ON THIS PAGE
Specify How to Display Configuration Groups and Interface Ranges
Display the Source Group for Inherited Configuration Group Elements
Display the Source Interface Range for Inherited Configuration Elements
Summary of Attributes for Configuration Group and Interface Range Inheritance
Examples: Specify the Output Format for Configuration Groups
Specify How to Display Inheritance for Configuration Groups and Interface Ranges Using the Junos XML Protocol
The following sections explain how to display groups and interface range configurations within their inheriting elements in configuration data that you request through a Junos XML protocol session. The sections also discuss how to view the source group or source interface range for configuration elements that are inherited from a group or interface range.
Understanding Groups and Interface Ranges
The <groups> element corresponds to the
[edit groups] configuration hierarchy. It encloses tag elements
representing configuration groups, each of which contains a set of
configuration statements that are appropriate at multiple locations in the
hierarchy. You use the apply-groups configuration statement or
<apply-groups> tag to insert a configuration group at the
appropriate location, achieving the same effect as directly inserting the statements
defined in the group. When a configuration group is applied to a configuration
hierarchy, the hierarchy is said to inherit the group's statements.
In addition to the groups defined at the [edit groups] hierarchy
level, Junos OS predefines a group called junos-defaults. This
group includes configuration statements judged appropriate for basic operations on
the device. By default, CLI commands that display the configuration do not display
the statements in the junos-defaults group. Similarly, the Junos
XML protocol server output for the <get-configuration>
operation does not display this group by default.
The <interface-range> element corresponds to the
[edit interfaces interface-range] configuration hierarchy. An
interface range is a set of interfaces to which you can apply a common configuration
profile. If an interface is a member of an interface range, it inherits the
configuration statements set for that range.
Specify How to Display Configuration Groups and Interface Ranges
By default, the Junos XML protocol server displays the element for each
user-defined configuration group as a child of the
<groups> element, instead of displaying them as
children of the elements to which they are applied. Similarly, the server
displays the elements for each user-defined interface range as a child of the
<interface-range> element, instead of displaying them
as children of the elements that are members of the interface range. This
display mode parallels the default behavior of the CLI configuration mode
show command, which displays [edit groups]
and [edit interfaces interface-range] as separate hierarchies
in the configuration.
A client application can request that the Junos XML protocol server display
elements inherited from user-defined groups or interface ranges within the
inheriting elements. To display the inherited elements, a client application
includes the inherit="inherit" attribute in the
<get-configuration> tag.
<rpc>
<get-configuration inherit="inherit"/>
<!-- OR -->
<get-configuration inherit="inherit">
<!-- tag elements for the configuration elements to return -->
</get-configuration>
</rpc>
To display the inherited elements for user-defined configuration groups and
interface ranges and also display the inherited elements from the
junos-defaults group, a client application includes the
inherit="defaults" attribute in the
<get-configuration> tag.
<rpc>
<get-configuration inherit="defaults"/>
<!-- OR -->
<get-configuration inherit="defaults">
<!-- tag elements for the configuration elements to return -->
</get-configuration>
</rpc>
When the client includes the inherit="inherit" attribute, the
output includes the same information as the output from the following CLI
configuration mode command. The output does not include configuration elements
inherited from the junos-defaults group.
user@host# show | display inheritance | except ##
When the client includes the inherit="defaults" attribute, the
output includes the same information as the output from the following CLI
configuration mode command:
user@host# show | display inheritance defaults | except ##
The Junos XML protocol server encloses its output in the
<rpc-reply> element. Depending on the requested
format, the server also includes an additional element. The server emits the
<configuration> element for Junos XML-tagged output,
the <configuration-text> element for formatted ASCII
output, or the <configuration-set> element for
configuration mode commands. The server does not enclose JSON data in additional
tags.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="URL">
<configuration attributes>
<!-- Junos XML tag elements representing configuration elements -->
</configuration>
<!-- OR -->
<configuration-text>
<!-- formatted ASCII configuration statements -->
</configuration-text>
<!-- OR -->
<configuration-set>
<!-- configuration mode commands -->
</configuration-set>
<!-- OR -->
<!-- JSON-formatted configuration data -->
</rpc-reply>You can combine the inherit attribute with one or more of the
following attributes in the <get-configuration/ tag:
-
changed -
database -
format -
groups -
interface-ranges -
junos:key
The application can also include the inherit attribute after
requesting an indicator for identifiers (as described in Request Identifiers for Configuration Elements Using the Junos XML Protocol).
