MX Series Router As Junos Multi-Access User Plane
Overview
Junos Multi-Access User Plane on a single MX Series router can function in four modes:
- As a combined SGW user plane (SGW-U) and PGW user plane (PGW-U) in a single MX series router. The combined SGW-U/PGW-U is referred to as a SAEGW-U (System Architecture Evolution Gateway-User Plane). The SAEGW-U interoperates with a third-party SAEGW-C through a combined Sxab interface.
- As a standalone SGW user plane (SGW-U). The SGW-U interoperates with a third-party SGW-C through a the Sxa interface and one or more Juniper or third-party PGW-Us over one or more S5/8-U interfaces.
- As a standalone PGW user plane (PGW-U) in a single MX router. The PGW-U interoperates with a third-party PGW-C through a the Sxb interface and one or more Juniper or third-party SGW-Us over one or more S5/8-U interfaces.
- As a standalone user plane function (UPF) for carrying 5G traffic. The UPF interoperates with a third-party session management function (SMF).
Configuring Junos Multi-Access User Plane on an MX Series router is essentially the same for each of these functions. This topic describes this configuration process.
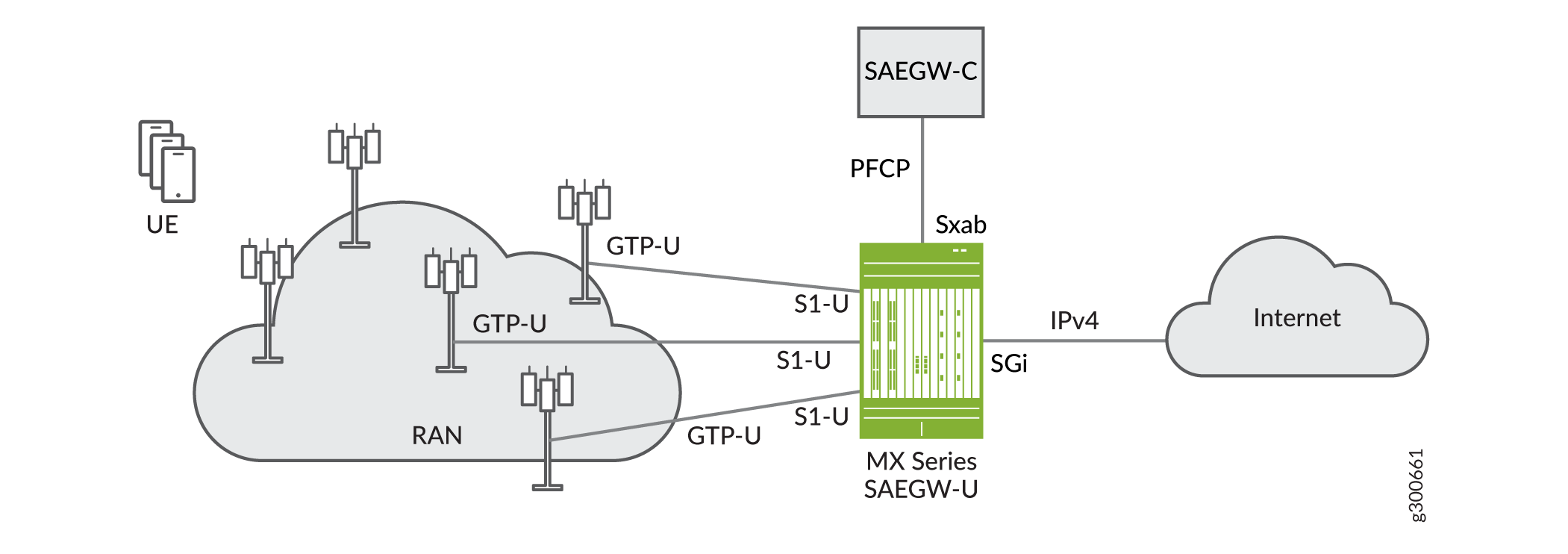
As Figure 1 shows, Juniper’s MX SAEGW-U interoperates with a third-party SAEGW-C through a combined Sxab interface.
