ON THIS PAGE
Broadcom BCM57608 Thor2 DCQCN configuration for RDMA Traffic
Configuring DCQN-ECN/PFC and TOS/DSCP for RDMA Traffic attributes directly
Configuring DCQN-ECN/PFC and TOS/DSCP for RDMA Traffic attributes using niccli
Non-volatile memory (NVM) options related to class of service.
Configuring DCQCN and RoCE traffic marking values using bnxt_setupcc.sh
Configuring the server to use the management interface for RCCL control traffic:
DCQCN configuration for RDMA Traffic on NICs
Broadcom BCM57608 Thor2 DCQCN configuration for RDMA Traffic
Default DCQN-ECN/PFC attributes in AMD servers.
The network interface adapters are configured with the following Class of Service (including DCQCN-ECN) parameters for RoCE traffic:
For Thor2 NIC adapter:
- RoCEv2 (RDMA over IPv4) enabled
- Congestion Control (ECN) and PFC enabled
- RoCE traffic tagged with DSCP 26 on PRIORITY 3
- RoCE CNP traffic tagged with DSCP 48 and PRIORITY 7
Mapping Broadcom and logical interface names to configure DCQN-ECN/PFC and TOS/DSCP for RDMA Traffic attributes in AMD servers
DCQCN ECN, PFC and traffic marking need to be configured on the interfaces connected to the GPU backend; that is on the gpu#_eth (#=0-7) interfaces only.
On the section Changing NIC attributes section of these document, we determined that the gpu#_eth interfaces in our servers, are Broadcom BCM97608 (shown below) NICs.
root@MI300X-01:/home/jnpr/SCRIPTS# cat devnames | grep gpu gpu0_eth:Broadcom Inc. and subsidiaries BCM57608 25Gb/50Gb/100Gb/200Gb/400Gb Ethernet (rev 11) gpu1_eth:Broadcom Inc. and subsidiaries BCM57608 25Gb/50Gb/100Gb/200Gb/400Gb Ethernet (rev 11) gpu2_eth:Broadcom Inc. and subsidiaries BCM57608 25Gb/50Gb/100Gb/200Gb/400Gb Ethernet (rev 11) gpu3_eth:Broadcom Inc. and subsidiaries BCM57608 25Gb/50Gb/100Gb/200Gb/400Gb Ethernet (rev 11) gpu4_eth:Broadcom Inc. and subsidiaries BCM57608 25Gb/50Gb/100Gb/200Gb/400Gb Ethernet (rev 11) gpu5_eth:Broadcom Inc. and subsidiaries BCM57608 25Gb/50Gb/100Gb/200Gb/400Gb Ethernet (rev 11) gpu6_eth:Broadcom Inc. and subsidiaries BCM57608 25Gb/50Gb/100Gb/200Gb/400Gb Ethernet (rev 11) gpu7_eth:Broadcom Inc. and subsidiaries BCM57608 25Gb/50Gb/100Gb/200Gb/400Gb Ethernet (rev 11)
All the steps for configuring Class of Service in this section will be focused on these Broadcom interfaces.
We will be using a combination of Linux system commands and Broadcom tools to enable, tune and monitor DCQCN ECN/PFC operation and RoCE traffic marking. For some of these commands we will need to find the Broadcom interface name associated with each gpu interface. Follow these steps to find these mappings:
- Find the PCI address of each gpu#_eth interface using the following logic:
for iface in $(ls /sys/class/net | grep -E 'gpu[0-9]+_eth'); do pci_addr=$(readlink -f /sys/class/net/$iface/device | awk -F '/' '{print $NF}') echo "$iface => $pci_addr" done1EXAMPLE:
root@MI300X-01:/home/jnpr/SCRIPTS# for iface in $(ls /sys/class/net | grep -E 'gpu[0-9]+_eth'); do pci_addr=$(readlink -f /sys/class/net/$iface/device | awk -F '/' '{print $NF}') echo "$iface => $pci_addr" done gpu0_eth => 0000:06:00.0 gpu1_eth => 0000:23:00.0 gpu2_eth => 0000:43:00.0 gpu3_eth => 0000:66:00.0 gpu4_eth => 0000:86:00.0 gpu5_eth => 0000:a3:00.0 gpu6_eth => 0000:c3:00.0 gpu7_eth => 0000:e6:00.0 - Find the bnxt_re# (#=0-7) devices that corresponds to each PCI address using the
following logic:
for pci in $(find /sys/class/infiniband -type l -exec basename {} \;); do pci_addr=$(readlink -f /sys/class/infiniband/$pci/device | awk -F '/' '{print $NF}') echo "$pci => $pci_addr" |grep bnxt doneEXAMPLE:
root@MI300X-01:/home/jnpr/SCRIPTS# for pci in $(find /sys/class/infiniband -type l -exec basename {} \;); do pci_addr=$(readlink -f /sys/class/infiniband/$pci/device | awk -F '/' '{print $NF}') echo "$pci => $pci_addr" |grep bnxt done bnxt_re5 => 0000:a3:00.0 bnxt_re3 => 0000:66:00.0 bnxt_re1 => 0000:23:00.0 bnxt_re6 => 0000:c3:00.0 bnxt_re4 => 0000:86:00.0 bnxt_re2 => 0000:43:00.0 bnxt_re0 => 0000:06:00.0 bnxt_re7 => 0000:e6:00.0 - MAP the GPU interface bnxt_re# or mlx5_# interface names.
Combine the outputs from steps 1 and 2 to create a full mapping from gpu#_eth to bnxt_re# or mlx5_#. You can see from the outputs that for example gpu0_eth corresponds to bnxt_re3 (0000:66:00.0)
You can use the following logic to simplify the process:
echo "GPU-to-NIC Mapping:"
for iface in $(ls /sys/class/net | grep -E 'gpu[0-9]+_eth'); do
pci_addr=$(readlink -f /sys/class/net/$iface/device | awk -F '/' '{print $NF}')
rdma_dev=$(find /sys/class/infiniband -type l -exec basename {} \; | while read rdma; do
rdma_pci=$(readlink -f /sys/class/infiniband/$rdma/device | awk -F '/' '{print $NF}')
if [[ "$pci_addr" == "$rdma_pci" ]]; then echo "$rdma"; fi
done)
echo "$iface => $pci_addr => $rdma_dev"
doneEXAMPLE:
root@MI300X-01:/home/jnpr/SCRIPTS# echo "GPU-to-NIC Mapping:"
for iface in $(ls /sys/class/net | grep -E 'gpu[0-9]+_eth'); do
pci_addr=$(readlink -f /sys/class/net/$iface/device | awk -F '/' '{print $NF}')
rdma_dev=$(find /sys/class/infiniband -type l -exec basename {} \; | while read rdma; do
rdma_pci=$(readlink -f /sys/class/infiniband/$rdma/device | awk -F '/' '{print $NF}')
if [[ "$pci_addr" == "$rdma_pci" ]]; then echo "$rdma"; fi
done)
echo "$iface => $pci_addr => $rdma_dev"
done
GPU-to-NIC Mapping:
gpu0_eth => 0000:06:00.0 => bnxt_re0
gpu1_eth => 0000:23:00.0 => bnxt_re1
gpu2_eth => 0000:43:00.0 => bnxt_re2
gpu3_eth => 0000:66:00.0 => bnxt_re3
gpu4_eth => 0000:86:00.0 => bnxt_re4
gpu5_eth => 0000:a3:00.0 => bnxt_re5
gpu6_eth => 0000:c3:00.0 => bnxt_re6
gpu7_eth => 0000:e6:00.0 => bnxt_re7Configuring DCQN-ECN/PFC and TOS/DSCP for RDMA Traffic attributes in AMD servers (Broadcom interfaces)
Some of the parameters related to DCQN-ECN/PFC and TOS/DSCP are listed in the following table:
Table 15. Server DCQCN configuration parameters
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | DEFAULT |
|---|---|---|
| cc_mode | 1 | |
| cnp_ecn | Enables/disables ECN | 0x1 (enabled) |
| cnp_dscp | DSCP value for RoCE congestion notification packets | 48 |
| cnp_prio | Priority for RoCE congestion notification packets | 7 |
| cnp_ratio_th | Defines the threshold ratio for generating CNPs. It determines the rate at which CNPs are sent in response to congestion, helping to control the feedback mechanism's aggressiveness. | 0x0 |
| ecn_enable | Enable congestion control. | 0x1 (enabled) |
| ecn_marking | Enables tagging of packets as ECN-enabled. ECN = 01 | 0x1 (enabled) |
| default_roce_mode | Sets the default RoCE mode for RDMA | RoCE v2 |
| default_roce_tos | Sets the default ToS value for RDMA traffic | 104 |
| roce_dscp | DSCP value for RoCE packets. | 26 |
| roce_prio | Priority for RoCE packets. | 3 |
| rtt | Time period (µs) over which cnp and transmitted packets counts accumulate. At the end of rtt, the ratio between CNPs and TxPkts is computed, and the CP is updated. | 40 μs. |
BCM95741X Ethernet network adapters support three transmit and receive queues for each Ethernet port: 0, 4, and 5.
BCM95750X Ethernet network adapters support eight transmit and receive queues for each Ethernet port: 0 through 7.
By default, all queues are configured for weighted-fair-queueing (WFQ), with priority 0 traffic mapped to queue 4.
When the RoCE bnxt_re driver is loaded, CoSQ 0 is configured for lossless traffic, and CoSQ 5 is changed from WFQ to strict priority (SP) for CNP processing.
RoCE and CNP traffic can be tagged with different DSCP values or use VLAN tags instead.
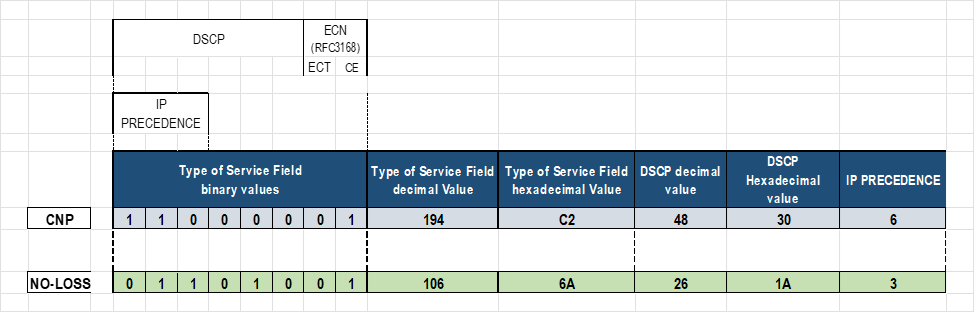
By default, the ToS field is set to 104, which means DSCP is set to 48 and the ECN bits are set to 10 (ECN-enabled).
These parameters can be adjusted using three different methods:
- Configuring DCQCN/RDMA marking values directly
- Configuring DCQCN/RDMA marking values using Broadcom tools such
as
niccli,orlldptooldirectly - Configuring DCQCN/RDMA marking values using
thebnxt_setupcc.shutility, which uses eitherniccliorlldptool(default) behind the scenes.
The following sections will describe the steps to make changes using these different options.
set class-of-service classifiers dscp mydscp forwarding-class CNP loss-priority low code-points 110000 set class-of-service classifiers dscp mydscp forwarding-class NO-LOSS loss-priority low code-points 011010 set class-of-service forwarding-classes class NO-LOSS pfc-priority 3
Configuring DCQN-ECN/PFC and TOS/DSCP for RDMA Traffic attributes directly
You can make changes to the DCQCN and traffic marking by directly editing the files that contain the values of each parameter. This method is the easiest, and does not require installation of any additional tools, however, it is not an option for PFC related parameters, nor is it supported on all types of network adapters.
