Auf dieser Seite
Beispiel: Konfigurieren von Communitys in einer Routingrichtlinie
Eine Community ist ein Routenattribut, das von BGP verwendet wird, um Routen mit ähnlichen Eigenschaften administrativ zu gruppieren.
Anforderungen
Vor der Konfiguration dieses Beispiels ist keine spezielle Konfiguration erforderlich, die über die Geräteinitialisierung hinausgeht.
- Aktualisiert und erneut validiert mit vMX auf Junos OS Version 21.1R1.
Überblick
Eine Hauptaufgabe des Community-Attributs besteht darin, ein administrativer Tag-Wert zu sein, der zum Zuordnen von Routen verwendet wird. Im Allgemeinen haben diese Routen einige gemeinsame Eigenschaften, dies ist jedoch nicht erforderlich. Communities sind ein flexibles Werkzeug innerhalb von BGP. Ein einzelner Community-Wert kann einer einzelnen Route oder mehreren Routen zugewiesen werden. Einer Route kann ein einzelner Community-Wert oder mehrere Werte zugewiesen werden. Netzwerke verwenden das Community-Attribut, um die Implementierung administrativer Routing-Richtlinien zu unterstützen. Der zugewiesene Wert einer Route kann es ermöglichen, dass sie in das Netzwerk aufgenommen oder aus dem Netzwerk abgelehnt wird oder dass Attribute geändert werden können.
Abbildung 1 zeigt Gerät R1, Gerät R2 und Gerät R3 als interne BGP (IBGP)-Peers im autonomen System (AS) 64510 an. Das Gerät R4 kündigt den Adressraum 172.16.0.0/21 aus AS 64511 an.
Topologie
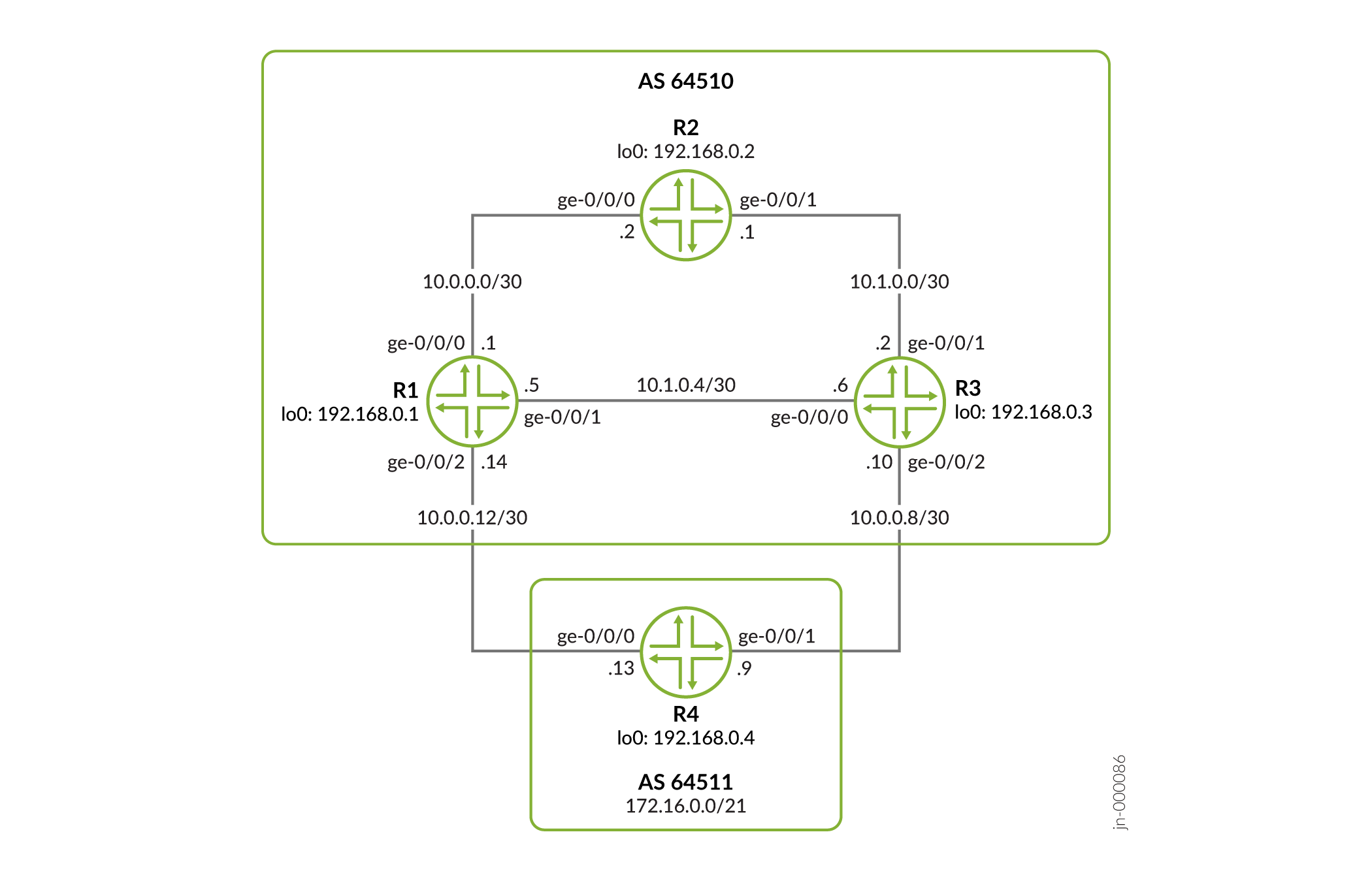
Die spezifischen Routen, die Gerät R1 von Gerät R4 empfängt, lauten wie folgt:
user@R1> show route receive-protocol bgp 10.0.0.13
inet.0: 24 destinations, 28 routes (24 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path
* 172.16.0.0/24 10.0.0.13 64511 I
* 172.16.1.0/24 10.0.0.13 64511 I
* 172.16.2.0/24 10.0.0.13 64511 I
* 172.16.3.0/24 10.0.0.13 64511 I
