Optional Configurations: DHCP Relay and Multicast
Use these examples to configure optional DHCP relay and multicast forwarding on your collapsed spine data center architecture.
Configure DHCP Relay (Optional)
Requirements
DHCP server.
The devices that you configured in How to Configure a Collapsed Spine with EVPN Multihoming.
Overview
Use this section to configure the spine switches to relay the
DHCP requests to the DHCP server. Enable DHCP relay in a routing instance
with the forward-only option. The forward-only option ensures that DHCP packets are forwarded on the switch but
that no DHCP server client bindings are created.
Topology
The DHCP server can be located anywhere in the data center or in a different data center. In this case, the DHCP server is connected to one of the ToR switches in DC1 and the IP address of the DHCP server is 192.168.201.10. The DHCP relay topology is shown in Figure 1.
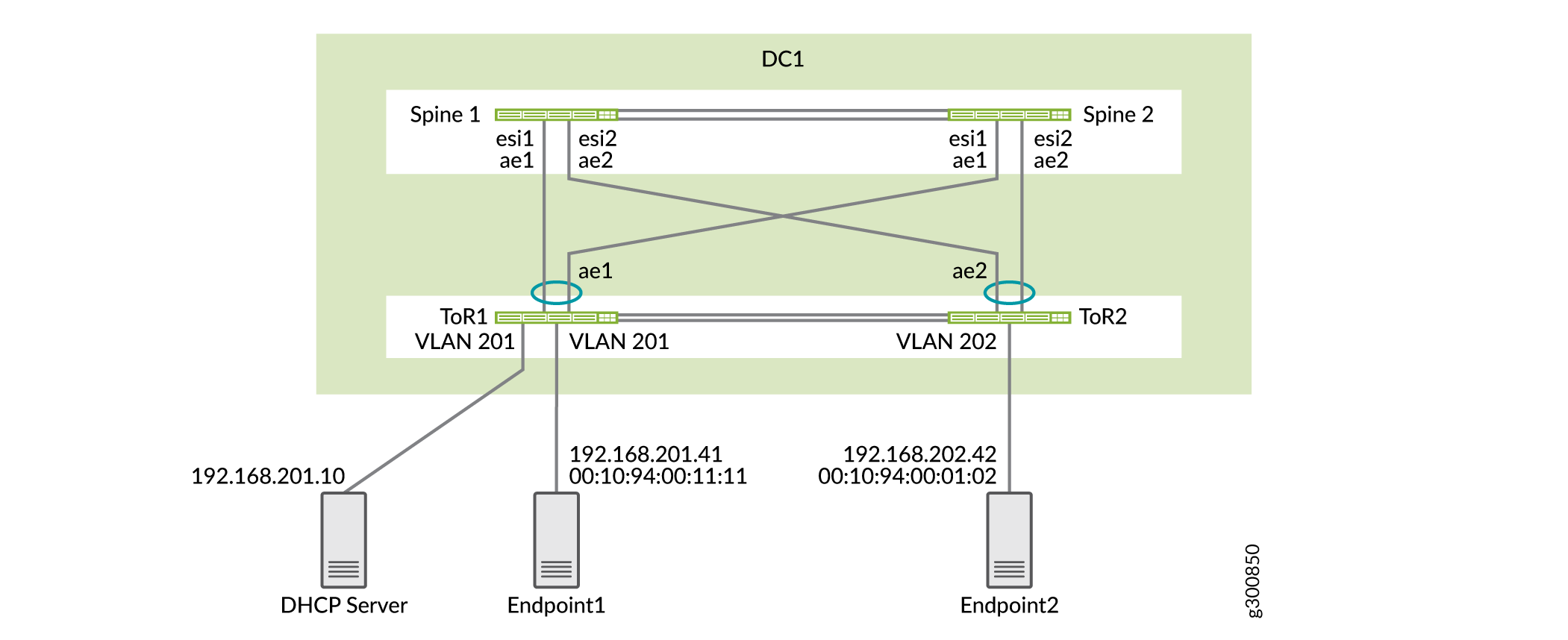
Configuration
Configure Spine 1
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure the DHCP relay on the first routing instance.
