Network Services SLE (Marvis Minis)
Use the Network Services SLE to gain insights into user connectivity experience at an organization or site level.
The Network Services SLE provides insights into the number of failed DNS, ARP, DHCP, or authentication attempts at an organization or site level based on the Marvis Minis validations. Marvis Minis simulates and validates user connectivity on active VLANs to ensure that users can reliably connect to the Internet and access necessary applications. Active VLANs refer to VLANs that are currently being used by clients to pass traffic.
For the validation on APs, Marvis Minis
-
Sends a DHCP request on a client VLAN to check if an IP address is successfully obtained.
-
Generates an ARP request to verify if the gateway is responsive, which is crucial for network communication.
-
Resolves DNS queries using all DNS server IP addresses provided in the DHCP offer. This step confirms that DNS is reachable and can resolve the application URLs, which is vital for translating domain names into IP addresses.
-
Checks application reachability by validating the accessibility of specific applications. You can define applications that need to be tested by Marvis Minis. You can define custom URLs/FQDNs in the organization or site settings. See Add Custom URLs for Marvis Minis Validation .
Marvis Minis considers an application as reachable if the response status code is either 200 (OK) or 408 (for default apps).
However, if you do not define any applications, then Marvis Minis validates accessibility to application by using default URLs such as captive.apple.com, connectivitycheck.gstatic.com, office.com, and teams.microsoft.com, along with verifying the reachability of Office365 services.
The final step in the connectivity validation process is explicitly releasing the DHCP lease on the tested VLAN. This ensures that resources are freed and available for other requests.
Classifiers
Marvis categorizes the results from the validations under the following classifiers to provide insights into failures detected during the connectivity phase.
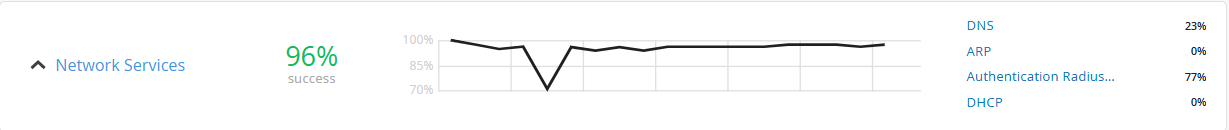
-
DHCP—DHCP request initiated by Marvis Minis for a client VLAN times out. This issue occurs when the DHCP server fails to respond within the expected timeframe, potentially due to network congestion, server misconfiguration, or connectivity issues.
-
Nack (Negative Acknowledgment)—The requested IP address could not be provided to the Marvis Minis. This could happen if the IP address is already in use by another device, if the request does not comply with the server's policy.
-
Renew Unresponsive—No response to a DHCP renew request When Marvis Minis attempts to renew its DHCP lease to maintain its IP address, it might not receive a response from the DHCP server. This can lead to connectivity interruptions, especially if the lease expires without renewal. Potential causes for unresponsiveness could include server outages or configuration errors on the server.
-
Incomplete—DHCP process did not complete. Marvis Minis could not obtain an IP address. This could be due to incomplete or incorrect DHCP configuration settings, network issues, or server-side errors that prevent the full exchange of DHCP messages required to establish a lease.
-
Unresponsive—No response to a DHCP Discover request which might result in Marvis Minis being unable to connect to the network. This can be caused due to server unavailability, or incorrect VLAN configurations that prevent the discover request from reaching the DHCP server.
-
-
ARP—Marvis Minis experienced problems related to ARP during the connectivity process.
Marvis Minis experienced issues with ARP resolution. The ARP process failed to resolve the IP address to the MAC address of the default gateway. This prevented Marvis Minis from successfully communicating with external networks, as the default gateway acts as a crucial point for routing traffic outside the local network.
-
DNS—DNS servers are not reachable, which indicates that attempts to resolve domain names to their corresponding IP addresses are failing. As a result, internet services relying on domain name resolution might be disrupted. This issue could be due to network configuration errors, server outages, or issues with the DNS settings on your device or network.
-
Authentication—Marvis Minis automatically learns all the RADIUS authentication servers configured for your network and validates server reachability. Using preset credentials, Marvis Minis initiates an authentication request to a RADIUS server. If the server rejects the authentication request, then it indicates that the server is available and reachable. This is currently supported only for switches.
