Installing a PAYG Conductor-managed Router in AWS
Introduction
This guide describes the process for deploying a PAYG (Pay As You Go) Session Smart Conductor and a Session Smart Router (SSR) in AWS.
Mist-managed SSR installations are now available through AWS. However, SSR Version 6.x installed as an AWS image will only support Mist-managed routers. It will not support a conductor-managed deployment. See Installing a Mist-Managed Router in AWS for details.
If you wish to install SSR Version 6.x on a conductor and conductor-managed router in AWS, the suggested procedure is to first install an earlier version of SSR software such as 5.x.x, and upgrade through the conductor.
The process for deploying Conductor-managed networks consists of the following steps:
- Selecting the AMI.
- Deploying a Session Smart Conductor.
- Deploying a Session Smart Router.
Proceed to the next section Selecting the AMI.
| Version | Supported Modes |
|---|---|
| 5.x | Conductor and Conductor-Managed Router |
| 6.x | Mist-Managed Router |
Selecting the AMI
There are different AMIs (images) available for the Juniper Session Smart Networking Platform offering:
- Private: For cases where there is no access to the SSR repositories (no internet connection) from the AWS environment where the software will be deployed, a Private Offer can be issued to your AWS account via the AWS Marketplace. To request access to a private offer, refer to Requesting access to a Private offer for additional information.
- Hourly: This provides a free trial period for 30 days and an hourly software cost after the trial expires. This plan is recommended for Proof of Concepts and Trials only. Software upgrades and deployments outside of the cloud, (on premises) require a token or certificate. The software can not be purchased via the marketplace. Refer to the Session Smart Networking Platform (PAYG) offering.
Once you have selected the AMI that better suits the needs of your deployment, proceed to the section Session Smart Conductor Deployment to deploy a Session Smart Conductor, or proceed to the section Session Smart Router Deployment to deploy a Session Smart Router.
SSR Version 6.x installed as an AWS image will only support Mist-managed routers. It will not support a conductor-managed deployment.
Requesting access to a Private Offer
There is no software cost associated with deploying the Private image, the cost of running the EC2 instance is the only cost (AWS compute cost). Please also note that software upgrades and deployments outside of the cloud (e.g., on premises) will not be possible without a token or certificate.
To request access to a Private offer:
- Locate the account ID of the AWS account where the deployment of the software is going to take place:
- Open the AWS Console.
- On the right at the top of the screen, click on the downward arrow next to your username, and the account ID will be displayed.
- Make a note of your account ID.
- Contact your Juniper Networks Sales representative and provide:
- The Account ID of the AWS account that will be used for the deployment.
- The version of the Session Smart Networking software. Your Juniper Sales representative will assist you if you don't know the version you need for your deployment.
-
Your Juniper Sales representative will email you the private offer.
-
When you receive the email containing the private offer, open it and review / accept the terms and conditions.
Session Smart Conductor Deployment
Use the following information to deploy a Session Smart Conductor in AWS.
Requirements
The following infrastructure must exist in your AWS account:
- A VPC where the Conductor will be deployed.
- The existing VPC is segmented with at least one subnet.
- The subnet is reachable for SSH and HTTPs access for administration purposes.
- The Session Smart Routers managed by this Conductor must be able to reach the IP address of the Conductor in this subnet.
Deployment
A Conductor can be deployed manually via the AWS Console or in an automated fashion using AWS CLI commands. This section describes both methods. Choose the method that better suits your needs.
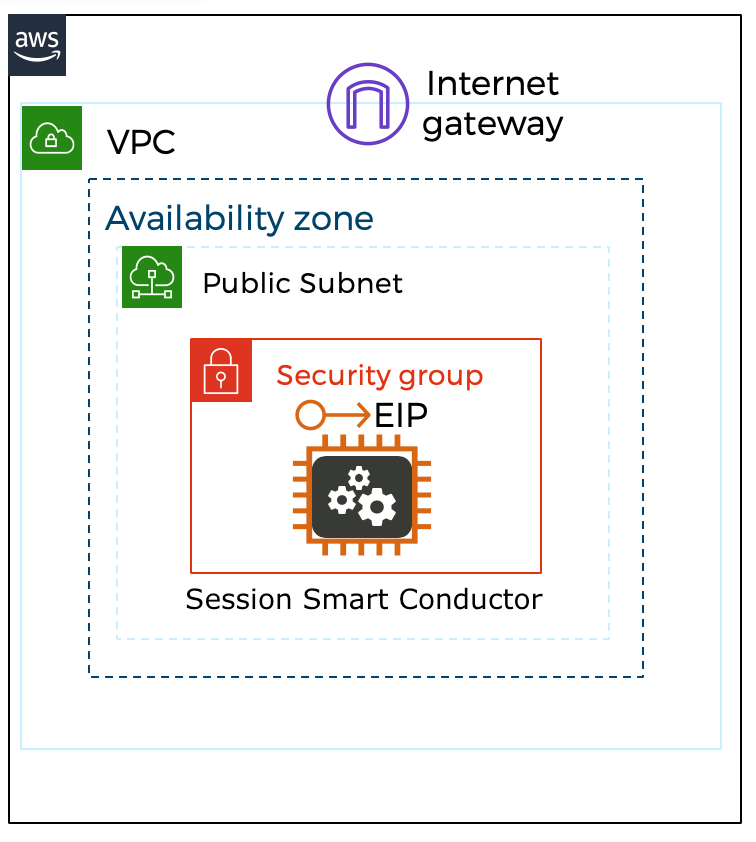
When deploying the Session Smart Conductor using the templates referenced in this section, the following infrastructure elements are created automatically to assist with the deployment process:
- EC2 instance using a Session Smart image available in the marketplace.
