Deploy Wi-Fi 7 with AP47
Explore the features and benefits of Wi-Fi 7. Learn about deploying Wi-Fi 7 in your network using the Juniper AP47.
AP47 Access Point Overview
The Juniper® AP47 High Performance Access Point is an indoor Wi-Fi 7 access point (AP) that provides virtual Bluetooth® Low Energy (vBLE) for enterprises that require increased channel width and capacity.
The AP47 has three IEEE 802.11be data radios, which deliver up to 4x4 multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) with four spatial streams. The AP47 also has a fourth 802.11be radio that is dedicated for scanning. The AP uses this radio for radio resource management (RRM), wireless security, and analytics.
The AP47 has a vBLE antenna array to enable location services such as asset visibility, wayfinding, and other services without battery-powered beacons. The AP47 includes two 802.15.4 capable radios, a built-in Global Navigation Satellite System/Global Positioning System (GNSS/GPS) radio, as well as Ultra-Wideband (UWB) capabilities.
The AP can operate simultaneously in the 2.4-GHz, 5-GHz, and 6-GHz bands. The AP is backward compatible with the 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax wireless standards.
AP47 Access Point Models
| Model | Antenna |
|---|---|
| AP47 | Internal omnidirectional |
| AP47D | Internal directional (60x60) |
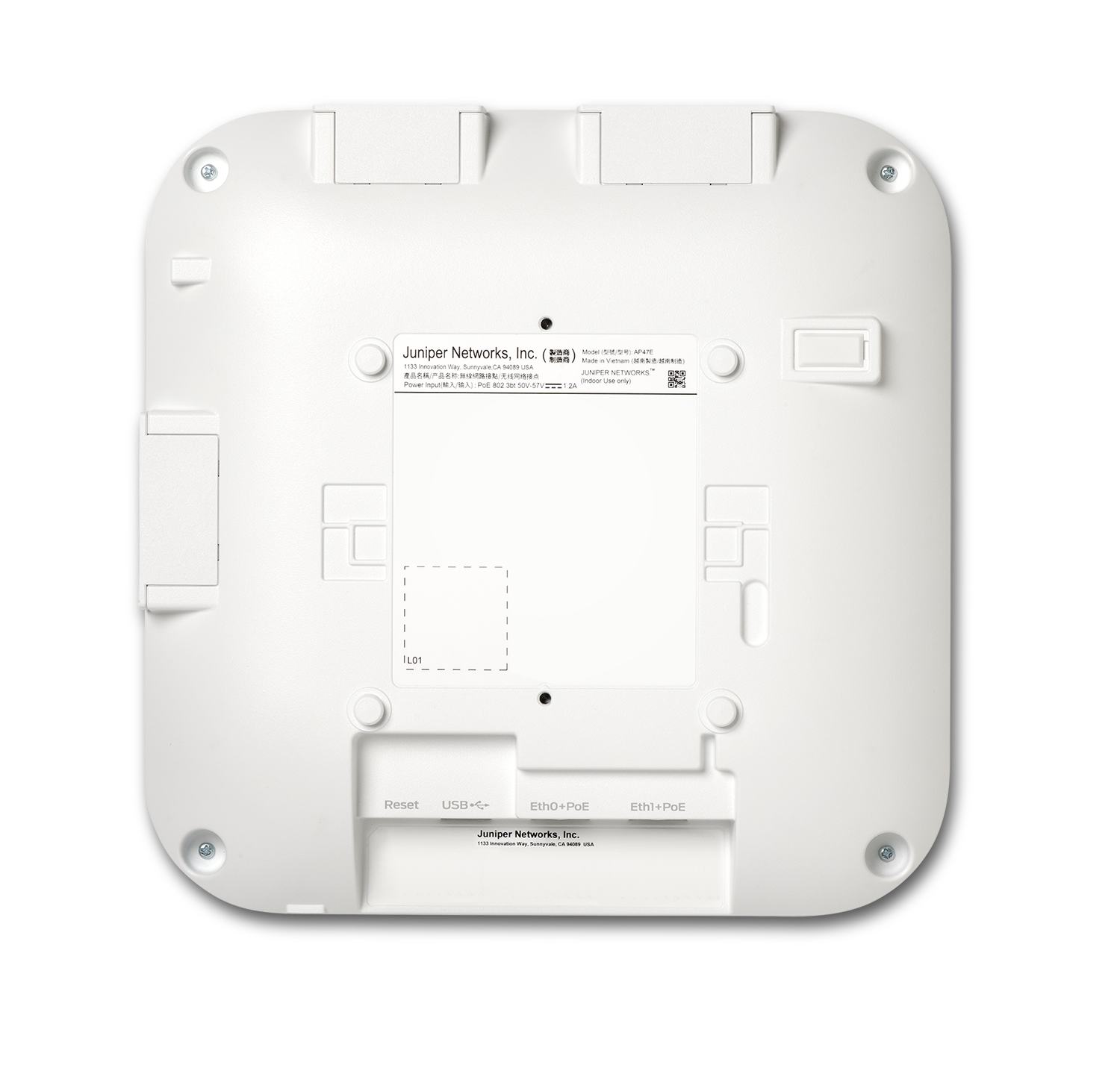
| AP47E | External |


Key Features of AP47 Access Points
-
Wi-Fi 7 support—The AP47 supports Wi-Fi 7, which allows for higher throughput and lower interference. Wi-Fi 7 can support 320 MHz wide radio channels in the 6GHz band and offers 4K QAM.
