BGP ピアリング セッション
外部BGPピアグループを使用するメリット
BGPは、現在使用されているルーティングプロトコルの中で、インターネット上のすべてのルートを運ぶのに適した唯一のプロトコルです。これは、BGPがTCP上で動作し、TCPのフロー制御を利用できることが大きな理由です。一方、内部ゲートウェイプロトコル(IGP)にはフロー制御はありません。IGPは、経路情報が多すぎると、解約を始めます。BGPでは、情報の送信速度が速すぎる隣接したスピーカーがある場合、TCPの確認応答を遅らせることで、その隣接したスピーカーを抑制することができます。
BGPのもう一つの利点は、(IS-ISと同様)タイプ、長さ、値(TLV)タプルと、ネットワーク層到達性情報(NLRI)を使用することで、その基礎となるプロトコルを変更することなく、外見上、無限の拡張性を実現していることです。
Junos OSでは、BGPは完全にポリシー主導です。オペレーターは、ピアリングするネイバーを明示的に設定し、ルートをBGPに明示的に受け入れる必要があります。さらに、ルーティングポリシーは、ルーティング情報のフィルタリングと変更に使用されます。このように、ルーティングポリシーは、ルーティングテーブルに対する完全な管理制御を提供します。
多数のBGPピアネイバーを設定するために有利な方法は、グループごとに複数のネイバーからなるピアグループを設定することです。
外部BGP(EBGP)グループの数が増えると、多数のBGPセッションをサポートする能力がCPUとメモリリソースのスケーリングの問題になる場合があります。一般的に、多数のEBGPグループをサポートするよりも、少数のEBGPグループをサポートするほうが良いです。これは、数百の EBGP グループについては、各グループに複数のピアが存在する少数の EBGP グループと比較した場合、より顕著になります。このスケーリング動作の理由は、Junos OSがグループ単位で発生するデータ構造を持っているためです。グループを追加する際、それらの数字を乗算し、使用可能なメモリの量を減らします。
BGPピアリングは、2つの独立した自律システム(AS)間で相互に有益なトラフィック交換関係を作成します。これは、サービスプロバイダの交換ポイントで特に便利です。この関係は、両方のネットワークでトランジットコストと機器リソースを削減するという主なメリットがあります。BGPピアグループを作成するその他のメリットには、トランジットプロバイダへの依存を減らすことで、BGP設定の複雑さを軽減し、ルート冗長性を増加させることが挙げられます。
BGPピアリングを使用して、リモートオフィスと本社などの2つのリモートネットワーク間でポイントツーポイントのトラフィック交換を作成できます。また、マージされた2つのオフィス間など、2つの異なるネットワークをすばやく接続するために使用することもできます。
外部BGPピアリングセッションを理解する
ピア自律システム(AS)間でポイントツーポイント接続を確立するには、ポイントツーポイントリンクの各インターフェイスに BGP セッションを設定します。一般的に、このようなセッションは、AS 外の隣接したホストとネットワークの出口点で行われます。 図 1に BGP ピアリングセッションの例を示します。
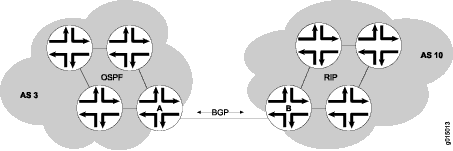
この図 1において、ルーターAはAS3のゲートウェイルーターであり、ルーターBはAS10のゲートウェイルーターです。いずれかのASの内部のトラフィックには、内部ゲートウェイプロトコル(IGP)が使用されます(例えば、OSPF)。ピアAS間でトラフィックをルーティングするには、BGPセッションを使用します。
BGP ルーティングデバイスをピアのグループに配置します。異なるピアグループは、異なるグループタイプ、AS 番号、ルートリフレクタークラスター識別子を持つことができます。
指定したBGPシステムのみをピアとして認識するBGPグループを定義するには、1つ以上のneighborステートメントを含めて、すべてのシステムのピアを静的に設定します。ピアネイバーのアドレスは、IPv6 アドレスまたは IPv4 アドレスのいずれかです。
BGPピアが確立された後、 の非BGPルートはBGPピアによって自動的に告知されません。各BGP対応機器では、ローカルルート、スタティックルート、IGPで学習したルートをBGP RIBにエクスポートして、他のピアにBGPルートとして告知するためのポリシー設定が必要です。BGPの広告ポリシーは、デフォルトではBGP以外の経路(ローカル経路など)をピアに広告しません。
SRXシリーズファイアウォールでは、指定されたインターフェイスまたはゾーンのインターフェイスすべてで、予期されるホストインバウンドトラトラフィックを有効にする必要があります。そうしないと、このデバイスを宛先とするインバウンドトラフィックはデフォルトで破棄されます。
たとえば、SRXシリーズファイアウォールにおける特定のゾーンでBGPトラトラフィックを許可するには、次のステップを使用します。
[edit] user@host# set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic protocols bgp
[edit] user@host# set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 host-inbound-traffic protocols bgp
関連項目
例:外部 BGP ポイント ツー ポイント ピア セッションの設定
この例では、BGP のポイントツーポイントのピアセッションを設定する方法を示しています。
要件
開始する前に、デフォルトの BGP ポリシーがネットワークに適していない場合は、ルーティングポリシーを設定して、受信する BGP ルートをフィルタリングしたり、BGP ルートを告知したりします。
概要
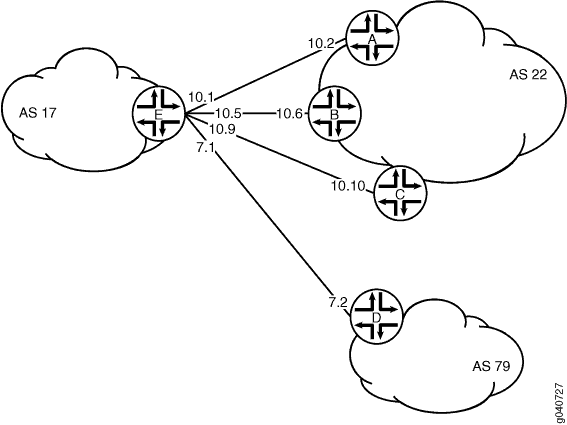
図 2は、BGP ピアセッションを持っているネットワークを示しています。サンプルネットワークでは、AS17 のデバイス E が、external-peersというピアのグループに BGP ピアセッションを持っています。ピア A、B、および C は、AS 22 に存在し、IP アドレスは、10.10.10.2、10.10.10.6、10.10.10.10 です。ピア D は、AS 79 に存在し、IP アドレスは、10.21.7.2です。この例では、デバイス E の設定を示しています。
トポロジー
設定
手順
CLIクイック構成
この例をすばやく設定するには、次のコマンドをコピーしてテキストファイルに貼り付け、改行を削除して、ネットワーク構成に合わせて必要な詳細を変更し、[edit]階層レベルのCLIにコマンドをコピー&ペーストしてください。
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 description to-A set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.10.10.1/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 5 description to-B set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 5 family inet address 10.10.10.5/30 set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 9 description to-C set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 9 family inet address 10.10.10.9/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 21 description to-D set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 21 family inet address 10.21.7.1/30 set protocols bgp group external-peers type external set protocols bgp group external-peers peer-as 22 set protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 10.10.10.2 set protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 10.10.10.6 set protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 10.10.10.10 set protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 10.21.7.2 peer-as 79 set routing-options autonomous-system 17
ステップバイステップでの手順
次の例では、設定階層のいくつかのレベルに移動する必要があります。CLIのナビゲーションについては、Junos OS CLIユーザーガイドの 設定モードでCLIエディターを使用する を参照してください。
BGP ピアセッションを設定する
ピア A、B、C、D へのインターフェースを設定します。
[edit interfaces] user@E# set ge-1/2/0 unit 0 description to-A user@E# set ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.10.10.1/30 user@E# set ge-0/0/1 unit 5 description to-B user@E# set ge-0/0/1 unit 5 family inet address 10.10.10.5/30 user@E# set ge-0/1/0 unit 9 description to-C user@E# set ge-0/1/0 unit 9 family inet address 10.10.10.9/30 user@E# set ge-1/2/1 unit 21 description to-D user@E# set ge-1/2/1 unit 21 family inet address 10.21.7.1/30
自律システム(AS)番号を設定します。
[edit routing-options] user@E# set autonomous-system 17
BGP グループを作成し、外部ネイバーアドレスを追加します。
[edit protocols bgp group external-peers] user@E# set neighbor 10.10.10.2 user@E# set neighbor 10.10.10.6 user@E# set neighbor 10.10.10.10
外部 AS の自律システム(AS)番号を指定します。
[edit protocols bgp group external-peers] user@E# set peer-as 22
ピア D を追加し、個々のネイバーレベルで AS 番号を設定します。
ネイバーの設定はグループの設定よりも優先されます。つまり、グループ内の他のすべてのネイバーに
peer-as 22が設定されているのに対し、ネイバー 10.21.7.2 にはpeer-as 79が設定されています。[edit protocols bgp group external-peers] user@E# set neighbor 10.21.7.2 peer-as 79
ピアタイプを外部 BGP(EBGP)に設定します。
[edit protocols bgp group external-peers] user@E# set type external
結果
コンフィギュレーションモードから、show interfacesshow protocols、、およびの各コマshow routing-optionsンドを入力し、コンフィギュレーションを確認します。出力結果に意図した設定内容が表示されない場合は、この例の手順を繰り返して設定を修正します。
[edit]
user@E# show interfaces
ge-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
description to-A;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.1/30;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 5 {
description to-B;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.5/30;
}
}
}
ge-0/1/0 {
unit 9 {
description to-C;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.9/30;
}
}
}
ge-1/2/1 {
unit 21 {
description to-D;
family inet {
address 10.21.7.1/30;
}
}
}
[edit]
user@E# show protocols
bgp {
group external-peers {
type external;
peer-as 22;
neighbor 10.10.10.2;
neighbor 10.10.10.6;
neighbor 10.10.10.10;
neighbor 10.21.7.2 {
peer-as 79;
}
}
}
[edit]
user@E# show routing-options
autonomous-system 17;
デバイスの設定が完了したら、設定モードから commit を入力します。
検証
設定が正常に機能していることを確認します。
BGP ネイバーの検証
目的
設定したインタフェースで BGP が動作していること、および各近隣アドレスで BGP セッションがアクティブになっていることを確認します。
アクション
オペレーショナルモードから、show bgp neighborコマンドを実行します。
user@E> show bgp neighbor
Peer: 10.10.10.2+179 AS 22 Local: 10.10.10.1+65406 AS 17
Type: External State: Established Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Options: <Preference PeerAS Refresh>
Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 10.10.10.2 Local ID: 10.10.10.1 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 0
BFD: disabled, down
Local Interface: ge-1/2/0.0
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 22)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 0
Accepted prefixes: 0
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 0
Last traffic (seconds): Received 10 Sent 6 Checked 1
Input messages: Total 8522 Updates 1 Refreshes 0 Octets 161922
Output messages: Total 8433 Updates 0 Refreshes 0 Octets 160290
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 10.10.10.6+54781 AS 22 Local: 10.10.10.5+179 AS 17
Type: External State: Established Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Options: <Preference PeerAS Refresh>
Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 10.10.10.6 Local ID: 10.10.10.1 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 1
BFD: disabled, down
Local Interface: ge-0/0/1.5
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 22)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 0
Accepted prefixes: 0
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 0
Last traffic (seconds): Received 12 Sent 6 Checked 33
Input messages: Total 8527 Updates 1 Refreshes 0 Octets 162057
Output messages: Total 8430 Updates 0 Refreshes 0 Octets 160233
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 10.10.10.10+55012 AS 22 Local: 10.10.10.9+179 AS 17
Type: External State: Established Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Options: <Preference PeerAS Refresh>
Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 10.10.10.10 Local ID: 10.10.10.1 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 2
BFD: disabled, down
Local Interface: fe-0/1/0.9
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 22)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 0
Accepted prefixes: 0
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 0
Last traffic (seconds): Received 15 Sent 6 Checked 37
Input messages: Total 8527 Updates 1 Refreshes 0 Octets 162057
Output messages: Total 8429 Updates 0 Refreshes 0 Octets 160214
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 10.21.7.2+61867 AS 79 Local: 10.21.7.1+179 AS 17
Type: External State: Established Flags: <ImportEval Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Options: <Preference PeerAS Refresh>
Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 10.21.7.2 Local ID: 10.10.10.1 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 3
BFD: disabled, down
Local Interface: ge-1/2/1.21
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 79)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 0
Accepted prefixes: 0