Display the Source Group for Inherited Configuration Group Elements
A client application can request that the Junos XML protocol server display the
configuration group from which each configuration element is inherited. To
display the source group, a client application combines the
inherit attribute with the groups="groups"
attribute in the <get-configuration> tag.
<rpc>
<get-configuration inherit="(defaults | inherit)" groups="groups"/>
<!-- OR -->
<get-configuration inherit="(defaults | inherit)" groups="groups">
<!-- tag elements indicating the configuration elements to return -->
</get-configuration>
</rpc>When you include both the inherit and
groups="groups" attributes in the request, the Junos XML
protocol server displays each configuration group element within its inheriting
element. In addition, the inherited element includes information that indicates
the source group. The format determines how the output displays the source group
information in the resulting configuration.
If the output is Junos XML format, the server includes the
junos:group="source-group" attribute
in the opening tags of configuration elements that are inherited from
configuration groups. The server encloses the data in
<rpc-reply> and
<configuration> elements.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="URL">
<configuration attributes>
<!-- For each inherited element -->
<!-- opening-tags-for-parents-of-the-element -->
<inherited-element junos:group="source-group">
<inherited-child-of-inherited-element junos:group="source-group">
<!-- inherited-children-of-child junos:group="source-group" -->
</inherited-child-of-inherited-element>
</inherited-element>
<!-- closing-tags-for-parents-of-the-element -->
</configuration>
</rpc-reply>If the output is formatted ASCII text, the server inserts three commented lines
with the information about the source group immediately preceding each inherited
element. The server encloses the data in <rpc-reply> and
<configuration-text> elements.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="URL">
<configuration-text>
*/ For each inherited element */
/* parent levels for the element */
##
## 'inherited-element' was inherited from group 'source-group'
##
inherited-element {
##
## 'inherited-child' was inherited from group 'source-group'
##
inherited-child {
... child statements of inherited-child ...
}
}
/* closing braces for parent levels of the element */
</configuration-text>
</rpc-reply>If the output is in JSON format, the server includes the
"junos:group" : "source-group"
attribute in the attribute list for the inherited element. The server encloses
the data in an <rpc-reply> element.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="URL">
{
"configuration" : {
/* JSON objects for parent levels of the element */
"inherited-child" : {
"@" : {
"junos:group" : "source-group"
},
"inherited-object" : [
{
"@" : {
"junos:group" : "source-group"
},
"name" : "identifier"
}
],
"@inherited-statement" : {
"junos:group" : "source-group"
}
}
/* closing braces for parent levels of the element */
}
}
</rpc-reply>When the groups="groups" attribute is combined with the
inherit="inherit" attribute, the XML output includes the
same information as the output from the following CLI configuration mode
command. The output does not include configuration elements inherited from the
junos-defaults group:
user@host# show | display inheritance | display xml groups
When the groups="groups" attribute is combined with the
inherit="defaults" attribute, the XML output includes the
same information as the output from the following CLI configuration mode
command:
user@host# show | display inheritance defaults | display xml groups
You can combine the inherit and groups
attributes with one or more of the following other attributes in the
<get-configuration> tag:
-
changed -
database -
format -
interface-ranges -
junos:key
The application can also include the inherit and
groups attributes after requesting an indicator for
identifiers (as described in Request Identifiers for Configuration Elements Using the Junos XML Protocol).
Display the Source Interface Range for Inherited Configuration Elements
A client application can request that the Junos XML protocol server display the
interface range from which each configuration element is inherited. To request
the source interface range, a client application combines the
inherit attribute with the
interface-ranges="interface-ranges" attribute in the
<get-configuration> tag.