To complete these changes for a specific interface, you must be under in the proper interface directory, following these steps:
- Create interface directories for qos related values
We determined the mappings between the gpu#_eth interfaces and the corresponding Broadcom interface names
GPU-to-NIC Mapping:
gpu0_eth => 0000:06:00.0 => bnxt_re0
gpu1_eth => 0000:23:00.0 => bnxt_re1
gpu2_eth => 0000:43:00.0 => bnxt_re2
gpu3_eth => 0000:66:00.0 => bnxt_re3
gpu4_eth => 0000:86:00.0 => bnxt_re4
gpu5_eth => 0000:a3:00.0 => bnxt_re5
gpu6_eth => 0000:c3:00.0 => bnxt_re6
gpu7_eth => 0000:e6:00.0 => bnxt_re7
We will use the Broadcom interface names to create the directories (rdma_cm and bnxt_re) where the DCQCN attributes as well as other parameters and statistics will be located for each interface.
The interface specific directories do not exist until created using the following commands:
cd /sys/kernel/config mkdir -p /rdma_cm/<Broadcom-interface-name> mkdir -p /bnxt_re/<Broadcom-interface-name>
Notice that these two directories must be present.
root@MI300X-01:/# cd /sys/kernel/config/ls bnxt_re rdma_cm
If the rdma_cm directory for example is missing, try the following:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# sudo modprobe rdma_cm root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# lsmod | grep rdma_cm rdma_cm 147456 0 iw_cm 61440 1 rdma_cm ib_cm 151552 1 rdma_cm ib_core 507904 6 rdma_cm,iw_cm,bnxt_re,ib_uverbs,mlx5_ib,ib_cm
EXAMPLE:
root@MI300X-01:/# cd /sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re# (NO FILES LISTED) root@MI300X-01:/# cd /sys/kernel/config/rdma_cm root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/rdma_cm# ls (NO FILES LISTED) root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# mkdir -p rdma_cm/bnxt_re0 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# mkdir -p bnxt_re/bnxt_re0 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# ls rdma_cm bnxt_re0 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# ls bnxt_re bnxt_re0 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# mkdir -p rdma_cm/bnxt_re1 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# mkdir -p bnxt_re/bnxt_re1 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# ls rdma_cm bnxt_re0 bnxt_re1 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# ls bnxt_re bnxt_re0 bnxt_re1
Repeat these steps for all the gpu interfaces.
NOTE: You must be a root user to make these changes.jnpr@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc$ sudo echo -n 0x1 > ecn_enable -bash: ecn_enable: Permission denied. jnpr@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc$ sudo bash root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# sudo echo -n 0x1 > ecn_enable root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc#
The new directories will contain values pertaining to ECN, ROCE traffic and other functions:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config# cd rdma_cm/bnxt_re0/ports/1 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/rdma_cm/bnxt_re0/ports/1# ls default_roce_mode default_roce_tos root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/rdma_cm/bnxt_re0/ports/1# cd /sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1 root@MI300X-02:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1$ ls cc tunables root@MI300X-02:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1$ ls tunables acc_tx_path cq_coal_en_ring_idle_mode dbr_pacing_algo_threshold en_qp_dbg snapdump_dbg_lvl user_dbr_drop_recov_timeout cq_coal_buf_maxtime cq_coal_normal_maxbuf dbr_pacing_enable gsi_qp_mode stats_query_sec cq_coal_during_maxbuf dbr_def_do_pacing dbr_pacing_time min_tx_depth user_dbr_drop_recov root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/# ls cc abs_max_quota act_cr_factor act_rel_cr_th actual_cr_shift_correction_en advanced ai_rate_incr ai_rtt_th1 ai_rtt_th2 apply bw_avg_weight cc_ack_bytes cc_mode cf_rtt_th cnp_dscp cnp_ecn cnp_prio cnp_ratio_th cp_bias cp_bias_en cp_exp_update_th cr_min_th cr_prob_fac cr_width disable_prio_vlan_tx ecn_enable ecn_marking exp_ai_rtts exp_crcp_ratio fair_cr_th fr_num_rtts g inact_th init_cp init_cr init_tr l64B_per_rtt lbytes_per_usec max_cp_cr_th max_quota min_quota min_time_bet_cnp random_no_red_en red_div red_rel_rtts_th reduce_cf_rtt_th reset_cc_cr_th roce_dscp roce_prio rt_en rtt rtt_jitter_en sc_cr_th1 sc_cr_th2 tr_lb tr_prob_fac tr_update_cyls tr_update_mode
You can find a description of some of these parameters, as well as their current value using
cat applywithin the/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc#directory.EXAMPLE:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat apply ecn status (ecn_enable) : Enabled ecn marking (ecn_marking) : ECT(1) congestion control mode (cc_mode) : DCQCN-P send priority vlan (VLAN 0) : Disabled running avg. weight(g) : 8 inactivity threshold (inact_th) : 10000 usec initial current rate (init_cr) : 0xc8 initial target rate (init_tr) : 0x320 cnp header ecn status (cnp_ecn) : ECT(1) rtt jitter (rtt_jitter_en) : Enabled link bytes per usec (lbytes_per_usec) : 0x7fff byte/usec current rate width (cr_width) : 0xe bits minimum quota period (min_quota) : 0x4 maximum quota period (max_quota) : 0x7 absolute maximum quota period(abs_max_quota) : 0xff 64B transmitted in one rtt (l64B_per_rtt) : 0xf460 roce prio (roce_prio) : 3 roce dscp (roce_dscp) : 26 cnp prio (cnp_prio) : 7 cnp dscp (cnp_dscp) : 48
- Enable RoCEv2 operation.
Even though RoCEv2 should be the default mode, the command to enable RoCEv2 is shown here.
NOTE: This change is made under the rdma_cm directoryroot@MI300X-01:/# cd /sys/kernel/config/rdma_cm/bnxt_re0/ports/1 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/rdma_cm/bnxt_re0/ports/1# ls default_roce_mode default_roce_tos root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/rdma_cm/bnxt_re0/ports/1# echo RoCE v2 > default_roce_mode
NOTE: Enter the value exactly as shown including the space: “RoCE v2” (case sensitive).After setting the parameter, apply the new values as follows:
echo -n 0x1 > apply
Verify the changes:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/rdma_cm/bnxt_re1/ports/1# cat default_roce_mode RoCE v2
-
Enable ECN response and notification functions.
Even though ECN should be enabled by default, the command to enable ECN is shown here.root@MI300X-01:/# cd /sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# echo -n 0x1 > ecn_enable
If needed, you can disable ECN by entering echo -n 0x0 > ecn_enable
instead.
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# echo -n 0x1 > ecn_enable
When ECN is enabled on the Broadcom interfaces, they will respond to CNP packets (RP) and will generate CNP packets when ECN-marked are received (NP).
To disable it, enter echo -n 0x0 > cnp_ecn
instead.
After setting the parameter, apply the new values:
echo -n 0x1 > apply
Verify the changes:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat ecn_enable 0x1
You can also enable the marking of both CNP and ROCE packets as ECN-eligible (meaning, these packets can be marked across the network when congestion occurs).
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat cnp_ecn 0x1
To summarize these attributes:
| ecn_enable | Enables/Disables the RP (response point) side of ECN. It enables the device to respond to CNP packets. Default = 1 (enable) |
| cnp_ecn | Configures marking CNP packets as ECN-eligible. Either a value of 01 or 10 for ECT field. |
| ecn_marking | Configures marking ROCE packets as ECN-eligible. Either a value of 01 or 10 for ECT field. |
- Configure the DSCP and PRIO values for CNP and RoCEv2 packets.
NOTE: Configuring these values manually, as shown below, is not an option for all types of Broadcom interface cards. For example, for BCM95741X devices you can use this method to configure the ECN, and RoCE priority values but on the BCM95750X/BCM97608 devices you can configure
roce_dscp, ecn_dscp.See Broadcom Ethernet Network Adapter Congestion Control Parameters
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# echo -n 0x30 > cnp_dscp # DSCP value as 48 (30 in HEX)
NOTE: These changes are made under the bnxt_re0 directory.echo -n 0x1a > roce_dscp # DSCP value as 26 (1a in HEX) echo -n 0x7 > cnp_prio echo -n 0x3 > roce_prio
NOTE: The following error indicates that changing the value of this parameter directly is not supported. In the case of BCM97608 roce_prio, and cnp_prio need to be configured usingbnxt_setupcc.sh(described later).root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# echo -n 0x3 > roce_prio bash: echo: write error: Invalid argument
After setting the parameter, apply the new values:
echo -n 0x1 > apply
Verify the changes:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat cnp_dscp 0x30 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat cnp_dscp 0x1a root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat cnp_prio 0x7 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat cnp_prio 0x3
- Configure the DCQCN algorithm (under the bnxt_re directory).
The default DCQCN Congestion Control (cc-mode) algorithm in Broadcom Ethernet network adapter is DCQCN-P. The mode can be changed using these commands:
NOTE: This change is made under the bnxt_re0 directory.To use DCQCN-P configure:
cd /sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc/ echo -n 1 > cc_mode echo -n 1 > apply cat apply
To use DCQCN-D configure:
root@MI300X-01:/ cd /sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc/ echo -n 0 > cc_mode echo -n 1 > apply
- Check all the attributes that were configured.
