Quantum Safe IPsec VPN
Learn how to use and configure the out-of-band key retrieval mechanisms in the IKED process to negotiate with quantum secured IKE and IPsec SAs.
Quantum Security Overview
The IPsec communication channel relies on the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocol. The IKE maintains security parameters to protect the data traffic. The security parameters include encryption and authentication algorithms, and associated keys.
The security protocols rely on asymmetric cryptographic algorithms such as Diffie Hellman (DH) or Elliptic Curve Diffie Hellman (ECDH) to establish keys are vulnerable to attacks.
To avoid security attacks, the RFC8784 introduces a method out-of-band method. The out-of-band method adds a secret key at the initiator and the responder. The secret key is Post-quantum Pre-shared Key (PPK).
-
You can use the PPK in addition to the authentication method in IKEv2.
-
PPK provides quantum resistance to any child SAs in initial negotiated IPsec SAs and any subsequent re-iked IPsec SAs.
-
With PPK and peer authentication key, initiator and responder can detect key mismatch.
Junos Key Manager Overview
You can use Junos Key Manager (JKM) to configure the static keys or dynamics keys to protect the data plane and control plane.
The JKM process acts as a key store and a proxy between the client or crypto application. The client or crypto application requires a key to establish an encrypted and authenticated quantum safe session with peer or application. The quantum safe uses the out-of-band key retrieval mechanism that lets two peers have the key. Different out-of-band mechanisms will have different protocols or methods to communicate. The JKM provides a common uniform interface for client or crypto applications to communicate.
Key Retrieval Mechanism
Two out-of-band key retrieval mechanisms in the IKED process to negotiate with quantum secured IKE and IPsec SAs.
-
Static Key—With static key profiles, you can configure a static key ID and a corresponding key. The same static key ID and key gets generated every time a request to JKM over a static key profile.
-
Quantum Key Manager—With quantum key manager key profiles, you can access the Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) devices and Quantum Network. The Quantum Network generates and exchange quantum keys between peers. Generates a different key ID and key every time on request to JKM over a quantum key manager key profile.
Use Key Profile for Quantum Safe IPsec VPN
With static key profiles, you can configure a static key ID and a corresponding key. To establish the quantum safe IPsec SAs, use the static key profile as Post-Quantum Pre-Shared Key (PPK) profile in the IPsec-VPN configuration. Uses the same key and key ID to re-authenticate existing IKE SA.
With quantum key manager key profile profiles, to access the Quantum Networks you need access to the QKD devices. The Quantum Network generates and exchanges quantum keys between peers. You can configure all the necessary parameters such as local SAE ID, URL to the QKD device, and so on. To establish IPsec SAs, use the quantum key manager key profile as Post-Quantum Pre-Shared Key (PPK) profile in the IPsec VPN configuration. Uses a different key and key ID to re-authenticate existing IKE SA.
Quantum Key Distribution
Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a secure key distribution method that uses quantum. Networks use quantum channels for generating the same key at both ends and monitor the quantum channel between the peers. These keys are dynamic, protects the data plane, and control plane.
Key Management Entity (KME) is the term we use to refer to the QKD devices on the management or control layer. QKD devices connect to each other through their quantum or QKD network. The KMEs connects over the public network through the secure channels for exchanging any control messages. The applications, Secure Application Entity (SAEs), and devices interact with KMEs through the secure channels as per ETSI specification. HTTPS combines with mutual TLS authentication and enables secure operations over the QKD network.