<rpc>
<get-configuration inherit="inherit" interface-ranges="interface-ranges"/>
<!-- OR -->
<get-configuration inherit="inherit" interface-ranges="interface-ranges">
<!-- tag elements for the configuration elements to return -->
</get-configuration>
</rpc>When you include both the inherit and
interface-ranges="interface-ranges" attributes in the
request, the Junos XML protocol server displays each interface range
configuration element within its inheriting element. In addition, the inherited
element includes information that indicates the source interface range. The
format determines how the output displays the source interface range information
in the resulting configuration.
If the output is Junos XML format, the server includes the
junos:interface-range="source-interface-range"
attribute in the opening tags of configuration elements that are inherited from
an interface range. The server encloses the data in
<rpc-reply> and
<configuration> elements.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="URL">
<configuration attributes>
<interfaces>
<!-- For each inherited element -->
<interface junos:interface-range="source-interface-range">
<inherited-element junos:interface-range="source-interface-range">
<inherited-child-of-inherited-element
junos:interface-range="source-interface-range">
<!-- inherited-children-of-child
junos:interface-range="source-interface-range" -->
</inherited-child-of-inherited-element>
</inherited-element>
</interface>
</interfaces>
</configuration>
</rpc-reply>If the output is formatted ASCII text, the server inserts three commented lines
with the information about the source interface range immediately preceding each
inherited element. The server encloses the data in
<rpc-reply> and
<configuration-text> elements.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="URL">
<configuration-text>
interfaces {
<!-- For each inherited element -->
##
## 'interface-name' was expanded from interface-range 'source-interface-range'
##
interface-name {
##
## 'inherited-element' was expanded from interface-range 'source-interface-range'
##
inherited-element {
inherited-child {
... child statements of inherited-child ...
}
}
}
}
</configuration-text>
</rpc-reply>If the output is JSON format, the server includes the
"junos:interface-range" : "source-interface-range"
attribute in the attribute list for the inherited element. The server encloses
the data in an <rpc-reply> element.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="URL">
{
"configuration" : {
/* JSON objects for parent levels of the element */
"inherited-child" : {
"@" : {
"junos:interface-range" : "source-interface-range"
},
"inherited-object" : [
{
"@" : {
"junos:interface-range" : "source-interface-range"
},
"name" : "identifier"
}
],
"@inherited-statement" : {
"junos:interface-range" : "source-interface-range"
}
}
/* closing braces for parent levels of the element */
}
}
</rpc-reply>When you combine the interface-ranges="interface-ranges"
attribute with the inherit="inherit" attribute, the XML output
includes the same information as the output from the following CLI configuration
mode command:
user@host# show | display inheritance | display xml interface-ranges
When you combine the interface-ranges="interface-ranges"
attribute with the inherit="defaults" attribute, the XML output
includes the same information as the output from the following CLI configuration
mode command:
user@host# show | display inheritance defaults | display xml interface-ranges
You can combine the inherit and
interface-ranges attributes with one or more of the
following other attributes in the <get-configuration/
tag:
-
changed -
database -
format -
groups -
junos:key
The application can also include the inherit and
interface-ranges attributes after requesting an indicator
for
identifiers.
Summary of Attributes for Configuration Group and Interface Range Inheritance
Table 1 summarizes the <get-configuration> attributes for
inheritance, the impact on the configuration data, and the CLI command that produces
equivalent output.
| Attribute | Additional Attribute | Description | CLI Command Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
|
– |
– |
Display groups and interface ranges as separate elements in the output instead of displaying them within their inheriting elements. |
|
|
|
– |
Display user-defined groups and interface ranges within the inheriting elements. |
|
|
|
Display user-defined groups and interface ranges within the inheriting elements. Display the source group for each inherited configuration group. |
|
|
|
|
Display user-defined groups and interface ranges within the inheriting elements. Display the source interface range for each inherited interface range. |
|
|
|
|
– |
Display user-defined groups and interface ranges and the
|
|
|
|
Display user-defined groups and interface ranges and the
|
|
|
|
|
Display user-defined groups and interface ranges and the
|
|
Examples: Specify the Output Format for Configuration Groups
The following sample configuration hierarchy defines a configuration group called
interface-group. The apply-groups
statement applies the statements in the group at the
[edit interfaces] hierarchy level.
