Verifying the IS-IS Protocol
Purpose
If your MPLS network is configured with IS-IS as the interior
gateway protocol (IGP), and the output of the show mpls lsp extensive command shows that there is a problem, check the IP and IS-IS layers.
Because IS-IS and IP are independent of each other, you can check
either layer first. For more information about checking the IP layer,
see Verifying the IP Layer.
After you have checked the IP layer and determined that there is still a problem, check the IS-IS layer, verify that IS-IS adjacencies are up, and make sure that the interfaces and IS-IS protocol are configured correctly.
To check the IS-IS protocol, follow these steps:
Verify the LSP
Purpose
Confirm that interfaces are configured for IS-IS, that the IS-IS protocol is configured correctly, and that adjacencies are established.
Action
To verify the label-switched path (LSP), enter the following command on the ingress, transit, and egress routers:
user@host> show mpls lsp extensive
Sample Output 1
command-name
user@R1> show mpls lsp extensive Ingress LSP: 1 sessions 10.0.0.6 From: 10.0.0.1, State: Dn, ActiveRoute: 0 , LSPname: R1-to-R6 ActivePath: (none) LoadBalance: Random Encoding type: Packet, Switching type: Packet, GPID: IPv4 Primary State: Dn 24 Oct 21 13:48:01 No Route toward dest [3 times] 23 Oct 21 13:47:44 Deselected as active 22 Oct 21 13:47:43 No Route toward dest[2 times] 21 Oct 21 13:47:43 ResvTear received 20 Oct 21 13:47:43 Down 19 Oct 21 13:47:43 10.1.13.2: No Route toward dest[2 times] 18 Oct 21 13:47:38 Record Route: 10.1.13.2 10.1.36.2 [...Output truncated...] Created: Tue Oct 19 21:22:53 2004 Total 1 displayed, Up 0, Down 1 Egress LSP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Transit LSP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
Sample Output 2
command-name
user@R3> show mpls lsp extensive Ingress LSP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Egress LSP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Transit LSP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
Sample Output 3
command-name
user@R6> show mpls lsp extensive
Ingress LSP: 1 sessions
10.0.0.1
From: 10.0.0.6, State: Dn, ActiveRoute: 0 , LSPname: R6-to-R1
ActivePath: (none)
LoadBalance: Random
Encoding type: Packet, Switching type: Packet, GPID: IPv4
Primary State: Dn
Will be enqueued for recomputation in 3 second(s).
13 Oct 21 14:23:33 CSPF failed: no route toward 10.0.0.1[90 times]
12 Oct 21 13:39:56 Deselected as active
11 Oct 21 13:39:56 CSPF: could not determine self
[...Output truncated...]
Created: Tue Oct 19 22:28:30 2004
Total 1 displayed, Up 0, Down 1
Egress LSP: 0 sessions
Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
Transit LSP: 0 sessions
Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
Meaning
The sample output shows that LSP R1-to-R6 and the reverse LSP R6-to-R1 are
down, and there are no LSP sessions on transit router R3.
Verify IS-IS Adjacencies and Interfaces
Purpose
When you check the IS-IS layer, you verify that IS-IS adjacencies are up and that the IS-IS interfaces are included at the protocol level.
