Configuring Junos OS on the SRX320
The SRX320 Firewall is shipped with the Juniper Networks Junos operating system (Junos OS) preinstalled and is ready to be configured when the SRX320 is powered on. You can perform the initial software configuration of the SRX320 by using one of the following methods:
-
Command-line interface (CLI)
-
Zero touch provisioning (ZTP) with a cloud-based provisioning service
-
J-Web GUI
Before you configure your new SRX320, we recommend that you understand the factory-default configuration. In many cases you are able to leverage the factory defaults to simplify your configuration tasks. In other cases, you might find it easier to start with a blank configuration when you find that the defaults don't align with your planned usage. See SRX320 Firewall Factory-Default Settings for details on the factory-default configuration.
Initial Configuration Using the CLI
You can use either the serial or the mini-USB console port on the device.
- Connect to the Serial Console Port
- Connect to the Mini-USB Console Port
- Configure the SRX320 Using the CLI
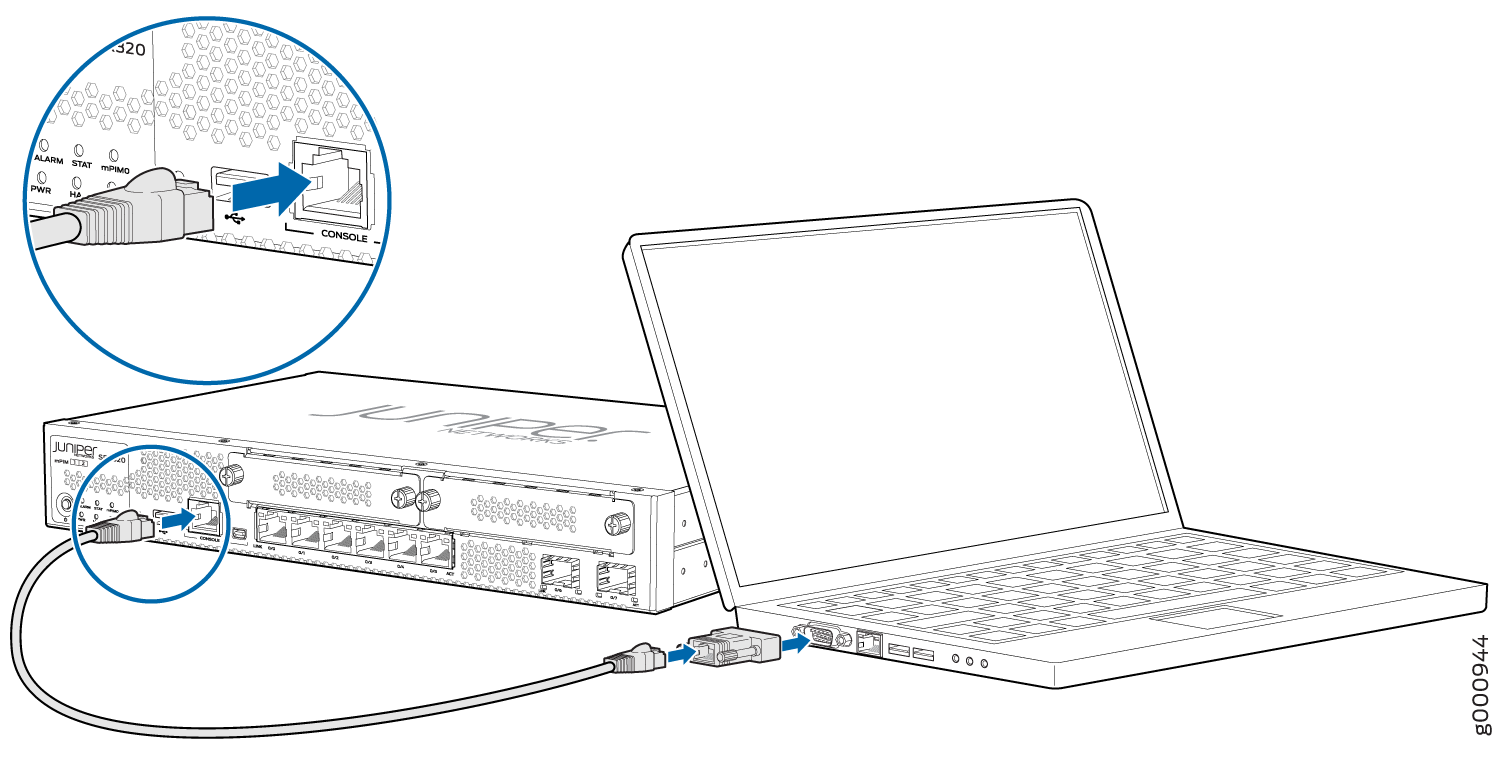
Connect to the Serial Console Port
To connect to the serial console port:
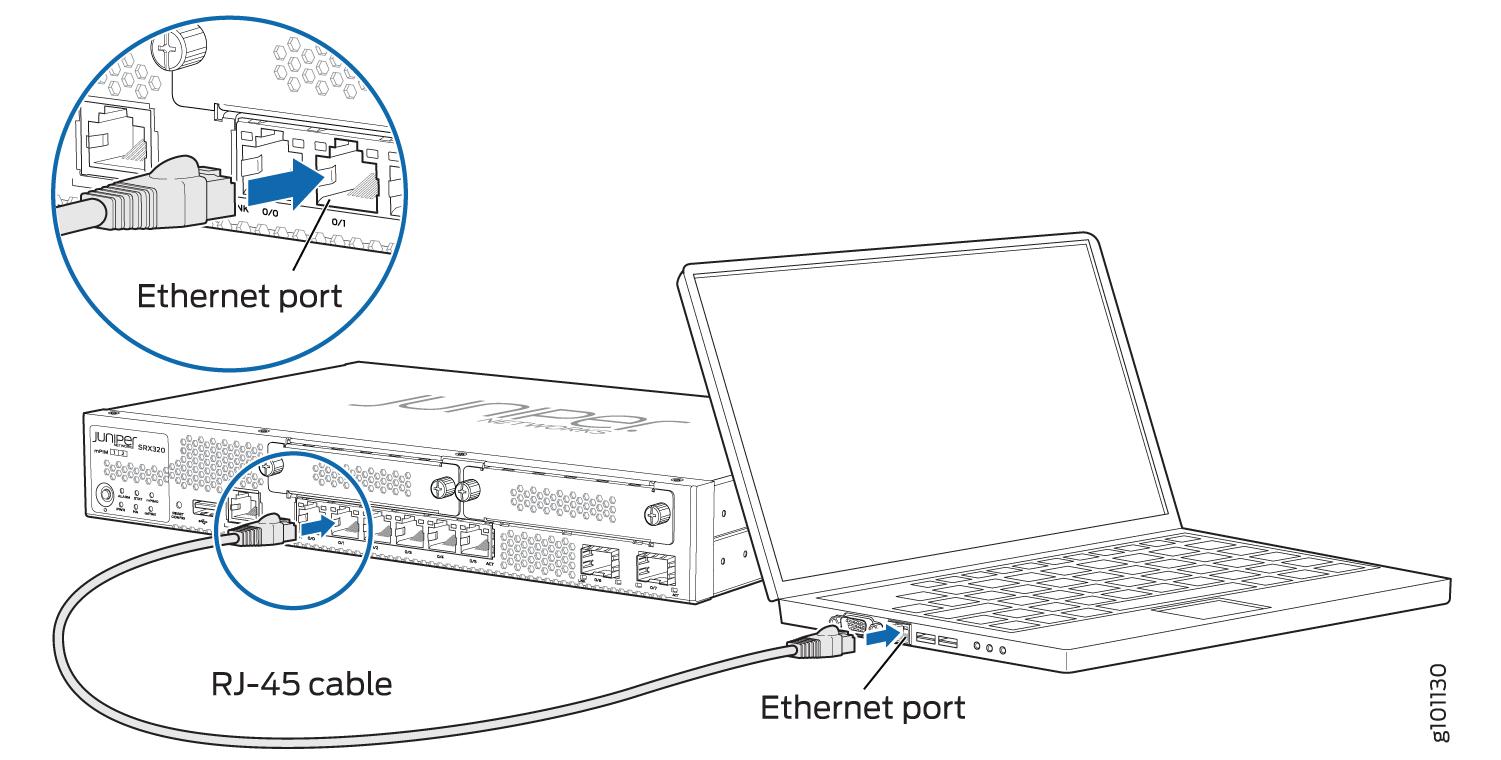
Connect to the Mini-USB Console Port
