How to Implement a Hybrid Cloud Strategy

Yes, the hybrid cloud can deliver better business outcomes. Here’s how.
According to Microsoft MVP and technology expert Brien Posey, organizations should make a plan to implement a hybrid cloud infrastructure to optimize costs and performance. He explains it all in this Eye on Tech webcast that you don’t want to miss.
You’ll learn
Advantages and shortcomings of the public cloud
Where private clouds fit in
How hybrid clouds can help
Who is this for?
Host

Transcript
0:05 Brien M. Posey: Hi, this is Brien Posey. And today
0:07 I want to talk about why a hybrid cloud might be
0:09 your best option. This presentation is designed to
0:14 be largely introductory in nature. And to that
0:17 end, there are several things that I want to
0:19 cover. I'm going to begin by talking a little bit
0:21 about the public cloud. Now, as I'm sure you know,
0:24 a lot of businesses have taken a cloud-first
0:26 approach to deploying IT workloads. And for good
0:29 reason, the cloud has a lot going for it. But at
0:32 the same time, there are also certain
0:34 disadvantages to running workloads in the public
0:36 cloud. So I want to spend a little bit of time
0:38 talking about some of the advantages and the
0:40 disadvantages associated with public cloud. From
0:44 there, I'm going to move on to a discussion of the
0:46 private cloud. The private cloud is a lot like the
0:49 public cloud, except for the IT resources reside
0:51 in your own data center. And like the public
0:54 cloud, there are certain advantages and
0:56 disadvantages to private cloud. And then finally,
1:00 I'm going to move on to a discussion of hybrid
1:02 cloud. Hybrid Cloud gives you the best of both
1:04 worlds. It gives you all of the advantages of
1:07 public cloud, as well as the advantages of private
1:10 cloud. So I'm going to be talking all about how
1:12 hybrid cloud may be the best option for you in
1:15 your own organization. Before I get into the main
1:21 part of this presentation, I just want to take a
1:23 moment and introduce myself and give you a little
1:25 bit of information about my background. Again, my
1:28 name is Brien Posey, and I'm a freelance
1:30 technology author and speaker. I'm also a 19 time
1:34 Microsoft MVP. Before I went freelance, I worked
1:37 as a network administrator for some of the largest
1:40 insurance companies in America. I was also the
1:43 lead network engineer for the United States
1:45 Department of Defense at Fort Knox. And I worked
1:48 as a CIO for a national chain of hospitals and
1:50 health care facilities. In addition to my IT
1:54 background, I've also spent the last several years
1:57 training as a commercial astronaut candidate in
1:59 preparation for a mission to study polar
2:01 mesospheric clouds from space. So that's just a
2:04 little bit about me. Let's get on with the
2:06 presentation. I want to begin the presentation by
2:11 talking a little bit about public cloud. I'm
2:14 guessing that most of you are probably already
2:16 familiar with public cloud. But I want to go ahead
2:18 and introduce the topic just in case because it is
2:20 going to come into play a little bit later on in
2:22 the discussion. There are actually a number of
2:25 different types of public clouds, everything from
2:27 Infrastructure as a Service clouds to Software as
2:29 a Service clouds. So for the purposes of this
2:33 discussion, when I refer to public cloud, I'm
2:36 going to be talking about Infrastructure as a
2:38 Service Cloud. Now, if you're not familiar with
2:40 Infrastructure as a Service clouds, the basic idea
2:44 is that the cloud provider gives subscribers the
2:46 ability to create various types of resources on
2:49 demand within the cloud. For example, a subscriber
2:53 might create virtual machine instances, they might
2:56 create databases, or they might provision various
2:58 managed services within the cloud. And the
3:02 subscriber is built based on the resources that
3:04 they use within the cloud. And that's actually one
3:10 of the really big advantages to public cloud is
3:12 that you're only paying for the resources that you
3:15 actually use, you never have to worry about
3:17 purchasing something and then not fully utilizing
3:20 it. Now, certainly, there are plenty of other
3:24 advantages to using public cloud. One of the big
3:27 advantages is that you don't have to worry about
3:29 buying any hardware. When you subscribe to a
3:32 public cloud, you're hosting resources on the
3:34 cloud providers hardware, so you don't have to
3:36 purchase that hardware yourself and deploy it in
3:38 your own data center. Similarly, the cloud
3:42 provider handles all of the hardware related
3:44 tasks. This might include purchasing the hardware,
3:47 getting it all deployed and set up. And all of the
3:50 ongoing hardware maintenance, such as replacing
3:52 failed hard drives, or refreshing aging hardware.
