Application Steering
Version History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 6.1.4-R2 | Application Steering introduced |
Application Steering provides the ability to configure unique steering policies for individual applications based on the application name, category, application signatures, URLs, and domains. Once the traffic has been classified, it can be steered across the available paths. Where traditional routing is destination based, Application Steering defines a policy associated with a specific application, providing a finer granularity for routing traffic. In addition, Application Steering is available for configurations where multiple applications point to the same port and destination.
Define the Application in the Service
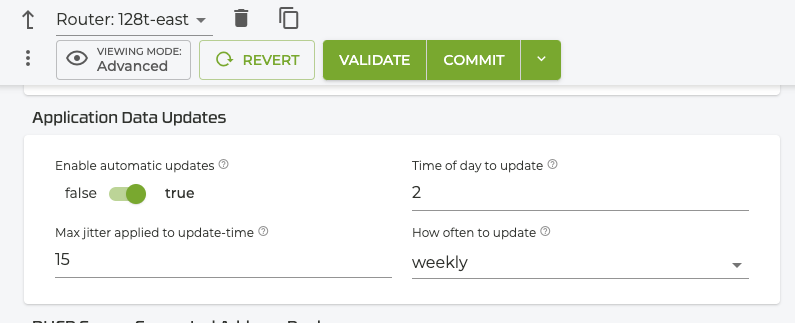
During the service configuration, applications are simply identified by name, for example Facebook. By default, the SSR automatically downloads domain and application datatsets weekly. The defaults (shown below) can be adjusted as necessary using the Application Data Updates panel or from the PCLI for each router. For additional information, see application-identification in the Element Reference section.
To steer the application, you can configure an access-policy to allow or deny the traffic, and a service-route to steer the traffic to a specific interface or next hop.
The following steps show configuring services, access policies, and service routes using only application names, and steering them to interfaces and specific next hops.
- Configure a service for the internet:
service internet
name internet
address 0.0.0.0/0
- Configure access policies
access-policy corp
source corp
access-policy corp
source guest
- Configure a service for the application you wish to steer, in this case we use Facebook, and an access policy that will not allow the application on the corporate network.
service facebook.internet
name facebook.internet
application-name facebook
access-policy corp
source corp
permission deny
For additional information about configuring heirarchical services, see Hierarchical Services
- Configure a service and an access policy for the Workday application, which will be allowed on the corporate network.
service workday.internet
name workday.internet
application-name Workday
access-policy corp
source corp
permission allow
Child Services
Beginning with version 6.1.4-R2, service routes can be configured on child services allowing sessions to be re-routed accordingly. Using the catch-all service for internet traffic (0.0.0.0/0) defined in step 1 above, and the workday.internet child service from step 4, we can define a service route for internet so that traffic takes both the broadband and lte paths. Then we can define another service route that specifically directs the workday.internet traffic over the SVR path to the head-end.
router myRouter
name myRouter
service-route internet-rte
name internet-rte
service-name internet
next-hop node1 broadband
node node1
interface broadband
next-hop node1 lte
node node1
interface lte
service-route workday.internet__headend
name workday.internet__headend
service-name workday.internet
peer headend
Category-based Steering
In addition to application based steering, traffic can be routed based on the application category. For example, steering all social-media traffic over broadband and the remaining internet traffic to the headend.
service social-media.internet
name social-media.internet
domain-name-category social-media
access-policy guest
source corp
permission allow
router myRouter
name myRouter
service-route social-media-rte
name social-media-rte
service-name social-media.internet
next-hop node1 broadband
node node1
interface broadband
service-route internet-rte
name internet-rte
service-name internet
peer headend