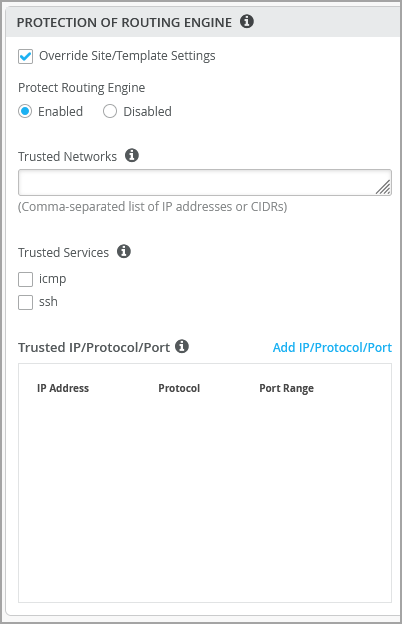
Protection of Routing Engine
The Protection of Routing Engine feature ensures that the Routing Engine accepts traffic only from trusted systems. Enabling this feature results in creation of a stateless firewall filter that discards all traffic destined for the Routing Engine, except those from the specified trusted sources. Protecting the Routing Engine involves filtering incoming traffic on the router’s lo0 interface. Enabling this feature on Juniper Switches is suggested as a best practice.
Configure Protection of Routing Engine
When Protection of Routing Engine is enabled, Mist by default ensures that the following services (if configured) are allowed to communicate with the switch: BGP, BFD, NTP, DNS, SNMP, TACACS, RADIUS, and Mist cloud connectivity.
If you want to additionally configure ICMP or SSH to access the switch from, you can enable them under Trusted Services. Note that enabling ICMP and SSH opens these protocols to all networks.
If you want to configure the commonly used IP networks to access the switch from, you can configure that under Trusted Networks. Use this option if you want to access the switch from the entire network.
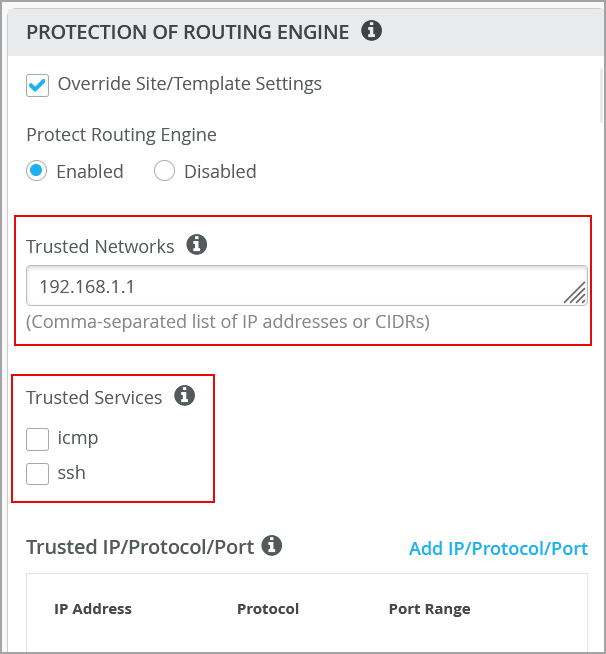
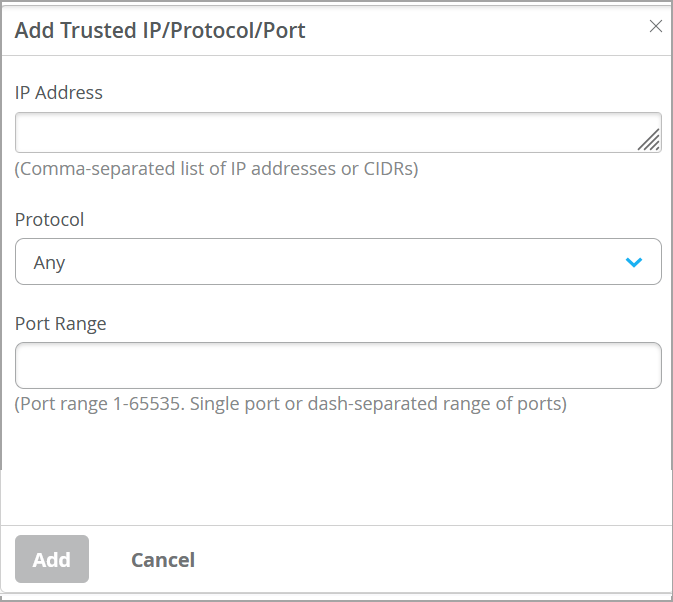
If you have other custom services (which are a specific combination of IP, Port and Protocol) that you would like to reach the switch from, you can configure them under Trusted IP/Port/Protocol. This option allows you to use a particular port and protocol to access the switch.
You can configure Protection of Routing Engine at the organization level (Organization > Switch Templates), at the site level (Site > Switch Configuration), and at the switch level (Switches > Switch Name).
