BGP 路由反射器
了解 BGP 路由反射器
本主题讨论如何使用路由反射器来简化配置并帮助扩展。减少不在流量转发路径中的路由反射器上的工作负载的另一种方法是在[edit protocols bgp family family-name]层次结构级别使用该no-install语句。从 Junos OS 15.1 版开始,该 no-install 语句消除了路由协议守护程序 (rpd) 与 Junos 系统中其他组件(如内核或分布式防火墙守护程序 (dfwd))之间的交互。通过禁止将关联 rpd 路由信息库 (RIB)(也称为路由表)中的任何路由发布到这些组件,可以消除这种交互。
在 Junos OS 15.1 版之前的版本中,您可以使用拒绝从 BGP 获知的路由的转发表导出策略,减少不在流量转发路径中的路由反射器上的工作负载。
由于内部 BGP (IBGP) 全网状网络要求,大多数网络使用路由反射器来简化配置。计算全网格所需会话数的公式为 v * (v - 1)/2,其中 v 是支持 BGP 的设备数。全网格模型不能很好地扩展。使用路由反射器,您可以将路由器分组到集群中,集群由自治系统 (AS) 特有的数字标识符标识。在群集中,您必须配置从单个路由器(路由反射器)到每个内部对等方的 BGP 会话。使用此配置,可以满足 IBGP 全网状网络的要求。
要在 AS 中使用路由反射,请将一个或多个路由器指定为路由反射器,通常为每个接入点 (POP) 指定一个路由器。路由反射器具有特殊的 BGP 功能,可以将从内部对等方获知的路由重新播发到其他内部对等方。因此,路由反射不需要所有内部对等方彼此完全网格化,而只需要路由反射器与所有内部对等方完全网格化。路由反射器及其所有内部对等方形成一个集群,如 所示 图 1。
对于某些瞻博网络设备,您必须在使用路由反射器的每台设备上安装高级 BGP 功能许可证。有关许可证的详细信息,请参阅 《软件安装和升级指南》。
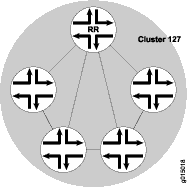
图 1 显示了配置为群集 127 路由反射器的路由器 RR。其他路由器是群集中指定的内部对等方。BGP 路由由任何内部对等方播发到路由器 RR。然后,RR 将这些路由重新播发到集群中的所有其他对等方。
您可以配置多个集群,并通过配置路由反射器的完整网格来链接它们(请参阅 图 2)。
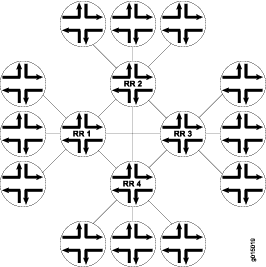
图 2 将路由反射器 RR 1、RR 2、RR 3 和 RR 4 显示为全网状内部对等方。当路由器将路由播发到 RR 1 时,RR 1 会将路由重新播发到其他路由反射器,而其他路由反射器又会将路由重新播发到 AS 中的其余路由器。路由反射允许路由在整个 AS 中传播,而不会因全网状网络要求而产生扩展问题。
支持多个集群的路由反射器不接受来自非客户端路由器的具有相同集群 ID 的路由。因此,您必须为冗余 RR 配置不同的集群 ID,以反映到其他集群的路由。
客户端是从路由反射器接收路由的 IBGP 路由器。非客户端是另一个 IBGP 邻接方。路由反射器仅将从非客户端获知的路由转发给其客户端,而不转发给非客户端。但是,路由反射器将从客户端获知的路由播发给客户端和非客户端。
但是,随着集群变大,带有路由反射器的全网格变得难以扩展,路由反射器之间的全网格也变得难以扩展。为了帮助解决此问题,可以将路由器群集一起分组为群集群集以进行分层路由反射(请参阅 图 3)。
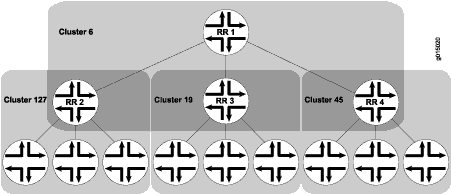
图 3 将 RR 2、RR 3 和 RR 4 分别显示为群集 127、19 和 45 的路由反射器。网络管理员没有将这些路由反射器完全网格化,而是将它们配置为另一个集群(集群 6)的一部分,RR 1 是其路由反射器。当路由器将路由播发到 RR 2 时,RR 2 会将路由重新播发到其自己的集群中的所有路由器,然后将路由重新播发到 RR 1。RR 1 将路由重新播发到其群集中的路由器,这些路由器通过其群集向下传播路由。
另请参阅
示例:配置路由反射器
此示例说明如何配置路由反射器。
要求
在配置此示例之前,不需要除设备初始化之外的特殊配置。
概述
通常,支持 BGP (IBGP) 的内部设备需要完全网状化,因为 IBGP 不会将更新重新播发到其他支持 IBGP 的设备。全网格是通过在每个启用 IBGP 的设备上配置多个 neighbor 语句来实现的逻辑网格。全网格不一定是物理全网格。在大型部署中,维护完整网格(逻辑或物理)不能很好地扩展。
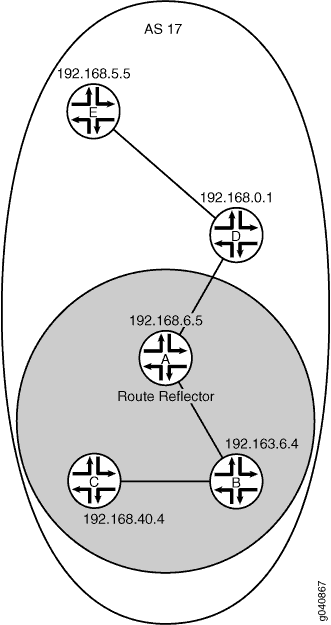
图 4 显示了以设备 A 充当路由反射器的 IBGP 网络。设备 B 和设备 C 是路由反射器的客户端。设备 D 和设备 E 位于群集外部,因此它们不是路由反射器的客户端。
在设备 A(路由反射器)上,必须通过包含 neighbor 客户端(设备 B 和设备 C)和非客户端(设备 D 和设备 E)的语句,与所有启用 IBGP 的设备形成对等关系。您还必须包含 cluster 语句和集群标识符。群集标识符可以是任何 32 位值。此示例使用路由反射器的环路接口 IP 地址。
在设备 B 和设备 C(路由反射器客户端)上,您只需要一个 neighbor 与路由反射器(设备 A)形成对等关系的语句。
在设备 D 和设备 E(非客户端)上,您需要为每个非客户端设备(D 到 E 和 E-to-D)提供语句 neighbor 。您还需要路由 neighbor 反射器(D 到 A 和 E 到 A)的语句。设备 D 和设备 E 不需要 neighbor 客户端设备(设备 B 和设备 C)的语句。
设备 D 和设备 E 被视为非客户端,因为它们彼此之间显式配置了对等关系。要使其成为 RRroute 反射器客户端,请从设备 D 上的配置中删除该 neighbor 192.168.5.5 语句,然后从设备 E 上的配置中删除该 neighbor 192.168.0.1 语句。
配置
程序
CLI 快速配置
要快速配置此示例,请复制以下命令,将其粘贴到文本文件中,删除所有换行符,更改与您的网络配置匹配所需的任何详细信息,然后将命令复制并粘贴到层次结构级别的 CLI [edit] 中。
设备 A
set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 1 description to-B set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.10.10.1/30 set interfaces fe-0/0/1 unit 3 description to-D set interfaces fe-0/0/1 unit 3 family inet address 10.10.10.9/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 192.168.6.5/32 set protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.168.6.5 set protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-ospf set protocols bgp group internal-peers cluster 192.168.6.5 set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.163.6.4 set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.40.4 set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.5.5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.1 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/0.1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/1.3 set policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2 from protocol ospf set policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2 then accept set routing-options router-id 192.168.6.5 set routing-options autonomous-system 17
设备 B