172.16.4.0/24 10.0.0.13 64511 I
172.16.5.0/24 10.0.0.13 64511 I
172.16.6.0/24 10.0.0.13 64511 I
172.16.7.0/24 10.0.0.13 64511 I
Die Administratoren von AS 64511 möchten einen bestimmten Benutzerdatenverkehr von Gerät R1 und anderen Benutzerdatenverkehr von Gerät R3 empfangen. Um dieses administrative Ziel zu erreichen, fügt Gerät R4 den Community-Wert 64511:1 an einige Routen an, die es sendet, und fügt den Community-Wert 64511:3 an andere Routen an, die es sendet. Routing-Richtlinien innerhalb von AS 64510 werden mithilfe eines Community-Übereinstimmungskriteriums konfiguriert, um die lokale Präferenz der empfangenen Routen in neue Werte zu ändern, die den BGP-Routenauswahlalgorithmus ändern. Die Route mit dem höchsten lokalen Präferenzwert wird bevorzugt.
Auf Gerät R1 wird Routen mit dem Community-Wert 64511:1 die lokale Präferenz 200 und Routen mit dem Community-Wert 64511:3 die lokale Präferenz 50 zugewiesen. Auf Gerät R3 geschieht umgekehrt, sodass Routen mit dem Community-Wert 64511:3 die lokale Präferenz 200 und Routen mit dem Community-Wert 64511:1 die lokale Präferenz 50 zugewiesen wird. Diese Information wird dann über IBGP sowohl von der Vorrichtung R1 als auch von der Vorrichtung R3 an die Vorrichtung R2 übermittelt.
CLI-Schnellkonfiguration Zeigt die Konfiguration für alle Geräte in Abbildung 1an.
Im Abschnitt Schritt-für-Schritt-Konfiguration werden die Konfigurationsschritte auf den Geräten R1 und R4 beschrieben.
Konfiguration
CLI-Schnellkonfiguration
Um dieses Beispiel schnell zu konfigurieren, kopieren Sie die folgenden Befehle, fügen Sie sie in eine Textdatei ein, entfernen Sie alle Zeilenumbrüche, ändern Sie alle Details, die für Ihre Netzwerkkonfiguration erforderlich sind, und kopieren Sie dann die Befehle und fügen Sie sie in die CLI auf Hierarchieebene [edit] ein.
