NAT for Multicast Flows
To implement multicast group address translation, either static NAT or destination NAT is used. With the help of NAT, source addresses in IPv4 are translated to IPv4 multicast group destination addresses.
Understanding NAT for Multicast Flows
Network Address Translation (NAT) can be used to translate source addresses in IPv4 multicast flows and to translate IPv4 multicast group destination addresses.
Either static NAT or destination NAT can be used to perform
multicast group address translation. Static NAT allows connections
to be originated from either side of the network, but translation
is limited to one-to-one addresses or between blocks of addresses
of the same size. No address pools are necessary. Use the static configuration statement at the [edit security nat] hierarchy level to configure static NAT
rule sets for multicast traffic. Destination NAT allows connections
to be initiated only for incoming network connections—for example,
from the Internet to a private network. Use the destination configuration statement at the [edit security nat] hierarchy
level to configure destination NAT pools and rule sets.
Source NAT for multicast traffic is supported only by using
IP address shifting to translate the original source IP address to
an IP address from a user-defined address pool. This type of translation
is one-to-one, static, and without port address translation. If the
original source IP address range is larger than the IP address range
in the user-defined pool, untranslated packets are dropped. The mapping
does not provide bidirectional mapping, which static NAT provides.
Use the source configuration statement at the [edit
security nat] hierarchy level to configure source NAT pools
and rule sets. When you define the source NAT pool for this type of
source NAT, use the host-address-base option to specify
the start of the original source IP address range.
See Also
Example: Configuring NAT for Multicast Flows
This example shows how to configure a Juniper Networks device for address translation of multicast flows.
Requirements
Before you begin:
Configure network interfaces on the device. See the Interfaces User Guide for Security Devices.
Create security zones and assign interfaces to them. See Understanding Security Zones.
-
Configure the device for multicast forwarding. See the Multicast Overview.
Overview
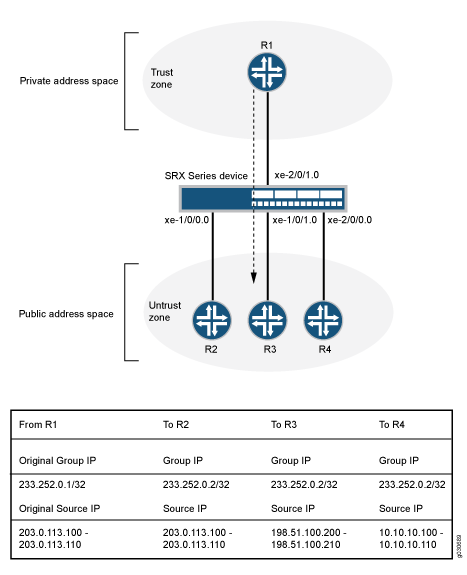
This example uses the trust security zone for the private address space and the untrust security zone for the public address space. Figure 1 depicts a typical deployment of the Juniper Networks device for multicast forwarding. The source router R1 sends multicast packets with source addresses in the range 203.0.113.100 through 203.0.113.110 and the group address 233.252.0.1/32 toward the Juniper Networks device. The source router R1 is in the private network (trust zone) upstream of the Juniper Networks device. There are several receivers in the public network (untrust zone) downstream of the device.
The Juniper Networks device translates incoming multicast packets from R1 before forwarding them out on the downstream interfaces. The following translations are applied:
For the interface to R2, the source address is untranslated, and the group address is translated to 233.252.0.2/32.
For the interface to R3, the source address is translated to an address in the range 198.51.100.200 through 198.51.100.210, and the group address is translated to 233.252.0.2/32.
For the interface to R4, the source address is translated to an address in the range 10.10.10.100 through 10.10.10.110, and the group address is translated to 233.252.0.2/32.
