High Availability Design for Session Smart Routers
Use this design guide to deploy high availability Session Smart Routers at the edge.
Juniper® Networks Session Smart™ High Availability (HA) Design Guide is for administrators who want to deploy HA Juniper Session Smart Routers at the Edge, but not for Whitebox setups.
In this documentation you’ll find step-by-step guidance for setting up a highly available hub and spoke deployment using Juniper® Mist WAN Assurance. Since this HA deployment builds upon the topology referenced in the Juniper Session Smart WAN Assurance Configuration Guide, you'll need to configure your network with that topology first. Building upon the reference topology in the Juniper Session Smart WAN Assurance Configuration Guide, you'll learn how to setup Session Smart Routers in an HA cluster configuration.
Devices in an HA pair must be identical. An HA pair with two SSR120s will work. An HA pair with one SSR120 and one SSR102-AE will not work.
Overview
You will deploy a highly available Hub and Spoke as shown in Figure 1. Here we see the Session Smart highly available Juniper Mist WAN Assurance topology for this HA Design Guide.
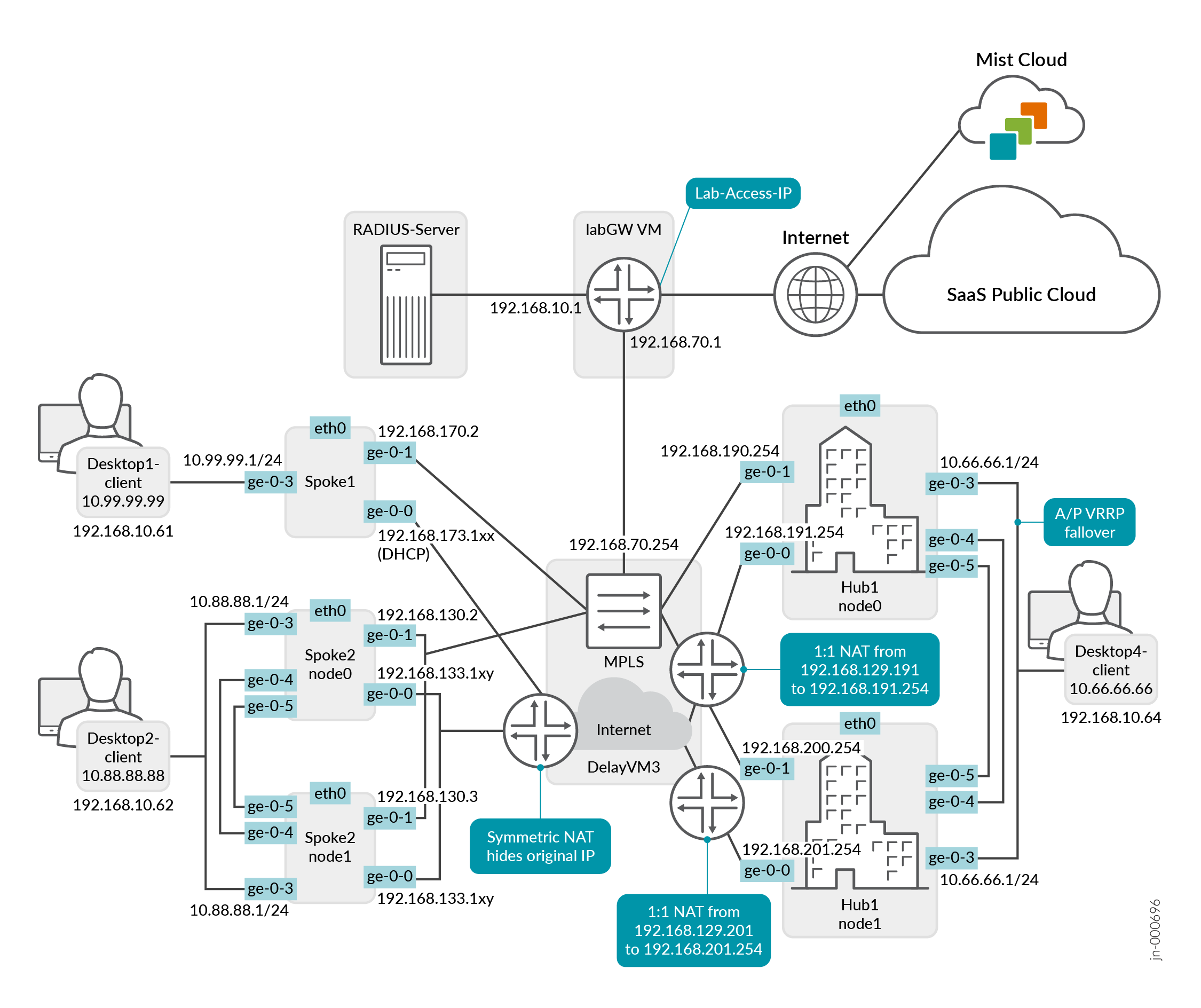
Before you get started, be sure you’ve setup the topology described in the Juniper WAN Assurance Configuration Guide.