The following procedure lists steps for configuring Protection of Routing Engine at the switch level.
To configure Protection of Routing Engine at the switch level:
Configuration Commands (CLIs)
"set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_mist_obssh from source-port [ 2200 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_mist_obssh then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dhcp from source-port [ 67 68 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dhcp from destination-port [ 67 68 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dhcp from protocol udp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dhcp then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bgp from source-prefix-list bgp_neighbors", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bgp from source-prefix-list bgp_vrf_neighbors", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bgp from destination-port [ 179 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bgp from protocol tcp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bgp then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bfd from source-prefix-list bgp_neighbors", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bfd from source-prefix-list bgp_vrf_neighbors", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bfd from destination-port [ 3784 4784 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bfd from protocol udp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bfd then accept", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_src from protocol udp", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_src from source-port 123", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_src then accept", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_dest from protocol udp", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_dest from destination-port 123", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_dest then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dns from source-port [ 53 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dns from protocol [ tcp udp ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dns then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_radius from source-prefix-list radius_servers", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_radius from destination-port [ 1812 1813 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_radius from protocol udp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_radius then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_tacacs from source-prefix-list tacacs_servers", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_tacacs from destination-port [ 49 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_tacacs from protocol tcp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_tacacs then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_snmp_clients from source-prefix-list snmp_clients", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_snmp_clients from destination-port [ 161 10161 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_snmp_clients from protocol udp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_snmp_clients then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts from source-prefix-list 10-216-192-1_32", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts from source-prefix-list 100-100-100-2_32", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts from source-prefix-list 8-8-8-8_32", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term otherwise then discard", "set groups top interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet filter input protect_re",
Verify Protection of Routing Engine Configuration
- Protection of Routing Engine (Trusted Networks Configuration)
- Protection of Routing Engine (Trusted Services Configuration)
Protection of Routing Engine (Trusted Networks Configuration)
Configuration commands (CLI)
set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts from source-prefix-list 10-216-192-1_32 set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts from source-prefix-list 100-100-100-2_32 set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts from source-prefix-list 8-8-8-8_32 set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts then accept set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term otherwise then log set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term otherwise then syslog set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term otherwise then discard
APIs
“switch_mgmt”: {
“protect_re”: {
“enabled”: true,
“trusted_hosts”: [
“10.216.192.1”,
“100.100.100.2”,
“8.8.8.8”
],
“allowed_services”: [],
“custom”: []
},
Use the show bgp summary command to get a summary of the status
of BGP connections:
{master:0}
mist@Border-switch-R2-U21> show bgp summary
Warning: License key missing; One or more members of the VC require ‘bgp’ license
Threading mode: BGP I/O
Default eBGP mode: advertise - accept, receive - accept
Groups: 2 Peers: 4 Down peers: 0
Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending
inet.0
10 6 0 0 0 0
bgp.evpn.0
68 34 0 0 0 0
Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Accepted/Damped...
10.255.240.3 65002 101 103 0 1 42:08 Establ
inet.0: 3/5/5/0
10.255.240.5 65003 35 33 0 3 11:51 Establ
inet.0: 3/5/5/0
100.100.100.2 65002 206 209 0 0 1:06:18 Establ
bgp.evpn.0: 25/34/34/0
default-switch.evpn.0: 22/30/30/0
default_evpn.evpn.0: 0/0/0/0
100.100.100.3 65003 57 55 0 3 11:48 Establ
bgp.evpn.0: 9/34/34/0
default-switch.evpn.0: 8/30/30/0
default_evpn.evpn.0: 0/0/0/0
To test the Trusted Networks functionality, ping 100.100.100.2 from the switch, as shown below. You can see that all the transmitted packets are received without any packet loss.
mist@Border-switch-R2-U21> ping 100.100.100.2
PING 100.100.100.2 (100.100.100.2): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 100.100.100.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=2.695 ms
64 bytes from 100.100.100.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=8.756 ms
64 bytes from 100.100.100.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=13.312 ms
64 bytes from 100.100.100.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=9.025 ms
--- 100.100.100.2 ping statistics ---
4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 2.695/8.447/13.312/3.781 ms
{master:0}
mist@Border-switch-R2-U21> ssh root@100.100.100.3
{master:0}
mist@Border-switch-R2-U21> ssh root@100.100.100.2
Password:
Last login: Fri Feb 3 04:57:20 2023 from 10.255.240.2
--- JUNOS 21.3R1.9 Kernel 64-bit JNPR-12.1-20210828.6e5b1bf_buil
root@CORE-1:RE:0%Also, ping or ssh a network other than the trusted networks. As you can see below, the ping shows 100 percent packet loss.