Root Cause Analysis for the Network Services SLE
You can use the information across the following tabs that display when you click v beside Network Services.
-
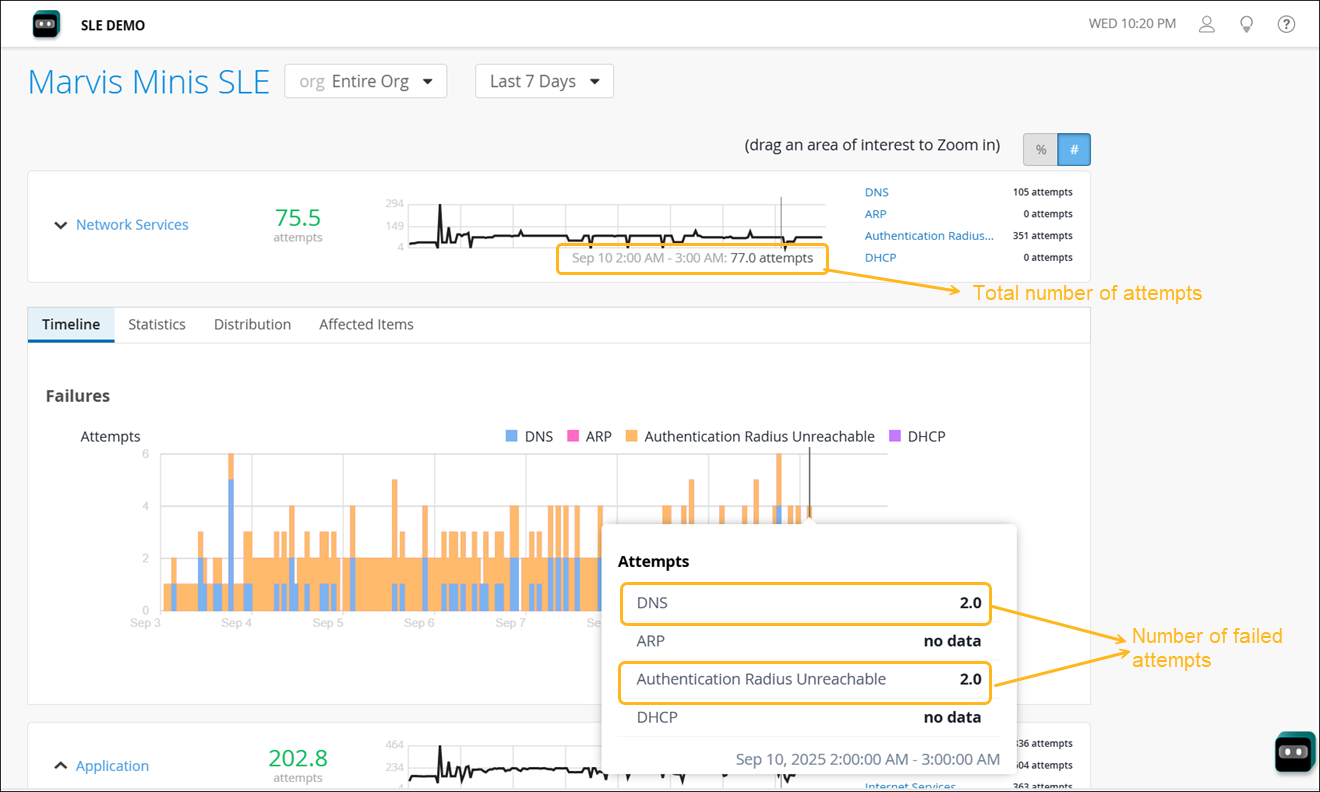
Timeline—See exactly when the issues occurred.
Here is an example of how Marvis displays the timeline for the Network Services SLE. You can view the total number of attempts and the number of failed attempts for a specific date and time by hovering your mouse over the graph. In this example you can see that a total of 77 attempts were made to connect to the network on September 10 between 2 AM and 3 AM of which 2 DNS attempts and 2 attempts to reach the authentication server failed.
