ON THIS PAGE
Install and Configure Junos Space, Security Director, and Log Collector
Install and Configure SRX Series, EX Series, and QFX Series Devices
Install and Configure Microsoft Windows Server and Active Directory
Download, Deploy, and Configure Policy Enforcer Virtual Machine
Obtain an ATP Cloud license and Create an ATP Cloud Web Portal Account
Install Root CA on the ATP Cloud Supported SRX Series Devices
Download, Deploy, and Configure the ForeScout CounterACT Virtual Machine
Configure the Policy Enforcer Connector for Third-Party Switches
Use Case Implementation: Juniper Connected Security Automated Threat Remediation with ForeScout CounterACT and Juniper Networks Devices
This use case shows how to integrate and configure a ForeScout CounterACT security appliance, a Windows 7 supplicant, a Juniper Networks vSRX virtual firewall, a Juniper Networks EX4300 switch, and a Juniper Networks QFX series switch into a Juniper Connected Security.
To implement this use case for threat remediation (block or quarantine) of infected hosts with ForeScout CounterACT, perform the following required set of installation, configuration, and verification steps:
Requirements
This use case uses the following hardware and software components:
vSRX virtual firewall running Junos OS Release 15.1X49-D110.4 or later
a QFX series switch running Junos OS Release 15.1X53-D60.4 or later
an EX4300 switch running Junos OS Release 15.1R5.5 or later
Advanced Threat Prevention Cloud (ATP Cloud)
Junos Space Network Management Platform, Release 17.2R1 or later
Junos Space Security Director, Release 17.2R2 or later
Log Collector, Release 17.2R2 or later
Policy Enforcer, Release 17.2R2 or later
ForeScout CounterACT version 7.0.0-513-2.3.0-1605
A virtual machine (VM) running Windows 7 with 2x dual NIC hosts
For a list of supported devices, please refer to the Policy Enforcer Release Notes.
Use Case Topology
The use case topology is illustrated in Figure 1
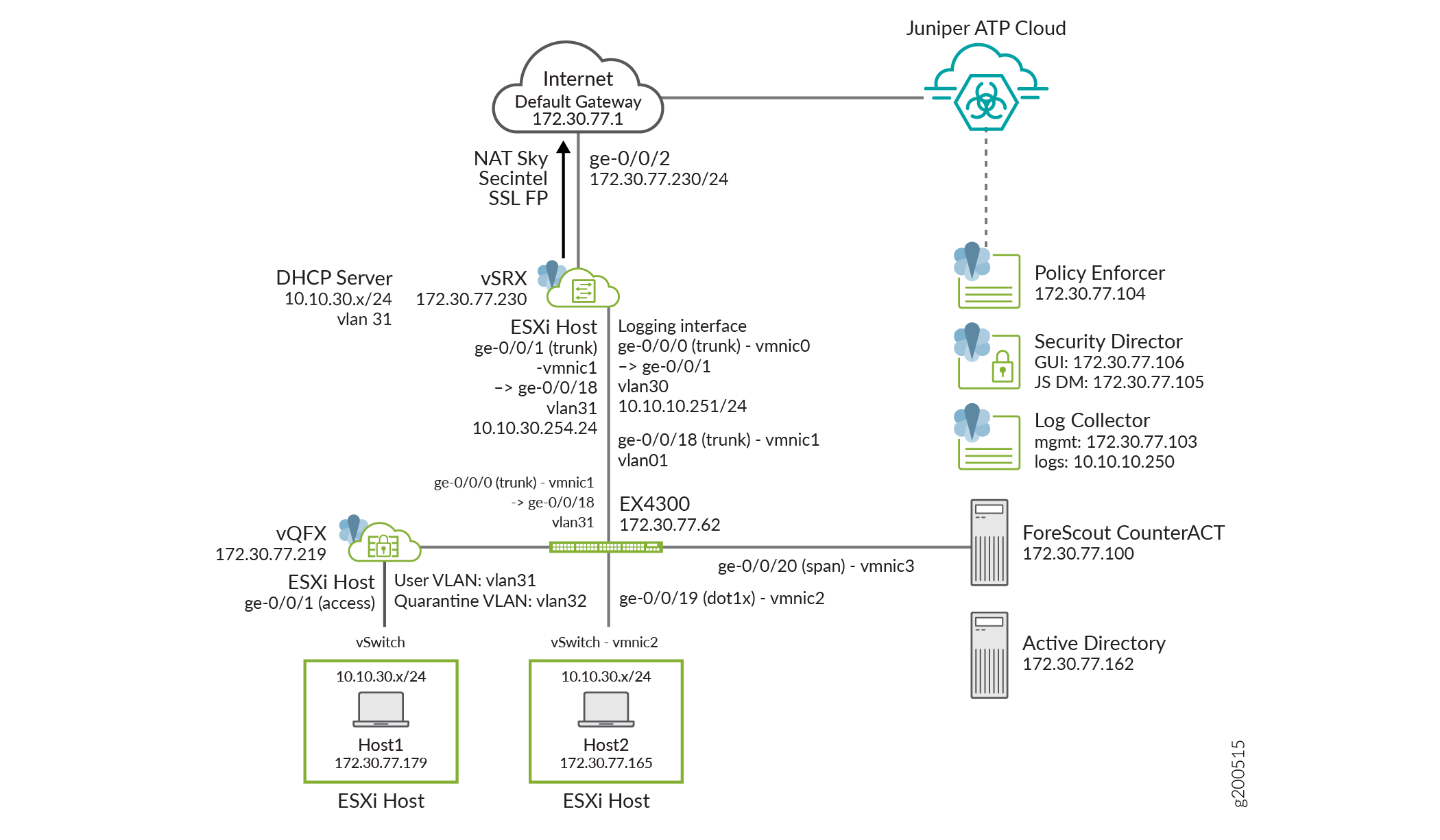
The Forescout CounterACT security appliance applies an agentless approach to network security and integrates with Juniper Connected Security to block or quarantine infected hosts on Juniper Networks’ devices, third-party switches, and wireless access controllers that support and do not support 802.1X protocol integration.
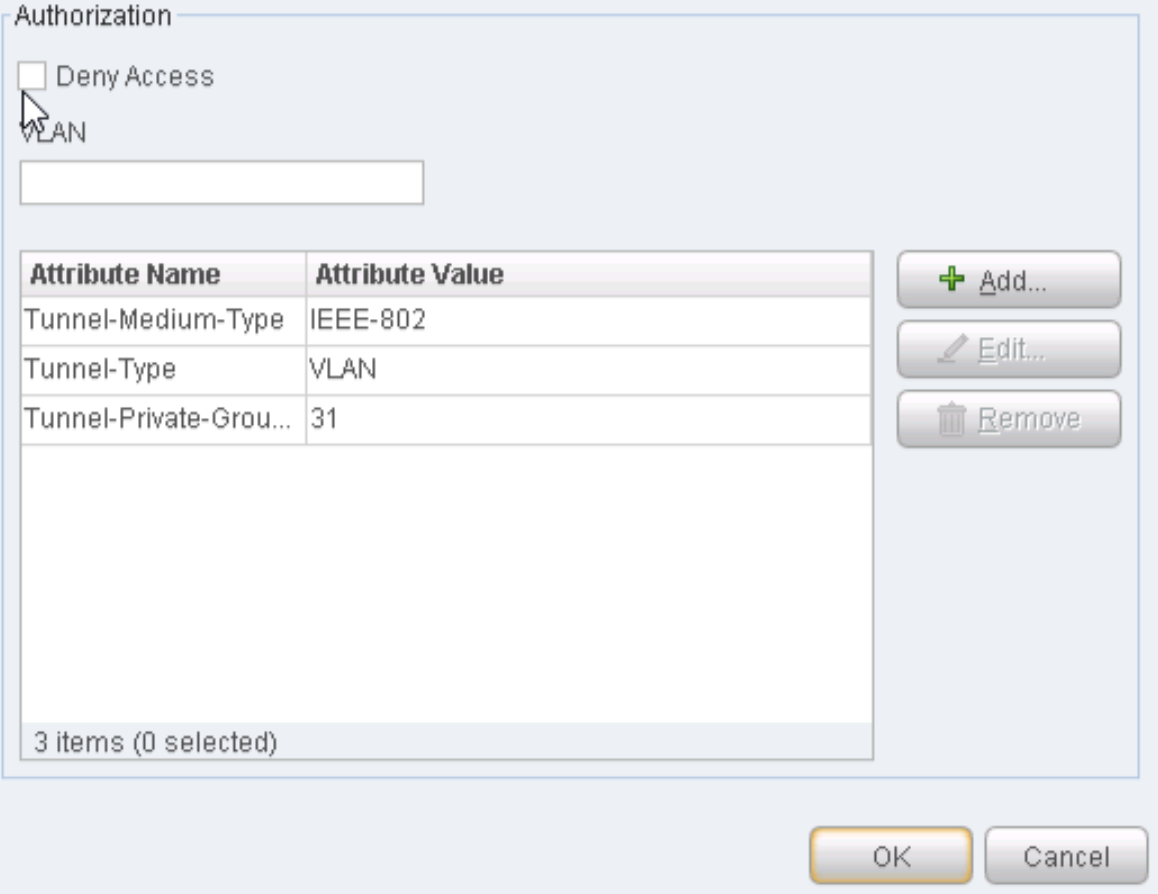
In this use case, the infected end user is quarantined into the user vlan VLAN31 on the EX4300 switch. The EX4300 switch has enabled ForeScout CounterACT and has 802.1X authentication enabled on ge-0/0/19. The end user authenticates to the network using 802.1X.
The following events occur in this use case:
- The infected endpoint is detected by ATP Cloud.
- Policy Enforcer downloads the infected host feed, and then enforces the infected host policy through CounterACT.
- CounterACT queries the server for endpoint details for the infected host’s IP address.
- CounterACT sends a message to the EX4300 switch, telling it to terminate the session by blocking or quarantining vlan31.
- Enforcement occurs on the EX4300 switch on which the endpoint is authenticated.
- CounterACT inventories the applications, services, and processes running on the device, checks the OS version and registry settings, and verifies the presence of security agents. As a result, a complete profile of the device and its security status is obtained.
Install and Configure Junos Space, Security Director, and Log Collector
This section shows how to install and configure Junos Space, Security Directory, and Log Collector for this use cases. These applications are used in this use case to provide the centralized policy and management application for consistent network security policies.
This section covers the following procedures:
- Install Junos Space, Security Director, and Log Collector
- Configure Basic Junos Space Networking
- Install the required DMI Schemas on Security Director
Install Junos Space, Security Director, and Log Collector
- Download the Junos Space Network Management Platform image from https://www.juniper.net/support/downloads/?p=space#sw.
- Install Junos Space using the instructions at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos-space17.2/information-products/pathway-pages/junos-space-virtual-appliance-pwp.html.
- Install Junos Security Director using the instructions at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos-space17.2/topics/task/multi-task/junos-space-sd-log-collector-installing.html.
- Install Log Collector using the instructions at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos-space17.2/topics/task/multi-task/junos-space-sd-log-collector-installing.html.
Configure Basic Junos Space Networking
To configure basic Junos Space Networking in this use case:
- Configure relevant routes, netmask, gateway, DNS, and NTP so that all components except Log Collector can connect to the Internet.
- Ensure all components are in same time zone.
- Ensure that SSH is enabled.
- Ensure that Security Director can connect to the ATP Cloud server, Policy Enforcer, and all devices.
For additional information on configuring Junos Space, see Junos Space Network Management Platform Documentation.
Install the required DMI Schemas on Security Director
Download and install the correct matching Junos OS schemas to manage the Juniper Networks’ devices:
- Add the DMI schemas for the Juniper Networks’ devices using the instructions at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos-space17.2/platform/topics/task/operational/dmi-schemas-adding-updating.html.
- Ensure that device software version and schema version match for all managed devices (SRX Series and EX Series devices).
Install and Configure SRX Series, EX Series, and QFX Series Devices
To install and configure vSRX virtual firewalls, EX Series switches, and QFX Series switches for this use case:
Install and Configure Microsoft Windows Server and Active Directory
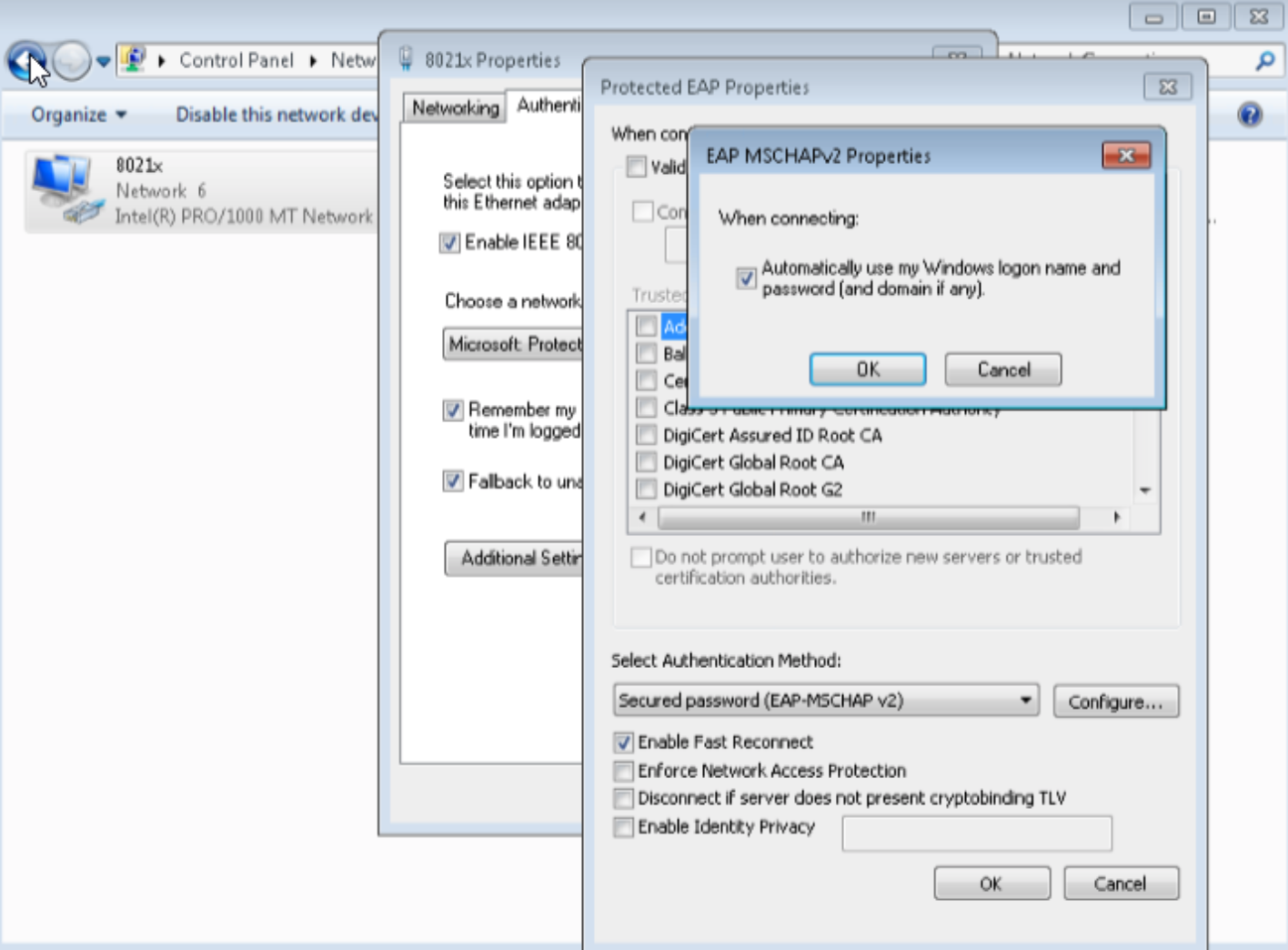
Because ForeScout CounterACT does not have a local user database to use for 802.1X authentication, you must install and configure a Windows Server 2008R2 with Active Directory.
- To set up and configure Windows Server 2008R2, click https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/iis/install/installing-iis-7/install-windows-server-2008-and-windows-server-2008-r2.
- To set up and configure Active Directory, click https://www.petri.com/installing-active-directory-windows-server-2008.
- Create a user domain account to use later during 802.1X authentication.