Action
To verify the functioning of adjacent interfaces, enter the following commands from the relevant routers:
user@host> show isis adjacency user@host> show isis interface
Sample Output 1
command-name
user@R1> show isis adjacency Interface System L State Hold (secs) SNPA so-0/0/0.0 R2 2 Up 20 so-0/0/1.0 R5 2 Up 23 so-0/0/2.0 R3 2 Up 26 user@R3> show isis adjacency Interface System L State Hold (secs) SNPA so-0/0/0.0 R4 2 Up 23 so-0/0/1.0 R2 2 Up 21 so-0/0/2.0 R1 2 Up 19 so-0/0/3.0 R6 2 Down 0 user@R6> show isis adjacency IS-IS instance is not running
Sample Output 2
command-name
user@R1> show isis interface IS-IS interface database: Interface L CirID Level 1 DR Level 2 DR L1/L2 Metric lo0.0 0 0x1 Passive Passive 0/0 so-0/0/0.0 2 0x1 Disabled Point to Point 10/10 so-0/0/1.0 2 0x1 Disabled Point to Point 10/10 so-0/0/2.0 2 0x1 Disabled Point to Point 10/10 user@R3> show isis interface IS-IS interface database: Interface L CirID Level 1 DR Level 2 DR L1/L2 Metric lo0.0 0 0x1 Passive Passive 0/0 so-0/0/0.0 2 0x1 Disabled Point to Point 10/10 so-0/0/1.0 2 0x1 Disabled Point to Point 10/10 so-0/0/2.0 2 0x1 Disabled Point to Point 10/10 so-0/0/3.0 2 0x1 Disabled Point to Point 10/10 user@R6> show isis interface IS-IS interface database: Interface L CirID Level 1 DR Level 2 DR L1/L2 Metric lo0.0 0 0x1 Passive Passive 0/0 so-0/0/0.0 1 0x1 Point to Point Disabled 10/10 so-0/0/1.0 1 0x1 Down Disabled 10/10 so-0/0/2.0 1 0x1 Point to Point Disabled 10/10 so-0/0/3.0 1 0x1 Point to Point Disabled 10/10
Meaning
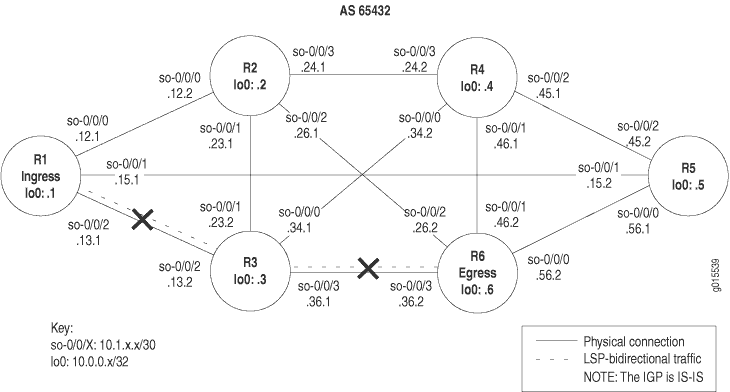
Sample Output 1 shows that ingress router R1 has established adjacencies with the relevant routers. Transit router R3 does not have an adjacency with egress router R6, and egress router R6 has no adjacencies established in the network shown in MPLS Network Broken at the IP and IGP Layers, indicating that the problem might be at the IS-IS protocol level.
Sample Output 2 shows that R1 and R2 are Level 2 routers, in contrast to R6 which is a Level 1 router. When a router is configured explicitly as a Level 1 or Level 2 router, it does not communicate with routers configured at a different level. Level 1 routers communicate with other Level 1 routers within their area, while Level 2 routers communicate with other Level 2 routers, and toward other autonomous systems. Because all the routers in this network are configured for Level 2, they cannot form an adjacency with R6, which is incorrectly configured as a Level 1 router.
See Also
Verify the IS-IS Configuration
Purpose
When you have determined that the problem is probably at the IS-IS protocol level, check the IS-IS configuration of the routers in your network.
Action
To verify the IS-IS configuration, enter the following command from the relevant routers:
user@host> show configuration protocols isis
Sample Output
command-name
user@R1> show configuration protocols isis
level 1 disable;
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface so-0/0/1.0;
interface so-0/0/2.0;
interface lo0.0; {
passive
user@R3> show configuration protocols isis
level 1 disable;
interface all {
level 2 metric 10;
}
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
interface lo0.0; {
passive
user@R6> show configuration protocols isis
level 2 disable; <<< Incorrect level disabled
interface all {
level 2 metric 10;
}
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
interface lo0.0; {
passive
Meaning
The sample output shows that R6 has Level 2 disabled,
while R1 and R3 have Level 1 disabled. For IS-IS adjacencies to establish,
routers need to be at the same level. Another common configuration
error is to omit the loopback interface (lo0) from the configuration
at the [edit protocols isis] hierarchy level. IS-IS does
not function correctly if the loopback interface (lo0) is not configured
at this level. In addition, including the passive statement
ensures that protocols are not run over the loopback interface (lo0)
and that the loopback interface (lo0) is advertised correctly throughout
the network.