Interfaces
The Interfaces use the following pattern for each node:
Node0: ge-0/0/x
Node1: ge-1/0/x
WAN Interfaces for HA hubs require static IP addresses. Spokes reach out across the overlay to these WAN interface endpoints.
HA Interfaces
Each path and Node in an HA network require their own designated WAN interface. This ensures active/active usage, meaning that these interfaces stay active and engaged, no matter what. WAN interfaces on spoke devices can contain either a static IP address or be linked to a DHCP-lease, giving you flexibility in how you manage them.
In certain scenarios, you may be limited to just one WAN IP address, especially for MPLS Networks. In these cases, you can configure the interface as a shared VRRP interface between two Nodes. This sets up an active/passive usage of the links, maintaining the balance and ensuring continuity. A second IP address for that second node enhances your setup's performance even further.
LAN Interfaces
You’ll need to define the LAN interfaces for both HA hubs and spokes are as redundant interfaces, and then specify the interfaces together as ge-0/0/x, ge-1/0/x. This will make them VRRP Interfaces.
Redundant VRRP Interfaces are only Active/Passive, meaning only the currently active Session Smart Router interface will broadcast VRRP.
The redundant VRRP interfaces must be in the same Layer 2 domain and need a single static IP address. The Active/Passive Interfaces will have a shared MAC address. Based on the device, the system decides who will be node0 and who will be node1.
- The lowest MAC address will be selected for node0.
- For Redundant VRRP interfaces, you can define which node is the primary, but we recommend leaving the default to node0 for consistency.
It's important to be aware of the two specific Ethernet interfaces that handle HA synchronization and fabric data exchange on the supported devices. See the Session Smart documentation https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/session-smart-router/docs/concepts_ha_theoryofoperation.
The HA synchronization link ensures that the two devices are chronologically synchronized and can swap appropriately in the event of an interface or device failure. The synchronization interface serves as the back-or-midplane of a chassis-based router.
The fabric interface is a forwarding interface between two nodes in a router and is used when the ingress interface and egress interface for a given session are active on different nodes. The synchronization and fabric interfaces are usually the two last ports of the system. You must wire them back-to-back with direct patch cables.
Configure High Availability
The following steps outline the process of adding the HA Hub Site.
To add a highly available hub we’ll need to create the first HA Site for the redundant interfaces. Later, we’ll clone this one for redundancy. Remember this HA Node will be the first device in a pair for path failover in the event of an issue or failure.
You should have already configured Networks, Applications, Sites, Variables, Hub Profiles and WAN Edge Templates. If these steps are new to you, please follow the Mist WAN Configuration Guide first before proceeding with the HA design guide. See WAN Assurance Configuration Overview.
Create a New Hub Profile
Now it's time to add the second hub profile for your high available hub configuration. In this step, you'll create a new hub profile by cloning the existing profile. Then, you’ll modify the cloned profile to meet new requirements for the HA hub.
Define the VRRP Interfaces
Next, you’ll define a Network for the redundant LAN interfaces for VRRP and cluster support.
Configure Traffic Steering Profile
Traffic steering rules direct the flow of data traffic from one location or device to another. These rules help control how data packets are routed within a network, ensuring efficient and optimized data delivery. Traffic steering rules can be set up for various purposes, such as load balancing, traffic optimization, security, and quality of service (QoS) management. This is the Mist expression of “how” we send our “who” Networks to our “what” Applications.