Download, Deploy, and Configure Policy Enforcer Virtual Machine
To download, deploy, and configure the Policy Enforcer Virtual Machine:
- Download the Policy Enforcer virtual machine image from http://www.juniper.net/support/downloads/?p=sdpe to the management station where the vSphere client is installed.
- On the vSphere client, select File > Deploy OVF Template from the menu bar.
- Click Browse to locate the OVA file that was downloaded.
- Click Next and follow the instructions in the installation wizard.
- Once the installation is complete, log in to the virtual
machine using
rootandabc123as the username and password, respectively. - Configure the network settings, NTP information, and customer information, and complete the wizard.
For more detailed instructions, see https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/release-independent/policy-enforcer/topics/task/installation/policy-enforcer-vm-config.html.
Identify and Connect Policy Enforcer to Security Director
To identify and connect Policy Enforcer to Security Director:
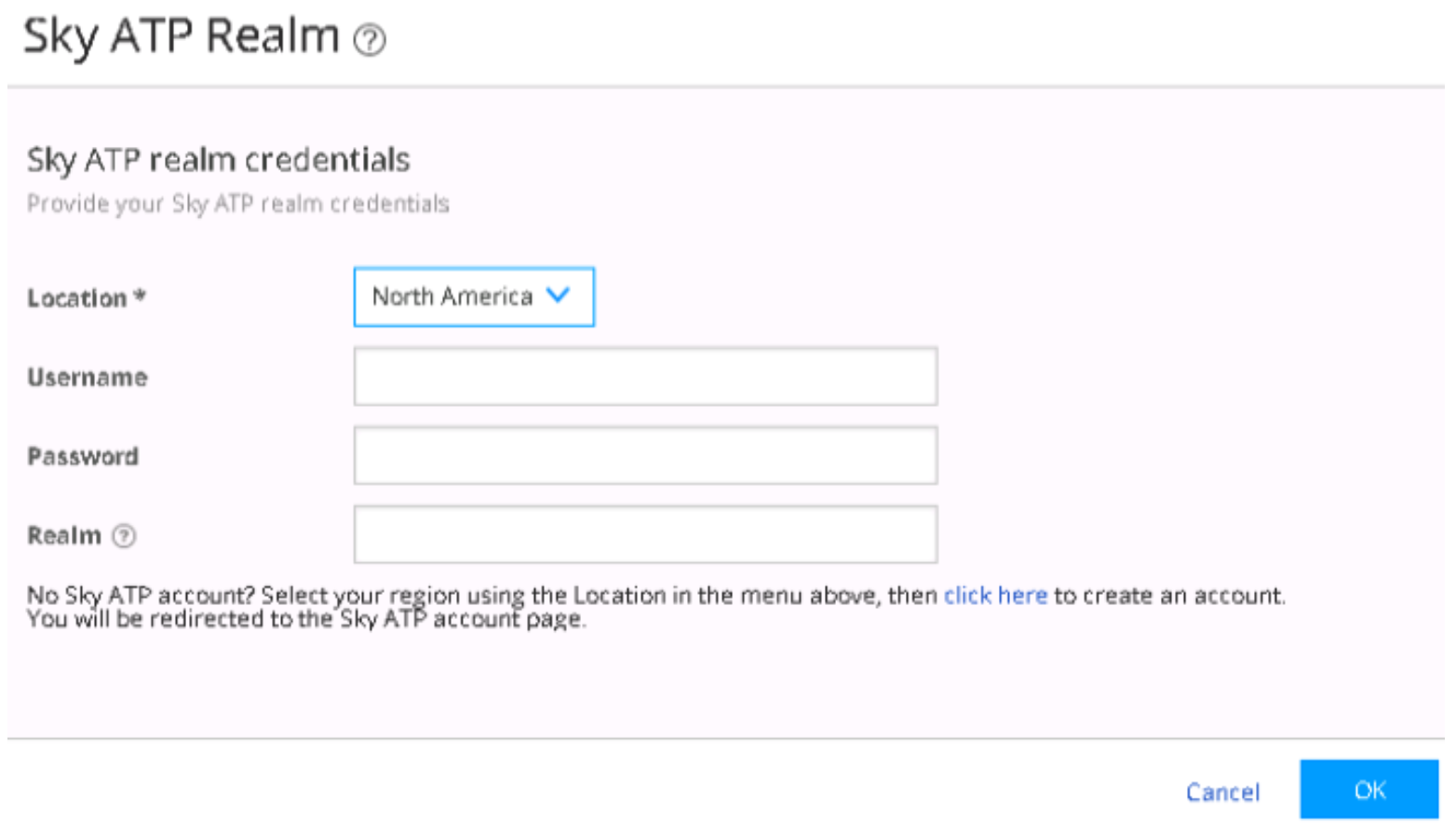
Obtain an ATP Cloud license and Create an ATP Cloud Web Portal Account
To obtain an ATP Cloud license and create an ATP Cloud Web Portal account:
Install Root CA on the ATP Cloud Supported SRX Series Devices
This section is required only if you are enabling HTTPS inspection as part of a malware profile or threat prevention policy.
This section covers the following topics:
- Generate Root CA Certificate using Junos OS CLI or OpenSSL on a UNIX Device
- Configure a Certificate Authority Profile Group
- Export and Import Root CA Certificate into a Web Browser
Generate Root CA Certificate using Junos OS CLI or OpenSSL on a UNIX Device
Use only one of these options.
To generate a root CA certificate using the Junos OS CLI on the SRX device:
Or
To generate a root CA certificate using OpenSSL on a UNIX device:
Generate a PKI public key or private key pair for a local digital certificate.
% openssl req -x509 -nodes -sha256 -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout ssl-inspect-ca.key -out ssl-inspect-ca.crt
Copy the key pair onto the SRX device or devices.
On the SRX device(s), import the key pair.
user@host> request security pki local-certificate load key ssl-inspect-ca.key filename ssl-inspect-ca.crt certificate-id ssl-inspect-ca
Apply the loaded certificate as root-ca in the SSL proxy profile.
user@host> set services ssl proxy profile ssl-inspect-profile root-ca ssl-inspect-ca
Configure a Certificate Authority Profile Group
To configure a Certificate Authority (CA) profile group.
Export and Import Root CA Certificate into a Web Browser
To export and import the Root CA Certificate into a web browser:
Or
If you are using a UNIX device, import the certificate into the browser:
% sudo cp ssl-inspect-ca.crt /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/ ssl-inspect-ca.crt % sudo update-ca-certificates
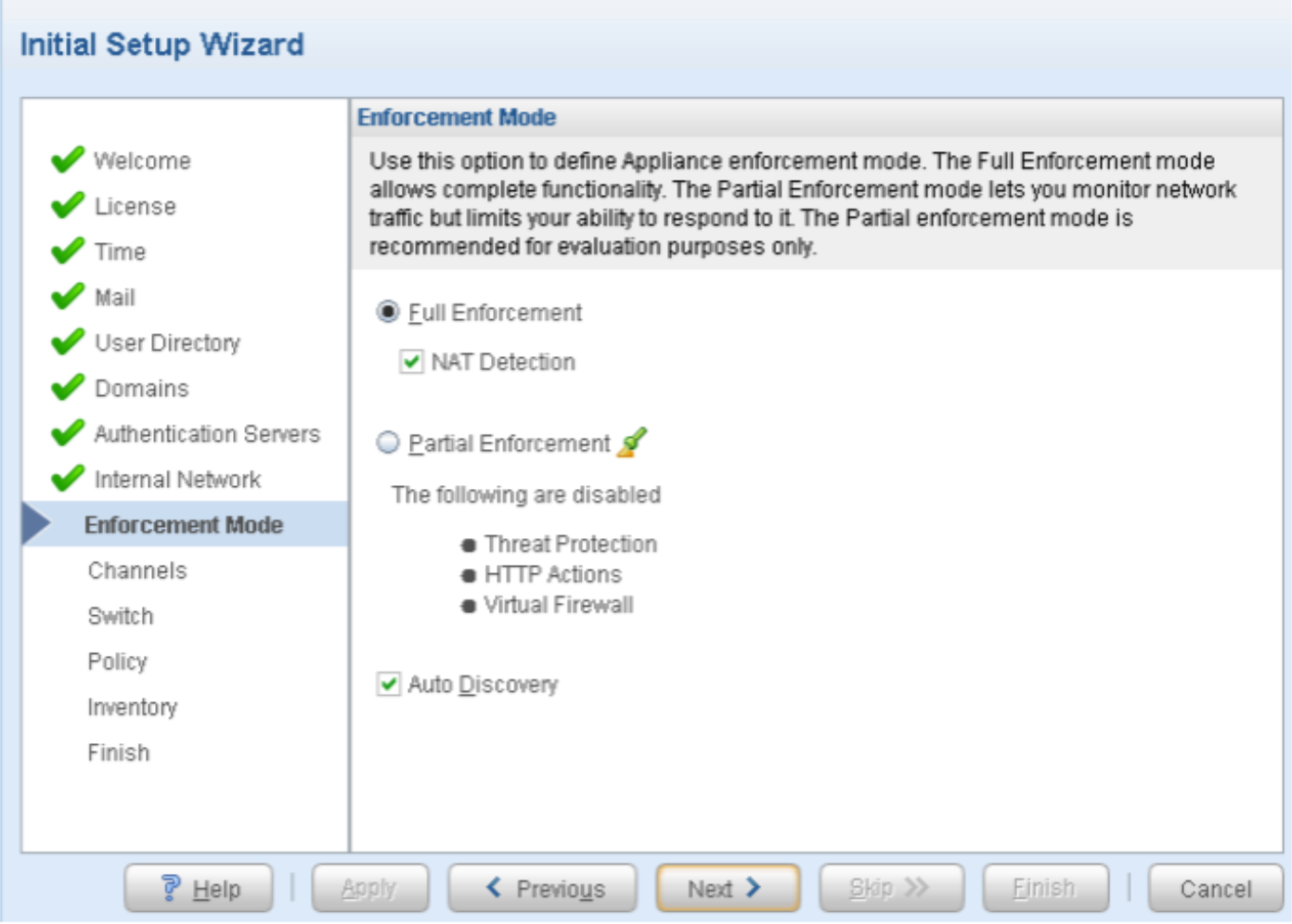
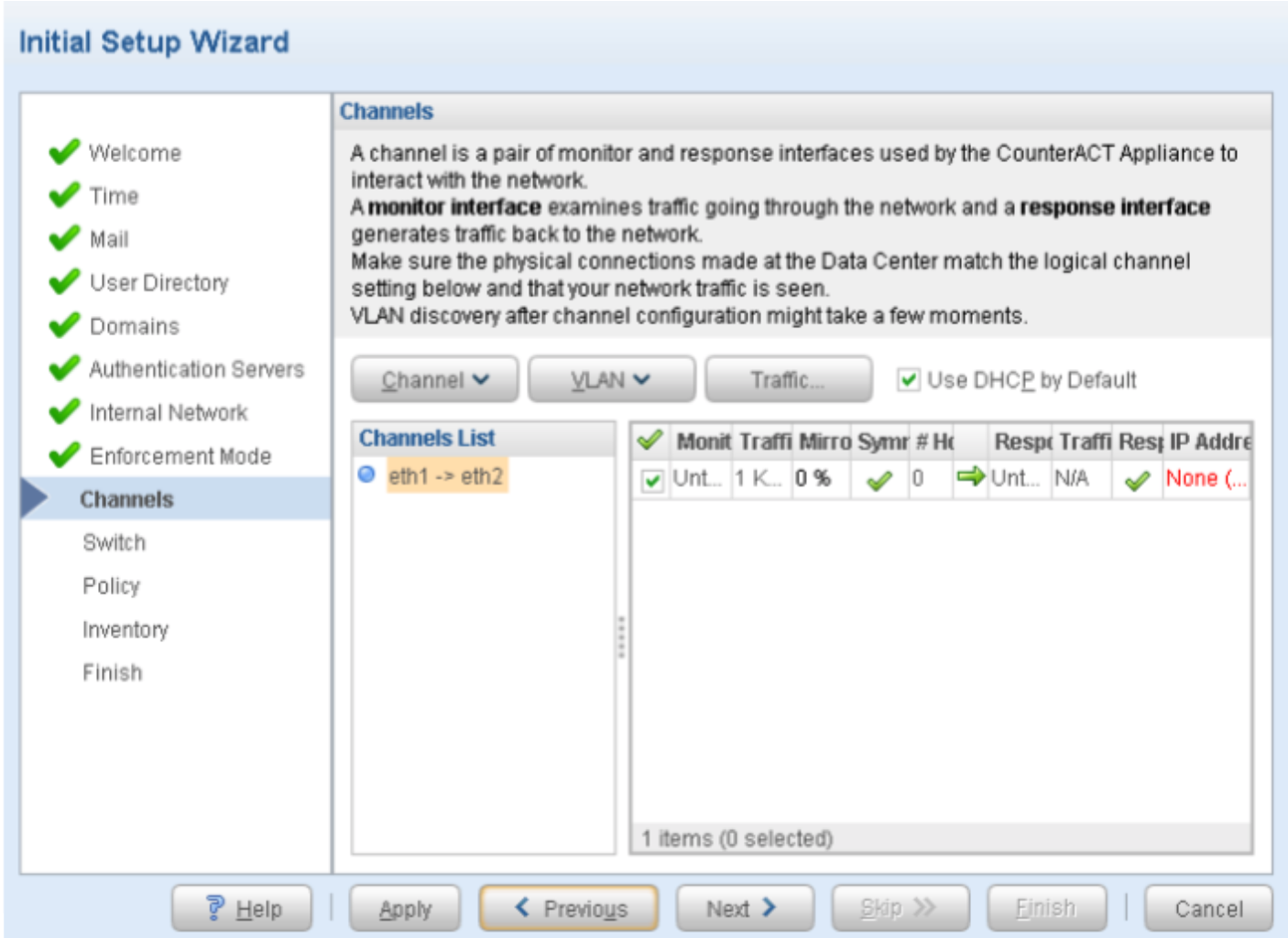
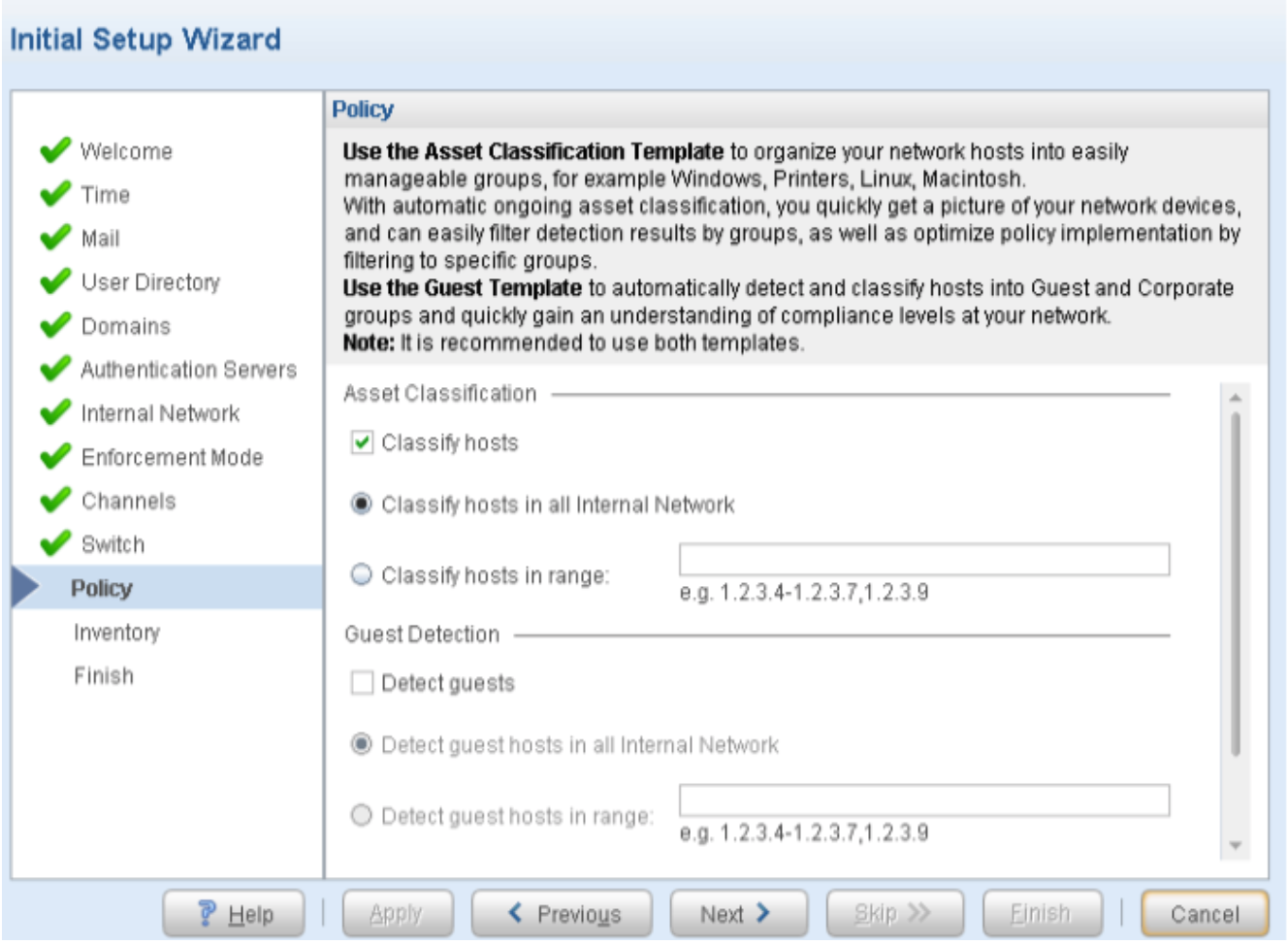
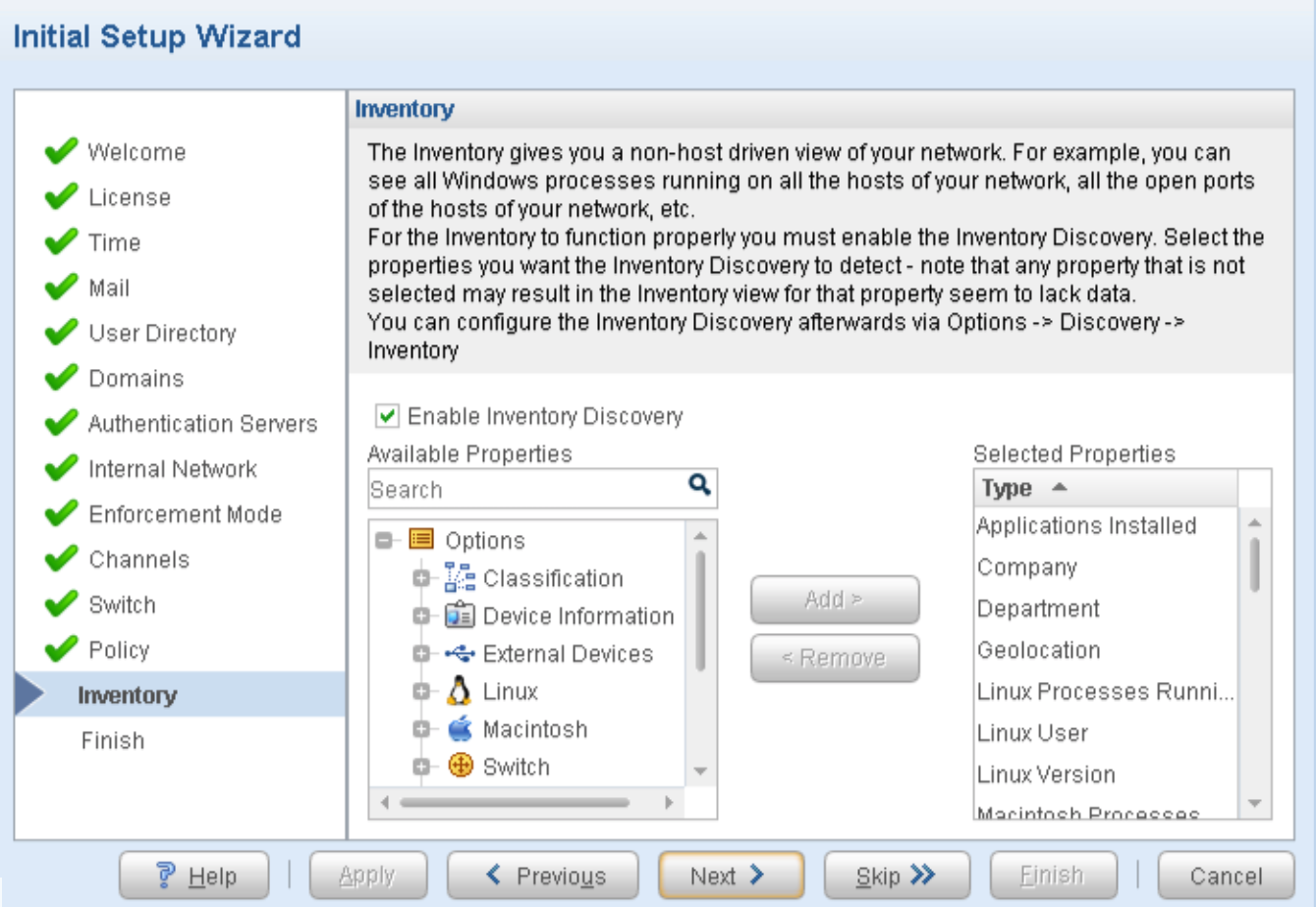
Download, Deploy, and Configure the ForeScout CounterACT Virtual Machine
This section covers the following topics:
- Prerequisite Tasks
- Install and Configure CounterACT Software
- Install and Configure CounterACT Plugins
- Configure User Directory Plugin
- Configure Switch Plugin
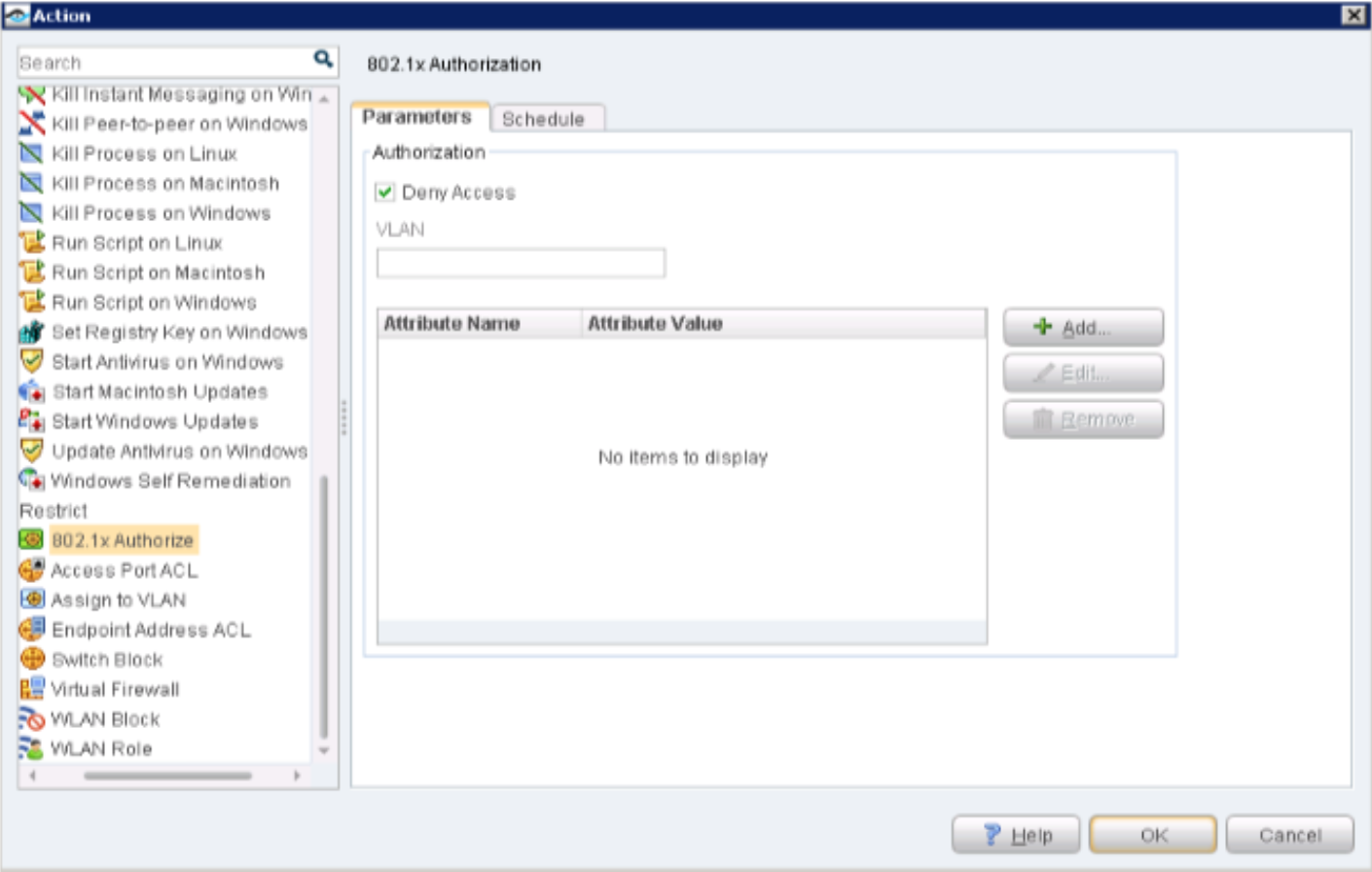
- Configure 802.1X Plugin
- Configure Windows 7 Supplicant
- Test and Troubleshoot 802.1X Authentication
- Configure Data Exchange Plugin
- Configure Web API Plugin
- Verify Plugins
- Configure Automated Threat Remediation Policies
Prerequisite Tasks
Before you begin this procedure, complete the following tasks:
Install and Configure CounterACT Software
To install and configure ForeScout CounterACT software:
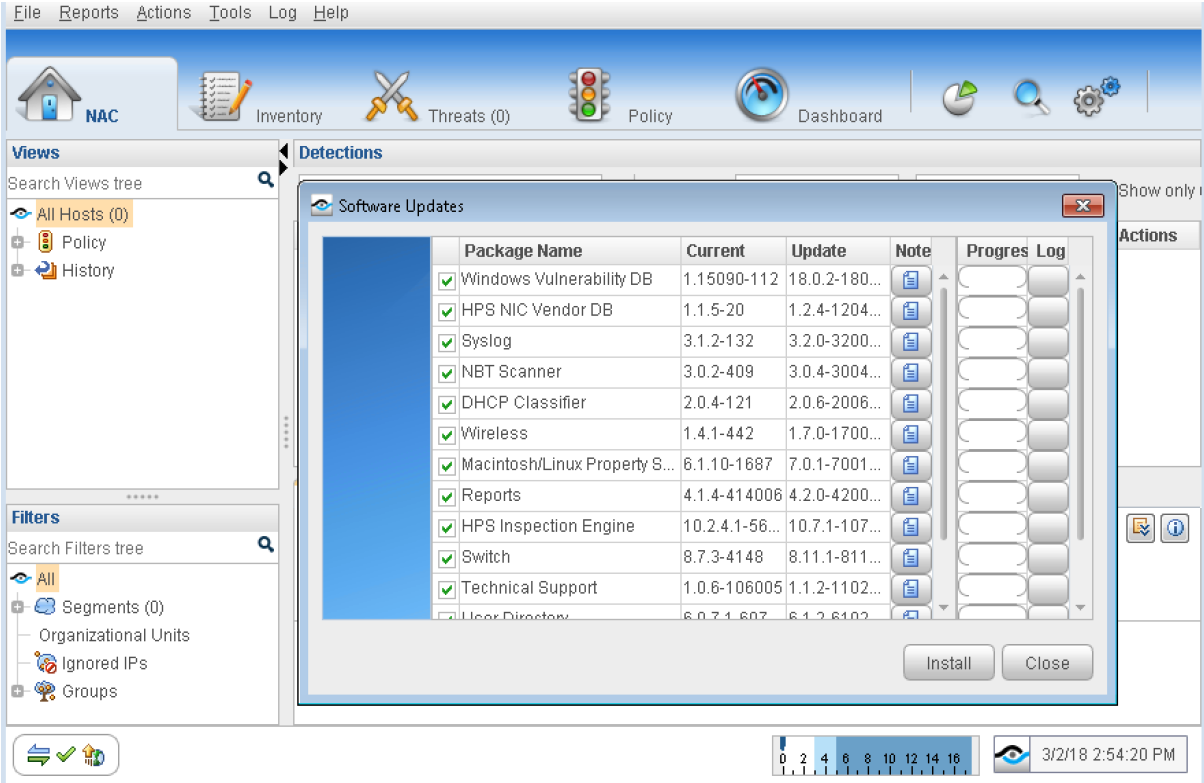
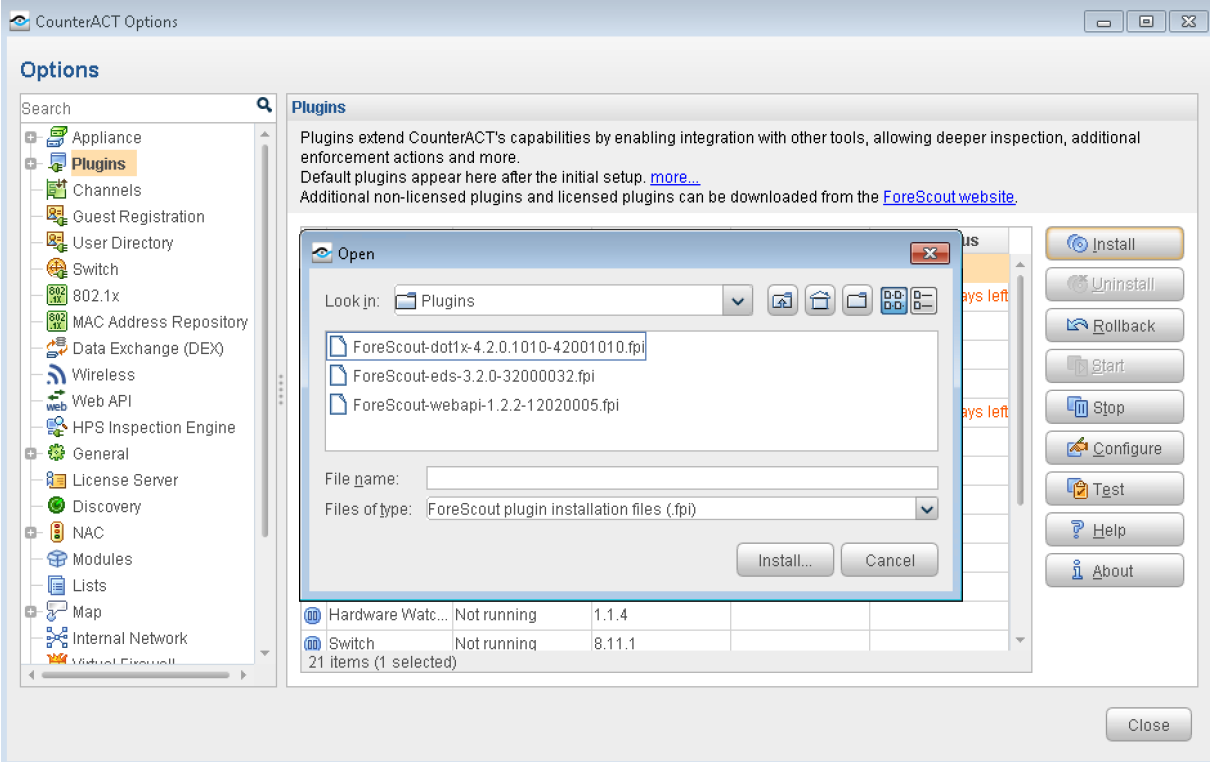
Install and Configure CounterACT Plugins
CounterACT is delivered with several bundled plugins:
ForeScout-dot1x-4.2.0.1010-42001010.fpi
ForeScout-eds-3.2.0-32000032.fpi
ForeScout-webapi-1.2.2-12020005.fpi
These plugins link CounterACT to the network infrastructure (switches, domain servers, and user directories), and provide core endpoint detection and management functionality, including a comprehensive set of host properties and actions.
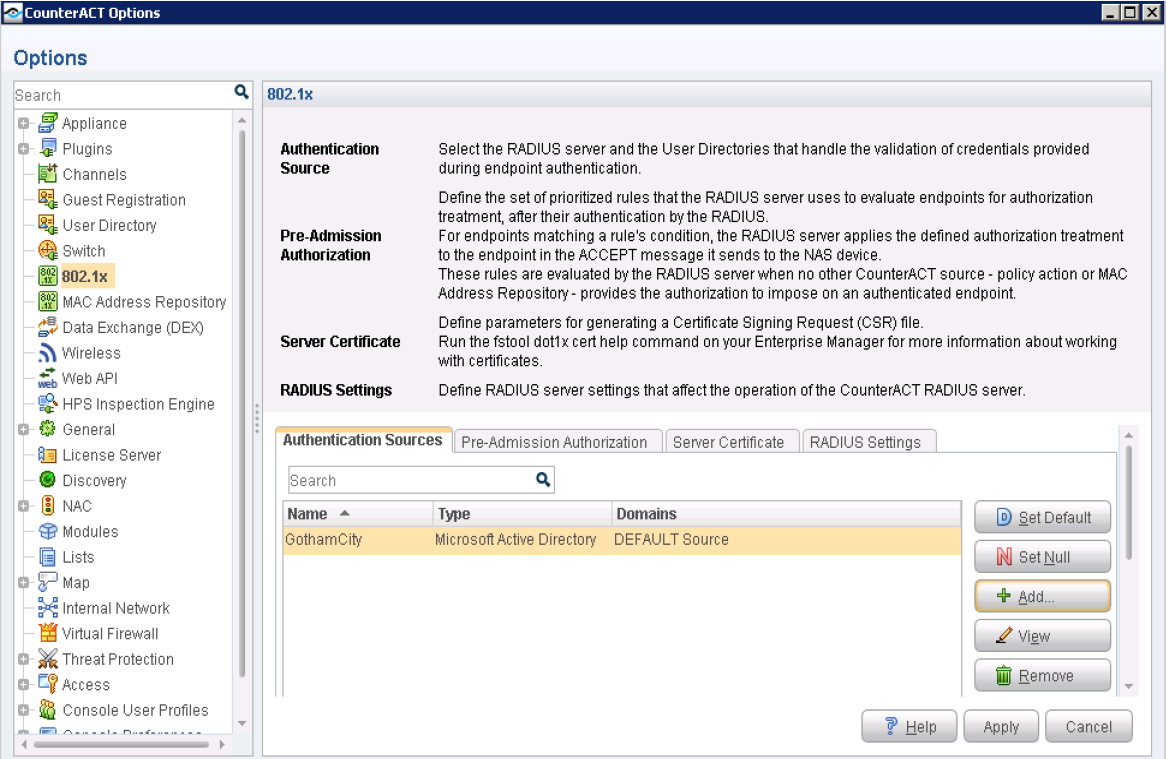
Configure User Directory Plugin
The User Directory Plugin resolves endpoint user details and performs endpoint authentication through authentication and directory servers.
To configure the User Directory servers:
Configure Switch Plugin
The Switch Plugin queries each switch for:
Switch port attributes and information about connected endpoints.
ARP table to discover new endpoints connected to the switch.
The information can be obtained via CLI and/or SNMP.
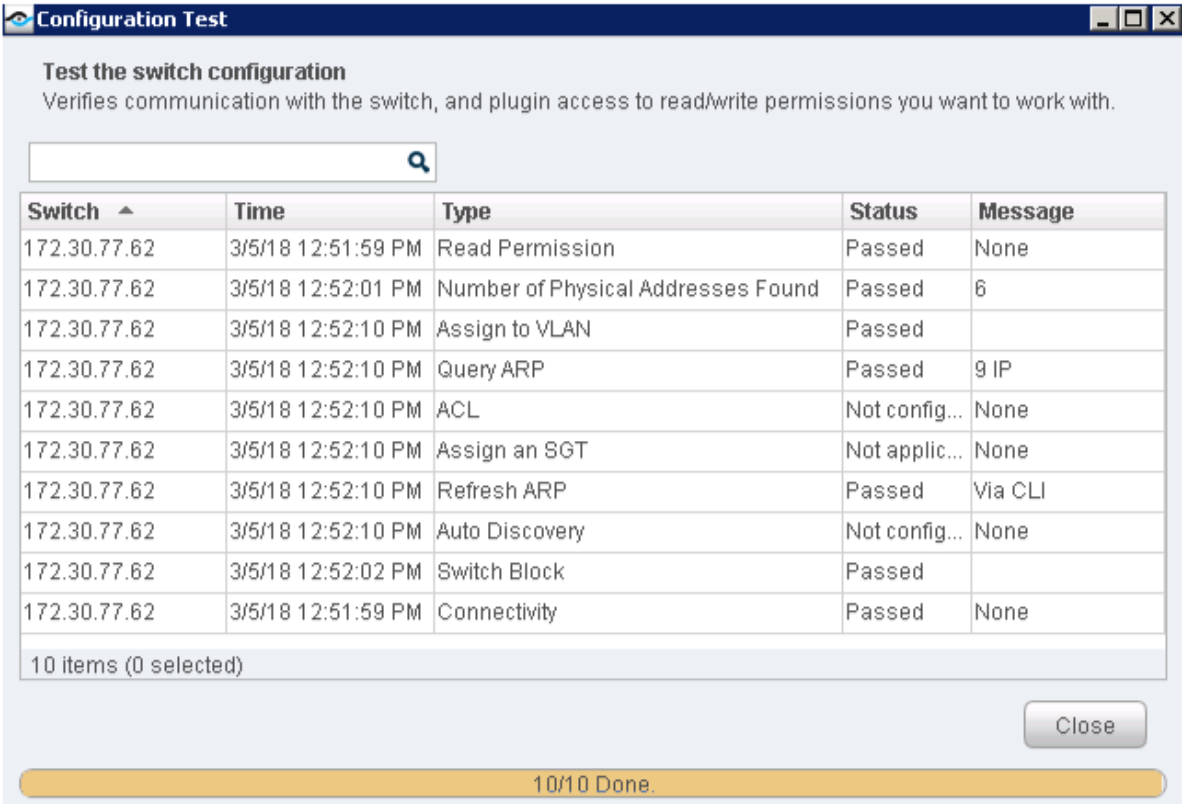
To configure the Switch Plugin for the EX4300 switch:
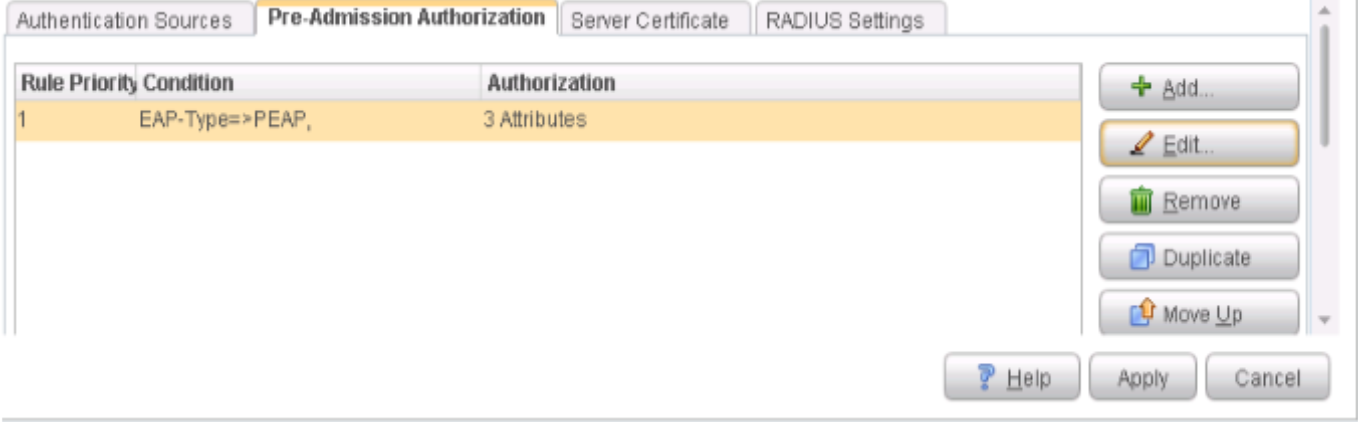
Configure 802.1X Plugin
The 802.1X Plugin enables CounterACT to authenticate 802.1X switch or wireless connections to the network. The plugin is compatible with the IEEE 802.1X specification and the RADIUS authentication protocol.
To configure the 802.1X Plugin:
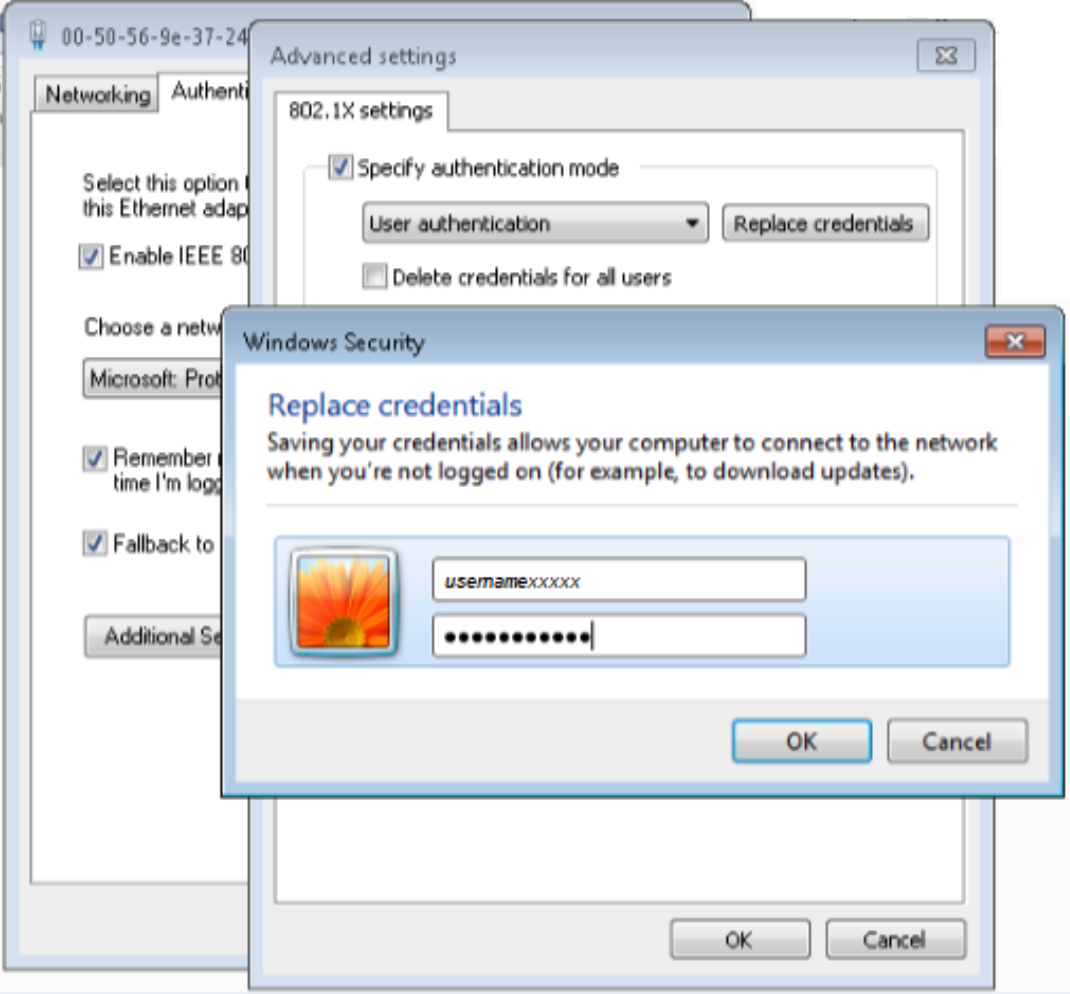
Configure Windows 7 Supplicant
You should have already installed the Microsoft Windows Server and Active Directory. Click Install and Configure Microsoft Windows Server and Active Directory to review the instructions.
To configure the Windows 7 Supplicant:
Test and Troubleshoot 802.1X Authentication
To test the 802.1X authentication against ForeScout CounterACT:
To troubleshoot 802.1X authentication issues:
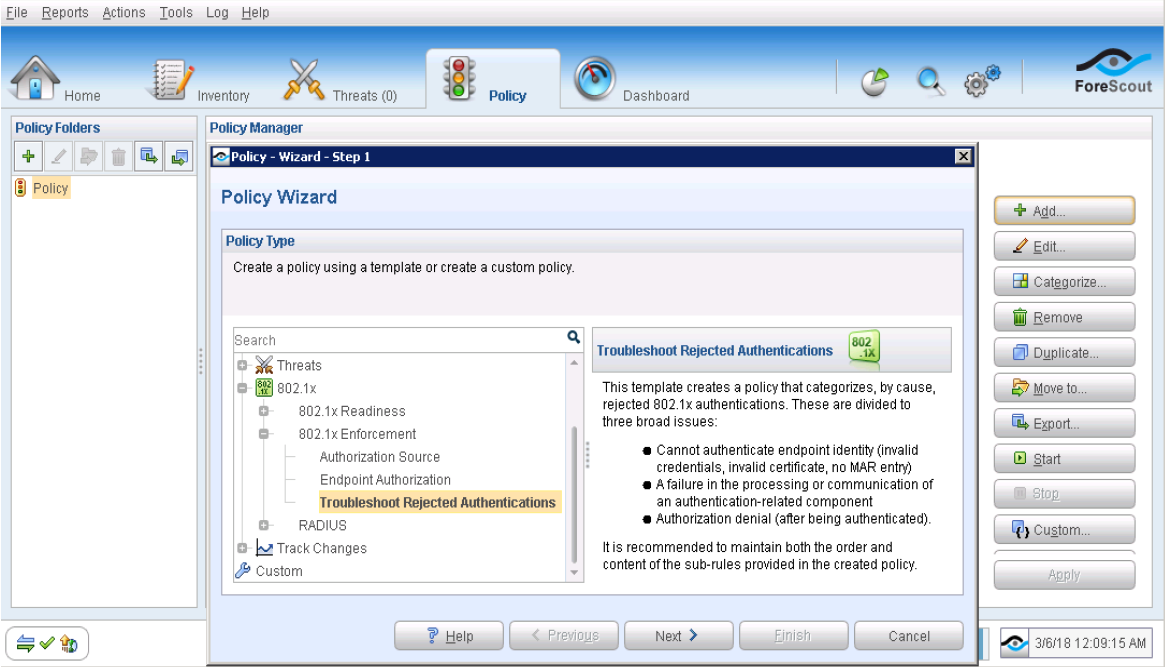
From the ForeScout CounterACT Console, click the Policy tab and create a policy using the Troubleshoot Rejected Authentications template (listed under 802.1X Enforcement).
Start your policy to troubleshoot the issue.
To view logs from the ForeScout CounterACT Console:
Select Log > Policy Log. From the Policy Log page, enter your Windows 7 supplicant’s MAC or IP address.
Figure 38: Policy Log Settings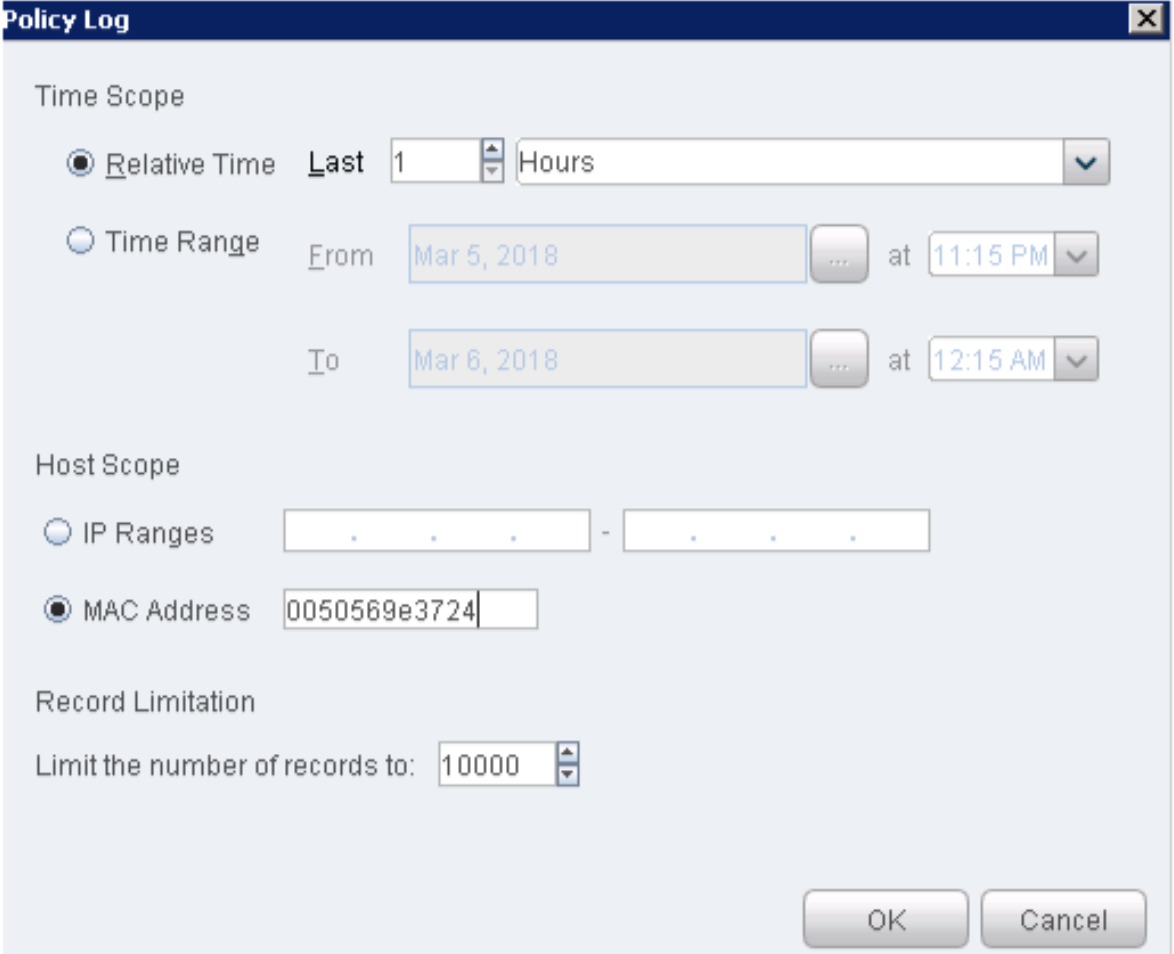
Click OK. The policy log files appear.
Figure 39: Policy Log Files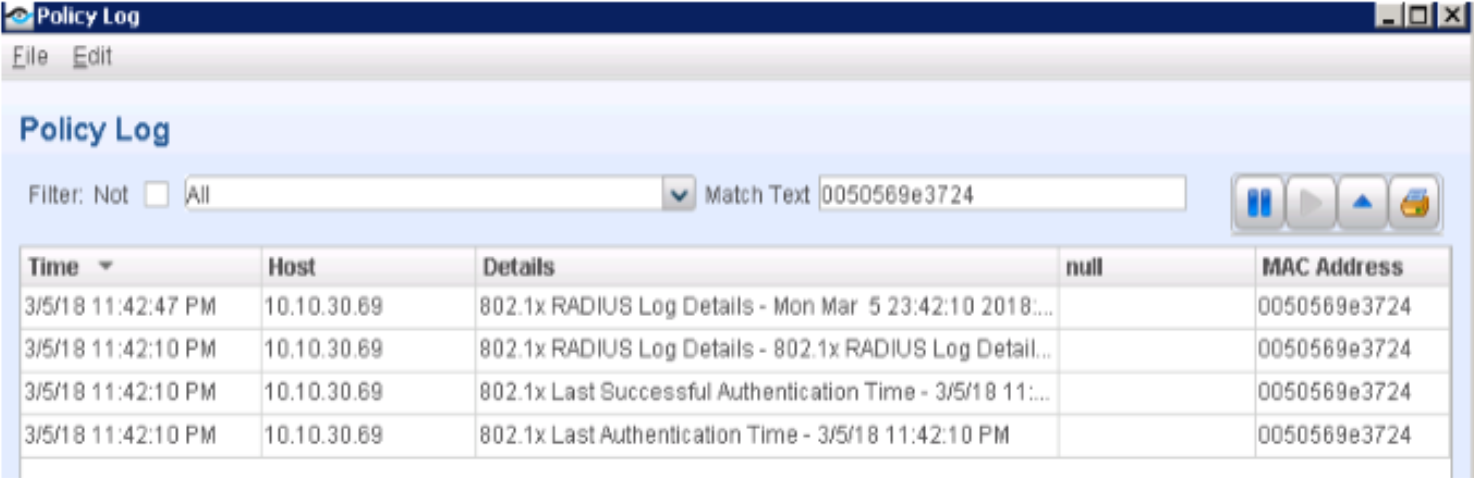
If 802.1X authentication works and your Windows 7 supplicant obtains an IP address from the DHCP server running on SRX, you can then generate some traffic to verify that your Windows 7 supplicant (for example, 10.10.30.69) appears on the Host list under the Home tab.
