What is a data center network?
What is a data center network?
A data center network consists of switches, routers, and other hardware components that work together to provide the connectivity and security needed to run applications and process data. As application requirements continue to change to address shifting business demands, data center networks mu st evolve as well. Traditional data center networks depend heavily on hardware and physical on-premises servers, which present storage, reliability, and latency issues in the face of a continuously growing volume of data. Furthermore, the only way to scale up a traditional network is to deploy larger switches and routers, which is both expensive and limited by the physical size of the data center. These larger, more complex devices also present greater risks; they are more prone to failures, and those failures have a wider impact (or “blast radius”) than do smaller devices.
Modern data center networks, on the other hand, incorporate virtualization to support applications and workloads across both physical and multicloud environments. Although modern networks still rely on physical components (routers, switches, firewalls, servers, etc.), they also depend on software components such as management and automation systems and analytics to reliably and efficiently deliver data and services among end users.
What Problems Does a Modern Data Center Network Solve?
The data center network plays a crucial role in an organization’s ability to meet business objectives. Modern data center networks incorporate intelligent automation and validation to support critical applications consistently and accurately and to address a range of operational issues, such as:
Vendor lock-in: Traditionally, vendor-specific requirements drove network design. The modern data center network, on the other hand, is vendor agnostic, allowing an organization’s business needs to drive the design and providing flexibility in vendor selection.
Human error: Manual operations are a primary cause of networking issues. Modern data center networks replace manual operations with automation to help assure reliability.
Complexity: Automation also helps to simplify network operations, enabling less-skilled networking staff to perform tasks that previously required specialized expertise. This reduces resource constraints and skills gaps.
Security breaches: Zero-trust data center security is an important aspect of the modern data center network that provides policy assurance, network segmentation, and compliance to prevent sensitive information from getting into the wrong hands.
Rigidity: The modern data center network has the agility and flexibility to adapt and scale as business needs change.
Inconsistencies: By consolidating information into one data set, the modern data center network ensures that all network operations are based on a single source of truth.
Data fog: Sorting through massive amounts of data makes troubleshooting a challenge. With advanced analytics built in, the modern data center network eliminates this challenge by enabling the network to quickly detect deviations and conditions of interest and provide actionable insights for fast root-cause identification.
How Do Modern Data Center Networks Work?
Modern data center networks are designed to address scalability and redundancy limitations that occur when traditional data center networks need to grow and evolve. This is achieved with an architecture consisting of an IP-based underlay that interconnects physical devices and a virtual overlay consisting of a control plane and a data plane to provide connectivity between endpoints.
Using a Clos — or spine-and-leaf — architecture for the underlay reduces latency and increases interconnectivity. Each leaf device is connected to each spine device, thus providing redundancy and resiliency. Since all the links are active, this architecture also offers equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) routing. Figure 1 illustrates the design of a simple Clos fabric.
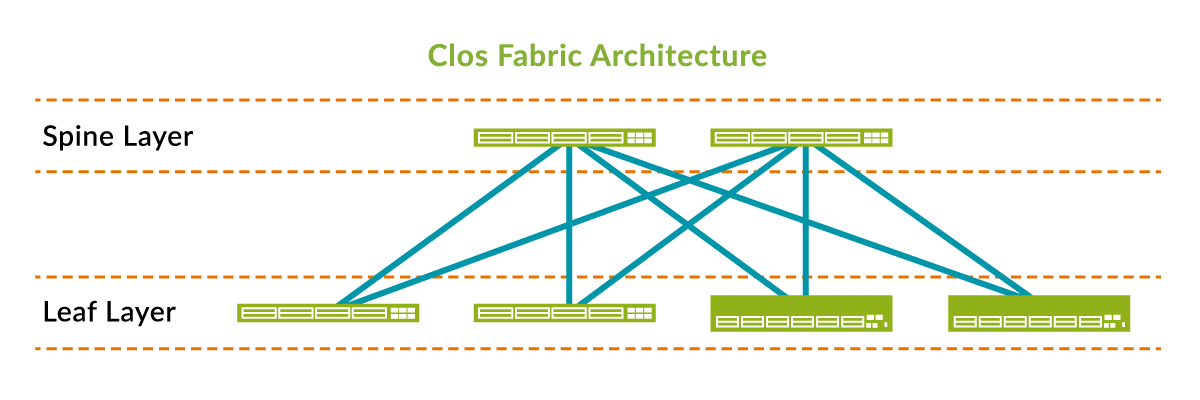
Figure 1: Example of a Clos architecture.
Notice how all spine nodes are linked to all leaf nodes. Flattening the data center network architecture in this way provides a number of benefits:
- Improves agility
- Reduces latency
- Maximizes bandwidth
- Minimizes bandwidth loss in the event of any link failures
Learn more about data center fabrics.
An Ethernet VPN (EVPN)-Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) overlay is built on top of the underlay infrastructure. EVPN-VXLAN is a standards-based data center fabric protocol that serves as the control plane to provide network mapping intelligence. EVPN-VXLAN using virtual and/or bare-metal servers enables deployment of much larger networks.