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 0
Last traffic (seconds): Received 28 Sent 24 Checked 47
Input messages: Total 8521 Updates 1 Refreshes 0 Octets 161943
Output messages: Total 8427 Updates 0 Refreshes 0 Octets 160176
Output Queue[0]: 0BGP グループの検証
目的
BGP グループが正しく設定されていることを確認します。
アクション
オペレーショナルモードから、show bgp groupコマンドを実行します。
user@E> show bgp group Group Type: External Local AS: 17 Name: external-peers Index: 0 Flags: <> Holdtime: 0 Total peers: 4 Established: 4 10.10.10.2+179 10.10.10.6+54781 10.10.10.10+55012 10.21.7.2+61867 inet.0: 0/0/0/0 Groups: 1 Peers: 4 External: 4 Internal: 0 Down peers: 0 Flaps: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending inet.0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BGP サマリー情報の検証
目的
BGP の設定が正しいことを確認します。
アクション
オペレーショナルモードから、show bgp summaryコマンドを実行します。
user@E> show bgp summary Groups: 1 Peers: 4 Down peers: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending inet.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Accepted/Damped... 10.10.10.2 22 8559 8470 0 0 2d 16:12:56 0/0/0/0 0/0/0/0 10.10.10.6 22 8566 8468 0 0 2d 16:12:12 0/0/0/0 0/0/0/0 10.10.10.10 22 8565 8466 0 0 2d 16:11:31 0/0/0/0 0/0/0/0 10.21.7.2 79 8560 8465 0 0 2d 16:10:58 0/0/0/0 0/0/0/0
例:IPv6 インターフェイスを持つ論理システムへの外部 BGP の設定
この例は、IPv6 インターフェイスを持つ論理システムに対して、外部 BGP(EBGP)ポイントツーポイント ピア セッションを設定する方法を説明します。
要件
この例では、デバイスの初期化以上の特別な設定は必要ありません。
概要
Junos OSは、IPv6 アドレスを用いて、EBGP ピア セッションをサポートします。IPv6 ピア セッションは、neighborステートメント内で IPv6 アドレスを指定する場合に設定可能です。この例では、EUI-64 を使用して、インターフェイスに自動的に適用される IPv6 アドレスを生成します。EUI-64 アドレスは、アドレスのインターフェイス識別子部分に IEEE EUI-64 フォーマットを使用する IPv6 アドレスです(最後の 64 ビット)。
あるいは、手動で割り当てられた 128 ビット IPv6 アドレスを使用して EBGP セッションを設定できます。
インターフェイスに 128 ビットのリンクローカル アドレスを使用する場合、local-interfaceステートメントを含める必要があります。このステートメントは、128 ビットの IPv6 リンクローカル アドレスのみに有効で、IPv6 EBGP リンクローカル ピア セッションを設定するには必須です。
リンクローカル アドレスを使用した EBGP ピアリングの設定は、直接接続されたインターフェイスにのみ適用可能です。マルチホップ ピアリングのサポートはありません。
インターフェイスがアップされた後、コマshow interfaces terseンドを使用して、インターフェイスに EUI-64 生成された IPv6 アドレスを表示できます。これらの生成されたアドレスは 、BGP neighborステートメントで使用しなければなりません。この例は、完全なエンドツーエンドの手順を示しています。
この例では、フレームリレー インターフェイス カプセル化が、論理トンネル(lt)インターフェイスに適用されています。この要件は、IPv6 アドレスがインターフェltイスで設定されている場合は、フレームリレーのカプセル化のみがサポートされているためです。
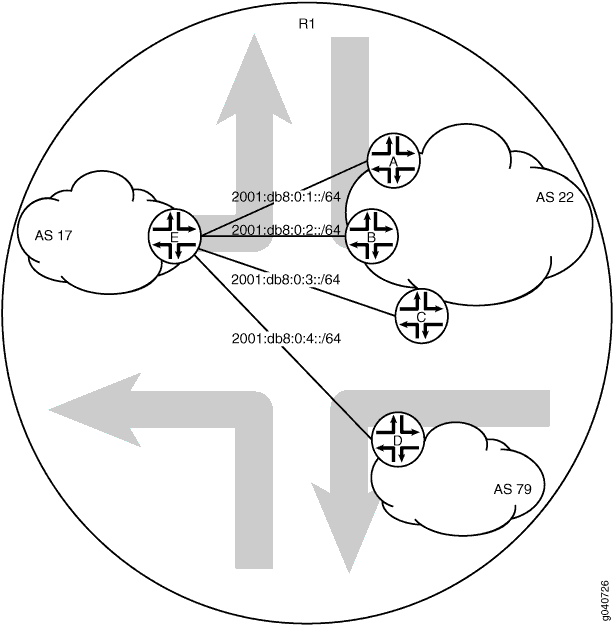
図 3は、BGP ピアセッションを持っているネットワークを示しています。サンプル ネットワークでは、ルーター R1 は 5 つの論理システムを設定しています。自律システム(AS)17 のデバイス E は、external-peersと呼ばれるピアのグループに BGP ピア セッションを有しています。ピア A、B、およびC は、AS 22 にあります。この例は、論理システム A と論理システム E の設定をステップバイステップで示しています。
トポロジー
設定
手順
CLIクイック構成
この例を迅速に設定するには、以下のコマンドをコピーして、テキストファイルに貼り付け、改行を削除し、ネットワーク設定に一致させる必要がある詳細情報を変更し、コマンドを [edit] 階層レベルでCLIにコピーアンドペーストして、設定モードから commit を入力します。
1 デバイスA 1
set logical-systems A interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 description to-E set logical-systems A interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 encapsulation frame-relay set logical-systems A interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 dlci 1 set logical-systems A interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 peer-unit 25 set logical-systems A interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 eui-64 set logical-systems A interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet6 address 2001:db8::1/128 set logical-systems A protocols bgp group external-peers type external set logical-systems A protocols bgp group external-peers peer-as 17 set logical-systems A protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:19da set logical-systems A protocols bgp group external-peers family inet6 unicast set logical-systems A routing-options router-id 172.16.1.1 set logical-systems A routing-options autonomous-system 22
1 デバイスB 1
set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6 description to-E set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6 encapsulation frame-relay set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6 dlci 6 set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6 peer-unit 5 set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:2::/64 eui-64 set logical-systems B interfaces lo0 unit 2 family inet6 address 2001:db8::2/128 set logical-systems B protocols bgp group external-peers type external set logical-systems B protocols bgp group external-peers peer-as 17 set logical-systems B protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 2001:db8:0:2:2a0:a502:0:5da set logical-systems B protocols bgp group external-peers family inet6 unicast set logical-systems B routing-options router-id 172.16.2.2 set logical-systems B routing-options autonomous-system 22
1 デバイスC 1
set logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 10 description to-E set logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 10 encapsulation frame-relay set logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 10 dlci 10 set logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 10 peer-unit 9 set logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 10 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:3::/64 eui-64 set logical-systems C interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet6 address 2001:db8::3/128 set logical-systems C protocols bgp group external-peers type external set logical-systems C protocols bgp group external-peers peer-as 17 set logical-systems C protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 2001:db8:0:3:2a0:a502:0:9da set logical-systems C protocols bgp group external-peers family inet6 unicast set logical-systems C routing-options router-id 172.16.3.3 set logical-systems C routing-options autonomous-system 22
1 デバイスD 1
set logical-systems D interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 7 description to-E set logical-systems D interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 7 encapsulation frame-relay set logical-systems D interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 7 dlci 7 set logical-systems D interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 7 peer-unit 21 set logical-systems D interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 7 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:4::/64 eui-64 set logical-systems D interfaces lo0 unit 4 family inet6 address 2001:db8::4/128 set logical-systems D protocols bgp group external-peers type external set logical-systems D protocols bgp group external-peers peer-as 17 set logical-systems D protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 2001:db8:0:4:2a0:a502:0:15da set logical-systems D protocols bgp group external-peers family inet6 unicast set logical-systems D routing-options router-id 172.16.4.4 set logical-systems D routing-options autonomous-system 79
1 デバイスE 1
set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 description to-B set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 encapsulation frame-relay set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 dlci 6 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 peer-unit 6 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:2::/64 eui-64 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 9 description to-C set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 9 encapsulation frame-relay set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 9 dlci 10 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 9 peer-unit 10 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 9 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:3::/64 eui-64 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 21 description to-D set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 21 encapsulation frame-relay set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 21 dlci 7 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 21 peer-unit 7 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 21 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:4::/64 eui-64 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 25 description to-A set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 25 encapsulation frame-relay set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 25 dlci 1 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 25 peer-unit 1 set logical-systems E interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 25 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 eui-64 set logical-systems E interfaces lo0 unit 5 family inet6 address 2001:db8::5/128 set logical-systems E protocols bgp group external-peers type external set logical-systems E protocols bgp group external-peers peer-as 22 set logical-systems E protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:1da set logical-systems E protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 2001:db8:0:2:2a0:a502:0:6da set logical-systems E protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 2001:db8:0:3:2a0:a502:0:ada set logical-systems E protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 2001:db8:0:4:2a0:a502:0:7da peer-as 79 set logical-systems E protocols bgp group external-peers family inet6 unicast set logical-systems E routing-options router-id 172.16.5.5 set logical-systems E routing-options autonomous-system 17
ステップバイステップでの手順
次の例では、設定階層のいくつかのレベルに移動する必要があります。CLI のナビゲーションについては、CLIユーザー・ガイド の コンフィギュレーション・モードでのCLIエディタの使用を参照してください。
BGP ピアセッションを設定する
そのコマ
show interfaces terseンドを実行して、物理ルーターに論理トンネル(lt)インターフェイスがあることを確認します。user@R1> show interfaces terse Interface Admin Link Proto Local Remote ... lt-0/1/0 up up ...