Figure 40: Policy Log 802.1X Authentication Confirmation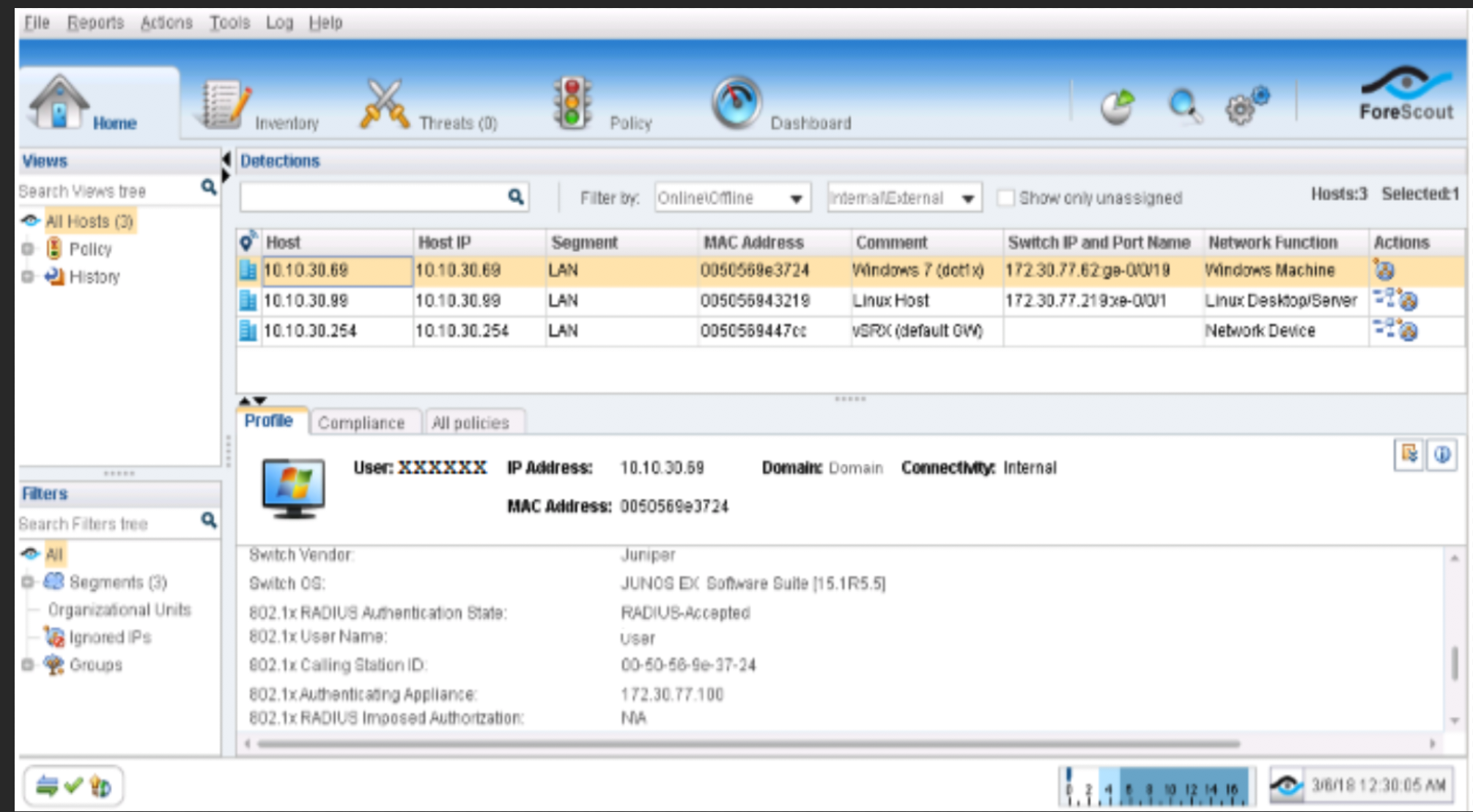 Note:
Note:Additionally, if you already configured the other host (Windows or Linux system) that is connected to the QFX switch and obtained an IP address from the DHCP server running on SRX, you can then generate some traffic for it, and the host address (for example, 10.10.30.99) will also appear on the Host list.
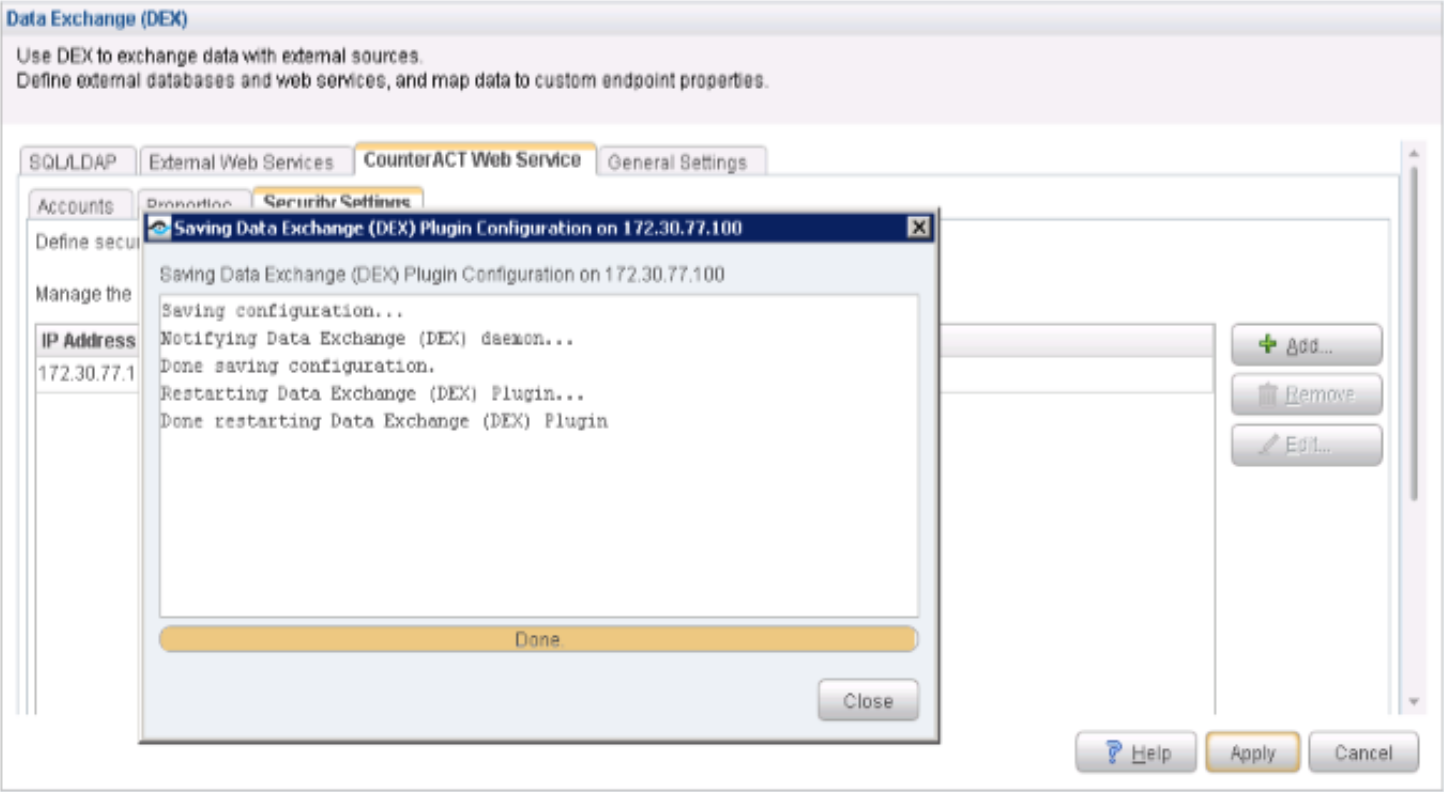
Configure Data Exchange Plugin
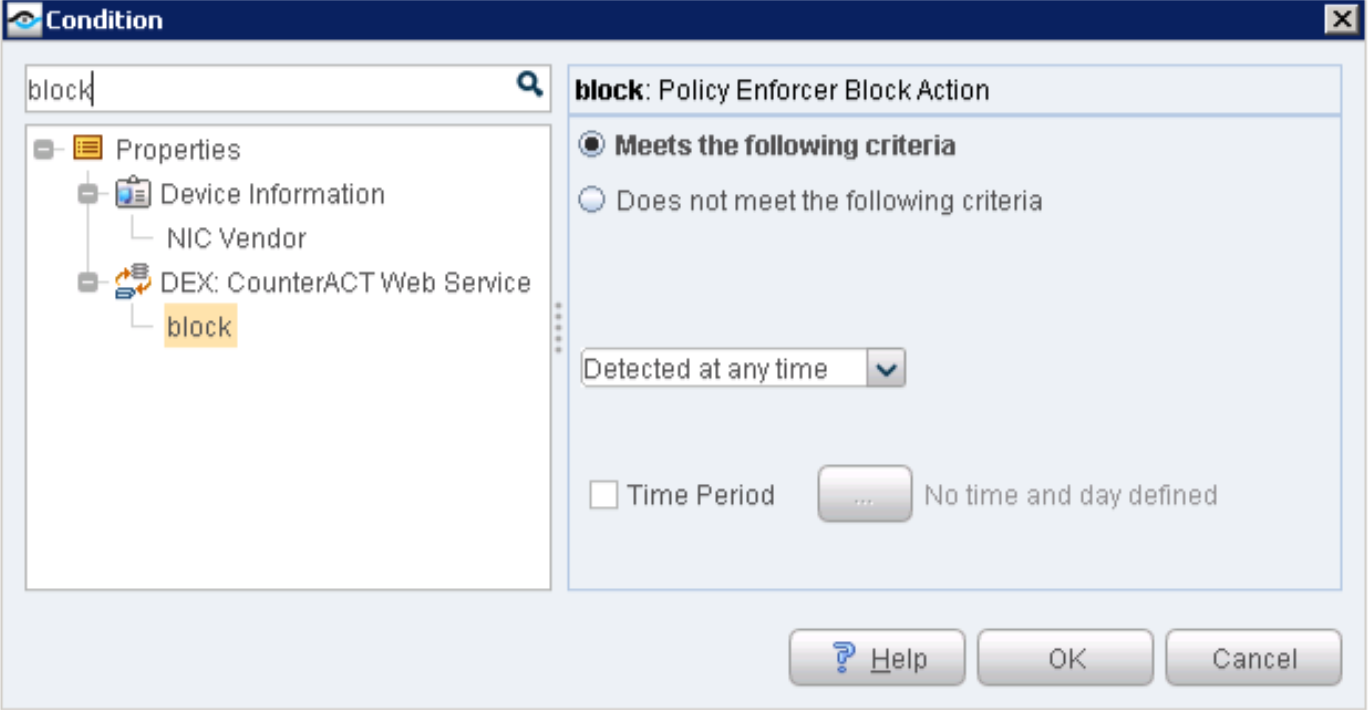
The Data Exchange (DEX) Plugin enables CounterACT to use web services to communicate with external entities. CounterACT queries external services and receives updates through the CounterACT web service hosted by the plugin. In this case DEX in conjunction with the ForeScout Connector will monitor PE for any communication.
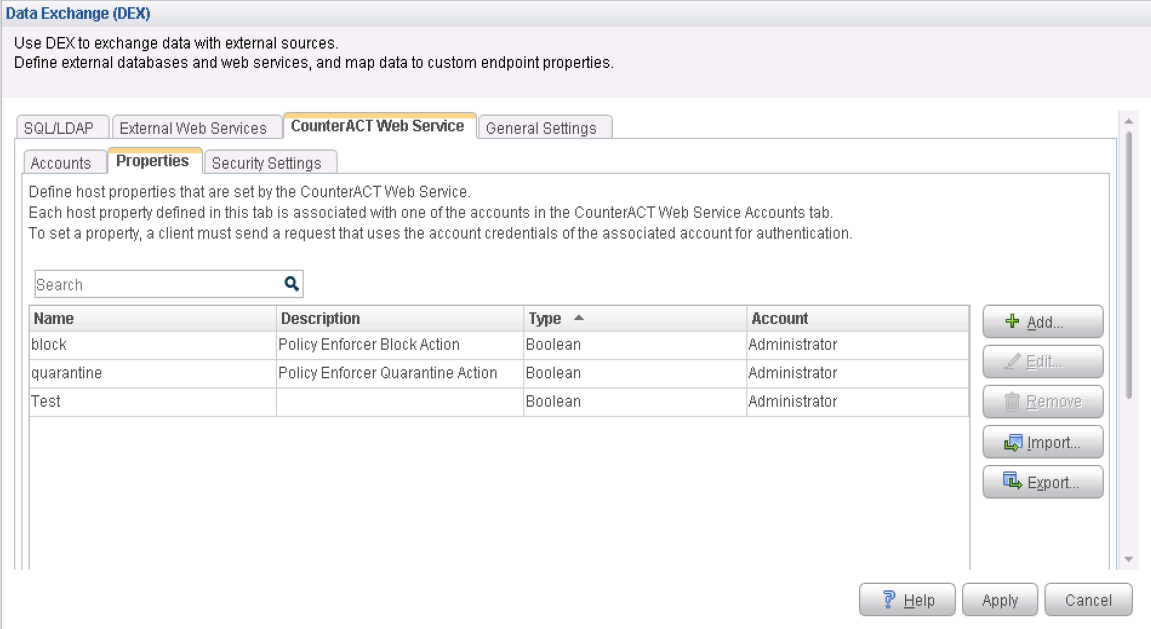
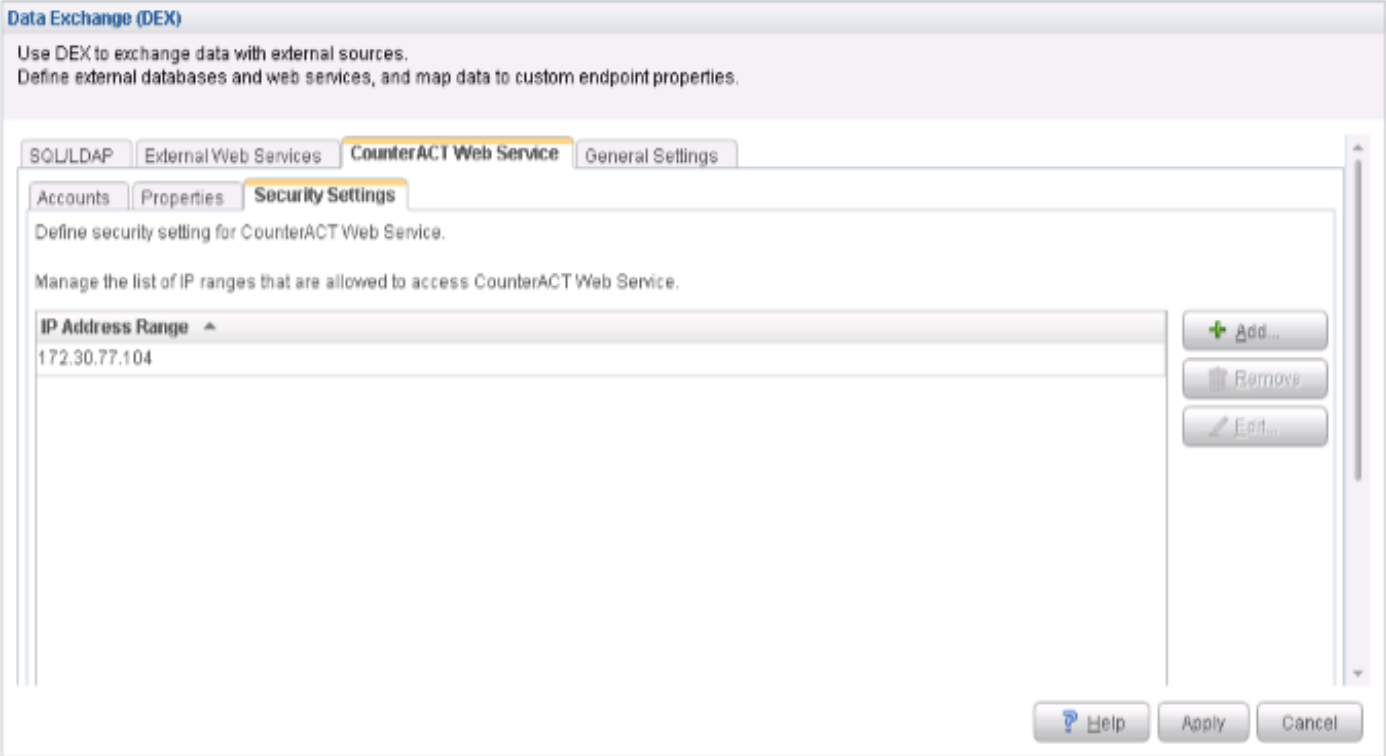
To configure the Data Exchange (DEX) Plugin:
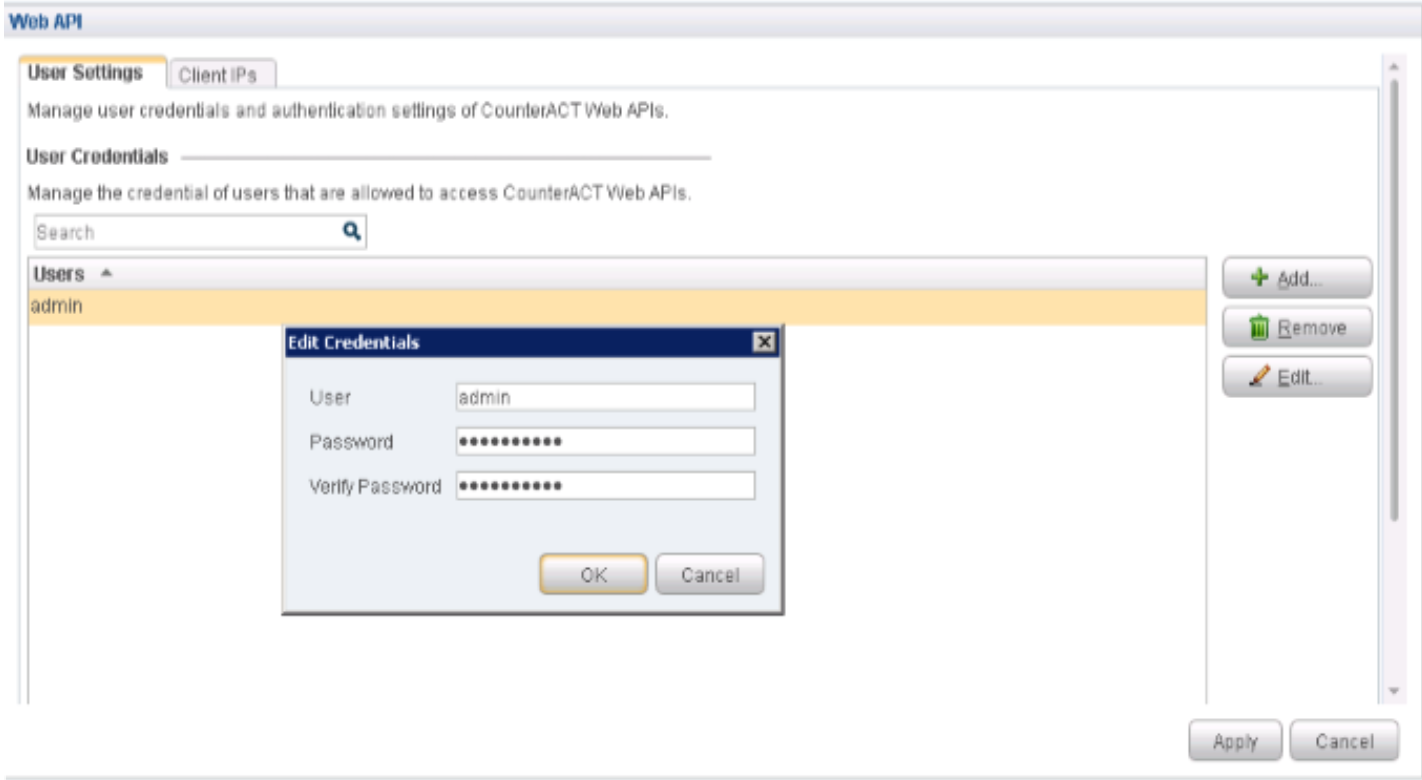
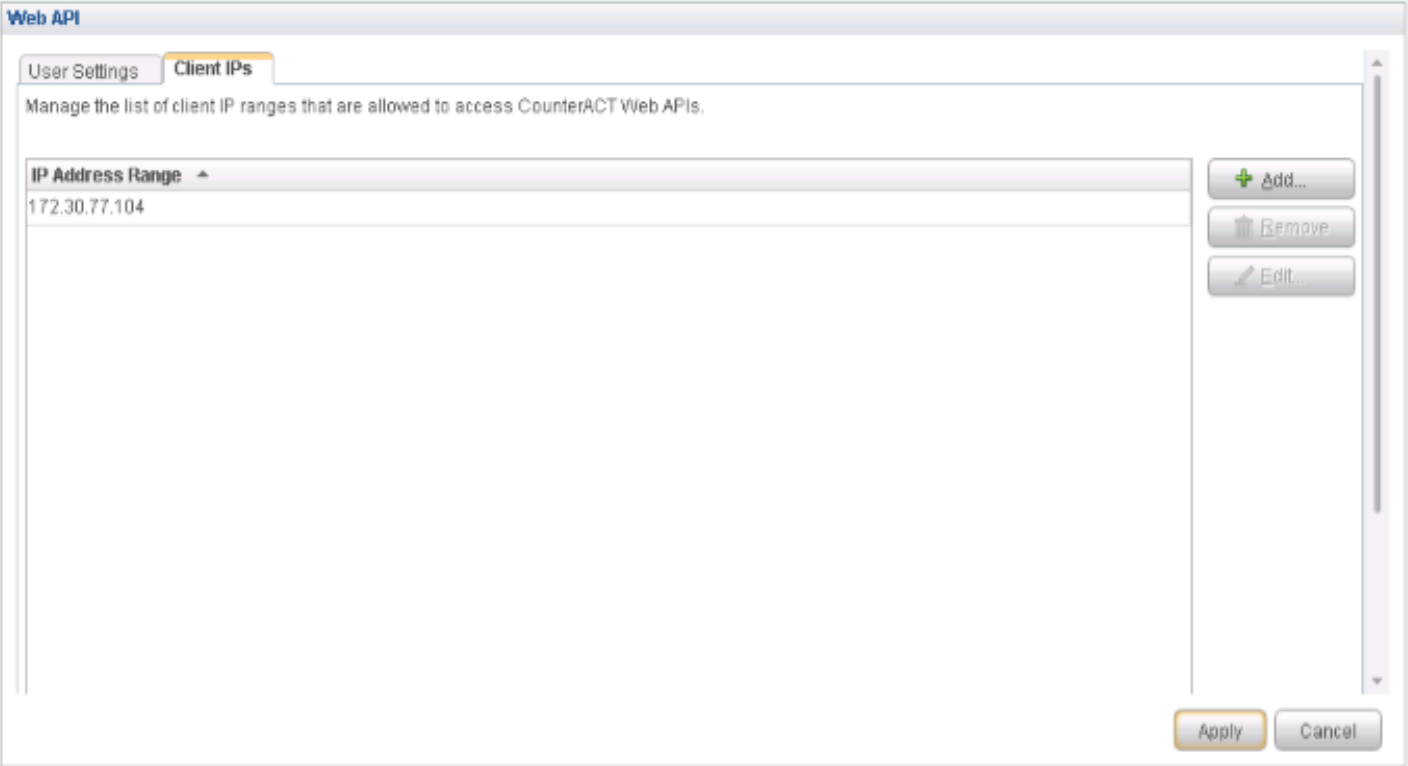
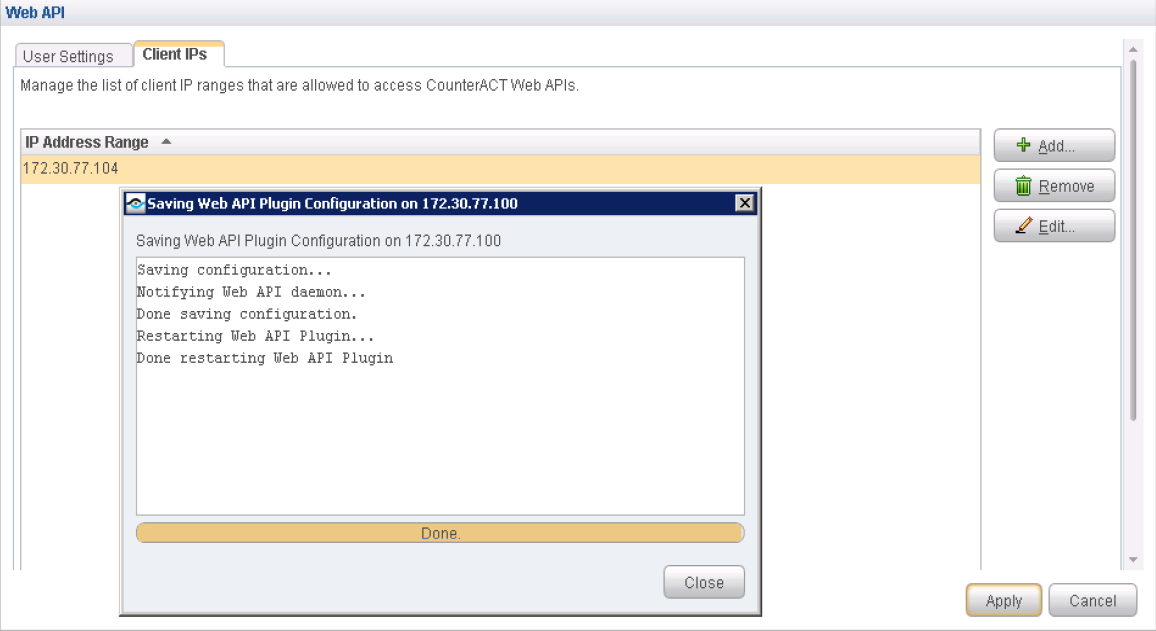
Configure Web API Plugin
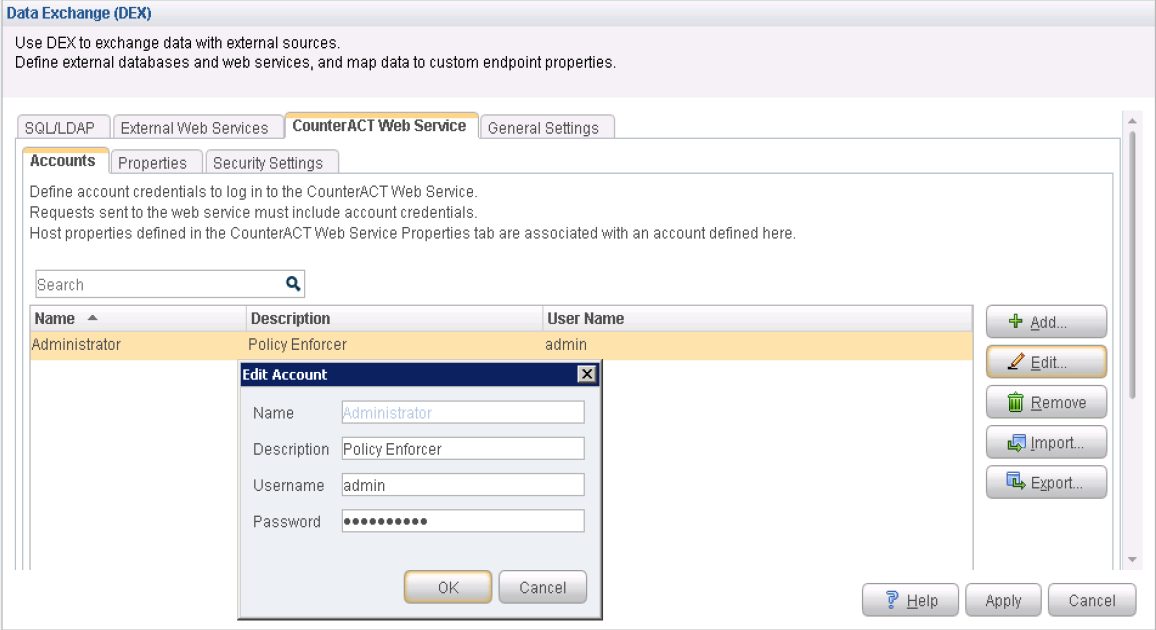
The Web API Plugin enables external entities to communicate with CounterACT using simple, yet powerful web service requests based on HTTP interaction. Configure the Web API Plugin to create an account for Policy Enforcer integration.
To configure the Web API Plugin:
Verify Plugins
To verify that all of the required plugins are running, select Tools > Options > Plugins. The Plugins page appears showing the status of each plugin.
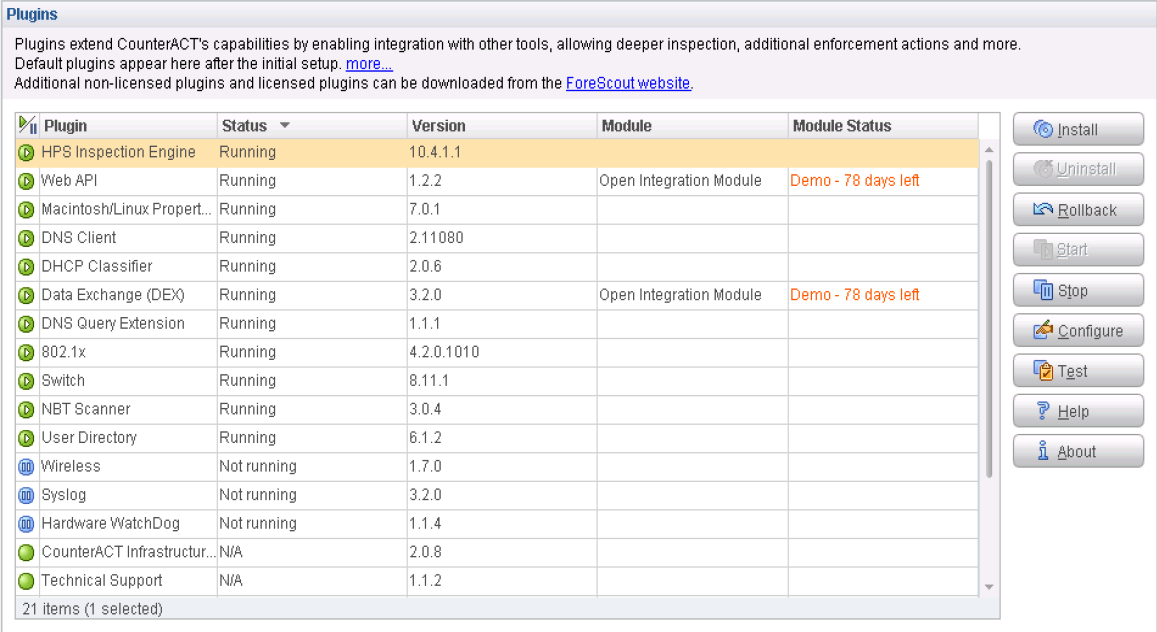
Configure Automated Threat Remediation Policies
Using Policy Manager, create these automated threat remediation policies:
NETCONF policies–used to connect hosts to the QFX switch.
802.1X policies–used to connect hosts to the EX4300 switch and used for 802.1X authentication.