set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay forward-only set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay server-group Server_Group1 192.168.201.10 set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 active-server-group Server_Group1 set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 route-suppression destination set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.201 set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.202 set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.203
Configure the DHCP relay on the second routing instance.
set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay forward-only set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay server-group Server_Group1 192.168.201.10 set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 active-server-group Server_Group1 set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 route-suppression destination set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.211 set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.212 set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.213
Verify the DHCP relay on Spine 1.
user@spine1> show dhcp relay statistics routing-instance JNPR_1_VRF Packets dropped: Total 50741 Invalid server address 0 dhcp-service total 50738 Messages received: BOOTREQUEST 3 DHCPDECLINE 0 DHCPDISCOVER 1 DHCPINFORM 0 DHCPRELEASE 0 DHCPREQUEST 2 DHCPLEASEACTIVE 0 DHCPLEASEUNASSIGNED 0 DHCPLEASEUNKNOWN 0 DHCPLEASEQUERYDONE 0 Messages sent: BOOTREPLY 2 DHCPOFFER 0 DHCPACK 2 DHCPNAK 0 DHCPFORCERENEW 0 DHCPLEASEQUERY 0 DHCPBULKLEASEQUERY 0
Configure Spine 2
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure the DHCP relay on the first routing instance.
set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay forward-only set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay forward-only-replies set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay server-group Server_Group1 192.168.201.10 set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 active-server-group Server_Group1 set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 route-suppression destination set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.201 set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.202 set routing-instances JNPR_1_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.203
Configure the DHCP relay on the second routing instance.
set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay forward-only set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay forward-only-replies set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay server-group Server_Group1 192.168.201.10 set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 active-server-group Server_Group1 set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 route-suppression destination set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.211 set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.212 set routing-instances JNPR_2_VRF forwarding-options dhcp-relay group Relay_Group1 interface irb.213
Verify the DHCP relay on Spine 2.
user@spine2> show dhcp relay statistics routing-instance JNPR_1_VRF Packets dropped: Total 50741 Invalid server address 0 dhcp-service total 50738 Messages received: BOOTREQUEST 3 DHCPDECLINE 0 DHCPDISCOVER 1 DHCPINFORM 0 DHCPRELEASE 0 DHCPREQUEST 2 DHCPLEASEACTIVE 0 DHCPLEASEUNASSIGNED 0 DHCPLEASEUNKNOWN 0 DHCPLEASEQUERYDONE 0 Messages sent: BOOTREPLY 2 DHCPOFFER 0 DHCPACK 2 DHCPNAK 0 DHCPFORCERENEW 0 DHCPLEASEQUERY 0 DHCPBULKLEASEQUERY 0
Configure Multicast for Intra-VNI Traffic (Optional)
Requirements
The devices that you configured in How to Configure a Collapsed Spine with EVPN Multihoming.
Overview
Use this section to configure your collapsed spine architecture to allow intra-VNI multicast traffic. The multicast source and receivers are part of the same VLAN.
The collapsed spine architecture with QFX5120 spine switches does not support inter-VNI multicast traffic.
Topology
This section includes the configuration for two multicast groups. The first is multicast group 224.0.0.66. As shown in Figure 2, the multicast source is Endpoint 62. The multicast receiver, Endpoint 61, is connected to ToR 2. Both the source and receiver are in the same VLAN, so traffic between them is intra-VNI multicast traffic.
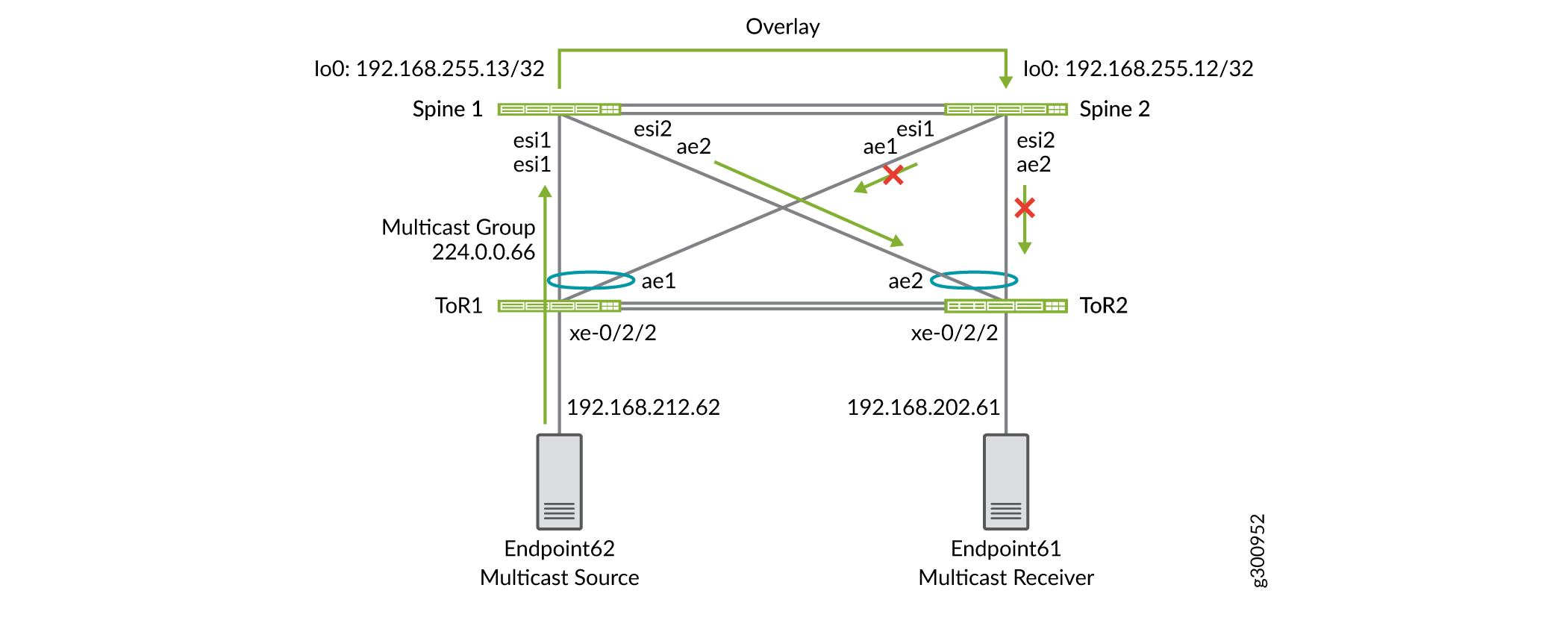
Configuration
- Configure Devices
- Verification for Multicast Group 224.0.0.66
- Verification for Multicast Group 224.0.0.65
Configure Devices
Step-by-Step Procedure
Enable IGMP snooping for all VLANs on both spine switches.
set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-201 immediate-leave set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-202 immediate-leave set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-211 immediate-leave set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-212 immediate-leave
Configure the ToR switches with IGMP snooping for all VLANs.
set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-201 immediate-leave set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-201 interface ae1.0 multicast-router-interface set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-202 immediate-leave set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-202 interface ae1.0 multicast-router-interface set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-211 immediate-leave set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-211 interface ae1.0 multicast-router-interface set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-212 immediate-leave set protocols igmp-snooping vlan VLAN-212 interface ae1.0 multicast-router-interface
Verification for Multicast Group 224.0.0.66
Step-by-Step Procedure
Verify IGMP snooping membership on ToR 2.
user@tor2> show igmp snooping membership Instance: default-switch Vlan: VLAN-201 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0 Vlan: VLAN-202 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0 Learning-Domain: default Interface: xe-0/2/2.0, Groups: 1 Group: 225.0.0.66 Group mode: Exclude Source: 0.0.0.0 Last reported by: 192.168.202.61 Group timeout: 177 Type: Dynamic Vlan: VLAN-211 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0 Vlan: VLAN-212 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0Verify IGMP snooping membership on Spine 1.
user@spine1> show igmp snooping evpn membership detail Instance: default-switch Vlan: VLAN-201, EVPN-Core-NH: 524301 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae2.0, Groups: 0 Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0 Vlan: VLAN-202, EVPN-Core-NH: 524303 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae2.0, Groups: 1 Group: 225.0.0.66 Group mode: Exclude Source: 0.0.0.0 Type: Local Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0 Vlan: VLAN-211, EVPN-Core-NH: 524307 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae2.0, Groups: 0 Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0 Vlan: VLAN-212, EVPN-Core-NH: 524298 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae2.0, Groups: 0 Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0Verify IGMP snooping membership on Spine 2.
user@spine2> show igmp snooping evpn membership detail Instance: default-switch Vlan: VLAN-201, EVPN-Core-NH: 524298 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae2.0, Groups: 0 Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0 Vlan: VLAN-202, EVPN-Core-NH: 524300 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae2.0, Groups: 1 Group: 225.0.0.66 Group mode: Exclude Source: 0.0.0.0 Type: Remote Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0 Vlan: VLAN-211, EVPN-Core-NH: 524304 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae2.0, Groups: 0 Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0 Vlan: VLAN-212, EVPN-Core-NH: 524306 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ae2.0, Groups: 0 Interface: ae1.0, Groups: 0Verify the designated forwarder on Spine 1. The output shows that Spine 1 is the designated forwarder for all Ethernet segments.
user@spine1> show evpn instance designated-forwarder Instance: default-switch Number of ethernet segments: 12 ESI: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:01:01 Designated forwarder: 192.168.255.13 ESI: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:01:02 Designated forwarder: 192.168.255.13 ESI: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:01:11 Designated forwarder: 192.168.255.13 ESI: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:01:12 Designated forwarder: 192.168.255.13Verify the multicast traffic flow on Spine 1.
Based on LAG hashing, ToR 1 sends the multicast traffic to Spine 1. The traffic reaches Spine 1 on the AE1 interface. Spine 1 forwards this traffic through AE2 based on IGMP group membership.
user@spine1> monitor interface traffic detail Interface Link Input packets (pps) Output packets (pps) ae1 Up 6742041146 (2946565) 3924 (1) ae2 Up 2536 (0) 6741411465 (2948357)
Verify the multicast traffic flow on Spine 2.
Based on LAG hashing, ToR 1 does not send the multicast traffic to Spine 2. Spine 2 receives this traffic from Spine 1 through the overlay, but it drops this traffic and does not forward it to AE2.
user@spine2> monitor interface traffic detail Interface Link Input packets (pps) Output packets (pps) ae1 Up 2547 (0) 3762 (1) ae2 Up 2462 (0) 3769 (1)
Verification for Multicast Group 224.0.0.65
Step-by-Step Procedure
Verify the designated forwarder on Spine 1. The output shows that Spine 1 is still the designated forwarder for all the Ethernet segments.
user@spine1> show evpn instance designated-forwarder Instance: default-switch Number of ethernet segments: 12 ESI: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:01:01 Designated forwarder: 192.168.255.13 ESI: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:01:02 Designated forwarder: 192.168.255.13 ESI: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:01:11 Designated forwarder: 192.168.255.13 ESI: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:01:12 Designated forwarder: 192.168.255.13Verify the multicast traffic flow on Spine 1.
Based on LAG hashing, ToR 1 does not send the multicast traffic to Spine 1, so there is no incoming traffic for this multicast group on Spine 1. Spine 1 receives the multicast stream from Spine 2 through the overlay. Spine 1 drops the traffic and does not forward it to AE2 because Spine 1 and Spine 2 are part of the same Ethernet segments for AE1 and AE2.
user@spine1> monitor interface traffic detail Interface Link Input packets (pps) Output packets (pps) et-0/0/51 Up 4750 (2947862) 4741 (3) ae1 Up 1027 (1) 1543 (1) ae2 Up 991 (0) 1537 (1)
Verify the multicast traffic flow on Spine 2.
Based on LAG hashing, ToR 1 sends the multicast traffic to Spine 2. Spine 2 is not the designated forwarder for the Ethernet segments, but Spine 2 still forwards this traffic to receivers on AE2 based on the local bias rules for multicast forwarding. See Overview of Selective Multicast Forwarding for more information about the EVPN multicast forwarding rules.
user@spine2> monitor interface traffic detail Interface Link Input packets (pps) Output packets (pps) et-0/0/51 Up 4603 (3) 3458201844 (2948641) ae1 Up 2985999842 (2948821) 1542 (1) ae2 Up 1009 (0) 2986000009 (2947024)
You have successfully configured multicast traffic forwarding on your network.