論理システム A で、インターフェイスのカプセル化、ピアユニット番号、および DLCI を設定して、論理システム E に到達します。
user@R1> set cli logical-system A Logical system: A [edit] user@R1:A> edit Entering configuration mode [edit] user@R1:A# edit interfaces [edit interfaces] user@R1:A# set lt-0/1/0 unit 1 encapsulation frame-relay user@R1:A# set lt-0/1/0 unit 1 dlci 1 user@R1:A# set lt-0/1/0 unit 1 peer-unit 25
論理システム A で、Peer E へのリンクに対するネットワーク アドレスを設定し、ループバック インターフェイスを設定します。
[edit interfaces] user@R1:A# set lt-0/1/0 unit 1 description to-E user@R1:A# set lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 eui-64 user@R1:A# set lo0 unit 1 family inet6 address 2001:db8::1/128
論理システム E で、インターフェイスのカプセル化、ピアユニット番号、および DLCI を設定し、論理システム A に到達します。
user@R1> set cli logical-system E Logical system: E [edit] user@R1:E> edit Entering configuration mode [edit] user@R1:E# edit interfaces [edit interfaces] user@R1:E# set lt-0/1/0 unit 25 encapsulation frame-relay user@R1:E# set lt-0/1/0 unit 25 dlci 1 user@R1:E# set lt-0/1/0 unit 25 peer-unit 1
論理システム E で、Peer A へのリンクに対するネットワーク アドレスを設定し、ループバック インターフェイスを設定します。
[edit interfaces] user@R1:E# set lt-0/1/0 unit 25 description to-A user@R1:E# set lt-0/1/0 unit 25 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 eui-64 user@R1:E# set lo0 unit 5 family inet6 address 2001:db8::5/128
コマ
show interfaces terseンドを実行して、EUI-64 によって生成された IPv6 アドレスを表示します。2001 のアドレスは、BGP の
neighborステートメントの、この例で使用されています。注:fe80 アドレスは、リンクローカル アドレスで、この例では使用されていません。
user@R1:A> show interfaces terse Interface Admin Link Proto Local Remote Logical system: A betsy@tp8:A> show interfaces terse Interface Admin Link Proto Local Remote lt-0/1/0 lt-0/1/0.1 up up inet6 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:1da/64 fe80::2a0:a502:0:1da/64 lo0 lo0.1 up up inet6 2001:db8::1 fe80::2a0:a50f:fc56:1dauser@R1:E> show interfaces terse Interface Admin Link Proto Local Remote lt-0/1/0 lt-0/1/0.25 up up inet6 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:19da/64 fe80::2a0:a502:0:19da/64 lo0 lo0.5 up up inet6 2001:db8::5 fe80::2a0:a50f:fc56:1da他の論理システムに対して、このインターフェイス設定を繰り返します。
外部 BGP セッションの設定
ステップバイステップでの手順
次の例では、設定階層のいくつかのレベルに移動する必要があります。CLI のナビゲーションについては、CLIユーザー・ガイド の コンフィギュレーション・モードでのCLIエディタの使用を参照してください。
BGP ピアセッションを設定する
論理システム A で、BGP グループを作成し、外部ネイバーアドレスを追加します。
[edit protocols bgp group external-peers] user@R1:A# set neighbor 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:19da user@R1:A# set family inet6 unicast
論理システム E で、BGP グループを作成し、外部ネイバーアドレスを追加します。
[edit protocols bgp group external-peers] user@R1:E# set neighbor 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:1da user@R1:E# set family inet6 unicast
論理システム A で、外部 AS の自律システム(AS)番号を指定します。
[edit protocols bgp group external-peers] user@R1:A# set peer-as 17
論理システム E で、外部 AS の自律システム(AS)番号を指定します。
[edit protocols bgp group external-peers] user@R1:E# set peer-as 22
論理システム A で、EBGP にピアタイプを設定します。
[edit protocols bgp group external-peers] user@R1:A# set type external
論理システム E で、EBGP にピアタイプを設定します。
[edit protocols bgp group external-peers] user@R1:E# set type external
論理システム A で、自律システム(AS)番号とルーター ID を設定します。
[edit routing-options] user@R1:A# set router-id 172.16.1.1 user@R1:A# set autonomous-system 22
論理システム E で、AS 番号とルーター ID を設定します。
[edit routing-options] user@R1:E# set router-id 172.16.5.5 user@R1:E# set autonomous-system 17
ピア A、B、C、および D に対して、これらの手順を繰り返します。
結果
設定モードから、show logical-systemsコマンドを入力して設定を確認します。出力結果に意図した設定内容が表示されない場合は、この例の手順を繰り返して設定を修正します。
[edit]
user@R1# show logical-systems
A {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 1 {
description to-E;
encapsulation frame-relay;
dlci 1;
peer-unit 25;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 {
eui-64;
}
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 1 {
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8::1/128;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group external-peers {
type external;
peer-as 17;
neighbor 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:19da;
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 172.16.1.1;
autonomous-system 22;
}
}
B {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 6 {
description to-E;
encapsulation frame-relay;
dlci 6;
peer-unit 5;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:0:2::/64 {
eui-64;
}
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 2 {
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8::2/128;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group external-peers {
type external;
peer-as 17;
neighbor 2001:db8:0:2:2a0:a502:0:5da;
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 172.16.2.2;
autonomous-system 22;
}
}
C {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 10 {
description to-E;
encapsulation frame-relay;
dlci 10;
peer-unit 9;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:0:3::/64 {
eui-64;
}
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 3 {
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8::3/128;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group external-peers {
type external;
peer-as 17;
neighbor 2001:db8:0:3:2a0:a502:0:9da;
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 172.16.3.3;
autonomous-system 22;
}
}
D {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 7 {
description to-E;
encapsulation frame-relay;
dlci 7;
peer-unit 21;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:0:4::/64 {
eui-64;
}
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 4 {
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8::4/128;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group external-peers {
type external;
peer-as 17;
neighbor 2001:db8:0:4:2a0:a502:0:15da;
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 172.16.4.4;
autonomous-system 79;
}
}
E {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 5 {
description to-B;
encapsulation frame-relay;
dlci 6;
peer-unit 6;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:0:2::/64 {
eui-64;
}
}
}
unit 9 {
description to-C;
encapsulation frame-relay;
dlci 10;
peer-unit 10;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:0:3::/64 {
eui-64;
}
}
}
unit 21 {
description to-D;
encapsulation frame-relay;
dlci 7;
peer-unit 7;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:0:4::/64 {
eui-64;
}
}
}
unit 25 {
description to-A;
encapsulation frame-relay;
dlci 1;
peer-unit 1;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 {
eui-64;
}
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 5 {
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8::5/128;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group external-peers {
type external;
peer-as 22;
neighbor 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:1da;
neighbor 2001:db8:0:2:2a0:a502:0:6da;
neighbor 2001:db8:0:3:2a0:a502:0:ada;
neighbor 2001:db8:0:4:2a0:a502:0:7da {
peer-as 79;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 172.16.5.5;
autonomous-system 17;
}
}
デバイスの設定が完了したら、設定モードから commit を入力します。
検証
設定が正常に機能していることを確認します。
BGP ネイバーの検証
目的
設定したインタフェースで BGP が動作していること、および各近隣アドレスで BGP セッションがアクティブになっていることを確認します。
アクション
オペレーショナルモードから、show bgp neighborコマンドを実行します。
user@R1:E> show bgp neighbor
Peer: 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:1da+54987 AS 22 Local: 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:19da+179 AS 17
Type: External State: Established Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: Open Message Error
Options: <Preference PeerAS Refresh>
Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Error: 'Open Message Error' Sent: 20 Recv: 0
Peer ID: 172.16.1.1 Local ID: 172.16.5.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 0
BFD: disabled, down
Local Interface: lt-0/1/0.25
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet6-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet6-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet6-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Peer does not support Restarter functionality
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet6-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet6-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet6-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 22)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet6.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 0
Accepted prefixes: 0
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 0
Last traffic (seconds): Received 7 Sent 18 Checked 81
Input messages: Total 1611 Updates 1 Refreshes 0 Octets 30660
Output messages: Total 1594 Updates 0 Refreshes 0 Octets 30356
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 2001:db8:0:2:2a0:a502:0:6da+179 AS 22 Local: 2001:db8:0:2:2a0:a502:0:5da+55502 AS 17
Type: External State: Established Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: Open Message Error