Gerät R1
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.5/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.14/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set policy-options policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R1-routes from community R1_PREFERRED set policy-options policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R1-routes then local-preference 200 set policy-options policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R3-routes from community R3_PREFERRED set policy-options policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R3-routes then local-preference 50 set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 1 from route-filter 10.0.0.12/30 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 1 then accept set policy-options community R3_PREFERRED members 64511:3 set policy-options community R1_PREFERRED members 64511:1 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int export send-direct set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols bgp group ext type external set protocols bgp group ext import change-local-preference set protocols bgp group ext peer-as 64511 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.0.0.13 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1 set routing-options autonomous-system 64510
Gerät R2
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.1/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.2/32 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 64510
Gerät R3
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.6/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.2/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.10/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.3/32 set policy-options policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R3-routes from community R3_PREFERRED set policy-options policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R3-routes then local-preference 200 set policy-options policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R1-routes from community R1_PREFERRED set policy-options policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R1-routes then local-preference 50 set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 1 from route-filter 10.0.0.8/30 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 1 then accept set policy-options community R1_PREFERRED members 64511:1 set policy-options community R3_PREFERRED members 64511:3 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.3 set protocols bgp group int export send-direct set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group ext type external set protocols bgp group ext import change-local-preference set protocols bgp group ext peer-as 64511 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.0.0.9 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.3 set routing-options autonomous-system 64510
Gerät R4
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.13/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.9/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.4/32 set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 1 from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 1 from route-filter 172.16.0.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 1 from route-filter 172.16.1.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 1 from route-filter 172.16.2.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 1 from route-filter 172.16.3.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 1 then community add R1_PREFERRED set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 1 then accept set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 2 from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 2 from route-filter 172.16.4.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 2 from route-filter 172.16.5.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 2 from route-filter 172.16.6.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 2 from route-filter 172.16.7.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 2 then community add R3_PREFERRED set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 2 then accept set policy-options policy-statement send-static term 3 then reject set policy-options community R3_PREFERRED members 64511:3 set policy-options community R1_PREFERRED members 64511:1 set protocols bgp group to-R1 type external set protocols bgp group to-R1 export send-static set protocols bgp group to-R1 peer-as 64510 set protocols bgp group to-R1 neighbor 10.0.0.14 set protocols bgp group to-R3 type external set protocols bgp group to-R3 export send-static set protocols bgp group to-R3 peer-as 64510 set protocols bgp group to-R3 neighbor 10.0.0.10 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.4 set routing-options autonomous-system 64511 set routing-options static route 172.16.0.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.1.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.2.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.3.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.4.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.5.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.6.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.7.0/24 reject
Schritt-für-Schritt-Anleitung
Im folgenden Beispiel müssen Sie durch verschiedene Ebenen in der Konfigurationshierarchie navigieren. Informationen zum Navigieren in der CLI finden Sie Verwenden des CLI-Editors im Konfigurationsmodus im Junos OS CLI-Benutzerhandbuch.
So konfigurieren Sie Gerät R1:
-
Konfigurieren Sie die Schnittstellen.
[edit interfaces] user@R1# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 user@R1# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.5/30 user@R1# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.14/30 user@R1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32
-
Konfigurieren Sie IGP-Verbindungen (Internal Gateway Protocol) zu den Geräten R2 und R3.
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@R1# set interface ge-0/0/0.0 user@R1# set interface ge-0/0/1.0 user@R1# set interface lo0.0 passive
-
Konfigurieren Sie die IBGP-Verbindungen zu den Geräten R2 und R3.
[edit protocols bgp group int] user@R1# set type internal user@R1# set local-address 192.168.0.1 user@R1# set export send-direct user@R1# set neighbor 192.168.0.2 user@R1# set neighbor 192.168.0.3
-
Konfigurieren Sie die EBGP-Verbindung zum Gerät R4.
[edit protocols bgp group ext] user@R1# set type external user@R1# set import change-local-preference user@R1# set peer-as 64511 user@R1# set neighbor 10.0.0.13
-
Konfigurieren Sie die Richtlinie
send-direct.Auf diese Richtlinie wird in der IBGP-Konfiguration verwiesen und sie ermöglicht die externe Erreichbarkeit von Gerät R2. Eine Alternative besteht darin, eine
next-hop selfRichtlinie für Gerät R1 und Gerät R3 zu konfigurieren.[edit policy-options policy-statement send-direct term 1] user@R1# set from protocol direct user@R1# set from route-filter 10.0.0.12/30 exact user@R1# set then accept
-
Konfigurieren Sie die Richtlinie, die die lokale Präferenz für Routen mit angegebenen Community-Tags ändert.
[edit policy-options ] user@R1# set policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R1-routes from community R1_PREFERRED user@R1# set policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R1-routes then local-preference 200 user@R1# set policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R3-routes from community R3_PREFERRED user@R1# set policy-statement change-local-preference term find-R3-routes then local-preference 50 user@R1# set community R3_PREFERRED members 64511:3 user@R1# set community R1_PREFERRED members 64511:1
-
Konfigurieren Sie die AS-Nummer (Autonomous System) und die Router-ID.
[edit routing-options] user@R1# set router-id 192.168.0.1 user@R1# set autonomous-system 64510
So konfigurieren Sie das Gerät R4:
-
Konfigurieren Sie die Schnittstellen.