set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 2 description to-A set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.10.10.2/30 set interfaces fe-0/0/1 unit 5 description to-C set interfaces fe-0/0/1 unit 5 family inet address 10.10.10.5/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 2 family inet address 192.163.6.4/32 set protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.163.6.4 set protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-ospf set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.6.5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.2 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/0.2 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/1.5 set policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2 from protocol ospf set policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2 then accept set routing-options router-id 192.163.6.4 set routing-options autonomous-system 17
设备 C
set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 6 description to-B set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 6 family inet address 10.10.10.6/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet address 192.168.40.4/32 set protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.168.40.4 set protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-ospf set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.6.5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.3 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/0.6 set policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2 from protocol ospf set policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2 then accept set routing-options router-id 192.168.40.4 set routing-options autonomous-system 17
设备 D
set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 4 description to-A set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 4 family inet address 10.10.10.10/30 set interfaces fe-0/0/1 unit 7 description to-E set interfaces fe-0/0/1 unit 7 family inet address 10.10.10.13/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 4 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-ospf set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.6.5 set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.5.5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.4 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/0.4 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/1.7 set policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2 from protocol ospf set policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2 then accept set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1 set routing-options autonomous-system 17
设备 E
set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 8 description to-D set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 8 family inet address 10.10.10.14/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 5 family inet address 192.168.5.5/32 set protocols bgp group internal-peers type internal set protocols bgp group internal-peers local-address 192.168.5.5 set protocols bgp group internal-peers export send-ospf set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group internal-peers neighbor 192.168.6.5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.5 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/0.8 set policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2 from protocol ospf set policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2 then accept set routing-options router-id 192.168.5.5 set routing-options autonomous-system 17
分步过程
配置路由反射器
分步过程
下面的示例要求您在各个配置层级中进行导航。有关导航 CLI 的信息,请参阅《Junos OS CLI 用户指南》中的在配置模式下使用 CLI 编辑器。
要使用瞻博网络设备 A 作为路由反射器在网络中配置 IBGP,请执行以下操作:
配置接口。
[edit interfaces] user@A# set fe-0/0/0 unit 1 description to-B user@A# set fe-0/0/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.10.10.1/30 user@A# set fe-0/0/1 unit 3 description to-D user@A# set fe-0/0/1 unit 3 family inet address 10.10.10.9/30 user@A# set lo0 unit 1 family inet address 192.168.6.5/32
配置 BGP,包括集群标识符以及与自治系统 (AS) 中所有启用 IBGP 的设备的邻居关系。
同时应用将 OSPF 路由重新分发到 BGP 的策略。
[edit protocols bgp group internal-peers] user@A# set type internal user@A# set local-address 192.168.6.5 user@A# set export send-ospf user@A# set cluster 192.168.6.5 user@A# set neighbor192.163.6.4 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.40.4 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.0.1 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.5.5
