ON THIS PAGE
Maintaining PTX5000 Interface Modules
Maintaining the PTX5000 FPCs
Purpose
For optimum PTX5000 performance, verify the condition of the FPCs.
Action
On a regular basis:
Check the LEDs on the FPC. During normal operation:
The green OK LED located the bottom of the FPC lights steadily when the FPC is online and functioning normally. The green OK LED blinks during startup.
Issue the CLI
show chassis fpccommand to check the status of installed FPCs. The valueOnlinein the column labeledStateindicates that the FPC is functioning normally.Issue the CLI
show chassis environment fpccommand to check the temperature and power of installed FPCs. The temperature values should be below the preconfigured thresholds. The power values provide Information about the voltage supplied to the FPC. The left column displays the required power, in volts. The right column displays the measured power, in millivolts.Issue the
show chassis fabric topologycommand. During normal operations, the output for the command shows that the state of the online SIBs and FPCs links are in theOKstate.
Holding PTX5000 FPCs
Preventing Damage to FPCs
Many components on the FPC are fragile. Failure to handle FPCs as specified in this document can cause irreparable damage.
To prevent damage when handling or carrying FPCs:
As you carry the FPC, do not bump it against anything. FPC components are fragile.
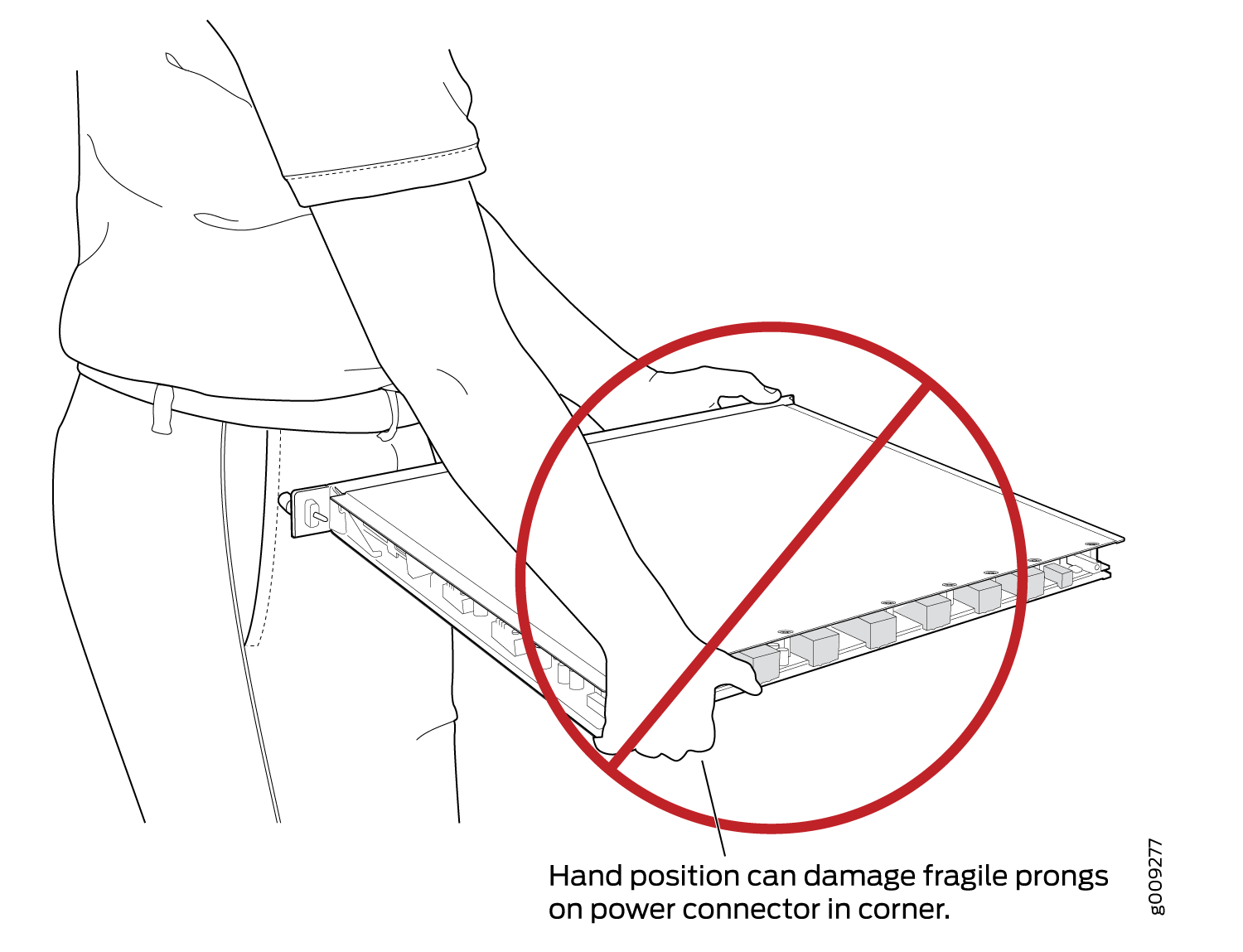
Do not grasp the FPC anywhere except places that this document indicates. In particular, never grasp the connector edge, especially at the power connector in the corner where the connector and bottom edges meet (see Figure 1).