[edit interfaces] user@R4# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.13/30 user@R4# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.9/30 user@R4# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.4/32
-
Konfigurieren Sie die EBGP-Verbindung zu Gerät R1 und Gerät R3.
[edit protocols bgp] user@R4# set group to-R1 type external user@R4# set group to-R1 export send-static user@R4# set group to-R1 peer-as 64510 user@R4# set group to-R1 neighbor 10.0.0.14 user@R4# set group to-R3 type external user@R4# set group to-R3 export send-static user@R4# set group to-R3 peer-as 64510 user@R4# set group to-R3 neighbor 10.0.0.10
-
Konfigurieren Sie die Community-Tags.
[edit policy-options ] user@R4# set community R3_PREFERRED members 64511:3 user@R4# set community R1_PREFERRED members 64511:1
-
Konfigurieren Sie die Richtlinie
send-static.Auf diese Richtlinie wird in den EBGP-Verbindungen zu Gerät R1 und Gerät R3 verwiesen. Die Richtlinie fügt die Community 64511:1 (PREFERRED) an einige Routen und die Community 64511:3 (NOT_PREFERRED) an andere Routen an.
[edit policy-options] user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 1 from protocol static user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 1 from route-filter 172.16.0.0/24 exact user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 1 from route-filter 172.16.1.0/24 exact user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 1 from route-filter 172.16.2.0/24 exact user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 1 from route-filter 172.16.3.0/24 exact user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 1 then community add R1_PREFERRED user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 1 then accept user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 2 from protocol static user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 2 from route-filter 172.16.4.0/24 exact user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 2 from route-filter 172.16.5.0/24 exact user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 2 from route-filter 172.16.6.0/24 exact user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 2 from route-filter 172.16.7.0/24 exact user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 2 then community add R3_PREFERRED user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 2 then accept user@R4# set policy-statement send-static term 3 then reject
-
Konfigurieren Sie die statischen Routen.
[edit routing-options static] user@R4# set route 172.16.0.0/24 reject user@R4# set route 172.16.1.0/24 reject user@R4# set route 172.16.2.0/24 reject user@R4# set route 172.16.3.0/24 reject user@R4# set route 172.16.4.0/24 reject user@R4# set route 172.16.5.0/24 reject user@R4# set route 172.16.6.0/24 reject user@R4# set route 172.16.7.0/24 reject
-
Konfigurieren Sie die AS-Nummer (Autonomous System) und die Router-ID.
[edit routing-options] user@R4# set router-id 192.168.0.4 user@R4# set autonomous-system 64511
Ergebnisse
Bestätigen Sie im Konfigurationsmodus Ihre Konfiguration, indem Sie die show interfacesBefehle , show protocols, show policy-optionsund show routing-options eingeben. Wenn die Ausgabe nicht die gewünschte Konfiguration anzeigt, wiederholen Sie die Anweisungen in diesem Beispiel, um die Konfiguration zu korrigieren.
Gerät R1
user@R1# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.1/30;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.0.5/30;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.14/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.1/32;
}
}
}
user@R1# show protocols
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.0.1;
export send-direct;
neighbor 192.168.0.2;
neighbor 192.168.0.3;
}
group ext {
type external;
import change-local-preference;
peer-as 64511;
neighbor 10.0.0.13;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
user@R1# show policy-options
policy-statement change-local-preference {
term find-R1-routes {
from community R1_PREFERRED;
then {
local-preference 200;
}
}
term find-R3-routes {
from community R3_PREFERRED;
then {
local-preference 50;
}
}
}
policy-statement send-direct {
term 1 {
from {
protocol direct;
route-filter 10.0.0.12/30 exact;
}
then accept;
}
}
community R3_PREFERRED members 64511:3;
community R1_PREFERRED members 64511:1;
user@R1# show routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1; autonomous-system 64510;
Gerät R4
user@R4# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.13/30;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.9/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.4/32;
}
}
}
user@R4# show protocols
bgp {
group to-R1 {
type external;
export send-static;
peer-as 64510;
neighbor 10.0.0.14;
}
group to-R3 {
type external;
export send-static;
peer-as 64510;
neighbor 10.0.0.10;
}
}
user@R4# show policy-options
policy-statement send-static {
term 1 {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 172.16.0.0/24 exact;
route-filter 172.16.1.0/24 exact;
route-filter 172.16.2.0/24 exact;
route-filter 172.16.3.0/24 exact;
}
then {
community add R1_PREFERRED;
accept;
}
}
term 2 {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 172.16.4.0/24 exact;
route-filter 172.16.5.0/24 exact;
route-filter 172.16.6.0/24 exact;
route-filter 172.16.7.0/24 exact;
}
then {
community add R3_PREFERRED;
accept;
}
}
term 3 {
then reject;
}
}
community R3_PREFERRED members 64511:3;
community R1_PREFERRED members 64511:1;
user@R4# show routing-options
router-id 192.168.0.4;
autonomous-system 64511;
static {
route 172.16.0.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.1.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.2.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.3.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.4.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.5.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.6.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.7.0/24 reject;
}
Wenn Sie mit der Konfiguration der Geräte fertig sind, rufen Sie den Konfigurationsmodus auf commit .
