What is Open RAN?
What is Open RAN?
Open RAN is an ongoing shift in mobile network architectures that enables service providers the use of non-proprietary subcomponents from a variety of vendors. An Open RAN, or open radio access network, is made possible by a set of industry-wide standards that telecom suppliers can follow when producing related equipment. Open RAN enables programmable, intelligent, disaggregated, virtualized, and interoperable functions. Specifically, the proprietary remote radio head (RRH) and baseband units (BBUs) are now disaggregated to radio units (RUs), distributed units (DUs), and centralized units (CUs), many of which can be virtualized or containerized. The interfaces between these new components are open and interoperable.
The O-RAN Alliance defines the specifications for all Open RAN components and the interfaces between them. Founded in 2018, the O-RAN Alliance is a progressive, global community comprising mobile network operators, manufacturers, vendors, and research and academic organizations working in telecommunications spaces all over the world. Similar terms, such as Open-RAN, ORAN, oran, or O-RAN, are also used in relation to Open RAN. Typically, Open RAN refers to the disaggregated radio access network with open interfaces between network components sourced from multiple suppliers, whereas O-RAN refers to the O-RAN Alliance and its work.
What Problems Does Open RAN Solve for Service Providers?
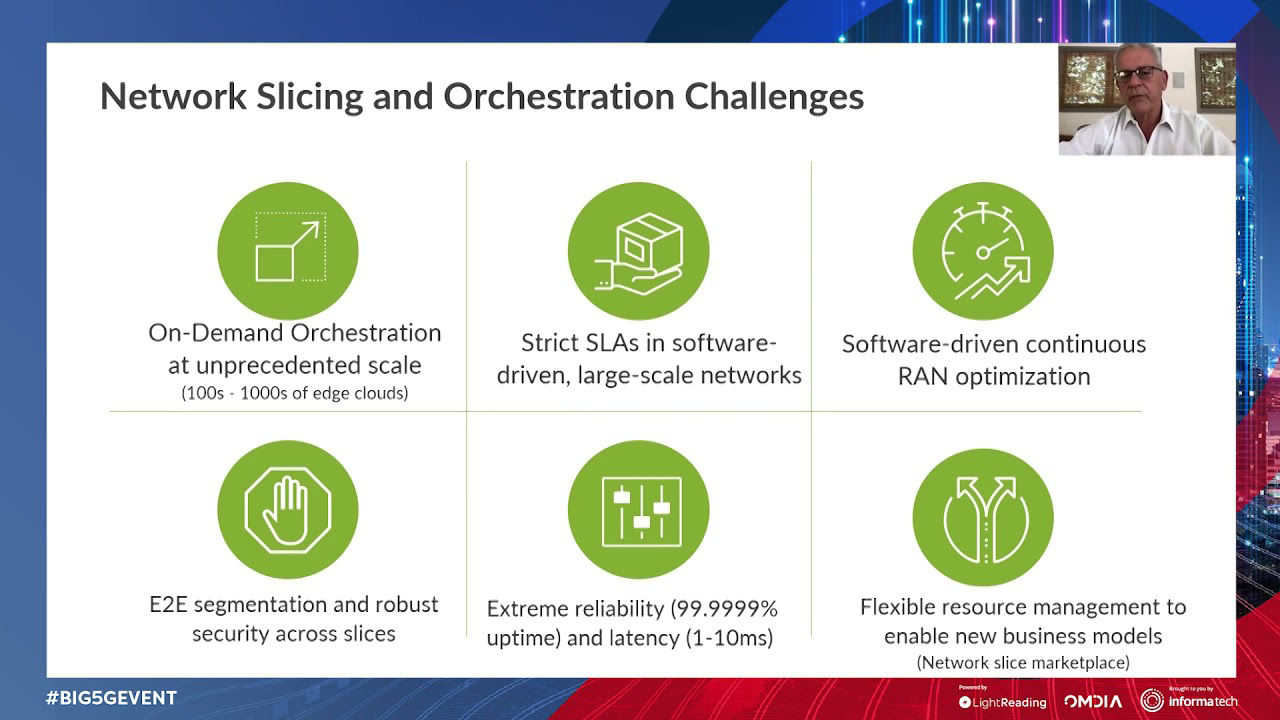
With Open RAN, the main driver for service providers is to increase vendor diversity and avoid lock-in. This happens when service providers are “locked in” using a single vendor to supply their equipment and software because switching suppliers isn’t straightforward. Now, service providers want to move away from single-vendor solutions towards open, multi-vendor networks with enhanced control and flexibility.