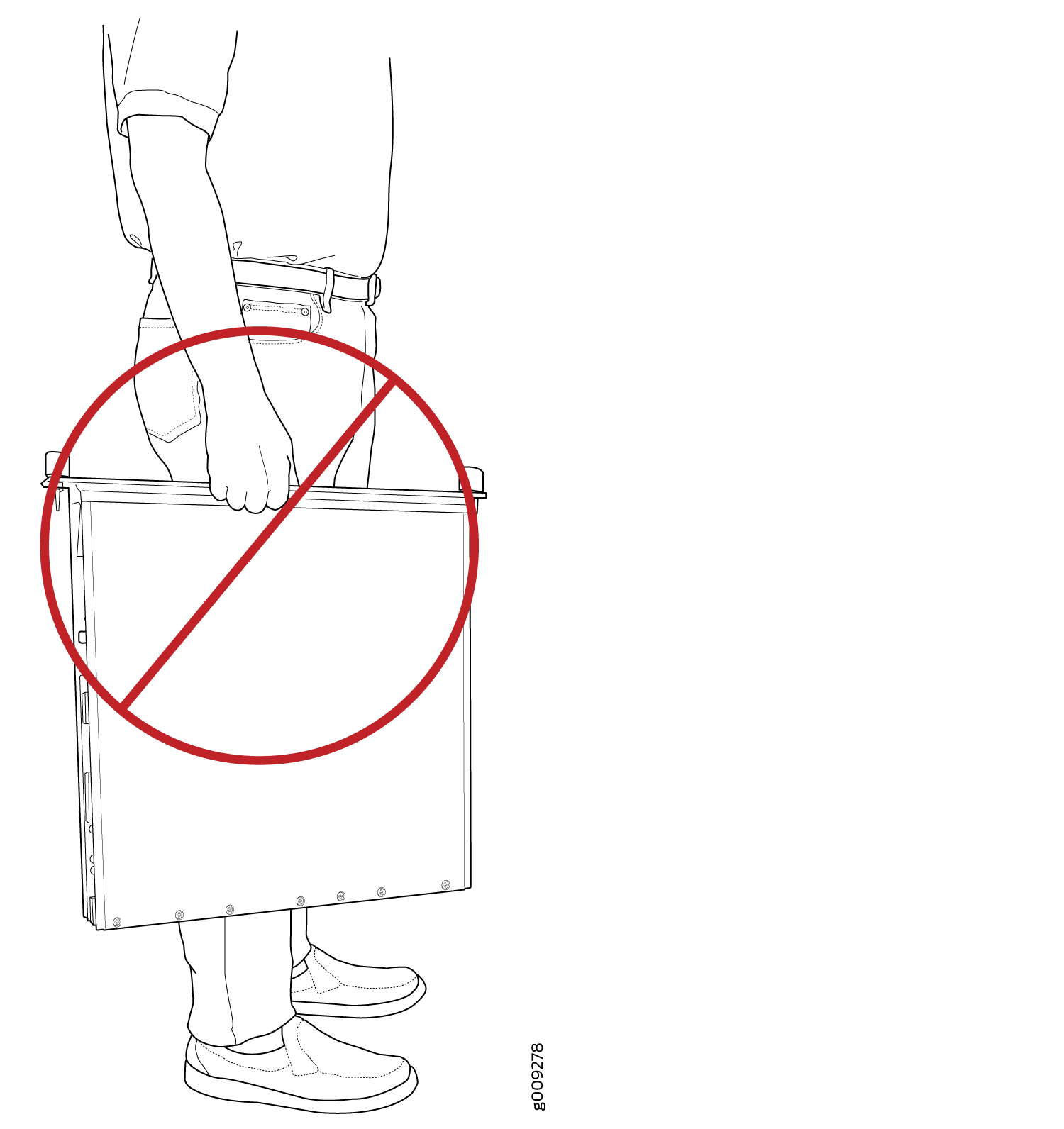
Do not carry the FPC by the faceplate with only one hand (see Figure 2).