To create an automated threat remediation NETCONF policy or 802.1X policy:
Configure the Policy Enforcer Connector for Third-Party Switches
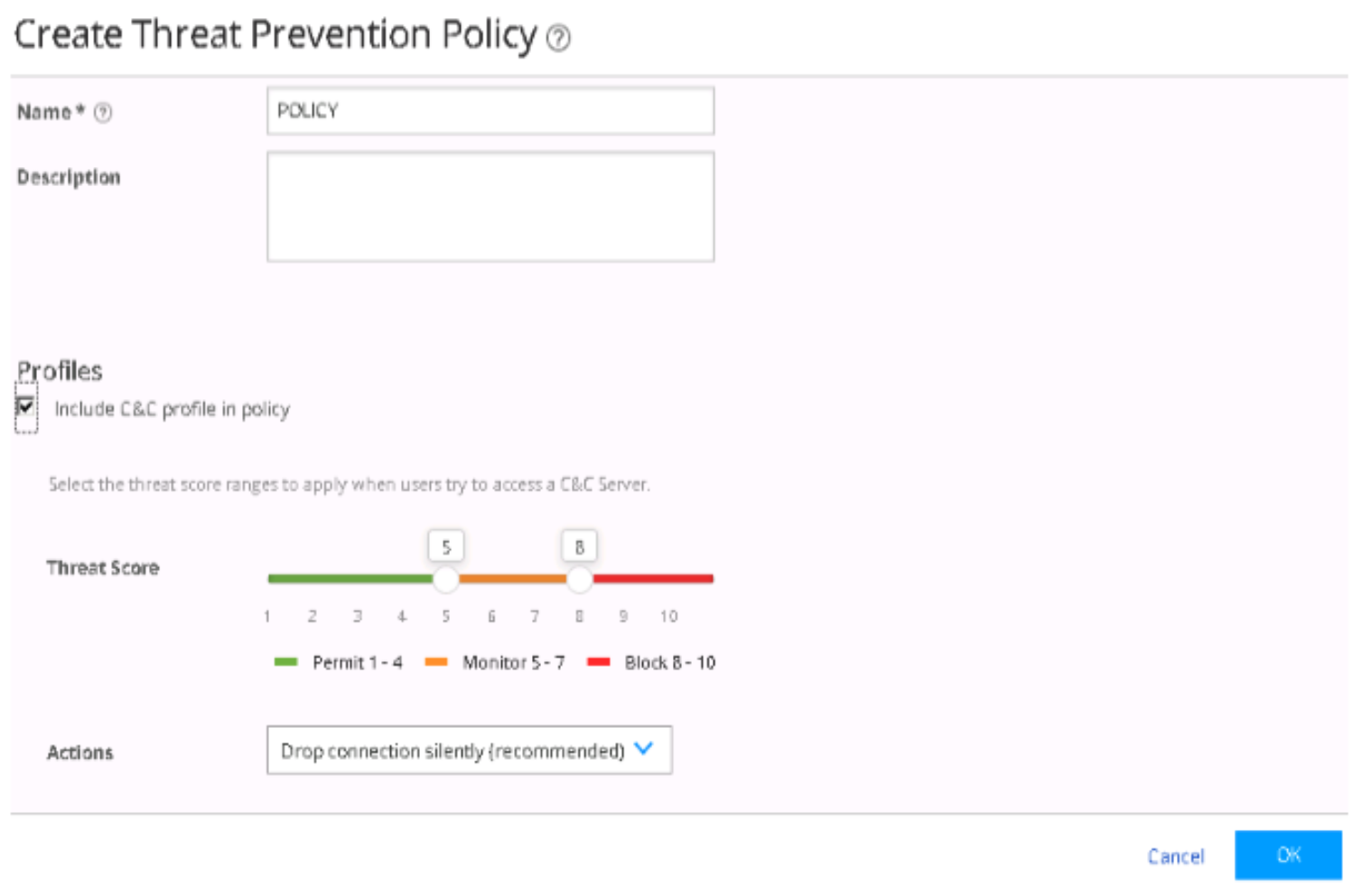
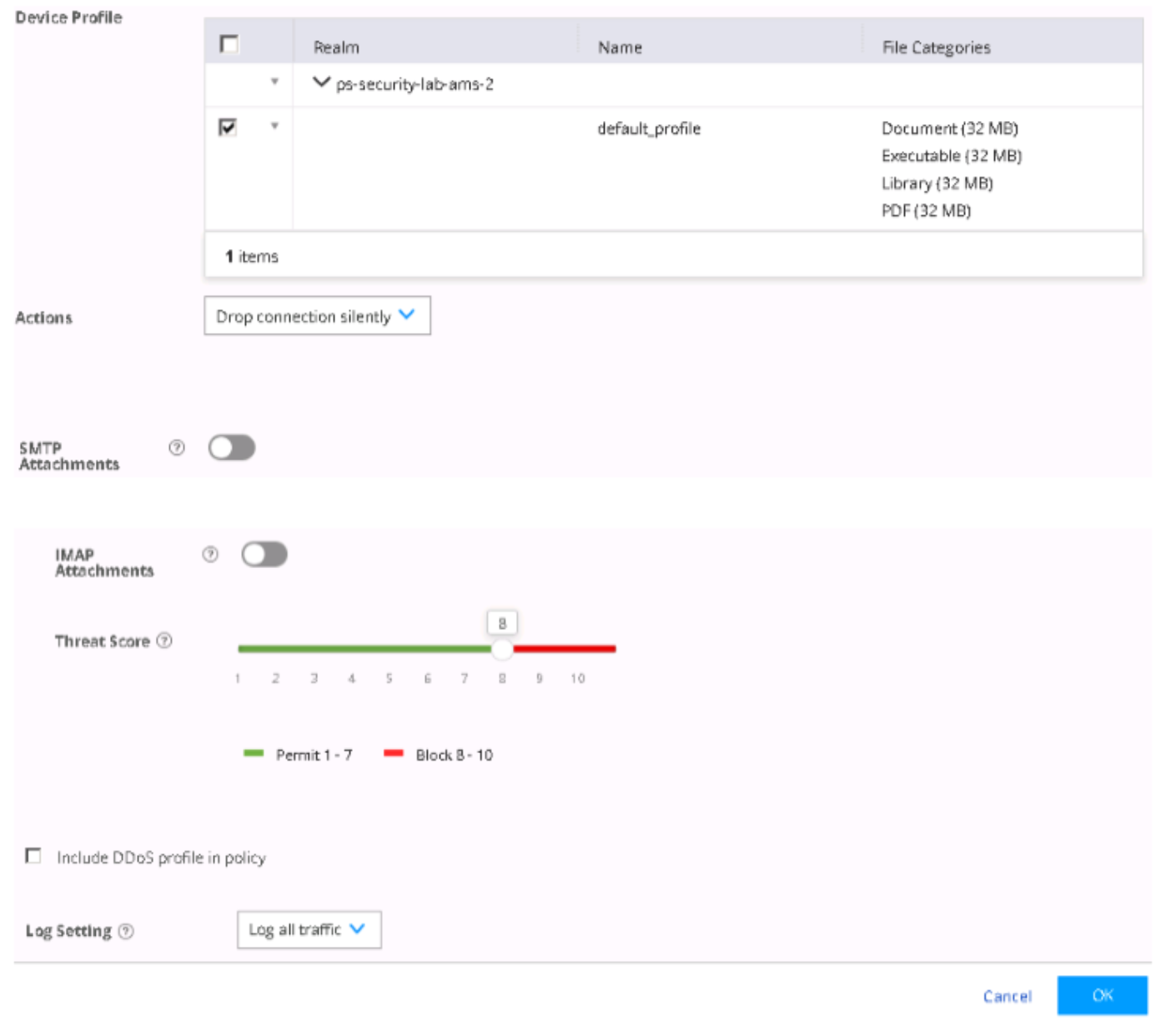
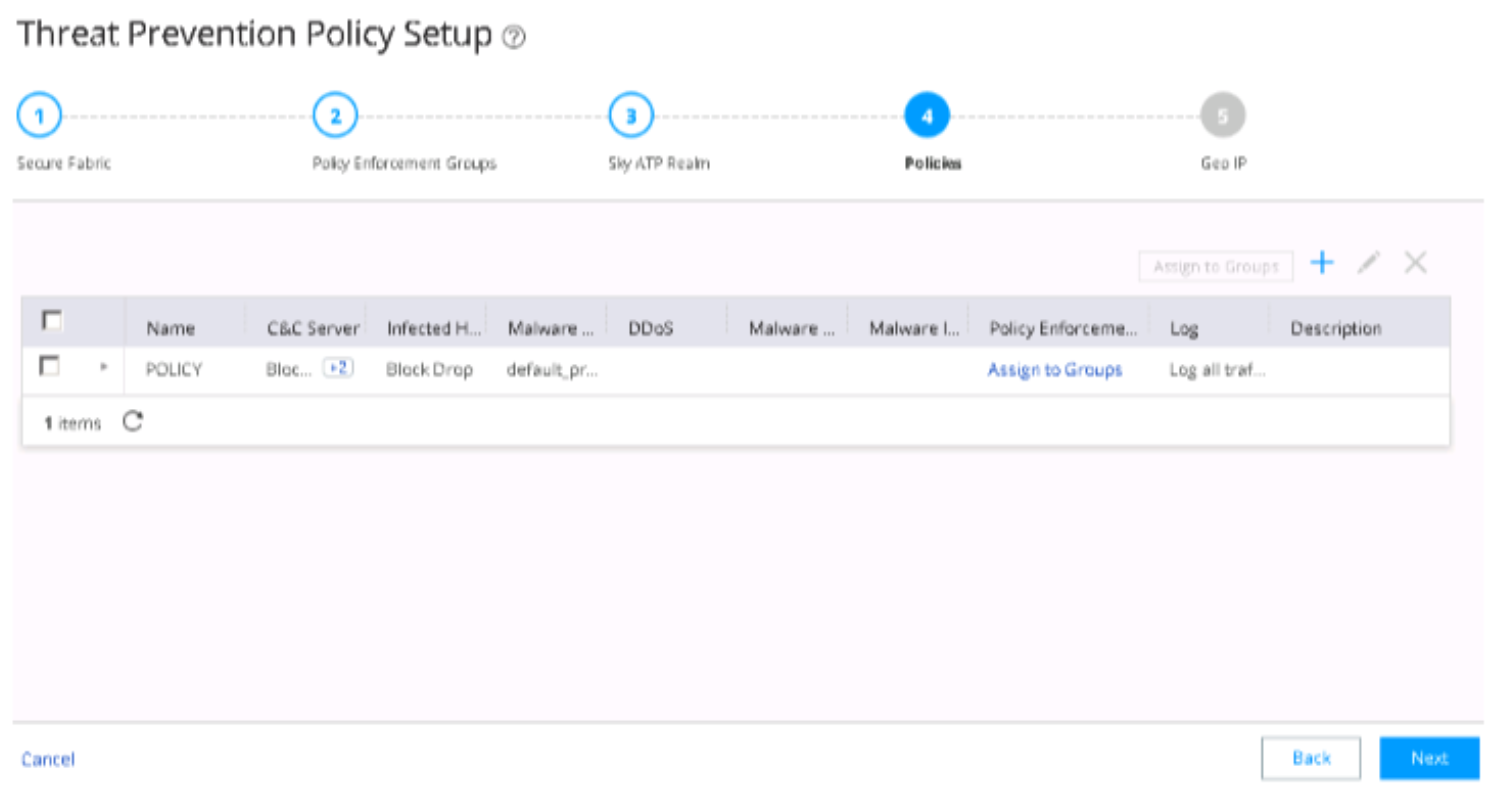
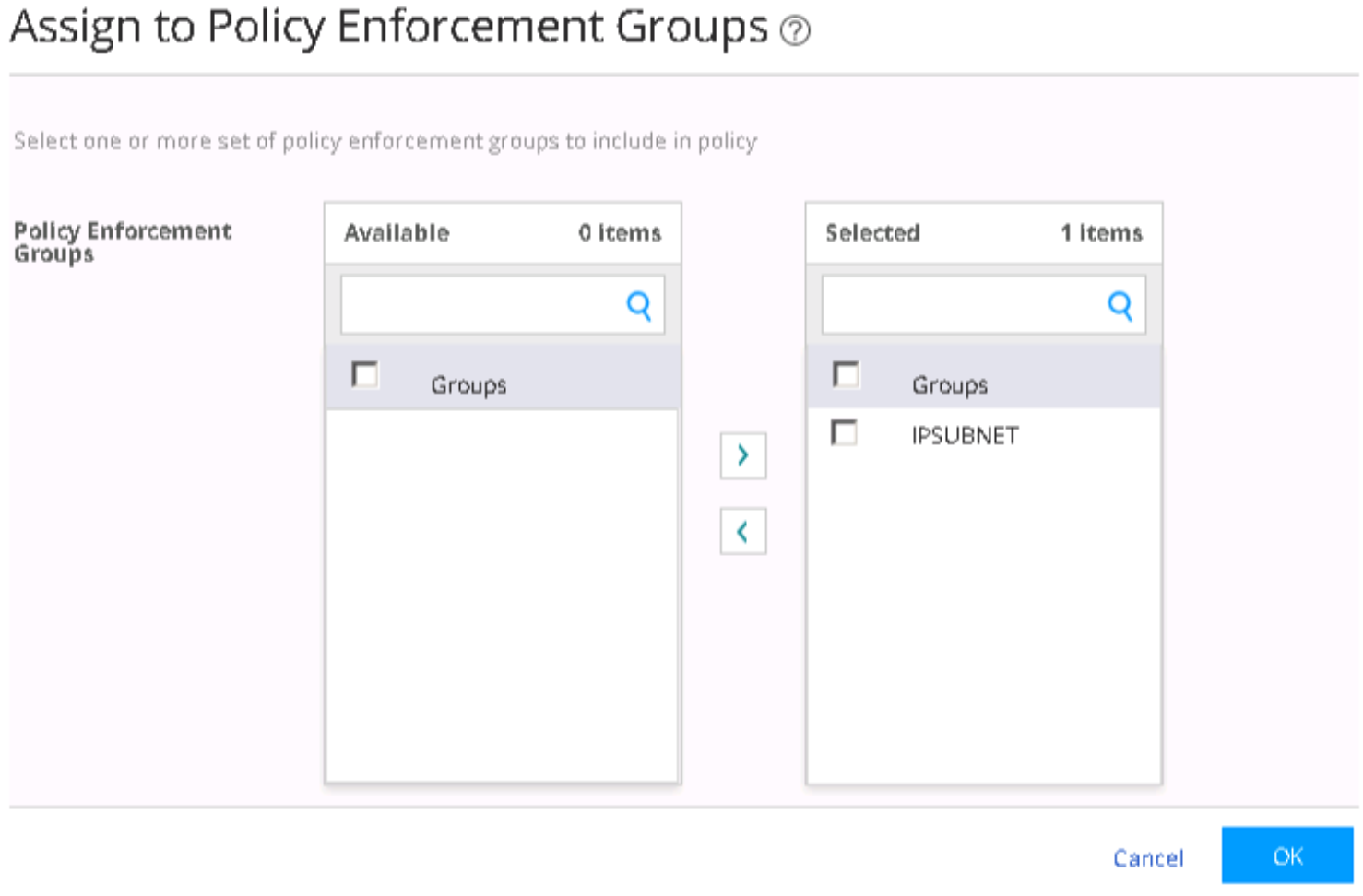
Configure ATP Cloud with Threat Prevention Policies
To configure ATP Cloud and set up threat prevention policies:
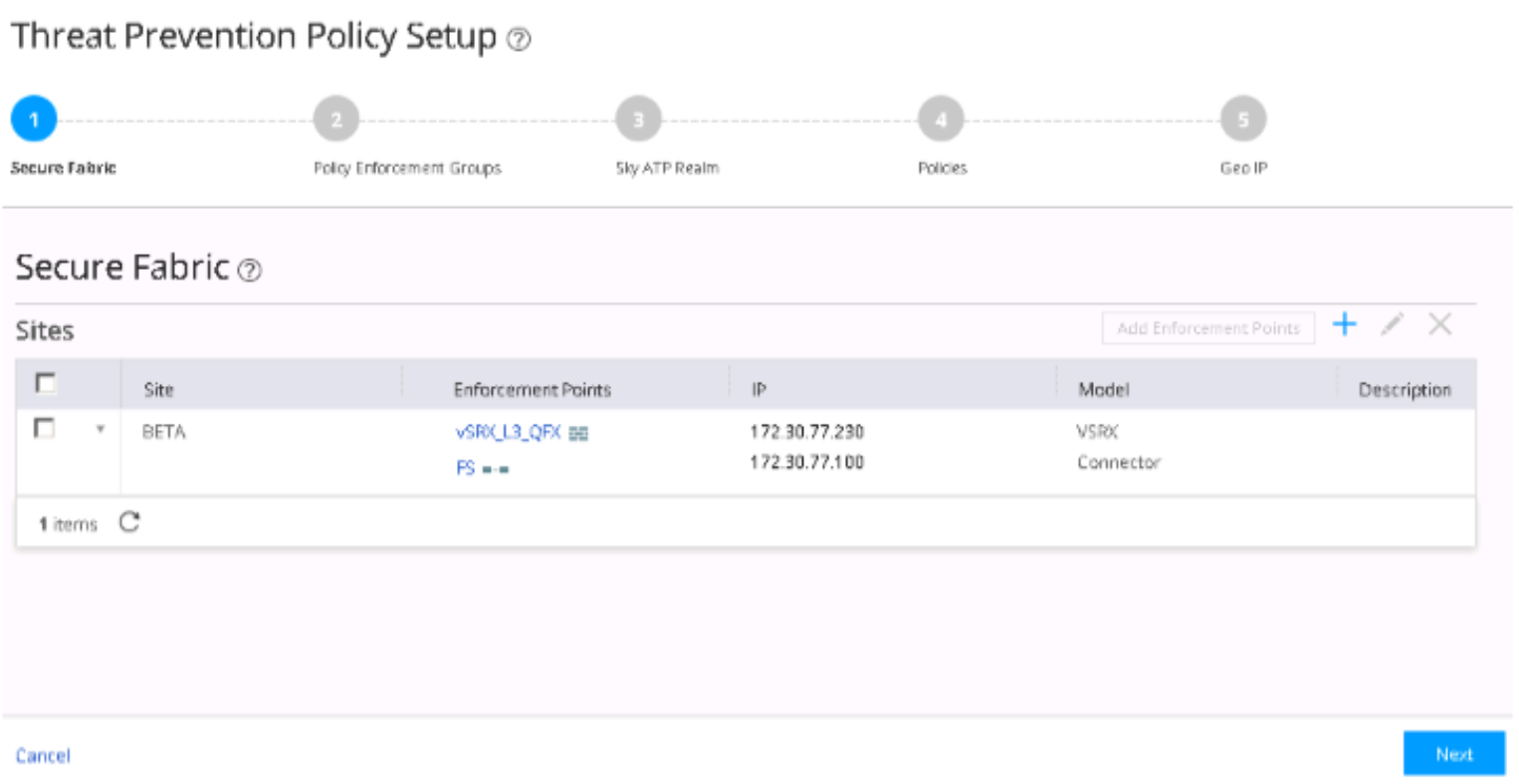
Configure a secure fabric. A secure fabric is a collection of sites which contain network devices (switches, routers, firewalls, and other security devices) used in policy enforcement groups.
Define a site and add endpoints to it (switches and firewalls).
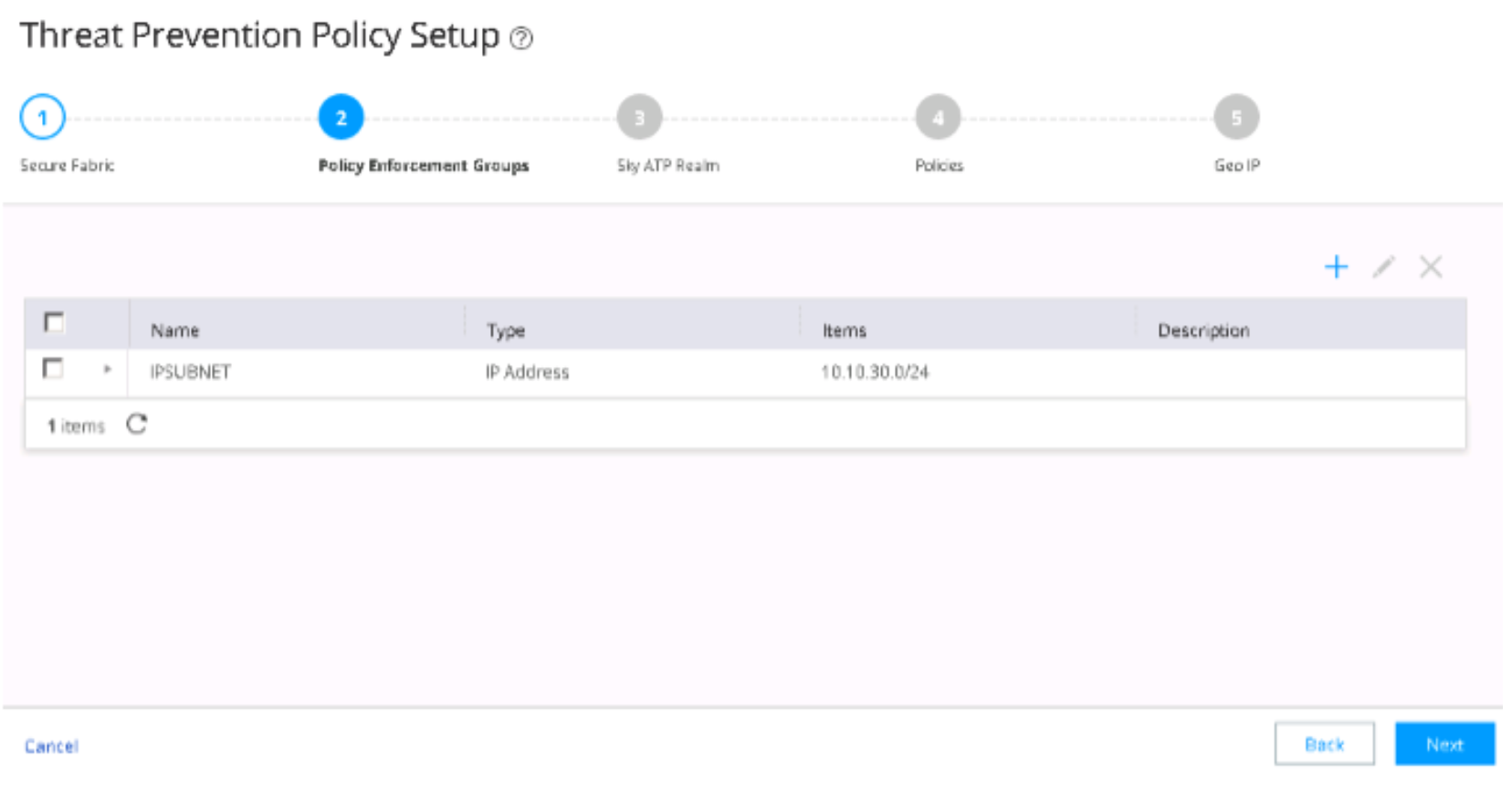
Configure policy enforcement groups. A policy enforcement group is a grouping of endpoints to which threat prevention policies are applied.
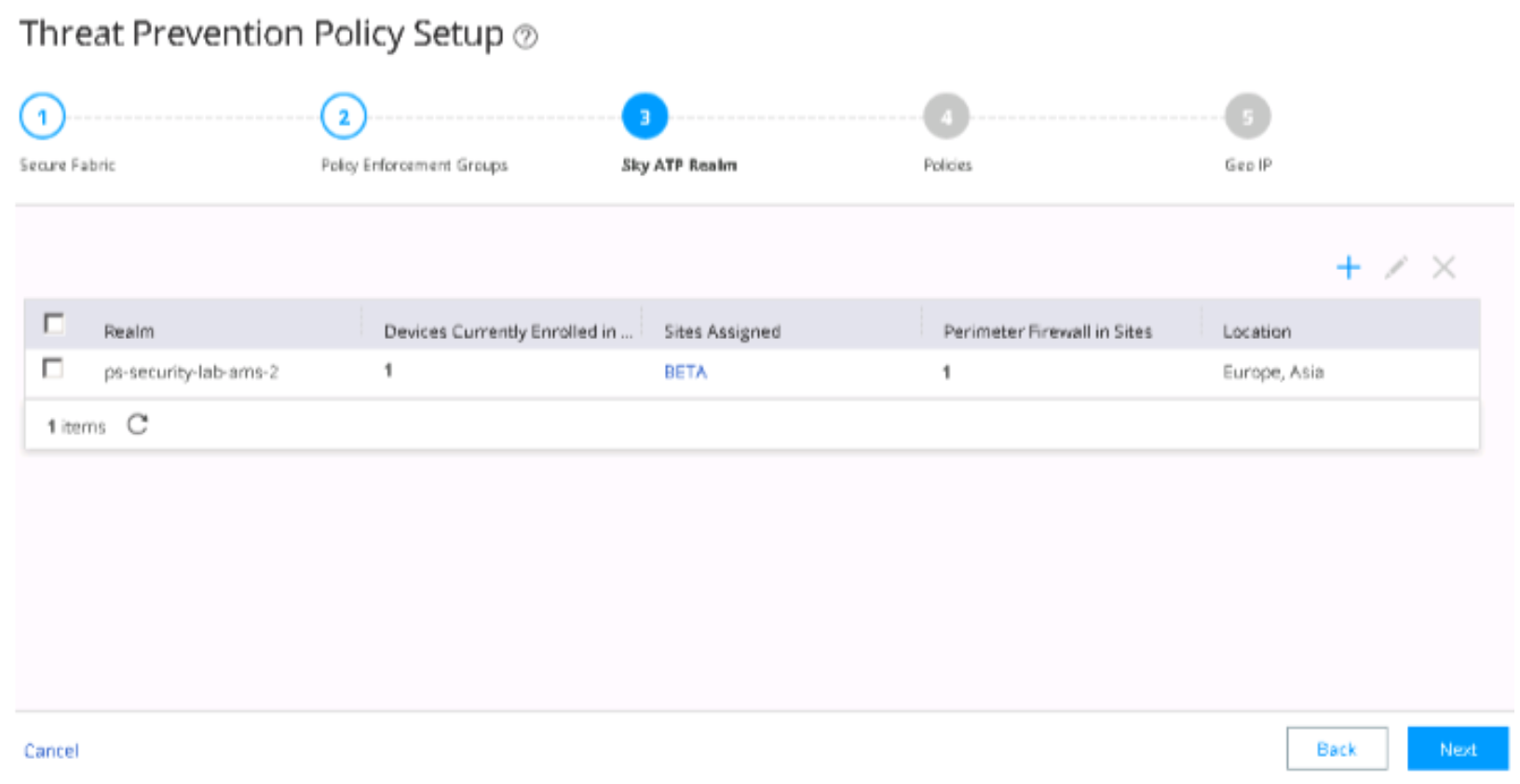
Create a threat prevention policy.
Apply threat prevention policies to policy enforcement groups
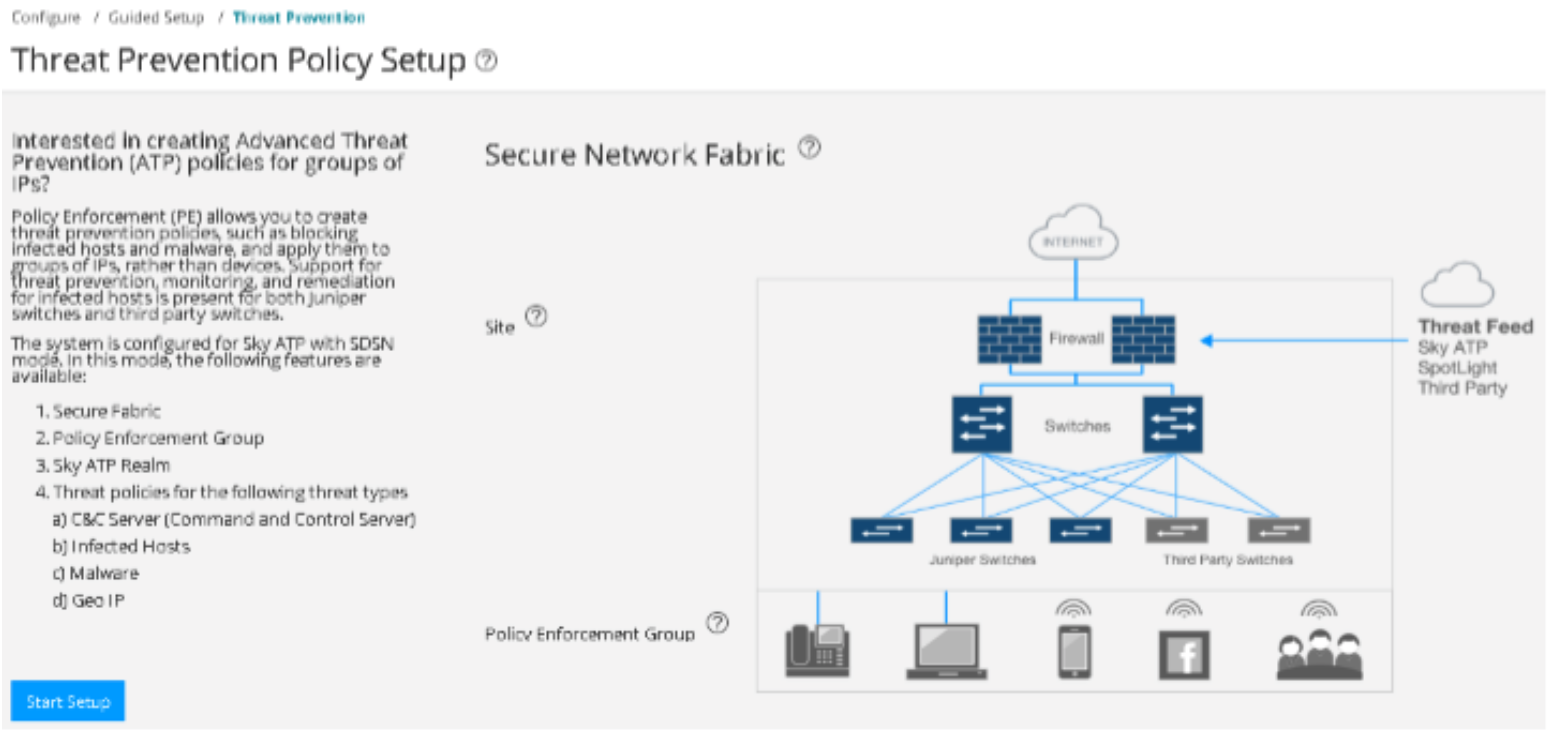
If you are using Policy Enforcer for threat prevention with ATP Cloud, Guided Setup is the most efficient way to complete the initial configuration.
To perform the configuration using Guided Setup:
Use Case Verification
To verify the use case configuration, perform the following actions:
- Verify the Enrollment of Devices in ATP Cloud on an SRX Series Device
- Verify the Enrollment of Policy Enforcer and SRX Series Devices in ATP Cloud
- Verify the Enrollment of Devices with ATP Cloud in Security Director
- Verify ForeScout CounterACT Functionality to Block Infected Endpoint (with 802.1X Authentication)
- Verify ForeScout CounterACT Functionality to Quarantine Infected Endpoint (with 802.1X Authentication)
- Verify ForeScout CounterACT Functionality to Block Infected Endpoint (with NETCONF)
- Verify ForeScout CounterACT Functionality to Quarantine Infected Endpoint (with NETCONF)
Verify the Enrollment of Devices in ATP Cloud on an SRX Series Device
Purpose
Verify that the SRX Series device is connected to the ATP Cloud server.
Action
On the SRX device, use the show services advanced-anti-malware
status CLI command.
user@host> show services advanced-anti-malware status
Server connection status:
Server hostname: srxapi.eu-west-1.sky.junipersecurity.net
Server port: 443
Control Plane:
Connection time: 2018-02-25 13:37:09 CET
Connection status: Connected
Service Plane:
fpc0
Connection active number: 1
Connection retry statistics: 280
Meaning
The CLI output displays the Connection status as Connected. The Server hostname field displays
the ATP Cloud server hostname.
Verify the Enrollment of Policy Enforcer and SRX Series Devices in ATP Cloud
Purpose
Verify that Policy Enforcer and the SRX Series device are enrolled with ATP Cloud.
Action
In ATP Cloud, navigate to the Enrolled Devices page and review the connection information for enrolled devices, including the serial number, model number, tier level (free, basic, premium) enrollment status in ATP Cloud, last telemetry activity, and last activity seen.
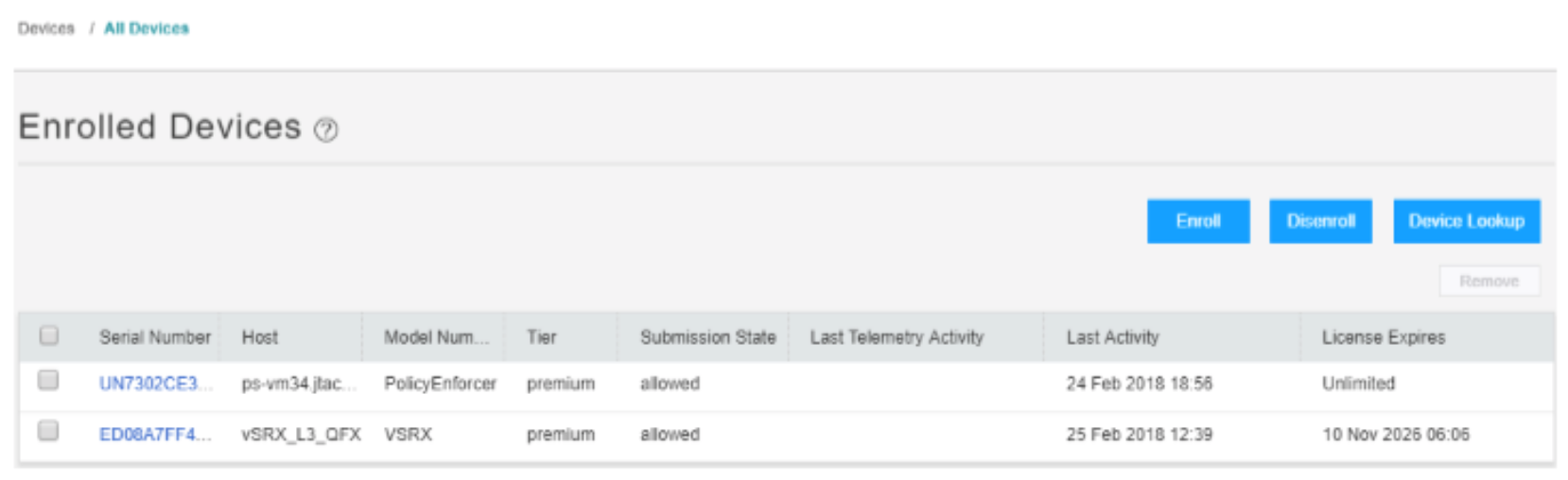
Meaning
The Host field displays details for the enrolled firewall (vSRX_L3_QFX) and for the Policy Enforcer device. You can click the serial numbers for more details.
Verify the Enrollment of Devices with ATP Cloud in Security Director
Purpose
Verify that the SRX Series device enrolled with ATP Cloud in Security Director.
Action
In Security Directory, navigate to Devices > Secure Fabric.
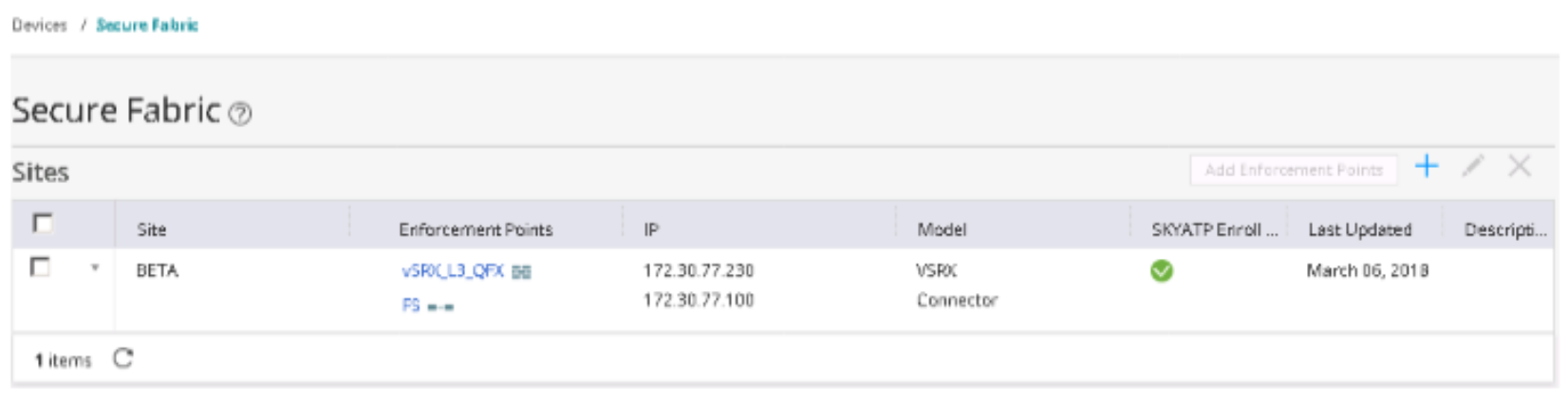
Meaning
A green dot with checkmark displays in the SkyATP Enroll Status field and confirms the enrollment of the SRX Series device with the ATP Cloud realm.
Verify ForeScout CounterACT Functionality to Block Infected Endpoint (with 802.1X Authentication)
Purpose
Test the ForeScout CounterACT integration and functionality when an endpoint is infected. In this example, you verify when the enforcement policy is configured to block the infected host with 802.1X authentication.
Action
A client VM or physical PC is required to trigger an attack.
Before the attack, confirm the following:
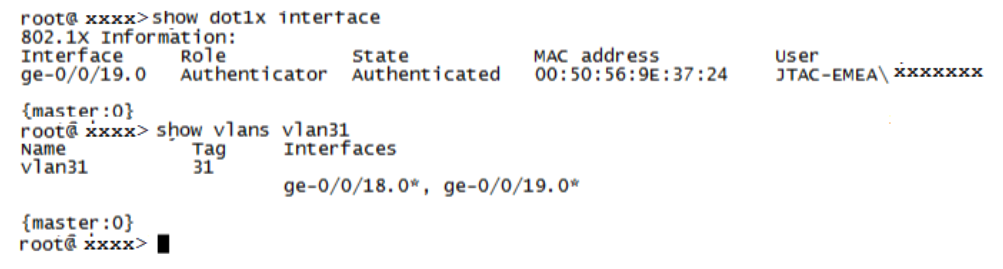
Confirm that Windows Supplicant is authenticated and in User VLAN (vlan31).
user@host> show vlans 31 Name Tag Interfaces vlan31 31 ge-0/0/0/18.0*, ge-0/0/0/19.0* user@host>
Confirm that the endpoint 10.10.30.69 can ping to Internet (IP address 8.8.8.8) and Layer 2 connected default gateway (10.10.30.254). Before the attack, the endpoint starts continuous pings to other endpoints on the LAN and Internet.
The endpoint pings the C&C server on the Internet from Windows Supplicant (in this example from the IP address 184.75.221.43).