- The Conductor is deployed with a single network interface identified as the control interface.
- There is a network security group associated with the control interface.
- The control interface has a unique and static public IP address.
The following image shows the infrastructure elements deployed:
AWS Console
To deploy the Session Smart Networking software via the AWS Console:
- Click on the Session Smart Networking Platform offering selected during the previous section Selecting the AMI.
- Click on the Continue to Subscribe button and accept the terms and conditions.
- Click on the Continue to Configuration button.
- In the Fulfillment Option drop down box select CloudFormation Template, select the template Juniper Session Smart Conductor and select the desired region.
- Click on the Continue to Launch button.
- In the Choose Action box, select Launch CloudFormation and click on the button Launch.
- Answer the following 3 questions to launch the deployment of a Conductor. For additional information, refer to Launch the Template.
- What name do you want to give it?
- Enter the name in the Stack name field (for example: Conductor).
- Where do you want to deploy it?
- Select the VPC in the region.
- Select the subnet within the VPC.
- Who is going to be the administrator?
- Select the IAM user key.
- Click the Next button.
- Click on the Create stack button to launch the deployment.
Once the deployment completes, information is provided in the Outputs tab.
Click on the HTTPS URL of the HTTPSLogin field to login to the Conductor GUI (In some cases when using Chrome, the self-signed certificate may return an unsafe connection. Click through the message.). The credentials are admin for username and the password is 128Tadmin. To login to the instance via SSH, use t128 as the username and the SSH public key of the IAM user provided in the template.
Be sure to change the password that conforms to your business' password requirements and criteria.
AWS CLI
To deploy the Session Smart Networking software via the AWS CLI:
- Click on the Session Smart Networking Platform offering selected during the previous section Selecting the AMI.
- Click on the Continue to Subscribe button and accept the terms and conditions.
- Click on the Continue to Configuration button.
- In the Fulfillment Option drop down box select CloudFormation Template, select the template Juniper Session Smart Conductor and select the desired region.
- Click on the Continue to Launch button.
- In the Choose Action box, select Launch CloudFormation and click on the button Launch.
- Copy the URL of the template located in the field Amazon S3 URL to the clipboard.
Launch the deployment with the corresponding AWS CLI commands making use of the S3 URL of the template identified previously. For additional information, refer to Launch the Template.
Once the deployment completes, information is provided in the Outputs tab.
Click on the HTTPS URL of the HTTPSLogin field to login to the Conductor GUI (In some cases when using Chrome, the self-signed certificate may return an unsafe connection. Click through the message.). The credentials are admin for username and the password is 128Tadmin. To login to the instance via SSH, use t128 as the username and the SSH public key of the IAM user provided in the template.
Be sure to change the password that conforms to your business' password requirements and criteria.
Adding a Token to enable upgrades and deployments on-premises
Adding a token to your deployment enables on-premises upgrades and deployments. Use the following steps to add the token credentials.
- SSH to the EC2 intance of Conductor (Linux).
- Run in Linux the following command to add a token credential:
install128t repo authenticate --username <your username> --token <your token>
If a token or certificate is not in your possession, please contact your Juniper Sales representative.
Proceed to the next section Session Smart Router Deployment to deploy a Session Smart Router.
Session Smart Router Deployment
Use the following guide to deploy a Session Smart Router in AWS.
Requirements
The following infrastructure must exist in your AWS account:
- A VPC where the Session Smart Router will be deployed.
- The existing VPC is segmented with at least three subnets. The role of each subnet is described below
- Enable enhanced network with ENA for maximum throughput performance. For SSR routers, execute the following command from your local computer
aws ec2 modify-instance-attribute --instance-id instance_id --ena-support
Public Subnet
This subnet must provide connectivity to enable communication with external/remote SSR peers. For Mist managed deployments, this subnet should also provide access to the Mist cloud infrastructure.
Private Subnet
This subnet must provide connectivity to internal workloads within the cloud.
Management Subnet
This subnet is used for conductor-managed deployments, and has the following requirements:
- The subnet is reachable for SSH for administration purposes.
- The interface of the Conductor that manages this router must be reachable from this subnet.
Please note that deploying Session Smart Routers without a valid token or certificate is limited to deployments within the cloud. If your use case also requires the deployment of an on-premises SSR, please contact your Juniper sales representative.
Deployment
A Session Smart Router can be deployed manually via the AWS Console or in an automated fashion using AWS CLI commands. This section describes both methods. Choose the method that better suits your needs.