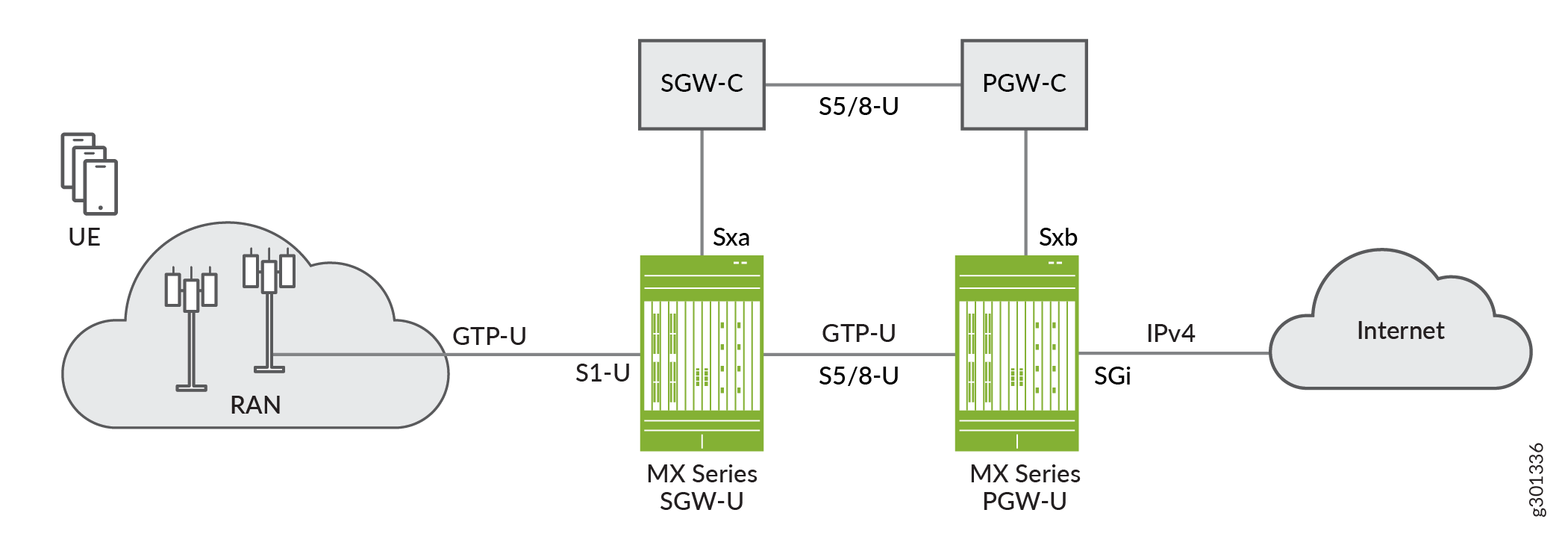
As Figure 2 shows, the SGW-U interoperates with a third-party SGW-C through a the Sxa interface and one or more Juniper or third-party PGW-Us over one or more S5/8-U interfaces. The PGW-U interoperates with a third-party PGW-C through a the Sxb interface and one or more Juniper or third-party SGW-Us over one or more S5/8-U interfaces.
As Figure 3 shows, Juniper’s MX UPF interoperates with a third-party SMF through the N4 interface.