Figure 77: Confirming Ping from Windows Supplicant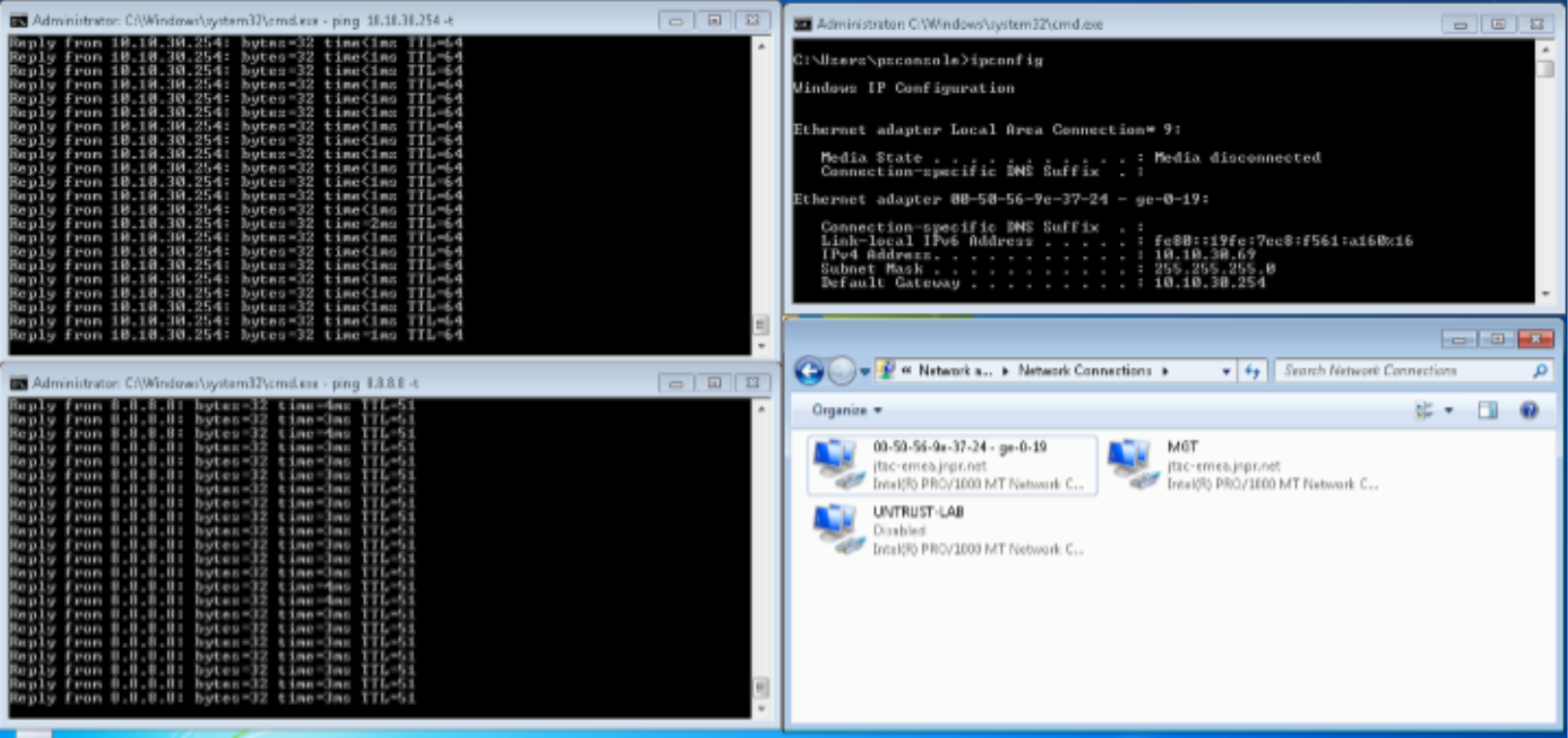
After the attack, the 802.1X session is terminated with RADIUS CoA on the EX4300 switch initiated by ForeScout CounterACT.
Confirm the following:
Confirm that Windows Supplicant cannot connect to the Internet or the LAN anymore.
Figure 78: Confirming Ping from Windows Supplicant is Blocked After the Attack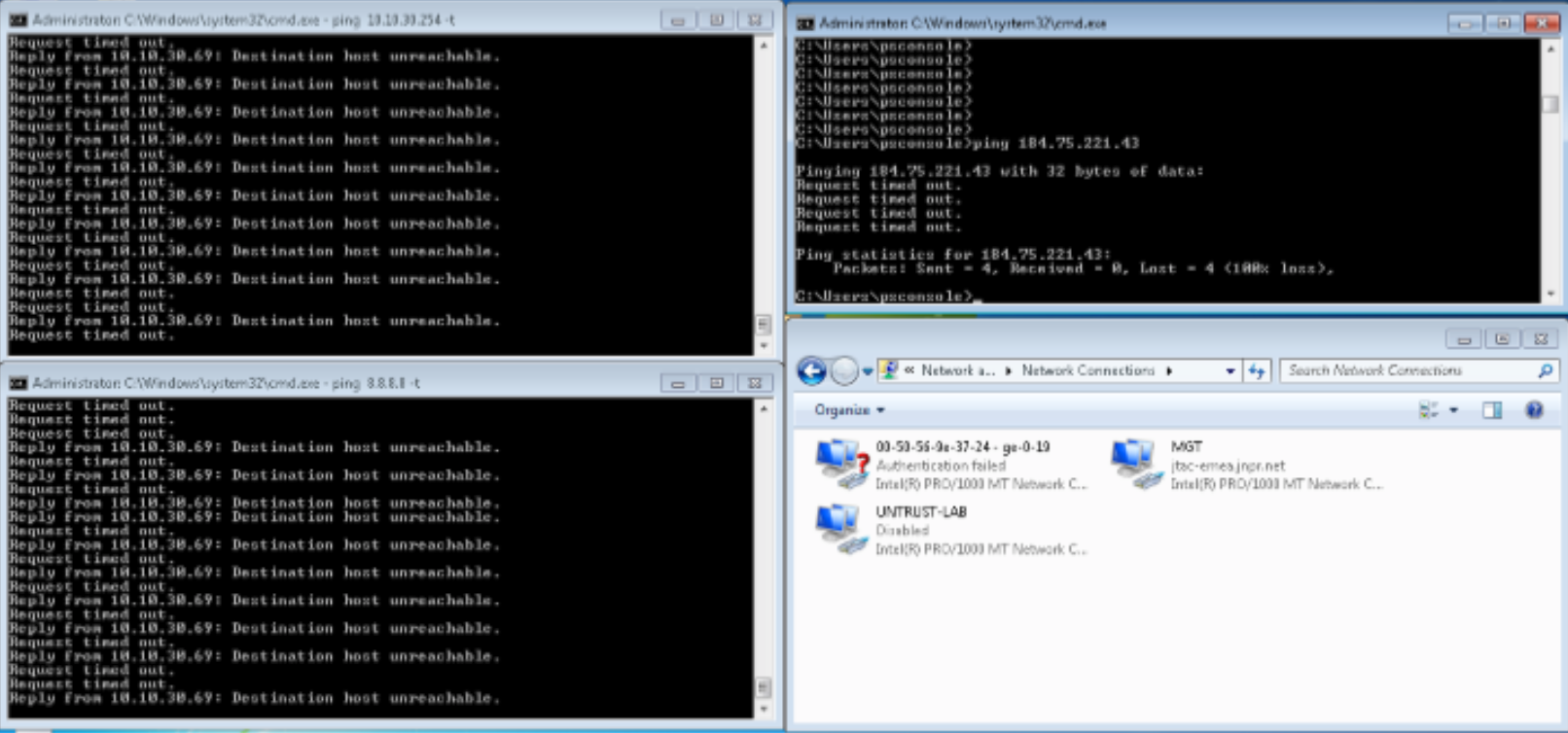
After the RADIUS CoA disconnect message, confirm that the Windows Supplicant is not in User VLAN (vlan31) anymore but in the default VLAN.
Confirm that further authentication requests are rejected by ForeScout CounterACT.
user@host> show vlans default Name Tag Interfaces default ge-0/0/0/19.0* user@host> user@host> show vlans 31 Name Tag Interfaces vlan31 31 ge-0/0/0/18.0* user@host>
Confirm the SDSN BLOCK (dot1x) policy match and automated threat remediation action details by navigating to ForeScout CounterACT > Home.
Figure 79: 802.1X SDSN Block Policy Match Verification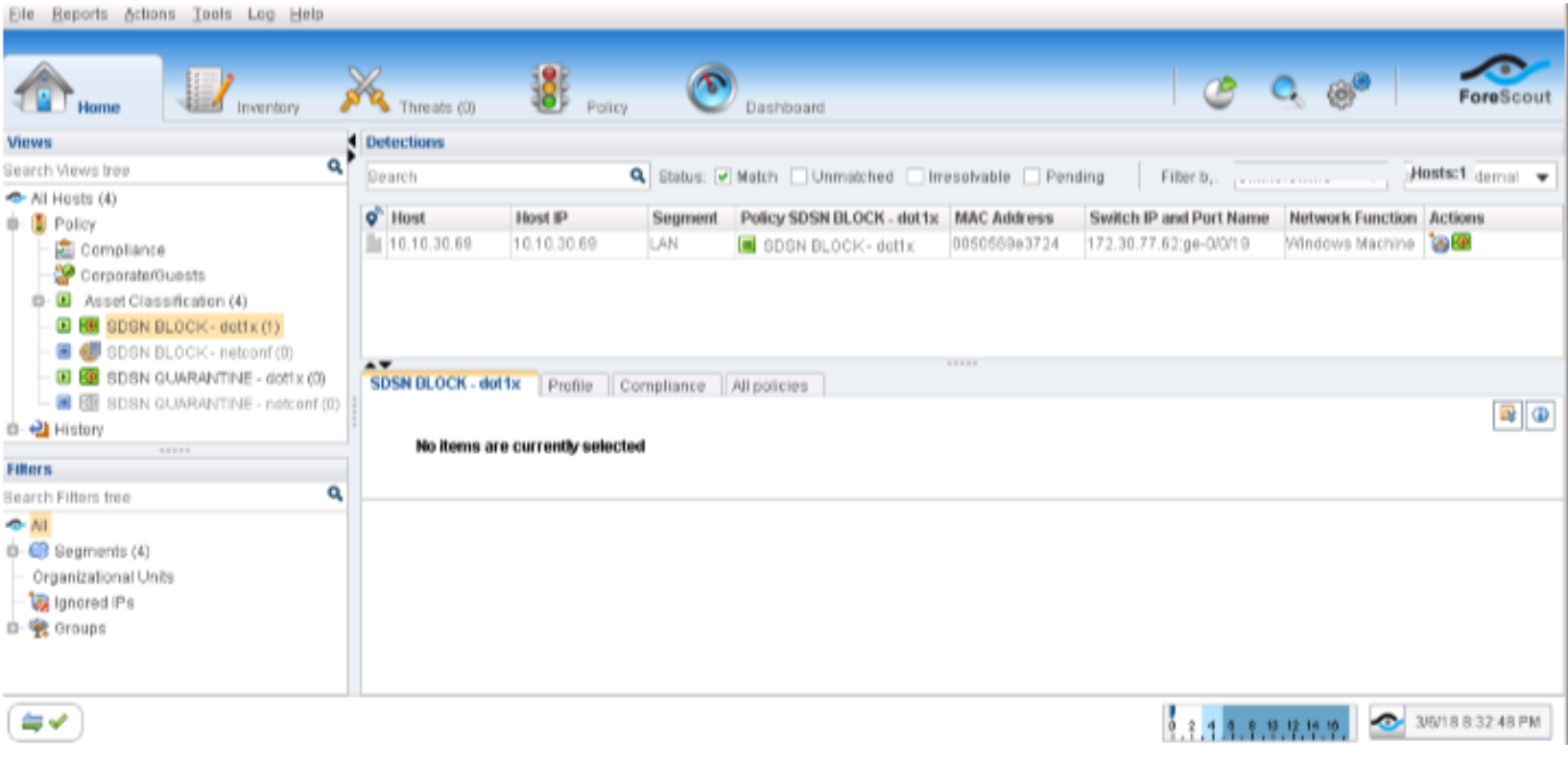
Navigate to Log > Host Log. Review the details for the SDSN BLOCK (dot1x) policy.
Figure 80: 802.1X Host Log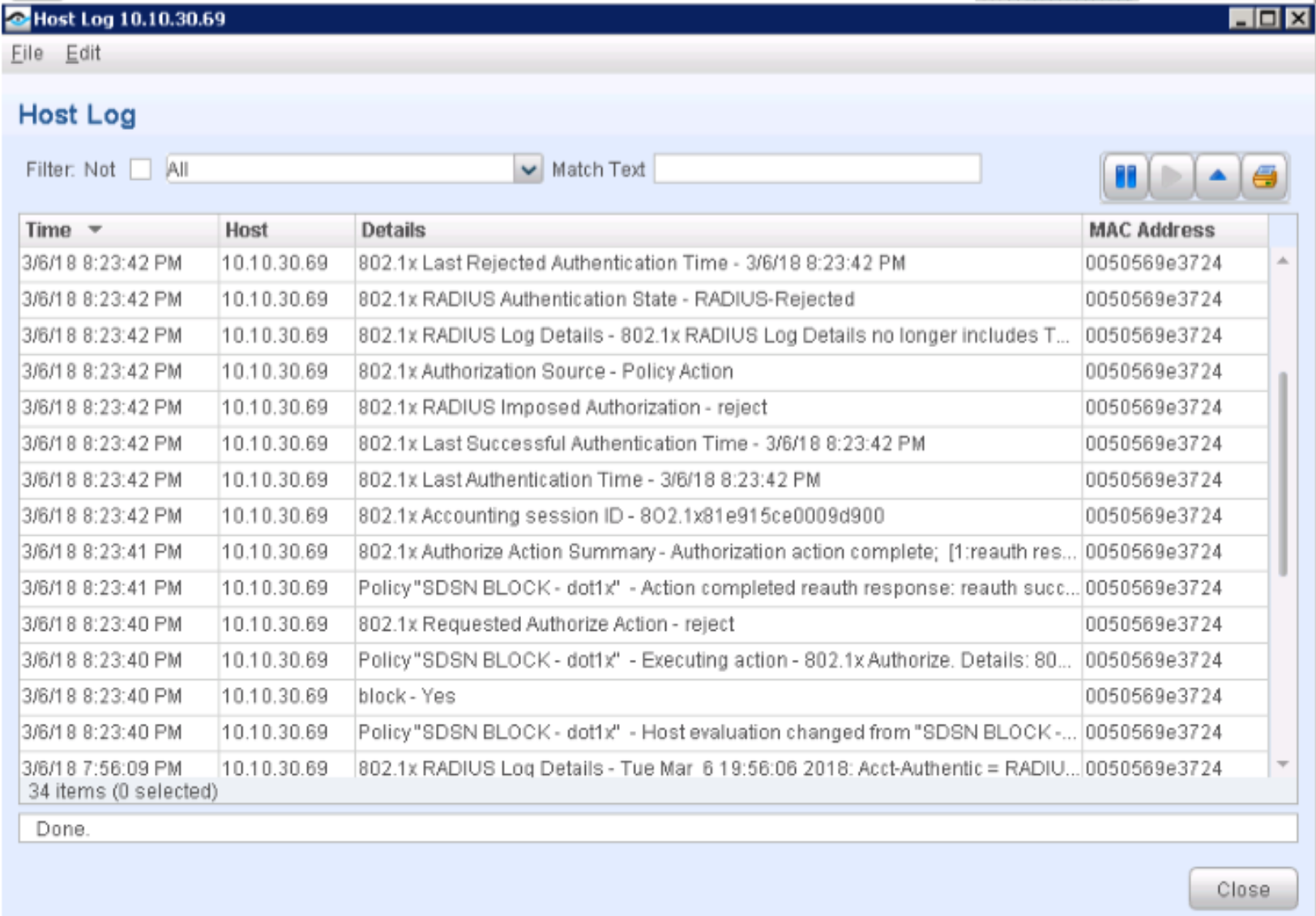
Confirm that the Windows Supplicant’s IP address was also added to the Infected-Hosts Feed on the SRX Series device to block Internet access.
user@vSRX_L3> show security dynamic-address category-name Infected-Hosts No. IP-start IP-end Feed Address 1 10.10.30.69 10.10.30.69 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-2150001a Total number of matching entries: 1 user@vSRX_L3>
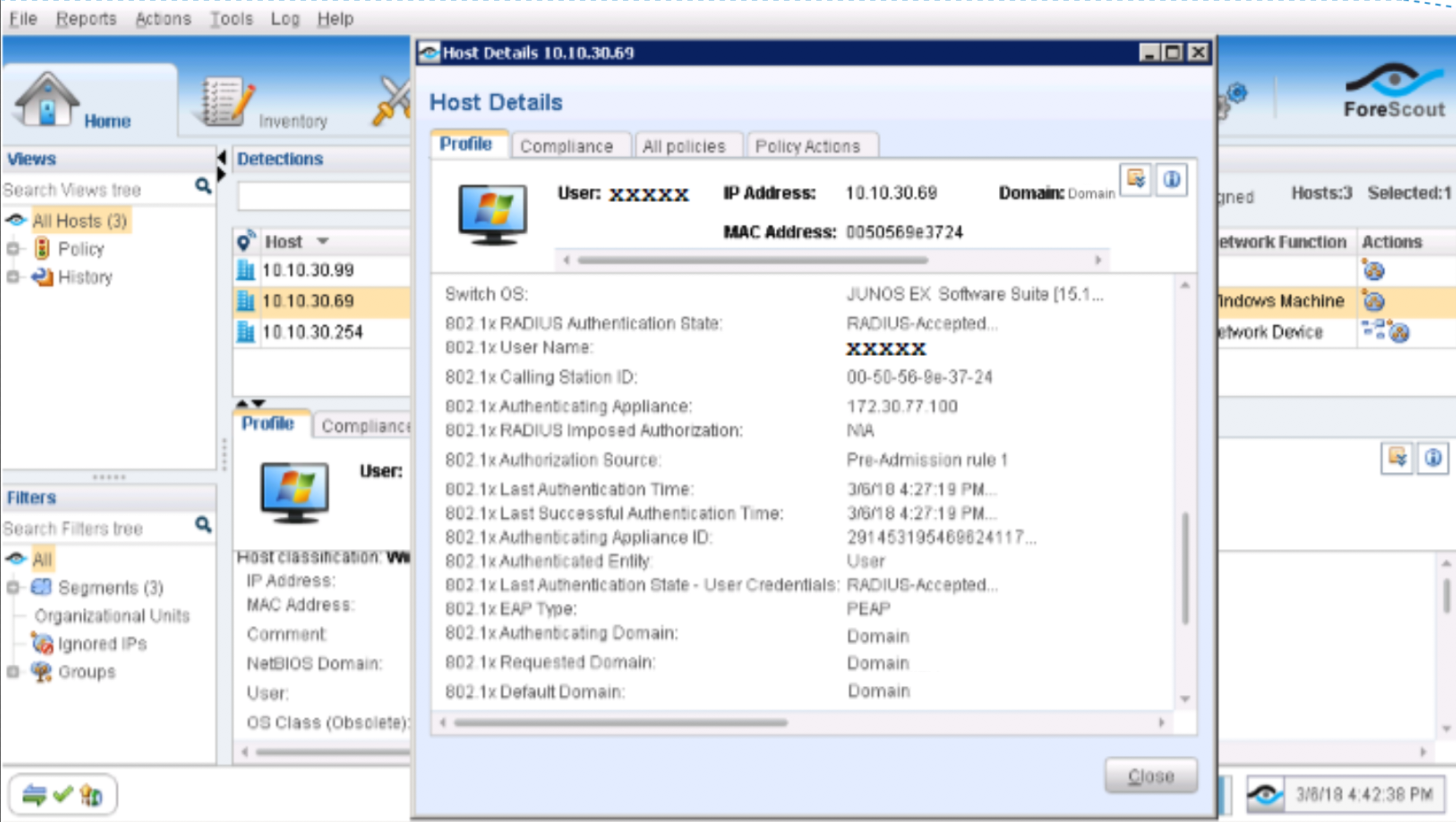
In the ATP Cloud portal, navigate to Monitor > Hosts. Confirm the host IP address (10.10.30.69), MAC-ID, and switch port of the Windows Supplicant.
Figure 81: ATP Cloud Host Monitoring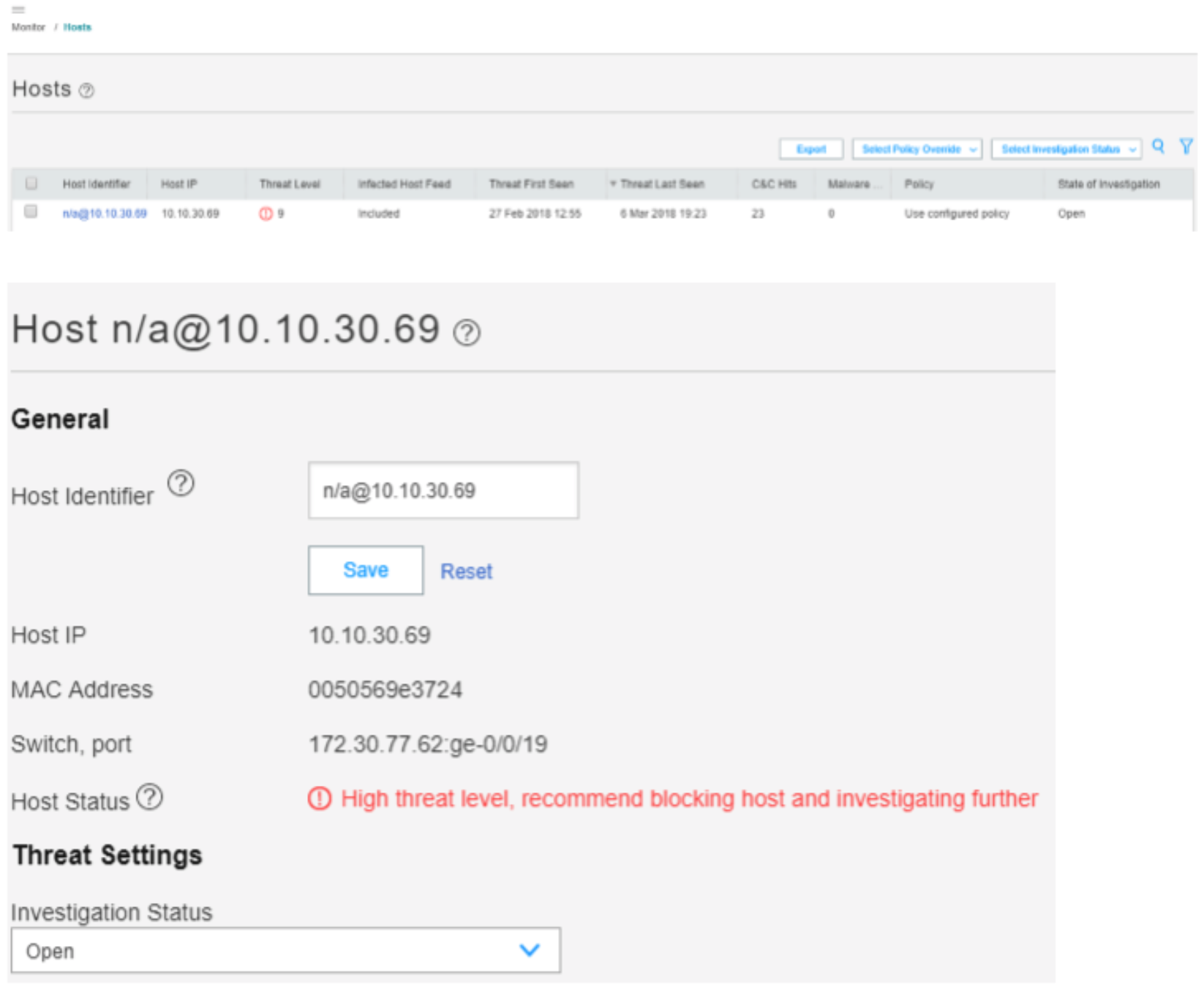
Meaning
All ping sessions show that the traffic is blocked after the threat was detected, confirming that the automated threat remediation use case is working properly.
The Hosts page lists compromised hosts and their associated threat levels. The output confirms that ATP Cloud and Security Director have detected the infected host. You can monitor and mitigate malware detections on a per host basis.
Verify ForeScout CounterACT Functionality to Quarantine Infected Endpoint (with 802.1X Authentication)
Purpose
Test the ForeScout CounterACT integration and functionality when an endpoint is infected. In this example, you verify when the enforcement policy is configured to quarantine the infected host with 802.1X authentication.
Action
A client VM or physical PC is required to trigger an attack.
Before the attack, confirm the following:
Release the infected host on the ATP Cloud portal or in Security Director (Monitor > Threat Prevention > Hosts).
Ensure that Internet or LAN access is restored for the Windows Supplicant.
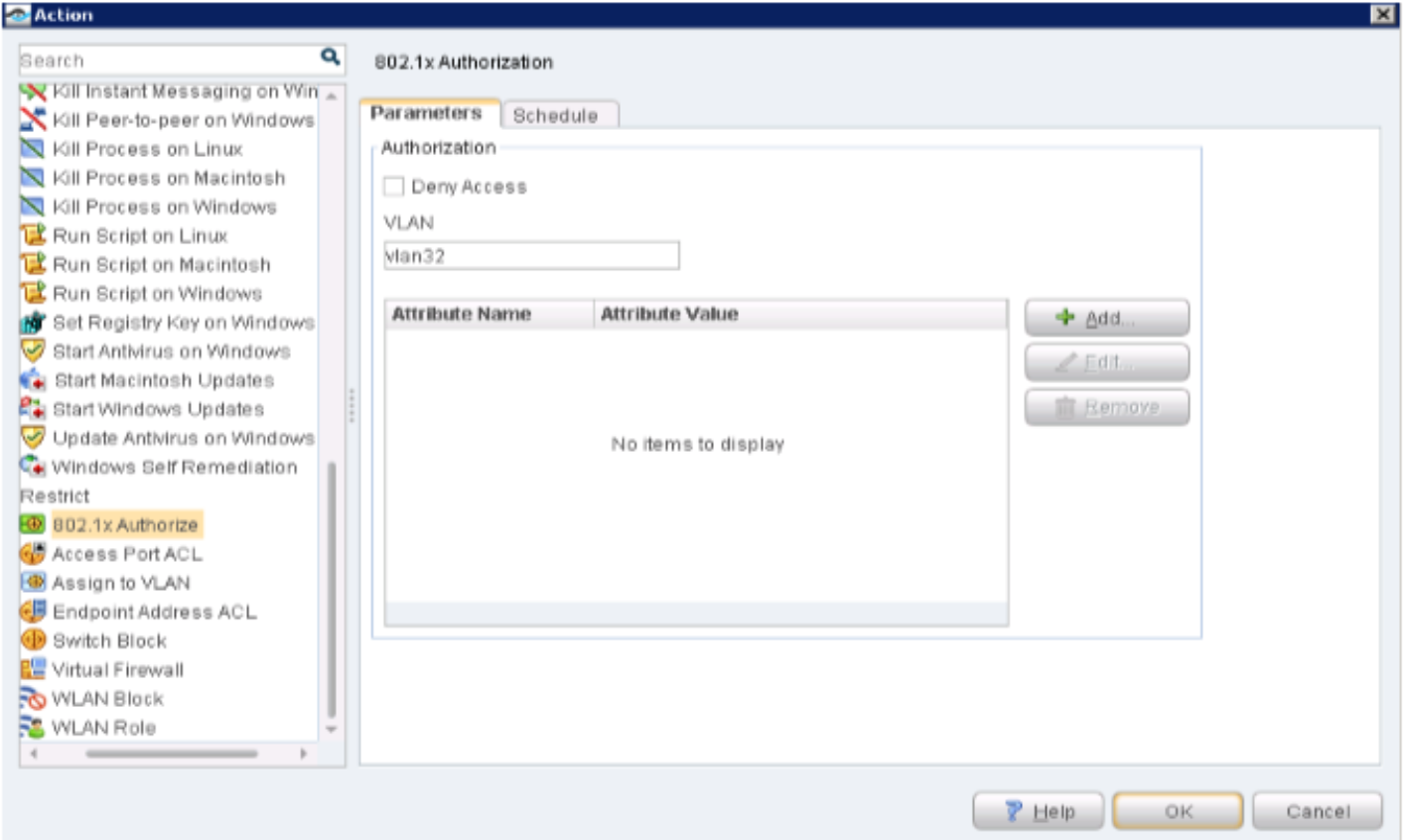
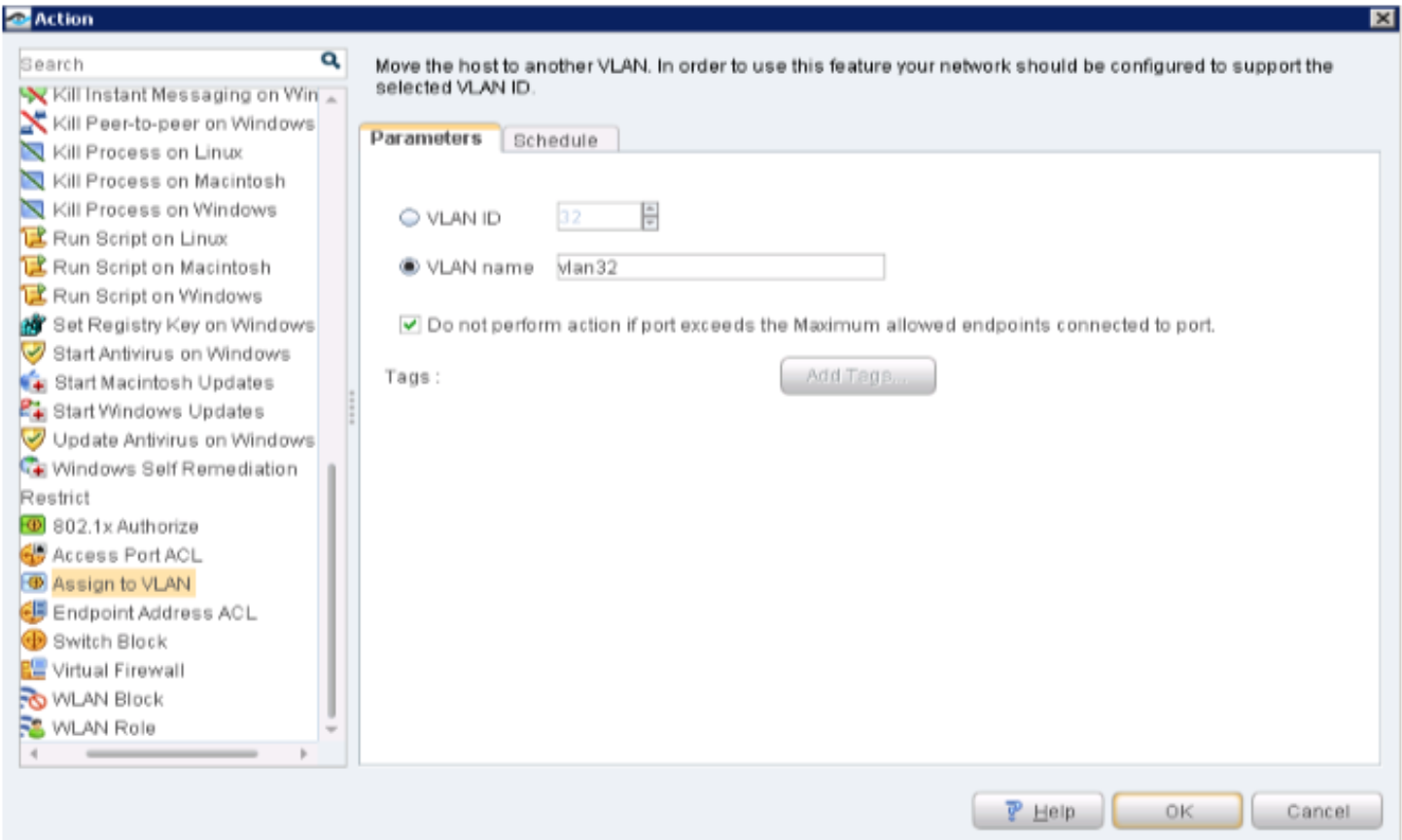
On the Policy Enforcer > Threat Prevention Policy page, change infected host profile actions to Quarantine and add the VLAN ID as vlan32. Click OK.
Figure 82: Threat Prevention Policy Pre-Attack Configuration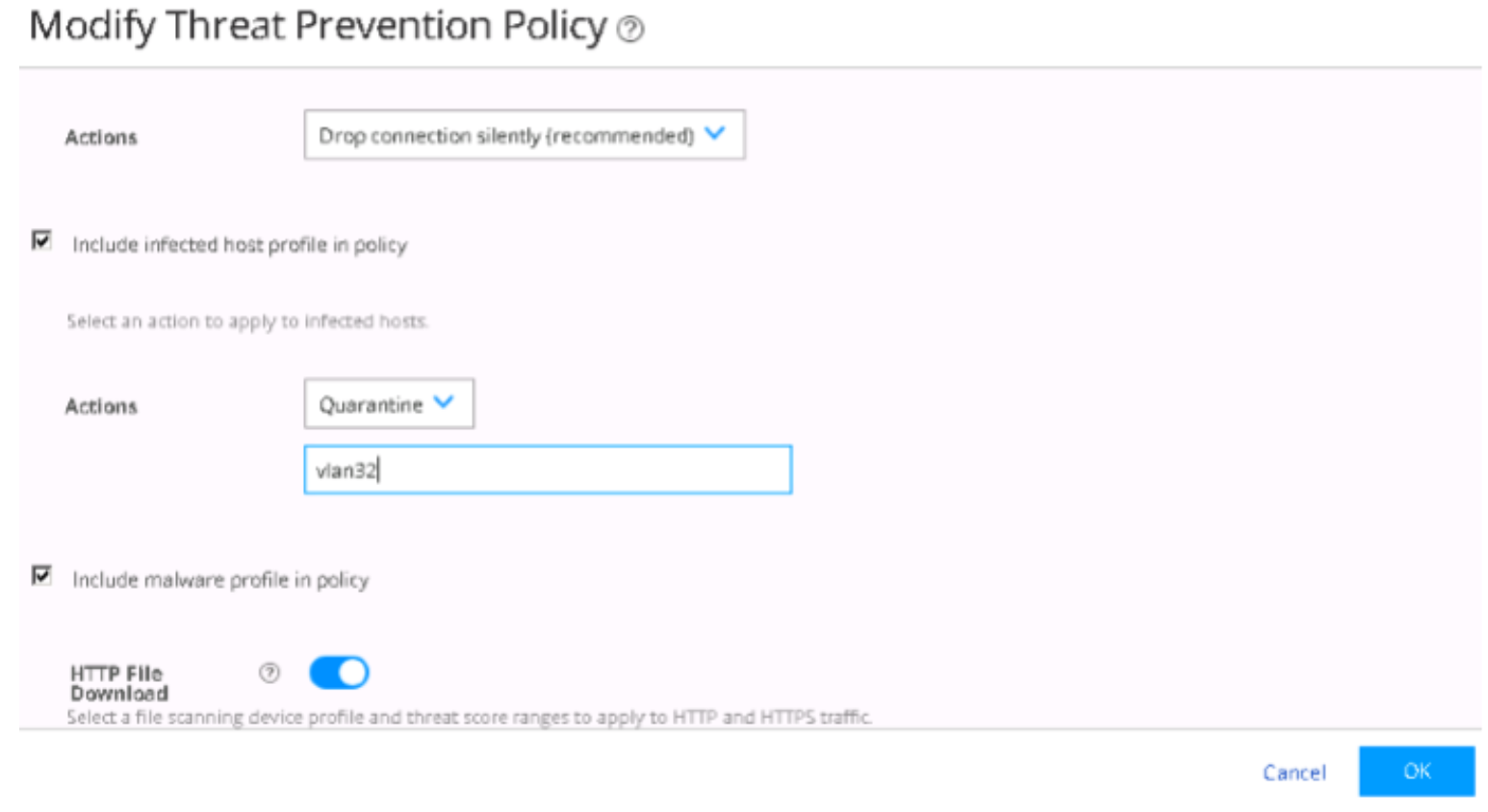
Confirm that Windows Supplicant is authenticated and in User VLAN (vlan31).
user@host> show vlans 31 Name Tag Interfaces vlan31 31 ge-0/0/0/18.0*, ge-0/0/0/19.0* user@host>
Confirm that the endpoint 10.10.30.69 can ping to Internet (IP address 8.8.8.8) and Layer 2 connected default gateway (10.10.30.254). Before the attack, the endpoint starts continuous pings to other endpoints on the LAN and Internet.
