Use Postman to Connect to the WebSocket API
Postman is a platform that is designed to make it easy to work with APIs. This topic walks you through how to use Postman to connect to the Mist WebSocket API and stream data.
Postman is an API platform that makes it easy for you to complete API related tasks, including sending and receiving data from a WebSocket server. This topic covers how to get set up in Postman and how to leverage it so that you can use the Mist WebSocket API to stream data.
See
Postman Setup
To use Postman, you can use the Postman website or download the Postman application as described in Download Postman.
- Sign in to Postman (or create an account) from the Postman website or application. This allows you to save your environment. See the Create Your Environment section further down in this topic.
- Once your account is created, you get access to your workspace. This is where you can save your API calls and configure your environment to interact with the Mist API.
Import the Mist API Collection
Next, import the Mist API Collection. Juniper Mist has built a list of Postman API calls that you can import directly into your Postman workspace. This list is maintained and matches what the API documentation lists.
- Navigate to the Juniper Mist Postman collections page and select the Mist Cloud Websockets collection.
- Once the collection is opened, click on Fork as described in Fork collections and environments in Postman. This enables you to create a copy of the collection in your own workspace and still receive updates when the main collection is updated.
- In the top left corner of Postman, you should see that the collection has now been forked into your workspace. Expand the collection and its subsections to see how all the WebSocket APi requests are organized.
Create Your Environment