For example, in a load balancing scenario, Traffic Steering rules might determine how incoming data traffic is distributed across multiple servers to prevent overload on any single server and ensure even distribution of the workload. In a security context, Traffic Steering rules could be used to direct certain types of traffic through specific security checkpoints or firewalls for inspection before allowing them into the network.
For your Traffic Steering network, keep in mind Session Smart Secure Vector Routing™. Your Session Smart routers are constantly communicating with one another with synchronous and asynchronous Bidirectional Forwarding Detection for liveness and path health for path selection in real-time. Traffic Steering then is an order of what paths you’d like traffic to take.
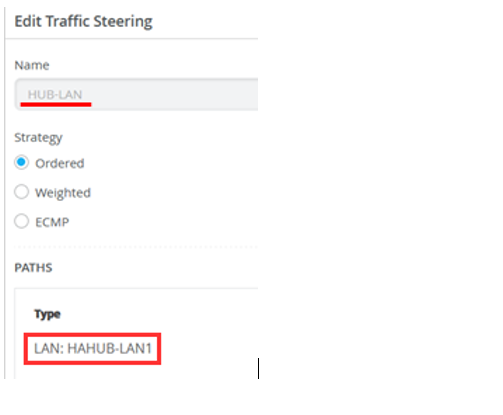
Scroll down to the TRAFFIC STEERING pane and edit the entry to change the rule for HUB-LAN to Paths / Type: LAN: HAHUB-LAN1
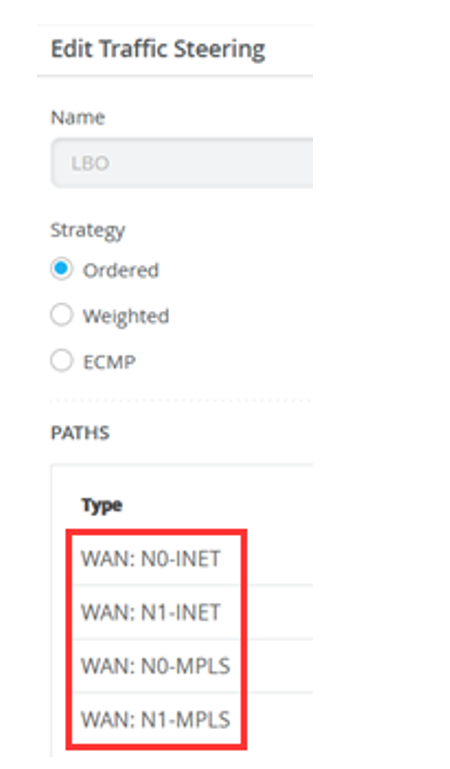
For LBO
- WAN: N0-INET
- WAN: N1-INET
- WAN: N0-MPLS
- WAN: N1-MPLS
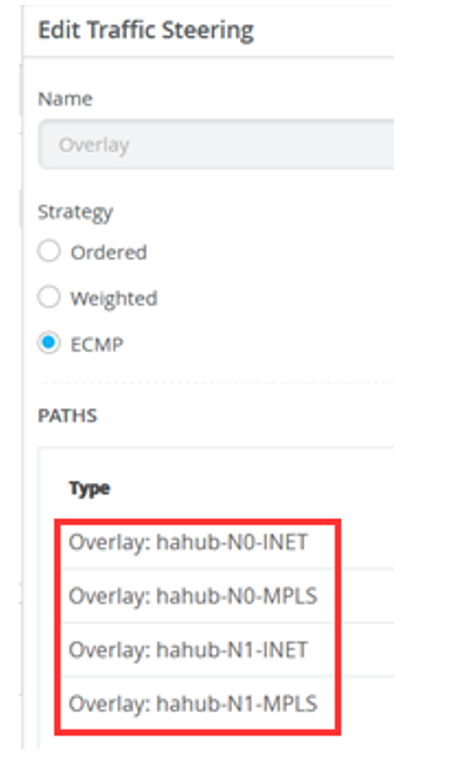
For Overlay
- Overlay: hahub-N0-INET
- Overlay: hahub-N0-MPLS
- Overlay: hahub-N1-INET
- Overlay: hahub-N1-MPLS
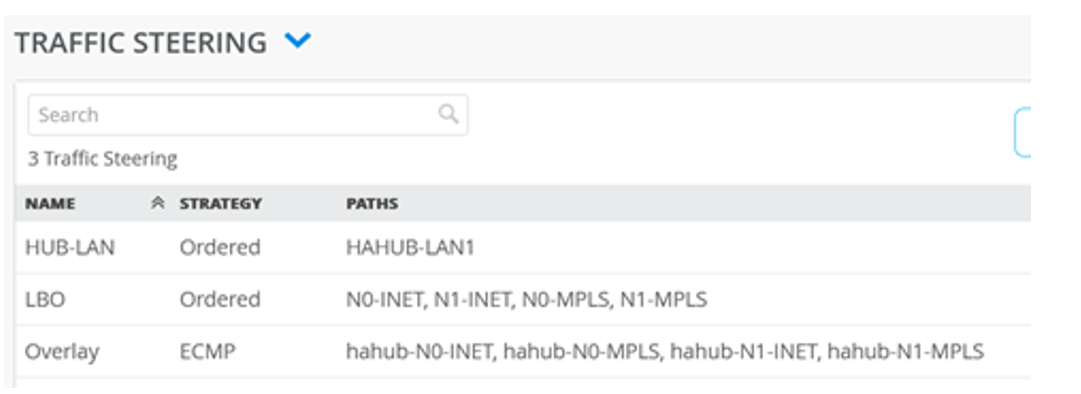