The following command shows all the interface parameters:
root@MI300X-01:/ cd /sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc/ echo -n 1 > advanced echo -n 1 > apply cat apply
For more information on the DCQCN algorithm in Broadcom Ethernet network adapter check the following documents: Changing Congestion Control Mode Settings and RoCE Congestion Control
EXAMPLE:
We have highlighted some ECN/CNP related parameters:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config#
cd /sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc/
echo -n 1 > advanced
echo -n 1 > apply
cat apply
ecn status (cnp_ecn) : Enabled
ecn marking (ecn_marking) : ECT(1)
congestion control mode (cc_mode) : DCQCN-P
send priority vlan (VLAN 0) : Disabled
running avg. weight(g) : 8
inactivity threshold (inact_th) : 10000 usec
initial current rate (init_cr) : 0xc8
initial target rate (init_tr) : 0x320
round trip time (rtt) : 45 usec
cnp header ecn status (cnp_ecn) : ECT(1)
rtt jitter (rtt_jitter_en) : Enabled
link bytes per usec (lbytes_per_usec) : 0x7fff byte/usec
current rate width (cr_width) : 0xe bits
minimum quota period (min_quota) : 0x4
maximum quota period (max_quota) : 0x7
absolute maximum quota period(abs_max_quota) : 0xff
64B transmitted in one rtt (l64B_per_rtt) : 0xf460
minimum time between cnps (min_time_bet_cnp) : 0x0 usec
initial congestion probability (init_cp) : 0x3ff
target rate update mode (tr_update_mode) : 1
target rate update cycle (tr_update_cyls) : 0x0
fast recovery rtt (fr_num_rtts) : 0x5 rtts
active increase time quanta (ai_rate_incr) : 0x1
reduc. relax rtt threshold (red_rel_rtts_th) : 0x2 rtts
additional relax cr rtt (act_rel_cr_th) : 0x50 rtts
minimum current rate threshold (cr_min_th) : 0x0
bandwidth weight (bw_avg_weight) : 0x5
actual current rate factor (act_cr_factor) : 0x0
current rate level to max cp (max_cp_cr_th) : 0x3ff
cp bias state (cp_bias_en) : Disabled
log of cr fraction added to cp (cp_bias) : 0x3
cr threshold to reset cc (reset_cc_cr_th) : 0x32a
target rate lower bound (tr_lb) : 0x1
current rate probability factor (cr_prob_fac) : 0x3
target rate probability factor (tr_prob_fac) : 0x5
current rate fairness threshold (fair_cr_th) : 0x64
reduction divider (red_div) : 0x1
rate reduction threshold (cnp_ratio_th) : 0x0 cnps
extended no congestion rtts (exp_ai_rtts) : 0x8 rtt
log of cp to cr ratio (exp_crcp_ratio) : 0x7
use lower rate table entries (rt_en) : Disabled
rtts to start cp track cr (cp_exp_update_th) : 0x1a4 rtt
first threshold to rise ai (ai_rtt_th1) : 0x40 rtt
second threshold to rise ai (ai_rtt_th2) : 0x80 rtt
actual rate base reduction threshold (cf_rtt_th) : 0x15e rtt
first severe cong. cr threshold (sc_cr_th1) : 0x0
second severe cong. cr threshold (sc_cr_th2) : 0x0
cc ack bytes (cc_ack_bytes) : 0x44
reduce to init rtts threshold(reduce_cf_rtt_th) : 0x3eb rtt
random no reduction of cr (random_no_red_en) : Enabled
actual cr shift correction (actual_cr_shift_correction_en) : Enabled
roce prio (roce_prio) : 3
roce dscp (roce_dscp) : 26
cnp prio (cnp_prio) : 7
cnp dscp (cnp_dscp) : 0
Configuring DCQN-ECN/PFC and TOS/DSCP for RDMA Traffic attributes using niccli
You can make changes to the DCQCN and traffic marking using the NICCLI Configuration Utility.
niccli is a management tool for Broadcom Ethernet
network adapters that provides detailed information, including
type, status, serial number, and firmware version. It also enables
the configuration of interface attributes such as DCQCN-ECN, PFC,
and TOS/DSCP for optimizing RDMA traffic.
Installing the NICCLI Configuration Utility
root@MI300X-01:/$ which niccli /usr/bin/niccli root@MI300X-01:/usr/bin$ ls niccli -l lrwxrwxrwx 1 18896 1381 18 Sep 25 18:52 niccli -> /opt/niccli/niccli
You can obtain a summary of the interface adapters and ethernet
ports that can be managed with niccli present on the server using
niccli listdev, or list-eth as show in the example
below.
root@MI300X-01:/home/jnpr# niccli --listdev
1 ) Supermicro PCIe 400Gb Single port QSFP56-DD Ethernet Controller (Adp#1 Port#1)
Device Interface Name : gpu0_eth
MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:75:D0
PCI Address : 0000:06:00.0
2 ) Supermicro PCIe 400Gb Single port QSFP56-DD Ethernet Controller (Adp#2 Port#1)
Device Interface Name : gpu1_eth
MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:79:20
PCI Address : 0000:23:00.0
3 ) Supermicro PCIe 400Gb Single port QSFP56-DD Ethernet Controller (Adp#3 Port#1)
Device Interface Name : gpu2_eth
MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:7D:F0
PCI Address : 0000:43:00.0
4 ) Supermicro PCIe 400Gb Single port QSFP56-DD Ethernet Controller (Adp#4 Port#1)
Device Interface Name : gpu3_eth
MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:7E:20
PCI Address : 0000:66:00.0
5 ) Supermicro PCIe 400Gb Single port QSFP56-DD Ethernet Controller (Adp#5 Port#1)
Device Interface Name : gpu4_eth
MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:75:10
PCI Address : 0000:86:00.0
6 ) Supermicro PCIe 400Gb Single port QSFP56-DD Ethernet Controller (Adp#6 Port#1)
Device Interface Name : gpu5_eth
MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:7D:C0
PCI Address : 0000:A3:00.0
7 ) Supermicro PCIe 400Gb Single port QSFP56-DD Ethernet Controller (Adp#7 Port#1)
Device Interface Name : gpu6_eth
MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:84:90
PCI Address : 0000:C3:00.0
8 ) Supermicro PCIe 400Gb Single port QSFP56-DD Ethernet Controller (Adp#8 Port#1)
Device Interface Name : gpu7_eth
MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:83:10
PCI Address : 0000:E6:00.0
root@MI300X-01:/home/jnpr# niccli --list-eth
BoardId Interface PCIAddr
1) BCM57608 gpu0_eth 0000:06:00.0
2) BCM57608 gpu1_eth 0000:23:00.0
3) BCM57608 gpu2_eth 0000:43:00.0
4) BCM57608 gpu3_eth 0000:66:00.0
5) BCM57608 gpu4_eth 0000:86:00.0
6) BCM57608 gpu5_eth 0000:A3:00.0
7) BCM57608 gpu6_eth 0000:C3:00.0
8) BCM57608 gpu7_eth 0000:E6:00.0You can use niccli in either oneline
mode, interactive mode, or batch
mode. The niccli -h help provides a high
level description of these modes. In this section, we will show
some examples of how to use the oneline and
interactive modes for DCQCN-ECN, PFC, and TOS/DSCP
configuration.
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# niccli --help
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI - Help Option
--help / -h Displays the following help page.
Utility provides three modes of execution,
1. Interactive Mode
To launch in interactive mode :
<NIC CLI executable> [-i <index of the target>] | -pci <NIC pci address>
After launching in interactive mode, execute 'help' command to
display the list of available commands.
2. Oneline Mode
To launch in Oneline mode :
<NIC CLI executable> [-i <index of the target>] | -pci <NIC pci address> <command>
To list available commands in Oneline mode :
<NIC CLI executable> [-i <index of the target>] | -pci <NIC pci address> help
Legacy Nic command syntax :
To launch in Oneline mode :
<NIC CLI executable> [-dev [<index of the target> | <mac addr> | <NIC pci address>]] <command>
To list available commands in Oneline mode :
<NIC CLI executable> [-dev [<index of the target> | <mac addr> | <NIC pci address>]] help
3. Batch Mode
To launch in batch mode :
<NIC CLI executable> [-i <index of the target>] | -pci <NIC pci address> --batch <batch file>
NOTE: Batch mode requires flat text file with utility supported commands.
Commands have to be provided in ascii format with the valid parameters.
Supported commands can be listed using One-Line mode or Interactive mode
Upon failure of any commands, utility will exit without continuing with other commands
List available targets for Oneline or Batch mode
<NIC CLI executable> --list
<NIC CLI executable> --listdevEntering
niccli with no options allows you to work in the
interactive mode, where you select an adapter/interface (by index)
and then the proper <command> (e.g. show,
get_qos, set_map) to obtain information or make changes to the
selected interface.
You can identify the interface index corresponding to each
interface using the method described in the Mapping Broadcom interface
name with logical interface name section. This will give you
the mappings between interfaces and pcie address which you can then
correlate with the output of niccli below.
Once identified, enter the interface index (first column in the output) as shown in the example below.
EXAMPLE:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# niccli
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BoardId MAC Address FwVersion PCIAddr Type Mode
1) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:75:D0 230.2.49.0 0000:06:00.0 NIC PCI
2) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:79:20 230.2.49.0 0000:23:00.0 NIC PCI
3) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:7D:F0 230.2.49.0 0000:43:00.0 NIC PCI
4) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:7E:20 230.2.49.0 0000:66:00.0 NIC PCI
5) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:75:10 230.2.49.0 0000:86:00.0 NIC PCI
6) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:7D:C0 230.2.49.0 0000:A3:00.0 NIC PCI
7) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:84:90 230.2.49.0 0000:C3:00.0 NIC PCI
8) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:83:10 230.2.49.0 0000:E6:00.0 NIC PCI
Enter the target index to connect with : 1
BCM57608>
Once you are at the prompt for the selected NIC, you can enter commands such as show, device_health_check, listdev, and listeth)
BCM57608> show
NIC State : Up
Device Type : THOR2
PCI Vendor ID : 0x14E4
PCI Device ID : 0x1760
PCI Revision ID : 0x11
PCI Subsys Vendor ID : 0x15D9
PCI Subsys Device ID : 0x1D42
Device Interface Name : gpu0_eth
MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:75:D0
Base MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:75:D0
Serial Number : OA248S074777
Part Number : AOC-S400G-B1C
PCI Address : 0000:06:00.0
Chip Number : BCM57608
Chip Name : THOR2
Description : Supermicro PCIe 400Gb Single port QSFP56-DD Ethernet Controller
---more---
BCM57608> devid
Device Interface Name : gpu0_eth
PCI Vendor ID : 0x14E4
PCI Device ID : 0x1760
PCI Revision ID : 0x11
PCI Subsys Vendor ID : 0x15D9
PCI Subsys Device ID : 0x1D42
PCI Address : 0000:06:00.0
BCM57608> device_health_check
Device Health Information :
SBI Mismatch Check : OK
SBI Booted Check : OK
SRT Mismatch Check : OK
SRT Booted Check : OK
CRT Mismatch Check : OK
CRT Booted Check : OK
Second RT Image : CRT Image
Second RT Image Redundancy : Good
Image Fastbooted Check : OK
Directory Header Booted Check : OK
Directory Header Mismatch Check : OK
MBR Corrupt Check : OK
NVM Configuration : OK
FRU Configuration : OK
---------------------------------------------
Overall Device Health : Healthy
BCM57608> devid
Device Interface Name : gpu0_eth
PCI Vendor ID : 0x14E4
PCI Device ID : 0x1760
PCI Revision ID : 0x11
PCI Subsys Vendor ID : 0x15D9
PCI Subsys Device ID : 0x1D42
PCI Address : 0000:06:00.0niccli -i <interface-index> <command>
niccli -list command can be used to
determine the interface index.EXAMPLE
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# niccli --list
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BoardId MAC Address FwVersion PCIAddr Type Mode
1) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:75:D0 230.2.49.0 0000:06:00.0 NIC PCI
2) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:79:20 230.2.49.0 0000:23:00.0 NIC PCI
3) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:7D:F0 230.2.49.0 0000:43:00.0 NIC PCI
4) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:7E:20 230.2.49.0 0000:66:00.0 NIC PCI
5) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:75:10 230.2.49.0 0000:86:00.0 NIC PCI
6) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:7D:C0 230.2.49.0 0000:A3:00.0 NIC PCI
7) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:84:90 230.2.49.0 0000:C3:00.0 NIC PCI
8) BCM57608 7C:C2:55:BD:83:10 230.2.49.0 0000:E6:00.0 NIC PCIThe sudo niccli help provides an extensive list of
commands and options available for both interactive and one-line
mode.
root@MI300X-01:/home/jnpr# sudo niccli help
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Commands sets - Generic/Offline
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
list - Lists all the compatible devices
listdev - Lists all the compatible devices (NIC legacy syntax)
devid - Query Broadcom device id's.
pkgver - Display FW PKG version installed on the device.
verify - Verify FW packages & NVM
nvm-list - Display NVM components and its associated versions.
nvmview - View NVM directories data
list-eth - Lists all NIC devices with ethernet interface names
help - Lists the available commands
quit - Quits from the application
Commands for platform 'BCM57xxx Performance NIC' and interface 'Direct PCIe'
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
show - Shows NIC specific device information
coredump - Retrieves coredump data from device.