To connect to the mini-USB console port:
Configure the SRX320 Using the CLI
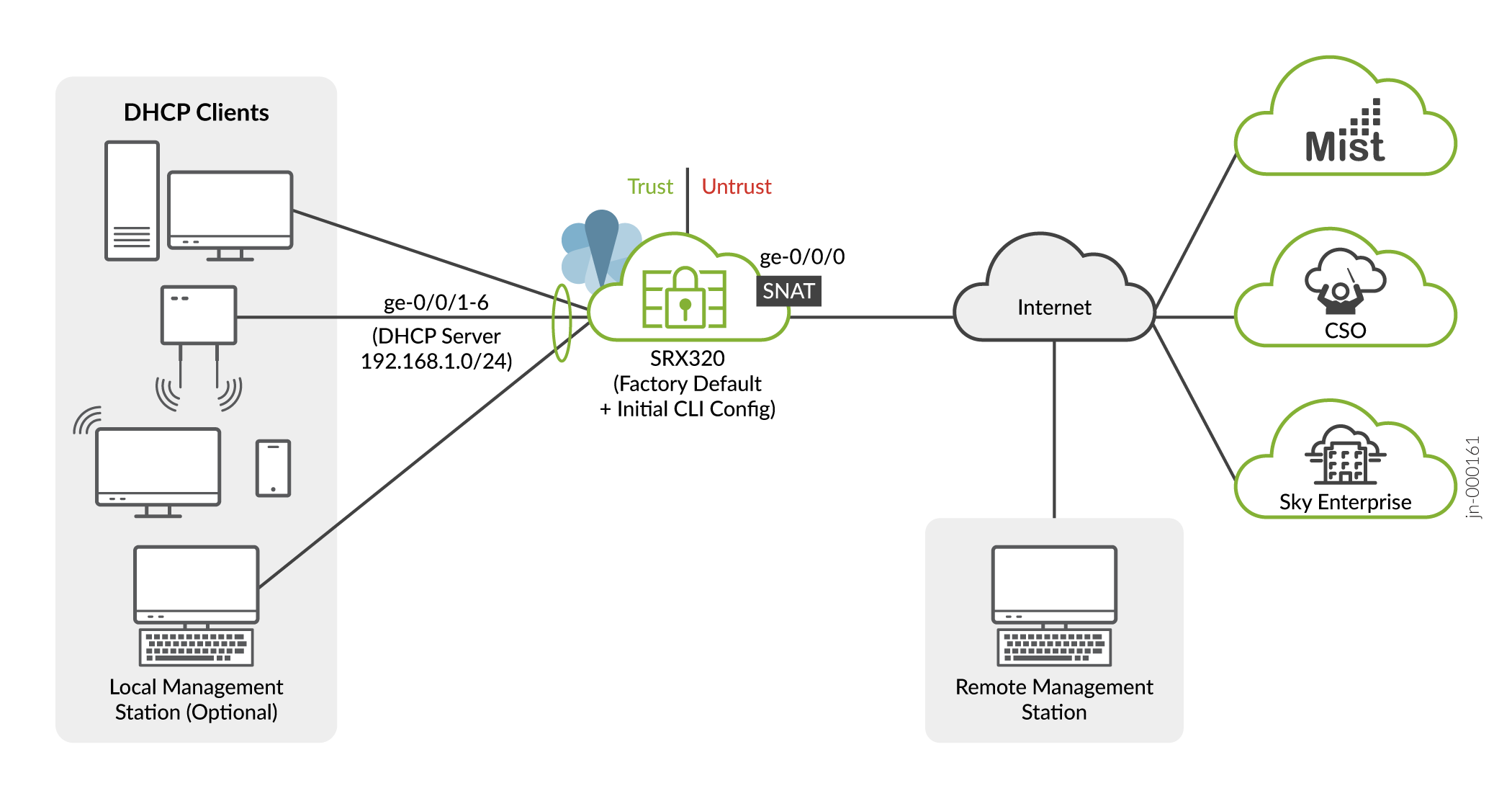
This section assumes you are performing initial configuration of a new SRX320 running a factory default configuration. We show you how to leverage the defaults to quickly get the SRX320 on the internet and able to be managed locally or remotely. See SRX320 Firewall Factory-Default Settings for details on the SRX320 factory defaults.
For this section, however, we assume the service provider does not support DHCP address assignment on the WAN interface. This allows us to show you how to configure an interface and static route using the Junos CLI.
To perform initial configuration on the SRX320 using the CLI:
Configure the SRX320 Using J-Web
Perform Initial Configuration Using J-Web
The J-Web user interface supports a setup wizard, which you can use to perform the initial configuration of the device.
Manage the SRX320 Using J-Web
After initial device configuration is complete you can use J-Web to perform ongoing configuration, management, and health monitoring of your SRX320 device.
For more information, see the SRX J-Web documentation for your release at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/product/us/en/j-web-srx-series.
Configure the Device Using ZTP with Juniper Networks Network Service Controller
You can configure using ZTP for Junos OS Release 19.2 and earlier releases.
You can use ZTP to complete the initial configuration of the SRX320 in your network automatically, with minimum intervention.
Network Service Controller is a component of the Juniper Networks Contrail Service Orchestration platform that simplifies and automates the design and implementation of custom network services that use an open framework.
For more information, refer to the Network Service Controller section in the datasheet at http://www.juniper.net/assets/us/en/local/pdf/datasheets/1000559-en.pdf.
To configure the device automatically using ZTP:
To complete the ZTP process, ensure that the SRX320 is connected to the Internet.
If you already have the authentication code, enter the code in the webpage displayed.
Figure 3: Authentication Code Page
On successful authentication, the initial configuration is applied and committed on the SRX320. Optionally, the latest Junos OS image is installed on the SRX320 before the initial configuration is applied.
If you do not have the authentication code, you can use the J-Web setup wizard to configure the SRX320. Click Skip to J-Web and configure the SRX320 using J-Web.