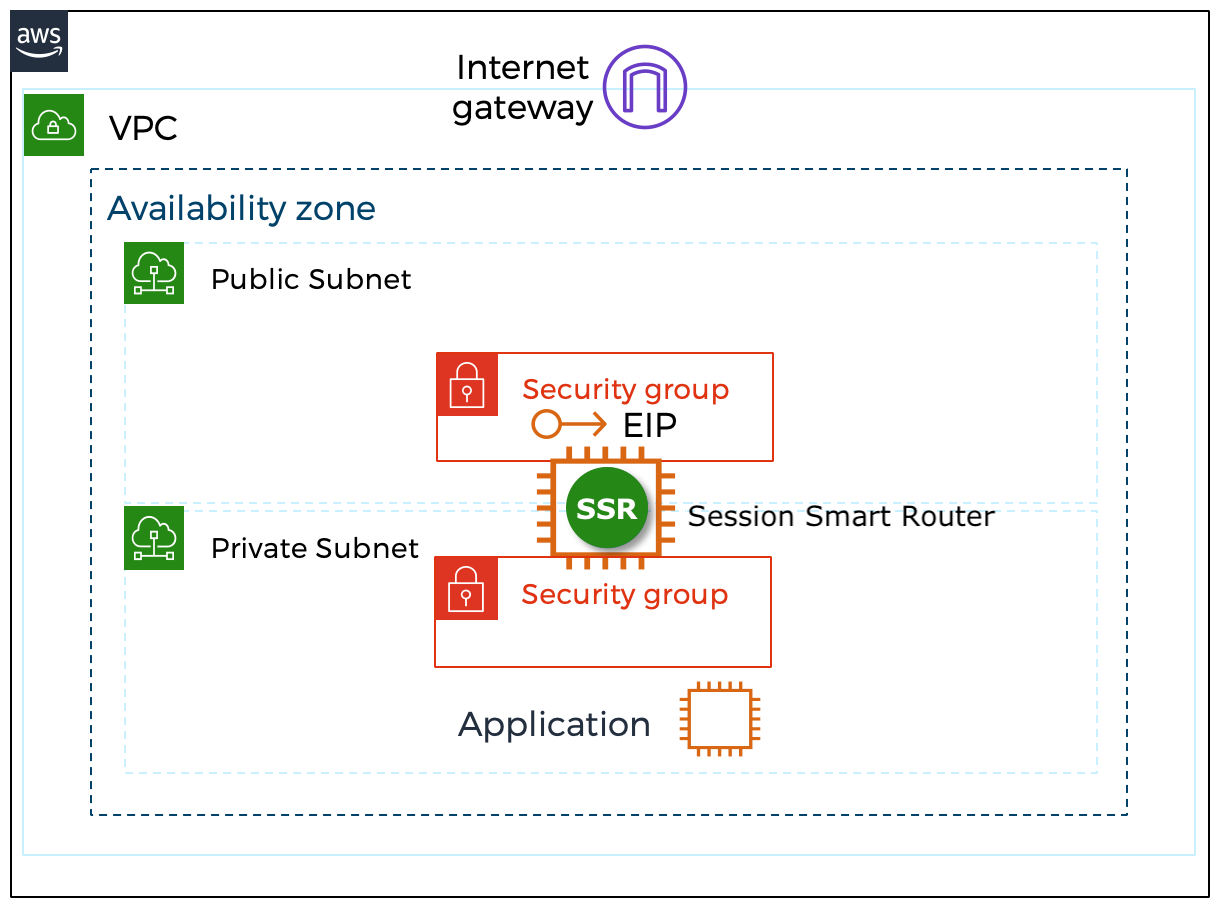
When deploying the Session Smart Router using the templates referenced in this section, the following infrastructure elements are created automatically to assist with the deployment process:
- EC2 instance using a Session Smart image available in the marketplace.
- The router is deployed with appropriate network interfaces as described here
- Each network interface has a network security group associated. The network security groups are configured in accordance with the requirements to deploy a fabric with Session Smart Networking software.
- The public and management interfaces have a unique and static public IP address associated.
The following image shows the infrastructure elements deployed:
AWS Console
To deploy the Session Smart Networking software via the AWS Console:
- Click on the Session Smart Networking Platform offering selected during the previous section Selecting the AMI.
- Click on the Continue to Subscribe button and accept the terms and conditions.
- Click on the Continue to Configuration button.
- In the Fulfillment Option drop down box select CloudFormation Template, select the template Juniper Session Smart Router and select the desired region.
- Click on the Continue to Launch button.
- In the Choose Action box, select Launch CloudFormation and click on the button Launch.
- Answer the following 4 questions to launch the deployment of an SSR. For additional information refer to Launch the Template.
- What name do you want to give it?
- Provide it in the Stack name field (for example: SSR_1_Router).
- Where do you want to deploy it?
- Select the VPC in the region.
- Select the public, private, and management subnets within the VPC.
- Which Session Smart Conductor is going to manage it?
- Provide the IP address of the primary node of Conductor in the Conductor Primary Control IP field. If the Conductor is highly available, provide the IP address of the secondary conductor node in the Conductor Secondary Control IP field. Please check the public IP address assigned to the Conductor deployed in the previous section.
- Who is going to be the administrator?
- Select the IAM user key.
- Click the Next button.
- Click on the Create stack button to launch the deployment.
Once the deployment completes, information is provided in the Outputs tab.
If the Session Smart Networking Platform offering selected for the deployment is a Private AMI or an Hourly AMI, and IP address/es to an existing Conductor have been provided in the template, the non-interactive, Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) method is triggered. After the VM is deployed, an additional 2-3 minutes are required before the ZTP process initializes. When the ZTP process is ready, there will be an asset in the Conductor to be associated with the router configuration.
Login to the Conductor via HTTPs to associate the pending asset with the configuration of the router. If the asset is not associated with a router, an unmanaged router will be deployed, and must be initialized manually. To login to the instance via SSH, use t128 as the username and the SSH public key of the IAM user provided in the template.