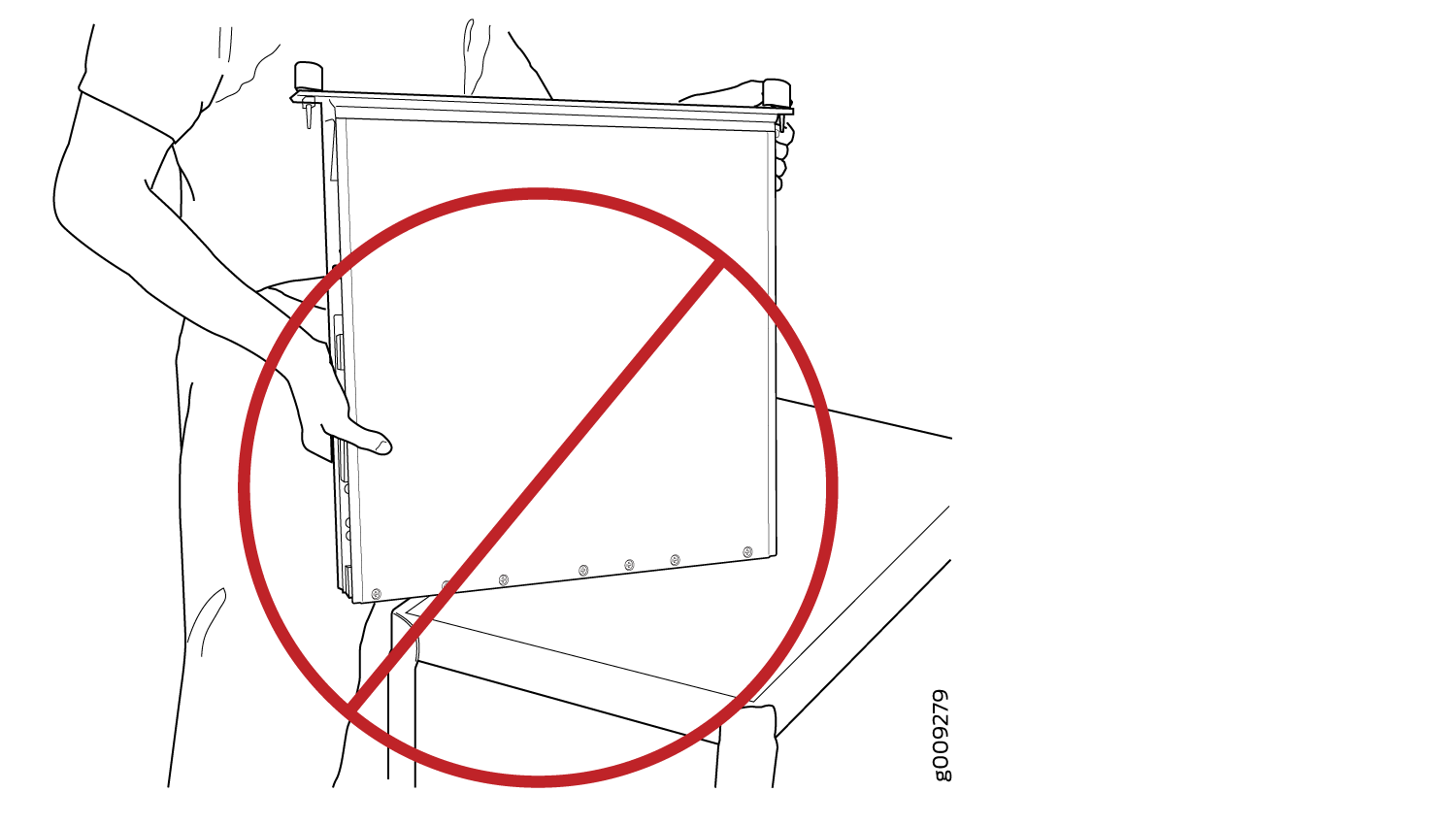
Do not rest any edge of an FPC directly against a hard surface (see Figure 3). If you must rest the FPC temporarily on an edge while changing its orientation between vertical and horizontal, use your hand as a cushion between the edge and the surface.