配置静态路由或内部网关协议 (IGP)。
此示例使用 OSPF。
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@A# set interface lo0.1 passive user@A# set interface fe-0/0/0.1 user@A# set interface fe-0/0/1.3
配置将 OSPF 路由重新分发到 BGP 的策略。
[edit policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2] user@A# set from protocol ospf user@A# set then accept
配置路由器 ID 和自治系统 (AS) 编号。
[edit routing-options] user@A# set router-id 192.168.6.5 user@A# set autonomous-system 17
结果
在配置模式下,输入 show interfaces 、show protocols、show policy-options 和 show routing-options 命令,以确认您的配置。如果输出未显示预期的配置,请重复此示例中的说明,以便进行更正。
user@A# show interfaces
fe-0/0/0 {
unit 1 {
description to-B;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.1/30;
}
}
}
fe-0/0/1 {
unit 3 {
description to-D;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.9/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 1 {
family inet {
address 192.168.6.5/32;
}
}
}
user@A# show protocols
bgp {
group internal-peers {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.6.5;
export send-ospf;
cluster 192.168.6.5;
neighbor 192.163.6.4;
neighbor 192.168.40.4;
neighbor 192.168.0.1;
neighbor 192.168.5.5;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.1 {
passive;
}
interface fe-0/0/0.1;
interface fe-0/0/1.3;
}
}
user@A# show policy-options
policy-statement send-ospf {
term 2 {
from protocol ospf;
then accept;
}
}
user@A# show routing-options router-id 192.168.6.5; autonomous-system 17;
如果完成设备配置,请从配置模式输入 commit。
如果其他非客户端设备来自瞻博网络,请对您正在配置的群集中的每个非客户端 BGP 对等方重复这些步骤。否则,请参阅设备的文档以获取说明。
配置客户端对等方
分步过程
下面的示例要求您在各个配置层级中进行导航。有关导航 CLI 的信息,请参阅《Junos OS CLI 用户指南》中的在配置模式下使用 CLI 编辑器。
要配置客户端对等方:
配置接口。
[edit interfaces] user@B# set fe-0/0/0 unit 2 description to-A user@B# set fe-0/0/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.10.10.2/30 user@B# set fe-0/0/1 unit 5 description to-C user@B# set fe-0/0/1 unit 5 family inet address 10.10.10.5/30 user@B# set lo0 unit 2 family inet address 192.163.6.4/32
配置与路由反射器的 BGP 邻居关系。
同时应用将 OSPF 路由重新分发到 BGP 的策略。
[edit protocols bgp group internal-peers] user@B# set type internal user@B# set local-address 192.163.6.4 user@B# set export send-ospf user@B# set neighbor 192.168.6.5
配置 OSPF。
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@B# set interface lo0.2 passive user@B# set interface fe-0/0/0.2 user@B# set interface fe-0/0/1.5
配置将 OSPF 路由重新分发到 BGP 的策略。
[edit policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2] user@B# set from protocol ospf user@B# set then accept
配置路由器 ID 和 AS 编号。
[edit routing-options] user@B# set router-id 192.163.6.4 user@B# set autonomous-system 17
结果
在配置模式下,输入 show interfaces 、show protocols、show policy-options 和 show routing-options 命令,以确认您的配置。如果输出未显示预期的配置,请重复此示例中的说明,以便进行更正。
user@B# show interfaces
fe-0/0/0 {
unit 2 {
description to-A;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.2/30;
}
}
}
fe-0/0/1 {
unit 5 {
description to-C;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.5/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 2 {
family inet {
address 192.163.6.4/32;
}
}
}
user@B# show protocols
bgp {
group internal-peers {
type internal;
local-address 192.163.6.4;
export send-ospf;
neighbor 192.168.6.5;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.2 {
passive;
}
interface fe-0/0/0.2;
interface fe-0/0/1.5;
}
}
user@B# show policy-options
policy-statement send-ospf {
term 2 {
from protocol ospf;
then accept;
}
}
user@B# show routing-options router-id 192.163.6.4; autonomous-system 17;
如果完成设备配置,请从配置模式输入 commit。
如果其他客户端设备来自瞻博网络,则对正在配置的群集中的每个客户端 BGP 对等方重复这些步骤。否则,请参阅设备的文档以获取说明。
配置非客户端对等方
分步过程
下面的示例要求您在各个配置层级中进行导航。有关导航 CLI 的信息,请参阅《Junos OS CLI 用户指南》中的在配置模式下使用 CLI 编辑器。
要配置非客户端对等方:
配置接口。
[edit interfaces] user@D# set fe-0/0/0 unit 4 description to-A user@D# set fe-0/0/0 unit 4 family inet address 10.10.10.10/30 user@D# set fe-0/0/1 unit 7 description to-E user@D# set fe-0/0/1 unit 7 family inet address 10.10.10.13/30 user@D# set lo0 unit 4 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32
配置 BGP 邻居与 RRroute 反射器和其他非客户端对等方的关系。
同时应用将 OSPF 路由重新分发到 BGP 的策略。