Deploying O-RAN gives providers a clear path towards fully programmable, intelligent, and multi-vendor RAN. With the help of a RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC), providers can control and optimize RAN functions with integrated applications. Specifically, a RIC is a software-defined component of the Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) architecture that enables the onboarding of service provider, vendor, and third-party apps. These applications are accessible in an “app store” and help service providers automate and optimize RAN operations at scale. Applications also support innovative use cases that lower mobile operators’ total cost of ownership (TCO) and enhance customers’ quality of experience (QoE).
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies can also be deployed with Open RAN RIC architecture. These AI/ML functions enable faster, innovative services and lower TCO.
How Does Open RAN Work?
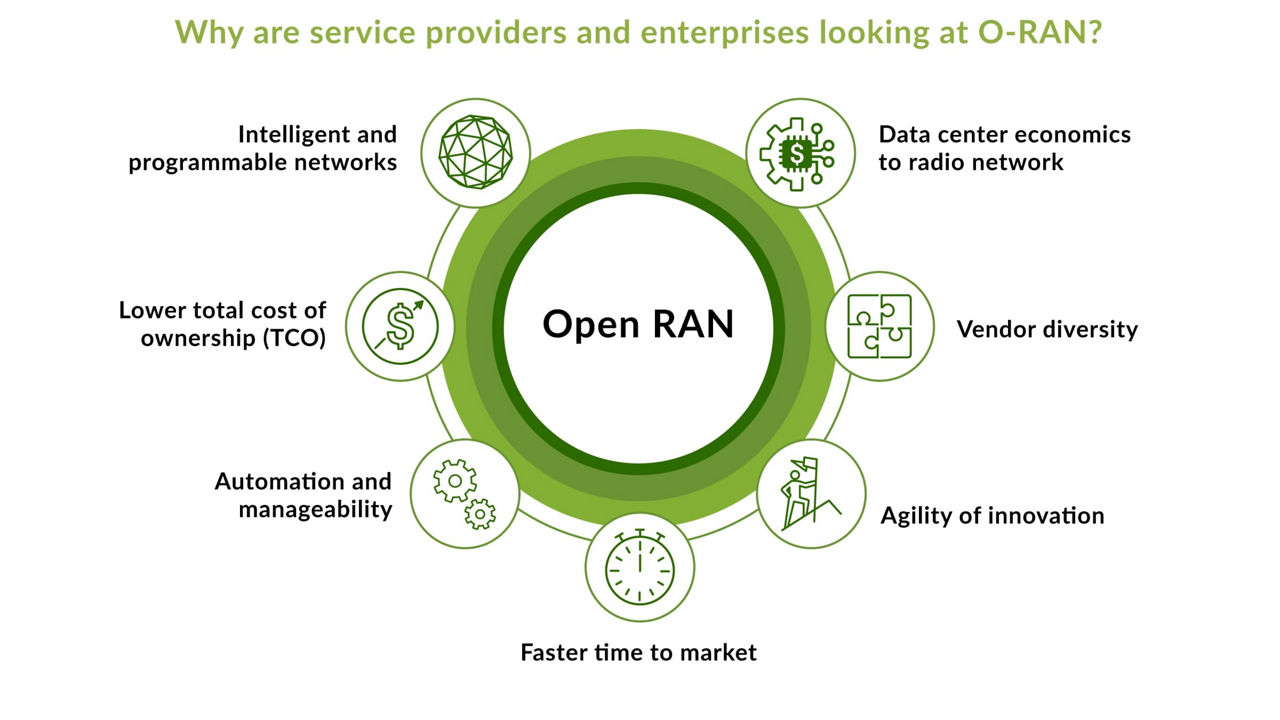
Let’s consider the evolution of legacy networks towards Open RAN. The legacy non-virtualized sites (pictured below) contain remote radio head (RRH) and baseband units (BBUs) co-located at a physical location. The RRH processes incoming and outgoing radio signals and the BBUs facilitate the digital signal processing of uplink and downlink data traffic. BBUs connect to the core via a backhaul transport network.