[edit]
groups {
interface-group {
interfaces {
so-1/1/1 {
encapsulation ppp;
}
}
}
}
apply-groups interface-group;
interfaces {
fxp0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.4.207/24;
}
}
}
}
When you execute the <get-configuration/> operation but
omit inherit attribute, the output includes the
<groups> and <apply-groups>
elements as separate items. The <groups> element encloses
the elements defined in the interface-group configuration
group. The placement of the <apply-groups> element
directly above the <interfaces> element indicates that
the [edit interfaces] hierarchy inherits the statements defined
in the interface-group configuration group.

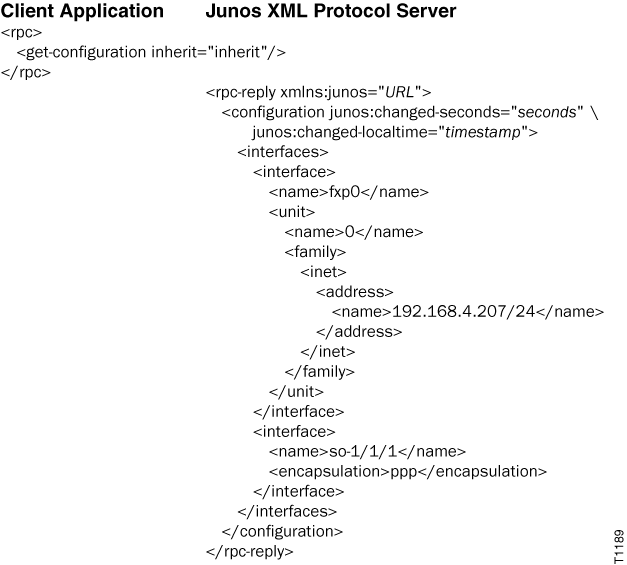
When you execute the <get-configuration/> operation and
include the inherit attribute, the
<interfaces> element encloses the elements defined in
the interface-group configuration group. The output does not
display the <groups> and
<apply-groups> elements separately.
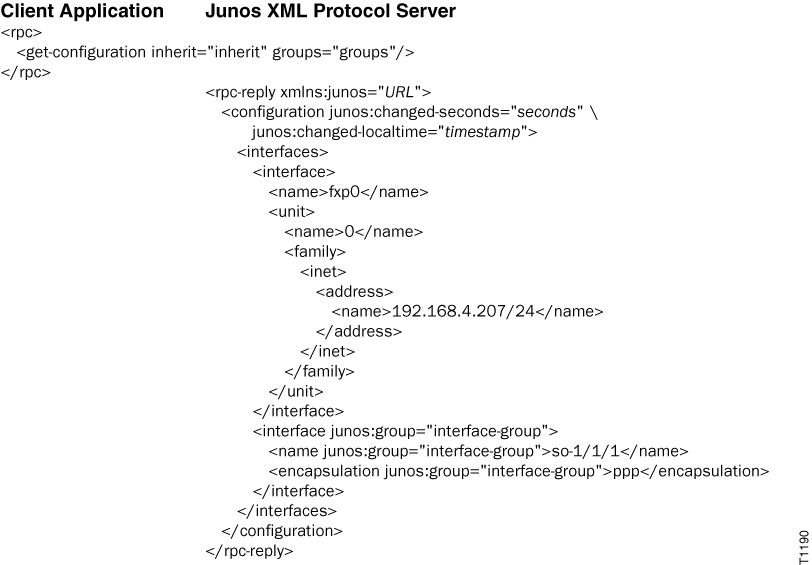
The following example executes the <get-configuration/>
operation and combines the groups="groups" attribute with the
inherit attribute. In the output, the
<interfaces> element encloses the elements defined in
the interface-group configuration group. The output also
provides information about the source group for the inherited elements. The
junos:group="interface-group" attribute indicates the
source group.