Options: <Preference PeerAS Refresh>
Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Error: 'Open Message Error' Sent: 26 Recv: 0
Peer ID: 172.16.2.2 Local ID: 172.16.5.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 2
BFD: disabled, down
Local Interface: lt-0/1/0.5
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet6-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet6-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet6-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Peer does not support Restarter functionality
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet6-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet6-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet6-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 22)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet6.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 0
Accepted prefixes: 0
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 0
Last traffic (seconds): Received 15 Sent 8 Checked 8
Input messages: Total 1610 Updates 1 Refreshes 0 Octets 30601
Output messages: Total 1645 Updates 0 Refreshes 0 Octets 32417
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 2001:db8:0:3:2a0:a502:0:ada+55983 AS 22 Local: 2001:db8:0:3:2a0:a502:0:9da+179 AS 17
Type: External State: Established Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Options: <Preference PeerAS Refresh>
Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 172.16.3.3 Local ID: 172.16.5.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 3
BFD: disabled, down
Local Interface: lt-0/1/0.9
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet6-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet6-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet6-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Peer does not support Restarter functionality
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet6-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet6-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet6-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 22)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet6.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 0
Accepted prefixes: 0
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 0
Last traffic (seconds): Received 21 Sent 21 Checked 67
Input messages: Total 1610 Updates 1 Refreshes 0 Octets 30641
Output messages: Total 1587 Updates 0 Refreshes 0 Octets 30223
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 2001:db8:0:4:2a0:a502:0:7da+49255 AS 79 Local: 2001:db8:0:4:2a0:a502:0:15da+179 AS 17
Type: External State: Established Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Options: <Preference PeerAS Refresh>
Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 172.16.4.4 Local ID: 172.16.5.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 1
BFD: disabled, down
Local Interface: lt-0/1/0.21
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet6-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet6-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet6-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Peer does not support Restarter functionality
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet6-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet6-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet6-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 79)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet6.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 0
Accepted prefixes: 0
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 0
Last traffic (seconds): Received 6 Sent 17 Checked 25
Input messages: Total 1615 Updates 1 Refreshes 0 Octets 30736
Output messages: Total 1593 Updates 0 Refreshes 0 Octets 30337
Output Queue[0]: 0意味
IPv6 ユニキャスト ネットワーク層到達可能性情報(NLRI)は、ネイバー間で交換されています。
BGP グループの検証
目的
BGP グループが正しく設定されていることを確認します。
アクション
オペレーショナルモードから、show bgp groupコマンドを実行します。
user@R1:E> show bgp group Group Type: External Local AS: 17 Name: external-peers Index: 0 Flags: <> Holdtime: 0 Total peers: 4 Established: 4 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:1da+54987 2001:db8:0:2:2a0:a502:0:6da+179 2001:db8:0:3:2a0:a502:0:ada+55983 2001:db8:0:4:2a0:a502:0:7da+49255 inet6.0: 0/0/0/0 Groups: 1 Peers: 4 External: 4 Internal: 0 Down peers: 0 Flaps: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending inet6.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 inet6.2 0 0 0 0 0 0
意味
グループ タイプは外部で、グループには 4 つのピアがあります。
BGP サマリー情報の検証
目的
BGP ピア関係が確立されていることを確認します。
アクション
オペレーショナルモードから、show bgp summaryコマンドを実行します。
user@R1:E> show bgp summary Groups: 1 Peers: 4 Down peers: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending inet6.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 inet6.2 0 0 0 0 0 0 Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Accepted/Damped... 2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:1da 22 1617 1600 0 0 12:07:00 Establ inet6.0: 0/0/0/0 2001:db8:0:2:2a0:a502:0:6da 22 1616 1651 0 0 12:06:56 Establ inet6.0: 0/0/0/0 2001:db8:0:3:2a0:a502:0:ada 22 1617 1594 0 0 12:04:32 Establ inet6.0: 0/0/0/0 2001:db8:0:4:2a0:a502:0:7da 79 1621 1599 0 0 12:07:00 Establ inet6.0: 0/0/0/0
意味
ダウン ピア:0 の出力は、BGP ピアが確立された状態であることを示しています。
ルーティングテーブルのチェック
目的
inet6.0 ルーティング テーブルに、ローカル ルートとダイレクト ルートが読み込まれていることを確認します。
アクション
オペレーショナルモードから、show routeコマンドを実行します。
user@R1:E> show route
inet6.0: 15 destinations, 18 routes (15 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
2001:db8::5/128 *[Direct/0] 12:41:18
> via lo0.5
2001:db8:0:1::/64 *[Direct/0] 14:40:01
> via lt-0/1/0.25
2001:db8:0:1:2a0:a502:0:19da/128
*[Local/0] 14:40:01
Local via lt-0/1/0.25
2001:db8:0:2::/64 *[Direct/0] 14:40:02
> via lt-0/1/0.5
2001:db8:0:2:2a0:a502:0:5da/128
*[Local/0] 14:40:02
Local via lt-0/1/0.5
2001:db8:0:3::/64 *[Direct/0] 14:40:02
> via lt-0/1/0.9
2001:db8:0:3:2a0:a502:0:9da/128
*[Local/0] 14:40:02
Local via lt-0/1/0.9
2001:db8:0:4::/64 *[Direct/0] 14:40:01
> via lt-0/1/0.21
2001:db8:0:4:2a0:a502:0:15da/128
*[Local/0] 14:40:01
Local via lt-0/1/0.21
fe80::/64 *[Direct/0] 14:40:02
> via lt-0/1/0.5
[Direct/0] 14:40:02
> via lt-0/1/0.9
[Direct/0] 14:40:01
> via lt-0/1/0.21
[Direct/0] 14:40:01
> via lt-0/1/0.25
fe80::2a0:a502:0:5da/128
*[Local/0] 14:40:02
Local via lt-0/1/0.5
fe80::2a0:a502:0:9da/128
*[Local/0] 14:40:02
Local via lt-0/1/0.9
fe80::2a0:a502:0:15da/128
*[Local/0] 14:40:01
Local via lt-0/1/0.21
fe80::2a0:a502:0:19da/128
*[Local/0] 14:40:01
Local via lt-0/1/0.25
fe80::2a0:a50f:fc56:1da/128
*[Direct/0] 12:41:18
> via lo0.5意味
inet6.0 ルーティング テーブルには、ローカル ルートとダイレクト ルートが含まれています。ルーティング テーブルに他のタイプのルートを読み込むには、ルーティング ポリシーを設定する必要があります。
内部 BGP ピアリングセッションの理解
2つのBGP対応デバイスが同じ自律システム(AS)内にある場合、BGPセッションは内部BGPセッション、またはIBGPセッションと呼ばれます。BGPは、IBGPと外部BGP(EBGP)セッションで同じメッセージ・タイプを使用しますが、各メッセージをいつ送信するか、また各メッセージをどのように解釈するかのルールは若干異なっています。こう言った理由で、IBGPとEBGPを別々のプロトコルと呼ぶ人もいます。
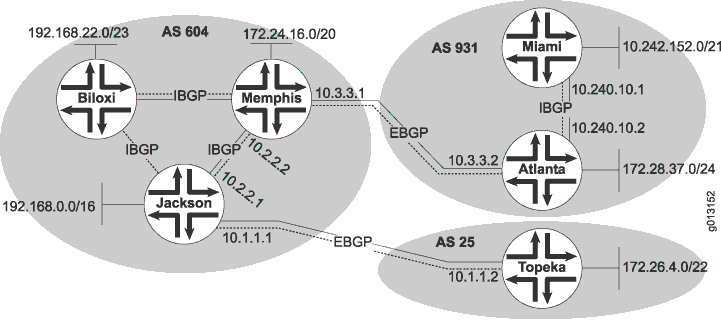
図 4において、Device Jackson、Device Memphis、およびDevice Biloxiは、互いにIBGPピア・セッションを持っています。同様に、Device MiamiとDevice Atlantaは、互いにIBGPピア・セッションを持っています。
IBGPの目的は、EBGPのルート広告をネットワーク全体に転送するための手段を提供することです。理論的には、このタスクを達成するために、すべてのEBGPルートをOSPFやIS-ISなどの内部ゲートウェイ・プロトコル(IGP)に再配信することができます。しかし、インターネットには多数のEBGPルートがあり、IGP の動作も加わるため、本番環境ではこの方法は推奨されません。つまり、これだけ多くのルートがあると、IGPは混乱するかクラッシュしてしまいます。
一般に、IBGPピア間の接続はループバック・インタフェース(lo0)を使用して確立します。ループバック インターフェースは、機器が動作している限り、常にアップしています。ループバック・アドレスへのルートがある場合、IBGPピアリング・セッションはアップしたままになります。物理インターフェース・アドレスを代わりに使用し、そのインターフェースがアップ・ダウンする場合、IBGPピアリング・セッションもアップ・ダウンします。このように、ループバック・インタフェースは、リンク冗長性を持つデバイスであれば、物理インタフェースやリンクがダウンした場合のフォールト・トレランスを提供します。
IBGPネイバーは直接接続されている必要はありませんが、完全にメッシュ化されている必要があります。この場合、フルメッシュ化とは、各機器がネイバーピア関係で他のすべての機器と論理的に接続されていることを意味します。neighbor文はメッシュを作成します。IBGPの完全なメッシュ要件のため、AS内のすべてのIBGPデバイス間で個々のピアリングセッションを設定する必要があります。フル・メッシュは物理的なリンクである必要はありません。むしろ、各ルーティング・デバイスでのコンフィギュレーションは、ピア・セッションのフルメッシュを(複数の neighbor というステートメントを使用して)作成する必要があります。
コンフェデレーションまたはルートリフレクションを設定すれば、フルメッシュの要件は免除されます。
フルメッシュの要件を理解するために、IBGPで学習したルートを別のIBGPピアに再広告できないことを考えます。IBGPルートの再広告を防止し、フルメッシュを必要とする理由は、AS内のルーティングループを回避するためです。ASパス属性は、BGPルーティングデバイスがループを回避するための手段です。EBGPピアからルートを受信したときだけ,ローカルAS番号でパス情報を調べます。属性はAS境界を越えて変更されるだけなので、このシステムは適切に機能します。ただし、属性は複数のAS境界でのみ変更されるため、AS内で問題が発生します。たとえば、ルーティングデバイスA、B、Cがすべて同じASにあるとします。デバイスAは、EBGPピアからルートを受信して、デバイスBにルートを送信し、デバイスBはそれをアクティブ・ルートとして読み込みます。その後、ルートはデバイスCに送信されます。デバイスCはローカルにルートをインストールしてデバイスAに送り返します。デバイスAがルートをインストールすると、AS内でループが形成されます。これらの広告の間,ASパス属性は変更されないので,ルーティング・デバイスはループを検出することができません。したがって、BGPプロトコル設計者が決めた方針では、ルーティングループを絶対に形成しない唯一の保証は、AS内でIBGPが学習したルートがIBGPピアによってアドバタイズされるのを防ぐことでした。ルート到達性に関しては、IBGPピアが完全にメッシュ化されています。
IBGPはマルチホップ接続をサポートしているため、IBGPネイバーをAS内の任意の場所に配置でき、多くの場合、リンクは共有されません。再帰的ルート探索により、ループバック・ピアリング・アドレスをIP転送のネクスト・ホップとすることで、解決します。ルックアップ・サービスは、スタティック・ルート、OSPFなどのIGP、またはBGPルートによって提供されます。