A postman environment allows you to store variables in a profile that you can reuse across multiple API calls and collections. You must create an environment and define variables before you begin in Postman.
Connect to the WebSocket API
Now that you have set up Postman with all of the necessary information, it's time
to test the connection to the WebSocket API. You can do this using the
GET /api/v1/self call to be returned with
information about your privileges and accounts. You can view steps on how to
this in Test Your First API Call, or see full documentation on this here.
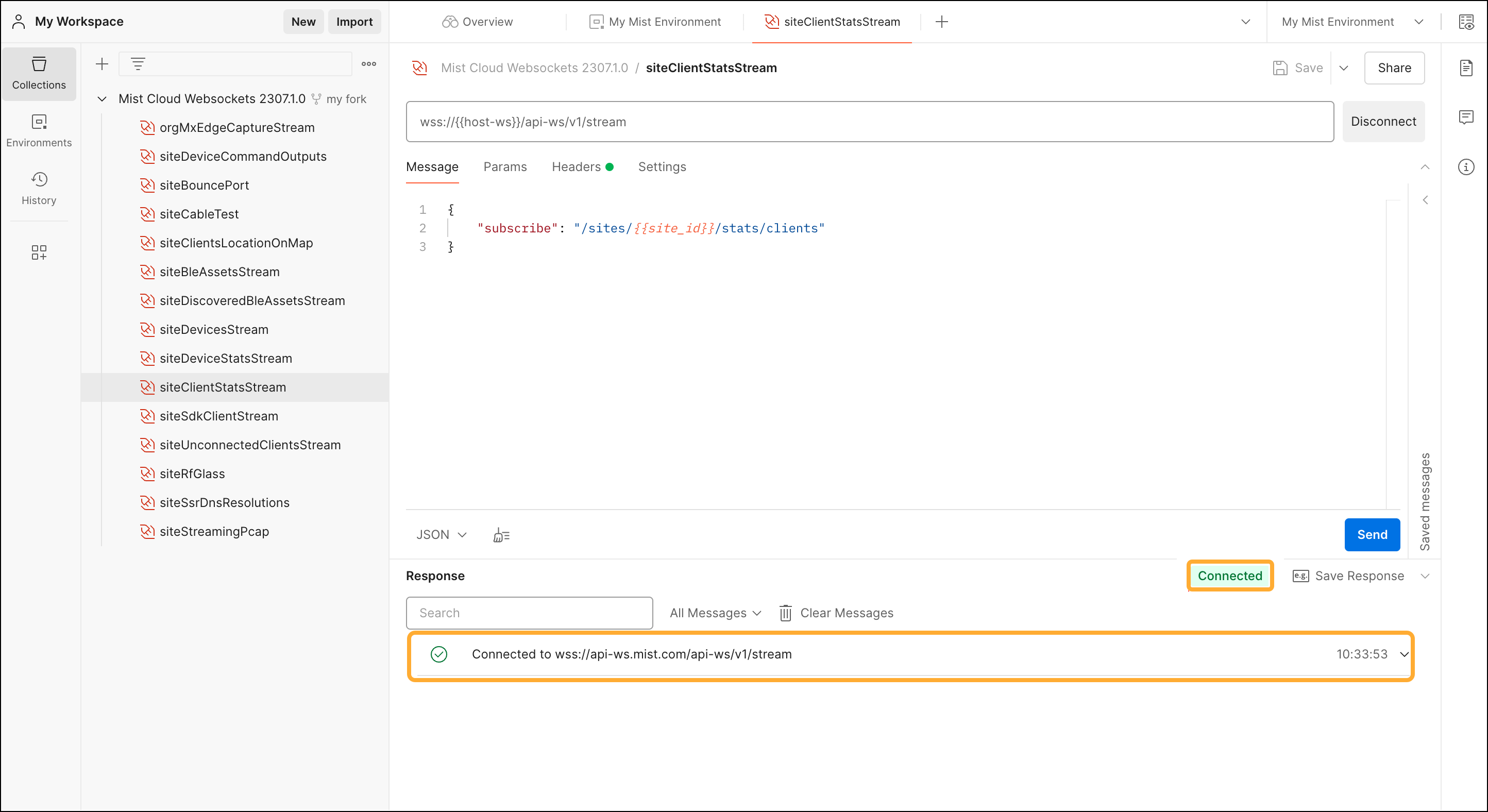
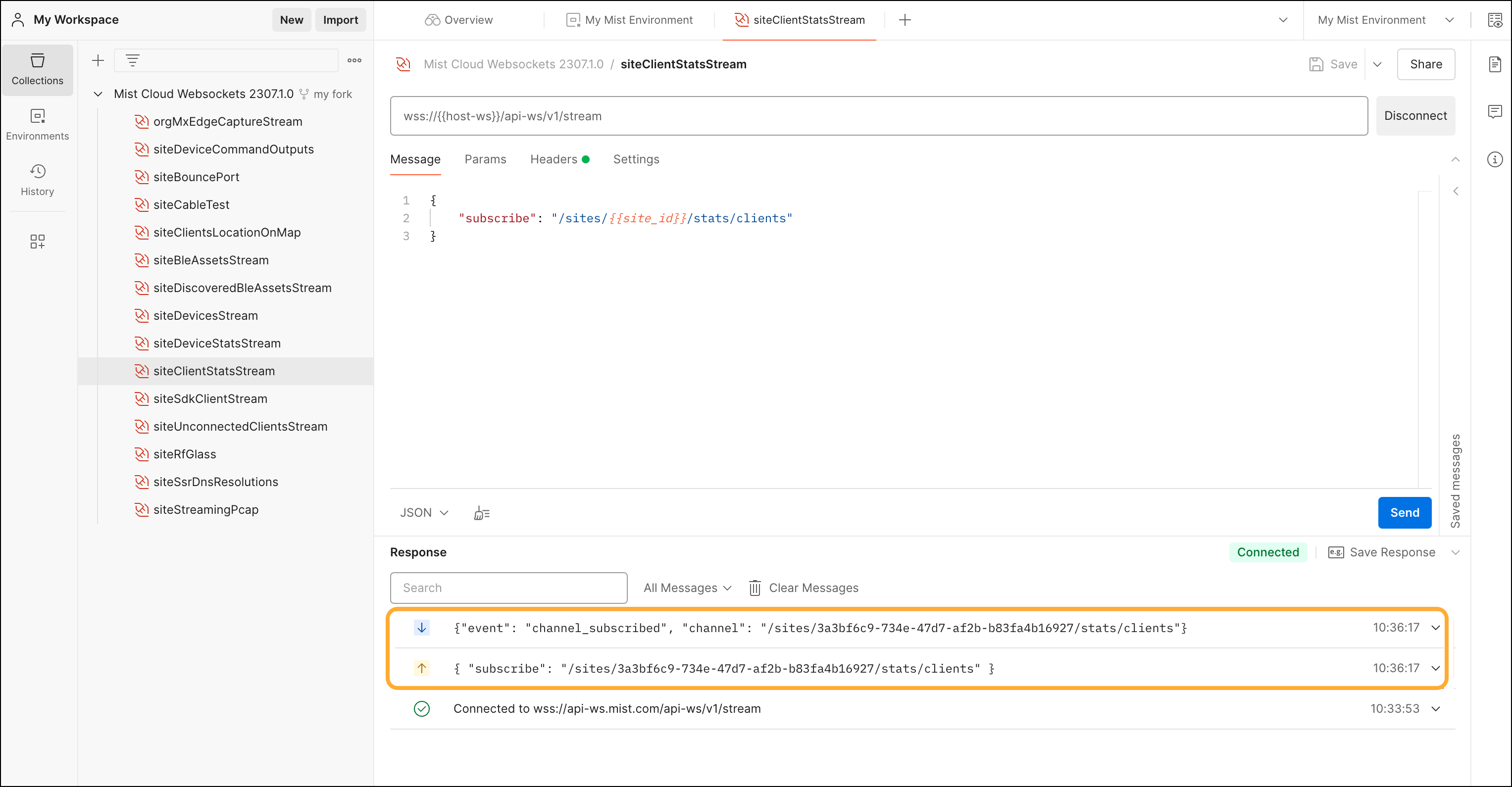
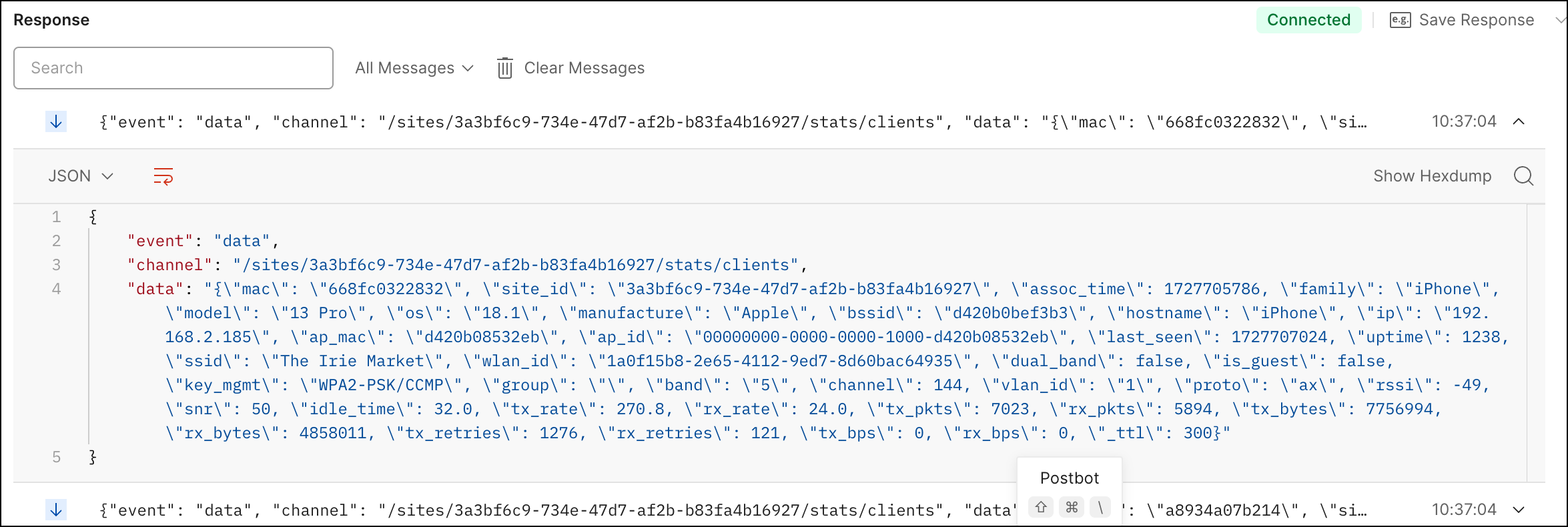
Let's say the first set of data you want to stream is related to Wi-Fi client
statistics. To stream this data, you must connect to the WebSocket API and then
subscribe to the /sites/<i>{{site_id}}</i>/stats/clients
channel.
In order to test your connection to the Juniper Mist WebSocket API, follow these steps: