Next-Generation MVPN Data Plane Overview
A next-generation multicast virtual private network (MVPN) data plane is composed of provider tunnels originated by and rooted at the sender provider edge (PE) routers and the receiver PE routers as the leaves of the provider tunnel.
A provider tunnel can carry data for one or more VPNs. Those provider tunnels that carry data for more than one VPN are called aggregate provider tunnels and are outside the scope of this topic. Here, we assume that a provider tunnel carries data for only one VPN.
This topic covers two types of tunnel technologies: IP generic routing encapsulation (GRE) provider tunnels signaled by Protocol Independent Multicast-Sparse Mode (PIM-SM) any-source multicast (ASM) and MPLS provider tunnels signaled by RSVP-Traffic Engineering (RSVP-TE).
When a provider tunnel is signaled by PIM, the sender PE router runs another instance of the PIM protocol on the provider’s network (P-PIM) that signals a provider tunnel for that VPN. When a provider tunnel is signaled by RSVP-TE, the sender PE router initiates a point-to-multipoint label-switched path (LSP) toward receiver PE routers by using point-to-multipoint RSVP-TE protocol messages. In either case, the sender PE router advertises the tunnel signaling protocol and the tunnel ID to other PE routers via BGP by attaching the provider multicast service interface (PMSI) attribute to either the Type 1 intra-AS autodiscovery routes (inclusive provider tunnels) or Type 3 S-PMSI autodiscovery routes (selective provider tunnels).
The sender PE router goes through two steps when setting up the data plane. First, using the PMSI attribute, it advertises the provider tunnel it is using via BGP. Second, it actually signals the tunnel using whatever tunnel signaling protocol is configured for that VPN. This allows receiver PE routers to bind the tunnel that is being signaled to the VPN that imported the Type 1 intra-AS autodiscovery route. Binding a provider tunnel to a VRF table enables a receiver PE router to map the incoming traffic from the core network on the provider tunnel to the local target VRF table.
The PMSI attribute contains the provider tunnel type and an identifier. The value of the provider tunnel identifier depends on the tunnel type. Table 1 identifies the tunnel types specified in Internet draft draft-ietf-l3vpn-2547bis-mcast-bgp-08.txt.
|
Tunnel Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
No tunnel information present |
|
1 |
RSVP-TE point-to-multipoint LSP |
|
2 |
Multicast LDP point-to-multipoint LSP |
|
3 |
PIM-SSM tree |
|
4 |
PIM-SM tree |
|
5 |
PIM-Bidir tree |
|
6 |
Ingress replication |
|
7 |
Multicast LDP multipoint-to-multipoint LSP |
Inclusive Provider Tunnels
This section describes various types of provider tunnels and attributes of provider tunnels.
- PMSI Attribute of Inclusive Provider Tunnels Signaled by PIM-SM
- PMSI Attribute of Inclusive Provider Tunnels Signaled by RSVP-TE
PMSI Attribute of Inclusive Provider Tunnels Signaled by PIM-SM
When the Tunnel Type field of the PMSI attribute is set to 4
(PIM-SM Tree), the tunnel identifier field contains <Sender
Address, P-Multicast Group Address>. The Sender Address field is set to the router ID of the sender PE router. The P-multicast
group address is set to a multicast group address from the service
provider’s P-multicast address space and uniquely identifies
the VPN. A receiver PE router that receives an intra-AS autodiscovery
route with a PMSI attribute whose tunnel type is PIM-SM is required
to join the provider tunnel.
For example, if the service provider deploys PIM-SM provider tunnels (instead of RSVP-TE provider tunnels), Router PE1 advertises the following PMSI attribute:
PMSI: 0:PIM-SM:label[0:0:0]:Sender10.1.1.1 Group 239.1.1.1
PMSI Attribute of Inclusive Provider Tunnels Signaled by RSVP-TE
When the tunnel type field of the PMSI attribute is set to 1
(RSVP-TE point-to-multipoint LSP), the tunnel identifier field contains
an RSVP-TE point-to-multipoint session object as described in RFC
4875. The session object contains the <Extended Tunnel ID,
Reserved, Tunnel ID, P2MP ID> associated with the point-to-multipoint
LSPs.
The PE router that originates the PMSI attribute is required to signal an RSVP-TE point-to-multipoint LSP and the sub-LSPs. A PE router that receives this PMSI attribute must establish the appropriate state to properly handle the traffic received over the sub-LSP.
For example, Router PE1 advertises the following PMSI attribute:
PMSI: Flags 0:RSVP-TE:label[0:0:0]:Session_13[10.1.1.1:0:6574:10.1.1.1]
Selective Provider Tunnels (S-PMSI Autodiscovery/Type 3 and Leaf Autodiscovery/Type 4 Routes)
A selective provider tunnel is used for mapping a specific C-multicast flow (a (C-S, C-G) pair) onto a specific provider tunnel. There are a variety of situations in which selective provider tunnels can be useful. For example, they can be used for putting high-bandwidth VPN multicast data traffic onto a separate provider tunnel rather than the default inclusive provider tunnel, thus restricting the distribution of traffic to only those PE routers with active receivers.
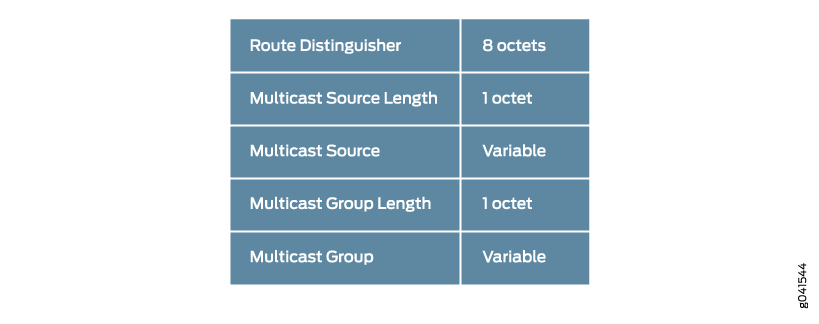
In BGP next-generation multicast virtual private networks (MVPNs), selective provider tunnels are signaled using Type 3 Selective-PMSI (S-PMSI) autodiscovery routes. See Figure 1 and Table 2 for details. The sender PE router sends a Type 3 route to signal that it is sending traffic for a particular (C-S, C-G) flow using an S-PMSI provider tunnel.
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Route Distinguisher |
Set to the route distinguisher configured on the router originating this route. |
|
Multicast Source Length |
Set to 32 for IPv4 and to 128 for IPv6 C-S IP addresses. |
|
Multicast Source |
Set to the C-S IP address. |
|
Multicast Group Length |
Set to 32 for IPv4 and to 128 for IPv6 C-G addresses. |
|
Multicast Group |
Set to the C-G address. |
The S-PMSI autodiscovery (Type 3) route carries a PMSI attribute
similar to the PMSI attribute carried with intra-AS autodiscovery
(Type 1) routes. The Flags field of the PMSI attribute
carried by the S-PMSI autodiscovery route is set to the leaf information
required. This flag signals receiver PE routers to originate a Type
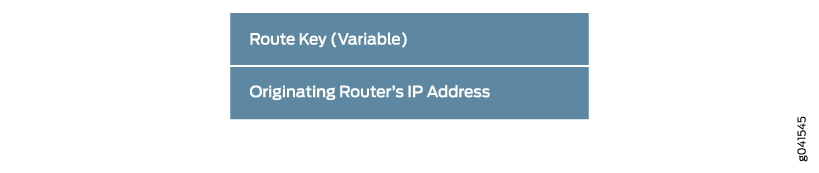
4 leaf autodiscovery route (Figure 2) to join the
selective provider tunnel if they have active receivers. See Table 3 for details of
leaf autodiscovery route type MCAST-VPN NLRI format descriptions.
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Route Key |
Contains the original Type 3 route received. |
|
Originating Router’s IP Address |
Set to the IP address of the PE router originating the leaf autodiscovery route This is typically the primary loopback address. |