関連項目
例:内部 BGP ピア セッションの設定
この例では、内部 BGP ピア セッションを設定する方法を示します。
要件
この例を構成する前に、デバイスの初期化以上の特別な構成は必要ありません。
概要
この例では、内部 BGP(IBGP)ピア セッションを設定します。ループバック インターフェース(lo0)は、IBGP ピア間の接続を確立するために使用されます。ループバック インターフェースは、機器が動作している限り、常にアップしています。ループバックア ドレスへのルートがある場合、IBGP ピア セッションはアップしたままになります。物理インターフェース アドレスを代わりに使用し、そのインターフェースがアップ/ダウンする場合、IBGP ピア セッションもアップ/ダウンします。したがって、リンク冗長性を持つデバイスの場合、ループバック インタフェースは、物理インタフェースまたはリンクの 1 つがダウンした場合にフォールト トレランスを提供します。
あるデバイスがリモート デバイスのループバック インターフェース アドレスとピアリングするとき、ローカル デバイスは BGP アップデート メッセージがリモート デバイスのループバック インターフェース アドレスから来る(ソースとなる)ことを期待します。ステートlocal-addressメントを使用すると、BGP アップデート メッセージのソース情報を指定することができます。local-address文を省略した場合、BGP 更新メッセージの予想送信元は装置の送信元アドレス選択ルールに基づき,通常は egress インタフェース アドレスが予想送信元となります。この場合,予想されるソース アドレス(ピアの egress インタフェース)と実際のソース(ピアの loopback インタフェース)の間にミスマッチが存在するため,ピア セッションは確立されません。予想される送信元アドレスと実際の送信元アドレスが一致するように、local-address文にループバック インターフェース アドレスを指定します。
IBGP はマルチホップ接続をサポートしているため、IBGP ネイバーは自律システム(AS)内のどこにでも存在でき、リンクを共有しないことがよくあります。再帰的ルート探索により、ループバック ピアのアドレスが IP 転送のネクストホップに解決されます。この例では、このサービスは OSPF によって提供されます。IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol)ネイバーは直接接続されている必要はありませんが、完全にメッシュ化されている必要があります。この場合、フルメッシュ化とは、各機器がネイバーピア関係で他のすべての機器と論理的に接続されていることを意味します。neighbor文はメッシュを作成します。
コンフェデレーションまたはルートリフレクションを設定すれば、フルメッシュの要件は免除されます。
BGP ピアが確立された後,BGP ピアが自動的にローカル ルートをアドバタイズすることはありません。BGP 対応機器では,ローカル,スタティック,または IGP で学習したルートを BGP ルーティング情報ベース(RIB)にエクスポートし,他のピアに BGP ルートとしてアドバタイズするためのポリシー設定が必要です。BGPの広告ポリシーは、デフォルトではBGP以外の経路(ローカル経路など)をピアに広告しません。
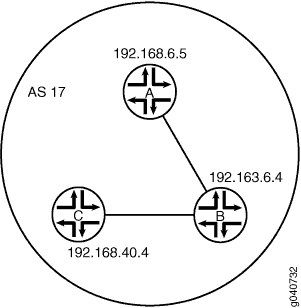
internal-peersサンプルネットワークでは、AS17 の機器はグループで完全にメッシュ化されています。デバイスのループバックアドレスは192.168.6.5、192.163.6.4、192.168.40.4です。
図 5は、内部ピア セッションを持つ典型的なネットワークを示しています。
設定
CLIクイック構成
この例をすばやく設定するには、次のコマンドをコピーしてテキストファイルに貼り付け、改行を削除して、ネットワーク構成に合わせて必要な詳細を変更し、[edit]階層レベルのCLIにコマンドをコピー&ペーストしてください。
1 デバイスA 1
set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 1 description to-B set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.10.10.1/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 192.168.6.5/32 set protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set protocols bgp group internal-peers description “connections to B and C” set protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.168.6.5 set protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-direct set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.163.6.4 set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.40.4 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.1 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/1/0.1 set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 then accept set routing-options router-id 192.168.6.5 set routing-options autonomous-system 17
1 デバイスB 1
set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 2 description to-A set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.10.10.2/30 set interfaces ge-0/1/1 unit 5 description to-C set interfaces ge-0/1/1 unit 5 family inet address 10.10.10.5/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 2 family inet address 192.163.6.4/32 set protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set protocols bgp group internal-peers description “connections to A and C” set protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.163.6.4 set protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-direct set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.40.4 set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.6.5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.2 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/1/0.2 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/1/1.5 set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 then accept set routing-options router-id 192.163.6.4 set routing-options autonomous-system 17
1 デバイスC 1
set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 6 description to-B set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 6 family inet address 10.10.10.6/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet address 192.168.40.4/32 set protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set protocols bgp group internal-peers description “connections to A and B” set protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.168.40.4 set protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-direct set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.163.6.4 set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.6.5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.3 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/1/0.6 set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 then accept set routing-options router-id 192.168.40.4 set routing-options autonomous-system 17
デバイス A を設定する
ステップバイステップでの手順
次の例では、設定階層のいくつかのレベルに移動する必要があります。CLIのナビゲーションについては、Junos OS CLIユーザーガイドの 設定モードでCLIエディターを使用する を参照してください。
装置 A で内部 BGP ピア セッションを設定する場合。
インターフェイスを設定します。
[edit interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 1] user@A# set description to-B user@A# set family inet address 10.10.10.1/30 [edit interfaces] user@A# set lo0 unit 1 family inet address 192.168.6.5/32
BGP を設定します。
機器 A と機器 C が直接接続されていないにもかかわらず、機器Bと機器 C の両方についての
neighbor文が含まれている。[edit protocols bgp group internal-peers] user@A# set type internal user@A# set description “connections to B and C” user@A# set local-address 192.168.6.5 user@A# set export send-direct user@A# set neighbor 192.163.6.4 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.40.4
OSPFを設定します。
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@A# set interface lo0.1 passive user@A# set interface ge-0/1/0.1
直接ルートを受け入れるポリシーを設定します。
このシナリオの他の有用なオプションは、OSPF またはローカル ルートで学習したルートを受け入れることかもしれません。
[edit policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2] user@A# set from protocol direct user@A# set then accept
ルーターID、AS番号を設定する。
[edit routing-options] user@A# set router-id 192.168.6.5 user@A# set autonomous-system 17
結果
設定モードから、show interfaces 、show policy-options、show protocols、およびshow routing-options のコマンドを入力して設定を確認します。出力結果に意図した設定内容が表示されない場合は、この例の手順を繰り返して設定を修正します。
user@A# show interfaces
ge-0/1/0 {
unit 1 {
description to-B;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.1/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 1 {
family inet {
address 192.168.6.5/32;
}
}
}
user@A# show policy-options
policy-statement send-direct {
term 2 {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
user@A# show protocols
bgp {
group internal-peers {
type internal;
description “connections to B and C”;
local-address 192.168.6.5;
export send-direct;
neighbor 192.163.6.4;
neighbor 192.168.40.4;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.1 {
passive;
}
interface ge-0/1/0.1;
}
}
user@A# show routing-options router-id 192.168.6.5; autonomous-system 17;
デバイスの設定が完了したら、設定モードから commit を入力します。
デバイス B の設定
ステップバイステップでの手順
次の例では、設定階層内のさまざまなレベルに移動する必要があります。設定モードでのCLIエディターの使用CLIのナビゲーションについては、「1 コンフィグレーション・モードでのCLIエディタの使用」1 を参照してください。
機器 B に内部 BGP ピアセッションを設定する。
インターフェイスを設定します。
[edit interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 2] user@B# set description to-A user@B# set family inet address 10.10.10.2/30 [edit interfaces ge-0/1/1] user@B# set unit 5 description to-C user@B# set unit 5 family inet address 10.10.10.5/30 [edit interfaces] user@B# set lo0 unit 2 family inet address 192.163.6.4/32
BGP を設定します。
機器 A と機器 C が直接接続されていないにもかかわらず、機器Bと機器 C の両方についての
neighbor文が含まれている。[edit protocols bgp group internal-peers] user@B# set type internal user@B# set description “connections to A and C” user@B# set local-address 192.163.6.4 user@B# set export send-direct user@B# set neighbor 192.168.40.4 user@B# set neighbor 192.168.6.5
OSPFを設定します。
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@B# set interface lo0.2 passive user@B# set interface ge-0/1/0.2 user@B# set interface ge-0/1/1.5
直接ルートを受け入れるポリシーを設定します。
このシナリオの他の有用なオプションは、OSPF またはローカル ルートで学習したルートを受け入れることかもしれません。
[edit policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2] user@B# set from protocol direct user@B# set then accept
ルーターID、AS番号を設定する。
[edit routing-options] user@B# set router-id 192.163.6.4 user@B# set autonomous-system 17
結果
設定モードから、show interfaces 、show policy-options、show protocols、およびshow routing-options のコマンドを入力して設定を確認します。出力結果に意図した設定内容が表示されない場合は、この例の手順を繰り返して設定を修正します。
user@B# show interfaces
ge-0/1/0 {
unit 2 {
description to-A;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.2/30;
}
}
}
ge-0/1/1 {
unit 5 {
description to-C;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.5/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 2 {
family inet {
address 192.163.6.4/32;
}
}
}
user@B# show policy-options
policy-statement send-direct {
term 2 {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
user@B# show protocols
bgp {
