GRES on Junos Multi-Access User Plane
Graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES) in Junos OS enables a router with redundant Routing Engines to continue forwarding packets even if one Routing Engine fails. GRES preserves interface and kernel information. Traffic is not interrupted.
MX204 routers do not support GRES.
To preserve routing during a switchover, GRES must be combined with either:
Graceful restart protocol extensions
Nonstop active routing (NSR)
For Junos Multi-Access User Plane, GRES switchover protects the PFCP KeepAlive protocol. The new primary Routing Engine starts answering peer keepalives.
Any updates to the primary Routing Engine are replicated to the backup Routing Engine as soon as they occur.
Primary Role switches to the backup Routing Engine if:
The primary Routing Engine kernel stops operating.
The primary Routing Engine experiences a hardware failure.
The administrator initiates a manual switchover.
To quickly restore or to preserve routing protocol state information during a switchover, GRES must be combined with either graceful restart or nonstop active routing, respectively. For more information about graceful restart, see Graceful Restart Concepts. For more information about nonstop active routing, see Nonstop Active Routing Concepts.
If the backup Routing Engine does not receive a keepalive from the primary Routing Engine after 2 seconds, it determines that the primary Routing Engine has failed; and assumes primary role.
The Packet Forwarding Engine:
Seamlessly disconnects from the old primary Routing Engine
Reconnects to the new primary Routing Engine
Does not reboot
Does not interrupt traffic
The new primary Routing Engine and the Packet Forwarding Engine then become synchronized. If the new primary Routing Engine detects that the Packet Forwarding Engine state is not up to date, it resends state update messages.
Successive Routing Engine switchover events must be a minimum of 240 seconds (4 minutes) apart after both Routing Engines have come up.
If the router or switch displays a warning message similar to Standby Routing Engine is not ready for graceful switchover. Packet
Forwarding Engines that are not ready for graceful switchover might
be reset , do not attempt switchover. If you choose
to proceed with switchover, only the Packet Forwarding Engines that
were not ready for graceful switchover are reset. None of the FPCs
should spontaneously restart. We recommend that you wait until the
warning no longer appears and then proceed with the switchover.
We do not recommend performing a commit operation on the backup Routing Engine when GRES is enabled on the router or switch.
We do not recommend enabling GRES on the backup Routing Engine in any scenario.
Figure 1 shows the system architecture of graceful Routing Engine switchover and the process a routing platform follows to prepare for a switchover.
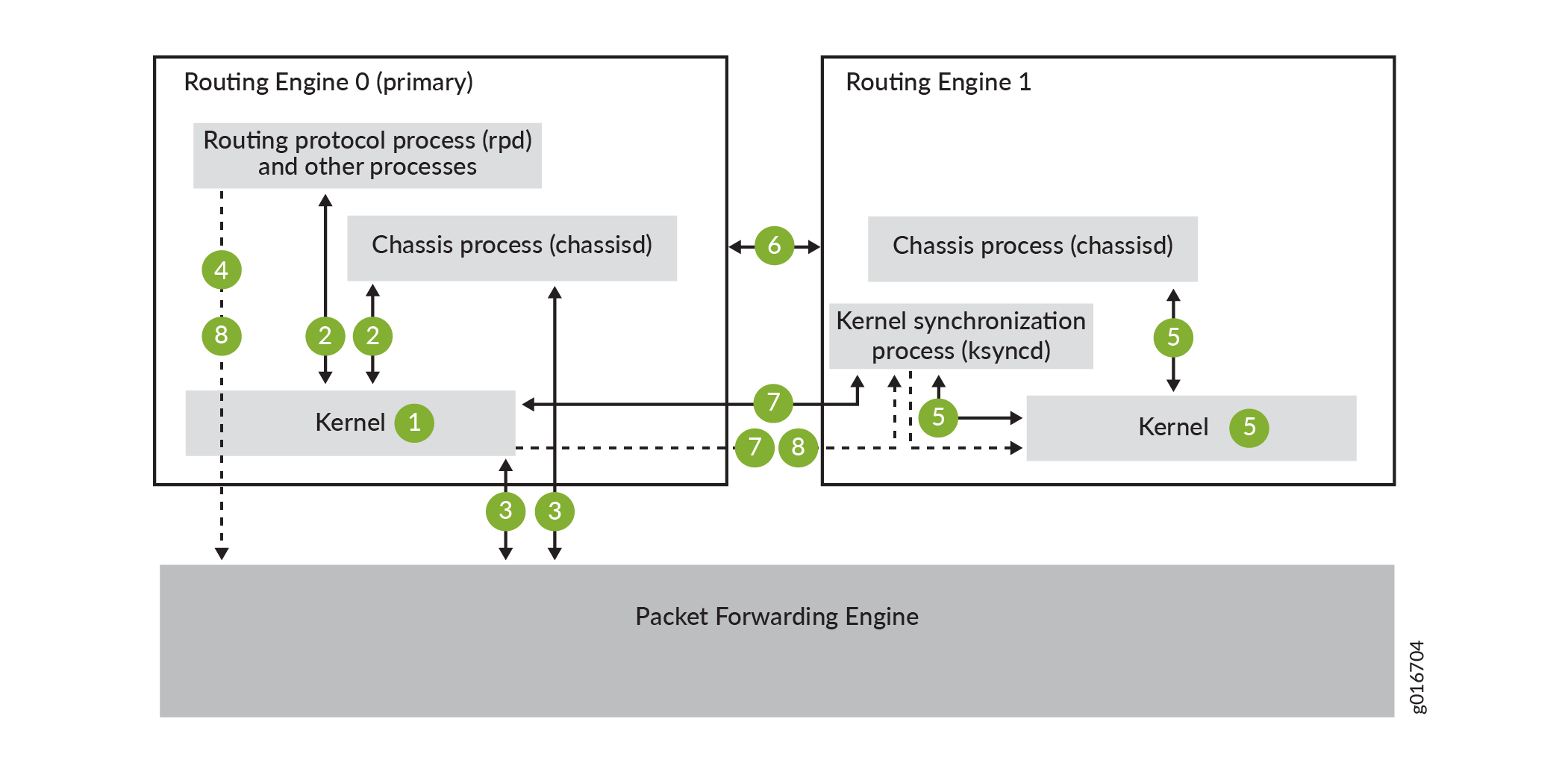
Check GRES readiness by executing both:
The
request chassis routing-engine master switch checkcommand from the primary Routing EngineThe
show system switchovercommand from the Backup Routing Engine
The switchover preparation process for GRES is as follows:
The primary Routing Engine starts.
The routing platform processes (such as the chassis process [chassisd]) start.
The Packet Forwarding Engine starts and connects to the primary Routing Engine.
All state information is updated in the system.
The backup Routing Engine starts.
The system determines whether GRES has been enabled.
The kernel synchronization process (ksyncd) synchronizes the backup Routing Engine with the primary Routing Engine.
After ksyncd completes the synchronization, all state information and the forwarding table are updated.
Figure 2 shows the effects of a switchover on the routing (or switching )platform.
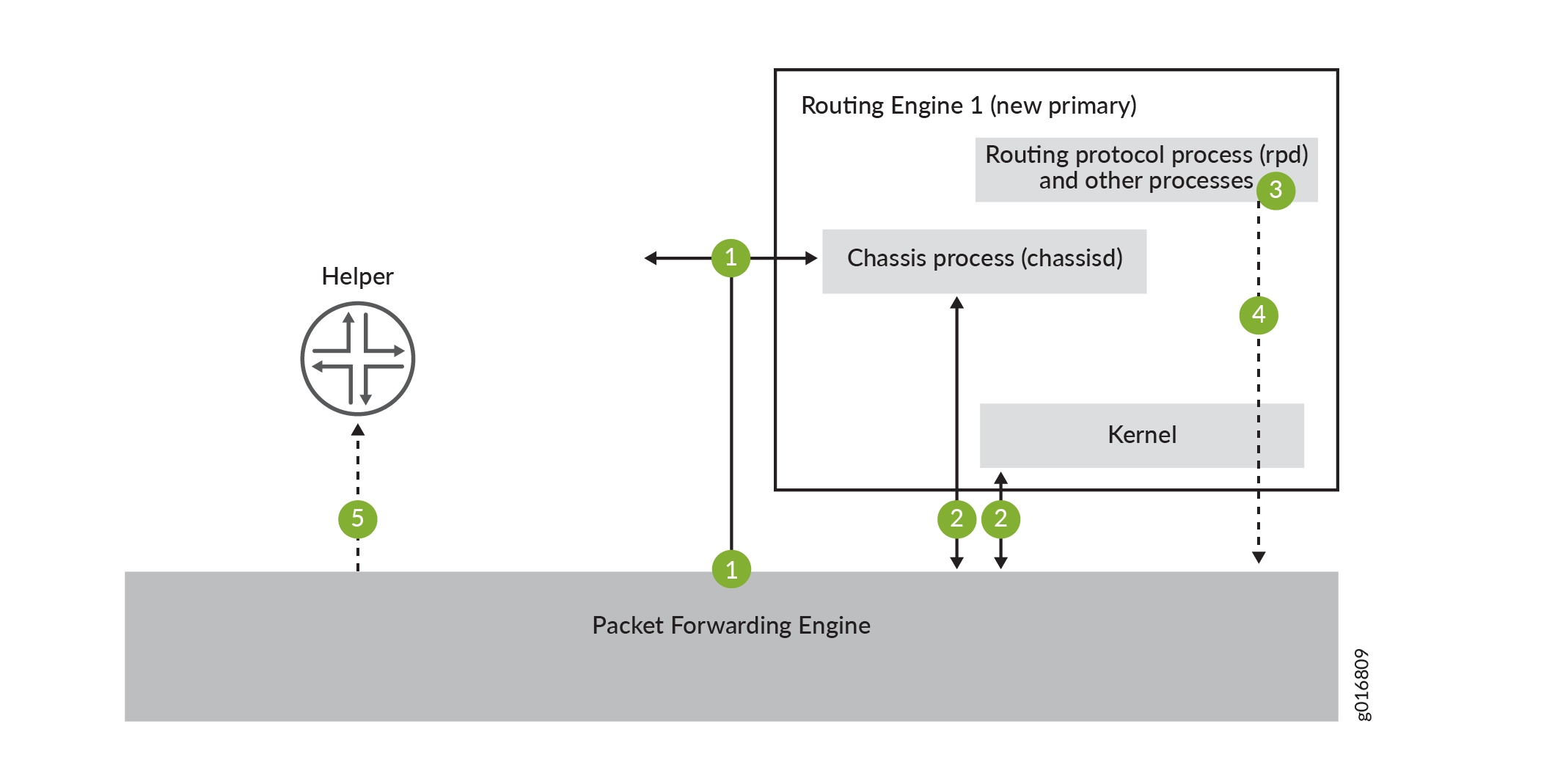
A switchover process consists of the following steps:
When keepalives from the primary Routing Engine are lost, the system switches over gracefully to the backup Routing Engine.
The Packet Forwarding Engine connects to the backup Routing Engine, which becomes the new primary.
Routing platform processes that are not part of GRES (such as the routing protocol process rpd) restart.
State information learned from the point of the switchover is updated in the system.
If configured, graceful restart protocol extensions collect and restore routing information from neighboring peer helper routers.
For MX Series routers using enhanced subscriber management, the new backup Routing Engine (the former primary Routing Engine) will reboot when a graceful Routing Engine switchover is performed. This cold restart resynchronizes the backup Routing Engine state with that of the new primary Routing Engine, preventing discrepancies in state that might have occurred during the switchover.
In Junos Multi-Access User Plane configuration, if the mobile-edge configuration is committed and then GRES needs to be enabled or disabled, a reboot of the entire chassis is required.
In Junos Multi-Access User Plane, any subscriber session
whose Session State is not ESTABLISHED, a graceful restart logs out that subscriber and cleans up any state.
The SAEGW-C will need to reestablish this session
Feature |
Benefits |
Considerations |
|---|---|---|
Dual Routing Engines only (no features enabled) |
|
|
GRES enabled |
|
|
GRES and NSR enabled |
|
|
GRES and graceful restart enabled |
|
|
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