3:58 Another advantage to the public cloud is that the
4:00 cloud makes it extremely easy to deploy new
4:02 workloads. For example, if an organization needs
4:05 to deploy a new virtual machine, they can
4:07 typically do that with just a few mouse clicks.
4:12 The public cloud also provides almost infinite
4:14 scalability. If a workload needs to scale, you can
4:18 easily provision additional resources to meet the
4:21 needs of that workload. And you can deep provision
4:25 resources just as easily. And this is really nice,
4:28 because in a public cloud environment, there is no
4:31 guilt associated with the de provisioning of
4:32 resources. If you retire a workload on premises,
4:36 then you may have hardware that's going to sit
4:39 unused after that. So you're not fully
4:41 capitalizing on the investment that you made in
4:43 that hardware. Well, in a public cloud, you don't
4:45 have to worry about that because you never
4:47 actually purchased the hardware. You're simply
4:50 paying for the resources that you use on that
4:52 hardware. And when you're done with a particular
4:54 workload, you can step away from it and not have
4:57 to worry about what happens with the hardware. And
5:01 then another advantage is that large public clouds
5:03 tend to be extremely reliable and secure.
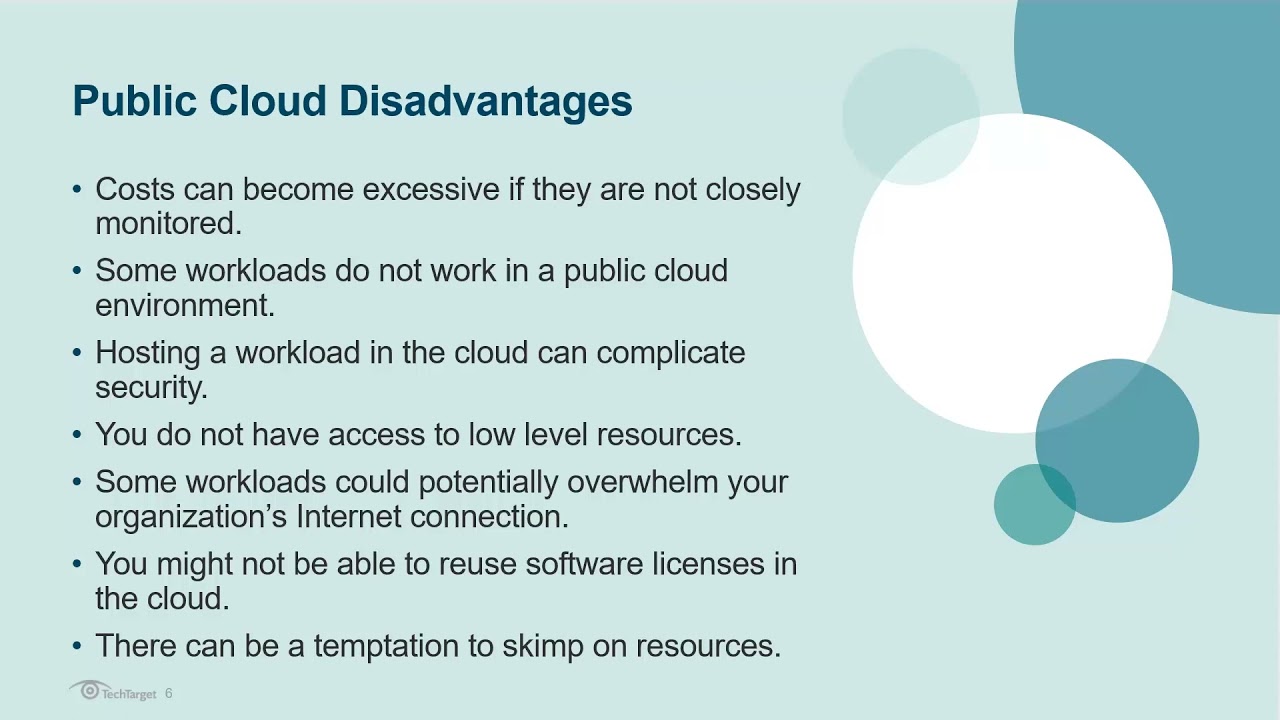
5:09 Just as there are advantages to hosting certain
5:12 workloads in the public cloud, there can also
5:14 potentially be some disadvantages that you need to
5:16 be aware of. One such disadvantage is cost. From
5:21 the very beginning, the public cloud has been
5:23 marketed as being the inexpensive option for
5:25 hosting it workloads. And in a lot of cases,
5:29 running a workload in the cloud can indeed save
5:31 you a lot of money. But you have to remember that
5:34 the public cloud providers bill you based on the
5:36 resources that you consume. So what this means is
5:39 that you have to be very careful to avoid
5:41 allocating excessive resources to a workload,
5:44 otherwise, it's going to cost you a lot more money
5:47 to run that workload than what is really
5:48 necessary. So you do have to keep an eye on cost