AWS CLI
To deploy the Session Smart Networking software via the AWS CLI:
- Click on the Session Smart Networking Platform offering selected during the previous section Selecting the AMI.
- Click on the Continue to Subscribe button and accept the terms and conditions.
- Click on the Continue to Configuration button.
- In the Fulfillment Option drop down box select CloudFormation Template, select the template Juniper Session Smart Router and select the desired region.
- Click on the Continue to Launch button.
- In the Choose Action box, select Launch CloudFormation and click on the button Launch.
- Copy to the clipboard the URL of the template located in the field Amazon S3 URL.
Launch the deployment with the corresponding AWS CLI commands making use of the S3 URL of the template identified previously. For additional information please refer to Launch the Template.
Conductor Managed Setup
If the Session Smart Networking Platform offering selected for the deployment is a Private AMI or an Hourly AMI, and IP address/es to an existing Conductor has been provided in the template, the non-interactive, Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) method is triggered. After the VM is deployed, an additional 2-3 minutes are required before the ZTP process initializes. When the ZTP process is ready, there will be an asset in the Conductor to be associated with the router configuration.
Login to Conductor via HTTPs to associate the pending asset with the configuration of the router. If the asset is not associated with a router, an unmanaged router will be deployed, and must be initialized manually. To login to the instance via SSH, use t128 as the username and the SSH public key of the IAM user provided in the template.
Network Interfaces Layout
The Session Smart Router Template deploys an EC2 instance for the SSR with three network interfaces. The template attaches the network interfaces to the EC2 instance in the following order: Management, Public, and Private. The network interfaces are mapped as follows:
| Network interface name | Subnet | PCI Address |
|---|---|---|
| eth0 | Management | 0000:00:05.0 |
| eth1 | Public | 0000:00:06.0 |
| eth2 | Private | 0000:00:07.0 |
Configuring a Device Interface
The following are the high level steps to configure a device interface on a SSR running in the AWS cloud.
- Disable Source / Destination Checking
- Determine the Device Interface Layout
- Configure and Assign the PCI Address Identifier to a Device Interface
- Configure the IP Addressing for every Network interface
- Configuration for every Network Interface with a Public IP Address (if a public IP address is associated to any of the network interfaces)
- Verify Connectivity
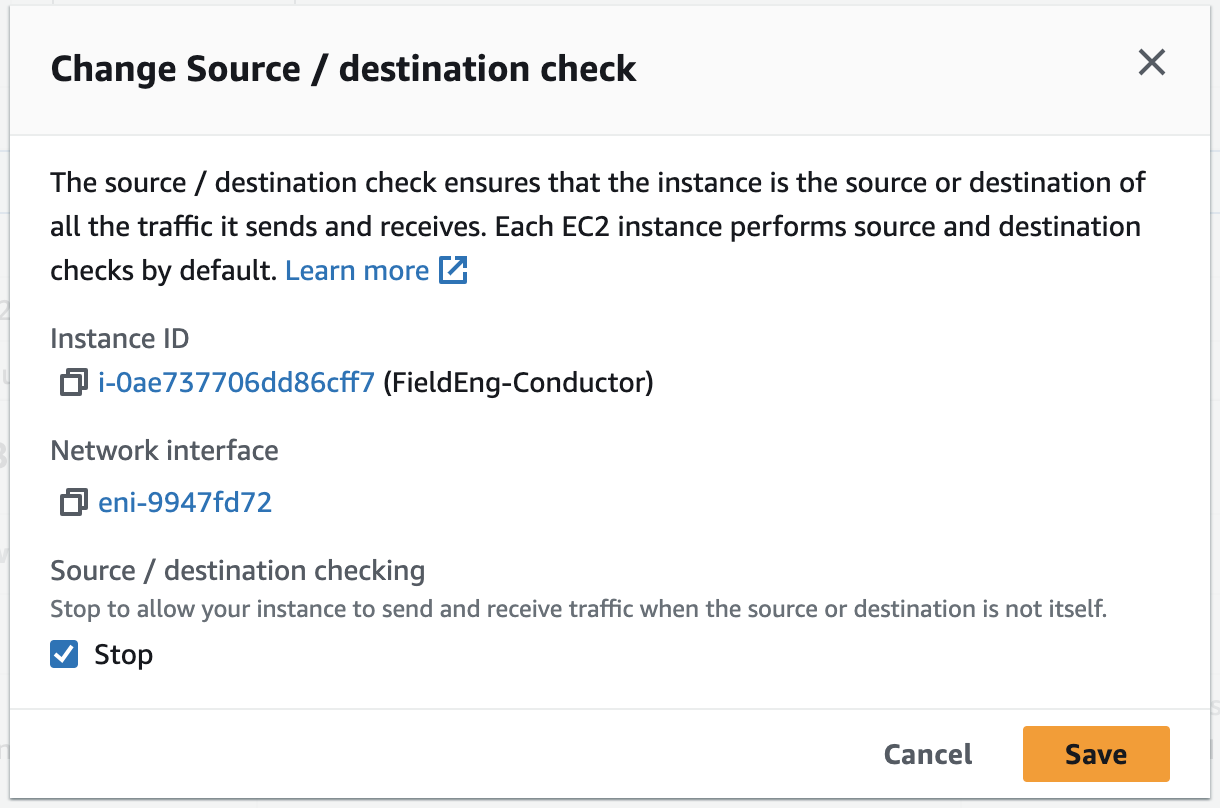
Source / Destination Check
Disabling Source / Destination checking allows the SSR AWS instance to send and receive traffic when it is not the source or destination. This feature is enabled by default. Perform the following steps to disable Source / Destination checking.