-
Dual Ethernet—The AP47 can connect to two Ethernet inputs at the same time, allowing for PoE redundancy and Ethernet failover.
-
Three models - AP47, AP47D, AP47E.
-
Dual 5 GHz or Dual 6 GHz support.
-
Dedicated scan radio.
-
U-NII-4 channel support.
-
Virtual Bluetooth Low Energy (vBLE) and Ultra-wideband (UWB) technologies for enhanced location use cases.
-
Dual 802.15.4-capable, multi-personality IoT radios.
-
Multiple sensors including pressure, accelerometer, temperature, and GPS.
For AP47 specifications, see the AP47 Datasheet.
Choose Between AP47, AP47D, and AP47E
Learn the differences between the different AP47 models to help you choose the best model for your deployment.
Juniper Networks offers three versions of the AP47:
-
The AP47 has traditional integrated omnidirectional antennas. It is the general usage AP in the lineup. It is used for general to high-density deployments for coverage in open areas such as conference rooms, open office spaces, retail spaces, etc.
-
The AP47D has 60x60° integrated directional antennas and is meant to be used in everyday deployments where you are looking for higher capacity. In many environments, AP47D can be used instead of AP47 to support higher AP density. For example in carpeted enterprise, education, or any environment where you are running into co-channel contention issues on 5 or 6 GHz due to the density of APs. AP47D provides better signal control and the capacity benefits of directional antennas without the added overhead of external antennas. AP47D is also a great fit for auditoriums, lecture halls or other high density environments that would benefit from a 60x60 pattern.
-
The AP47E allows for the use of external antennas and complete customization of the AP’s coverage pattern. It is suited for deployment in very high density areas where the direction of the signal needs to be controlled using different types of antennas or you where you may need a different coverage pattern than the 60x60. For example, in large public venues with a high density patch, or high racking warehousing through a warehouse style antenna. The AP47E uses the 14 lead antennas with three pluggable connectors (MPC). Because the AP47E has dual 5 and dual 6 GHz capability, it uses different external antennas than the AP45E.
Power Options for the AP47
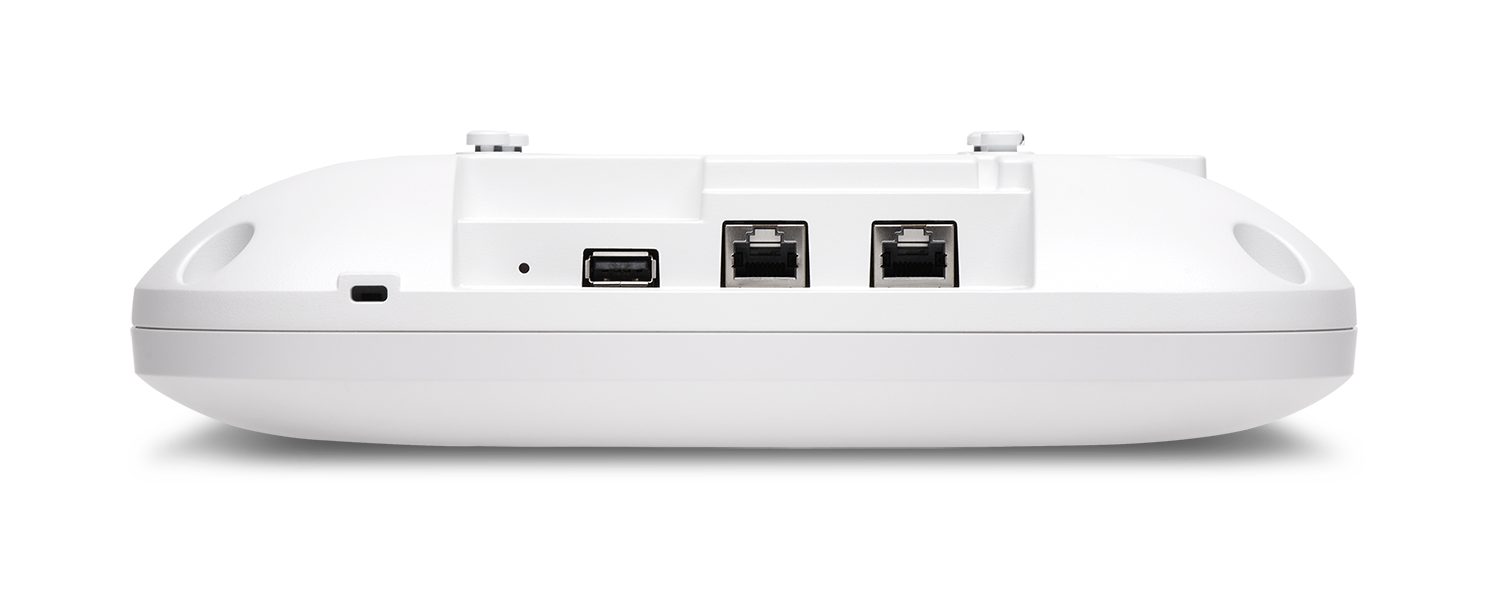
The AP47 has dual 10 GbE multigigabit Ethernet ports, both of which support power over Ethernet (PoE) in.

The AP47 requires 802.3bt power (Class 6 - 60W) for full functionality. It requires approximately 29 Watts of power at the powered device (PD) for full Wi-Fi functionality. When powered by 802.3at power, the AP operates with reduced functionality. The three Wi-Fi radios operate at 2x2:2, or 4x4:4 with any two Wi-Fi radios enabled. The AP47 keeps the scanning radio, and the BLE, GPS, and UWB radios active at all times, regardless of the power source.
Either or both of the ports can be used to power the AP using PoE. You can see the functionality differences below:
-
802.3bt Power Source
-
Single 802.3bt in – Full functionality
-
Dual 802.3bt in – Full functionality
-
-
802.3.at Power Source
-
Single 802.3at in – Reduced Wi-Fi functionality – Three 2x2 or Two 4x4
-
Dual 802.3at in – Full functionality
-
-
Mixed Power Source
-
One 802.3bt in and one 802.3at in – Full functionality
-
NOTE: When two 802.3bt sources power the AP, the device supports full Ethernet and PoE redundancy. When two 802.3at sources power the AP, a power-sharing configuration is created, where the AP merges power from both ports to ensure full functionality.
In the power-sharing configuration, the AP maintains full Ethernet redundancy; however, it may experience a brownout or reboot if one power source fails. Internal testing has proven that brownouts or reboots are rare occurrences. To ensure maximum redundancy, use 802.3bt power sources.
Ensure you use 802.3bt or 802.3at compliant PoE switches or injectors to power the AP47.
See PoE Requirements for Juniper Mist APs for AP47 power requirements.
Ethernet Redundancy and Connecting the AP47 to the Network
The two 10 Gbps Ethernet ports on the AP47 not only provide PoE redundancy but also support redundant Ethernet links to ensure continued operation during infrastructure outages or upgrades in mission critical environments. The AP47 supports single uplink, dual uplink, individual uplink and downlink, and dual downlink connectivity.
Single Uplink
For single uplink we recommend that you connect Eth0 to the network uplink for simplicity and consistency. However, there is no restriction on using Eth1 to connect to the network uplink on an AP47.
If you enforce a MAC limit on your AP switch ports, such as when you tunnel traffic to a Mist Edge, you must configure the MAC limit to two or more.
Dual Uplink
If you leverage dual uplinks, here are a few good things to know:
-
Connecting the AP47 to the network requires no switch configuration. You can connect the AP to the same switch or different switches. Ensure the L2 VLAN is the same on both switch ports so clients don’t need to obtain new IP addresses if a failover occurs.
-
New AP47s arrive configured with dual uplinks in an active-standby configuration.
-
You can configure uplink, downlink and dual downlink (mesh relay) connectivity by manually configuring the port VLANs in the Mist portal.
-
-
The AP47 employs passive failover detection based on link status and activity which results in three to five-second failover.
-
The AP47 is capable of non-traffic-impacting (hitless) PoE failover when you use dual 802.3bt power sources.
-
If you use two 802.3at or mixed 802.3at and 802.3bt power sources, the AP47 combines the received power for full functionality. The AP may brownout or reboot in the event it needs to reduce functionality due to a single power source failure.
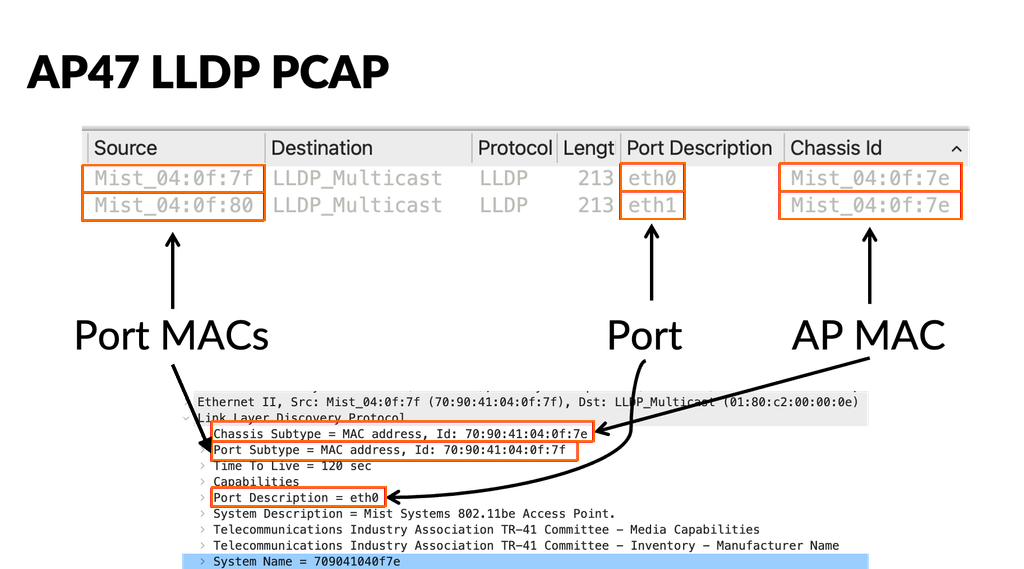
AP47 Ethernet MAC Addresses
-
The AP47 uses three MAC addresses for Ethernet, because it supports multiple uplinks. The MAC address for the AP wireless interface is known as the AP MAC address, then each Ethernet port MAC address is incremented by 1. For example:
-
AP MAC Address = 70:90:41:XX:XX:7E
-
AP Eth0 MAC Address = 70:90:41:XX:XX:7F
-
AP Eth1 MAC Address = 70:90:41:XX:XX:80
-
-
The AP47 uses the AP MAC address for switch virtual interfaces (SVIs) and IP communication, such as DHCP, ARP, DNS, NTP, AP Management, L2TPv3, and RADIUS.
-
The AP47 uses the unique Ethernet port MACs for link-local packets, such as LLDP and Dot1x Supplicant.
-
Connected switches use the AP47's multiple MAC addresses primarily when you configure switch-side MAC-based policies. For example:
-
To perform MAC authentication bypass (MAB) authentication against the APs, add both the AP MAC address and the port MAC addresses to your switch's MAB database,
-
If you leverage LLDP, the Chassis ID is the AP MAC address.
-
If you enforce a MAC limit on your AP switch ports, such as when tunneling traffic to a Mist Edge, set the MAC limit to two or more: one for the Ethernet MAC and one for the AP MAC.
-
-
If you leverage 802.1X authentication against the APs with dual uplinks, both ports authenticate to the network independently of each other. Thus, two separate auths appear in your RADIUS server.
Wi-Fi 7 Deployment Considerations
The AP47 supports Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be Extremely High Throughput), which provides higher throughput and lower interference as compared to other Wi-Fi standards. Wi-Fi 7 also introduces several new features such as 4K Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM), Multi Resource Unit (Multi-RU), and Multi-Link Operation (MLO) among others.
With the introduction of Wi-Fi 6E, the Wi-Fi Alliance enforced the use of WPA3 in the 6 GHz band. With Wi-Fi 7, the use of WPA3 or OWE is mandatory on any WLAN in any band that has Wi-Fi 7 enabled.
The mandatory security items in Wi-Fi 7 are:
-
WPA3 or OWE
-
Management Frame Protection
-
GCMP256 Cipher
-
Beacon Protection
-
Authentication and Key Management (AKM) type 24 (SAE-GDH) or type 25 (FT+SAE-GDH) with the use of WPA3 Personal
The GCMP256 encryption protocol is mandatory on every Wi-Fi 7 BSS, regardless of the security type.
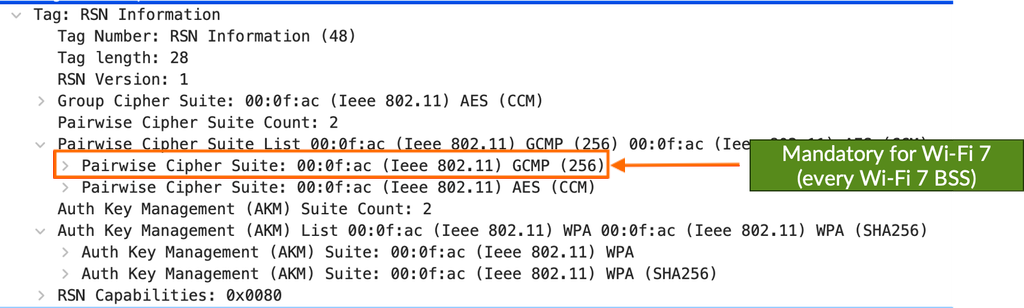
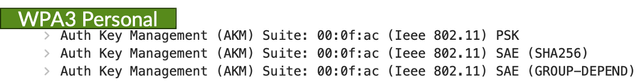
When you create WLANs in the Mist UI, Wi-Fi 7 is enabled by default and Mist automatically enables the mandatory Wi-Fi 7 security features.
For additional information about Wi-Fi 7, see: Wi-Fi (802.11be) Technology.
Tri-Band Radio Operation on the AP47
The AP47 has three Wi-Fi 7 data radios and supports the following modes of operation:
-
Tri-band mode—This mode operates simultaneously in the 2.4-GHz, 5-GHz, and 6-GHz bands.
-
2.4 GHz band—channels 1-13
-
5 GHz band—channels 36-177
-
6 GHz band—channels 1-233
-
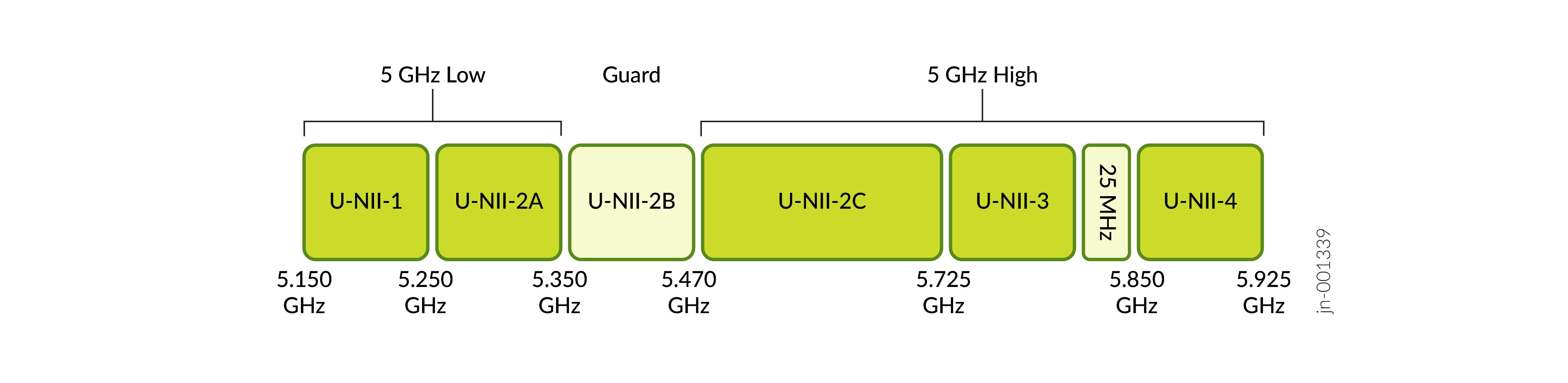
Dual 5 GHz mode—This mode splits the 5 GHz band into high channels and low channels.
-
5 GHz band (low)—U-NII-1 and U-NII-2A (channels 36-64)
-
5 GHz band (high)— U-NII-2C, U-NII-3, and U-NII-4 (channels 100-177)
-
6 GHz band—(channels 1-233)
-
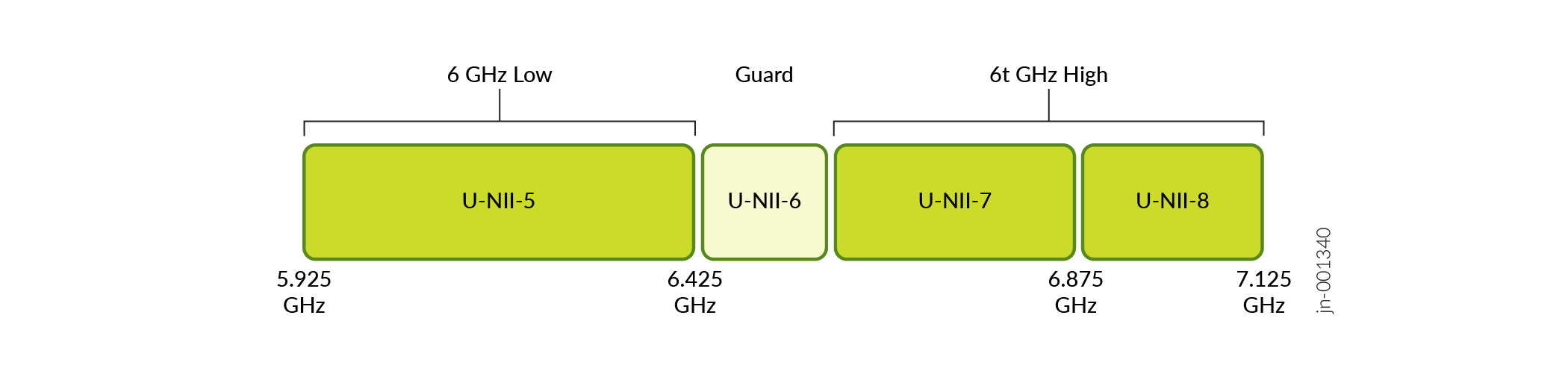
Dual 6 GHz mode—This mode splits the 6 GHz band into high channels and low channels.
-
5 GHz band—channels (36-177)
-
6 GHz band (low)—U-NII-5 (channels 1-93)
-
6 GHz band (high)—U-NII-7 and U-NII-8 (channels 117-233)
 Note: Dual 5 and dual 6 GHz mode support varies per country based on the allowed channels in the country.
Note: Dual 5 and dual 6 GHz mode support varies per country based on the allowed channels in the country.-
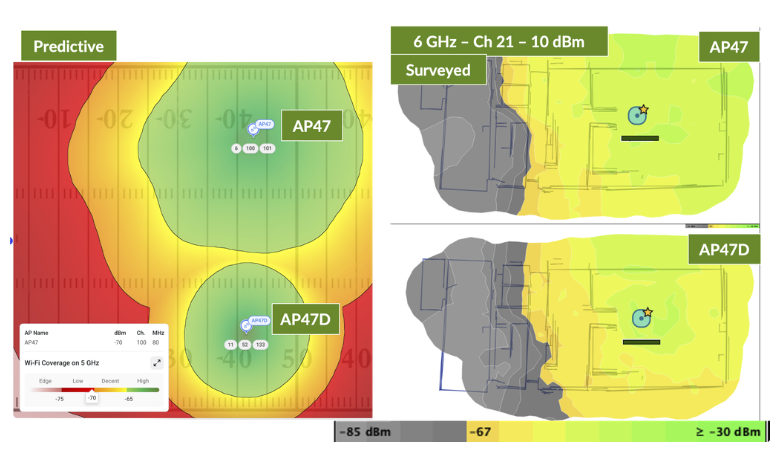
GPS and GNSS Support on the AP47
The AP47 supports L1 and L5 based Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). The reason for including a Global Positioning System (GPS) chip on the AP is to support Standard Power use cases in 6 GHz. These use cases require suppling geolocation information to the Automated Frequency Coordination (AFC) system. However, GNSS reception indoors can be challenging, especially as your AP placement approaches the center of a building..
You will achieve the strongest GNSS reception indoors when you deploy AP47s near the edge of the building or close to exterior windows.