Take Appropriate Action
Problem
Description
Depending on the error you encountered in your investigation, you must take the appropriate action to correct the problem. In the example below, the routers are configured to function at different levels of the IS-IS protocol.
Solution
To correct the error in this example, enter the following commands:
Sample Output
[edit protocols isis]
user@R6# show
level 2 disable;
interface all {
level 2 metric 10;
}
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
interface lo0.0; {
passive
[edit protocols isis]
user@R6# delete level 2
[edit protocols isis]
user@R6# set level 1 disable
[edit protocols isis]
user@R6# show
level 1 disable;
interface all {
level 2 metric 10;
}
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
interface lo0.0; {
passive
[edit protocols isis]
user@R6# commit
commit complete
[edit protocols isis]
user@R6# run show isis adjacency
Interface System L State Hold (secs) SNPA
so-0/0/0.0 R5 2 Up 22
so-0/0/1.0 R4 2 Up 22
so-0/0/2.0 R2 2 Up 22
so-0/0/3.0 R3 2 Up 22
Meaning
The sample output shows that the configuration error on egress router R6 has been corrected, and IS-IS adjacencies are now established.
See Also
Verify the LSP Again
Purpose
After taking the appropriate action to correct the error, the label-switched path (LSP) needs to be checked again to confirm that the problem in the RSVP layer has been resolved.
Action
To verify that the LSP is up and traversing the network as expected, enter the following command from the ingress, egress, and transit routers:
user@host> show mpls lsp extensive
Sample Output 1
command-name
user@R1> show mpls lsp extensive
Ingress LSP: 1 sessions
10.0.0.6
From: 10.0.0.1, State: Up, ActiveRoute: 1 , LSPname: R1-to-R6
ActivePath: (primary)
LoadBalance: Random
Encoding type: Packet, Switching type: Packet, GPID: IPv4
*Primary State: Up
Computed ERO (S [L] denotes strict [loose] hops): (CSPF metric: 20)
10.1.13.2 S 10.1.36.2 S
Received RRO (ProtectionFlag 1=Available 2=InUse 4=B/W 8=Node 10=SoftPreempt):
10.1.13.2 10.1.36.2
5 Oct 21 15:52:07 Selected as active path
4 Oct 21 15:52:07 Record Route: 10.1.13.2 10.1.36.2
3 Oct 21 15:52:07 Up
2 Oct 21 15:52:07 Originate Call
1 Oct 21 15:52:07 CSPF: computation result accepted
Created: Thu Oct 21 15:52:06 2004
Total 1 displayed, Up 1 , Down 0
Egress LSP: 1 sessions
10.0.0.1
From: 10.0.0.6, LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0
LSPname: R6-to-R1 , LSPpath: Primary
Suggested label received: -, Suggested label sent: -
Recovery label received: -, Recovery label sent: -
Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: 3, Label out: -
Time left: 142, Since: Thu Oct 21 15:41:59 2004
Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak Infbps m 20 M 1500
Port number: sender 2 receiver 39082 protocol 0
PATH rcvfrom: 10.1.13.2 (so-0/0/2.0) 17 pkts
Adspec: received MTU 1500
PATH sentto: localclient
RESV rcvfrom: localclient
Record route: 10.1.36.2 10.1.13.2 <self>
Total 1 displayed, Up 1 , Down 0
Transit LSP: 0 sessions
Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
Sample Output 2
command-name