Holding PTX5000 FPCs Vertically
An FPC configured with PICs installed can weigh as much as 50 lb (22.7 kg). Be prepared to accept the full weight of the FPC as you lift it.
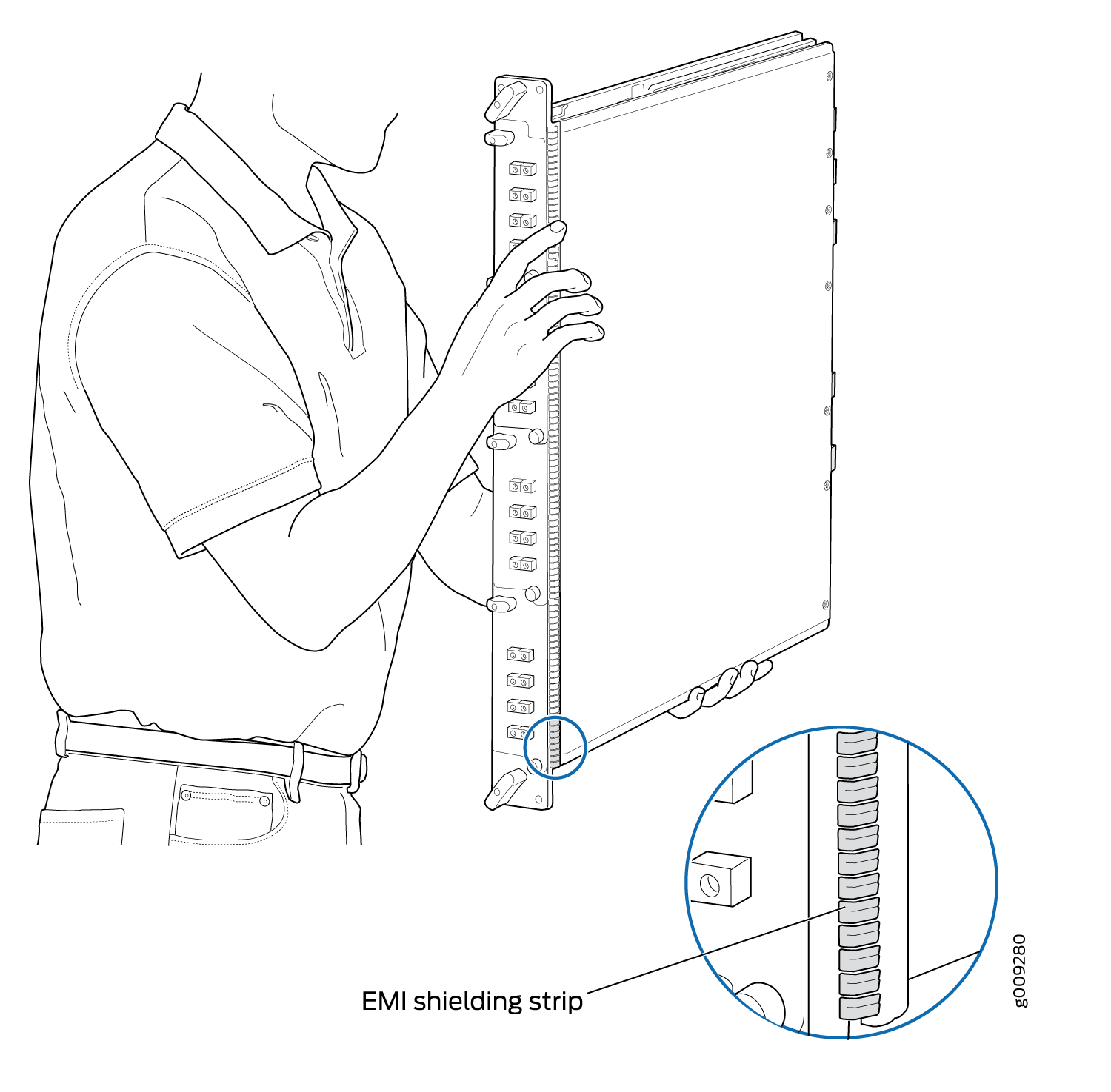
You hold an FPC vertically when installing it into the chassis. To hold an FPC vertically (see Figure 4):
- Orient the FPC so that the faceplate faces you.