Another important aspect of a modern data center is automation. Although networking teams have long recognized the value of automation to address labor-intensive operational tasks and reduce human error, most conventional automation tools focus only on specific tasks and generate configurations that apply only to the organization’s current network. Changes to the network mean that scripts must be changed as well. And if the network includes hardware from multiple vendors, the organization must maintain multiple scripts doing the same thing.
To overcome these issues and simplify operations, networking teams rely on intent-based networking (IBN) software to design, deploy, and operate their modern data centers. This software takes the networking team’s intent — the expressed business objectives — and converts it into actionable network policies that are then executed as device-specific configurations, regardless of hardware vendor. The software also validates outcomes, continuously monitors the network to ensure it maintains compliance with the intent, and makes adjustments throughout the network lifecycle (Day 0 through Day 2+).
Learn more about intent-based networking.
Juniper Data Center Networks In Action
Juniper has everything a networking team needs to design, build, deploy, and operate a modern data center network. Whether your organization is starting from scratch or upgrading an existing network, our primary goal is to enhance the reliability of your network infrastructure and operations, lower your operational costs, and achieve faster time to market. We do this by providing intent-based networking software and specially programmed switching, routing, and security solutions. Besides our hardware having access to the neatly structured yet versatile Junos OS, our systems also have IP fabric, threat prevention, and EVPN-VXLAN capabilities.
Juniper Apstra
Juniper Apstra intent-based networking software automates and validates the design, deployment, and operations of networks across a range of vendors, any topology, and any data center location. Apstra accelerates everyday operations with a single source of truth, powerful analytics, and root-cause identification so you can quickly pinpoint and resolve issues. Apstra significantly reduces deployment times with validated templates and zero-touch provisioning (ZTP). It also averts outages with predictive insights, shortens time to resolution, and diminishes human error with change control and fast, all-network rollback.
Switches
Juniper carries a range of switches for use in data center network fabrics. Our switches enable you to scale your data center network easily to:
- Add more users
- Improve network speed
- Accommodate larger data transfers
- Add layers of security
- Optimize the cloud
- Implement machine learning and AI
We use Mist AI in our switches to lead assessments by using real-time data to make predictions designed to save time, resources, and money. Our stackable switches are also easy to integrate with other systems and offer both wired and wireless connections, including EVPN-VXLAN. For the switch families, we have the EX and QFX series. The EX series are ethernet switches with cloud integration and aggregation core layers that work well with enterprise branch, campus, and data center networks. The QFX network switches offer open programmability with Junos OS and allow for end-to-end automation with Juniper Apstra software. You can design spine and leaf fabrics with the QFX series, as they have core, data center gateway, and data center interconnect capability.
Routers
Juniper has a range of edge-ready routers that can be as robust or nimble as needed. Juniper routers maintain operational consistency and can integrate with or improve networking systems. Paired with Junos OS and automation software, these routers are future proof. We have the MX Universal series, which offers SDN-enabled routers that can handle growth. There’s also the PTX series, which offer core capabilities, ultra-high-power efficiency, and exceptional performance in 100G and 400G networks. The PTX series is also optimized for WAN core and data center use. For those needing universal metro routers, we offer those too. Our ACX series works for users by making network overlays a thing of the past. For those who want to maximize automation and machine learning, we offer session smart routers. Attach a gateway to your network to further secure your routers. Lastly, we have physical, virtual, and containerized firewalls.
Junos OS
The Junos operating system sets our hardware apart. Unlike other systems that may have multiple versions of varying operating systems, Junos OS is system wide. All our equipment contains Junos operating system, making it easy for them to connect. This OS also learns and uses real-time analytics to optimize performance. Some other things Junos OS offers:
Automation frameworks: Integrate Junos OS with ease. It’s compatible with multiple infrastructures, including:
- Ansible
- Chef
- Puppet
- PyEZ
- Salt
Programmability: Mold the Junos OS to business specifications with the Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) API. Here, operators can program the OS to manage network access and data plane services. JET API works across our portfolio, this includes external servers too.
Telemetry: With the Junos Telemetry Interface (JTI), programmers will notice a distributed network analytic engine that can accumulate, organize, and provide real-time network data and event information. This helps operators prepare for the future and optimize their networks accordingly.
Data Center Network FAQs
What does a data center network do? What is it used for?
A data center network enables operators to supply digital services to end users. It does all this with the help of networking hardware like routers, switches, and gateways. These products can come with artificial intelligence, machine learning, firewalls, and management and automation software to streamline and secure network operations.
Why do we need data center networks?
Data center networks deliver crucial services and applications to end users. Anyone who goes online is dependent on data center networks. In today’s information-hungry world, demand continually grows for more computing power, faster processing speed, and larger storage space. As a result, optimizing network performance and scalability is a challenge that networking teams constantly face.
What data center networking solutions does Juniper offer?
Juniper offers a range of products for modernizing and automating your data center network.
Juniper Apstra software automates and validates your data center network from Day 0 through Day 2 and beyond to improve operational reliability, speed, and flexibility. Apstra is the only intent-based networking software to support multiple vendors. The software also supports virtually any topology and any data center location.
Juniper’s switching, routing, and security platforms deliver scalability, reliability, and threat protection for data center fabrics, gateways, and data center interconnect (DCI). Junos OS powers all of Juniper’s physical and virtual hardware, providing more operational efficiency and service agility.