group internal-peers {
type internal;
description “connections to A and C”;
local-address 192.163.6.4;
export send-direct;
neighbor 192.168.40.4;
neighbor 192.168.6.5;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.2 {
passive;
}
interface ge-0/1/0.2;
interface ge-0/1/1.5;
}
}
user@B# show routing-options router-id 192.163.6.4; autonomous-system 17;
デバイスの設定が完了したら、設定モードから commit を入力します。
デバイス C の設定
ステップバイステップでの手順
次の例では、設定階層のいくつかのレベルに移動する必要があります。CLIのナビゲーションについては、Junos OS CLIユーザーガイドの 設定モードでCLIエディターを使用する を参照してください。
機器 C に内部 BGP ピアセッションを設定する。
インターフェイスを設定します。
[edit interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 6] user@C# set description to-B user@C# set family inet address 10.10.10.6/30 [edit interfaces] user@C# set lo0 unit 3 family inet address 192.168.40.4/32
BGP を設定します。
機器 A と機器 C が直接接続されていないにもかかわらず、機器Bと機器 C の両方についての
neighbor文が含まれている。[edit protocols bgp group internal-peers] user@C# set type internal user@C# set description “connections to A and B” user@C# set local-address 192.168.40.4 user@C# set export send-direct user@C# set neighbor 192.163.6.4 user@C# set neighbor 192.168.6.5
OSPFを設定します。
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@C# set interface lo0.3 passive user@C# set interface ge-0/1/0.6
直接ルートを受け入れるポリシーを設定します。
このシナリオの他の有用なオプションは、OSPF またはローカル ルートで学習したルートを受け入れることかもしれません。
[edit policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2] user@C# set from protocol direct user@C# set then accept
ルーターID、AS番号を設定する。
[edit routing-options] user@C# set router-id 192.168.40.4 user@C# set autonomous-system 17
結果
設定モードから、show interfaces 、show policy-options、show protocols、およびshow routing-options のコマンドを入力して設定を確認します。出力結果に意図した設定内容が表示されない場合は、この例の手順を繰り返して設定を修正します。
user@C# show interfaces
ge-0/1/0 {
unit 6 {
description to-B;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.6/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 3 {
family inet {
address 192.168.40.4/32;
}
}
}
user@C# show policy-options
policy-statement send-direct {
term 2 {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
user@C# show protocols
bgp {
group internal-peers {
type internal;
description “connections to A and B”;
local-address 192.168.40.4;
export send-direct;
neighbor 192.163.6.4;
neighbor 192.168.6.5;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.3 {
passive;
}
interface ge-0/1/0.6;
}
}
user@C# show routing-options router-id 192.168.40.4; autonomous-system 17;
デバイスの設定が完了したら、設定モードから commit を入力します。
検証
設定が正常に機能していることを確認します。
BGP ネイバーの検証
目的
設定したインタフェースで BGP が動作していること、および各近隣アドレスで BGP セッションがアクティブになっていることを確認します。
アクション
動作モードからshow bgp neighborコマンドを入力します。
user@A> show bgp neighbor
Peer: 192.163.6.4+179 AS 17 Local: 192.168.6.5+58852 AS 17
Type: Internal State: Established Flags: Sync
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Export: [ send-direct ]
Options: Preference LocalAddress Refresh
Local Address: 192.168.6.5 Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 192.163.6.4 Local ID: 192.168.6.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 0
BFD: disabled, down
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 17)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 3
Accepted prefixes: 3
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 2
Last traffic (seconds): Received 25 Sent 19 Checked 67
Input messages: Total 2420 Updates 4 Refreshes 0 Octets 46055
Output messages: Total 2411 Updates 2 Refreshes 0 Octets 45921
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 192.168.40.4+179 AS 17 Local: 192.168.6.5+56466 AS 17
Type: Internal State: Established Flags: Sync
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Export: [ send-direct ]
Options: Preference LocalAddress Refresh
Local Address: 192.168.6.5 Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 192.168.40.4 Local ID: 192.168.6.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 1
BFD: disabled, down
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 17)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 2
Accepted prefixes: 2
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 2
Last traffic (seconds): Received 7 Sent 21 Checked 24
Input messages: Total 2412 Updates 2 Refreshes 0 Octets 45867
Output messages: Total 2409 Updates 2 Refreshes 0 Octets 45883
Output Queue[0]: 0BGP グループの検証
目的
BGP グループが正しく設定されていることを確認します。
アクション
動作モードからshow bgp groupコマンドを入力します。
user@A> show bgp group Group Type: Internal AS: 17 Local AS: 17 Name: internal-peers Index: 0 Flags: <Export Eval> Export: [ send-direct ] Holdtime: 0 Total peers: 2 Established: 2 192.163.6.4+179 192.168.40.4+179 inet.0: 0/5/5/0 Groups: 1 Peers: 2 External: 0 Internal: 2 Down peers: 0 Flaps: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending inet.0 5 0 0 0 0 0
BGP サマリー情報の検証
目的
BGP の設定が正しいことを確認します。
アクション
動作モードからshow bgp summaryコマンドを入力します。
user@A> show bgp summary Groups: 1 Peers: 2 Down peers: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending inet.0 5 0 0 0 0 0 Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Accepted/Damped... 192.163.6.4 17 2441 2432 0 0 18:18:52 0/3/3/0 0/0/0/0 192.168.40.4 17 2432 2430 0 0 18:18:48 0/2/2/0 0/0/0/0
BGP ルートがルーティングテーブルにインストールされていることを確認する
目的
エクスポートポリシーの設定によって,BGP ルートがピアのルーティングテーブルにインストールされることを確認します。
アクション
動作モードからshow route protocol bgpコマンドを入力します。
user@A> show route protocol bgp
inet.0: 7 destinations, 12 routes (7 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.10.10.0/30 [BGP/170] 07:09:57, localpref 100, from 192.163.6.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via ge-0/1/0.1
10.10.10.4/30 [BGP/170] 07:09:57, localpref 100, from 192.163.6.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via ge-0/1/0.1
[BGP/170] 07:07:12, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via ge-0/1/0.1
192.163.6.4/32 [BGP/170] 07:09:57, localpref 100, from 192.163.6.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via ge-0/1/0.1
192.168.40.4/32 [BGP/170] 07:07:12, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via ge-0/1/0.1例:論理システムでの内部 BGP ピアリング セッションの設定
この例では、論理システムで内部 BGP ピアセッションを構成する方法を示します。
要件
この例では、デバイスの初期化以上の特別な設定は必要ありません。
概要
この例では、内部 BGP(IBGP)ピアリング セッションを設定します。
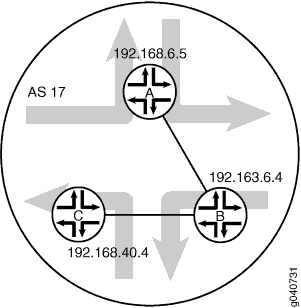
internal-peersサンプルネットワークでは、AS17 の機器はグループで完全にメッシュ化されています。デバイスのループバックアドレスは192.168.6.5、192.163.6.4、192.168.40.4です。
図 6は、内部ピア セッションを持つ典型的なネットワークを示しています。
設定
CLIクイック構成
この例をすばやく設定するには、次のコマンドをコピーしてテキストファイルに貼り付け、改行を削除して、ネットワーク構成に合わせて必要な詳細を変更し、[edit]階層レベルのCLIにコマンドをコピー&ペーストしてください。
set logical-systems A interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 description to-B set logical-systems A interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems A interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 peer-unit 2 set logical-systems A interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.10.10.1/30 set logical-systems A interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 192.168.6.5/32 set logical-systems A protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set logical-systems A protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.168.6.5 set logical-systems A protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-direct set logical-systems A protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.163.6.4 set logical-systems A protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.40.4 set logical-systems A protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.1 passive set logical-systems A protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lt-0/1/0.1 set logical-systems A policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 from protocol direct set logical-systems A policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 then accept set logical-systems A routing-options router-id 192.168.6.5 set logical-systems A routing-options autonomous-system 17 set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 description to-A set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 peer-unit 1 set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.10.10.2/30 set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 description to-C set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 peer-unit 6 set logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 family inet address 10.10.10.5/30 set logical-systems B interfaces lo0 unit 2 family inet address 192.163.6.4/32 set logical-systems B protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set logical-systems B protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.163.6.4 set logical-systems B protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-direct set logical-systems B protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.40.4 set logical-systems B protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.6.5 set logical-systems B protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.2 passive set logical-systems B protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lt-0/1/0.2 set logical-systems B protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lt-0/1/0.5 set logical-systems B policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 from protocol direct set logical-systems B policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 then accept set logical-systems B routing-options router-id 192.163.6.4 set logical-systems B routing-options autonomous-system 17 set logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6 description to-B set logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6 peer-unit 5 set logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6 family inet address 10.10.10.6/30 set logical-systems C interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet address 192.168.40.4/32 set logical-systems C protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set logical-systems C protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.168.40.4 set logical-systems C protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-direct set logical-systems C protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.163.6.4 set logical-systems C protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.6.5 set logical-systems C protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.3 passive set logical-systems C protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lt-0/1/0.6 set logical-systems C policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 from protocol direct set logical-systems C policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2 then accept set logical-systems C routing-options router-id 192.168.40.4 set logical-systems C routing-options autonomous-system 17
デバイス A
ステップバイステップでの手順
次の例では、設定階層のいくつかのレベルに移動する必要があります。CLI のナビゲーションについては、CLIユーザー・ガイド の コンフィギュレーション・モードでのCLIエディタの使用を参照してください。
装置 A で内部 BGP ピア セッションを設定する場合。
インターフェイスを設定します。
[edit logical-systems A interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1] user@R1# set description to-B user@R1# set encapsulation ethernet user@R1# set peer-unit 2 user@R1# set family inet address 10.10.10.1/30 user@R1# set family inet address 192.168.6.5/32 user@R1# up user@R1# up [edit logical-systems A interfaces] user@R1# set lo0 unit 1 family inet address 192.168.6.5/32 user@R1# exit [edit] user@R1# edit logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0 [edit logical-systems B interfaces lt-0/1/0] user@R1# set unit 2 description to-A user@R1# set unit 2 encapsulation ethernet user@R1# set unit 2 peer-unit 1 user@R1# set unit 2 family inet address 10.10.10.2/30 user@R1# set unit 5 description to-C user@R1# set unit 5 encapsulation ethernet user@R1# set unit 5 peer-unit 6 user@R1# set family inet address 10.10.10.5/30 user@R1# up [edit logical-systems B interfaces] user@R1# set lo0 unit 2 family inet address 192.163.6.4/32 user@R1# exit [edit] user@R1# edit logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6 [edit logical-systems C interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 6] set description to-B set encapsulation ethernet set peer-unit 5 set family inet address 10.10.10.6/30 user@R1# up user@R1# up [edit logical-systems C interfaces] set lo0 unit 3 family inet address 192.168.40.4/32
BGP を設定します。
論理システム A では、論理システム A と機器 C が直接接続されていないにもかかわらず、機器 B と機器 C の両方に
neighborステートメントが含まれています。[edit logical-systems A protocols bgp group internal-peers] user@R1# set type internal user@R1# set local-address 192.168.6.5 user@R1# set export send-direct user@R1# set neighbor 192.163.6.4 user@R1# set neighbor 192.168.40.4 [edit logical-systems B protocols bgp group internal-peers] user@R1# set type internal user@R1# set local-address 192.163.6.4 user@R1# set export send-direct user@R1# set neighbor 192.168.40.4 user@R1# set neighbor 192.168.6.5 [edit logical-systems C protocols bgp group internal-peers] user@R1# set type internal user@R1# set local-address 192.168.40.4 user@R1# set export send-direct user@R1# set neighbor 192.163.6.4 user@R1# set neighbor 192.168.6.5
OSPFを設定します。
[edit logical-systems A protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@R1# set interface lo0.1 passive user@R1# set interface lt-0/1/0.1 [edit logical-systems A protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@R1# set interface lo0.2 passive user@R1# set interface lt-0/1/0.2 user@R1# set interface lt-0/1/0.5 [edit logical-systems A protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@R1# set interface lo0.3 passive user@R1# set interface lt-0/1/0.6
直接ルートを受け入れるポリシーを設定します。
このシナリオの他の有用なオプションは、OSPF またはローカル ルートで学習したルートを受け入れることかもしれません。
[edit logical-systems A policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2] user@R1# set from protocol direct user@R1# set then accept [edit logical-systems B policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2] user@R1# set from protocol direct user@R1# set then accept [edit logical-systems C policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 2] user@R1# set from protocol direct user@R1# set then accept
ルーターIDと自律システム(AS)番号を設定する。
[edit logical-systems A routing-options] user@R1# set router-id 192.168.6.5 user@R1# set autonomous-system 17 [edit logical-systems B routing-options] user@R1# set router-id 192.163.6.4 user@R1# set autonomous-system 17 [edit logical-systems C routing-options] user@R1# set router-id 192.168.40.4 user@R1# set autonomous-system 17
結果
設定モードから、show logical-systemsコマンドを入力して設定を確認します。出力結果に意図した設定内容が表示されない場合は、この例の設定手順を繰り返して設定を修正します。
user@R1# show logical-systems
A {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 1 {
description to-B;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 2;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.1/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 1 {
family inet {
address 192.168.6.5/32;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group internal-peers {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.6.5;
export send-direct;
neighbor 192.163.6.4;
neighbor 192.168.40.4;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.1 {
passive;
}
interface lt-0/1/0.1;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement send-direct {
term 2 {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 192.168.6.5;
autonomous-system 17;
}
}
B {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 2 {
description to-A;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 1;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.2/30;
}
}
unit 5 {
description to-C;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 6;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.5/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 2 {
family inet {
address 192.163.6.4/32;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group internal-peers {
type internal;
local-address 192.163.6.4;
export send-direct;
neighbor 192.168.40.4;
neighbor 192.168.6.5;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.2 {
passive;
}
interface lt-0/1/0.2;
interface lt-0/1/0.5;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement send-direct {
term 2 {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 192.163.6.4;
autonomous-system 17;
}
}
C {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 6 {
description to-B;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 5;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.6/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 3 {
family inet {
address 192.168.40.4/32;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group internal-peers {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.40.4;
export send-direct;
neighbor 192.163.6.4;
neighbor 192.168.6.5;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.3 {
passive;
}
interface lt-0/1/0.6;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement send-direct {
term 2 {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 192.168.40.4;
autonomous-system 17;
}
}
デバイスの設定が完了したら、設定モードから commit を入力します。
検証
設定が正常に機能していることを確認します。
BGP ネイバーの検証
目的
設定したインタフェースで BGP が動作していること、および各近隣アドレスで BGP セッションがアクティブになっていることを確認します。
アクション
オペレーションモードから、show bgp neighborコマンドを入力します。
user@R1> show bgp neighbor logical-system A
Peer: 192.163.6.4+179 AS 17 Local: 192.168.6.5+58852 AS 17
Type: Internal State: Established Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Export: [ send-direct ]
Options: <Preference LocalAddress Refresh>
Local Address: 192.168.6.5 Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 192.163.6.4 Local ID: 192.168.6.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 0
BFD: disabled, down
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 17)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 3