[edit protocols bgp group internal-peers] user@D# set type internal user@D# set local-address 192.168.0.1 user@D# set export send-ospf user@D# set neighbor 192.168.6.5 user@D# set neighbor 192.168.5.5
配置 OSPF。
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@D# set interface lo0.4 passive user@D# set interface fe-0/0/0.4 user@D# set interface fe-0/0/1.7
配置将 OSPF 路由重新分发到 BGP 的策略。
[edit policy-options policy-statement send-ospf term 2] user@D# set from protocol ospf user@D# set then accept
配置路由器 ID 和 AS 编号。
[edit routing-options] user@D# set router-id 192.168.0.1 user@D# set autonomous-system 17
结果
在配置模式下,输入 show interfaces 、show protocols、show policy-options 和 show routing-options 命令,以确认您的配置。如果输出未显示预期的配置,请重复此示例中的说明,以便进行更正。
user@D# show interfaces
fe-0/0/0 {
unit 4 {
description to-A;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.10/30;
}
}
}
fe-0/0/1 {
unit 7 {
description to-E;
family inet {
address 10.10.10.13/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 4 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.1/32;
}
}
}
user@D# show protocols
bgp {
group internal-peers {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.0.1;
export send-ospf;
neighbor 192.168.6.5;
neighbor 192.168.5.5;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.4 {
passive;
}
interface fe-0/0/0.4;
interface fe-0/0/1.7;
}
}
user@D# show policy-options
policy-statement send-ospf {
term 2 {
from protocol ospf;
then accept;
}
}
user@D# show routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1; autonomous-system 17;
如果完成设备配置,请从配置模式输入 commit。
如果其他非客户端设备来自瞻博网络,则对正在配置的群集中的每个非客户端 BGP 对等方重复这些步骤。否则,请参阅设备的文档以获取说明。
验证
确认配置工作正常。
验证 BGP 邻居
目的
验证 BGP 是否在配置的接口上运行,以及是否已为每个邻居地址建立 BGP 会话。
操作
在操作模式下,输入 show bgp neighbor 命令。
user@A> show bgp neighbor
Peer: 192.163.6.4+179 AS 17 Local: 192.168.6.5+62857 AS 17
Type: Internal State: Established (route reflector client)Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Export: [ send-ospf ]
Options: <Preference LocalAddress Cluster Refresh>
Local Address: 192.168.6.5 Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 192.163.6.4 Local ID: 192.168.6.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 0
BFD: disabled, down
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 17)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 6
Accepted prefixes: 1
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 6
Last traffic (seconds): Received 5 Sent 3 Checked 19
Input messages: Total 2961 Updates 7 Refreshes 0 Octets 56480
Output messages: Total 2945 Updates 6 Refreshes 0 Octets 56235
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 192.168.0.1+179 AS 17 Local: 192.168.6.5+60068 AS 17
Type: Internal State: Established (route reflector client)Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Export: [ send-ospf ]
Options: <Preference LocalAddress Cluster Refresh>
Local Address: 192.168.6.5 Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 192.168.0.1 Local ID: 192.168.6.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 3
BFD: disabled, down
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 17)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 6
Accepted prefixes: 1
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 6
Last traffic (seconds): Received 18 Sent 20 Checked 12
Input messages: Total 15 Updates 5 Refreshes 0 Octets 447
Output messages: Total 554 Updates 4 Refreshes 0 Octets 32307
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 192.168.5.5+57458 AS 17 Local: 192.168.6.5+179 AS 17
Type: Internal State: Established (route reflector client)Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Export: [ send-ospf ]
Options: <Preference LocalAddress Cluster Refresh>
Local Address: 192.168.6.5 Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 192.168.5.5 Local ID: 192.168.6.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 2
BFD: disabled, down
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 17)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 7
Accepted prefixes: 7
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 6
Last traffic (seconds): Received 17 Sent 3 Checked 9
Input messages: Total 2967 Updates 7 Refreshes 0 Octets 56629