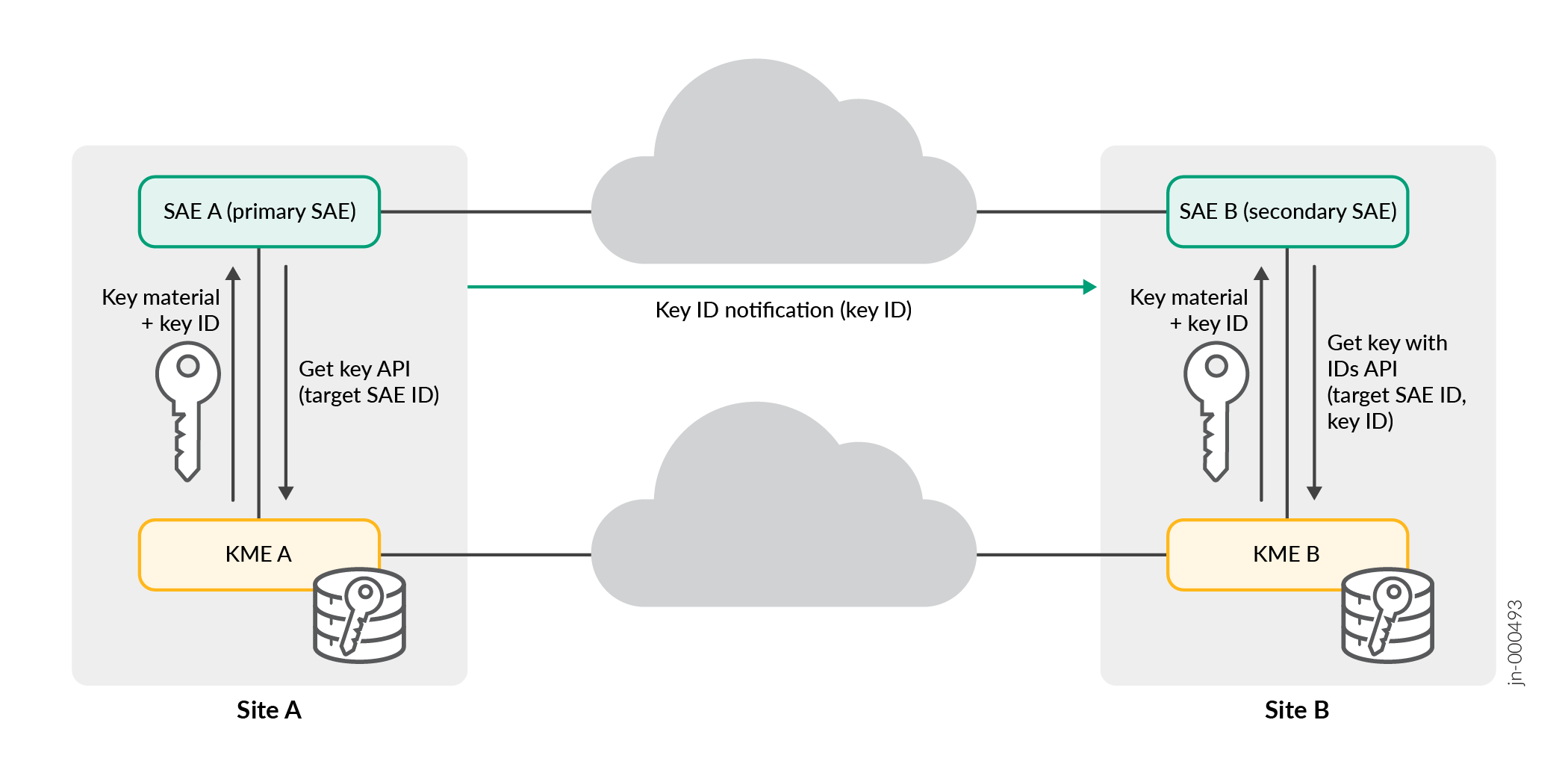
In the Figure 1 describes how the two devices interacting with their corresponding QKD devices to establish a quantum secured session
-
SAE A role is primary. SAE A acts as the initiator to establish a quantum secured session with SAE B.
-
The SAE B role is secondary. SAE B acts as the responder.
-
The SAE A request the KME A through the Get key API to generate and share a new quantum key with SAE B with target SAE ID.
-
The KME A performs the operation and responds to SAE A with the generated key ID and key material.
-
KME B receives the key material and the generated ID key over the QKD network.
-
The SAE A initiates secured session with SAE B directly using the same key and key ID.
-
An exchange of messages establishes a secure session with SAE B.
-
SAE A sends the key ID in plaintext or encrypted for the corresponding quantum key that is used to secure the session with SAE B.