Accepted prefixes: 3
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 2
Last traffic (seconds): Received 16 Sent 1 Checked 63
Input messages: Total 15713 Updates 4 Refreshes 0 Octets 298622
Output messages: Total 15690 Updates 2 Refreshes 0 Octets 298222
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 192.168.40.4+179 AS 17 Local: 192.168.6.5+56466 AS 17
Type: Internal State: Established Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Export: [ send-direct ]
Options: <Preference LocalAddress Refresh>
Local Address: 192.168.6.5 Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 192.168.40.4 Local ID: 192.168.6.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 1
BFD: disabled, down
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 17)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 2
Accepted prefixes: 2
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 2
Last traffic (seconds): Received 15 Sent 22 Checked 68
Input messages: Total 15688 Updates 2 Refreshes 0 Octets 298111
Output messages: Total 15688 Updates 2 Refreshes 0 Octets 298184
Output Queue[0]: 0BGP グループの検証
目的
BGP グループが正しく設定されていることを確認します。
アクション
オペレーションモードから、show bgp groupコマンドを入力します。
user@A> show bgp group logical-system A Group Type: Internal AS: 17 Local AS: 17 Name: internal-peers Index: 0 Flags: <Export Eval> Export: [ send-direct ] Holdtime: 0 Total peers: 2 Established: 2 192.163.6.4+179 192.168.40.4+179 inet.0: 0/5/5/0 Groups: 1 Peers: 2 External: 0 Internal: 2 Down peers: 0 Flaps: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending inet.0 5 0 0 0 0 0
BGP サマリー情報の検証
目的
BGP の設定が正しいことを確認します。
アクション
オペレーションモードから、show bgp summaryコマンドを入力します。
user@A> show bgp summary logical-system A Groups: 1 Peers: 2 Down peers: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending inet.0 5 0 0 0 0 0 Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Accepted/Damped... 192.163.6.4 17 15723 15700 0 0 4d 22:13:15 0/3/3/0 0/0/0/0 192.168.40.4 17 15698 15699 0 0 4d 22:13:11 0/2/2/0 0/0/0/0
BGP ルートがルーティングテーブルにインストールされていることを確認する
目的
エクスポート ポリシー設定が機能していることを確認します。
アクション
オペレーションモードから、show route protocol bgpコマンドを入力します。
user@A> show route protocol bgp logical-system A
inet.0: 7 destinations, 12 routes (7 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.10.10.0/30 [BGP/170] 4d 11:05:55, localpref 100, from 192.163.6.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via lt-0/1/0.1
10.10.10.4/30 [BGP/170] 4d 11:05:55, localpref 100, from 192.163.6.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via lt-0/1/0.1
[BGP/170] 4d 11:03:10, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via lt-0/1/0.1
192.163.6.4/32 [BGP/170] 4d 11:05:55, localpref 100, from 192.163.6.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via lt-0/1/0.1
192.168.40.4/32 [BGP/170] 4d 11:03:10, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via lt-0/1/0.1Overview: 同じリンク ローカル アドレスを使用した、異なるリンクでの複数のシングル ホップ EBGP セッションの設定(IPv6)
データ センターやクラウドなどの複雑なネットワークでは、リンクやノードの数が多いため、リンク ローカル アドレスが広く使われています。リンク ローカル アドレスを使用するジュニパー機器に複数のシングル ホップ BGP セッションを展開できることは、大きなメリットです。
Junos OS Release 20.4R1 以降では、同じ IPv6 リンクローカル アドレスを使用する複数の直接接続ピア上の異なるリンクで、シングル ホップの EBGP セッションを有効にすることができます。EBGP セッションごとに、Juniper デバイスの一意のピアアドレスを持つ必要はなくなりました。
例:同一の IPv6 リンクローカルアドレスを使用して、異なるリンク上で複数のシングルホップ EBGP セッションを設定します。
この例では、同じ IPv6 リンクローカルアドレスを使用して、異なるリンク上で複数のシングルホップ EBGP セッションを設定する方法を示します。
要件
この例では、以下のハードウェアとソフトウェアのコンポーネントを使用しています。
2つのMXシリーズルーター
Junos OS リリース 20.4R1 以降のバージョン
概要
Junos OS Release 20.4R1 以前では、リンクローカルアドレスで BGP ピアを設定することはできますが、異なるインターフェイスで同じリンクローカルアドレスを使用するように、複数の BGP ピアを設定することはできませんでした。Junos OS 20.4R1 以降では、同じリンクローカルアドレスを使用して、異なるリンク上で複数のシングルホップ EBGP セッションを有効にすることができます。
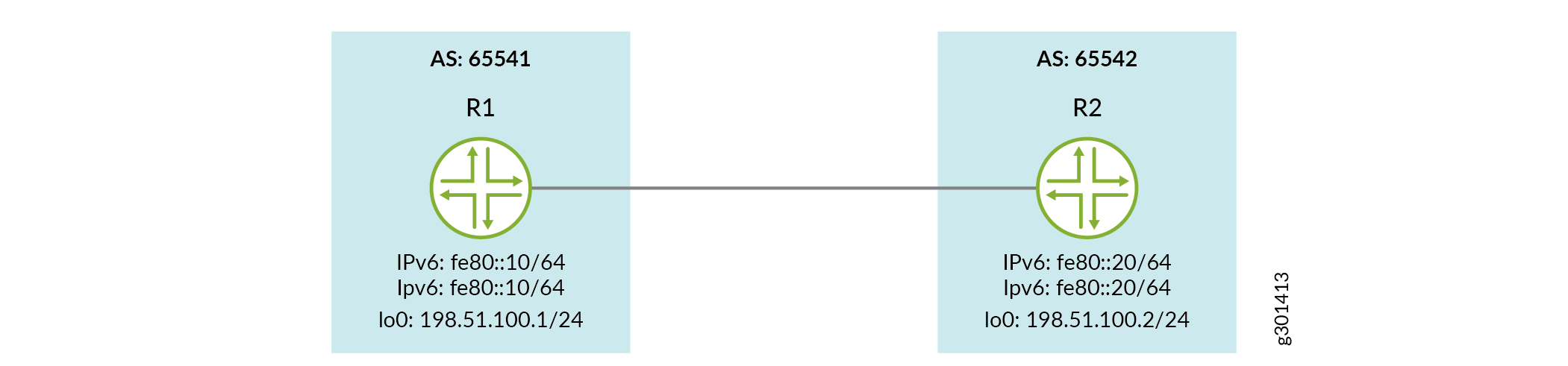
トポロジー
設定
この例では、同じ IPv6 リンクローカルアドレスを使用する 2 つの異なるリンク上で、複数のシングルホップ EBGP セッションを設定します。
CLIクイック構成
R1
set interfaces ge-0/0/1set interfaces ge-0/0/1 description R1-to-R2-Linkset interfaces ge-0/0/1 vlan-taggingset interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 1 vlan-id 1set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 1 family inet6 address fe80::10/64set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 2 vlan-id 2set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 2 family inet6 address fe80::10/64set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 198.51.100.1/24 primaryset routing-options router-id 198.51.100.1set routing-options autonomous-system 65541set protocols bgp group external peer-as 65542set protocols bgp group external local-as 65541set protocols bgp group external neighbor fe80::20%ge-0/0/1.1set protocols bgp group external neighbor "fe80::20%ge-0/0/1.2
R2
set interfaces ge-0/0/1set interfaces ge-0/0/1 description R2-to-R1-Linkset interfaces ge-0/0/1 vlan-taggingset interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 1 vlan-id 1set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 1 family inet6 address fe80::20/64set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 2 vlan-id 2set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 2 family inet6 address fe80::20/64set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 198.51.100.2/24 primaryset routing-options router-id 198.51.100.2set routing-options autonomous-system 65542set protocols bgp group external peer-as 65541set protocols bgp group external local-as 65542set protocols bgp group external neighbor fe80::10%ge-0/0/1.1set protocols bgp group external neighbor fe80::10%ge-0/0/1.2
同一の IPv6 リンクローカルアドレスを使用して、複数のリンク上でシングルホップの EBGP セッションを設定します。
ステップバイステップでの手順
R1 と R2 の VLAN タグ、VLAN ID、ループバック、IPv6 のリンクローカルアドレスなどの基本的な設定を行います。
単一のインターフェイスで、複数のユニットを設定するには、次の手順に従います。
R1
set interfaces ge-0/0/1set interfaces ge-0/0/1 description R1-to-R2-Linkset interfaces ge-0/0/1 vlan-taggingset interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 1 vlan-id 1set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 1 family inet6 address fe80::10/64set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 2 vlan-id 2set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 2 family inet6 address fe80::10/64set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 198.51.100.1/24 primaryR2
set interfaces ge-0/0/1set interfaces ge-0/0/1 description R2-to-R1-Linkset interfaces ge-0/0/1 vlan-taggingset interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 1 vlan-id 1set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 1 family inet6 address fe80::20/64set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 2 vlan-id 2set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 2 family inet6 address fe80::20/64set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 198.51.100.2/24 primaryR1 および R2 で BGP を有効にするルーティングオプションを設定します。
R1
set routing-options router-id 198.51.100.1set routing-options autonomous-system 65541R2
set routing-options router-id 198.51.100.2set routing-options autonomous-system 65542set protocols bgp group group neighbor peeraddress%localinterface.unitR1 と R2 の複数のリンクに、形式の同じリンクローカル IPv6 アドレスを使用して EBGP を設定します。R1
set protocols bgp group external peer-as 65542set protocols bgp group external local-as 65541set protocols bgp group external neighbor fe80::20%ge-0/0/1.1set protocols bgp group external neighbor "fe80::20%ge-0/0/1.2R2
set protocols bgp group external peer-as 65541set protocols bgp group external local-as 65542set protocols bgp group external neighbor fe80::10%ge-0/0/1.1set protocols bgp group external neighbor fe80::10%ge-0/0/1.2設定モード
commitからを入力します。
結果
以下のようなデバイスで、以下の設定を照合して、設定を検証します。
R1 デバイスでの設定を検証する方法は、以下のようになります。
user@R1# show interfaces
ge-0/0/1 {
description R1-to-R2-Link;
vlan-tagging;
unit 1 {
vlan-id 1;
family inet6 {
address fe80::10/64;
}
}
unit 2 {
vlan-id 2;
family inet6 {
address fe80::10/64;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 198.51.100.1/24 {
primary;
}
}
}
}
user@R1# show protocols
bgp {
group external {
peer-as 65542;
local-as 65541;
neighbor "fe80::20%ge-0/0/1.1";
neighbor "fe80::20%ge-0/0/1.2";
}
}
user@R1# show routing-options
router-id 198.51.100.1; autonomous-system 65541;
検証
EBGP リンクローカル サポートの検証
目的
そのコマshow bgp summaryンドを使用して、同じリンクローカルアドレスを持つデバイス上で、異なるインターフェイスを介して作成された EBGP セッションを確認します。
アクション
user@R1> show bgp summary
Threading mode: BGP I/O
Default eBGP mode: advertise - accept, receive - accept
Groups: 1 Peers: 2 Down peers: 0
Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending
inet6.0
0 0 0 0 0 0
Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Accepted/Damped...
fe80::20%ge-0/0/1.1 65542 115 114 0 0 50:59 Establ
inet6.0: 0/0/0/0
fe80::20%ge-0/0/1.2 65542 114 114 0 0 50:58 Establ
inet6.0: 0/0/0/0意味
この出力は、R1 の設定された 2 つのローカルインターフェース(ge-0/0/1.1とge-0/0/1.2)を介して、R2 の同じ IPv6 リンクローカルアドレス(fe80::20)で 2 つの EBGP セッションが確立されていることを示しています。