Output messages: Total 2943 Updates 6 Refreshes 0 Octets 56197
Output Queue[0]: 0
Peer: 192.168.40.4+53990 AS 17 Local: 192.168.6.5+179 AS 17
Type: Internal State: Established (route reflector client)Flags: <Sync>
Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive
Last Error: None
Export: [ send-ospf ]
Options: <Preference LocalAddress Cluster Refresh>
Local Address: 192.168.6.5 Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170
Number of flaps: 0
Peer ID: 192.168.40.4 Local ID: 192.168.6.5 Active Holdtime: 90
Keepalive Interval: 30 Peer index: 1
BFD: disabled, down
NLRI for restart configured on peer: inet-unicast
NLRI advertised by peer: inet-unicast
NLRI for this session: inet-unicast
Peer supports Refresh capability (2)
Restart time configured on the peer: 120
Stale routes from peer are kept for: 300
Restart time requested by this peer: 120
NLRI that peer supports restart for: inet-unicast
NLRI that restart is negotiated for: inet-unicast
NLRI of received end-of-rib markers: inet-unicast
NLRI of all end-of-rib markers sent: inet-unicast
Peer supports 4 byte AS extension (peer-as 17)
Peer does not support Addpath
Table inet.0 Bit: 10000
RIB State: BGP restart is complete
Send state: in sync
Active prefixes: 0
Received prefixes: 7
Accepted prefixes: 7
Suppressed due to damping: 0
Advertised prefixes: 6
Last traffic (seconds): Received 5 Sent 23 Checked 52
Input messages: Total 2960 Updates 7 Refreshes 0 Octets 56496
Output messages: Total 2943 Updates 6 Refreshes 0 Octets 56197
Output Queue[0]: 0验证 BGP 组
目的
验证是否正确配置了 BGP 组。
操作
在操作模式下,输入 show bgp group 命令。
user@A> show bgp group Group Type: Internal AS: 17 Local AS: 17 Name: internal-peers Index: 0 Flags: <> Export: [ send-ospf ] Options: <Cluster> Holdtime: 0 Total peers: 4 Established: 4 192.163.6.4+179 192.168.40.4+53990 192.168.0.1+179 192.168.5.5+57458 inet.0: 0/26/16/0 Groups: 1 Peers: 4 External: 0 Internal: 4 Down peers: 0 Flaps: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending inet.0 26 0 0 0 0 0
验证 BGP 摘要信息
目的
验证 BGP 配置是否正确。
操作
在操作模式下,输入 show bgp summary 命令。
user@A> show bgp summary Groups: 1 Peers: 4 Down peers: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending inet.0 26 0 0 0 0 0 Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Accepted/Damped... 192.163.6.4 17 2981 2965 0 0 22:19:15 0/6/1/0 0/0/0/0 192.168.0.1 17 36 575 0 0 13:43 0/6/1/0 0/0/0/0 192.168.5.5 17 2988 2964 0 0 22:19:10 0/7/7/0 0/0/0/0 192.168.40.4 17 2980 2964 0 0 22:19:14 0/7/7/0 0/0/0/0
验证路由表信息
目的
验证路由表是否包含 IBGP 路由。
操作
在操作模式下,输入 show route 命令。
user@A> show route
inet.0: 12 destinations, 38 routes (12 active, 0 holddown, 10 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.10.10.0/30 *[Direct/0] 22:22:03
> via fe-0/0/0.1
[BGP/170] 22:20:55, MED 2, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
[BGP/170] 22:20:51, MED 3, localpref 100, from 192.168.5.5
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
10.10.10.1/32 *[Local/0] 22:22:03
Local via fe-0/0/0.1
10.10.10.4/30 *[OSPF/10] 22:21:13, metric 2
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
[BGP/170] 22:20:51, MED 4, localpref 100, from 192.168.5.5
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
10.10.10.8/30 *[Direct/0] 22:22:03
> via fe-0/0/1.3
[BGP/170] 22:20:51, MED 2, localpref 100, from 192.168.5.5
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
[BGP/170] 22:20:55, MED 3, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
10.10.10.9/32 *[Local/0] 22:22:03
Local via fe-0/0/1.3
10.10.10.12/30 *[OSPF/10] 22:21:08, metric 2
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
[BGP/170] 22:20:55, MED 4, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
192.163.6.4/32 *[OSPF/10] 22:21:13, metric 1
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
[BGP/170] 22:20:55, MED 1, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
[BGP/170] 22:20:51, MED 3, localpref 100, from 192.168.5.5
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
192.168.0.1/32 *[OSPF/10] 22:21:08, metric 1
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
[BGP/170] 22:20:51, MED 1, localpref 100, from 192.168.5.5