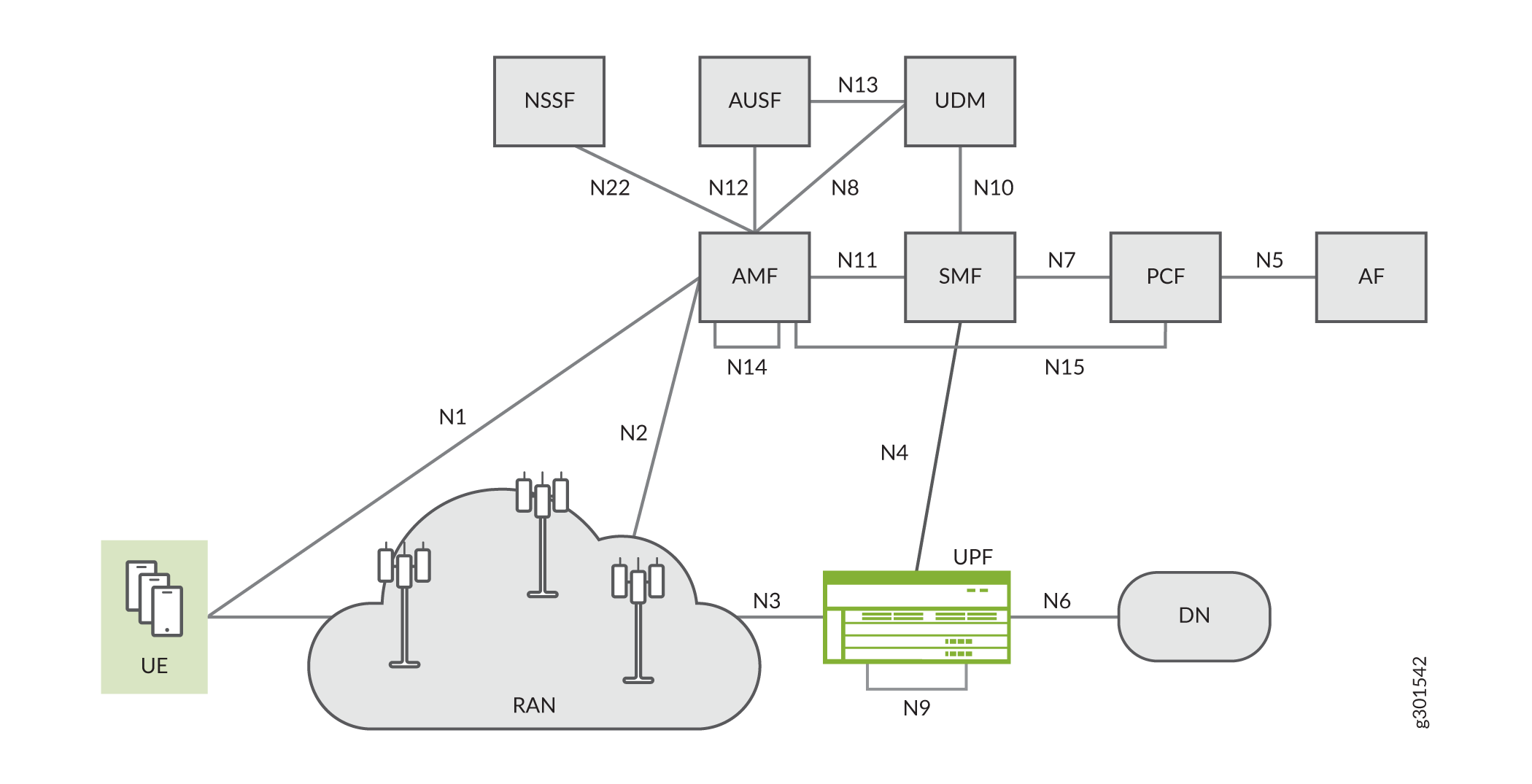
The MX as SAEGW-U, SGW-U, PGW-U or UPF supports the following CUPS interfaces:
-
Sxab/Sxa/Sxb/N4—Packet Forwarding Control Protocol (PFCP) enables communication between the Junos Multi-Access User Plane and the control plane. PFCP encodes TLV messages for transport over UDP/IP. This interface can also transport user data packets (GTP-U based) between the user plane and control plane. Junos Multi-Access User Plane runs PFCP as the control protocol with the third-party control plane to set up data paths for wireless subscribers.
-
S1-U/N3—This interface is the data path between an eNodeB and the Junos Multi-Access User Plane. Application data packets from end-user equipment are encapsulated over GTP. For upstream packets, Junos Multi-Access User Plane is responsible for GTP tunnel termination and forwarding the user packets to the core. For downstream packets from core, Junos Multi-Access User Plane adds the GTP header and forwards to eNodeB(s). The data plane handles IP packets encapsulated in GTP-U from/to eNodeBs that arrive for the mobile subscribers and performs routing to/from the external Internet.