user@R3> show mpls lsp extensive Ingress LSP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Egress LSP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Transit LSP: 2 sessions 10.0.0.1 From: 10.0.0.6, LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 1 LSPname: R6-to-R1 , LSPpath: Primary Suggested label received: -, Suggested label sent: - Recovery label received: -, Recovery label sent: 3 Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: 100528, Label out: 3 Time left: 125, Since: Thu Oct 21 15:29:26 2004 Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak Infbps m 20 M 1500 Port number: sender 2 receiver 39082 protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: 10.1.36.2 (so-0/0/3.0) 17 pkts Adspec: received MTU 1500 sent MTU 1500 PATH sentto: 10.1.13.1 (so-0/0/2.0) 17 pkts RESV rcvfrom: 10.1.13.1 (so-0/0/2.0) 17 pkts Explct route: 10.1.13.1 Record route: 10.1.36.2 <self> 10.1.13.1 10.0.0.6 From: 10.0.0.1, LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 1 LSPname: R1-to-R6 , LSPpath: Primary Suggested label received: -, Suggested label sent: - Recovery label received: -, Recovery label sent: 3 Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: 100544, Label out: 3 Time left: 147, Since: Thu Oct 21 15:39:33 2004 Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak Infbps m 20 M 1500 Port number: sender 1 receiver 47963 protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: 10.1.13.1 (so-0/0/2.0) 4 pkts Adspec: received MTU 1500 sent MTU 1500 PATH sentto: 10.1.36.2 (so-0/0/3.0) 4 pkts RESV rcvfrom: 10.1.36.2 (so-0/0/3.0) 4 pkts Explct route: 10.1.36.2 Record route: 10.1.13.1 <self> 10.1.36.2 Total 2 displayed, Up 2, Down 0
Sample Output 3
command-name
user@R6> show mpls lsp extensive
Ingress LSP: 1 sessions
10.0.0.1
From: 10.0.0.6, State: Up, ActiveRoute: 1, LSPname: R6-to-R1
ActivePath: (primary)
LoadBalance: Random
Encoding type: Packet, Switching type: Packet, GPID: IPv4
*Primary State: Up
Computed ERO (S [L] denotes strict [loose] hops): (CSPF metric: 20)
10.1.36.1 S 10.1.13.1 S
Received RRO (ProtectionFlag 1=Available 2=InUse 4=B/W 8=Node 10=SoftPreempt):
10.1.36.1 10.1.13.1
18 Oct 21 15:34:18 Selected as active path
17 Oct 21 15:34:17 Record Route: 10.1.36.1 10.1.13.1
16 Oct 21 15:34:17 Up
15 Oct 21 15:34:17 Originate Call
14 Oct 21 15:34:17 CSPF: computation result accepted
[...Output truncated...]
Created: Tue Oct 19 22:28:30 2004
Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
Egress LSP: 1 sessions
10.0.0.6
From: 10.0.0.1, LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0
LSPname: R1-to-R6 , LSPpath: Primary
Suggested label received: -, Suggested label sent: -
Recovery label received: -, Recovery label sent: -
Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: 3, Label out: -
Time left: 126, Since: Thu Oct 21 15:44:25 2004
Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak Infbps m 20 M 1500
Port number: sender 1 receiver 47963 protocol 0
PATH rcvfrom: 10.1.36.1 (so-0/0/3.0) 4 pkts
Adspec: received MTU 1500
PATH sentto: localclient
RESV rcvfrom: localclient
Record route: 10.1.13.1 10.1.36.1 <self>
Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
Transit LSP: 0 sessions
Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
Meaning
Sample Outputs 1 and 3 from ingress router R1 and egress router R6 show that the LSP is now traversing the network along the expected path, from R1 through R3 to R6, and the reverse LSP, from R6 through R3 to R1. In addition, Sample Output 2 from transit router R3 shows that there are two transit LSP sessions, one from R1 to R6, and the other from R6 to R1.