The Traffic steering rules now combine the interfaces of the two nodes as shown in Figure 23.
Modify Application Policies
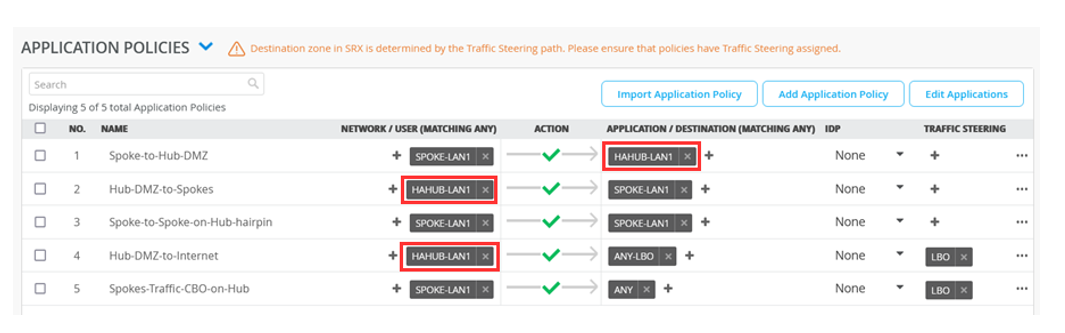
The Application Policies are like the ones for hub1 or hub2. But this time, you’ll change what was HUB1-LAN1 to HAHUB-LAN1. The changes are noted in bold font.
For example, wherever applicable, change HUB1-LAN to HAHUB-LAN1.
| No. | Rule Name | Network | Action | Destination | Steering |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spoke-to-Hub-DMZ | SPOKE-LAN1 | Pass | HAHUB-LAN1 | N/A |
| 2 | Hub-DMZ-to-Spokes | HAHUB-LAN1 | Pass | SPOKE-LAN1 | N/A |
| 3 | Spoke-to-Spoke-on-Hub-hairpin | SPOKE-LAN1 | Pass | SPOKE-LAN1 | N/A |
| 4 | Hub-DMZ-to-Internet | HAHUB-LAN1 | Pass | ANY-LBO | LBO |
| 5 | Spokes-Traffic-CBO-on-Hub | SPOKE-LAN1 | Pass | ANY | LBO |
Figure 24 shows the details of the updated application policies after you save your changes.
Create Spoke Templates
Create the Second Spoke Template
Now it’s time to clone our WAN Edge Template for our redundant spoke Node.
Onboard your Devices
You can Claim or Adopt to onboard devices into your organization inventory. For details on getting your Session Smart Router up and running in the Mist cloud, see SSR Series Devices.