snapdump - Retrieves snapdump data from device.
version - Display the current version of the application
txfir - Network Interface Card Transmission Finite
- Impulse Response
msixmv - Display and configure the number of MSIX max
- vectors values for VF's per each PF
scan - Scan PCI devices in the topology
pcie - Show/Execute pcie operation
nvm - NVRAM Option Management
pfalloc - Configure and Query for the number of PFs per PCIe
- endpoint
rfd - Restores NVM configuration to factory defaults
backuppowercfg - Backup Power Configuration
tsio - TSIO function capability on the pin
ingressqos - Query and configure the ingressqos parameters
egressqos - Query and configure the egressqos parameters
dutycycle - Set duty cycle on TSIO outgoing signal
dllsource - Set the DLL source for PHC
vf - Configure and Query for a trusted VF
rxportrlmt - Configure the receive side port rate limit
rxrlmt - Query the configured receive side rate control parameters
rxeprlmt - Configure the receive side rate control parameters for a given endpoint
txpartitionrlmt - Query and Configure the transmit side partition rate limit applies to traffic
- sent from a partition, which is one PF and all of its child VFs
txportrlmt - Query and Configure the transmit side of port rate limit
txeprlmt - Query and Configure the PCIe endpoint transmit rate control
vf - Configure and Query for a trusted VF
pfc - Configure the priority-based flow control for a given priority
apptlv - Configure the priority for the AppTLV
tcrlmt - Configure the rate limit for each traffic class
ets - Configure the enhanced transmission selection, priority to traffic class and bandwidths
up2tc - Configure the user priorities to traffic classes
getqos - Query the configured enhanced transmission selection, priority to traffic class and bandwidths
listmap - List the priority to traffic class and queueid mapping
dscp2prio - Query the dscp to priority mapping
reset - Reset the device
synce - Configure the synchronous ethernet profile
dscdump - Retrieves dscdump for device
ptp - PTP extended parameters operation
prbs_test - Run PRBS loopback test
serdes - Plots the serdes pci and ethernet eye and prints the horizontal and vertical margin values
Legacy NVM commands : - Query commands
--------------------- - ---------------
device_info - Query Broadcom device information and default hardware
- resources profile version.
device_temperature - Query the device temperature in Celsius.
get_backup_power_config - Query backup power configuration of the device.
moduleinfo - Query the PHY module information.
nvm_measurement - Query the active NVM configuration.
get_ptp_extended - Query the PTP extended parameters.
getoption - Query current NVM configuration option settings
- of a device.
pcie_counters - Display the pcie counters.
saveoptions - Save NVM configuration options on the device
- to a file.
get_sync_ethernet - Get the synchronous ethernet frequency profile
get_txfir - Query the TX FIR settings.
cert_provision_state - Query the imported certificate chain on the device.
read - Read the NVM item data and write its contents to a file.
mh_pf_alloc - Query the number of PFs per PCIe endpoint.
- This command is supported only on Thor devices.
get_tsio_function_pin - Query TSIO function capability on the pin.
Legacy NVM commands : - Debug commands
--------------------- - ---------------
device_health_check - Checks the device health.
backup - Backup NVM contents to a file
Legacy NVM commands : - Configuration commands
--------------------- - ---------------
reset_ap - Reset management processor.
setoption - Configure NVM configuration option settings
- of a device.
msix_max_vectors - Configure the number of MSI-X max vectors per
- VF for each PF.
loopback - Query/perform loopback config.
add_ntuple_filter - Add ntuple flow filter.
free_ntuple_filter - Free ntuple flow filter.
cfgtunnel - query/config custom tunnel port/rss.
write - Create or overwrite NVM data item with a file.
set_txfir - Configures the TX FIR settings
set_ptp_extended - Set PTP extended parameters
mh_pf_alloc - Query/Configure the number of PFs per PCIe endpoint.
- This command is supported only on Thor devices.
restore_factory_defaults - Restores NVM configuration to factory defaults
resmgmt - Query and Configure resources of the device.
Legacy NVM commands : - FW update commands
--------------------- - ---------------
fw_sync - Synchronize primary & secondary FW images
livepatch - Query, Activate and Deactivate the patch in live
install - Install/Update FW
Legacy QoS Rx commands : - Rx Qos commands
--------------------- - ---------------
rx_port_ratelimit - The user can configure rx rate control that applies to all traffic in a rx CoS queue group.
rx_endpoint_ratelimit - The user can configure endpoint rx rate control that applies to all traffic in a rx CoS queue group.
get_rx_ratelimits - The user can query the rx rate limits.
Legacy QoS Tx commands : - Tx Qos commands
--------------------- - ---------------
partition_tx_ratelimit - This command is used to configure partition tx rate limit.
get_partition_tx_ratelimit - This command is used to query the partition rate limit configuration for a given partition.
get_tx_port_ratelimit - This command is used to query the tx side of port rate limit.
tx_port_ratelimit - This command is used to configure the tx side of port rate limit
tx_endpoint_ratelimit - This command is used to configure PCIe endpoint tx rate limit.
get_tx_endpoint_ratelimits - This command is used to query the tx endpoint rate limits.
Legacy DCB commands : - Data Center Bridging commands
--------------------- - ---------------
set_pfc - This command is used to enable PFC on a given priority
set_apptlv - This command is used to configure the priority of the AppTLV.
ratelimit - This command is used to configure the rate limit for each traffic class.
set_ets - This command is used to configure the DCB parameters.
set_map - This command is used to configure the priority to traffic class.
get_qos - This command is used to query the DCB parameters.
dump - This command is used to dump the priority to cos mapping.
get_dscp2prio - This command is used to query the dscp to priority mapping.The following examples show you how to
use niccli to obtain information about a specific
interface.
- Check interface status.
The
niccli -i <interface> showprovides details about the interface such as type, MAC address, firmware, serial number, device health, temperature and so on.EXAMPLE:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# sudo niccli -i 1 show ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- NIC State : Up Device Type : THOR2 PCI Vendor ID : 0x14E4 PCI Device ID : 0x1760 PCI Revision ID : 0x11 PCI Subsys Vendor ID : 0x15D9 PCI Subsys Device ID : 0x1D42 Device Interface Name : gpu0_eth MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:75:D0 Base MAC Address : 7C:C2:55:BD:75:D0 Serial Number : OA248S074777 Part Number : AOC-S400G-B1C PCI Address : 0000:06:00.0 Chip Number : BCM57608 Chip Name : THOR2 Description : Supermicro PCIe 400Gb Single port QSFP56-DD Ethernet Controller Firmware Name : PRIMATE_FW Firmware Version : 230.2.49.0 RoCE Firmware Version : 230.2.49.0 HWRM Interface Spec : 1.10.3 Kong mailbox channel : Not Applicable Active Package Version : 230.2.52.0 Package Version on NVM : 230.2.52.0 Active NVM config version : 0.0.5 NVM config version : 0.0.5 Reboot Required : No Firmware Reset Counter : 0 Error Recovery Counter : 0 Crash Dump Timestamp : Not Available Secure Boot : Enabled Secure Firmware Update : Enabled FW Image Status : Operational Crash Dump Available in DDR : No Device Temperature : 57 Celsius PHY Temperature : Not Available Optical Module Temperature : 65 Celsius Device Health : Good
- Check QoS settings
The sudo niccli -i <interface-index> dscp2prio and sudo
niccli -i 1 listmap -pri2cos commands show mappings between DSCP and Priority
vales, and between priority vales, traffic classes (TC) and the output queues.
root@MI300X-01:/home/jnpr# sudo niccli -i 1 dscp2prio
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
dscp2prio mapping:
priority:7 dscp: 48
priority:3 dscp: 26
root@MI300X-01:/home/jnpr# sudo niccli -i 2 listmap -pri2cos
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Base Queue is 0 for port 0
----------------------------
Priority TC Queue ID
------------------------
0 0 4
1 0 4
2 0 4
3 1 0
4 0 4
5 0 4
6 0 4
7 2 5 The outputs in the example show the defaults for:
- Queues status. Only queues 0, 1, and 2 are enabled.
- Priority to DSCP mappings: priority 7 => DSCP 48 & priority 3 => DSCP 26.
- Priority to TC (traffic class) and queue mappings: priority 7 => TC2 (queue 0) => DSCP 48 & priority 3 => TC1 (queue 5) => DSCP 26.
The sudo niccli -i <interface-index> get_qos
command provides a summary of the QoS configuration on the
interface.
EXAMPLE:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IEEE 8021QAZ ETS Configuration TLV:
PRIO_MAP: 0:0 1:0 2:0 3:1 4:0 5:0 6:0 7:2
TC Bandwidth: 50% 50% 0%
TSA_MAP: 0:ets 1:ets 2:strict
IEEE 8021QAZ PFC TLV:
PFC enabled: 3
IEEE 8021QAZ APP TLV:
APP#0:
Priority: 7
Sel: 5
DSCP: 48
APP#1:
Priority: 3
Sel: 5
DSCP: 26
APP#2:
Priority: 3
Sel: 3
UDP or DCCP: 4791
TC Rate Limit: 100% 100% 100% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%| IEEE 802.1Qaz ETS Configuration TLV: shows the Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS) configuration | |
|---|---|
| PRIO_MAP: 0:0 1:0 2:0 3:1 4:0 5:0 6:0 7:2 |
Maps priorities to Traffic Classes (TC) Priority 0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 6 → TC 0 Priority 3 → TC 1 Priority 7 → TC 2 |
| TC Bandwidth: 50% 50% 0% |
Allocates bandwidth percentages to traffic classes. TC 0: 50% of the total bandwidth. TC 1: 50%. TC 2: 0%. |
| TSA_MAP: 0:ets 1:ets 2:strict |
Together with TC Bandwidth, TSA_MAP allocates resources and defines service priority for each TC. Equivalent to schedulers & scheduler-map in Junos. Specifies the Transmission Selection Algorithm (TSA) used for each TC: TC 0 and TC 1 use ETS (Enhanced Transmission Selection) and share the available bandwidth 50/50 TC 2 uses strict priority, meaning TC 2 traffic will always be sent first |
| IEEE 802.1Qaz PFC TLV: defines traffic classification using the APP TLV (Type-Length-Value) format | |
| PFC enabled: 3 |
Indicates that PFC is enabled on priority 3. Other priorities do not have PFC enabled. PFC ensures that traffic with this priority can pause instead of being dropped during congestion. |
| IEEE 802.1Qaz APP TLV | |
|
APP#0: Priority: 7 Sel: 5 DSCP: 48 APP#1: Priority: 3 Sel: 5 DSCP: 26 APP#2: Priority: 3 Sel: 3 UDP or DCCP: 4791 |
Maps traffic to Traffic Classes. Equivalent to multifield classifiers in Junos. APP#0: Traffic marked with DSCP = 48 is mapped to priority 7 APP#1: Traffic marked with DSCP = 48 is mapped to priority 3 APP#2: UDP or DCCP traffic with port = 4791 (RoCEv2) is mapped to priority 3 |
| TC Rate Limit: 100% 100% 100% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% |
TC 0, TC 1, and TC 2 can use up to 100% of the bandwidth allocated to them. TC 3 through TC 7 are set to 0%, meaning they are not currently configured to transmit traffic. |
If needed, change the priority to traffic class mappings or the applications to traffic class mappings.