- Place one hand around the FPC faceplate about a quarter of the way down from the top edge. To avoid deforming the electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding strip, do not press hard on it.
- Place your other hand at the bottom edge of the FPC.
Holding PTX5000 FPCs Horizontally
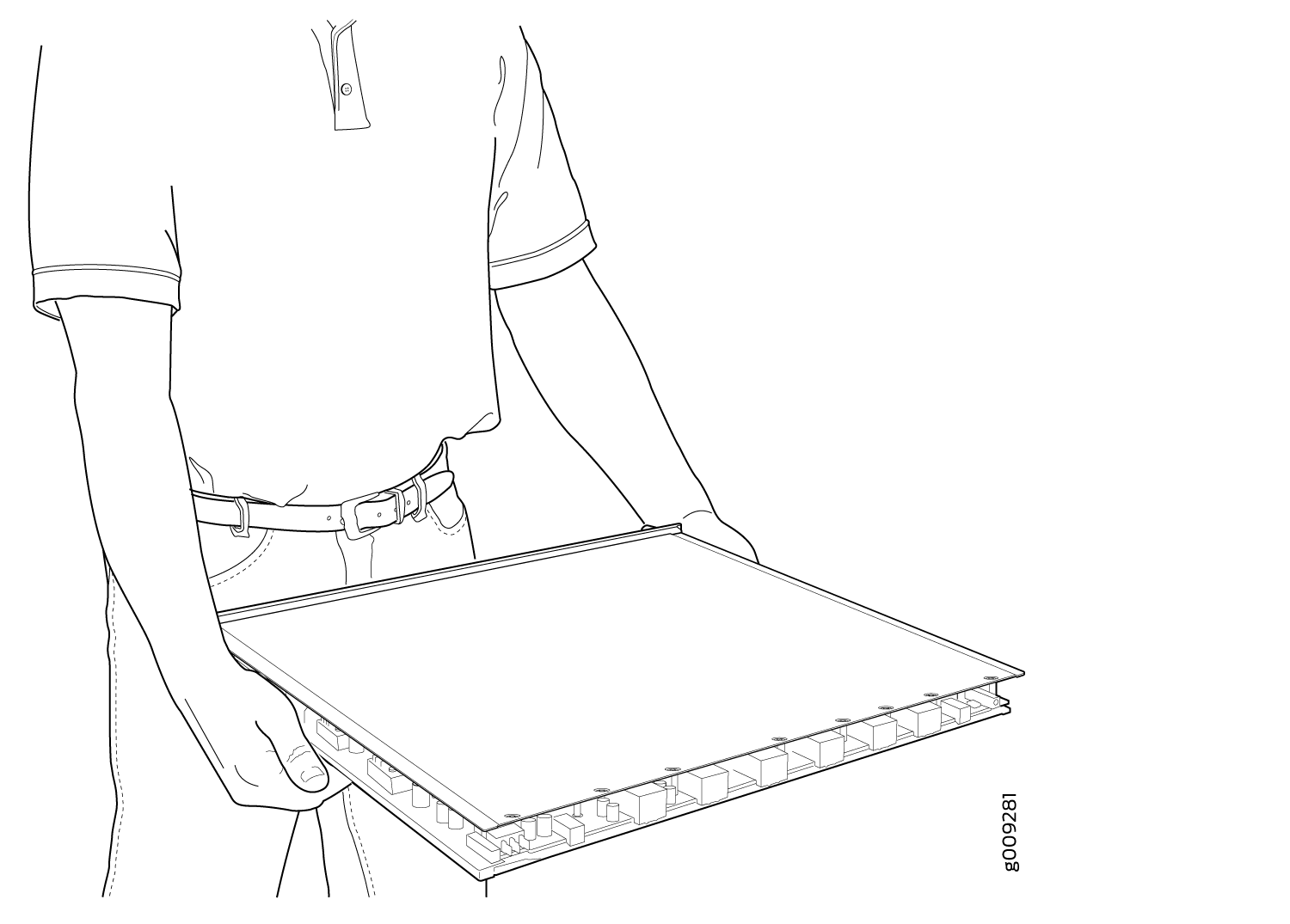
To hold an FPC horizontally:
- Orient the FPC so that the faceplate is facing you.