Verifizierung
Vergewissern Sie sich, dass die Konfiguration ordnungsgemäß funktioniert.
Überprüfen der auf Gerät R4 gesendeten Routen
Zweck
Überprüfen Sie auf Gerät R4 die Routen, die an Gerät R1 und Gerät R3 gesendet wurden.
Action!
user@R4> show route advertising-protocol bgp 10.0.0.14 extensive
inet.0: 13 destinations, 13 routes (13 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
* 172.16.0.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R1 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:1
* 172.16.1.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R1 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:1
* 172.16.2.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R1 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:1
* 172.16.3.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R1 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:1
* 172.16.4.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R1 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:3
* 172.16.5.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R1 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:3
* 172.16.6.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R1 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:3
* 172.16.7.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R1 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:3
user@R4> show route advertising-protocol bgp 10.0.0.10 extensive
inet.0: 13 destinations, 13 routes (13 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
* 172.16.0.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R3 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:1
* 172.16.1.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R3 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:1
* 172.16.2.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R3 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:1
* 172.16.3.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R3 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:1
* 172.16.4.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R3 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:3
* 172.16.5.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R3 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:3
* 172.16.6.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R3 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:3
* 172.16.7.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group to-R3 type External
Nexthop: Self
AS path: [64511] I
Communities: 64511:3
Bedeutung
Gerät R4 hat die Routen mit den Communities 64511:1 und 64511:3 getaggt und an Gerät R1 und R3 gesendet.
Überprüfen der auf Gerät R2 empfangenen Routen
Zweck
Überprüfen Sie auf Gerät R2 die Routen, die von Gerät R1 und Gerät R3 empfangen wurden.
Action!
user@R2> show route receive-protocol bgp 192.168.0.1 inet.0: 25 destinations, 25 routes (25 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path * 10.0.0.12/30 192.168.0.1 100 I * 172.16.0.0/24 10.0.0.13 200 64511 I * 172.16.1.0/24 10.0.0.13 200 64511 I * 172.16.2.0/24 10.0.0.13 200 64511 I * 172.16.3.0/24 10.0.0.13 200 64511 I
user@R2> show route receive-protocol bgp 192.168.0.3 inet.0: 25 destinations, 25 routes (25 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path * 10.0.0.8/30 192.168.0.3 100 I * 172.16.4.0/24 10.0.0.9 200 64511 I * 172.16.5.0/24 10.0.0.9 200 64511 I * 172.16.6.0/24 10.0.0.9 200 64511 I * 172.16.7.0/24 10.0.0.9 200 64511 I
user@R2> show route match-prefix 172.16.*
inet.0: 25 destinations, 25 routes (25 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
172.16.0.0/24 *[BGP/170] 1w3d 00:02:11, localpref 200, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via ge-0/0/0.0
172.16.1.0/24 *[BGP/170] 1w3d 00:02:11, localpref 200, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via ge-0/0/0.0
172.16.2.0/24 *[BGP/170] 1w3d 00:02:11, localpref 200, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via ge-0/0/0.0
172.16.3.0/24 *[BGP/170] 1w3d 00:02:11, localpref 200, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via ge-0/0/0.0
172.16.4.0/24 *[BGP/170] 1w3d 00:01:50, localpref 200, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.2 via ge-0/0/1.0
172.16.5.0/24 *[BGP/170] 1w3d 00:01:50, localpref 200, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.2 via ge-0/0/1.0
172.16.6.0/24 *[BGP/170] 1w3d 00:01:50, localpref 200, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.2 via ge-0/0/1.0
172.16.7.0/24 *[BGP/170] 1w3d 00:01:50, localpref 200, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.2 via ge-0/0/1.0
Bedeutung
Gerät R2 enthält die Routen mit den erwarteten lokalen Einstellungen und die erwarteten aktiven Routen, die durch die Sternchen (*) gekennzeichnet sind.