Figure 83: Confirming Ping from Windows Supplication Before the Attack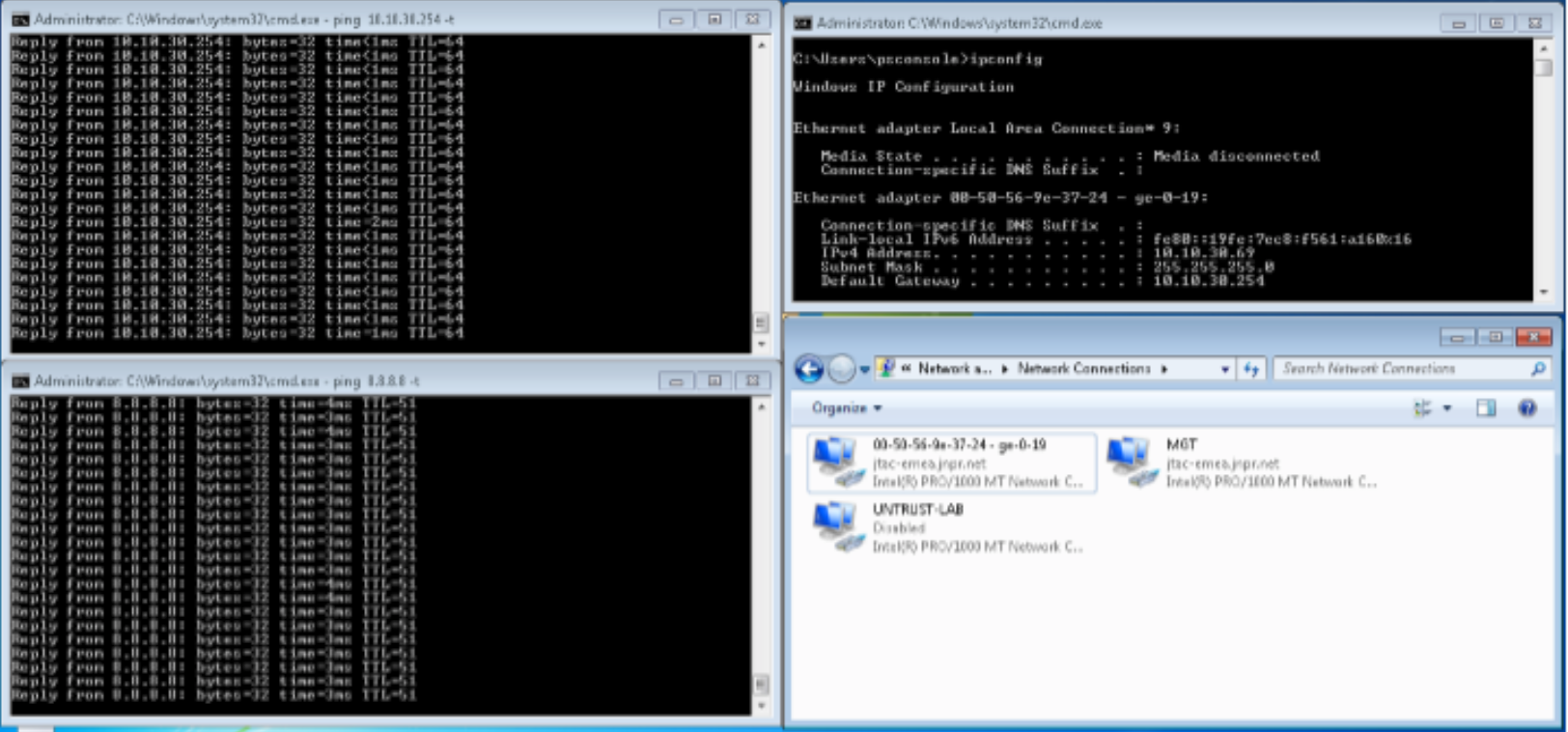
The endpoint pings the C&C server on the Internet from Windows Supplicant (in this example from the IP address 184.75.221.43).
After the attack, the 802.1X session is terminated with RADIUS CoA on the EX4300 switch initiated by ForeScout CounterACT.
Confirm the following:
Confirm that Windows Supplicant re-authenticates and is automatically moved into Quarantine VLAN (vlan32). As a result, the Windows Supplicant cannot connect to the Internet or the LAN anymore.
Figure 84: Confirm Traffic is Moved to Quarantine VLAN After Attack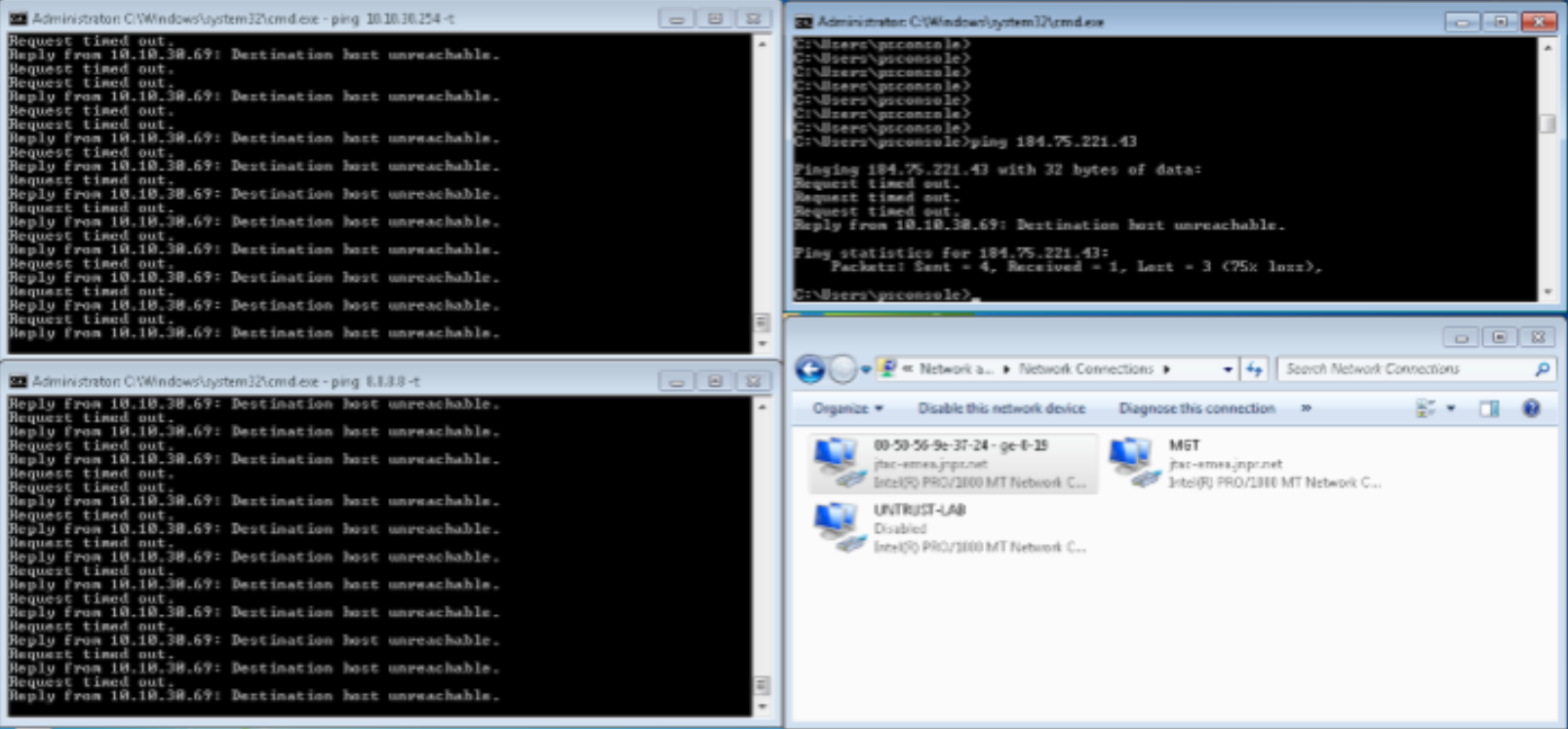
After the RADIUS CoA disconnect message and re-authentication, confirm that the Windows Supplicant is now in Quarantine VLAN (vlan32).
Confirm that further authentication requests are rejected by ForeScout CounterACT.
user@host> show vlans default Name Tag Interfaces default ge-0/0/0/19.0* user@host> user@host> show vlans 32 Name Tag Interfaces vlan32 32 ge-0/0/0/19.0* user@host>
Confirm the SDSN QUARANTINE (dot1x) policy match and automated threat remediation action details by navigating to ForeScout CounterACT > Home.
Figure 85: 802.1X SDSN Quarantine Policy Match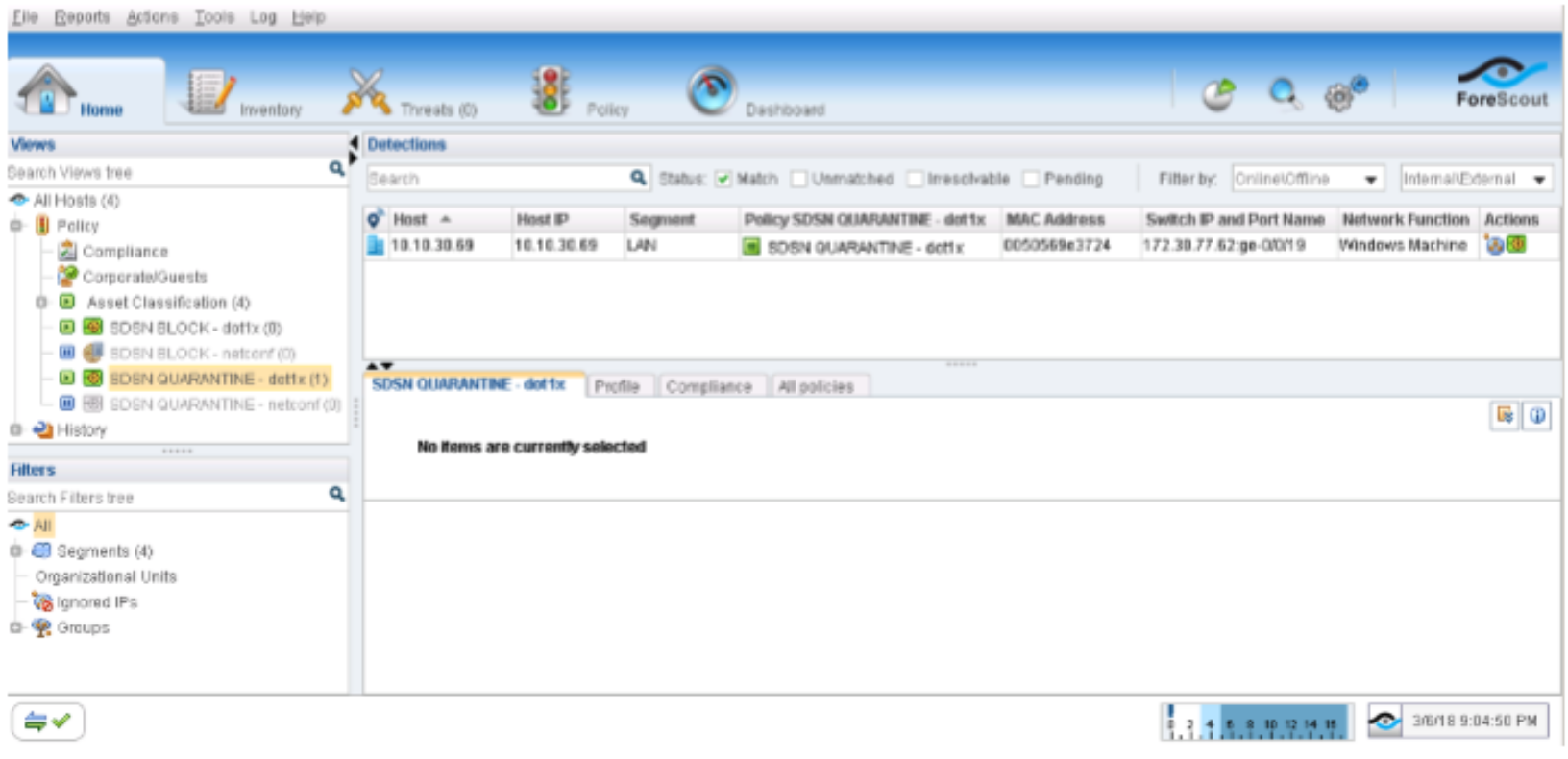
Navigate to Log > Host Log. Review the details for the SDSN QUARANTINE (dot1x) policy.
Figure 86: 802.1X SDSN Quarantine Host Log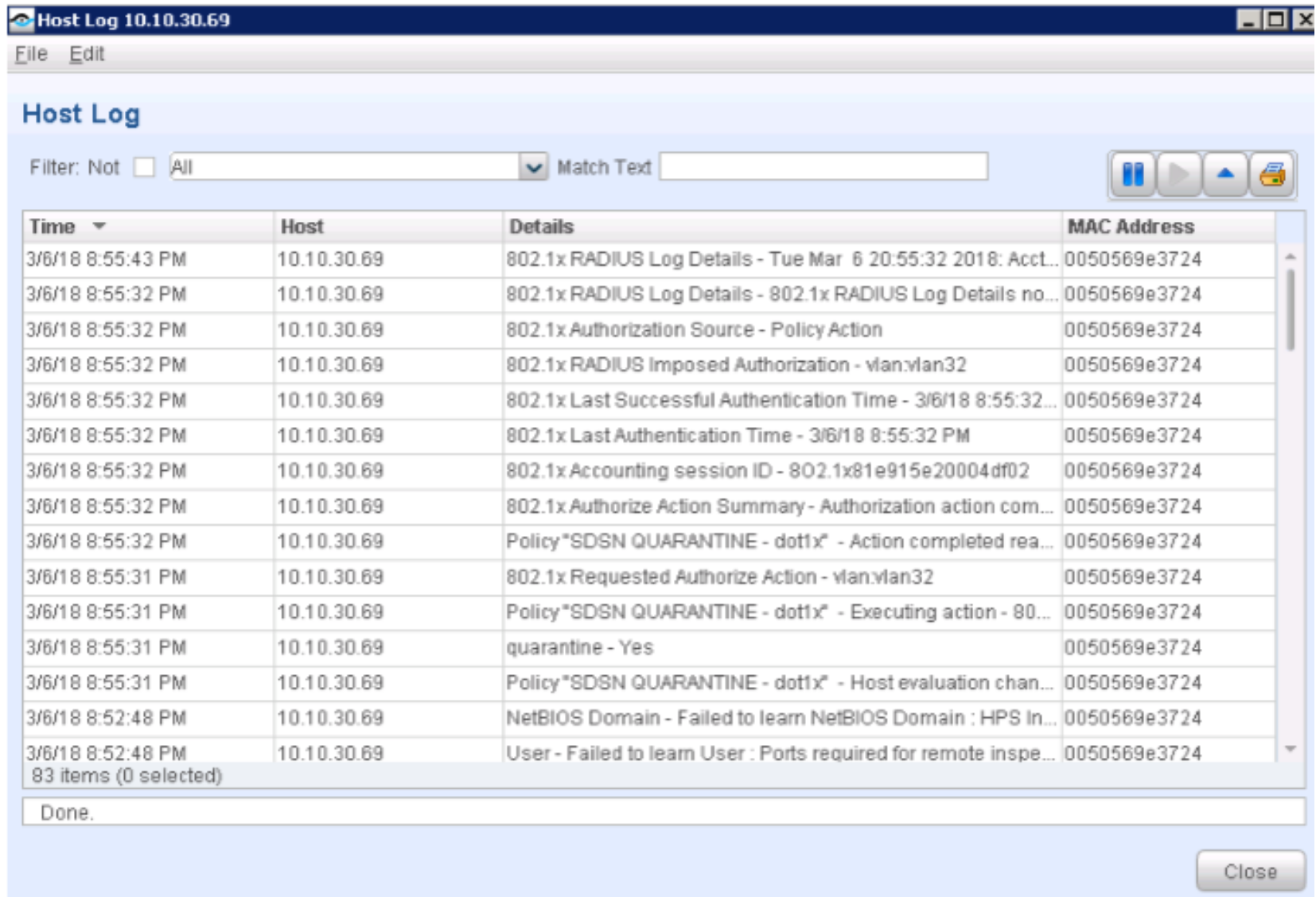
Confirm that the Windows Supplicant’s IP address was also added to the Infected-Hosts Feed on the SRX Series device to block Internet access.
user@vSRX_L3> show security dynamic-address category-name Infected-Hosts No. IP-start IP-end Feed Address 1 10.10.30.69 10.10.30.69 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-2150001a Total number of matching entries: 1 user@vSRX_L3>
In the ATP Cloud portal, navigate to Monitor > Hosts. Confirm the host IP address (10.10.30.69), MAC-ID, and switch port of the Windows Supplicant.
Figure 87: Confirming Host Details in ATP Cloud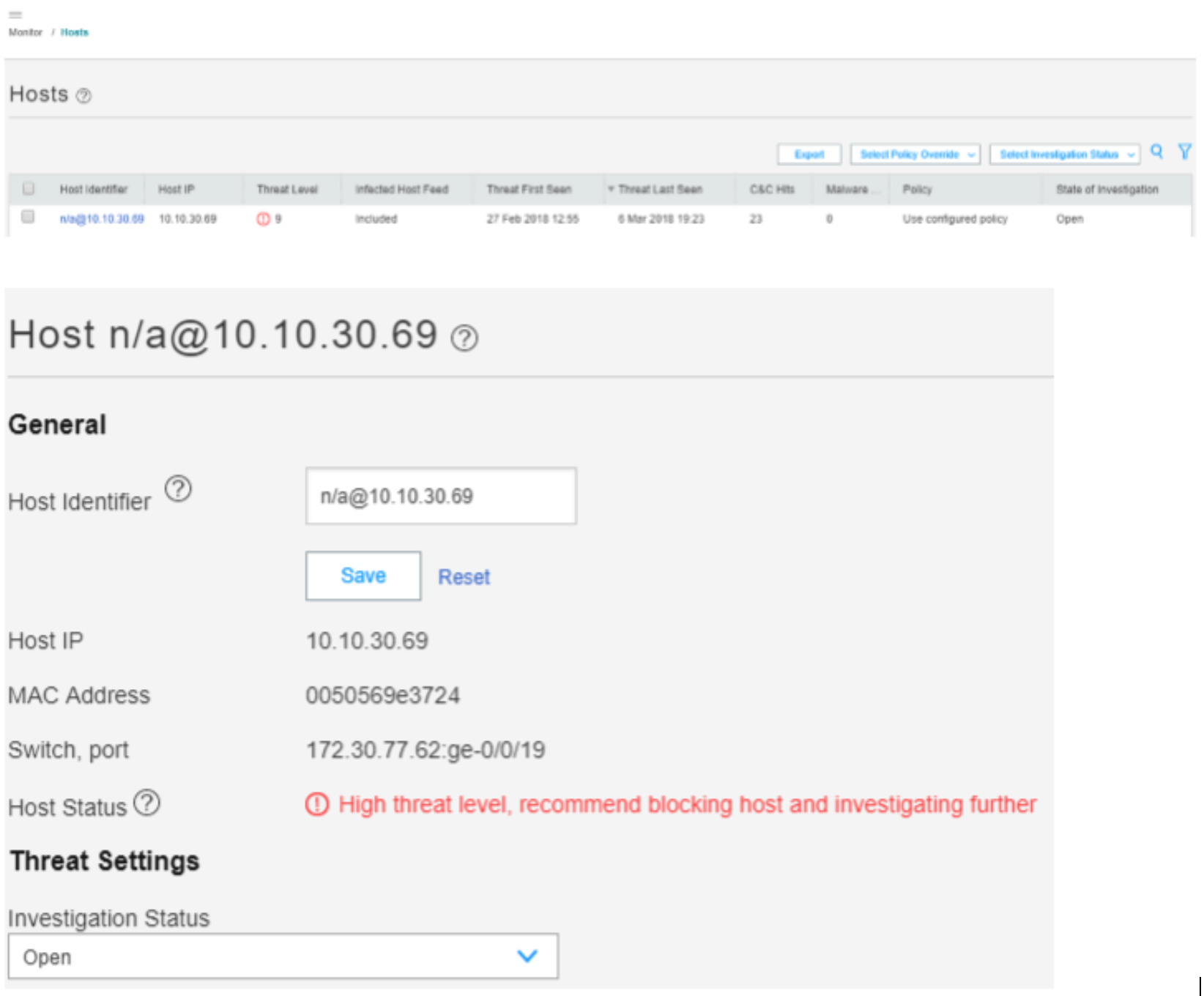
Meaning
The output shows that the ATP Cloud infected host feed containing the Windows Supplicant’s IP address 10.10.30.69 has been successfully downloaded, resulting in the SRX device taking an action to quarantine the IP address.
The Hosts page lists compromised hosts and their associated threat levels. The output confirms that ATP Cloud and Security Director have detected and quarantined the infected host. You can monitor and mitigate malware detections on a per host basis. You can also drill down and verify why the host is marked as infected (for this use case, the C&C server IP address). For malware, details of the downloaded file display.
Verify ForeScout CounterACT Functionality to Block Infected Endpoint (with NETCONF)
Purpose
Test the ForeScout CounterACT integration and functionality when an endpoint is infected. In this example, you verify when the enforcement policy is NETCONF, and it is configured block the infected host.
Action
A client VM or physical PC is required to trigger an attack.
Before the attack, confirm the following:
On the Policy Enforcer > Threat Prevention Policy page, change infected host profile actions to Drop connection silently. Click OK.
Figure 88: Drop Connection Silently Option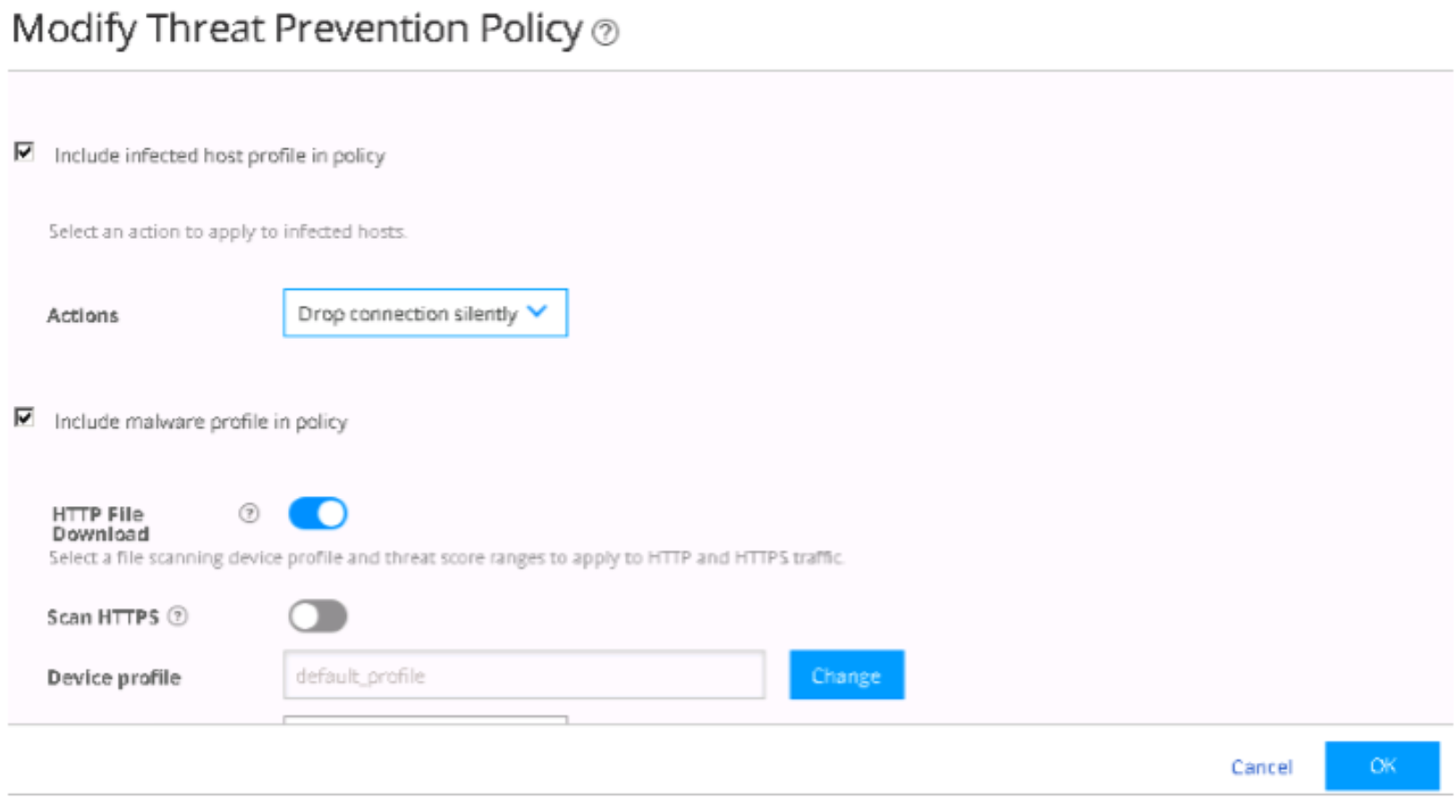
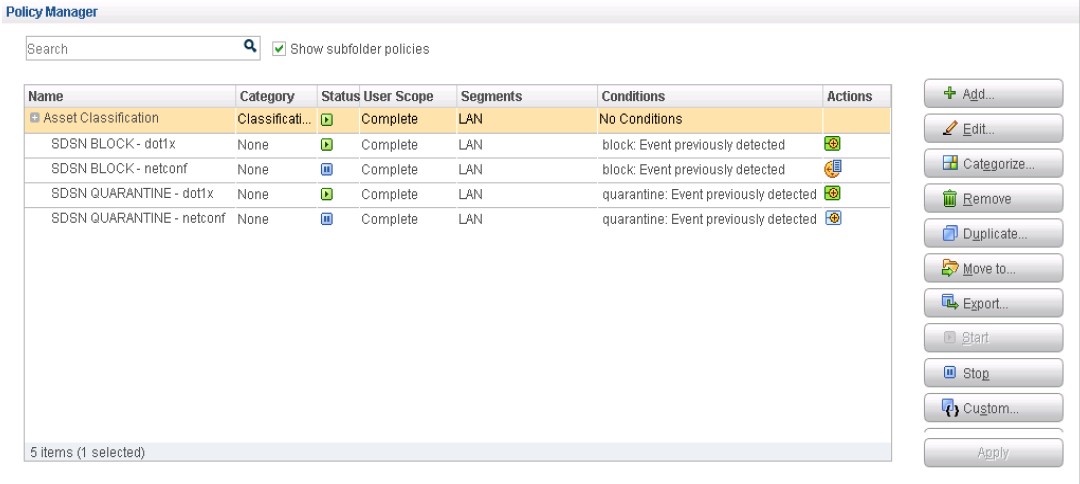
Navigate to the Policies tab. From the Console, stop both SDSN BLOCK–dot1x and SDSN QUARANTINE–dot1x polices, and start both SDSN BLOCK–NETCONF and SDSN QUARANTINE–NETCONF policies.
Figure 89: Policies Tab in Policy Manager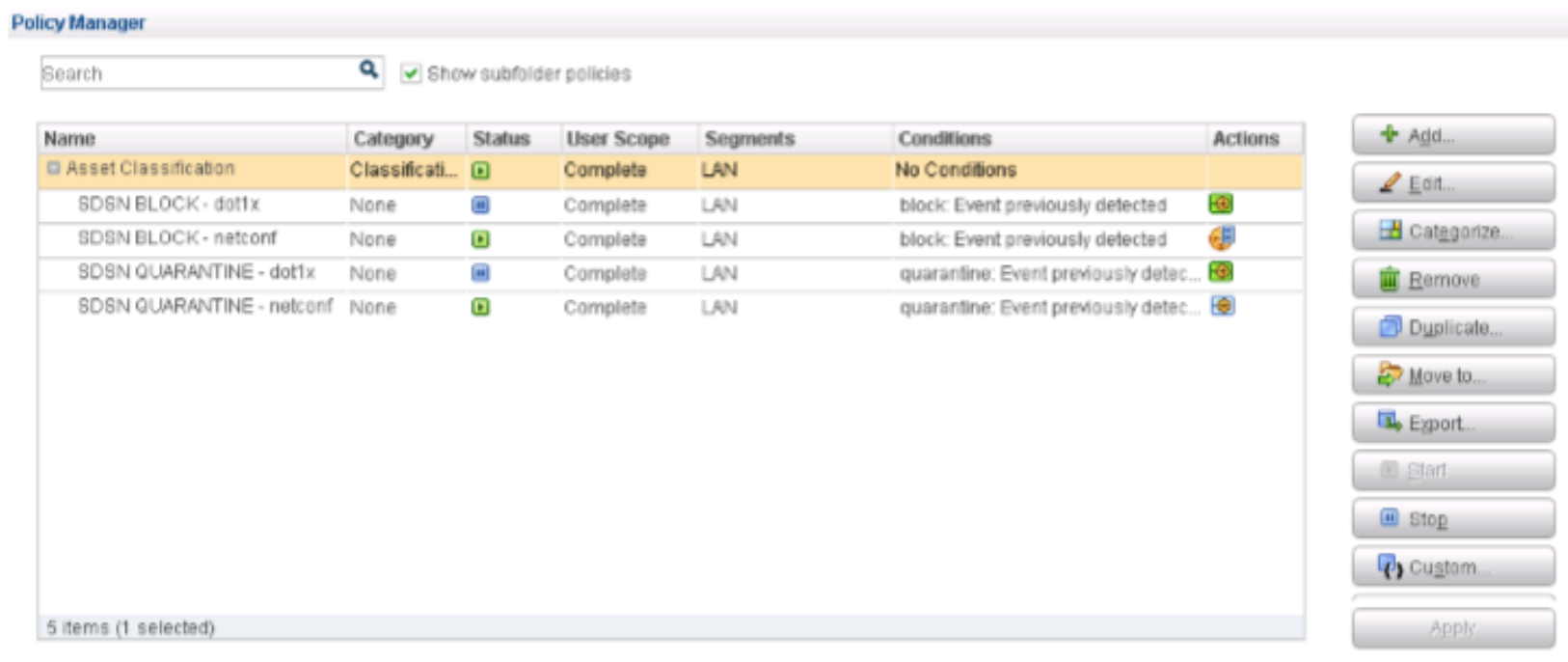
Confirm that the Linux host is in User VLAN (vlan31) with IP address 10.10.30.99.
Figure 90: Linux Host Confirmation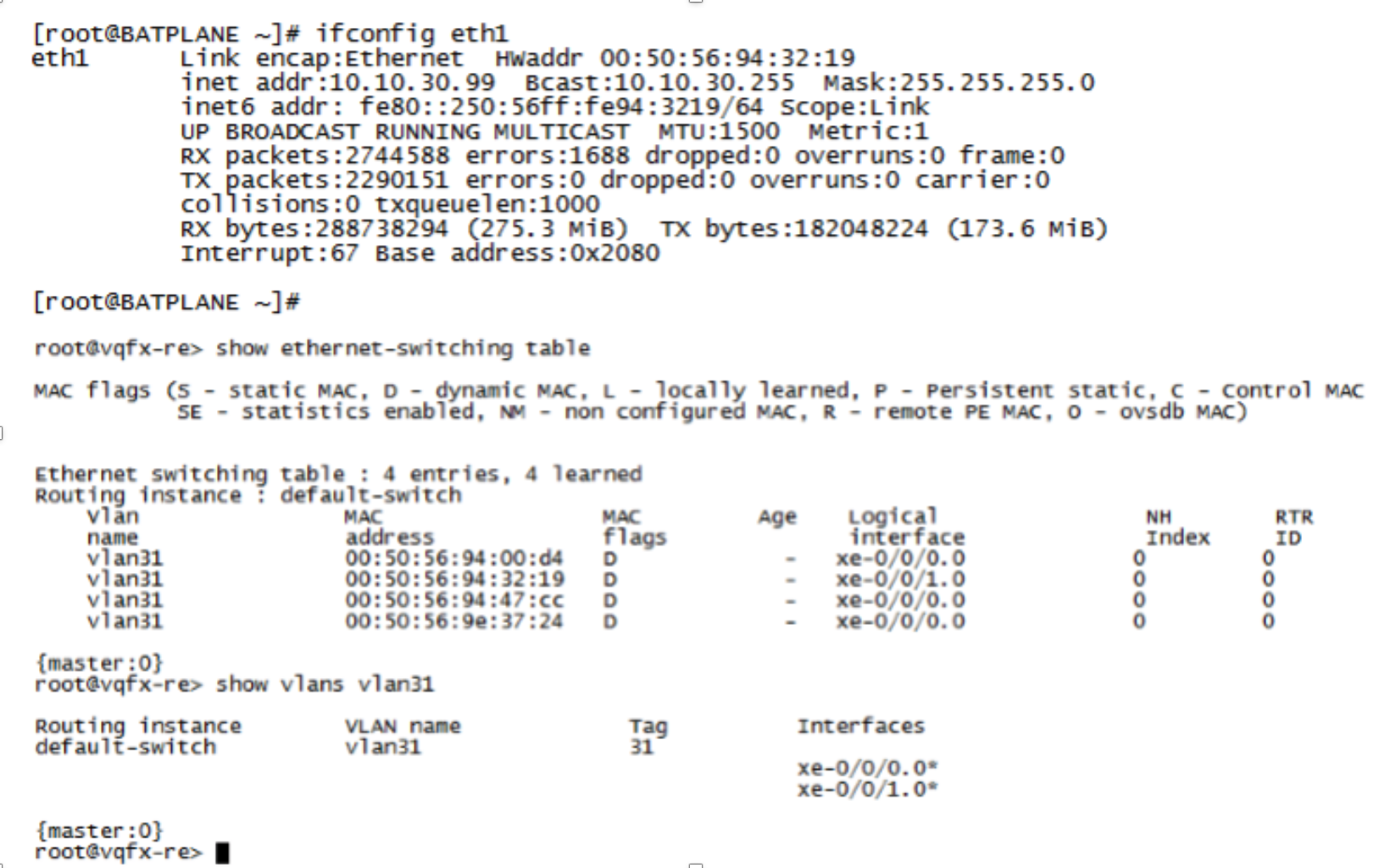
Confirm that the endpoint 10.10.30.99 can ping to Internet (IP address 8.8.8.8) and Layer 2 connected default gateway (10.10.30.254). Before the attack, the endpoint starts continuous pings to other endpoints on the LAN and Internet.