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
[BGP/170] 22:20:55, MED 3, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
192.168.5.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 22:21:08, metric 2
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
[BGP/170] 00:15:24, MED 1, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
[BGP/170] 22:20:55, MED 4, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
192.168.6.5/32 *[Direct/0] 22:22:04
> via lo0.1
[BGP/170] 22:20:51, MED 2, localpref 100, from 192.168.5.5
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
[BGP/170] 22:20:55, MED 2, localpref 100, from 192.168.40.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
192.168.40.4/32 *[OSPF/10] 22:21:13, metric 2
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
[BGP/170] 22:20:55, MED 1, localpref 100, from 192.163.6.4
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.2 via fe-0/0/0.1
[BGP/170] 22:20:51, MED 4, localpref 100, from 192.168.5.5
AS path: I
> to 10.10.10.10 via fe-0/0/1.3
224.0.0.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 22:22:07, metric 1
MultiRecv了解属于两个不同集群的路由反射器
路由反射的目的是在内部 BGP (IBGP) 路由设备未完全网状化时防止环路。为此,RR 会违反正常 BGP 操作的规则之一:它们将从内部 BGP 对等方获知的路由重新播发到其他内部 BGP 对等方。
通常,单个 RR 仅是一个集群的成员。例如,在分层 RR 设计中,第 2 层 RR 可以是第 1 层 RR 的客户端,但它们不能是彼此的客户端。
但是,当两个 RR 是彼此的客户端,并且路由从一个集群反映到另一个集群时,集群列表中仅包含一个集群 ID。这是因为在这种情况下,在群集列表中拥有一个群集 ID 足以防止环路。
表 1 汇总路由反射器在使用群集 ID 填充反射路由的群集列表时使用的规则。
路由反射方案 |
配置 |
|---|---|
将路由从其中一个客户端反射到非客户端路由器时 客户端 -> RR -> 非客户端 |
RR 在反射路由的集群列表中填充与该客户端关联的集群 ID。 |
将路由从非客户端路由器反射到客户端路由器时 非客户端 -> RR -> 客户端 |
RR 在反射路由的集群列表中填充与该客户端关联的集群 ID。 |
将路由从客户端路由器反射到不同群集中的另一个客户端路由器时 client1 -> RR -> client2(不同的集群) |
RR 在将群集 ID 反映到客户端 2 之前,会在群集列表中填充与 client1 关联的群集 ID。不会添加与客户端 2 关联的群集 ID。 |
将路由从客户端路由器反射到不同自治系统中的非客户端路由器时。 例如,如果配置了第 2 层 RR 和 2 个 BGP 组(一个用于 RR 客户端,另一个用于第 1 层 RR),并且要反映从一个自治系统到另一个自治系统的路由。 客户端 -> RR -> 非客户端(不同 AS) |
在反映到非客户端设备的路由之前,RR 不会使用群集 ID 填充群集列表,因为群集 ID 特定于一个自治系统。 |
另请参阅
示例:配置属于两个不同集群的路由反射器
此示例说明如何配置属于两个不同群集的路由反射器 (RR)。这不是常见方案,但在某些情况下可能很有用。
要求
配置设备接口和内部网关协议 (IGP)。有关包含接口和 IGP 配置的 RR 设置示例,请参阅 示例:配置路由反射器。
概述
在此示例中,设备 RR1 是设备 R3 和设备 RR2 的路由反射器。路由反射器 RR1 分配了两个不同的群集 ID,一个是 RR1-R3 的 10.13.1.3,RR1-RR2 的 10.12.1.2。
设备 RR2 是设备 R4 的路由反射器。
考虑图 图 5。
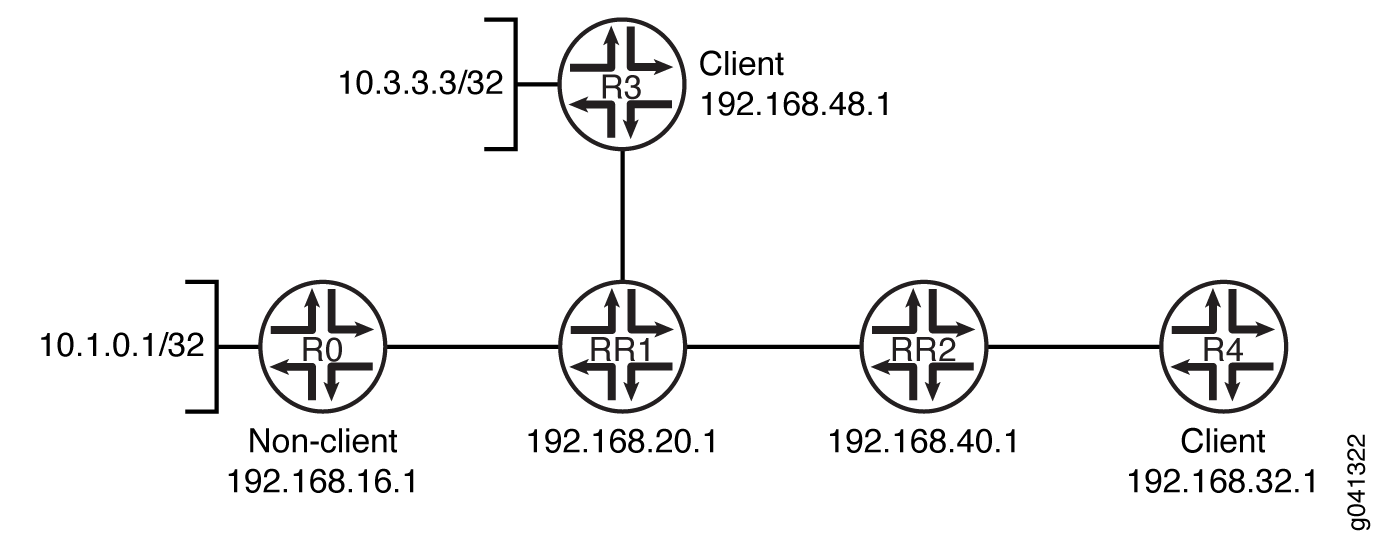
此示例显示了设备 RR1 和设备 RR2 上的 BGP 配置。
配置
程序
CLI 快速配置
要快速配置此示例,请复制以下命令,将其粘贴到文本文件中,删除所有换行符,更改与您的网络配置匹配所需的任何详细信息,然后将命令复制并粘贴到层次结构级别的 CLI [edit] 中。
设备 RR1
set protocols bgp group RR1_client type internal set protocols bgp group RR1_client local-address 192.168.20.1 set protocols bgp group RR1_client cluster 10.13.1.3 set protocols bgp group RR1_client neighbor 192.168.48.1 set protocols bgp group Non_client type internal set protocols bgp group Non_client local-address 192.168.20.1 set protocols bgp group Non_client neighbor 192.168.16.1 set protocols bgp group RR1_to_RR2 type internal set protocols bgp group RR1_to_RR2 local-address 192.168.20.1 set protocols bgp group RR1_to_RR2 cluster 10.12.1.2 set protocols bgp group RR1_to_RR2 neighbor 192.168.40.1
设备 RR2
set protocols bgp group RR2_client type internal set protocols bgp group RR2_client local-address 192.168.40.1 set protocols bgp group RR2_client cluster 10.24.2.4 set protocols bgp group RR2_client neighbor 192.168.32.1 set protocols bgp group RR2_to_RR1 type internal set protocols bgp group RR2_to_RR1 local-address 192.168.40.1 set protocols bgp group RR2_to_RR1 neighbor 192.168.20.1
配置设备 RR1
分步过程
下面的示例要求您在各个配置层级中进行导航。有关导航 CLI 的信息,请参阅《Junos OS CLI 用户指南》中的在配置模式下使用 CLI 编辑器。
要配置设备 RR1:
-
配置与设备 R3 的对等关系。
[edit protocols bgp group RR1_client] user@RR1# set type internal user@RR1# set local-address 192.168.20.1 user@RR1# set cluster 10.13.1.3 user@RR1# set neighbor 192.168.48.1
-
配置与设备 R0 的对等关系。
[edit protocols bgp group Non_client] user@RR1# set type internal user@RR1# set local-address 192.168.20.1 user@RR1# set neighbor 192.168.16.1
-
配置与设备 RR2 的对等关系。
[edit protocols bgp group RR1_to_RR2] user@RR1# set type internal user@RR1# set local-address 192.168.20.1 user@RR1# set cluster 10.12.1.2 user@RR1# set neighbor 192.168.40.1
结果
在配置模式下,输入 show protocols 命令以确认您的配置。如果输出未显示预期的配置,请重复此示例中的说明,以便进行更正。