Some service providers evolved their networks to a new topology, called Centralized RAN, or C-RAN. Here, BBUs are grouped in a central location, like a data center. The centralized BBUs are connected to RRHs through a fronthaul transport network. Centralized BBUs provide OpEx savings in terms of power and cooling and simplify the management of the radio network. This is physical pooling of BBUs with no cloud involved.
Then there is virtualized RAN, also known as vRAN or V-RAN, in which BBU functions are moved to the cloud to increase agility and scalability with more control.
Until Open RAN, the interfaces between BBU and RRH were proprietary, meaning that only one vendor could provide both BBU and RRH. Open RAN disaggregated this architecture and introduced open interfaces. Instead of RRH and BBU, the functions are disaggregated into radio unit (RU), distributed unit (DU), and centralized unit (CU), with open interfaces between them. The RU, DU, and CU functions can also be virtualized or containerized. A new element, the RIC, adds intelligence to the networks. The RIC is basically an app store for the base station. Service providers can use the RIC to onboard third-party rApps/xApps that enhance RAN functions at scale with AI/ML technologies while addressing innovative use cases. This can result in lower TCO and better QoE.
Juniper Implementation of Open RAN
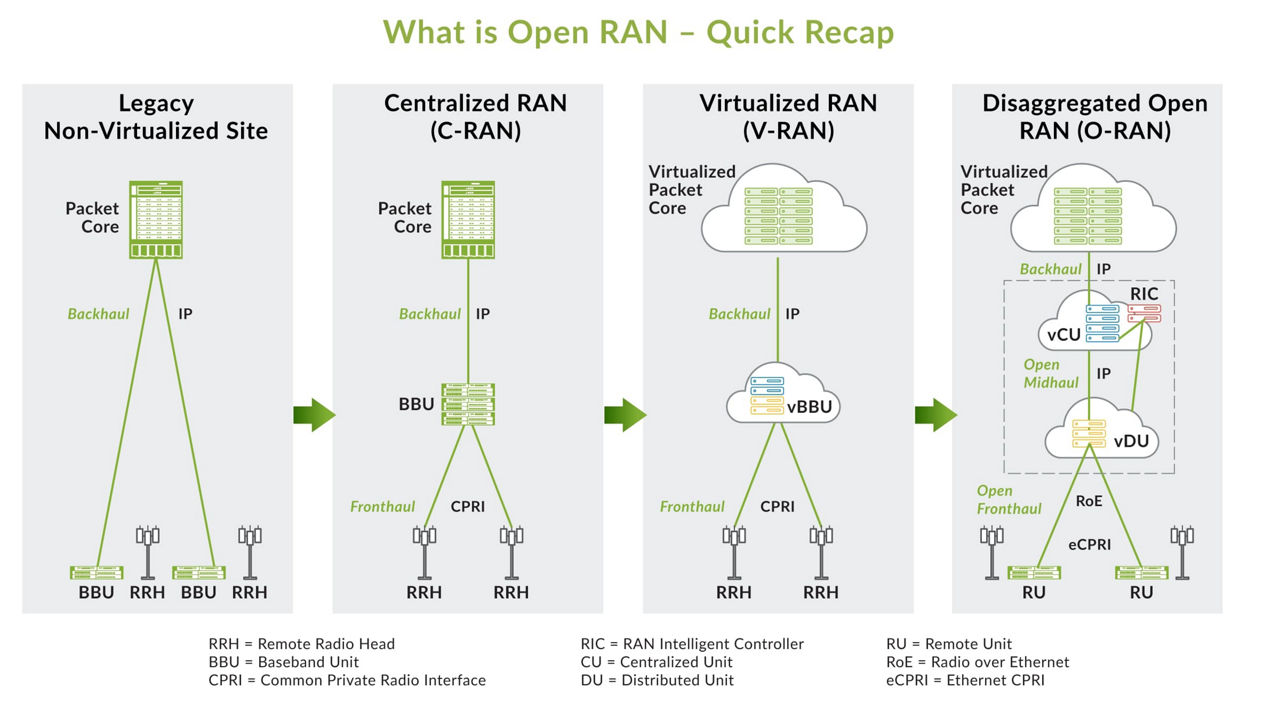
Juniper is an active proponent of Open RAN across different industry and standards organizations. We are contributing to 6 out of 10 working groups in the O-RAN Alliance. Juniper is also chair for the O-RAN Slicing Task Group, co-chair for the Use Cases Task Group, and editor and contributor to several O-RAN specification documents.