5:52 in order to avoid surprise billing. Another
5:57 potential disadvantage to be aware of is that
5:59 there are going to be some workloads that simply
6:01 don't work all that well, in a public cloud
6:03 environment. This can be especially true for
6:06 legacy workloads. And those workloads might be
6:09 better suited for remaining on premises. Something
6:13 else to be aware of is that hosting a workload in
6:15 the cloud can complicate your security. Now, this
6:19 isn't to say that your security is going to be
6:21 weakened simply because you moved a workload to
6:23 the public cloud. As a matter of fact, the
6:25 opposite often happens, moving a workload to the
6:28 public cloud can in some ways, improve the
6:31 workload security, but just know that the
6:34 migration process will cause you to have to re
6:37 evaluate the workload security. And in some cases,
6:40 things can be a little bit more complicated.
6:45 Another potential disadvantage to be aware of is
6:48 that when you host a workload in the public cloud,
6:51 you don't have access to low level resources on
6:53 the server that the workload is running on. This
6:56 can limit your ability to customize the workloads
6:59 platform. For a lot of workloads, this isn't a big
7:02 deal, but it is something that you need to be
7:04 aware of. Another thing to keep in mind with
7:08 regard to hosting a workload in the public cloud
7:12 is that some workloads could potentially overwhelm
7:15 your organization's internet connection. Now,
7:18 certainly, this isn't true for all workloads. But
7:20 if you have a workload that generates a heavy
7:23 amount of internet traffic between your
7:25 organization and the cloud provider, that workload
7:28 is going to be competing with your end users and
7:30 with other applications for internet bandwidth. So
7:33 you just need to make sure that you've got plenty
7:35 of internet bandwidth to accommodate that
7:36 workload. And a moment ago, I mentioned that there
7:42 are some workloads that really don't work all that
7:44 well, in a public cloud environment. Sometimes
7:47 that happens, because a workload just doesn't
7:49 really mesh well with the cloud infrastructure.