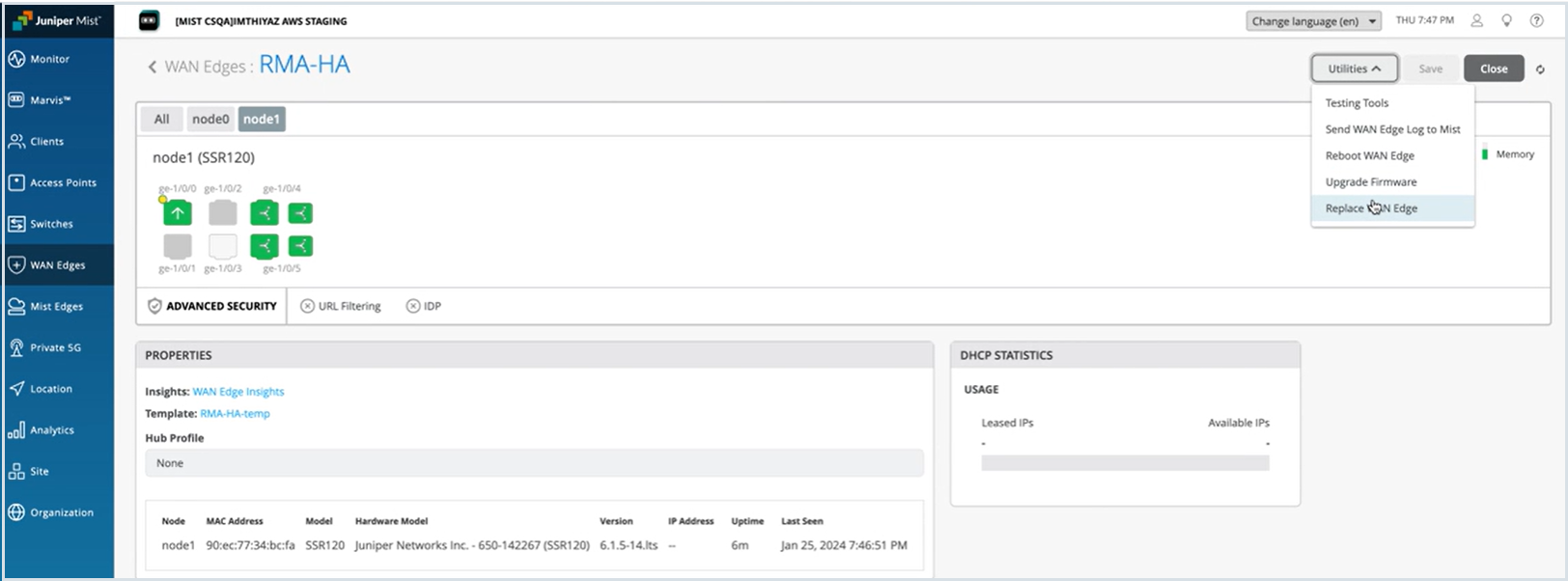
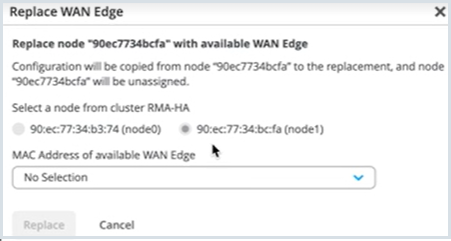
Replace an Session Smart Router Node in a High Availability Cluster
You can replace an Session Smart Router device from a high availability cluster setup with few simple steps.
Before you replace a Session Smart Router node from the cluster, you must:
- Remove the cluster fabric cables from the node being replaced and connect it to the new replacement node.
- Make sure that the replacement Session Smart Router is both the same model as the device being replaced and has a firmware version higher than 6.0
- If you are replacing a node with a new out-of-the box Session Smart Router,
ensure that you:
- Claim the new Session Smart Router to the same site where the Session Smart Router cluster is present.
- Upgrade the firmware of the Session Smart Router to a version above 6.0.
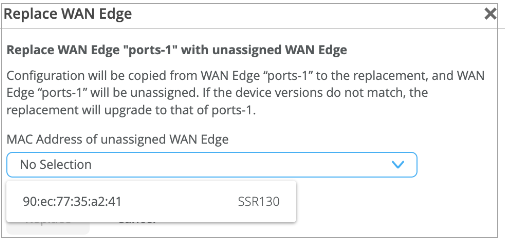
Replace a Standalone Session Smart Router
You can replace connected or disconnected Session Smart Router with another device of the same model.