mist@Border-switch-R2-U21> ssh root@100.100.100.3
{master:0}
mist@Border-switch-R2-U21> ssh root@100.100.100.4
{master:0}
mist@Border-switch-R2-U21> ping 100.100.100.3
PING 100.100.100.3 (100.100.100.3): 56 data bytes
--- 100.100.100.3 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100% packet loss
{master:0}
mist@Border-switch-R2-U21> ping 100.100.100.4
PING 100.100.100.4 (100.100.100.4): 56 data bytes
--- 100.100.100.4 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100% packet lossProtection of Routing Engine (Trusted Services Configuration)
Configuration commands (CLI)
"set groups top interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet filter input protect_re", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_mist_obssh from source-port [ 2200 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_mist_obssh then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dhcp from source-port [ 67 68 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dhcp from destination-port [ 67 68 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dhcp from protocol udp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dhcp then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bgp from source-prefix-list bgp_neighbors", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bgp from source-prefix-list bgp_vrf_neighbors", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bgp from destination-port [ 179 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bgp from protocol tcp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bgp then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bfd from source-prefix-list bgp_neighbors", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bfd from source-prefix-list bgp_vrf_neighbors", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bfd from destination-port [ 3784 4784 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bfd from protocol udp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_bfd then accept", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_src from protocol udp", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_src from source-port 123", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_src then accept", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_dest from protocol udp", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_dest from destination-port 123", "set firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ntp_dest then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dns from source-port [ 53 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dns from protocol [ tcp udp ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_dns then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_radius from source-prefix-list radius_servers", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_radius from destination-port [ 1812 1813 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_radius from protocol udp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_radius then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_tacacs from source-prefix-list tacacs_servers", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_tacacs from destination-port [ 49 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_tacacs from protocol tcp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_tacacs then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_snmp_clients from source-prefix-list snmp_clients", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_snmp_clients from destination-port [ 161 10161 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_snmp_clients from protocol udp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_snmp_clients then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts from source-prefix-list 10-216-192-1_32", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts from source-prefix-list 100-100-100-2_32", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts from source-prefix-list 8-8-8-8_32", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term trusted_hosts then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ssh from destination-port [ 22 ]", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ssh from protocol tcp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_ssh then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_icmp from protocol icmp", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term allow_icmp then accept", "set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term otherwise then discard",
APIs
“switch_mgmt”: {
“protect_re”: {
“enabled”: true,
“trusted_hosts”: [
“10.216.192.1”,
“100.100.100.2”,
“8.8.8.8”
],
“allowed_services”: [
“ssh”,
“icmp”
],
“custom”: []
},
To test the trusted services configuration, log in to a device which is not on the trusted network.
mist@Distribution-2-R2-U07-> ping 100.100.100.1
PING 100.100.100.1 (100.100.100.1): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 100.100.100.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=63 time=36.941 ms
64 bytes from 100.100.100.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=45.158 ms
--- 100.100.100.1 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 36.941/41.050/45.158/4.108 ms
{master:0}
mist@Distribution-2-R2-U07-> ssh root@100.100.100.1
Password:
Last login: Fri Feb 3 07:23:35 2023 from 10.216.201.35
--- JUNOS 22.2R1.12 Kernel 64-bit JNPR-12.1-20220623.dbb31e0_buil
root@Border-switch-R2-U21:RE:0%To check the discarded packet, run the following additional CLI commands on the device:
set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term otherwise then log set groups top firewall family inet filter protect_re term otherwise then syslog mist@Distribution-1-R2-U06-> show firewall log Log : Time Filter Action Interface Protocol Src Addr Dest Addr 13:20:01 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:19:56 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:19:51 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:19:45 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:19:40 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:19:35 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:19:30 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:18:26 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:18:19 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:18:18 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 13:18:14 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:18:12 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 13:18:09 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:18:04 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 13:18:01 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 13:18:00 pfe D vtep.32769 UDP 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 13:18:00 pfe D vtep.32769 UDP 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 13:18:00 pfe D vtep.32769 UDP 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 13:18:00 pfe D vtep.32769 UDP 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 13:18:00 pfe D vtep.32769 UDP 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 13:18:00 pfe D vtep.32769 UDP 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 13:18:00 pfe D vtep.32769 UDP 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 13:18:00 pfe D vtep.32769 UDP 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 14:17:31 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:17:30 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:17:28 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:17:28 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:17:26 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:17:23 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:17:18 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:17:16 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:17:15 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:17:12 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:17:10 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:17:09 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:17:07 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:17:06 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:17:05 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:17:03 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:17:02 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:17:01 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:16:57 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:16:52 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:16:51 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:16:50 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:16:46 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:16:45 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:16:44 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:16:41 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:16:41 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:16:40 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:16:38 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:16:36 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:16:36 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:16:31 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:16:26 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 10.216.199.80 255.255.255.255 14:16:26 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:16:25 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:16:20 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6 14:16:19 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 8.8.8.8 10.216.202.6 14:16:16 protect_re D vme.0 UDP 66.129.233.81 10.216.202.6
Read also: Example: Configuring a Stateless Firewall Filter to Accept Traffic from Trusted Sources and Example: Configuring a Stateless Firewall Filter to Protect Against TCP and ICMP Floods.