- On the Instances page, select the Launch Instances dropdown.
- Select Networking.
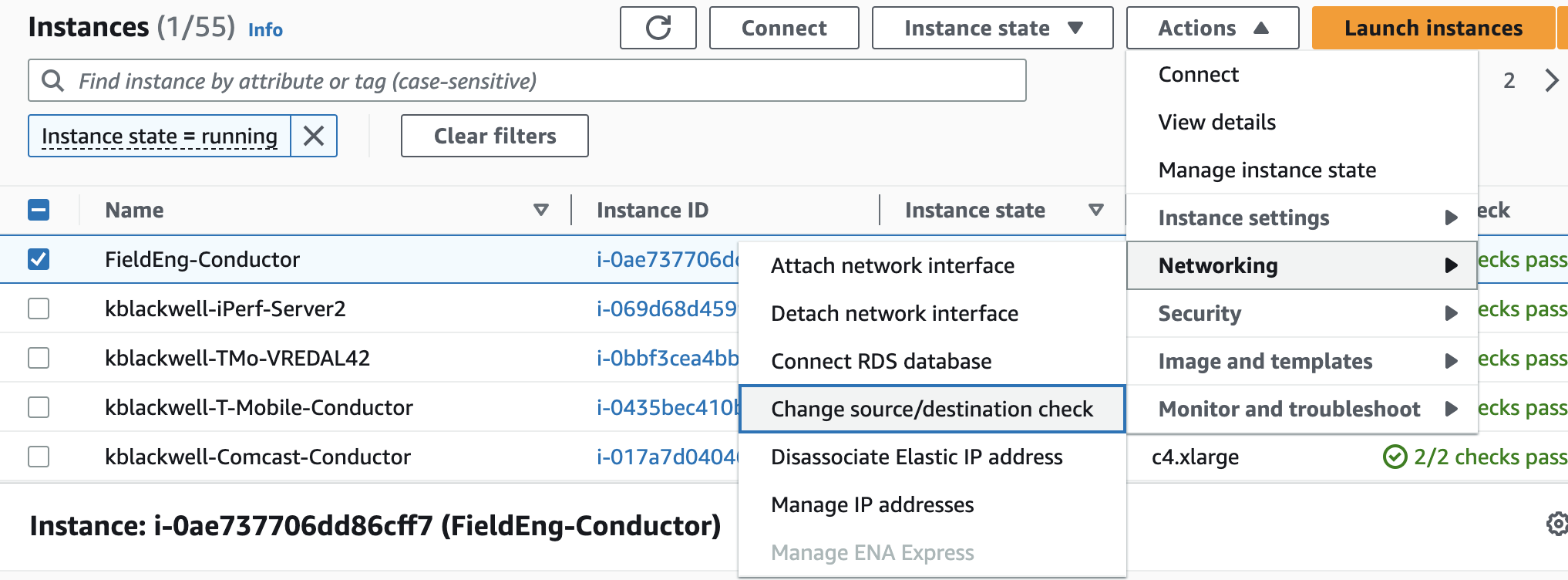
- From the pull out menu, select Change source/destination check.
- In the Change Source / Destination Check window, select Stop, and Save.
Determine the Device Interface Layout
Perform the following steps to identify the correct PCI address for each network interface attached to the EC2 instance:
- Login via SSH to the EC2 corresponding to the SSR.
- Run the following command in Linux:
sudo dpdk-devbind.py --status
The PCI address is the first column under Network devices using kernel driver. The network interfaces are listed in the order in which they are attached to the EC2 instance.
If you have used the Session Smart Router Template to deploy the SSR, the template attached the network interfaces to the EC2 instance in the order described in the previous section Network Interfaces Layout. Otherwise, if you did not use the template and instead launched an EC2 instance with a custom network interface layout, note the order in which the network interfaces are attached to your EC2 instance.
Assign the PCI Address Identifier to a Device Interface
For cloud deployments the recommendation is not to configure the management interface (the first network interface of the EC2 instance) as management over forwarding. In other words, the recommendation is not to configure the management interface on the router at all, so that management is out of band and remains managed by Linux.
Assign the PCI Address Identifier to a device interface using the Conductor CLI or GUI.
- Login to the CLI on the Conductor.
- Run the following commands to configure a device interface with a PCI Address for every forwarding interface (e.g. WAN and LAN) of the router:
configure authority router <router name> node <node name> device-interface <device interface name>
type ethernet
forwarding true
pci-address <device interface vmbus uuid>
top
-
Repeat the steps above for each forwarding device interface (e.g. WAN and LAN) and router running on AWS.
-
Validate and commit the changes.
validate
commit
Configure the IP Addressing for Network Interfaces
By default, AWS assigns a private IP address to each network interface attached to an EC2 instance. Therefore, the recommendation is to enable DHCP on every network interface managed by the SSR.
- Login to the CLI on the Conductor.