- Grasp the top edge with your left hand and the bottom edge with your right hand.
You can rest the faceplate of the FPC against your body as you carry it (see Figure 5).
Replacing a PTX5000 FPC
Removing a PTX5000 FPC
The PTX5000 holds up to eight FPCs, which are installed vertically in the front of the PTX5000. An empty FPC weighs between 24.5 lb (11.1 kg) and 38.5 lb (17.5 kg), and an FPC with PICs installed can weigh up to 50 lb (22.7 kg).
Each FPC slot not occupied by an FPC must be covered by an FPC blank panel. An FPC blank panel weighs 6.9 lb (3.1 kg).
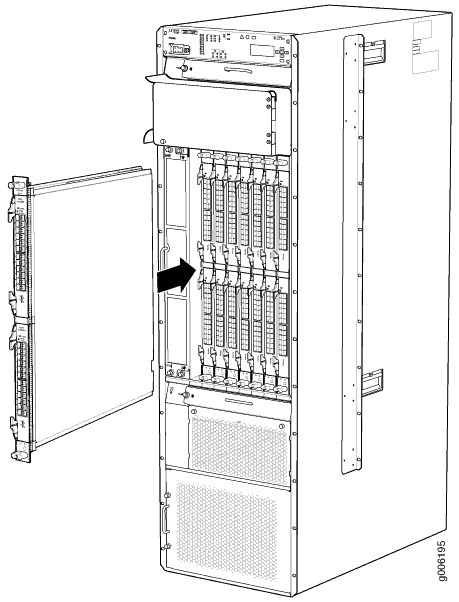
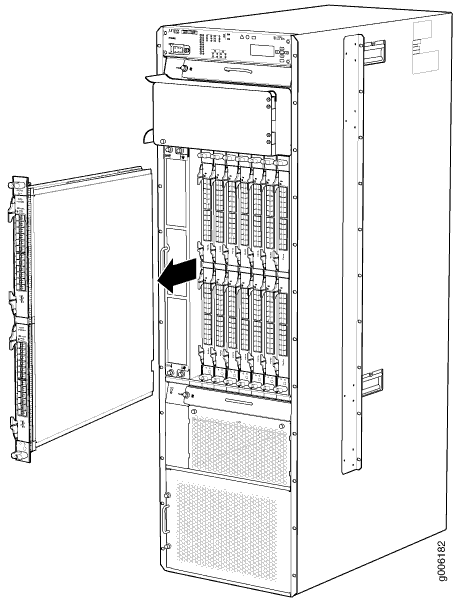
To remove an FPC (see Figure 6):
Installing a PTX5000 FPC
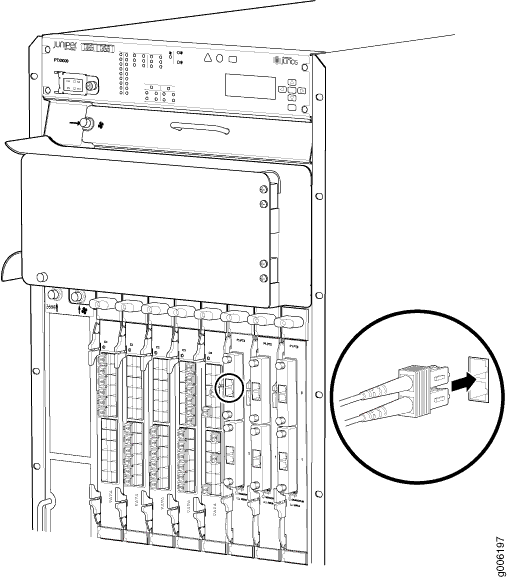
The FPC power connector is located in the corner where the bottom and the connector edges meet. If a power connector prong becomes bent, it no longer aligns with the socket connector on the midplane, and the FPC no longer functions.