-
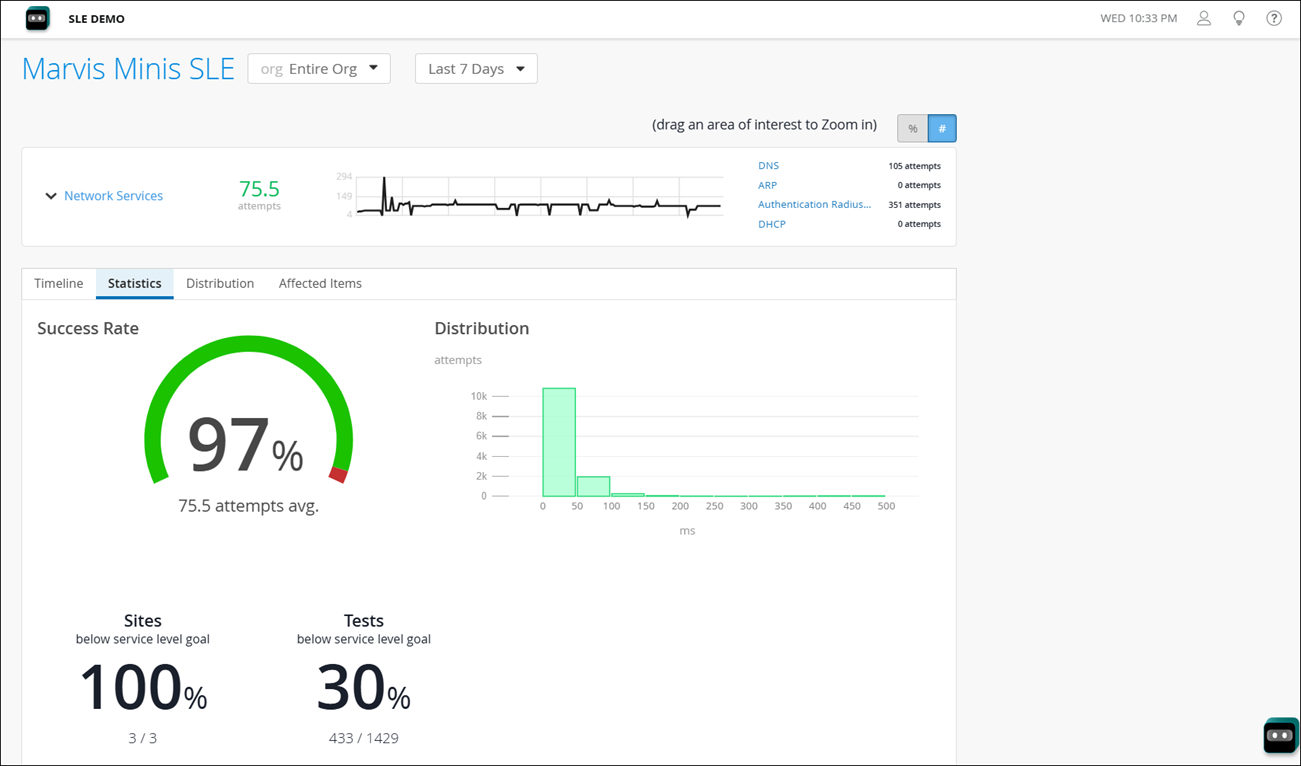
Statistics—See the success rate, number of sites experiencing failures and the latency information. The Distribution graph indicates the latency. In this example, you can see that 10000 connection attempts experienced a latency of 50 ms.
-
Distribution—See which sites and VLANs were affected.