Additionally, Juniper offers O-RAN-compliant products and solutions across the entire network. These include:
Open and Interoperable RIC Platform
Juniper’s open and interoperable RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) platform allows for easier integration with partners in the Open RAN ecosystem. Our RICs facilitate the onboarding of both Juniper and third-party rApps/xApps. This makes it easier for service providers to enable new business models and personalize their service experiences, as well as optimize CapEx and OpEx.
End-to-End Service Management and Orchestration
Our Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) is built to deliver end-to-end (E2E) network slicing with support for prescribed service-level agreements (SLAs) across the RAN, transport, and core networks. The solution supports multicloud, multi-domain, and multi-tenant deployment models. Our SMO complies with O-RAN SMO requirements and interfaces, as well as 3GPP’s Network Slicing Management Functions.
Low Latency and Reliable Fronthaul Transport Network
O-RAN Fronthaul requires tight end-to-end latency, (~100–150 microseconds), as well as small jitter of a few microseconds. Juniper’s ACX 7100 routers support Time Sensitive Networking Profile A for prioritized eCPRI or PTP packets, Class D timing, and transport features such as segment routing and EVPN.
Connected Security
Open RAN introduces new functions such as CU, DU, RU, RIC, SMO, and open interfaces between them that need to be secured. Also, disaggregation of the RAN requires protection of virtualization infrastructure against security threats. Juniper Service Provider Security protects users, applications, and infrastructure by extending threat intelligence to all network connection points.
Open Ecosystem
Open networks require joint innovation for widespread deployment of cost-effective, open, and best-of-breed infrastructure. Juniper is partnering with Rakuten and Intel to offer integrated routing and Open RAN in a single platform, stimulating cost and operational benefits for providers. Juniper and Intel are also collaborating on RIC platforms and applications to further improve customer experience, maximize ROI, and drive rapid Open RAN ecosystem innovation.
Open RAN FAQs
What does Open RAN mean?
Open RAN stands for open radio access network. Specifically, Open RAN is an ongoing shift in mobile network architectures that enables service providers the use of non-proprietary subcomponents from a variety of vendors. Specific proprietary components like remote radio head (RRH) and baseband units (BBUs) are now disaggregated to centralized units (CU), distributed units (DU), and radio units (RU). With Open RAN, the new disaggregated functions can also be virtualized or containerized. The O-RAN Alliance takes it a step further by ensuring that the interfaces between these components are open and interoperable.
What is the benefit of Open RAN?
Open RAN helps service providers avoid vendor lock-in while encouraging vendor diversity. Service providers don’t want to deploy single-vendor solutions for their radio access networks, where equipment and software are provided by a single vendor. The Open RAN approach provides a clear path towards fully programmable, intelligent, and multi-vendor RAN with the help of a RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC).
What is a RIC and why is it needed for Open RAN?
A RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) is a software-defined component of the Open RAN architecture that controls and optimizes RAN functions. The RIC is an important part of Open RAN disaggregation, bringing multi-vendor interoperability, intelligence, agility, and programmability to radio access networks. It enables the onboarding of third-party applications that automate and optimize RAN operations at scale while supporting innovative use cases that lower mobile operators’ total cost of ownership (TCO) and enhance customers’ quality of experience (QoE).
How does Juniper optimize Open RAN for users using RIC?
Juniper’s RIC platform extends our vision for automation, control, intelligence, and assurance to radio access networks. As a RAN-neutral vendor, Juniper’s approach is to create an open RIC platform that enables powerful rApps/xApps from Juniper as well as third parties, available in an Open RAN “app store.” This helps operators create new business models, personalize service experiences, and optimize CapEx and OpEx. Juniper’s solutions are architected with open interfaces on the northbound and southbound sides for easier integration with partner solutions in the Open RAN ecosystem.