7:52 But another reason why you might have trouble
7:54 making a workload work in a public cloud, is
7:56 because you might not be able to reuse your
7:58 software licenses in a cloud environment. Now,
8:01 again, this isn't true for every workload, but it
8:03 is something that's worth paying attention to. And
8:06 then finally, one last disadvantage is that there
8:09 can be a temptation to skimp on the resources that
8:12 are allocated to your application. Remember, in a
8:15 public cloud environment, you're paying for the
8:17 resources that you consume. So there can be a
8:21 temptation to cut some corners and not given
8:23 application, all of the resources that it really
8:25 needs, just in an effort to stretch the IT budget
8:28 a bit. So now that I've talked a little bit about
8:33 public clouds, I want to turn my attention to
8:36 private clouds. private clouds have a lot of
8:38 similarities to public clouds, in that they
8:41 provide authorized users with a self service
8:44 environment that allows them to create resources
8:47 on demand. For example, an authorized user might
8:51 create virtual machines based on a template that's
8:54 been put into place by an administrator within the
8:56 private cloud environment. The primary difference
9:00 between a private cloud and a public cloud is that
9:02 the private cloud is based on the organization's
9:05 own hardware. That's hardware that the
9:07 organization owns, that exists in the
9:09 organization's own data center. One of the most
9:14 important things to understand about a private
9:16 cloud environment is that although the environment
9:18 does indeed give you cloud like functionality,
9:21 you'll lose one of the key benefits that's
9:23 associated with public clouds, namely, Pay As You
9:26 Go pricing. Because remember, the private cloud is
9:29 based on hardware that exist in your own data
9:31 center. So that means that you have to purchase
9:33 all of the capacity that you're going to need in
9:35 advance of actually needing it. And you're also
9:38 going to have to handle all of the hardware
9:40 maintenance yourself. Whereas in a public cloud
9:42 environment, the cloud provider takes care of all
9:45 of the hardware acquisition, and all of the
9:47 hardware maintenance on your behalf. Now that I've
9:53 spent some time talking about both public cloud
9:55 and private cloud, and the advantages and
9:58 disadvantages of each one of them turned my
10:00 attention to hybrid cloud. Hybrid Cloud is
10:03 essentially a combination of public and private
10:06 cloud resources.
10:08 The public and private clouds are merged together
10:10 in a way that gives the organization's all of the
10:13 benefits of both technologies. It's a way of
10:15 getting the best of both worlds. And as you can
10:18 imagine, there are many compelling benefits to
10:21 choosing the hybrid cloud option. So I want to
10:23 talk about some of those benefits. One of the big
10:28 benefits to building a hybrid cloud is that it
10:31 doesn't require an organization to abandon its
10:34 existing hardware resources. Because very often
10:37 when an organization is running a workload on
10:39 premises, and they decide that they want to
10:41 migrate that workload to the cloud, then once the
10:44 workload has been migrated, they have to figure
10:46 out what to do with the hardware that the workload
10:48 had previously been running on. Remember, this is
10:51 hardware that the organization had bought and paid
10:53 for. And now it's just sitting idle. And because
10:56 the hardware is sitting idle, the organization's
10:58 no longer realizing a return on investment. From
11:01 that hardware. Oftentimes, the hardware ends up
11:04 being prematurely retired, simply because it no
11:07 longer has a workload to run. But in a hybrid
11:11 cloud, on premises resources are still used, and
11:14 they're combined with resources that reside in the
11:17 public cloud. So you can continue to make use of
11:20 that hardware that exists within your data center.
11:25 Another especially compelling benefit to building
11:28 a hybrid cloud is that our hybrid cloud gives you
11:31 flexibility, you're free to run a workload in the
11:34 location where it makes the most sense to do so.
11:37 And there are any number of criteria that might
11:40 establish where it makes the most sense to run a
11:42 given workload. One such criteria is cost, you may
11:46 find that it costs less to host a particular
11:48 workload on premises than in a public cloud. Of
11:52 course, the opposite can be true, too, you might
11:55 find that it's cheaper to run a given workload in
11:57 the public cloud than it is to run it in your own
12:00 data center. And in a hybrid cloud environment,
12:03 you have that flexibility of being able to place
12:05 that workload where it makes the most sense to do
12:08 so based on cost. Another factor that sometimes
12:13 plays into the decision as to where a particular
12:16 workload should be hosted, are your compliance
12:19 requirements. For example, there may be a
12:21 compliance mandate that requires a given workload
12:24 to be hosted on premises rather than it residing
12:27 in the public cloud. And if you have a hybrid
12:30 cloud environment, you're certainly free to do
12:32 that, you can place a workload where it needs to