user@RR1# show protocols
bgp {
group RR1_client {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.20.1;
cluster 10.13.1.3;
neighbor 192.168.48.1;
}
group Non_client {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.20.1;
neighbor 192.168.16.1;
}
group RR1_to_RR2 {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.20.1;
cluster 10.12.1.2;
neighbor 192.168.40.1;
}
}
如果完成设备配置,请从配置模式输入 commit。
配置设备 RR2
分步过程
下面的示例要求您在各个配置层级中进行导航。有关导航 CLI 的信息,请参阅《Junos OS CLI 用户指南》中的在配置模式下使用 CLI 编辑器。
要配置设备 RR2:
-
配置与设备 R4 的对等关系。
[edit protocols bgp group RR2_client] user@RR2# set type internal user@RR2# set local-address 192.168.40.1 user@RR2# set cluster 10.24.2.4 user@RR2# set neighbor 192.168.32.1
-
配置与设备 RR1 的对等关系。
[edit protocols bgp group RR2_to_RR1] user@RR2# set type internal user@RR2# set local-address 192.168.40.1 user@RR2# set neighbor 192.168.20.1
结果
在配置模式下,输入 show protocols 命令以确认您的配置。如果输出未显示预期的配置,请重复此示例中的说明,以便进行更正。
user@RR2# show protocols
bgp {
group RR2_client {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.40.1;
cluster 10.24.2.4;
neighbor 192.168.32.1;
}
group RR2_to_RR1 {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.40.1;
neighbor 192.168.20.1;
}
}
如果完成设备配置,请从配置模式输入 commit。
验证
确认配置工作正常。
检查为 Route 10 播发的集群 ID。3.3.3
目的
验证 BGP 是否在配置的接口上运行,以及是否已为每个邻居地址建立 BGP 会话。
操作
在操作模式下,输入 show route advertising-protocol bgp neighbor-address 命令。
user@RR1> show route advertising-protocol bgp 192.168.40.1 active-path 10.3.3.3 extensive
inet.0: 61 destinations, 61 routes (60 active, 0 holddown, 1 hidden)
* 10.3.3.3/32 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group RR1_to_RR2 type Internal
Nexthop: 192.168.48.1
Localpref: 100
AS path: [100] I
Cluster ID: 10.13.1.3
Originator ID: 192.168.48.1
意义
10.3.3.3/32 路由源自设备 RR1 的客户端对等方设备 R3。当此路由发送到 RR1 的客户端设备 RR2 时,路由具有 10。13.1.附加了 3 个群集 ID,即 RR1-R3 的群集 ID。
检查为路由 10.1 通告的集群 ID。0,1
目的
检查从设备 RR1 到设备 RR2 的路由播发。
操作
在操作模式下,输入 show route advertising-protocol bgp neighbor-address 命令。
user@RR1> show route advertising-protocol bgp 192.168.40.1 active-path 10.1.0.1/32 extensive
inet.0: 61 destinations, 61 routes (60 active, 0 holddown, 1 hidden)
* 10.1.0.1/32 (1 entry, 1 announced)
BGP group RR1_to_RR2 type Internal
Nexthop: 192.168.16.1
Localpref: 100
AS path: [100] I
Cluster ID: 10.12.1.2
Originator ID: 192.168.16.1意义
10.1.0.1/32 路由源自设备 RR1 的非客户端对等方设备 R0。当此路由发送到 RR1 的客户端设备 RR2 时,路由具有 10。12.1.附加了 2 个群集 ID,即 RR1-RR2 的群集 ID。
向不同集群中的另一个客户端(设备 R4)播发时,设备 RR1 会保留设备 RR2 中的入站集群 ID。
了解 BGP 最佳路由反射
您可以将 IS-IS 和 OSPF 配置为路由反射器上的内部网关协议 (IGP),将 BGP 最佳路由反射 (BGP-ORR) 配置为向 BGP-ORR 客户端组通告最佳路径。这是从客户端的角度使用最短 IGP 指标而不是路由反射器的视图来完成的。
共享相同或相似 IGP 拓扑的客户端组可以分组为一个 BGP 对等组。您可以配置为 optimal-route-reflection 在该 BGP 对等组中启用 BGP-ORR。您还可以将其中一个 反射器 节点配置为 BGP 对等组中的主节点 (igp-primary),以便使用该主节点中的 IGP 指标选择最佳路径并将其播发给同一 BGP 对等组中的客户端。或者,您也可以选择另一个 反射器 节点作为备份节点 (igp-backup),当主 反射器 节点 (igp-primary) 出现故障或无法访问时,将使用该节点。
要启用 BGP-ORR,请在 [edit protocols bgp group group-name] 层次结构级别包含optimal-route-reflection语句。
BGP-ORR 仅在 IGP 用于 BGP 路由解析时起作用。当 MPLSLDP/RSVP 用于路由解析时,BGP-ORR 不起作用。
要使 BGP-ORR 正常工作,应通过 IGP 解析 BGP 前缀。在正常的第 3 层 VPN、第 2 层 VPN、VPLS 或 MVPN 或 EVPN 场景中,前缀通过 inet.3 解析。在 inet.3 中,前缀的协议下一跃点的主要路由是 RSVP 或 LDP(而不是像 IS-IS 或 OSPF 这样的 IGP 协议)。要使 BGP-ORR 正常工作,您需要将路由器配置为使用 inet.0 对第 3 层 VPN、第 2 层 VPN、VPLS 或 MVPN 或 EVPN 前缀进行路由解析。您可以通过以下命令执行此操作:
-
对于第 3 层 VPN 前缀:
user@host# set routing-options resolution rib bgp.l3vpn.0 resolution-ribs inet.0
-
对于第 2 层 VPN 或 VPLS 前缀:
user@host# set routing-options resolution rib bgp.l2vpn.0 resolution-ribs inet.0
-
对于 EVPN 前缀:
user@host# set routing-options resolution rib bgp.evpn.0 resolution-ribs inet.0
-
对于 MVPN 前缀:
user@host# set routing-options resolution rib bgp.mvpn.0 resolution-ribs inet.0
另一种方法是将 IGP 路由泄漏到 inet.3 中,并使其成为 inet.3 中的主要路由。
使用以下 CLI 层次结构配置 BGP-ORR:
[edit protocols bgp]
group group-name{
optimal-route-reflection {
igp-primary ipv4-address;
igp-backup ipv4-address;
}
}
另请参阅
在路由反射器上配置 BGP 最佳路由反射以通告最佳路径
您可以将 IS-IS 和 OSPF 配置为路由反射器上的内部网关协议 (IGP),将 BGP 最佳路由反射 (BGP-ORR) 配置为向 BGP-ORR 客户端组通告最佳路径。这是从客户端的角度使用最短 IGP 指标而不是路由反射器的视图来完成的。
要启用 BGP-ORR,请在 [edit protocols bgp group group-name] 层次结构级别包含optimal-route-reflection语句。