Figure 91: Internet Ping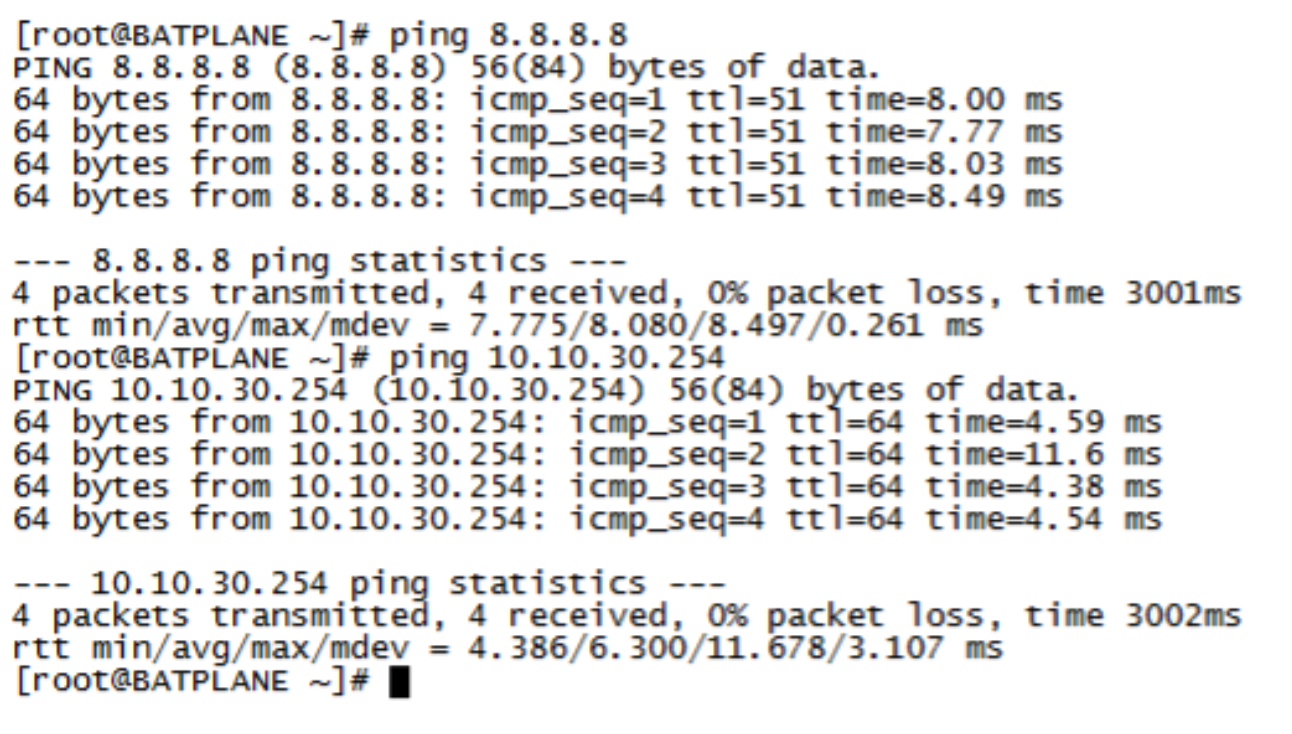
The endpoint pings the C&C server on the Internet from the Linux host (in this example from the IP address 184.75.221.43).
Figure 92: C&C Server Ping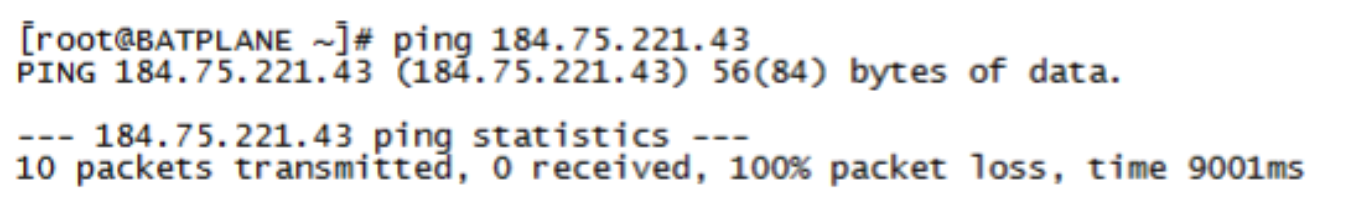
After the attack, ForeScout CounterACT applies ACL on the QFX switch using NETCONF. Confirm the following:
Confirm that the Linux host cannot connect to the Internet or the LAN anymore.
Figure 93: Confirming Disconnected Linux Host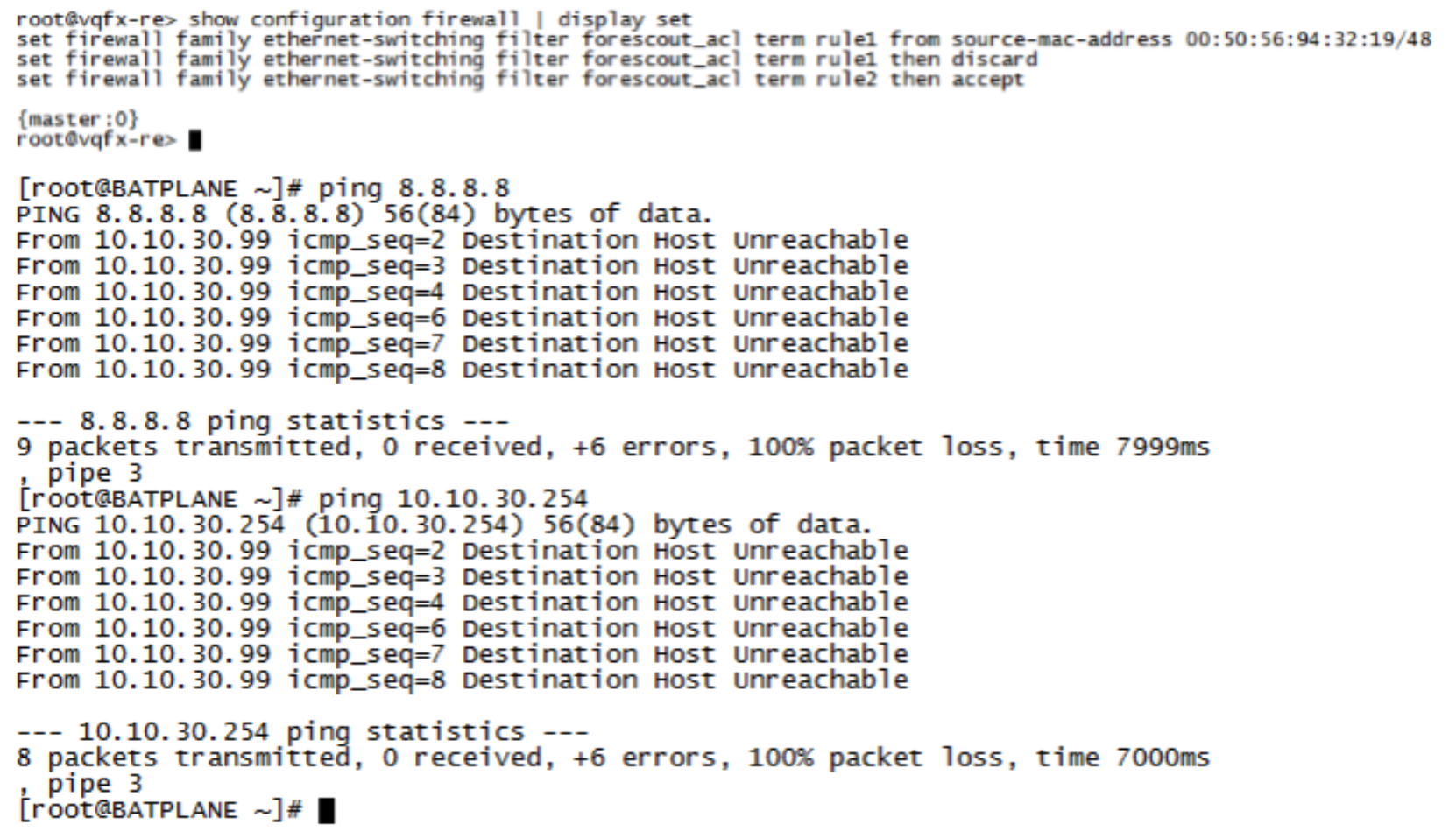
Confirm the SDSN BLOCK (NETCONF) policy match and automated threat remediation action details by navigating to ForeScout CounterACT > Home.
Figure 94: Confirming Policy Match and Automated Threat Remediation Details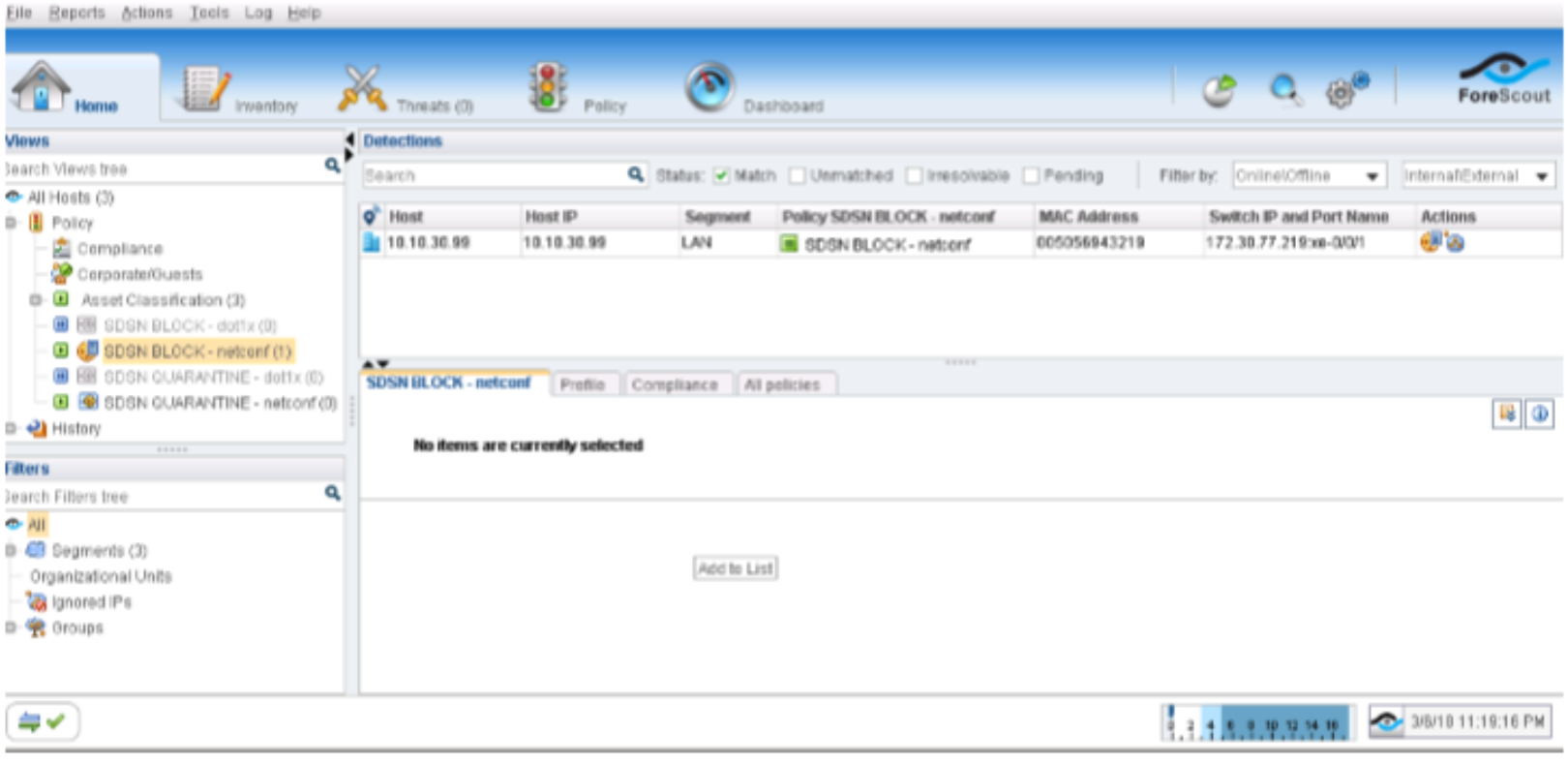
Navigate to Log > Host Log. Review the details for the SDSN BLOCK (NETCONF) policy.
Figure 95: SDSN Block Host Log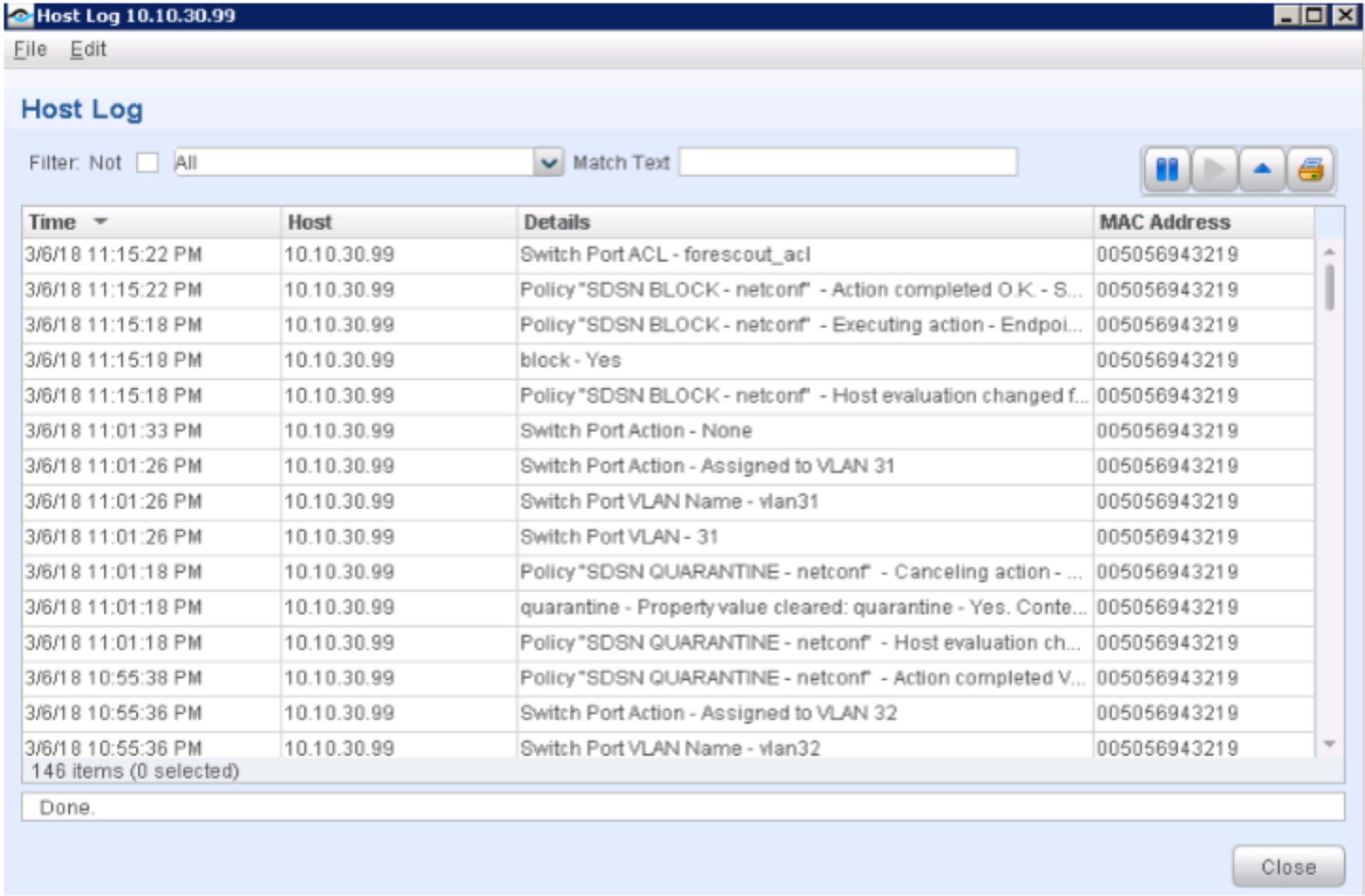
Confirm that the Linux host’s IP address was also added to the Infected-Hosts Feed on the SRX Series device to block Internet access.
user@vSRX_L3> show security dynamic-address category-name Infected-Hosts No. IP-start IP-end Feed Address 1 10.10.30.99 10.10.30.99 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-2150001a Total number of matching entries: 1 user@vSRX_L3>
In the ATP Cloud portal, navigate to Monitor > Hosts. Confirm the host IP address (10.10.30.99), MAC-ID, and switch port of the Linux host.
Figure 96: Confirming Host Information in ATP Cloud Portal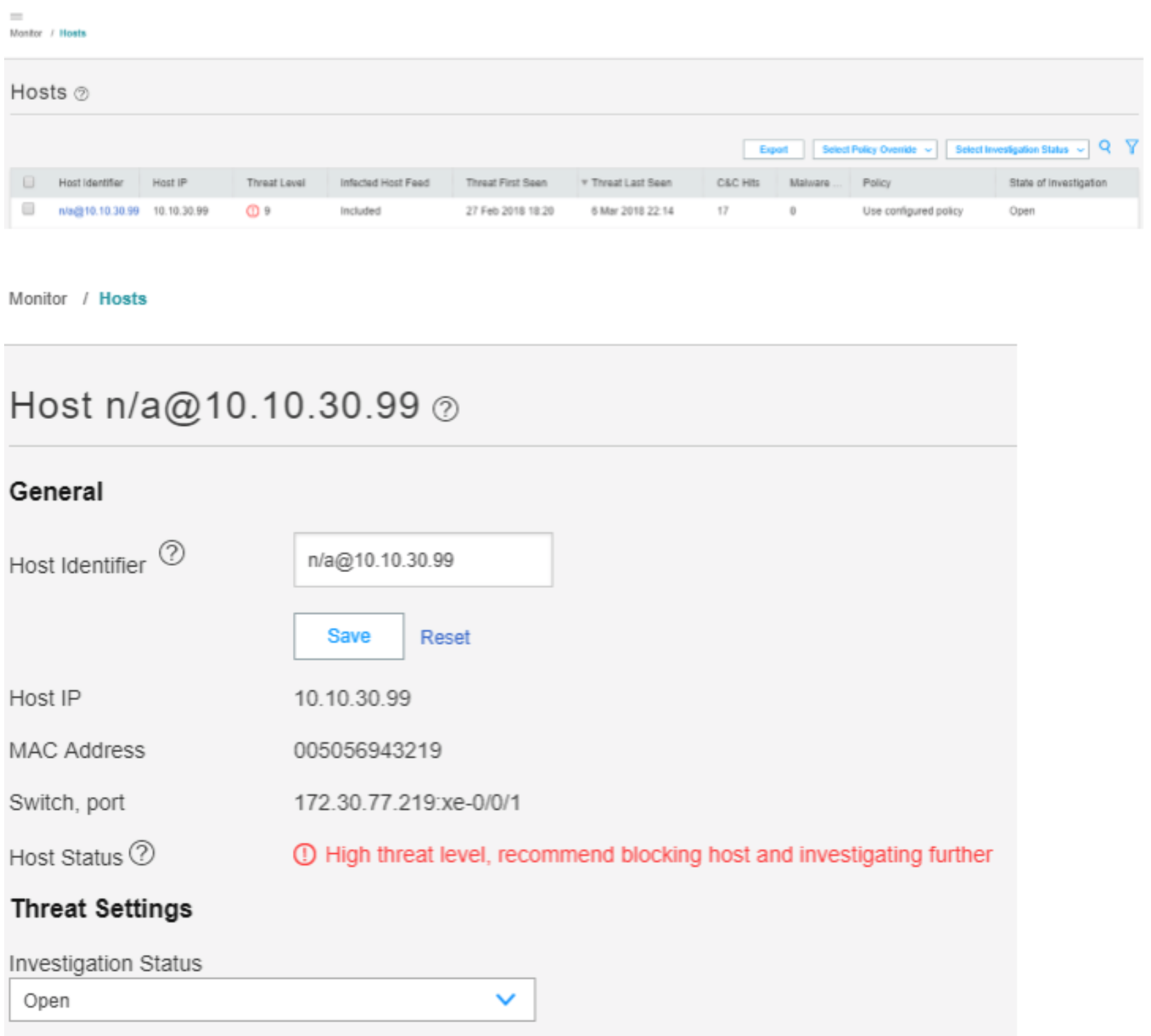
Meaning
All ping sessions show that the traffic is blocked after the threat was detected, confirming that the automated threat remediation use case is working properly.
The Hosts page lists compromised hosts and their associated threat levels. The output confirms that ATP Cloud and Security Director have detected the infected host. You can monitor and mitigate malware detections on a per host basis.
Verify ForeScout CounterACT Functionality to Quarantine Infected Endpoint (with NETCONF)
Purpose
Test the ForeScout CounterACT integration and functionality when an endpoint is infected. In this example, you verify when the enforcement policy NETCONF, and it is configured to quarantine the infected host.
Action
A client VM or physical PC is required to trigger an attack.
Before the attack, confirm the following:
Release the infected host on the ATP Cloud portal or in Security Director (Monitor > Threat Prevention > Hosts).
Ensure that Internet or LAN access is restored for the Linux host.
On the Policy Enforcer > Threat Prevention Policy page, change infected host profile actions to Quarantine and add the VLAN ID as vlan32. Click OK.
Figure 97: Changing Threat Prevention Policy to Quarantine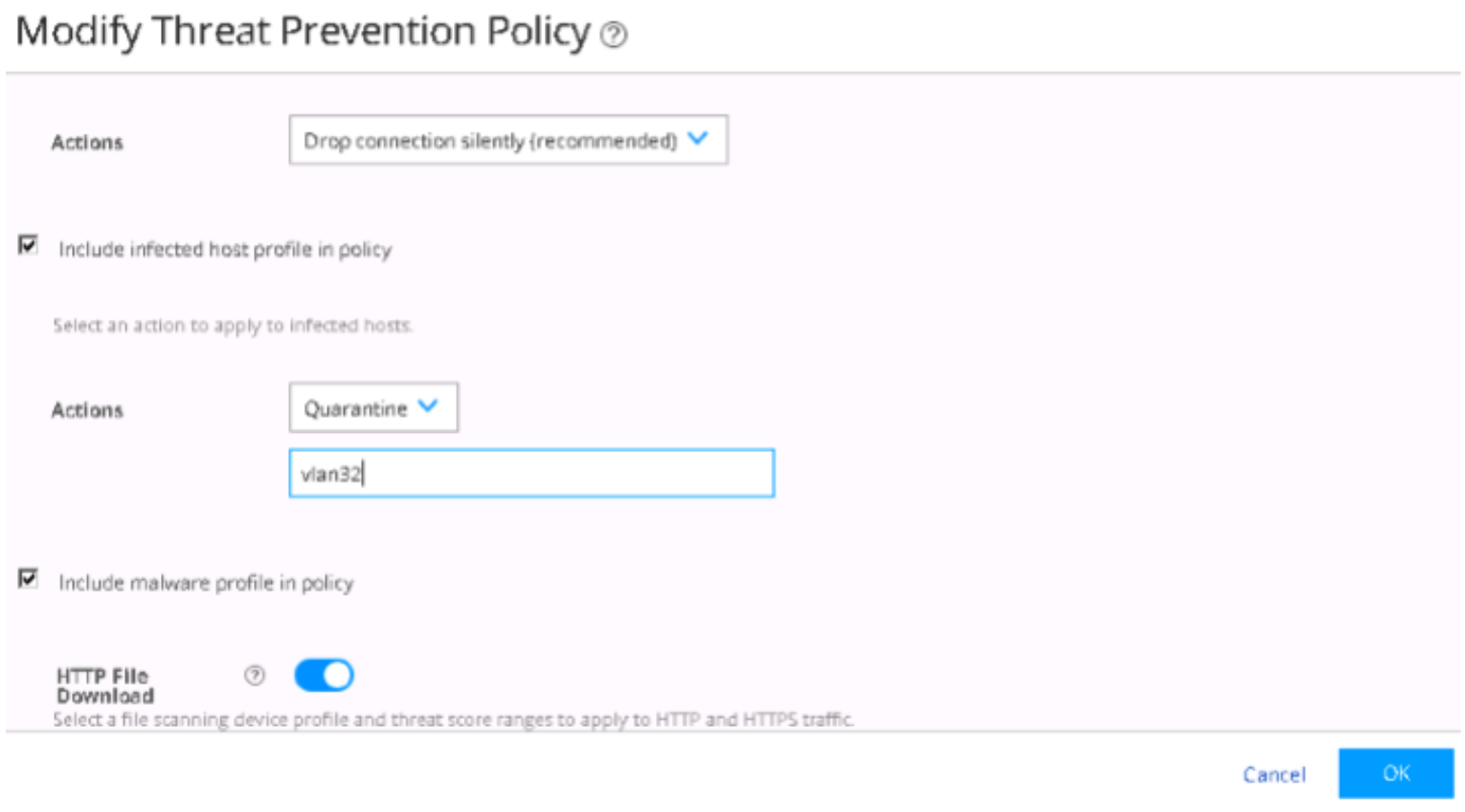
Confirm that the Linux host is in User VLAN (vlan31) with IP address 10.10.30.99.
Figure 98: Confirming Linux Host Details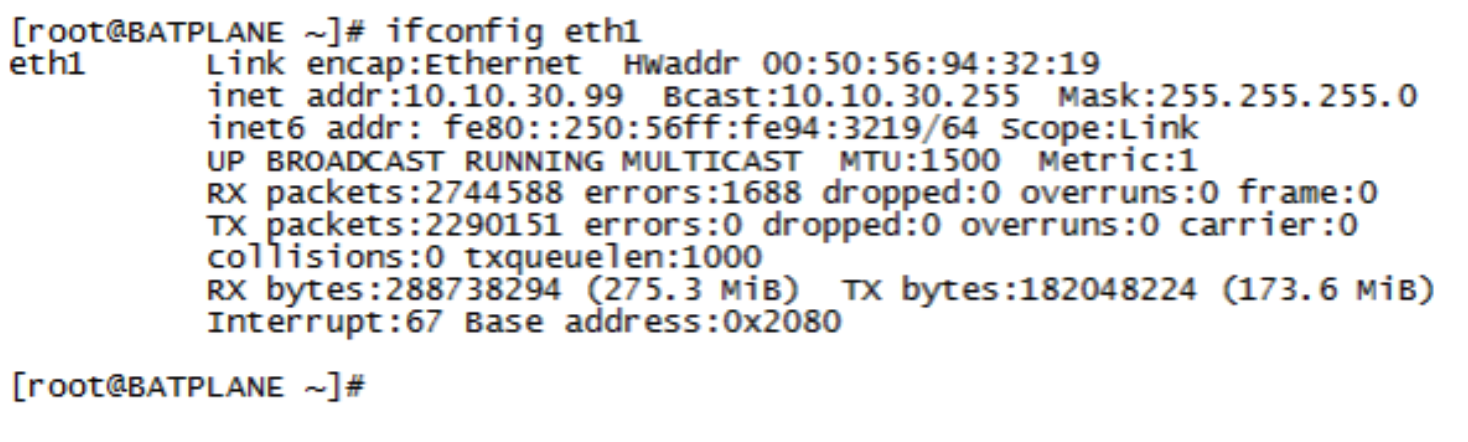
Confirm that the endpoint 10.10.30.99 can ping to Internet (IP address 8.8.8.8) and Layer 2 connected default gateway (10.10.30.254). Before the attack, the endpoint starts continuous pings to other endpoints on the LAN and Internet.
Figure 99: Confirming Internet Connectivity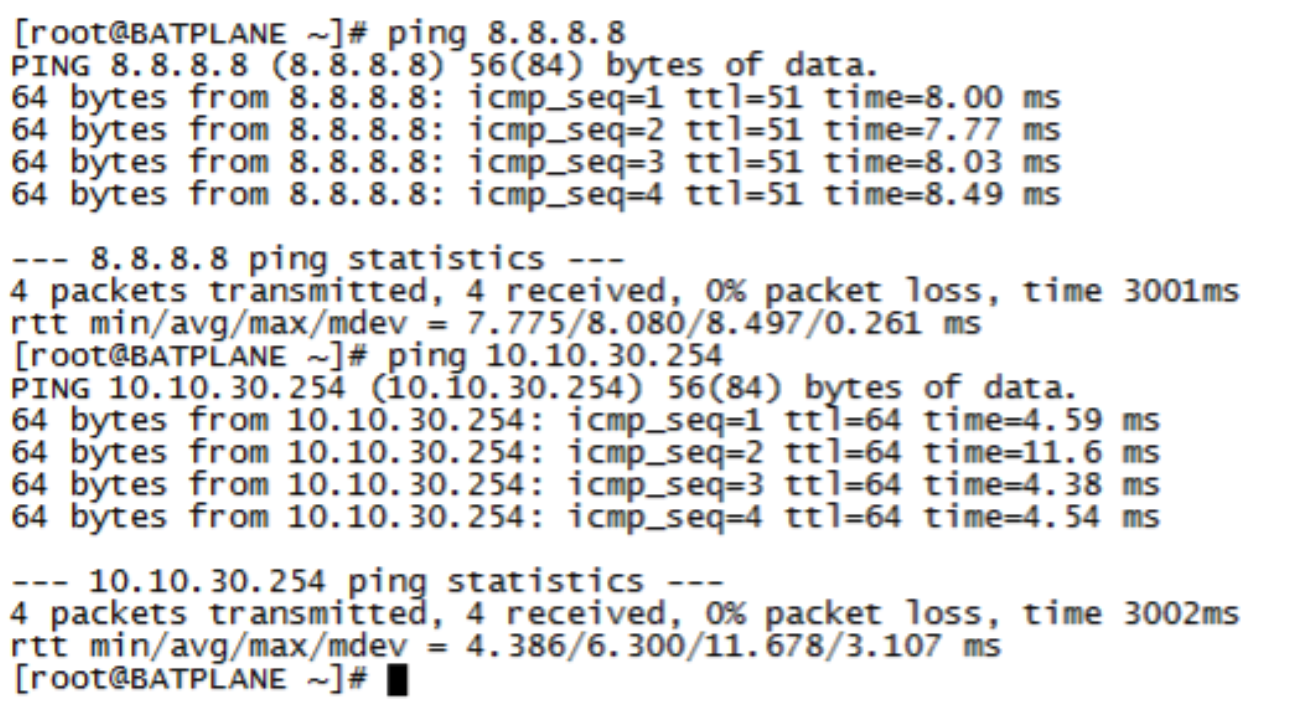
The endpoint pings the C&C server on the Internet from the Linux host (in this example from the IP address 184.75.221.43).
Figure 100: Confirming Connection to C&C Server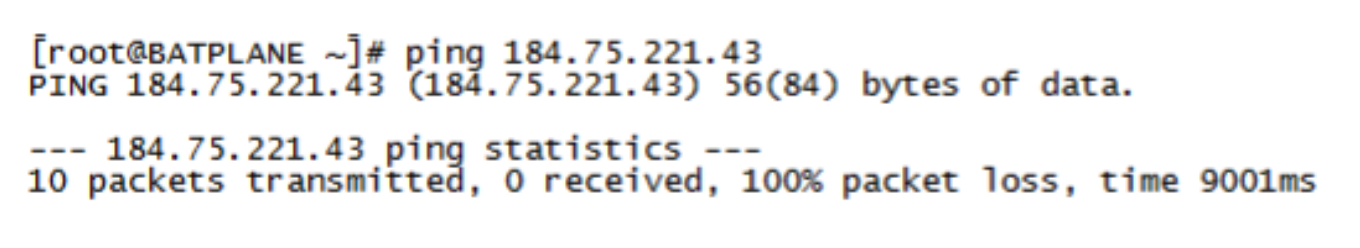
After the attack, ForeScout CounterACT changes the VLAN configuration of the interface connecting the Linux host from User VLAN (vlan31) to Quarantine VLAN (vlan32) on the QFX switch using NETCONF.
Confirm the following:
Confirm that the Linux host cannot connect to the Internet or the LAN anymore.
Figure 101: Confirming Linux Host Cannot Connect to Internet or LAN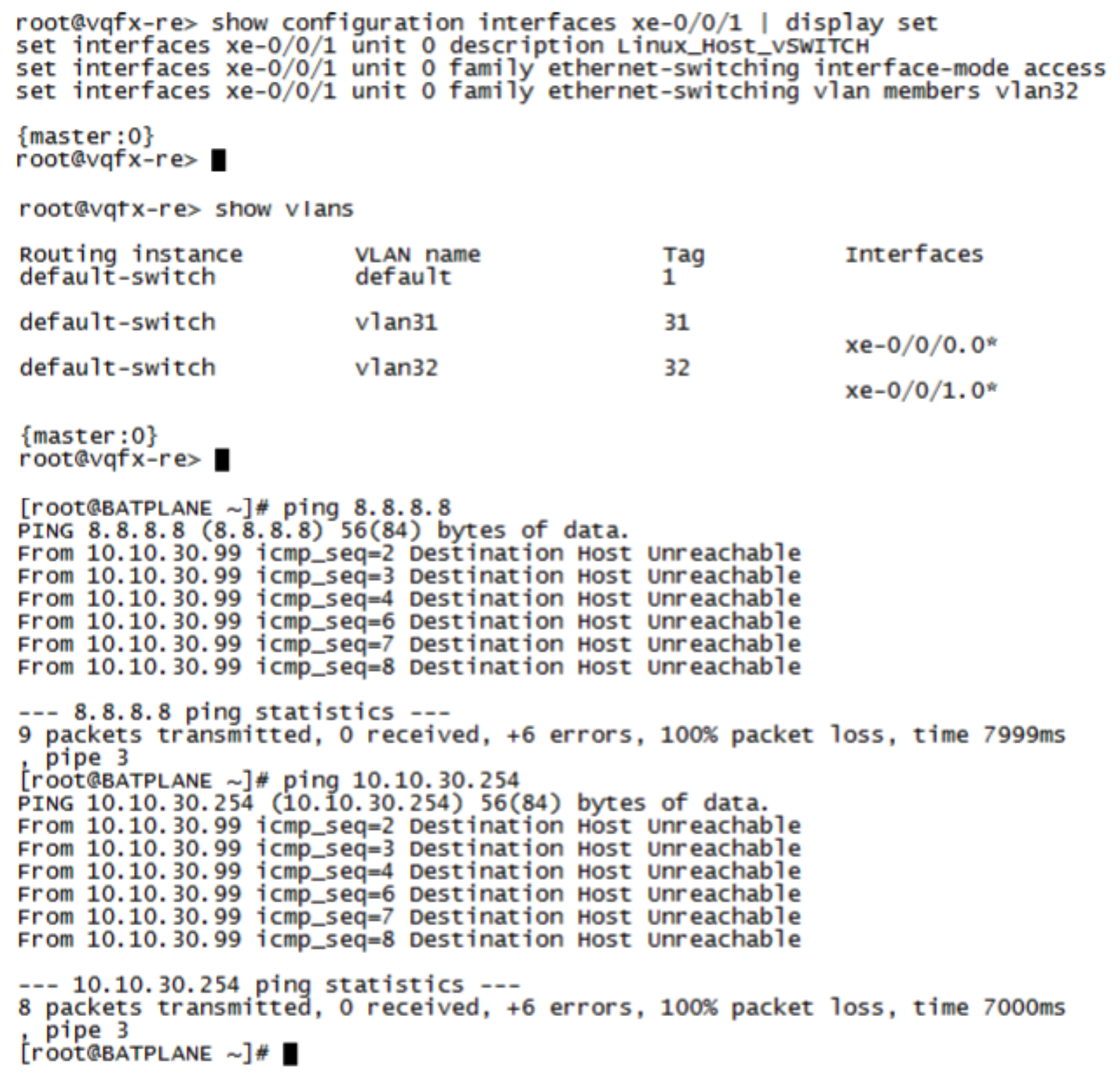
Confirm the SDSN QUARANTINE (NETCONF) policy match and automated threat remediation action details by navigating to ForeScout CounterACT > Home.