- Run the following commands to configure a network interface with DHCP on a router:
configure authority router <router name> node <node name> device-interface <device interface name> network-interface <network interface name>
dhcp v4
top
-
Repeat the steps above for each network interface and router running on AWS.
-
Validate and commit the changes.
validate
commit
If setting a static private IP address is a requirement, note that for every subnet AWS reserves the first IP address as the AWS subnet gateway. For example, if the prefix of a subnet in AWS is 192.168.0.1/24, then AWS reserves the IP address 192.168.1.1 for the gateway of the subnet, therefore, make sure the corresponding network interface of the Session Smart Router is configured with the gateway 192.168.1.1.
Configuration for Network Interfaces with a Public IP Address
When AWS associates a Public IP address with the elastic network interface of an EC2 instance, AWS does a 1:1 mapping between the Public IP address and the Private IP address for that elastic network interface. In other words, every network interface attached to the EC2 instance sits behind that Public IP, and all traffic destined to the Public IP is NATted and forwarded to the corresponding private IP address. For every elastic network interface that has a Public IP address associated (e.g. the WAN interface), the Neighborhood has to be configured so that the SSR is aware that forwarding is behind NAT.
- Login to the CLI on the Conductor.
- Run the following commands to configure the external-nat-address in the Neighborhood for every network interface with a Public IP address on a router:
configure authority router <router name> node <node name> device-interface <device interface name> network-interface <network interface name> neighborhood <neighborhood name>
external-nat-address <public IP address AWS assigned to the elastic network interface of the EC2 instance>
top
-
Repeat the steps above for each network interface with a Public IP address and router running on AWS.
-
Validate and commit the changes.
validate
commit
Verify Connectivity
-
Login via SSH to the EC2 instance of each router running on AWS.
-
Login to the SSR CLI.
su admin -
Ping the gateway of each device interface.
ping <gateway IP address> -
Confirm AWS gateways reply to ping successfully.
Source / Destination Check
Disabling Source / Destination checking allows the SSR AWS instance to send and receive traffic when it is not the source or destination. This feature is enabled by default. Perform the following steps to disable Source / Destination checking.
- On the Instances page, select the Launch Instances dropdown.
- Select Networking.

- From the pull out menu, select Change source/destination check.
- In the Change Source / Destination Check window, select Stop, and Save.

Launch the Template
This section describes how to fill out and launch the template using either the AWS marketplace or programmatically to deploy a Session Smart Conductor and SSR.
Session Smart Conductor
This section describes the parameters to complete the template to deploy a Session Smart Conductor, as well as how to launch it using the portal, or programmatically.
A description of the parameters of the template are listed in the following table:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Stack name | Fill out the Instance Name field to provide a name to the VM for the Conductor. |
| VPC ID | ID of the existing VPC where the Conductor is going to be deployed. |
| Control Subnet ID | ID of the control (public) subnet within the VPC. |
| Control Allowed CIDR | It is used to define a trusted source IP address range which represents the source IP addresses of the management interface of the SSRs to be managed. Connections originated from source IP addresses which are outside the range are not allowed, effectively protecting the Control Subnet. It is common to set this field to 0.0.0.0/0 (accepting traffic from all source IP addresses) for now, as the source IP addresses of the SSRs may not be known at this time. However, after the deployment and once these external IP addresses are known, it may be desirable to provision them explicitly in the corresponding security groups to increase the degree of security. |
| Instance size | Size of the EC2 instance. |
| Key Name | IAM user key (SSH public key) to login to the EC2 instance (Linux) via SSH. |
| Admin Allowed CIDR | It allows for restricting reachability to the control interface of the Conductor to a well known source IP address CIDR range for management purposes. It is common to set this field to 0.0.0.0/0 (accepting traffic from all source IP addresses) for now, as the source IP address/es where the Conductor will be administered from may not be known at this time. However, once the deployment completes, it is highly recommended to update the configuration of the network security group to allow only access from the source IP address/es where the Conductor will be administered. |
AWS Console
- Go to the Session Smart Networking Platform offering following the steps described in the section Selecting the AMI.
- Click on the Continue to Subscribe button and accept the terms and conditions.
- Click on the Continue to Configuration button.
- In the Fulfillment Option drop down box select CloudFormation Template, select the template Juniper Session Smart Conductor and select the desired region.
- Click on the Continue to Launch button.
- In the Choose Action box, select Launch CloudFormation and click on the button Launch.
- Click the Next button.
- Fill out the template. Review the section above to understand the parameters of the template.
- Continue clicking the Next button.
- Click Create Stack to start the deployment.
Once the deployment of the template is complete, information about the new Conductor deployment is provided in the Output tab.
The information listed in the Outputs tab is the following:
- Instance ID of the Conductor EC2 instance.
- Private IP address of the control interface.
- Public IP address of the control interface.
- HTTPs URL to login to the Conductor GUI. Please continue to the end of this section below for more information regarding the credentials to login.
- SSH command to login to the Linux VM. Please continue to the end of this section below for more information regarding the credentials to login.
When logging to the Linux instance via SSH use t128 as the username and the SSH public key of the IAM user provided in the template.
If a template of the Bring Your Own License image was used, SSH to the EC2 instance using t128 as the username as indicated in the SSHLogin field. Launch the software installation process with the command sudo install-ssr.
If a Conductor template of a Private or Hourly image was used, you can login to the application via HTTPs as indicated in the HTTPSLogin fields respectively, the username is admin and the password is 128Tadmin.