We recommend keeping the default settings and making sure they are consistent with the class-of-service configuration on the leaf nodes in the GPU backend fabric.
[edit class-of-service classifiers]
jnpr@gpu-backend-rack1-001-leaf1# show
dscp mydscp {
forwarding-class CNP {
loss-priority low code-points 110000; <= DSCP = 48
}
forwarding-class NO-LOSS {
loss-priority low code-points 011010; <= DSCP = 26
}
}
}
[edit class-of-service forwarding-classes]
jnpr@gpu-backend-rack1-001-leaf1# show
class CNP queue-num 3;
class NO-LOSS queue-num 4 no-loss pfc-priority 3;If there are any requirements to change the priority to traffic class mappings or the applications to traffic class mappings the following commands can be used:
Priority to traffic class mappings
BCM57608> help up2tc
DESCRIPTION :
This command is used to set the user priorities to traffic classes.
SYNTAX :
up2tc -p <priority[0-7]:tc>, ...>
-p: Comma separated list mapping user priorities to traffic classes.EXAMPLE:
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IEEE 8021QAZ ETS Configuration TLV:
PRIO_MAP: 0:1 1:1 2:0 3:0 4:1 5:1 6:0 7:0 <= default
---more---
BCM57608> up2tc -p 0:0,1:0,2:1,3:1,4:1,5:1,6:1,7:0
User priority to traffic classes are configured successfully.
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IEEE 8021QAZ ETS Configuration TLV:
PRIO_MAP: 0:0 1:0 2:1 3:1 4:1 5:1 6:1 7:0
---more---Applications to traffic class mappings
BCM57608> help apptlv
DESCRIPTION :
This command is used to configure the priority of the AppTLV
SYNTAX :
apptlv -add -app <priority,selector,protocol>
apptlv -del -app <priority,selector,protocol>EXAMPLE:
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
---more---
IEEE 8021QAZ APP TLV:
APP#1:
Priority: 7
Sel: 5
DSCP: 48
APP#2:
Priority: 3
Sel: 5
DSCP: 26
APP#3:
Priority: 3
Sel: 3
UDP or DCCP: 4791
BCM57608> apptlv -add -app 5,1,35093
AppTLV configured successfully.
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
---more---
IEEE 8021QAZ APP TLV:
APP#0:
Priority: 5
Sel: 1
Ethertype: 0x8915
APP#1:
Priority: 7
Sel: 5
DSCP: 48
APP#2:
Priority: 3
Sel: 5
DSCP: 26
APP#3:
Priority: 3
Sel: 3
UDP or DCCP: 4791
BCM57608> BCM57608> apptlv -del -app 5,1,35093
AppTLV deleted successfully.
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
---more---
IEEE 8021QAZ APP TLV:
APP#0:
Priority: 7
Sel: 5
DSCP: 48
APP#1:
Priority: 3
Sel: 5
DSCP: 26
APP#2:
Priority: 3
Sel: 3
UDP or DCCP: 4791
---more---If needed, change ETS configuration attributes
We recommend keeping the default settings and making sure they are consistent with the class-of-service configuration on the leaf nodes in the GPU backend fabric.
[edit class-of-service forwarding-classes]
jnpr@gpu-backend-rack1-001-leaf1# show
class CNP queue-num 3;
class NO-LOSS queue-num 4 no-loss pfc-priority 3;
BCM57608> help ets
DESCRIPTION :
This command is used to configure the enhanced transmission selection,
priority to traffic class and traffic class bandwidths.
SYNTAX :
ets -tsa <tc[0-7]:[ets|strict], ...> -up2tc <priority[0-7]:tc>, ...> -tcbw <list>
-tsa: Transmission selection algorithm, sets a comma separated list of traffic classes to
the corresponding selection algorithm. Valid algorithms include "ets" and "strict".
-up2tc: Comma separated list mapping user priorities to traffic classes.
-tcbw: Comma separated list of bandwidths for each traffic class the first value
being assigned to traffic class 0 and the second to traffic class 1 and so on.EXAMPLE:
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IEEE 8021QAZ ETS Configuration TLV:
PRIO_MAP: 0:1 1:1 2:0 3:0 4:1 5:1 6:0 7:0
TC Bandwidth: 50% 50% 0%
TSA_MAP: 0:ets 1:ets 2:strict
IEEE 8021QAZ PFC TLV:
PFC enabled: 3
---more---
BCM57608> ets -tsa 0:ets,1:ets,2:ets -up2tc 0:0,1:0,2:0,3:0,4:0,5:1,6:0,7:0 -tcbw 50,25,25
Enhanced transmission selection (ets) configured successfully.
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IEEE 8021QAZ ETS Configuration TLV:
PRIO_MAP: 0:0 1:0 2:0 3:0 4:0 5:1 6:0 7:0
TC Bandwidth: 50% 25% 25%
TSA_MAP: 0:ets 1:ets 2:etsIf needed, configure PFC
BCM57608> help pfc
DESCRIPTION :
This command is used to enable priority-based flow control on a given priority.
SYNTAX :
pfc -enable <pfc list>
The valid range is from 0 to 7. Where list is a comma-separated value for each pfc.
To disable the pfc, user needs to provide a value of 0xFF.EXAMPLE:
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
---more---
IEEE 8021QAZ PFC TLV:
PFC enabled: 3 <= default; PFC enabled for priority 3
---more---
BCM57608> pfc -enable 0xFF <= disables pfc on all priorities.
pfc configured successfully.
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
---more---
IEEE 8021QAZ PFC TLV:
PFC enabled: none <= pfc disabled on all priorities.
---more---
BCM57608> pfc -enable 5
pfc configured successfully.
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 1 get_qos
---more---
IEEE 8021QAZ PFC TLV:
PFC enabled: 5 <= PFC enabled for priority 5
---more---The following command attempts to enable the pfc on priority 5 and 6 and demonstrates that only one queue (one priority) can be configured as a lossless queue (PFC-enabled).
BCM57608> pfc -enable 5,6 ERROR: Hardware doesn't support more than 1 lossless queues to configure pfc. ERROR: Failed to enable pfc.
Configuring DCQCN and RoCE traffic marking values using bnxt_setupcc.sh
Using the
bnxt_setupcc.sh
utility, which can simplify the process.
The
bnxt_setupcc.sh
utility simplifies enabling or disabling both ECN and PFC, and
changing the values of DSCP and PRIO for both ROCE and CNP packets
for a given interface.
Under the hood it uses niccli (default) or
lldptool which can be selected as part of the
command.
You need to enter bnxt_setupcc.sh followed by your
selected options as described in the help menu:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# bnxt_setupcc.sh
Usage: bnxt_setupcc.sh [OPTION]...
-d RoCE Device Name (e.g. bnxt_re0, bnxt_re_bond0)
-i Ethernet Interface Name (e.g. p1p1 or for bond, specify slave interfaces like -i p6p1 -i p6p2)
-m [1-3] 1 - PFC only
2 - CC only
3 - PFC + CC mode
-v 1 - Enable priority vlan
-r [0-7] RoCE Packet Priority
-s VALUE RoCE Packet DSCP Value
-c [0-7] RoCE CNP Packet Priority
-p VALUE RoCE CNP Packet DSCP Value
-b VALUE RoCE Bandwidth percentage for ETS configuration - Default is 50%
-t [2] Default mode (Only RoCE v2 is supported - Input Ignored)
-C VALUE Set CNP Service Type
-u [1-3] Utility to configure QoS settings
1 - Use bnxtqos utility. Will disable lldptool if enabled. (default)
2 - Use lldptool
3 - Use Broadcom niccli utility. Will disable lldptool if enabled.
-h display helpEXAMPLE:
The default DSCP marking for CNP packets for interface gpu0 (bnxt_re0) is 0 as shown in the output below:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat apply | grep cnp ecn status (cnp_ecn) : Enabled cnp header ecn status (cnp_ecn) : ECT(1) minimum time between cnps (min_time_bet_cnp) : 0x0 usec rate reduction threshold (cnp_ratio_th) : 0x0 cnps cnp prio (cnp_prio) : 7 cnp dscp (cnp_dscp) : 0 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat apply | grep cc congestion control mode (cc_mode) : DCQCN-P cr threshold to reset cc (reset_cc_cr_th) : 0x32a cc ack bytes (cc_ack_bytes) : 0x44 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat cnp_prio 0x7 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat cnp_dscp 0x0
bnxt_setupcc.sh can be used to change it to the
value expected by the fabric (48) as follows:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# bnxt_setupcc.sh -d bnxt_re0 -i gpu0_eth -u 3 -p 48 -c 6 -s 26 -r 5 -m 3 ENABLE_PFC = 1 ENABLE_CC = 1 ENABLE_DSCP = 1 ENABLE_DSCP_BASED_PFC = 1 L2 50 RoCE 50 Using Ethernet interface gpu0_eth and RoCE interface bnxt_re0 Setting pfc/ets 0000:06:00.0 ---more--- AppTLV configured successfully.
Where:
- -u 3: Uses Broadcom niccli utility
- -p 48: Sets the DSCP value for CNP packets to 48 (0x30)
- -c: Configures the priority for CNP packets to 6
- -s: Defines the DSCP value for regular RoCE packets to 26 (0x1a)
- -r: Sets the priority for regular RoCE packets to 5
- -m 3: Configures both PFC and congestion control (ECN).
Verify the results with:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat apply | grep cnp ecn status (cnp_ecn) : Enabled cnp header ecn status (cnp_ecn) : ECT(1) minimum time between cnps (min_time_bet_cnp) : 0x0 usec rate reduction threshold (cnp_ratio_th) : 0x0 cnps cnp prio (cnp_prio) : 6 cnp dscp (cnp_dscp) : 48 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat apply | grep roce roce prio (roce_prio) : 5 roce dscp (roce_dscp) : 26 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat cnp_prio 0x6 root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat cnp_dscp 0x30 <= 48 is HEX root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat roce_dscp 0x1a <= 26 is HEX root@MI300X-01:/sys/kernel/config/bnxt_re/bnxt_re0/ports/1/cc# cat roce_prio 0x5
bnxt_setupcc.sh is installed and executable, but also
that at least one of the tools (niccli or
lldptool) is installed.The following example shows that bnxt_setupcc.sh
and niccli are installed, but lldptool is
not. It also shows examples of installing and using the
lldptool.
root@MI300X-01:/# which bnxt_setupcc.sh /usr/local/bin/bnxt_setupcc.sh root@MI300X-01:/usr/local/bin# ls bnxt_setupcc.sh -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 14761 Jan 17 18:06 bnxt_setupcc.sh root@MI300X-01:/$ which niccli /usr/bin/niccli root@MI300X-01:/usr/bin$ ls niccli -l lrwxrwxrwx 1 18896 1381 18 Sep 25 18:52 niccli -> /opt/niccli/niccli root@MI300X-01:/opt/niccli$ ls niccli -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 18896 1381 609 Sep 25 18:52 niccli root@MI300X-01:/$ which lldptool
The lldptool is used to check or modify the LLDP
(Link Layer Discovery Protocol) settings. To enable LLDP you need
to install lldpad, which also installs
lldptool automatically.
To install lldpad and
lldptool follow these steps:
- Install required dependencies.
Before installing lldpad, ensure that the necessary libraries are installed by running the following command:
sudo apt install libconfig9 libnl-3-200- libconfig9 – A configuration file processing library.
- libnl-3-200 – A library for interacting with the Linux Netlink interface.
- Install lldpad.