You can also verify correct FPC and PIC functioning by issuing
the show chassis fpc and show chassis fpc
pic-status commands, as described in Maintaining
the PTX5000 FPCs.
Maintaining the PTX5000 PICs
Purpose
For optimum performance, verify the condition of the PICs.
Action
On a regular basis:
Check the LEDs on PIC faceplates. The meaning of the LED states differs for various PICs. For more information, see the PTX Series Interface Module Reference. If the FPC that houses the PIC detects a PIC failure, the FPC generates an alarm message to be sent to the Routing Engine.
A PIC LED lit green indicates that the PIC is functioning normally.
Issue the CLI
show chassis fpc pic-statuscommand. The PIC slots in an FPC are numbered from 0 through 1, top to bottom.
Replacing a PTX5000 PIC
Removing a PTX5000 PIC
PICs are hot-insertable and hot-removable. When you remove a PIC, the PTX5000 continues to function, although the PIC interfaces being removed no longer function.
The PICs are located in the FPCs installed in the front of the PTX5000. A PIC weighs approximately 5 lb (2.3 kg).
To remove a PIC:
Installing a PTX5000 PIC
To install a PIC:
Maintaining the PTX5000 PIC Cables
Purpose
For optimum performance, verify the condition of the cables.
Action
Use the cable management system (shown in PTX5000 Cable Management System) to support cables and prevent cables from dislodging or developing stress points.
Place excess cable out of the way in the cable management system. Do not allow fastened loops of cable to dangle from the connector or cable management system, because this stresses the cable at the fastening point. Putting fasteners on the loops helps to maintain their shape.
Keep the cable connections clean and free of dust and other particles, which can cause drops in the received power level. Always inspect cables and clean them if necessary before connecting an interface.
Label both ends of the cables to identify them.
When you unplug a fiber-optic cable from a transceiver, always place a rubber safety plug over the transceiver on the faceplate and on the end of the cable.
Anchor fiber-optic cable to avoid stress on the connectors. When attaching fiber to a transceiver, be sure to secure the fiber so it is not supporting its own weight as it hangs to the floor. Never let fiber-optic cable hang free from the connector.
Avoid bending fiber-optic cable beyond its bend radius. An arc smaller than a few inches can damage the cable and cause problems that are difficult to diagnose.
Frequent plugging and unplugging of fiber-optic cable into and out of optical instruments, such as analyzers, can cause damage to the instruments that is expensive to repair. Instead, attach a short fiber extension to the optical equipment. Any wear and tear due to frequent plugging and unplugging is then absorbed by the short fiber extension, which is easy and inexpensive to replace.
Keep fiber-optic cable connections clean. Small microdeposits of oil and dust in the canal of the transceiver or cable connector could cause loss of light, reducing signal power and possibly causing intermittent problems with the optical connection.
Replacing a PTX5000 PIC Cable
Removing a PTX5000 PIC Cable
Removing and installing PIC cables does not affect router functionality, except that a PIC does not receive or transmit data while its cable is disconnected. To remove a PIC cable:
Installing a PTX5000 PIC Cable
Replacing a PTX5000 PIC CFP Transceiver
Removing a PTX5000 PIC CFP Transceiver
C form-factor pluggables (CFPs) are transceivers that can be removed from a PIC. CFP transceivers are hot-insertable and hot-removable. Removing a CFP transceiver does not interrupt PIC functioning, but the removed CFP transceiver no longer receives or transmits data.
To remove a CFP transceiver:
Installing a PTX5000 PIC CFP Transceiver
To install a replacement CFP:
Replacing a CFP2 Transceiver
Removing a CFP2 Transceiver
C form-factor pluggables (CFPs) are transceivers that can be removed from a PIC. CFP2 transceivers are hot-insertable and hot-removable. Removing a CFP2 transceiver does not interrupt PIC functioning, but the removed CFP2 transceiver no longer receives or transmits data.