This example describes the following configurations:
Destination NAT pool
dst-nat-poolthat contains the IP address 233.252.0.2/32.Destination NAT rule set
rs1with ruler1to match packets arriving on interface xe-2/0/1.0 with the destination IP address 233.252.0.1/32. For matching packets, the destination address is translated to the IP address in thedst-nat-poolpool.Source NAT pool
src-nat-shift-1that contains the IP address range 198.51.100.200/32 through 198.51.100.210/32. For this pool, the beginning of the original source IP address range is 203.0.113.100/32 and is specified with thehost-address-baseoption.Source NAT rule set
rs-shift1with ruler1to match packets from the trust zone to interface xe-1/0/1.0 with a source IP address in the 203.0.113.96/28 subnet. For matching packets that fall within the source IP address range specified by thesrc-nat-shift-1configuration, the source address is translated to the IP address in thesrc-nat-shift-1pool.Source NAT pool
src-nat-shift-2that contains the IP address range 10.10.10.100/32 through 10.10.10.110/32. For this pool, the beginning of the original source IP address range is 203.0.113.100/32 and is specified with thehost-address-baseoption.Source NAT rule set
rs-shift2with ruler1to match packets from the trust zone to interface xe-2/0/0.0 with a source IP address in the 203.0.113.96/28 subnet. For matching packets that fall within the source IP address range specified by thesrc-nat-shift-2configuration, the source address is translated to the IP address in thesrc-nat-shift-2pool.Proxy ARP for the addresses 203.0.113.100 through 203.0.113.110 on interface xe-1/0/0.0, addresses 198.51.100.200 through 198.51.100.210 on interface xe-1/0/1.0, and addresses 10.10.10.100 through 10.10.10.110 on interface xe-2/0/0.0. This allows the Juniper Networks security device to respond to ARP requests received on the interface for those addresses.
Security policy to permit traffic from the trust zone to the untrust zone.
Security policy to permit traffic from the untrust zone to the translated destination IP address in the trust zone.
Topology
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set security nat source pool src-nat-shift-1 address 198.51.100.200/32 to 198.51.100.210/32 set security nat source pool src-nat-shift-1 host-address-base 203.0.113.100/32 set security nat source pool src-nat-shift-2 address 10.10.10.100/32 to 10.10.10.110/32 set security nat source pool src-nat-shift-2 host-address-base 203.0.113.100/32 set security nat source rule-set rs-shift1 from zone trust set security nat source rule-set rs-shift1 to interface xe-1/0/1.0 set security nat source rule-set rs-shift1 rule r1 match source-address 203.0.113.96/28 set security nat source rule-set rs-shift1 rule r1 then source-nat pool src-nat-shift1 set security nat source rule-set rs-shift2 from zone trust set security nat source rule-set rs-shift2 to interface xe-2/0/0.0 set security nat source rule-set rs-shift2 rule r2 match source-address 203.0.113.96/28 set security nat source rule-set rs-shift2 rule r2 then source-nat pool src-nat-shift2 set security nat destination pool dst-nat-pool address 233.252.0.2/32 set security nat destination rule-set rs1 from interface xe-2/0/1.0 set security nat destination rule-set rs1 rule r1 match destination-address 233.252.0.1/32 set security nat destination rule-set rs1 rule r1 then destination-nat pool dst-nat-pool set security nat proxy-arp interface xe-1/0/0.0 address 203.0.113.100/32 to 203.0.113.110/32 set security nat proxy-arp interface xe-1/0/1.0 address 198.51.100.200/32 to 198.51.100.210/32 set security nat proxy-arp interface xe-2/0/0.0 address 10.10.10.100/32 to 10.10.10.110/32 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy internet-access match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy internet-access match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy internet-access match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy internet-access then permit set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy dst-nat-pool-access match source-address any set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy dst-nat-pool-access match destination-address 233.252.0.1/21 set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy dst-nat-pool-access match application any set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy dst-nat-pool-access then permit
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For instructions on how to do that, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode.
To configure the destination and source NAT translations for multicast flows:
Create a destination NAT pool.
[edit security nat destination] user@host# set pool dst-nat-pool address 233.252.0.2/32
Create a destination NAT rule set.
[edit security nat destination] user@host# set rule-set rs1 from interface xe-2/0/1.0
Configure a rule that matches packets and translates the destination address to the address in the destination NAT pool.
[edit security nat destination] user@host# set rule-set rs1 rule r1 match destination-address 233.252.0.1/32 user@host# set rule-set rs1 rule r1 then destination-nat pool dst-nat-pool
Create a source NAT pool.
[edit security nat source] user@host# set pool src-nat-shift-1 address 198.51.100.200 to 198.51.100.210
Specify the beginning of the original source IP address range.
[edit security nat source] user@host# set pool src-nat-shift-1 host-address-base 203.0.113.100
Create a source NAT rule set.
[edit security nat source] user@host# set rule-set rs-shift1 from zone trust user@host# set rule-set rs-shift1 to interface xe-1/0/1.0
Configure a rule that matches packets and translates the destination address to the address in the source NAT pool.
[edit security nat source] user@host# set rule-set rs-shift1 rule r1 match source-address 203.0.113.96/28 user@host# set rule-set rs-shift1 rule r1 then source-nat pool src-nat-shift1
Create a source NAT pool.