AWS CLI
Alternatively, it is possible to launch the template programmatically. Please adjust the content of the JSON file below to match the input of each template.
Create the parameters file conductor.parameters.json with the following command:
vi conductor.parameters.json
and paste the following JSON content, please adjust the values to your specific environment:
{
"StackName": "<instance name>",
"VpcId": "<ID of the VPC>",
"ControlSubnet": "<ID of the subnet within the VPC>",
"ControlAllowedCidr": "0.0.0.0/0",
"InstanceType": "c5.xlarge",
"KeyName": "<username>",
"AdminAllowedCidr": "0.0.0.0/0"
}
- Go to the Session Smart Networking Platform offering following the steps described in the section Selecting the AMI.
- Click on the Continue to Subscribe button and accept the terms and conditions.
- Click on the Continue to Configuration button.
- In the Fulfillment Option drop down box select CloudFormation Template, select the template Juniper Session Smart Conductor and select the desired region.
- Click on the Continue to Launch button.
- In the Choose Action box, select Launch CloudFormation and click on the button Launch.
- Copy to the clipboard the URL of the template located in the field Amazon S3 URL.
Launch the template running the following command:
aws ec2 create-launch-template \
--launch-template-name <template-file> \
--launch-template-data file://conductor.parameters.json
When logging to the Linux instance via SSH use t128 as the username and the SSH public key of the IAM user provided in the template.
If a template of the Bring Your Own License image was used, SSH to the EC2 instance using t128 as the username as indicated in the SSHLogin field. Launch the software installation process with the command sudo install-ssr.
If a Conductor template of a Private or Hourly image was used, you can login to the application via HTTPs as indicated in the HTTPSLogin fields respectively, the username is admin and the password is 128Tadmin.
Conductor-Managed Session Smart Router
This section describes the parameters to complete the template to deploy a conductor-managed SSR, as well as how to launch it using the portal, or programmatically.
A description of the parameters of the template are listed in the following table:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Stack name | Fill out the Instance Name field to provide a name to the VM for the Conductor. |
| VPC ID | ID of the existing VPC where the Conductor is going to be deployed. |
| Public Subnet ID | ID of the public subnet within the VPC. |
| Public Subnet Allowed CIDR | The IP CIDR range of the endpoints allowed to originate traffic to the Router's public interface in the public subnet. |
| Private Subnet ID | ID of the private subnet within the VPC. |
| Private Subnet Allowed CIDR | The IP CIDR range of the endpoints allowed to originate traffic to the Router's private interface in the private subnet. |
| Management Subnet ID | ID of the management subnet within the VPC. |
| Admin Allowed CIDR | It allows for restricting reachability to the control interface of the Conductor to a well known source IP address CIDR range for management purposes. It is common to set this field to 0.0.0.0/0 (accepting traffic from all source IP addresses) for now, as the source IP address/es where the Conductor will be administered from may not be known at this time. However, once the deployment completes, it is highly recommended to update the configuration of the network security group to allow only access from the source IP address/es where the Conductor will be administered. |
| Conductor Primary Control IP | If a Session Smart Conductor has already been deployed, fill out the field Conductor Primary Control IP with the IP address of the control interface of the primary node of Session Smart Conductor. The IP address of the control interface of Conductor should be reachable from the Management subnet selected above. It must be a valid IP address of the form x.x.x.x. If no Session Smart Conductor has been deployed yet or the intention is simply deploying an unmanaged router please refrain from entering any value in this field. |
| Conductor Secondary Control IP | If there is an existing Session Smart Conductor already deployed and the deployment of the Conductor is Highly Available, please enter the IP address of the control interface of the secondary node of Session Smart Conductor in the field Conductor Secondary Control IP. If the existing deployment of the Session Smart Conductor is not Highly Available, in other words if the Conductor is standalone, please refrain from entering any value in this field. |
| Instance size | Size of the EC2 instance. |
| Key Name | IAM user key (SSH public key) to login to the EC2 instance (Linux) via SSH. |
AWS Console
- Go to the Session Smart Networking Platform offering following the steps described in the section Selecting the AMI.
- Click on the Continue to Subscribe button and accept the terms and conditions.
- Click on the Continue to Configuration button.
- In the Fulfillment Option drop down box select CloudFormation Template, select the template Juniper Session Smart Router and select the desired region.
- Click on the Continue to Launch button.
- In the Choose Action box, select Launch CloudFormation and click on the button Launch.
- Click the Next button.
- Fill out the template. Review the section above to understand the parameters of the template.
- Continue clicking the Next button.
- Click Create Stack to start the deployment.
Once the deployment of the template is complete, information about the new router deployment is provided in the Output tab.
The information listed in the Outputs tab is the following:
- Instance ID of the Router EC2 instance.
- Public IP address of the management interface for administration purposes.
- SSH command to login to the Linux VM. Please continue to the end of this section below for more information regarding the credentials to login.
When logging to the Linux instance via SSH use t128 as the username and the SSH public key of the IAM user provided in the template.
If a template of the Bring Your Own License image was used, SSH to the EC2 instance using t128 as the username as indicated in the SSHLogin field. Launch the software installation process with the command sudo install-ssr.
If a Conductor template of a Private or Hourly image was used, you can login to the application via HTTPs as indicated in the HTTPSLogin fields respectively, the username is admin and the password is 128Tadmin.