Install lldpad by running the following command:
sudo apt install lldpad
This package enables LLDP on the system, allowing it to exchange network topology information with other devices.
- Enable lldpad.
Enable lldp using systemctl:
sudo systemctl enable lldpad
This creates a systemd service that ensures lldpad is always running after a reboot.
- Start the lldpad service
Activate lldp using systemctl:
sudo systemctl start lldpad
This activates lldpad immediately, allowing it to process LLDP packets.
NOTE:To restart lldpad manually, use:sudo systemctl restart lldpadTo disable lldpad from starting at boot, use:sudo systemctl disable lldpad - Verify the installation
Check the service status using systemctl
user@MI300X-01:/etc/apt$ sudo systemctl status lldpad
● lldpad.service - Link Layer Discovery Protocol Agent Daemon.
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/lldpad.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2025-02-14 00:16:40 UTC; 2min 2s ago
TriggeredBy: ● lldpad.socket
Docs: man:lldpad(8)
Main PID: 695860 (lldpad)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 629145)
Memory: 1.3M (peak: 2.0M)
CPU: 510ms
CGroup: /system.slice/lldpad.service
└─695860 /usr/sbin/lldpad -t
Feb 14 00:16:40 MI300X-01 systemd[1]: Started lldpad.service - Link Layer Discovery Protocol Agent Daemon..This ensures the tool is installed and ready to use. If everything is working properly, you should see an "active (running)" status.
You can use lldptool to enable or disable LLDP on an interface, and to check the LLDP status and the neighbors discovered on that interface. The lldptool -h shows you all the different options:
user@MI300X-01:/etc/apt$ lldptool -h
Usage:
lldptool <command> [options] [arg] general command line usage format
lldptool go into interactive mode
<command> [options] [arg] general interactive command format
Options:
-i [ifname] network interface
-V [tlvid] TLV identifier
may be numeric or keyword (see below)
-c <argument list> used with get TLV command to specify
that the list of configuration elements
should be retrieved
-d use to delete specified argument from
the configuration. (Currently
implemented for DCBX App TLV settings)
-n "neighbor" option for command
-r show raw message
-R show only raw messages
-g destination agent (may be one of):
- nearestbridge (nb) (default)
- nearestcustomerbridge (ncb)
- nearestnontpmrbridge (nntpmrb)
Commands:
license show license information
-h|help show command usage information
-v|version show version
-p|ping ping lldpad and query pid of lldpad
-q|quit exit lldptool (interactive mode)
-S|stats get LLDP statistics for ifname
-t|get-tlv get TLVs from ifname
-T|set-tlv set arg for tlvid to value
-l|get-lldp get the LLDP parameters for ifname
-L|set-lldp set the LLDP parameter for ifname
TLV identifiers:
chassisID : Chassis ID TLV
portID : Port ID TLV
TTL : Time to Live TLV
portDesc : Port Description TLV
sysName : System Name TLV
sysDesc : System Description TLV
sysCap : System Capabilities TLV
mngAddr : Management Address TLV
macPhyCfg : MAC/PHY Configuration Status TLV
powerMdi : Power via MDI TLV
linkAgg : Link Aggregation TLV
MTU : Maximum Frame Size TLV
LLDP-MED : LLDP-MED Settings
medCap : LLDP-MED Capabilities TLV
medPolicy : LLDP-MED Network Policy TLV
medLoc : LLDP-MED Location TLV
medPower : LLDP-MED Extended Power-via-MDI TLV
medHwRev : LLDP-MED Hardware Revision TLV
medFwRev : LLDP-MED Firmware Revision TLV
medSwRev : LLDP-MED Software Revision TLV
medSerNum : LLDP-MED Serial Number TLV
medManuf : LLDP-MED Manufacturer Name TLV
medModel : LLDP-MED Model Name TLV
medAssetID : LLDP-MED Asset ID TLV
CIN-DCBX : CIN DCBX TLV
CEE-DCBX : CEE DCBX TLV
evb : EVB Configuration TLV
evbcfg : EVB draft 0.2 Configuration TLV
vdp : VDP draft 0.2 protocol configuration
IEEE-DCBX : IEEE-DCBX Settings
ETS-CFG : IEEE 8021QAZ ETS Configuration TLV
ETS-REC : IEEE 8021QAZ ETS Recommendation TLV
PFC : IEEE 8021QAZ PFC TLV
APP : IEEE 8021QAZ APP TLV
PVID : Port VLAN ID TLV
PPVID : Port and Protocol VLAN ID TLV
vlanName : VLAN Name TLV
ProtoID : Protocol Identity TLV
vidUsage : VID Usage Digest TLV
mgmtVID : Management VID TLV
linkAggr : Link Aggregation TLV
uPoE : Cisco 4-wire Power-via-MDI TLV
user@MI300X-01:/etc/apt$ sudo lldptool -S -i gpu0_eth
Total Frames Transmitted = 0
Total Discarded Frames Received = 0
Total Error Frames Received = 0
Total Frames Received = 92
Total Discarded TLVs = 0
Total Unrecognized TLVs = 8
Total Ageouts = 0
user@MI300X-01:/etc/apt$ sudo lldptool -L -i gpu0_eth AMDinStatus=rxtx
AMDinStatus = rxtx
user@MI300X-01:/etc/apt$ sudo lldptool -S -i gpu0_eth
Total Frames Transmitted = 5
Total Discarded Frames Received = 0
Total Error Frames Received = 0
Total Frames Received = 94
Total Discarded TLVs = 0
Total Unrecognized TLVs = 8
Total Ageouts = 0
user@MI300X-01:/etc/apt$ sudo lldptool -t -i gpu0_eth
Chassis ID TLV
MAC: 7c:c2:55:bd:75:d0
Port ID TLV
MAC: 7c:c2:55:bd:75:d0
Time to Live TLV
120
IEEE 8021QAZ ETS Configuration TLV
Willing: yes
CBS: not supported
MAX_TCS: 3
PRIO_MAP: 0:0 1:0 2:0 3:0 4:0 5:0 6:0 7:0
TC Bandwidth: 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
TSA_MAP: 0:strict 1:strict 2:strict 3:strict 4:strict 5:strict 6:strict 7:strict
IEEE 8021QAZ PFC TLV
Willing: yes
MACsec Bypass Capable: no
PFC capable traffic classes: 1
PFC enabled: none
End of LLDPDU TLVCheck the Installing and Configuring Software Manually section of the Broadcom Ethernet Network Adapter User Guide or Installing the NICCLI Configuration Utility for more details.
Monitor interface and ECN/PFC operation:
Once you have the Broadcom name for a particular gpu as described at the beginning of this section, you can locate the directories where the interface’s operation status, as well as RoCE traffic and Congestion Control statistics are located.
- Navigate to the corresponding directory
/sys/class/infiniband/<Broadcom-interface-name>
EXAMPLE:
For gpu0_eth:
root@MI300X-01:/home/jnpr/SCRIPTS# cd /sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3 root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3# ls device fw_ver hca_type hw_rev node_desc node_guid node_type ports power subsystem sys_image_guid uevent root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3# ls device/net/gpu3_eth/ addr_assign_type address addr_len broadcast carrier carrier_changes carrier_down_count carrier_up_count device dev_id dev_port dormant duplex flags gro_flush_timeout ifalias ifindex iflink link_mode mtu name_assign_type napi_defer_hard_irqs netdev_group operstate phys_port_id phys_port_name phys_switch_id power proto_down queues speed statistics subsystem testing threaded tx_queue_len type uevent
Here you can check attributes such as operational state, address, mtu, speed, and interface statistics (including transmit and received packets, dropped packets, as well as ECN-marked packets, CNP packets received and CNP packets transmitted):
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3# cat device/net/gpu3_eth/operstate
up
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3# cat device/net/gpu3_eth/address
7c:c2:55:bd:7e:20
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3# cat device/net/gpu3_eth/mtu
9000
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3# cat device/net/gpu3_eth/speed
400000
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3# ls device/net/gpu3_eth/statistics
collisions multicast rx_bytes rx_compressed rx_crc_errors
rx_dropped rx_errors rx_fifo_errors rx_frame_errors rx_length_errors
rx_missed_errors rx_nohandler rx_over_errors rx_packets tx_aborted_errors
tx_bytes tx_carrier_errors tx_compressed tx_dropped tx_errors
tx_fifo_errors tx_heartbeat_errors tx_packets tx_window_errors tx_fifo_errors
rx_dropped rx_frame_errors rx_nohandlertx_aborted_errors tx_compressed tx_window_errors
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3# ls ports/1
cap_mask cm_rx_duplicates cm_rx_msgs cm_tx_msgs cm_tx_retries
counters gid_attrs gids hw_counters lid
lid_mask_count link_layer phys_state pkeys rate
sm_lid sm_sl state
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3# ls ports/1/counters/ -m
excessive_buffer_overrun_errors link_downed link_error_recovery
local_link_integrity_errors port_rcv_constraint_errors port_rcv_data
port_rcv_errors port_rcv_packets port_rcv_remote_physical_errors
port_rcv_switch_relay_errors port_xmit_constraint_errors port_xmit_data
port_xmit_discards port_xmit_packets port_xmit_wait
symbol_error VL15_dropped To check ECN statistics, check the related counters for the specific interface:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband/bnxt_re3# ls ports/1/hw_counters/ -m
active_ahs active_cqs active_mrs active_mws
active_pds active_qps active_rc_qps active_srqs
active_ud_qps bad_resp_err db_fifo_register dup_req
lifespan local_protection_err local_qp_op_err max_retry_exceeded
mem_mgmt_op_err missing_resp oos_drop_count pacing_alerts
pacing_complete pacing_reschedule recoverable_errors remote_access_err
remote_invalid_req_err remote_op_err res_cmp_err res_cq_load_err
res_exceed_max res_exceeds_wqe res_invalid_dup_rkey res_irrq_oflow
resize_cq_cnt res_length_mismatch res_mem_err res_opcode_err
res_rem_inv_err res_rx_domain_err res_rx_invalid_rkey res_rx_no_perm
res_rx_pci_err res_rx_range_err res_srq_err res_srq_load_err
res_tx_domain_err res_tx_invalid_rkey res_tx_no_perm res_tx_pci_err
res_tx_range_err res_unaligned_atomic res_unsup_opcode res_wqe_format_err
rnr_naks_rcvd rx_atomic_req rx_bytes rx_cnp_pkts
rx_ecn_marked_pkts rx_good_bytes rx_good_pkts rx_out_of_buffer
rx_pkts rx_read_req rx_read_resp rx_roce_discards
rx_roce_errors rx_roce_only_bytes rx_roce_only_pkts rx_send_req
rx_write_req seq_err_naks_rcvd to_retransmits tx_atomic_req
tx_bytes tx_cnp_pkts tx_pkts tx_read_req