[edit security nat source] user@host# set pool src-nat-shift-2 address 10.10.10.100 to 10.10.10.110
Specify the beginning of the original source IP address range.
[edit security nat source] user@host# set pool src-nat-shift-2 host-address-base 203.0.113.100/32
Create a source NAT rule set.
[edit security nat source] user@host# set rule-set rs-shift2 from zone trust user@host# set rule-set rs-shift2 to interface xe-2/0/0.0
Configure a rule that matches packets and translates the destination address to the address in the source NAT pool.
[edit security nat source] user@host# set rule-set rs-shift2 rule r2 match source-address 203.0.113.96/28 user@host# set rule-set rs-shift2 rule r2 then source-nat pool src-nat-shift2
Configure proxy ARP.
[edit security nat] user@host# set proxy-arp interface xe-1/0/0.0 address 203.0.113.100 to 203.0.113.110 user@host# set proxy-arp interface xe-1/0/1.0 address 198.51.100.200 to 198.51.100.210 user@host# set proxy-arp interface xe-2/0/0.0 address 10.10.10.100 to 10.10.10.110
Configure a security policy that allows traffic from the trust zone to the untrust zone.
[edit security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust] user@host# set policy internet-access match source-address any destination-address any application any user@host# set policy internet-access then permit
Configure a security policy that allows traffic from the untrust zone to the trust zone.
[edit security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust] user@host# set policy dst-nat-pool-access match source-address any destination-address 233.252.0.1/32 application any user@host# set policy dst-nat-pool-access then permit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show security nat and show security
policies commands. If the output does not display the intended
configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in this example
to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show security nat
source {
pool src-nat-shift-1 {
address {
198.51.100.200/32 to 198.51.100.210/32;
}
host-address-base 203.0.113.100/32;
}
pool src-nat-shift-2 {
address {
10.10.10.100/32 to 10.10.10.110/32;
}
host-address-base 203.0.113.100/32;
}
rule-set trust-to-untrust {
from zone trust;
to zone untrust;
rule source-nat-rule {
match {
source-address 0.0.0.0/0;
}
then {
source-nat {
interface;
}
}
}
}
rule-set rs-shift1 {
from zone trust;
to interface xe-1/0/1.0;
rule r1 {
match {
source-address 203.0.113.96/28;
}
then {
source-nat {
pool {
src-nat-shift1;
}
}
}
}
}
rule-set rs-shift2 {
from zone trust;
to interface xe-2/0/0.0;
rule r2 {
match {
source-address 203.0.113.96/28;
}
then {
source-nat {
pool {
src-nat-shift2;
}
}
}
}
}
}
destination {
pool dst-nat-pool {
address 233.252.0.1/32;
}
rule-set rs1 {
from interface xe-2/0/1.0;
rule r1 {
match {
destination-address 233.252.0.1/32;
}
then {
destination-nat pool dst-nat-pool;
}
}
}
}
proxy-arp {
interface xe-1/0/0.0 {
address {
203.0.113.100/32 to 203.0.113.110/32;
}
}
interface xe-1/0/1.0 {
address {
198.51.100.200/32 to 198.51.100.210/32;
}
}
interface xe-2/0/0.0 {
address {
10.10.10.100/32 to 10.10.10.110/32;
}
}
}
[edit]
user@host# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone untrust {
policy trust-to-untrust {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
policy internet-access {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
from-zone untrust to-zone trust {
policy dst-nat-pool-access {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address 233.252.0.1/21;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks:
- Verifying Destination NAT Pool Usage
- Verifying Destination NAT Rule Usage
- Verifying Source NAT Pool Usage
- Verifying Source NAT Rule Usage
- Verifying NAT Application to Traffic
Verifying Destination NAT Pool Usage
Purpose
Verify that there is traffic using IP addresses from the destination NAT pool.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security
nat destination pool all command. View the Translation hits
field to check for traffic using IP addresses from the pool.
Verifying Destination NAT Rule Usage
Purpose
Verify that there is traffic matching the destination NAT rule.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security
nat destination rule all command. View the Translation hits
field to check for traffic that matches the rule.
Verifying Source NAT Pool Usage
Purpose
Verify that there is traffic using IP addresses from the source NAT pool.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security
nat source pool all command. View the Translation hits field
to check for traffic using IP addresses from the pool.
Verifying Source NAT Rule Usage
Purpose
Verify that there is traffic matching the source NAT rule.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security
nat source rule all command. View the Translation hits field
to check for traffic that matches the rule.