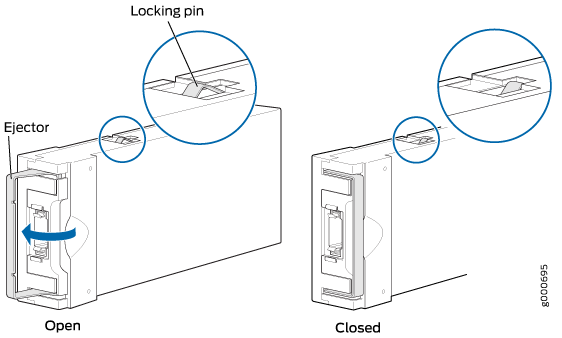
To remove a CFP2 transceiver (see Figure 10):
Installing a CFP2 Transceiver
To install a replacement CFP2:
Replacing a PTX5000 PIC SFP+ Transceiver
Removing a PTX5000 PIC SFP+ Transceiver
Small form-factor pluggables (SFPs) are transceivers that can be removed from a PIC. SFPs are hot-insertable and hot-removable. Removing an SFP does not interrupt PIC functioning, but the removed SFP no longer receives or transmits data.
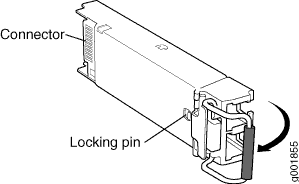
To remove an SFP+ transceiver (see Figure 11):
Installing a PTX5000 PIC SFP+ Transceiver
To install a replacement SFP+:
Replacing a QSFP28 Transceiver
Removing a QSFP28 Transceiver
28-Gbps quad small form-factor pluggable (QSFP28) are transceivers that can be removed from a PIC. QSFP28 transceivers are hot-insertable and hot-removable. Removing a QSFP28 transceiver does not interrupt PIC functioning, but the removed QSFP28 transceiver no longer receives or transmits data.
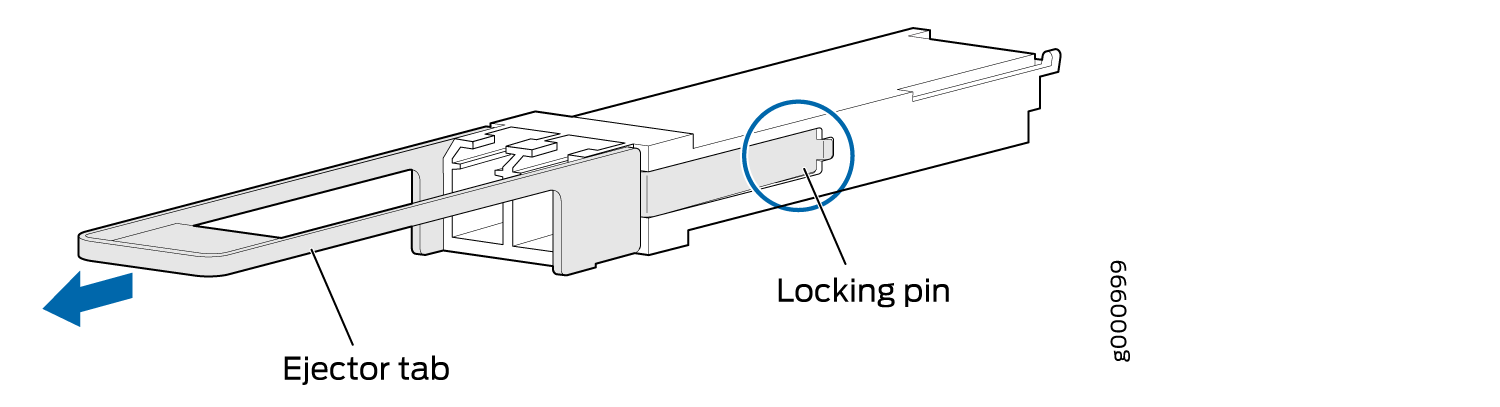
To remove a QSFP28 transceiver (see Figure 12):
Installing a QSFP28 Transceiver
To install a replacement QSFP28: