PoE Requirements for Juniper APs
Understand the Power over Ethernet (PoE) requirements to ensure that your access points (APs) receive sufficient power.
The following table lists the power over Ethernet (PoE) requirements for Juniper Mist Access Points (APs). The notes below the table provide additional information for understanding the dynamic power mode available with most Juniper APs.
| Generation | Model | Minimum Functionality | Full Functionality | Power in Watts for Full Functionality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi 7 | AP36 | 802.3at | 802.3bt | 29.3 watts |
| AP37 | 802.3at | 802.3bt | 29.3 watts | |
| AP47/D/E | 802.3at/bt | 802.3bt | 29.3 watts | |
| AP66 | dynamic | 25.5 watts | ||
| Wi-Fi 6E | AP64 | 802.3af | 802.3bt | 13 watts |
| AP45/45E | dynamic | 29.3 watts | ||
| AP34 | dynamic | 20.9 watts | ||
| AP24 | 802.3af | 802.3bt | 13 watts | |
| Wi-Fi 6 | AP63 | 802.3at | 802.3bt | 25.2 watts |
| AP43 | 802.3at | 802.3bt | 25.5 watts | |
| AP33 | 802.3af | 802.3at | 19.5 watts | |
| AP32 | 802.3af | 802.3at | 19.5 watts | |
| AP12 | 802.3af | 802.3at | 12.9 watts | |
| Wi-Fi 5 | AP61 | 802.3at | 802.3at | 19.5 watts |
| AP41 | 802.3at | 802.3at | 19.5 watts | |
| AP21 | 802.3af | 802.3at | 12.9 watts | |
| Other | BT11 | 802.3af | 802.3af | 5.5 watts |
|
* Power required at the power device to support all Wi-Fi radios and all spatial streams. |
||||
Full Power, Reduced Functionality, and Insufficient Power
Although you may be able to power up an AP from any given PoE interface, if the interface does not meet the requirement for full power, the performance of the AP will be unpredictable. In this case, a warning appears on the Access Points dashboard, indicating either that the AP is running with reduced functionality (dynamic power mode), or that the AP is only able to connect to the cloud.
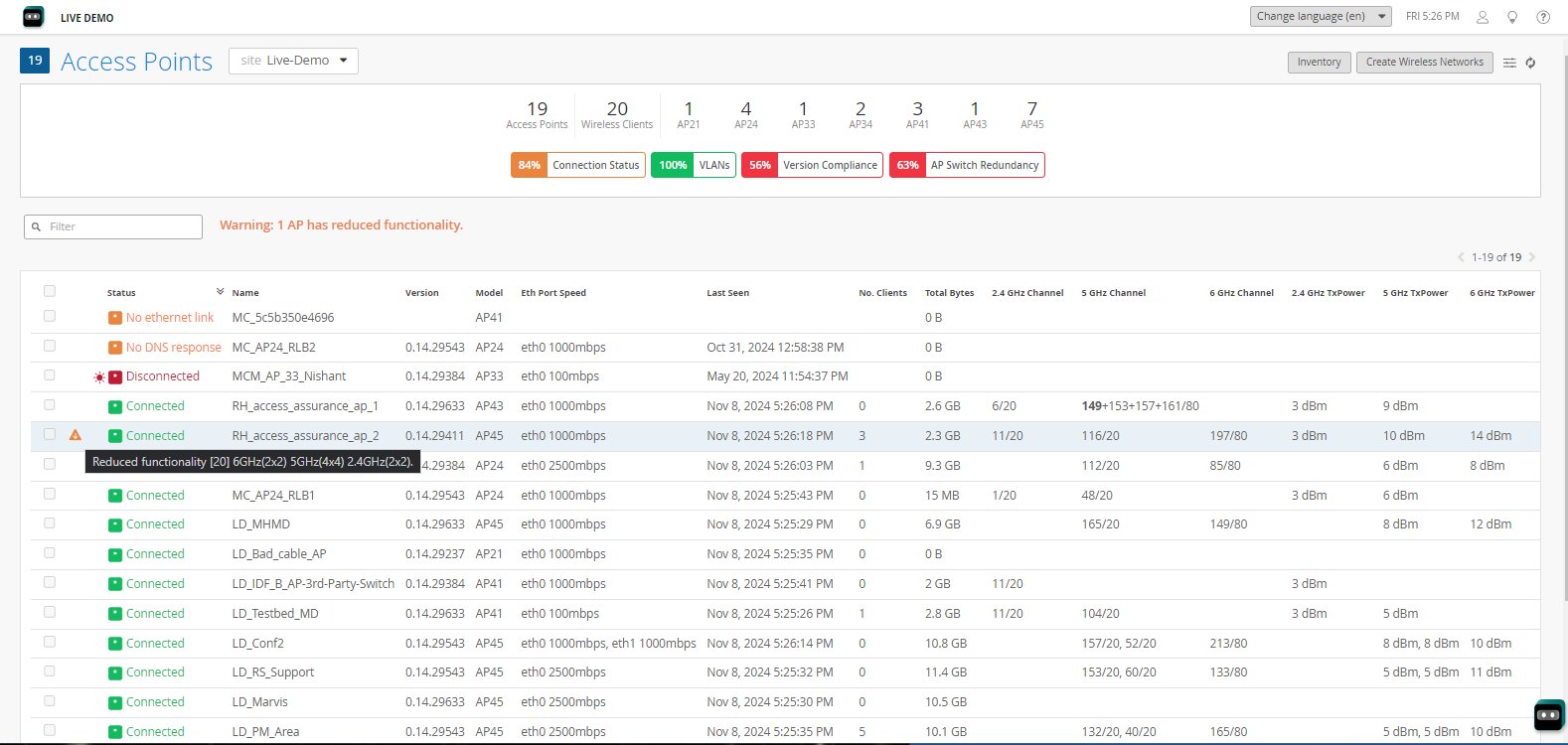
To see the exact power required, power requested, and power allocated for a given AP, click the AP name in the Access Point list, and in the screen that appears, scroll down to the Power Mode section.
Dynamic Power Mode
Many Juniper Mist APs can leverage a dynamic power mode which allows them to automatically reduce their operating capabilities according to the power available, for example by reducing from 4x4:4 spatial streams to 2x2:2 spatial streams.
-
AP47—The AP47 has two 10 multi-gigabit Ethernet ports, both of which support power over Ethernet (PoE) in. Either port, or both ports, can be used to power the AP. It requires 802.3bt power (approximately 29 watts at the PD ) for full Wi-Fi functionality and to power the USB port.
-
- Single 802.3bt in—Full functionality
- Both 802.3bt in—Full functionality. When both ports are connected, LLDP details and PoE statistics for the active and standby ports are available in the Connected Switch Properties section of the AP details page.
-
On 802.3at power, the AP will operate with reduced functionality. If all three Wi-Fi radios are enabled, they will operate at 2x2:2. If only two Wi-Fi radios are enabled, they will operate at 4x4:4 The scanning radio, BLE radios, GPS and UWB are always enabled regardless of power source.
- Single 802.3at in—Reduced Wi-Fi functionality—tri 2x2 or two 4x4
- Both 802.3at in—Full functionality
-
Mixed Power Source
- One 802.3bt in and one 802.3at in—Full functionality
-
-
Note: Regarding the failover behavior of AP47 when both Ethernet ports are used for uplink. There is full Ethernet and PoE redundancy support when the AP is powered by two 802.3bt sources. When the AP is powered by two 802.3at sources this is considered as power sharing—the power from both ports is combined for full functionality. In this case, there is full Ethernet redundancy, however the AP may brownout or reboot in the event one of the power sources fails. In lab testing this is a rare occurrence, however we want to call out for the highest redundancy, please ensure 802.3bt power sources are used.
Please ensure 802.3bt or 802.3at compliant PoE switches or injectors are used to power the AP47
-
AP45 or AP45E—Requires 802.3bt for full functionality. The dedicated scanning radio and BLE are always active regardless of power.
-
At 802.3at power, with any two data radios enabled, both will operate in 4×4 mode. In order to provide power to the USB with 802.3at power, only one radio can be enabled at start-up. With all three data radios enabled, the 2.4 GHz radio will run in 2×2 mode, the 5 GHz radio will run in 4×4 mode, and the 6 GHz radio will run in 2×2 mode. With all three data radios enabled and 5 GHz dual band also enabled, one 5 GHz radio will run in 2x2 mode and the other will run in 4×4 mode. For 5 GHz and 6 GHz dual band, both radios will run in 4×4 mode.
-
At 802.3af, an AP45 or AP45E can connect to the cloud, but only to let you know it needs more power.
-
-
AP61 or AP61E, AP63 or AP63E—Always require 802.3at or PoE+ (because these APs consume a maximum of 25.5W).
-
AP41 or AP41E, AP43 or AP43E—Always require 802.3at or PoE+ (because these APs consume a maximum of 25.5W).
-
AP37 and AP36—Requires 802.3bt for full functionality. On 802.3at power, the AP will operate with reduced functionality, which means a combination of 2x2 and 4x4 modes depending on which radios (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz) are active. At 802.3af, the AP can connect to the cloud, but only to let you know it needs more power.
-
AP34—At 802.3af, the AP can connect to the cloud, but only to let you know it needs more power.
-
AP33 and AP32—At 802.3af power, the 5-GHz radio operates in 2×2 mode instead of 4×4 mode. Eth0 port operates at a maximum speed of 1 Gbps Eth1 port is disabled.
-
AP24 and AP64—Always require 802.3af.
-
AP12 —Only requires 802.3at if using PoE out; otherwise, 802.3af power is sufficient.
More Information
PoE injects DC power onto a standard twisted pair Ethernet cable without disturbing the data traffic being transmitted over the same cable. The power sourcing equipment (PSE), such as a supported Juniper switch, supplies the power and the powered device (PD), such as a Juniper Mist AP, gets its power from the switch. Because Ethernet is an isolated network, each twisted pair connects to a different data transformer.
- The IEEE 802.3bt PoE standard provides for Ethernet cables to carry up to 90 watts of DC power for connected devices (by means of 4 twisted pairs).
- The IEEE 802.3at-2009 PoE+ PoE standard provides for up to 25.5 watts.
- The IEEE 802.3af-2003 PoE standard provides for up to 15.4 watts (by means of 2 twisted pairs).
When connecting to either an 802.3at or 802.3af interface, most Juniper Mist APs use hardware detection to determine the PoE interface type. AP45, AP43, and AP34 series will also detect BT power. After the hardware detection, the APs use LLDP, when available, to negotiate their specific power requirements.
Note that for most Cisco switches, LLDP is disabled by default so you must enable it on the interface before connecting an AP that requires 802.3at or higher, otherwise the interface will support 802.3af only.