Figure 102: Confirming Policy Match and Automated Threat Remediation Details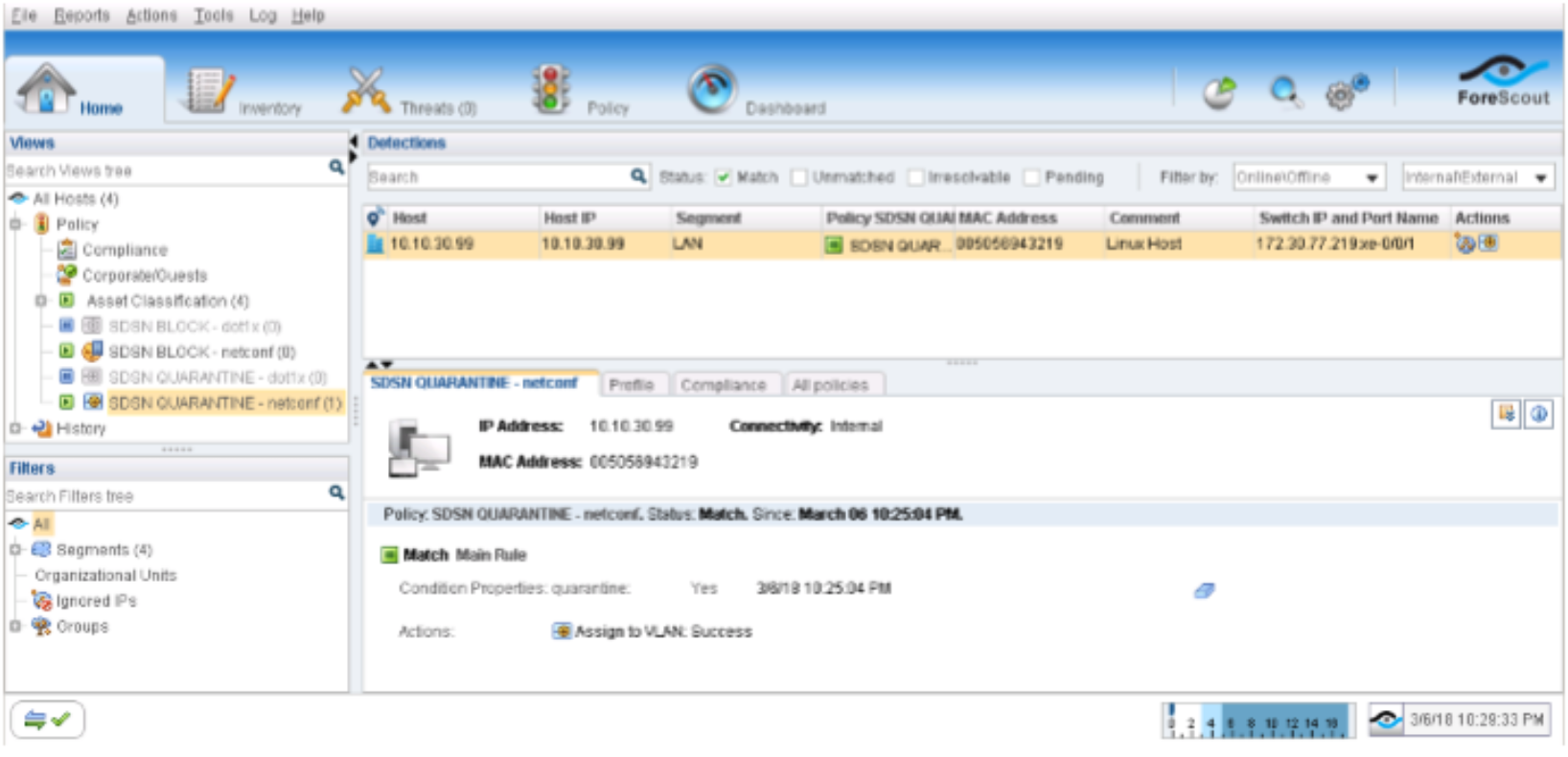
Navigate to Log > Host Log. Review the details for the SDSN BLOCK (NETCONF) policy.
Figure 103: SDSN Block Policy Host Log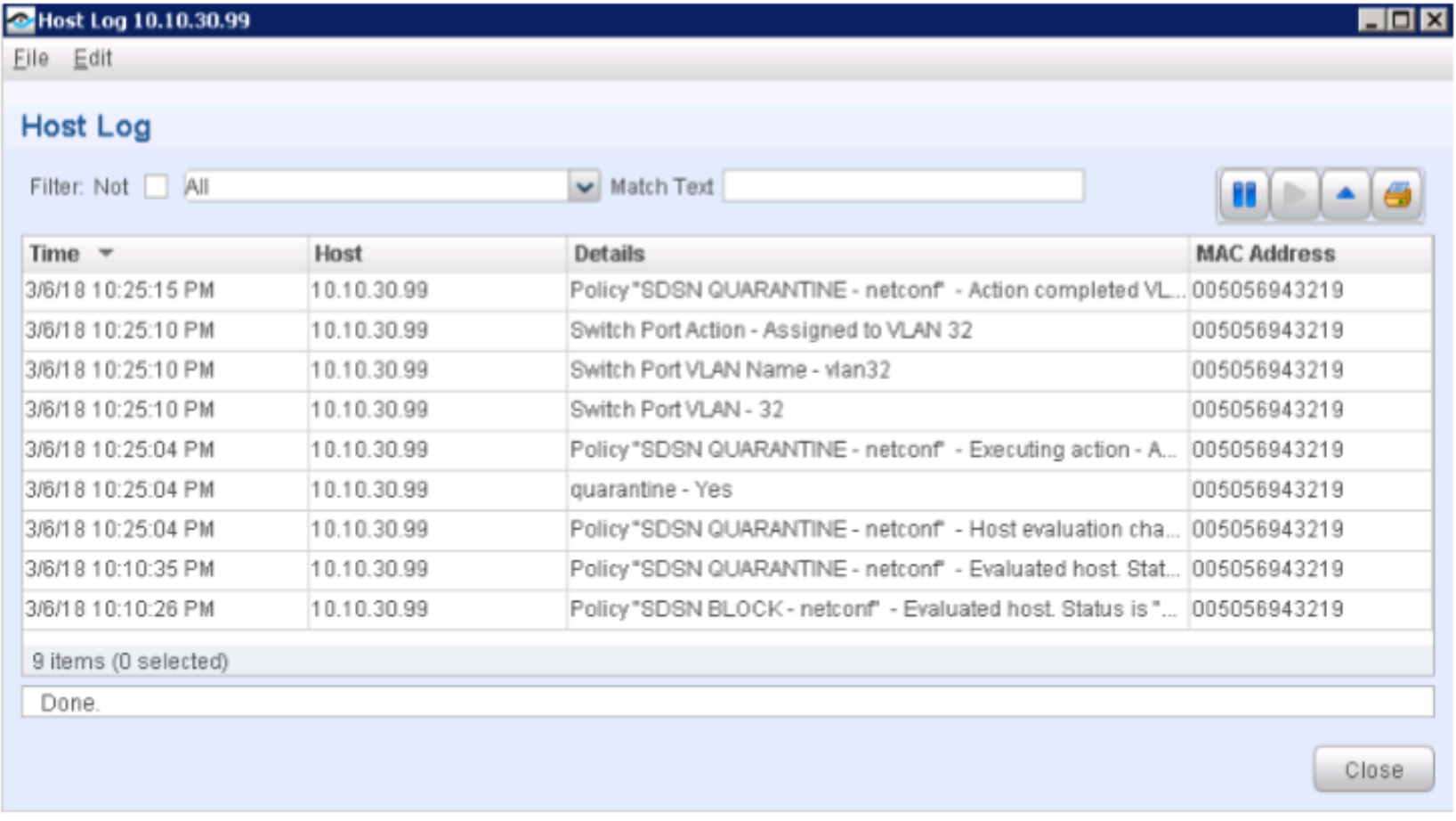
Confirm that the Linux host’s IP address was also added to the Infected-Hosts Feed on the SRX Series device to block Internet access.
user@vSRX_L3> show security dynamic-address category-name Infected-Hosts No. IP-start IP-end Feed Address 1 10.10.30.99 10.10.30.99 Infected-Hosts/1 ID-2150001a Total number of matching entries: 1 user@vSRX_L3>
In the ATP Cloud portal, navigate to Monitor > Hosts. Confirm the host IP address (10.10.30.99), MAC-ID, and switch port of the Linux host.
Figure 104: Confirming Host Details in ATP Cloud Portal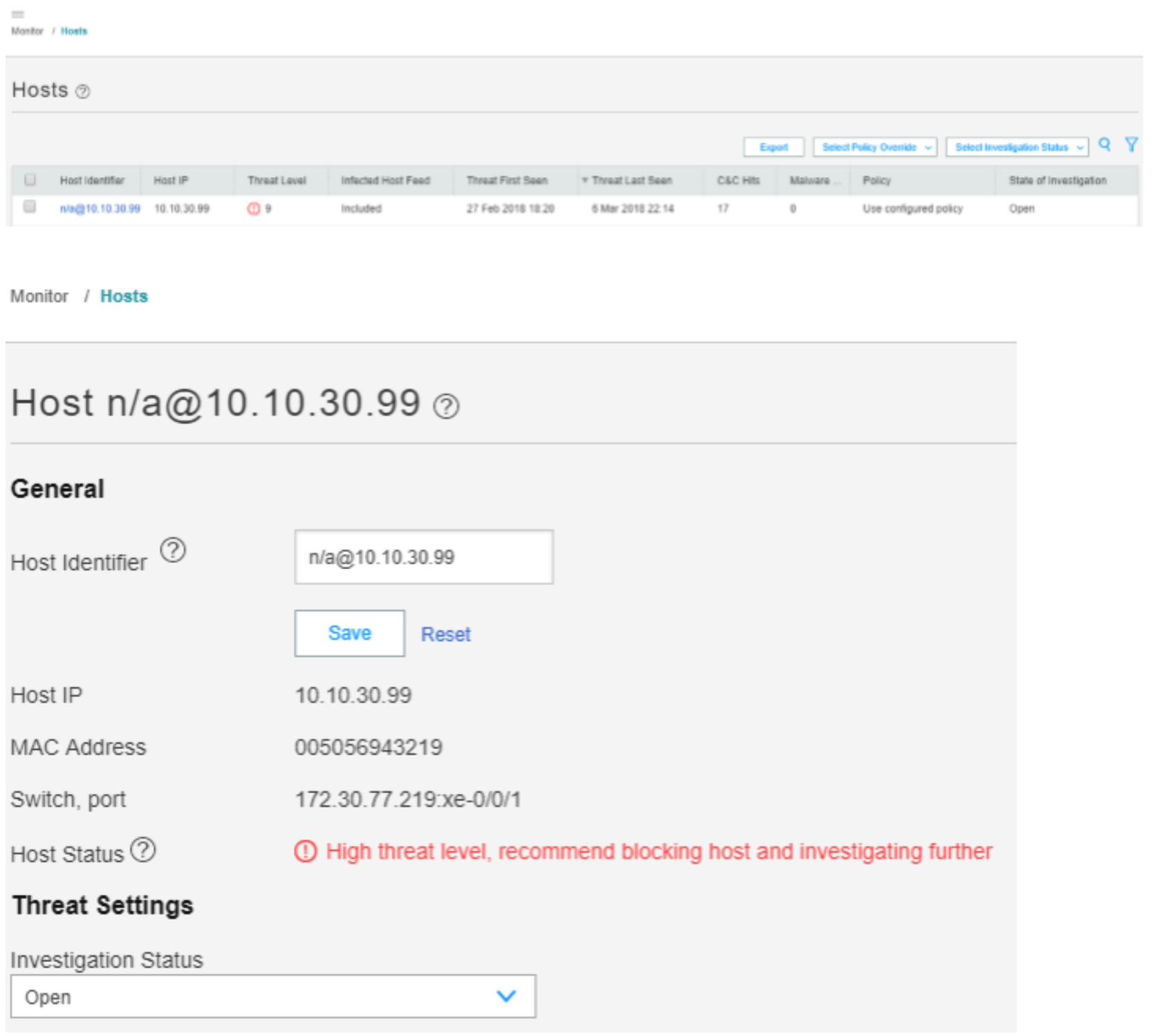
Meaning
The output shows that the ATP Cloud infected host feed containing the Linux host’s IP address 10.10.30.99 has been successfully downloaded, resulting in the SRX device taking an action to quarantine the IP address.
The Hosts page lists compromised hosts and their associated threat levels. The output confirms that ATP Cloud and Security Director have detected and quarantined the infected host. You can monitor and mitigate malware detections on a per host basis.
Appendix A: Device Configurations
This section provides the following device configurations:
- CLI Configuration for SRX Series Device
- CLI Configuration for EX4300 Switch
- CLI Configuration for QFX Switch
CLI Configuration for SRX Series Device
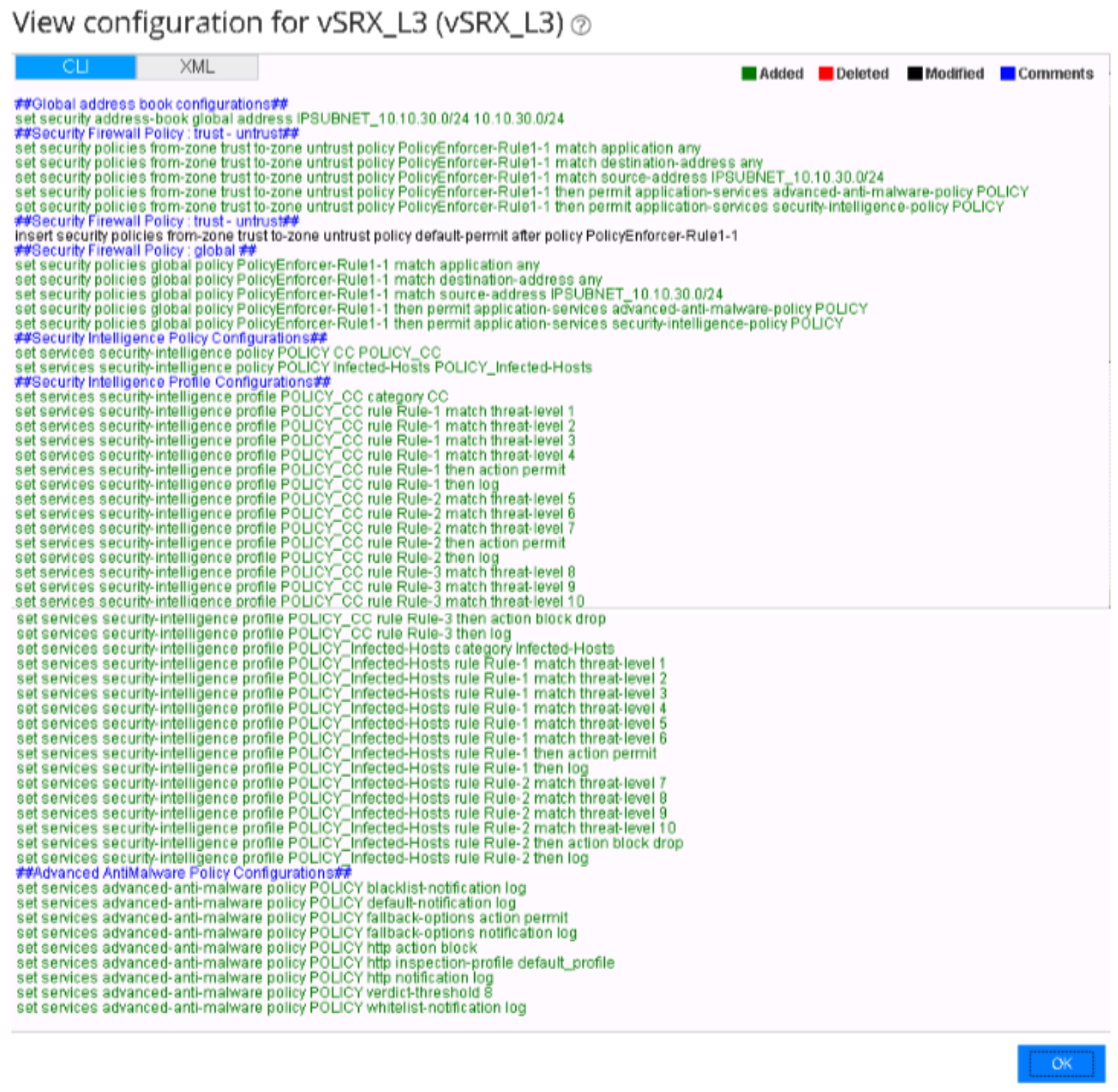
set version 15.1X49-D110.4 set system host-name vSRX_L3 set system time-zone Europe/Amsterdam set system root-authentication encrypted-password "$ABC123" set system name-server 172.29.143.60 set system services ssh max-sessions-per-connection 32 set system services netconf ssh set system services dhcp-local-server group wan-dhcp interface ge-0/0/1.0 set system services web-management http interface fxp0.0 set system syslog user * any emergency set system syslog file messages any any set system syslog file messages authorization info set system syslog file interactive-commands interactive-commands any set system syslog file default-log-messages any info set system syslog file default-log-messages match "(requested 'commit' operation)|(requested 'commit synchronize' operation)|(copying configuration to juniper.save)|(commit complete)|ifAdminStatus|(FRU power)|(FRU removal)|(FRU insertion)|(link UP)|transitioned|Transferred|transfer-file|(license add)|(license delete)|(package -X update)|(package -X delete)|(FRU Online)|(FRU Offline)|(plugged in)|(unplugged)|GRES" set system syslog file default-log-messages structured-data set system license autoupdate url https://ae1.juniper.net/junos/key_retrieval set system ntp boot-server 172.30.77.162 set system ntp server 172.30.77.162 set services application-identification set services ssl initiation profile aamw-ssl trusted-ca aamw-secintel-ca set services ssl initiation profile aamw-ssl trusted-ca aamw-cloud-ca set services ssl initiation profile aamw-ssl client-certificate aamw-srx-cert set services ssl initiation profile aamw-ssl actions crl disable set services security-intelligence url https://172.30.77.104:443/api/v1/manifest.xml set services security-intelligence authentication auth-token 22QDFN29DJQXK7ZD3V8Q21X34THWKBC7 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC category CC set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-1 match threat-level 1 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-1 match threat-level 2 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-1 match threat-level 3 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-1 match threat-level 4 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-1 then action permit set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-1 then log set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-2 match threat-level 5 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-2 match threat-level 6 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-2 match threat-level 7 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-2 then action permit set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-2 then log set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-3 match threat-level 8 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-3 match threat-level 9 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-3 match threat-level 10 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-3 then action block drop set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_CC rule Rule-3 then log set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts category Infected-Hosts set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-1 match threat-level 1 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-1 match threat-level 2 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-1 match threat-level 3 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-1 match threat-level 4 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-1 match threat-level 5 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-1 match threat-level 6 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-1 then action permit set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-1 then log set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-2 match threat-level 7 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-2 match threat-level 8 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-2 match threat-level 9 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-2 match threat-level 10 set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-2 then action block drop set services security-intelligence profile POLICY_Infected-Hosts rule Rule-2 then log set services security-intelligence policy POLICY CC POLICY_CC set services security-intelligence policy POLICY Infected-Hosts POLICY_Infected-Hosts set services advanced-anti-malware connection url https://srxapi.eu-west-1.sky.junipersecurity.net set services advanced-anti-malware connection authentication tls-profile aamw-ssl set services advanced-anti-malware policy POLICY http inspection-profile default_profile set services advanced-anti-malware policy POLICY http action block set services advanced-anti-malware policy POLICY http notification log set services advanced-anti-malware policy POLICY verdict-threshold 8 set services advanced-anti-malware policy POLICY fallback-options action permit set services advanced-anti-malware policy POLICY fallback-options notification log set services advanced-anti-malware policy POLICY default-notification log set services advanced-anti-malware policy POLICY whitelist-notification log set services advanced-anti-malware policy POLICY blacklist-notification log set security log mode stream set security log format sd-syslog set security log report set security log source-address 10.10.10.251 set security log stream TRAFFIC category all set security log stream TRAFFIC host 10.10.10.250 set security log stream TRAFFIC host port 514 set security pki ca-profile aamw-ca ca-identity deviceCA set security pki ca-profile aamw-ca enrollment url http://ca.junipersecurity.net:8080/ejbca/publicweb/apply/scep/SRX/pkiclient.exe set security pki ca-profile aamw-ca revocation-check disable set security pki ca-profile aamw-ca revocation-check crl url http://va.junipersecurity.net/ca/deviceCA.crl set security pki ca-profile aamw-secintel-ca ca-identity JUNIPER set security pki ca-profile aamw-secintel-ca revocation-check crl url http://va.junipersecurity.net/ca/current.crl set security pki ca-profile aamw-cloud-ca ca-identity JUNIPER_CLOUD set security pki ca-profile aamw-cloud-ca revocation-check crl url http://va.junipersecurity.net/ca/cloudCA.crl set security address-book global address IPSUBNET_10.10.30.0/24 10.10.30.0/24 set security screen ids-option untrust-screen icmp ping-death set security screen ids-option untrust-screen ip source-route-option set security screen ids-option untrust-screen ip tear-drop set security screen ids-option untrust-screen tcp syn-flood alarm-threshold 1024 set security screen ids-option untrust-screen tcp syn-flood attack-threshold 200 set security screen ids-option untrust-screen tcp syn-flood source-threshold 1024 set security screen ids-option untrust-screen tcp syn-flood destination-threshold 2048 set security screen ids-option untrust-screen tcp syn-flood queue-size 2000 set security screen ids-option untrust-screen tcp syn-flood timeout 20 set security screen ids-option untrust-screen tcp land set security nat source rule-set OutBoundInternetTraffic from zone trust set security nat source rule-set OutBoundInternetTraffic to zone untrust set security nat source rule-set OutBoundInternetTraffic rule natALL match source-address 0.0.0.0/0 set security nat source rule-set OutBoundInternetTraffic rule natALL match destination-address 0.0.0.0/0 set security nat source rule-set OutBoundInternetTraffic rule natALL then source-nat interface set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy PolicyEnforcer-Rule1-1 match source-address IPSUBNET_10.10.30.0/24 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy PolicyEnforcer-Rule1-1 match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy PolicyEnforcer-Rule1-1 match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy PolicyEnforcer-Rule1-1 then permit applicationservices security-intelligence-policy POLICY set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy PolicyEnforcer-Rule1-1 then permit applicationservices advanced-anti-malware-policy POLICY set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy default-permit match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy default-permit match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy default-permit match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy default-permit then permit set security policies global policy PolicyEnforcer-Rule1-1 match source-address IPSUBNET_10.10.30.0/24 set security policies global policy PolicyEnforcer-Rule1-1 match destination-address any set security policies global policy PolicyEnforcer-Rule1-1 match application any set security policies global policy PolicyEnforcer-Rule1-1 then permit application-services securityintelligence-policy POLICY set security policies global policy PolicyEnforcer-Rule1-1 then permit application-services advanced-antimalware-policy POLICY set security zones security-zone trust tcp-rst set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services all set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic protocols all set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security zones security-zone untrust screen untrust-screen set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services all set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic protocols all set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 description LOGGING-INTERFACE-VLAN10 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.10.10.251/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 description LAN-VLAN31 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 vlan-tagging set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 vlan-id 31 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.10.30.254/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 description INTERNET-MANAGEMENT set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.30.77.230/23 set interfaces fxp0 unit 0 deactivate interfaces fxp0 set snmp trap-group space targets 172.30.77.106 set routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 172.30.77.1 set access address-assignment pool wan-1 family inet network 10.10.30.0/24 set access address-assignment pool wan-1 family inet range wan-1-range low 10.10.30.60 set access address-assignment pool wan-1 family inet range wan-1-range high 10.10.30.100 set access address-assignment pool wan-1 family inet dhcp-attributes maximum-lease-time 86400 set access address-assignment pool wan-1 family inet dhcp-attributes name-server 8.8.8.8 set access address-assignment pool wan-1 family inet dhcp-attributes name-server 172.30.77.162 set access address-assignment pool wan-1 family inet dhcp-attributes router 10.10.30.254
CLI Configuration for EX4300 Switch
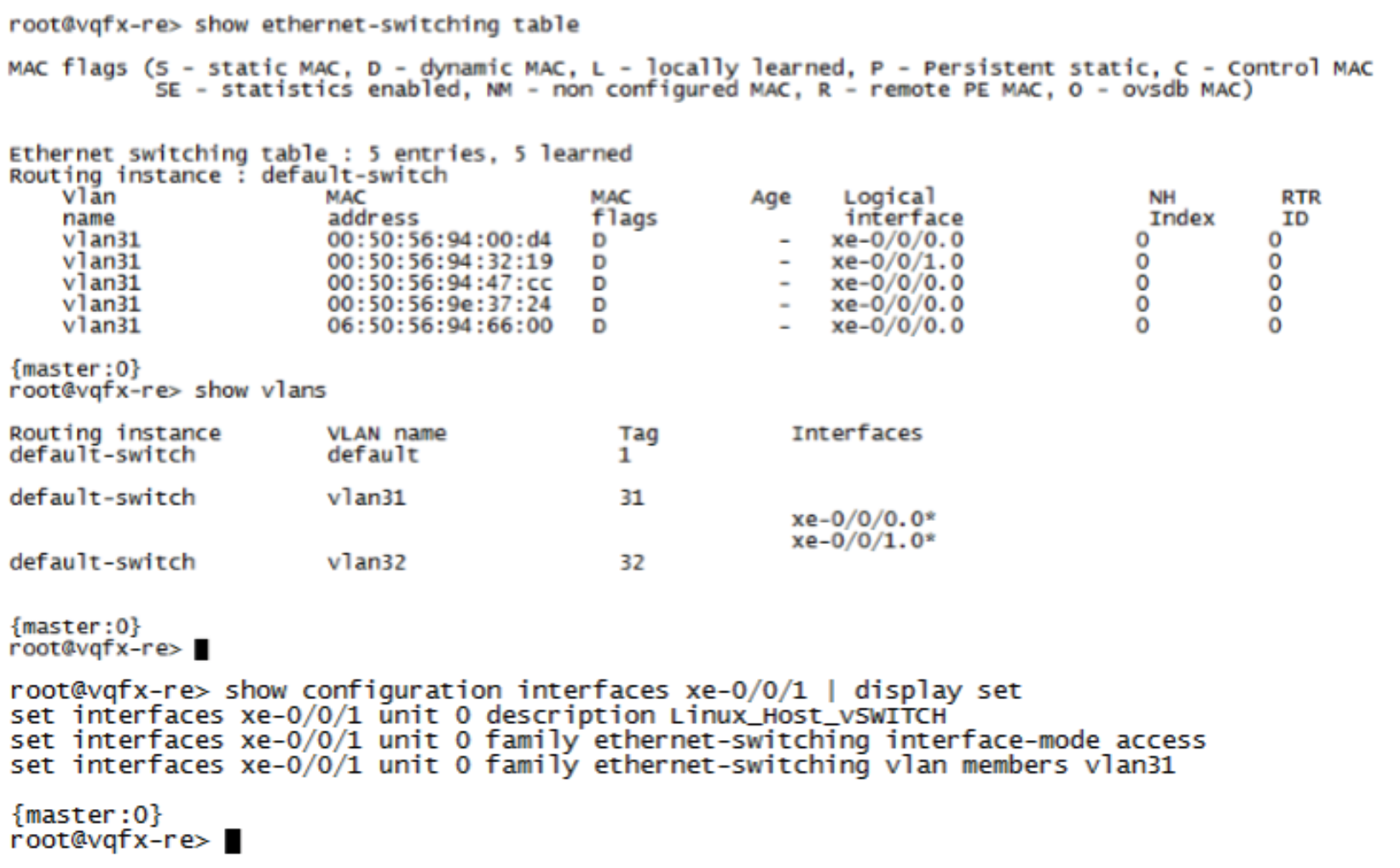
set version 15.1R5.5 set system host-name abernathy set system services ssh root-login allow set system services ssh protocol-version v2 set system services ssh max-sessions-per-connection 32 set system services netconf ssh set system ntp server 172.30.255.62 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 description PORT_TO_ESXi_vmnic0_vSRX_LOGGING set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members LOGGING set interfaces ge-0/0/18 description PORT_TO_ESXi_vmnic1_vSRX_vQFX_LAN set interfaces ge-0/0/18 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk set interfaces ge-0/0/18 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan31 set interfaces ge-0/0/19 description PORT_TO_ESXi_vmnic2_WINDOWS7_DOT1x set interfaces ge-0/0/19 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/19 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members default set interfaces ge-0/0/20 description SPAN_PORT_TO_ESXi_vmnic3_COUNTERACT_EXPERIMENTAL set interfaces ge-0/0/20 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/20 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members default set interfaces me0 unit 0 family inet address 172.30.77.62/23 set routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 172.30.77.1 set protocols igmp set protocols dot1x authenticator authentication-profile-name CounterACT set protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/19.0 supplicant multiple set protocols rstp set access radius-server 172.30.77.100 dynamic-request-port 3799 set access radius-server 172.30.77.100 secret "$ABC123" set access radius-server 172.30.77.100 source-address 172.30.77.62 set access profile CounterACT authentication-order radius set access profile CounterACT radius authentication-server 172.30.77.100 set access profile CounterACT radius accounting-server 172.30.77.100 set access profile CounterACT radius options nas-identifier 172.30.77.100 set access profile CounterACT accounting order radius set ethernet-switching-options analyzer mirror_traffic input ingress interface ge-0/0/18.0 set ethernet-switching-options analyzer mirror_traffic input ingress interface ge-0/0/19.0 set ethernet-switching-options analyzer mirror_traffic input egress interface ge-0/0/18.0 set ethernet-switching-options analyzer mirror_traffic input egress interface ge-0/0/19.0 set ethernet-switching-options analyzer mirror_traffic output interface ge-0/0/20.0 set ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port vlan vlan31 examine-dhcp set vlans LOGGING description LOGGING set vlans LOGGING vlan-id 10 set vlans vlan31 description LAN-VLAN31 set vlans vlan31 vlan-id 31 set vlans vlan32 description QUARANTINE set vlans vlan32 vlan-id 32 set poe interface all
CLI Configuration for QFX Switch
set system host-name vqfx-re set system root-authentication encrypted-password "$ABC123" set system root-authentication ssh-rsa "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA6NF8iallvQVp22WDkTkyrtvp9eWW6A8YVr+kz4TjGYe7gHzIw+niNltGEFHzD8+v1I2YJ6oXevct1YeS0o9H ZyN1Q9qgCgzUFtdOKLv6IedplqoPkcmF0aYet2PkEDo3MlTBckFXPITAMzF8dJSIFo9D8HfdOV0IAdx4O7PtixWKn5y2hMNG0zQPyUecp4pzC6ki vAIhyfHilFR61RGL+GPXQ2MWZWFYbAGjyiYJnAmCP3NOTd0jMZEnDkbUvxhMmBYSdETk1rRgm+R4LOzFUGaHqHDLKLX+FIPKcF96hrucXzcWyLbI bEgE98OHlnVYCzRdK8jlqm8tehUc9c9WhQ== vagrant insecure public key" set system login user vagrant uid 2000 set system login user vagrant class super-user set system login user vagrant authentication ssh-rsa "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA6NF8iallvQVp22WDkTkyrtvp9eWW6A8YVr+kz4TjGYe7gHzIw+niNltGEFHzD8+v1I2YJ6oXevct1YeS0o9H ZyN1Q9qgCgzUFtdOKLv6IedplqoPkcmF0aYet2PkEDo3MlTBckFXPITAMzF8dJSIFo9D8HfdOV0IAdx4O7PtixWKn5y2hMNG0zQPyUecp4pzC6ki vAIhyfHilFR61RGL+GPXQ2MWZWFYbAGjyiYJnAmCP3NOTd0jMZEnDkbUvxhMmBYSdETk1rRgm+R4LOzFUGaHqHDLKLX+FIPKcF96hrucXzcWyLbI bEgE98OHlnVYCzRdK8jlqm8tehUc9c9WhQ== vagrant insecure public key" set system services ssh root-login allow set system services ssh max-sessions-per-connection 32 set system services netconf ssh set system services rest http port 8080 set system services rest enable-explorer set system syslog user * any emergency set system syslog file messages any notice set system syslog file messages authorization info set system syslog file interactive-commands interactive-commands any set system syslog file default-log-messages any any set system syslog file default-log-messages match "(requested 'commit' operation)|(requested 'commit synchronize' operation)|(copying configuration to juniper.save)|(commit complete)|ifAdminStatus|(FRU power)|(FRU removal)|(FRU insertion)|(link UP)|transitioned|Transferred|transfer-file|(license add)|(license delete)|(package -X update)|(package -X delete)|(FRU Online)|(FRU Offline)|(plugged in)|(unplugged)|QF_NODE|QF_SERVER_NODE_GROUP|QF_INTERCONNECT|QF_DIRECTOR|QF_NETWORK_NODE_GROUP|(Master Unchanged, Members Changed)|(Master Changed, Members Changed)|(Master Detected, Members Changed)|(vc add)|(vc delete)|(Master detected)|(Master changed)|(Backup detected)|(Backup changed)|(interface vcp-)" set system syslog file default-log-messages structured-data set system extensions providers juniper license-type juniper deployment-scope commercial set system extensions providers chef license-type juniper deployment-scope commercial set interfaces xe-0/0/0 description UPLINK-via-ESXi-vmnic1-to-EX4300 set interfaces xe-0/0/0 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk set interfaces xe-0/0/0 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan31 set interfaces xe-0/0/1 unit 0 description Linux_Host_vSWITCH set interfaces xe-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access set interfaces xe-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan31 set interfaces em0 unit 0 family inet address 172.30.77.219/23 set interfaces em1 unit 0 family inet address 169.254.0.2/24 set forwarding-options storm-control-profiles default all set routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 172.30.77.1 set protocols igmp-snooping vlan default set vlans default vlan-id 1 set vlans vlan31 vlan-id 31 set vlans vlan32 vlan-id 32 set poe interface xe-0/0/1
Appendix B: Troubleshooting Adding Third-Party Connector
If you encounter problems while adding the third-party connector, review the following log files for troubleshooting information.
This section covers the following third-party connector issues:
Troubleshooting Policy Enforcer
To troubleshoot Policy Enforcer, review these logs:
/srv/feeder/connectors/forescout/logs/forescout_connector.log/srv/feeder/log/controller.logIf the following log message displays in the
forescout_connector.logfile:DEBUG response content of API: {"status":"NOT_FOUND","code":404,"message":"failed to read properties file /usr/local/forescout/plugin/webapi/local.properties"}Then navigate to the ForeScout CounterACT CLI and enter this command:
chmod 777 /usr/local/forescout/plugin/webapi/local.properties
Troubleshooting ForeScout CounterACT
To enable debugging on the CLI for the DEX (eds) and Web API plugins, enter the following commands:
fstool eds debug 10fstool webapi debug 10
Review the following log files:
/usr/local/forescout/log/plugin/eds/usr/local/forescout/log/plugin/webapi