-
S5/8-U—The S5/8-U interface is the data path between an SGW-U and a PGW-U.
-
N9—Interface between two UPFs.
-
SGi/N6—Interface to the core Internet, supporting IPv4.
Junos Multi-Access User Plane provides purely the user plane function in the form of an MX router that interacts with a third-party control plane function. The MX router receives instructions from the control plane through the Sxab/Sxa/Sxb/N4 interface using PFCP. Based on those instructions, the MX routing engine manages user plane sessions and programs data paths in the anchor PFEs. For the MX router to provide the user plane functionality, it must contain the following minimum elements:
-
At least one anchor PFE interface–An anchor PFE interface is a line card interface that has no physical interface connection, but rather provides the core processing of data traffic by doing the following:
-
Encoding/decoding of GTP-U packets. The anchor PFE interface decodes GTP-U packets from eNodeBs and forwards them to the core network and encodes IPv4 packets from the core network and forwards them to eNodeBs.
-
Enforces class of service and firewall filter rules on subscriber sessions
-
Collects statistics on data usage for charging/accounting purpose
-
-
At least one signalling/control interface-This is the Sxab/Sxa/Sxb/N4 interface in the CUPS architecture. The signalling/control interface is a physical interface that does the following:
-
Sends/receives PFCP packets to/from the control plane
-
-
At least one ingress interface-This is the S1-U or N3 or the S5/8-U or N9 interface in the CUPS architecture, depending on where the device is in the data stream. The ingress interface is a physical interface that does the following:
-
As the S1-U or N3 interface, forwards GTP-U packets between eNodeBs and the anchor PFE.
-
As the S5/8-U or N9 interface, receives GTP-U packets from the downstream UPF.
-
-
At least one egress interface-This is the SGi or N6 or the S5/8-U or N9 interface in the CUPS architecture, depending on where the device is in the data stream. The egress interface is a physical interface that does the following:
-
As the SGi or N6 interface, forwards IPv4 packets between the anchor PFE and the core network.
-
As the S5/8-U or N9 interface, sends GTP-U packets to the upstream UPF.
-
You can configure all interface types on the same line card, as long as that line card supports all of the interface types. See Table 1 for a list of line card support by interface type.