tx_read_resp tx_roce_discards tx_roce_errors tx_roce_only_bytes
tx_roce_only_pkts tx_send_req tx_write_req unrecoverable_err
watermark_ahs watermark_cqs watermark_mrs watermark_mws
watermark_pds watermark_qps watermark_rc_qps watermark_srqs
watermark_ud_qps
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband#
for iface in /sys/class/infiniband/*/ports/1/hw_counters/rx_ecn_marked_pkts; do
echo "$(basename $(dirname $(dirname $(dirname $(dirname "$iface"))))) : $(cat "$iface")"
done
bnxt_re0 : 0
bnxt_re1 : 1102
bnxt_re2 : 532
bnxt_re3 : 707
bnxt_re4 : 474
bnxt_re5 : 337
bnxt_re6 : 970
bnxt_re7 : 440
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband#
for iface in /sys/class/infiniband/*/ports/1/hw_counters/tx_cnp_pkts; do
echo "$(basename $(dirname $(dirname $(dirname $(dirname "$iface"))))) : $(cat "$iface")"
done
bnxt_re0 : 0
bnxt_re1 : 1102
bnxt_re2 : 532
bnxt_re3 : 707
bnxt_re4 : 474
bnxt_re5 : 337
bnxt_re6 : 970
bnxt_re7 : 440
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband#
for iface in /sys/class/infiniband/*/ports/1/hw_counters/rx_cnp_pkts; do
echo "$(basename $(dirname $(dirname $(dirname $(dirname "$iface"))))) : $(cat "$iface")"
done
bnxt_re0 : 0
bnxt_re1 : 830
bnxt_re2 : 0
bnxt_re3 : 375
bnxt_re4 : 734
bnxt_re5 : 23
bnxt_re6 : 2395
bnxt_re7 : 2291ethtool -s <InterfaceIndex> |egrep "pfc_frames|roce_pause"|more
EXAMPLE:
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband# for iface in $(ls /sys/class/net/ | grep '^gpu'); do
echo "$iface :"
sudo ethtool -S "$iface" | egrep "pfc_frames|roce_pause"
done
gpu0_eth :
rx_pfc_frames: 0
tx_pfc_frames: 22598
continuous_roce_pause_events: 0
resume_roce_pause_events: 0
gpu1_eth :
rx_pfc_frames: 0
tx_pfc_frames: 194626
continuous_roce_pause_events: 0
resume_roce_pause_events: 0
gpu2_eth :
rx_pfc_frames: 0
tx_pfc_frames: 451620
continuous_roce_pause_events: 0
resume_roce_pause_events: 0
gpu3_eth :
rx_pfc_frames: 0
tx_pfc_frames: 492042
continuous_roce_pause_events: 0
resume_roce_pause_events: 0
gpu4_eth :
rx_pfc_frames: 0
tx_pfc_frames: 407113
continuous_roce_pause_events: 0
resume_roce_pause_events: 0
gpu5_eth :
rx_pfc_frames: 0
tx_pfc_frames: 290378
continuous_roce_pause_events: 0
resume_roce_pause_events: 0
gpu6_eth :
rx_pfc_frames: 0
tx_pfc_frames: 228918
continuous_roce_pause_events: 0
resume_roce_pause_events: 0
gpu7_eth :
rx_pfc_frames: 0
tx_pfc_frames: 477572
continuous_roce_pause_events: 0
resume_roce_pause_events: 0
root@MI300X-01:/sys/class/infiniband#
for iface in $(ls /sys/class/net/ | grep '^gpu'); do
echo "$iface :"
sudo ethtool -S "$iface" | grep cos | grep -v ": 0"
done
gpu0_eth :
rx_bytes_cos0: 9529443988084
rx_packets_cos0: 3319036491
rx_bytes_cos4: 18230144638154
rx_packets_cos4: 5955503873
rx_discard_bytes_cos4: 3032625534
rx_discard_packets_cos4: 736191
tx_bytes_cos0: 27757371721830
tx_packets_cos0: 9297694711
tx_bytes_cos4: 604920
tx_packets_cos4: 2628
gpu1_eth :
rx_bytes_cos0: 27969554019118
rx_packets_cos0: 9565740297
rx_bytes_cos4: 4193860
rx_packets_cos4: 47350
tx_bytes_cos0: 27738638134736
tx_packets_cos0: 9184463836
tx_bytes_cos4: 619484
tx_packets_cos4: 2686
tx_bytes_cos5: 81548
tx_packets_cos5: 1102
gpu2_eth :
rx_bytes_cos0: 27961559203510
rx_packets_cos0: 9438688373
rx_bytes_cos4: 4134654
rx_packets_cos4: 46526
tx_bytes_cos0: 27177768852872
tx_packets_cos0: 9028738664
tx_bytes_cos4: 619444
tx_packets_cos4: 2686
tx_bytes_cos5: 39368
tx_packets_cos5: 532
gpu3_eth :
rx_bytes_cos0: 27886187894460
rx_packets_cos0: 9394306658
rx_bytes_cos4: 4161424
rx_packets_cos4: 46910
tx_bytes_cos0: 27963541263338
tx_packets_cos0: 9314918707
tx_bytes_cos4: 619624
tx_packets_cos4: 2688
tx_bytes_cos5: 52318
tx_packets_cos5: 707
gpu4_eth :
rx_bytes_cos0: 27760098268028
rx_packets_cos0: 9493708902
rx_bytes_cos4: 4190302
rx_packets_cos4: 47275
tx_bytes_cos0: 27943026331154
tx_packets_cos0: 9175330615
tx_bytes_cos4: 619068
tx_packets_cos4: 2683
tx_bytes_cos5: 35076
tx_packets_cos5: 474
gpu5_eth :
rx_bytes_cos0: 27742656661456
rx_packets_cos0: 9603877462
rx_bytes_cos4: 4136456
rx_packets_cos4: 46558
tx_bytes_cos0: 27862529155204
tx_packets_cos0: 9053600792
tx_bytes_cos4: 619318
tx_packets_cos4: 2686
tx_bytes_cos5: 24938
tx_packets_cos5: 337
gpu6_eth :
rx_bytes_cos0: 27204139187706
rx_packets_cos0: 9417550449
rx_bytes_cos4: 4309610
rx_packets_cos4: 48912
tx_bytes_cos0: 27939647032856
tx_packets_cos0: 9122722262
tx_bytes_cos4: 619248
tx_packets_cos4: 2685
tx_bytes_cos5: 71780
tx_packets_cos5: 970
gpu7_eth :
rx_bytes_cos0: 27985967658372
rx_packets_cos0: 9636086344
rx_bytes_cos4: 4303716
rx_packets_cos4: 48823
tx_bytes_cos0: 27949102839310
tx_packets_cos0: 9149097911
tx_bytes_cos4: 619138
tx_packets_cos4: 2684
tx_bytes_cos5: 32560
tx_packets_cos5: 440
BCM57608> sudo niccli -i 2 listmap -pri2cos
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NIC CLI v231.2.63.0 - Broadcom Inc. (c) 2024 (Bld-94.52.34.117.16.0)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Base Queue is 0 for port 0
----------------------------
Priority TC Queue ID
------------------------
0 0 4
1 0 4
2 0 4
3 1 0
4 0 4
5 0 4
6 0 4
7 2 5 Configuring the server to use the management interface for RCCL control traffic:
ROCm Communication Collectives Library (RCCL) creates TCP sessions to coordinate processes and exchange Queue Pair information for RoCE, GIDs (Global IDs), Local and remote buffer addresses, RDMA keys (RKEYs for memory access permissions)
These TCP sessions are created when the job starts and by default use one of the GPU interfaces (same interfaces used for RoCEv2 traffic).
Example:
jnpr@MI300X-01:~$ netstat -atn | grep 10.200 | grep "ESTABLISHED" tcp 0 0 10.200.4.8:47932 10.200.4.2:43131 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 10.200.4.8:46699 10.200.4.2:37236 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 10.200.2.8:60502 10.200.13.2:35547 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 10.200.4.8:37330 10.200.4.2:55355 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 10.200.4.8:56438 10.200.4.2:53947 ESTABLISHED ---more---
It is recommended that the management interface connected to the (Frontend Fabric) is used. To achieve this, include the following when starting a job: export NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME="mgmt_eth". The same environment variable applies to both NCCL and RCCL.
Example:
jnpr@MI300X-01:~$ netstat -atn | grep 10.10.1 | grep "ESTABLISHED" tcp 0 0 10.10.1.0:44926 10.10.1.2:33149 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 10.10.1.0:46705 10.10.1.0:40320 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 10.10.1.0:54661 10.10.1.10:52452 ESTABLISHED ---more---
AMD Pollara DCQCN configuration for RDMA Traffic
For the AMD Pollara validation, DCQCN needs to be enabled and QOS has to be applied on the AMD NIC cards.
- Configure QOS on the NICs using the script. The DSCP parameters are equivalent to the
values suggested in Table 15. Server DCQCN configuration parameters.
jnpr@mi300-01:~$ cat /usr/local/bin/jnpr-setupqos.sh #!/bin/bash for i in $(sudo /usr/sbin/nicctl show port | grep Port | awk {'print $3'}); do sudo /usr/sbin/nicctl update port -p $i --pause-type pfc --rx-pause enable --tx-pause enable; done cts_dscp=48 cts_prio=2 data_dscp=26 data_prio=3 sudo nicctl update qos --classification-type dscp sudo nicctl update qos dscp-to-priority --dscp $cts_dscp --priority $cts_prio sudo nicctl update qos dscp-to-priority --dscp $data_dscp --priority $data_prio sudo nicctl update qos pfc --priority $cts_prio --no-drop enable sudo nicctl update qos pfc --priority $data_prio --no-drop enable sudo nicctl update qos dscp-to-purpose --dscp $cts_dscp --purpose xccl-cts - Using AMD
nicctlcommand line Utility below are the QOS parameters configured:jnpr@mi300-01:~$ sudo nicctl show qos | more NIC : 42424650-4c32-3530-3130-313346000000 (0000:06:00.0) Port : 0490812b-9860-4242-4242-000011010000 Classification type : DSCP DSCP-to-priority : DSCP bitmap : 0xfffefffffbffffff ==> priority : 0 DSCP bitmap : 0x0001000000000000 ==> priority : 2 DSCP bitmap : 0x0000000004000000 ==> priority : 3 DSCP : 0-25, 27-47, 49-63 ==> priority : 0 DSCP : 48 ==> priority : 2 DSCP : 26 ==> priority : 3 DSCP-to-purpose : 48 ==> xccl-cts PFC : PFC priority bitmap : 0xc PFC no-drop priorities : 2,3 Scheduling : -------------------------------------------- Priority Scheduling Bandwidth Rate-limit Type (in %age) (in Gbps) -------------------------------------------- 0 DWRR 0 N/A 2 DWRR 0 N/A 3 DWRR 0 N/A NIC : 42424650-4c32-3530-3130-313844000000 (0000:23:00.0) Port : 0490812b-9fb0-4242-4242-000011010000 Classification type : DSCP DSCP-to-priority : DSCP bitmap : 0xfffefffffbffffff ==> priority : 0 DSCP bitmap : 0x0001000000000000 ==> priority : 2 DSCP bitmap : 0x0000000004000000 ==> priority : 3 DSCP : 0-25, 27-47, 49-63 ==> priority : 0 DSCP : 48 ==> priority : 2 DSCP : 26 ==> priority : 3 DSCP-to-purpose : 48 ==> xccl-cts PFC : PFC priority bitmap : 0xc PFC no-drop priorities : 2,3 --More-- - The
rdma linkcommand can be used to check if the roce-devices association to the AMD Pollara NIC cards exist.jnpr@mi300-01:~$ rdma link | grep gpu link rocep9s0/1 state ACTIVE physical_state LINK_UP netdev gpu0_eth link rocep38s0/1 state ACTIVE physical_state LINK_UP netdev gpu1_eth link rocep70s0/1 state ACTIVE physical_state LINK_UP netdev gpu2_eth link roceo1/1 state ACTIVE physical_state LINK_UP netdev gpu3_eth link rocep137s0/1 state ACTIVE physical_state LINK_UP netdev gpu4_eth link rocep166s0/1 state ACTIVE physical_state LINK_UP netdev gpu5_eth link rocep198s0/1 state ACTIVE physical_state LINK_UP netdev gpu6_eth link rocep233s0/1 state ACTIVE physical_state LINK_UP netdev gpu7_eth
The roce-devices are created when the ionic_rdma kernel module is loaded and should create the below roce-device file for each NIC card.