12:35 go based on your compliance mandates. one more
12:39 factor that often plays into the decision as to
12:42 where a particular workload should be hosted is
12:45 simply the workload logistics. For example, if you
12:48 have a very bandwidth intensive application, you
12:51 may want to keep that application in your own data
12:53 center so that you're not consuming an excessive
12:56 amount of internet bandwidth. At the same time, if
13:00 you have a workload that depends on a number of
13:02 other managed services residing in the public
13:04 cloud, then it might make more sense to host that
13:07 particular application in the public cloud. The
13:10 bottom line is that a hybrid cloud environment
13:12 gives you the flexibility to run that workload
13:14 wherever it makes the most sense to do so. Yet
13:20 another benefit to building a hybrid cloud is that
13:23 hybrid clouds give you on demand scalability, but
13:25 without the hardware investment. Now, as you'll
13:28 recall, hybrid clouds make use of hardware that's
13:31 running on premises, but they also make use of
13:33 resources in the public cloud. So if you suddenly
13:37 need to scale up a workload, you don't necessarily
13:40 need to go out and purchase more hardware, you
13:42 could use resources residing within the public
13:45 cloud to help you to scale that workload. If at a
13:48 later time you need to scale that workload back
13:50 down. Well, then you could simply d provision
13:52 resources in the public cloud and bring the entire
13:55 workload back on premises. The point is that the
13:58 hybrid cloud gives you the ability to demand scale
14:01 your workload either up or down, without
14:04 necessarily having to purchase additional
14:06 hardware. Another benefit is that hybrid clouds
14:12 can improve an organization's agility. Remember,
14:15 hybrid clouds use resources residing both locally
14:18 in the organization's own data center and in the
14:20 public cloud. And having all these resources at
14:23 your disposal makes it very, very easy to
14:26 provision and deploy new workloads at a moment's
14:28 notice, thereby helping to make the organization
14:31 far more agile than it might otherwise be. Yet
14:37 another benefit to the hybrid cloud is that when
14:39 properly configured, a hybrid cloud can help an
14:42 organization to achieve business continuity and
14:44 disaster recovery capabilities that might
14:46 otherwise be out of reach. One of the most popular
14:50 use cases for hybrid cloud is to configure
14:52 workloads that are running on premises to
14:54 automatically fail over to the public cloud,
14:57 should something happen in the organization's own
14:59 datacenter
15:01 hybrid clouds are often also used for disaster
15:04 recovery purposes. For example, workloads running
15:07 on premises might be backed up to public cloud
15:09 resources. These are just a couple of different
15:12 examples of some of the ways that organizations
15:15 achieve business continuity and disaster recovery
15:17 capabilities through the hybrid cloud. And one
15:23 more benefit to building a hybrid cloud is that
15:25 hybrid clouds are really good for accommodating
15:27 temporary workloads. If for example, an
15:30 organization needed to provision a new workload,
15:33 but they knew going in that that particular
15:35 workload was going to be temporary in nature, then
15:38 the hybrid cloud would make it very easy for the
15:40 organization to deploy the resources that were
15:42 needed by that workload. And then to reclaim those
15:45 resources once the workload is no longer needed.
15:49 So those are just a few of the many benefits to
15:51 building a hybrid cloud. Throughout this
15:56 presentation, I've stressed the idea that there
15:58 are three main types of clouds, public, private,
16:01 and hybrid. And in the vast majority of cases,
16:04 hybrid cloud is the preferred model. Now, having
16:08 said that, hybrid cloud does have some
16:10 disadvantages just as public and private cloud
16:12 have disadvantages. The main disadvantage to
16:15 building a hybrid cloud is that some hardware is
16:17 going to be required. That means that if you don't
16:20 already have hardware in your data center, you're
16:22 going to need to purchase some hardware. And
16:25 because of that, hybrid cloud probably isn't going
16:27 to be the best choice for startups. If you've got
16:31 a startup organization, it's generally going to be
16:33 more cost effective to deploy workloads in a
16:35 public cloud. But if you do have hardware in your
16:39 own data center, then you can certainly use that
16:41 hardware to build a hybrid cloud. Now, if you're
16:44 interested in building a hybrid cloud, and you
16:47 don't already have hardware or don't have enough
16:49 hardware, there is another option available. There
16:52 are vendors that will give you consumption based
16:55 pricing for data center hardware. So that's just
16:58 something to think about. The bottom line is that
17:03 in the vast majority of cases, hybrid cloud is the
17:05 preferred solution because it gives you the
17:07 greatest degree of flexibility for your workloads.
17:12 So I hope you found this presentation to be
17:14 informative. I'm Brien Posey, thanks for watching.