共享相同或相似 IGP 拓扑的客户端组可以分组为一个 BGP 对等组。您可以配置为 optimal-route-reflection 在该 BGP 对等组中启用 BGP-ORR。
要配置 BGP-ORR,请执行以下操作:
使用以下 CLI 命令监控 BGP-ORR 的配置并对其进行故障排除:
show bgp group—查看 BGP-ORR 的主配置和备份配置。show isis bgp-orr—查看 IS-IS BGP-ORR 指标 (RIB)。show ospf bgp-orr—查看 OSPF BGP-ORR 指标 (RIB)。show ospf route— 查看 OSPF 路由表中的条目show route- 查看路由表中的活动条目。show route advertising protocol bgp peer— 验证是否正在根据 BGP-ORR 规则播发路由。
另请参阅
BGP 路由服务器概述
BGP 路由服务器是相当于内部 IBGP (IBGP) 路由反射器的外部 BGP (EBGP),可简化网络中所需的直接点对点 EBGP 会话数量。EBGP 路由服务器在 BGP 属性传播方面是透明的,因此,如果路由来自直接连接的 EBGP 对等方,则从路由服务器接收的路由将携带一组 BGP 属性(NEXT_HOP、AS_PATH、MULTI_EXIT_DISC、AIGP 和社区)。
与 IBGP 路由反射器一样,EBGP 路由服务器使用路由服务器功能连接到 EBGP 对等方之间的直接转发路径之外的网络。这种连接可以通过直接物理链路,也可以通过 VPLS LAN 或 EVPN 等第 2 层网络,也可以通过点对点 EBGP 链路的 IP 交换矩阵提供对等方环路地址的可访问性(通常在数据中心网络中)。
BGP 协议经过增强,可提供具有 RFC 7947 中所述的以下功能的路由服务器功能:
NEXT_HOP、AS_PATH、MULTI_EXIT_DISC、AIGP 和社区的属性透明度。
每客户端策略控制和多个路由服务器 RIB,用于缓解路径隐藏。
BGP 可编程性利用路由服务器功能。BGP JET bgp_route_service.proto API 已得到增强,可支持路由服务器功能,如下所示:
对 EBGP 路由服务器进行编程。
将路由注入特定路由服务器 RIB,以便有选择地将其播发到特定于客户端的 RIB 中的客户端组。
BGP JET bgp_route_service.proto API 包含一个对等类型对象,用于将各个路由标识为 EBGP 或 IBGP(默认)。
路由服务器功能通常与地址族无关,尽管某些特定的 BGP 属性支持可能特定于地址族(例如,AIGP 仅支持标记单播地址族)。所有 EBGP 地址族都支持路由服务器功能。
BGP 属性透明度
通过修改常规 BGP 路由传播来支持路由服务器的 EBGP 属性透明度 [RFC7947],以便在传播路由时剥离或修改传递和非传递属性。
对正常 EBGP 行为的更改由 route-server-client CLI 配置控制。route-server-client[edit protocols bgp group group-name] 层次结构级别的 CLI 配置实现了路由服务器 BGP 属性透明度行为。
路由服务器为单跃点 EBGP 和多跃点配置提供属性透明度。因此,配置
route-server-client隐式包括用于单跃点和多跃点会话的功能no-nexthop-change。对于多跃点 BGP 会话,必须配置multihop关键字。route-server-client可以在 [edit protocol bgp] 层次结构的协议、组或邻居级别进行配置。仅当
route-server-client组类型为 external. 为internal组配置 时route-server-client,尝试提交时会发出配置错误。配置
route-server-client没有参数。普通 BGP 权限适用于
route-server-client配置。
就属性透明度而言,属性是独立处理的。即使路由服务器无法在未经修改的情况下发送下一跃点,也会透明地发送适用于这些属性的其他属性。
下面是一个示例 route-server-client 配置:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group R0 {
type external;
route-server-client;
family inet {
unicast;
}
peer-as 100;
neighbor 10.0.0.1;
}
}
}
下一跳
除非通过策略显式配置,否则不得通过强加下一跃点自身或以其他方式修改下一跃点来修改下一跃点属性。路由服务器必须根据 RFC 4271 的第三方下一跃点规则传播 BGP 下一跃点。
为以下路由服务器方案指定下一跃点行为:
在 LAN 和 WAN 互连的情况下,当路由服务器通过共享的 LAN 和 WAN 子网连接到客户端对等方时,路由服务器将播发收到的第三方下一跃点,而无需按照 RFC 4271 中的定义进行修改。
对于数据中心多跳互连,当路由服务器通过多跳互连连接到客户端对等方时,必须配置 EBGP 多跳,并且 CLI 配置的行为
no-nexthop-change由配置隐式施加route-server-client。根据 RFC 4271 中定义的可选第三方行为,路由服务器将播发收到的第三方下一跃点,无需修改。在其他情况下,例如路由服务器和客户端对等方之间的点对点单跃点连接,将使用正常的下一跃点播发过程来防止播发可能被 BGP 对等方拒绝的下一跃点(例如,默认情况下,大多数 BGP 实现拒绝非多点会话上子网地址未涵盖的下一跃点地址。
AS 路径
不得通过前置路由服务器的本地 AS 编号来修改 AS 路径。为对等方配置 CLI 会 route-server-client 抑制播发中本地 AS 编号的前置。此外, show route advertising-protocol bgp peer CLI 命令会针对作为路由服务器客户端的对等方进行更改,以便本地 AS 不显示在播发的指标中。
其他属性
MULTI_EXIT_DISC属性(可选、非传递)必须在收到时传播。
所有社区属性(包括无广告、禁止导出和不可传递扩展社区)都必须在收到时传播。
累积 IGP (AIGP) 属性(可选、非传递)必须在收到时传播。
注:Junos OS 仅支持 BGP-LU 地址族(IPv4 和 IPv6)的 AIGP。
BGP 路由服务器客户端 RIB
路由服务器客户端特定的 RIB 是 BGP Loc-RIB 的不同视图,可以包含与其他视图相同的目标的不同路由。路由服务器客户端通过其对等组,可以与单个特定于客户端的视图或共享的公共 RIB 相关联。
为了提供向同一目标的不同客户端播发不同路由的功能,从概念上讲,有必要允许在同一目标但不同的客户端/组上下文中出现 BGP 路径选择的多个实例。
为了通过每个客户端/组路径选择实现灵活策略控制的高级要求,BGP 路由服务器采用使用非转发路由实例 (NFI) 对 BGP 管道进行多实例的方法,包括 BGP 路径选择、Loc-RIB 和策略。路由服务器配置为在单独的非转发路由实例中配置的 BGP 组中对路由服务器客户端进行分组。此方法利用了以下事实:在路由实例中运行的 BGP 执行路径选择,并具有独立于在其他路由实例中运行的 BGP 的 RIB。
策略要求和注意事项
要在路由服务器客户端之间传播路由,将根据配置的策略在路由实例的 RIB 之间泄露路由。
用于策略控制的路由服务器配置包括以下注意事项:
路由服务器客户端应在同一主实例或路由实例中配置,以接收相同的 Loc-RIB 视图。
路由服务器客户端应在其自己的路由实例中进行配置,以接收完全唯一的 Loc-RIB 视图。
路由服务器客户端应在同一路由实例的不同 BGP 对等组中进行配置,以便在同一 Loc-RIB 视图上具有不同的导出策略。
默认情况下,要使路由服务器客户端特定的 RIB 视图从其他表接收所有路由,使用 配置了全网格
instance-import策略instance-any。使用包含以下内容的策略instance-any进行配置instance-import时:instance-any可用于:policy-statement ... term ... frompolicy-statement ... frompolicy-statement ... term ... topolicy-statement ... to
instance-any没有参数。在 以外的
instance-import策略中使用instance-any没有任何效果。
配置许多不同的路由实例和对等组会影响规模和性能。
[
edit protocols bgp group neighbor] 层次结构级别的 BGPforwarding-contextCLI 配置将 BGP 邻接方的路由实例拆分为配置实例和转发实例。BGPforwarding-contextCLI 配置还支持将 BGP 对等方配置为route-server-client非转发实例,其中指定的实例是能够转发不属于无转发类型的主实例或路由实例的任何实例。
另请参阅
变更历史表
是否支持某项功能取决于您使用的平台和版本。 使用 Feature Explorer 查看您使用的平台是否支持某项功能。
no-install 语句消除了路由协议守护程序 (rpd) 与 Junos 系统中其他组件(如内核或分布式防火墙守护程序 (dfwd))之间的交互。