jnpr@mi300-01:/sys/class/infiniband$ find /sys/class/infiniband -type l /sys/class/infiniband/rocep137s0 /sys/class/infiniband/rocep38s0 /sys/class/infiniband/rocep70s0 /sys/class/infiniband/roceo1 /sys/class/infiniband/rocep166s0 /sys/class/infiniband/rocep233s0 /sys/class/infiniband/rocep198s0 /sys/class/infiniband/rocep9s0
- To configure DCQCN on the AMD Pollara NICs, run below script with appropriate
parameters.
jnpr @mi300-01:~$ cat /usr/local/bin/jnpr-enable-dcqcn.sh #!/bin/bash TOKEN_BUCKET_SIZE=800000 AI_RATE=160 ALPHA_UPDATE_INTERVAL=1 ALPHA_UPDATE_G=512 INITIAL_ALPHA_VALUE=64 RATE_INCREASE_BYTE_COUNT=431068 HAI_RATE=300 RATE_REDUCE_MONITOR_PERIOD=1 RATE_INCREASE_THRESHOLD=1 RATE_INCREASE_INTERVAL=1 CNP_DSCP=48 ROCE_DEVICES=$(rdma link | grep gpu | awk '{ print $2 }' | awk -F/ '{ print $1 }' | paste -sd " ") for roce_dev in $ROCE_DEVICES do sudo nicctl update dcqcn -r $roce_dev -i 1 \ --token-bucket-size $TOKEN_BUCKET_SIZE \ --ai-rate $AI_RATE \ --alpha-update-interval $ALPHA_UPDATE_INTERVAL \ --alpha-update-g $ALPHA_UPDATE_G \ --initial-alpha-value $INITIAL_ALPHA_VALUE \ --rate-increase-byte-count $RATE_INCREASE_BYTE_COUNT \ --hai-rate $HAI_RATE \ --rate-reduce-monitor-period $RATE_REDUCE_MONITOR_PERIOD \ --rate-increase-threshold $RATE_INCREASE_THRESHOLD \ --rate-increase-interval $RATE_INCREASE_INTERVAL \ --cnp-dscp $CNP_DSCP Done - Using the nicctl command check the DCQCN profile for each roce-device.
jnpr@mi300-01:~$ sudo nicctl show dcqcn --roce-device rocep137s0 | more ROCE device : rocep137s0 DCQCN profile id : 7 Status : Disabled Rate reduce monitor period : 100 Alpha update interval : 100 Clamp target rate : 0 Rate increase threshold : 1 Rate increase byte count : 431068 Rate increase in AI phase : 200 Alpha update G value : 50 Minimum rate : 1 Token bucket size : 4000000 Rate increase interval : 10 Rate increase in HAI phase : 200 Initial alpha value : 64 DSCP value used for CNP : 48 DCQCN profile id : 5 Status : Disabled Rate reduce monitor period : 100 Alpha update interval : 100 Clamp target rate : 0 Rate increase threshold : 1 Rate increase byte count : 431068 Rate increase in AI phase : 200 Alpha update G value : 50 Minimum rate : 1 Token bucket size : 4000000 Rate increase interval : 10 Rate increase in HAI phase : 200 Initial alpha value : 64 DSCP value used for CNP : 48 DCQCN profile id : 3 Status : Disabled Rate reduce monitor period : 100 Alpha update interval : 100 Clamp target rate : 0 Rate increase threshold : 1 Rate increase byte count : 431068 Rate increase in AI phase : 200 Alpha update G value : 50 Minimum rate : 1 Token bucket size : 4000000 Rate increase interval : 10 Rate increase in HAI phase : 200 Initial alpha value : 64 DSCP value used for CNP : 48 --More—
- Finally run the rccl_test.sh script as below. The example below
shows the tests run for “All reduce”.
jnpr@mi300-01:/mnt/nfsshare/source/aicluster/rccl-tests$ ./run-rccl.sh Running all_reduce, channels 64, qps 1 ... Num nodes: 2 + tee --append /mnt/nfsshare/logs/rccl/MI300-RAILS-ALL/06062025_18_03_35/test.log + /opt/ompi/bin/mpirun --np 16 --allow-run-as-root -H MI300-01:8,MI300-02:8 --bind-to numa -x NCCL_IB_GID_INDEX=1 -x UCX_UNIFIED_MODE=y -x NCCL_IB_PCI_RELAXED_ORDERING=1 -x NCCL_GDR_FLUSH_DISABLE=1 -x RCCL_GDR_FLUSH_GPU_MEM_NO_RELAXED_ORDERING=0 -x PATH=/opt/ompi/bin:/opt/rocm/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin -x LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/home/dbarmann/pollara/rccl-7961624/build/release:/home/dbarmann/pollara/amd-anp-new/build:/opt/ompi/lib: -x UCX_NET_DEVICES=gpu0_eth,gpu1_eth,gpu2_eth,gpu3_eth,gpu4_eth,gpu5_eth,gpu6_eth,gpu7_eth -x NCCL_IB_HCA=rocep9s0,rocep38s0,rocep70s0,roceo1,rocep137s0,rocep166s0,rocep198s0,rocep233s0 --mca btl '^vader,openib' --mca btl_tcp_if_include mgmt_eth -x NCCL_MIN_NCHANNELS=64 -x NCCL_MAX_NCHANNELS=64 -x NCCL_IB_QPS_PER_CONNECTION=1 -x NCCL_TOPO_DUMP_FILE=/tmp/system_run2.txt -x HSA_NO_SCRATCH_RECLAIM=1 -x NCCL_GDRCOPY_ENABLE=0 -x NCCL_IB_TC=106 -x NCCL_IB_FIFO_TC=192 -x NCCL_IGNORE_CPU_AFFINITY=1 -x RCCL_LL128_FORCE_ENABLE=1 -x NCCL_PXN_DISABLE=0 -x NCCL_DEBUG=INFO -x NET_OPTIONAL_RECV_COMPLETION=1 -x NCCL_IB_USE_INLINE=1 -x NCCL_DEBUG_FILE=/mnt/nfsshare/logs/rccl/MI300-RAILS-ALL/06062025_18_03_35/nccl-debug.log -x 'LD_PRELOAD=/home/dbarmann/pollara/amd-anp-new/build/librccl-net.so /home/dbarmann/pollara/rccl-7961624/build/release/librccl.so' /mnt/nfsshare/source/aicluster/rccl-tests/build/all_reduce_perf -b 1024 -e 16G -f 2 -g 1 -n 20 -m 1 -c 1 -w 5_# nThread 1 nGpus 1 minBytes 1024 maxBytes 17179869184 step: 2(factor) warmup iters: 5 iters: 20 agg iters: 1 validation: 1 graph: 0_# rccl-tests: Version develop:b0a3841+ # Using devices # Rank 0 Group 0 Pid 18335 on mi300-01 device 0 [0000:05:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 1 Group 0 Pid 18336 on mi300-01 device 1 [0000:29:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 2 Group 0 Pid 18337 on mi300-01 device 2 [0000:49:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 3 Group 0 Pid 18340 on mi300-01 device 3 [0000:65:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 4 Group 0 Pid 18338 on mi300-01 device 4 [0000:85:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 5 Group 0 Pid 18341 on mi300-01 device 5 [0000:a9:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 6 Group 0 Pid 18342 on mi300-01 device 6 [0000:c9:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 7 Group 0 Pid 18339 on mi300-01 device 7 [0000:e5:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 8 Group 0 Pid 16249 on mi300-02 device 0 [0000:05:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 9 Group 0 Pid 16251 on mi300-02 device 1 [0000:29:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 10 Group 0 Pid 16250 on mi300-02 device 2 [0000:49:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 11 Group 0 Pid 16254 on mi300-02 device 3 [0000:65:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 12 Group 0 Pid 16255 on mi300-02 device 4 [0000:85:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 13 Group 0 Pid 16253 on mi300-02 device 5 [0000:a9:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 14 Group 0 Pid 16252 on mi300-02 device 6 [0000:c9:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # Rank 15 Group 0 Pid 16256 on mi300-02 device 7 [0000:e5:00] AMD Instinct MI300X # # out-of-place in-place # size count type redop root time algbw busbw #wrong time algbw busbw #wrong # (B) (elements) (us) (GB/s) (GB/s) (us) (GB/s) (GB/s) 1024 256 float sum -1 41.61 0.02 0.05 0 53.55 0.02 0.04 0 2048 512 float sum -1 43.79 0.05 0.09 0 50.54 0.04 0.08 0 4096 1024 float sum -1 45.75 0.09 0.17 0 45.21 0.09 0.17 0 8192 2048 float sum -1 46.50 0.18 0.33 0 47.75 0.17 0.32 0 16384 4096 float sum -1 60.52 0.27 0.51 0 48.90 0.34 0.63 0 32768 8192 float sum -1 49.68 0.66 1.24 0 52.57 0.62 1.17 0 65536 16384 float sum -1 53.75 1.22 2.29 0 52.74 1.24 2.33 0 131072 32768 float sum -1 69.16 1.90 3.55 0 56.83 2.31 4.32 0 262144 65536 float sum -1 69.31 3.78 7.09 0 63.17 4.15 7.78 0 524288 131072 float sum -1 77.16 6.79 12.74 0 80.51 6.51 12.21 0 1048576 262144 float sum -1 127.5 8.23 15.42 0 107.6 9.75 18.28 0 2097152 524288 float sum -1 125.0 16.78 31.46 0 130.9 16.02 30.04 0 4194304 1048576 float sum -1 149.5 28.06 52.61 0 148.4 28.26 52.99 0 8388608 2097152 float sum -1 222.9 37.63 70.55 0 231.6 36.21 67.90 0 16777216 4194304 float sum -1 321.3 52.21 97.90 0 326.2 51.43 96.43 0 33554432 8388608 float sum -1 436.2 76.93 144.25 0 447.0 75.06 140.75 0 67108864 16777216 float sum -1 678.9 98.85 185.35 0 684.6 98.02 183.79 0 134217728 33554432 float sum -1 1164.6 115.25 216.10 0 1148.1 116.90 219.19 0 268435456 67108864 float sum -1 1550.3 173.15 324.66 0 1563.9 171.65 321.84 0 536870912 134217728 float sum -1 2979.9 180.16 337.81 0 2977.6 180.30 338.07 0 1073741824 268435456 float sum -1 5824.8 184.34 345.64 0 5859.5 183.25 343.59 0 2147483648 536870912 float sum -1 11596 185.20 347.25 0 11611 184.94 346.77 0 4294967296 1073741824 float sum -1 520420 8.25 15.47 0 23190 185.21 347.27 0 8589934592 2147483648 float sum -1 46157 186.10 348.94 0 46150 186.13 349.00 0 17179869184 4294967296 float sum -1 568668 30.21 56.65 0 91823 187.10 350.81 0 # Errors with asterisks indicate errors that have exceeded the maximum threshold. # Out of bounds values : 0 OK # Avg bus bandwidth : 117.077 #