AWS CLI
Alternatively, it is possible to launch the template programmatically. Please adjust the content of the JSON file below to match the input of each template.
Create the parameters file router.parameters.json with the following command:
vi router.parameters.json
and paste the following JSON content, please adjust the values to your specific environment:
{
"StackName": "<instance name>",
"VpcId": "<ID of the VPC>",
"PublicSubnet": "<ID of the public subnet within the VPC>",
"PublicSubnetAllowedCidr": "0.0.0.0/0",
"PrivateSubnet": "<ID of the public subnet within the VPC>",
"PrivateSubnetAllowedCidr": "0.0.0.0/0",
"ManagementSubnet": "<ID of the management subnet within the VPC>",
"AdminAllowedCidr": "0.0.0.0/0",
"ConductorPrimaryControlIP": "<IP address of primary node of Conductor>",
"ConductorSecondaryControlIP": "<IP address of secondary node of Conductor>",
"InstanceType": "c5.xlarge",
"KeyName": "<username>"
}
- Go to the Session Smart Networking Platform offering following the steps described in the section Selecting the AMI.
- Click on the Continue to Subscribe button and accept the terms and conditions.
- Click on the Continue to Configuration button.
- In the Fulfillment Option drop down box select CloudFormation Template, select the template Juniper Session Smart Router and select the desired region.
- Click on the Continue to Launch button.
- In the Choose Action box, select Launch CloudFormation and click on the button Launch.
- Copy to the clipboard the URL of the template located in the field Amazon S3 URL.
Launch the template running the following command:
aws ec2 create-launch-template \
--launch-template-name <template-file> \
--launch-template-data file://router.parameters.json
When logging to the Linux instance via SSH use t128 as the username and the SSH public key of the IAM user provided in the template.
If a template of the Bring Your Own License image was used, SSH to the EC2 instance using t128 as the username as indicated in the SSHLogin field. Launch the software installation process with the command sudo install-ssr.
If a Conductor template of a Private or Hourly image was used, you can login to the application via HTTPs as indicated in the HTTPSLogin fields respectively, the username is admin and the password is 128Tadmin.
Deploying a Conductor or Router without Templates
- Launch a web browser and navigate to https://aws.amazon.com/
- Login to AWS with your account.
note
If you do not have an account, click Create an AWS Account to register.
- Click EC2 Dashboard and select your deployment region from the drop down list.
- Click Launch Instance.
- On the Step 1: Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) page, select the Amazon Marketplace tab and enter Session Smart Networking in the search bar.
- Locate the SSR image and click Select.
- On the Step 2: Choose and Instance Type page, choose an instance type.
- On the Step 3: Configure Instance Details page, click Subnet and select the desired subnet and retain the default values for the other fields.
note
If the desired subnet is not listed, click Create New Subnet to create one.
- Click Next: Add Storage.
Select Yes, I want to continue with this change and click Next.note
The You have changed your network setting window may appear.
- On the Step 4: Add Storage page, ensure the size is 128 GB (default value).
- Click Next: Add Tags. See Interface Tagging for additional tag configuration information.
- On the the Step 5: Add Tags page, click Add Tags.
- Click inside the Key column and select Name. Under the Value column enter the name for your instance.
- Click Next: Configure Security Group.
- On the Step 6: Configure Security Group page, click select an existing security group and choose one from the list.
note
If the desired security group is not listed you can create your own by selecting Create a new security group and following the prompts.
- For Mist managed routers, expand the Advanced Details and scroll down to the User data section. To onboard the router to the desired Mist org, you can add cloud-init user-data using the steps in the Cloud-init Onboarding section.
- Select Review and Launch.
- In the Boot from General Purpose window, select Continue and then click Next.
- On the Step 7: Review Instance Launch page, click Launch to finalize the instance.
- In the Select an existing key pair or create a new key pair dialog box, select Choose an existing key pair and select the desired key pair from the list.
note
If the desired key pair is not listed click Create a new key pair, enter a name in the Key pair name field and click Download Key Pair.
- Check the acknowledgment check box and then click Launch Instances.
- On the Launch Status page, click View Instances.
- Record the instances IP address.
- Launch a command window prompt.
- Enter the IP address of the instance. Result: The interactive SSR Installer application launches.
- When prompted by the installer, press the Enter key to select Begin.
Configuring a Default Route to an Internet Gateway
If the EC2 instance deployed for the Session Smart software does not have access to the Internet, verify a default route to an Internet Gateway exists:
- From the main toolbar, click Services to expand the Services list and select VPC.
- From the VPC Dashboard pane, click Your VPCs.
- From the VPC Dashboard pane, click Route Tables and then Create Route Table.
- In the Create Route Table dialog box, enter the following information and click Yes, Create.
- Name Tag: Enter a name for your route table
- VPC: Using the dropdown list, select the VPC to associate with the route table
- From the VPC Dashboard pane, select Internet Gateways and click Create Internet Gateway.
- In the Create Internet Gateway dialog box, enter an Internet Gateway name in the Name Tag field and click Yes, Create.
- On the Internet Gateways page, click Attach to VPC and assign the Internet Gateway to your VPC.
- From the VPC Dashboard pane, select Route Tables and click Edit.
- Click Add Another Route.
- In the 0.0.0.0/0 row, click the empty cell under the Target column and the local name automatically appears as a selectable option.
- Select it and click Save.