Configuring Junos Multi-Access User Plane on an MX Router
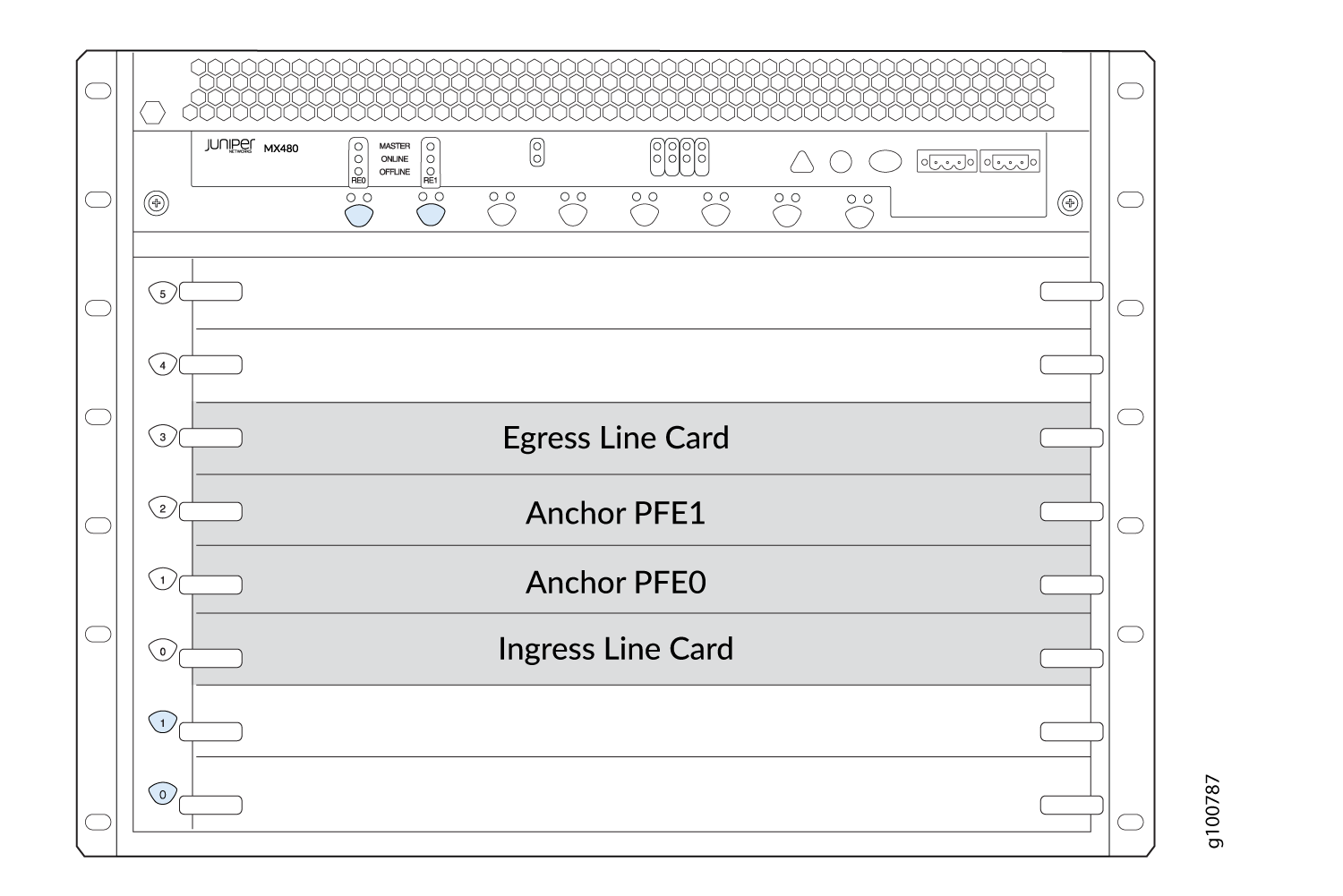
As Figure 4 shows, a standard setup of an MX router as either an SAEGW-U, an SGW-U, a PGW-U, or a UPF includes an ingress line card, and egress line card, and a recommended two anchor PFE line cards operating redundantly.
-
The ingress line card provides the S1-U interface (SAEGW-U, SGW-U), the S5/8-U interface (PGW-U), or the N3 interface (UPF). , The ingress line card also provides the Sxab interface (SAEGW-U), the Sxa interface (SGW-U), the Sxb interface (PGW-U), or the N4 interface (UPF).
-
The anchor PFE line cards provide the core processing of data traffic through internal
pfe-interfaces. At least one anchor PFE card is required, but two are recommended to provide redundancy. -
The egress line card provides the SGi interface (SAEGW-U, PGW-U), the S5/8-U interface (SGW-U), or the N6 interface (UPF).
-
You can configure all of this functionality on a single line card as long as that line card supports all of the Junos Multi-Access User Plane functionality. We show separate line cards here for simplicity and recommended setup.
To configure Junos Multi-Access User Plane on an MX router, perform the following configuration procedures in the listed order:
- DDoS Attack Protection Configuration
- GRES Configuration
- Chassis Configuration for the Anchor PFE Line Cards
- Interface Configuration
- Mobile Edge Configuration
DDoS Attack Protection Configuration
Define DDoS attack protection for PFCP protocol traffic.
GRES Configuration
The graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES) feature in Junos OS enables a router with redundant Routing Engines to continue forwarding packets, even if one Routing Engine fails. GRES preserves interface and kernel information. Traffic is not interrupted.
[edit chassis] user@host# set redundancy graceful-switchover user@host# commit
See Also
Chassis Configuration for the Anchor PFE Line Cards
Define each Packet Forwarding Engine (PFE) on each anchor PFE line card as an anchor interface.
Interface Configuration
Configure the interfaces needed.
Mobile Edge Configuration
Once you’ve configured all of the necessary interfaces, you can configure the MX router to be a UPF.
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