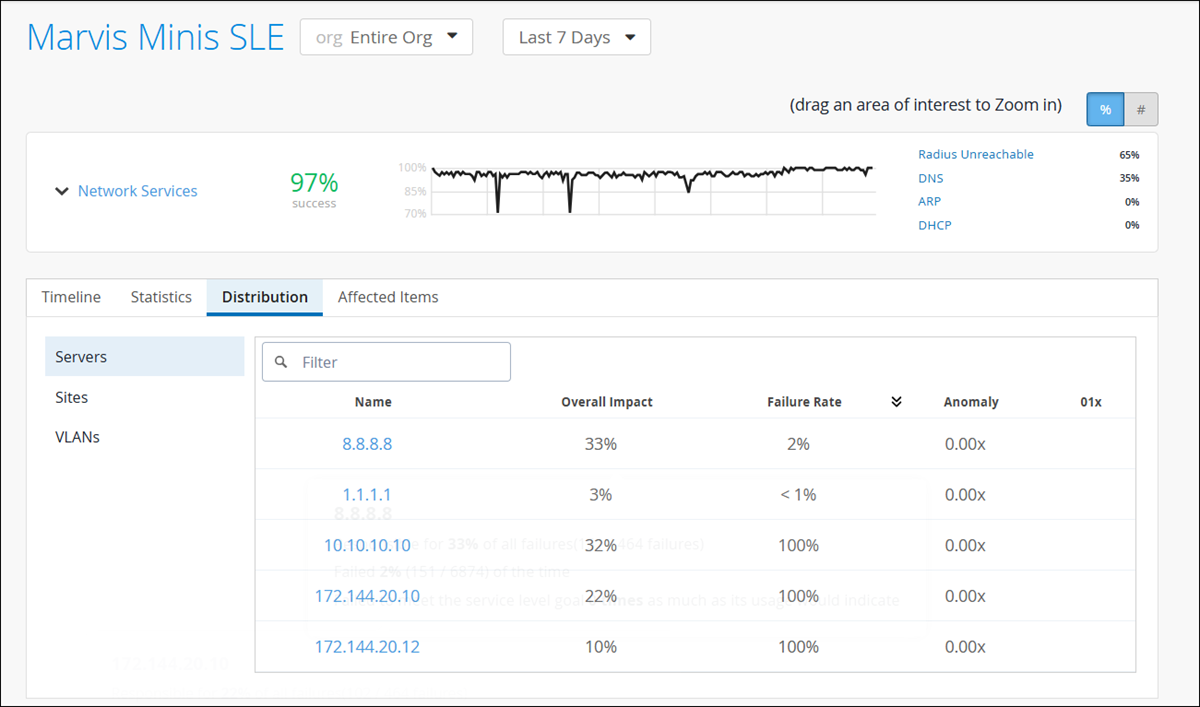
-
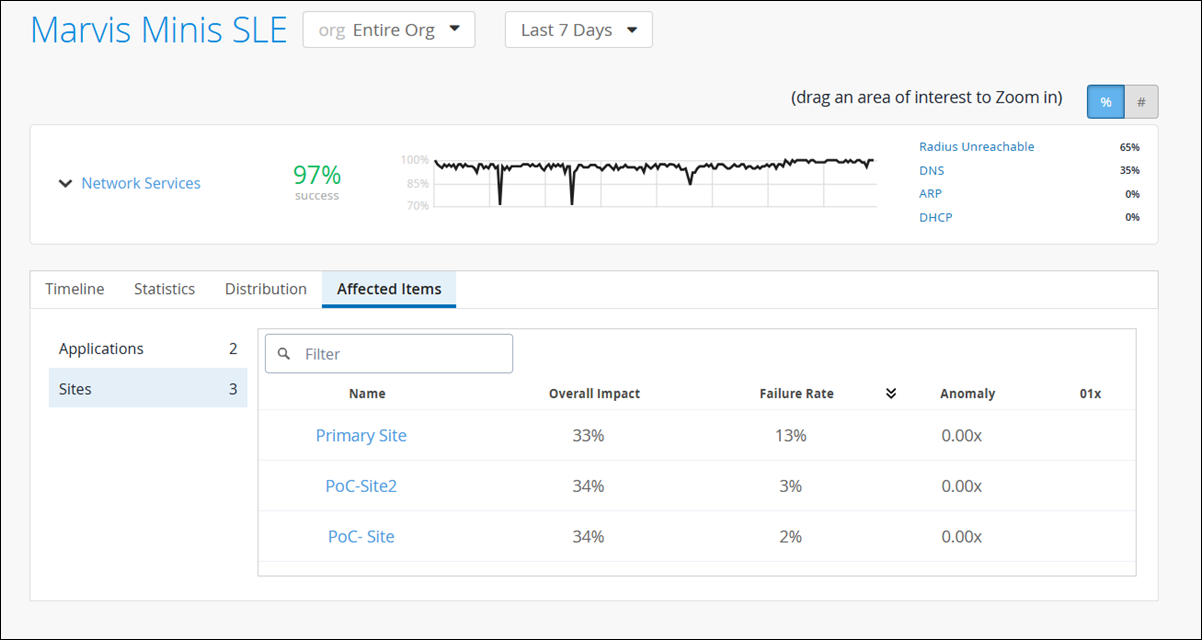
Affected Items—See which applications and sites were affected and how much each one contributed to the overall impact. Also see the individual failure rate for each application or site.