-
Once SAE B receives the key ID, the SAE B contacts KME B through the Get key with IDs API to get the corresponding quantum-key for the given key ID and target SAE ID or SAE A.
-
After SAE B gets the key, a fully quantum secured session establishes between SAE A and SAE B.
Configure Static Key Profile for Junos Key Manager
This example shows how to configure static key profile for Junos key manager. Configure the static keys on concerned gateways and do not need share static keys over the Internet to establish the IPsec tunnel.
Requirements
-
Hardware requirements —Juniper Networks® SRX1500 Firewall and higher-numbered device models or Juniper Networks® vSRX Virtual Firewall (vSRX3.0).
-
Software requirements—Junos OS Release 22.4R1 or later with JUNOS ike and JUNOS Key Manager packages.
Overview
With static key based profiles you need to configure a static key ID and a corresponding key. If you use the static key profile in the IPsec VPN object, when the re-authentication for existing IKE SA the same key and key ID are used.
Configuration
Configure the static key profile for Junos key manager.
user@host# set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 static key-id ascii-text test-ppk-id user@host# set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 static key ascii-text qjwbdip139u5mcy89m28pcgowerefnkjsdg
Verification
Purpose
Verify the static key profile and keys.
Action
From operational mode, enter the request security key-manager profiles get
profile-keys name km_profile_1 to view the static key profile and keys.
user@host> request security key-manager profiles get profile-keys name km_profile_1
- Response:
- Status: SUCCESS
- Name: km_profile_1
- Type: Static
- Key-size: 280 bits
- Key-count: 1
- Key-ids:
- test-ppk-id
- Keys:
- 716a776264697031333975356d637938396d32387063676f77657265666e6b6a736467From operational mode, enter the show security key-manager profiles name
km_profile_1 detail to view the static key profile details.
user@host> show security key-manager profiles name km_profile_1 detail
Name: km_profile_1, Index: 1, Type: Static
Configured-at: 10.09.23 (20:16:34)
Time-elapsed: 0 hrs 2 mins 21 secs
Request stats:
Received: 1
In-progress: 0
Success: 1
Failed: 0
Meaning
The request security key-manager profiles get profile-keys name
km_profile_1 displays the status, static key profile name, type, key size, key
ID, and keys.
The show security key-manager profiles name km_profile_1 detail displays
the static key profile name, type, and request status.
Example: Configure Static Keys Profile for Site-to-Site VPN
Use this configuration example to configure the static key profile. You can use the static key profile to secure an IPsec Site-to-Site VPN infrastructure.
You can secure an IPsec Site-to-Site VPN infrastructure by configuring the static key profile.
In this configuration example, the SRX1 and SRX2 devices use the static key profile to fetch the QKD keys on IPsec VPN. The QKD keys help to send traffic securely over the Internet.
|
Reading Time |
Less than an hour |
|
Configuration Time |
Less than an hour |
- Example Prerequisites
- Before You Begin
- Functional Overview
- Topology Overview
- Topology Illustration
- Step-By-Step Configuration on SRX Series Firewall Devices
- Verification
- Appendix 1: Set Commands on all Devices
- Appendix 2: Show Configuration Output on DUT
Example Prerequisites
|
Hardware requirements |
Juniper Networks® SRX1500 Firewall or higher-numbered device models or Juniper Networks® vSRX Virtual Firewall (vSRX3.0) |
|
Software requirements |
Junos OS Release 22.4R1 or later. |
Before You Begin
|
Benefits |
|
|
Useful Resources |
|
|
Know more |
|
|
Hands-on experience |
|
|
Learn more |
Functional Overview
| IPsec VPN |
Deploy a IPsec VPN topology where SRX Series Firewall devices are connected by VPN tunnels that send traffic through the IPsec VPN tunnel. The VPN tunnels are later configured to use quantum keys making them quantum-safe VPN tunnels. |
| IKE gateway |
Establish a secure connection, the IKE gateway uses the IKE policy to limit itself to the configured group of CAs (ca-profiles) while validating the certificate. |
| Proposals | |
| IKE proposal |
Define the algorithms and keys used to establish the secure IKE connection with the peer security gateway. IKE creates the dynamic SAs and negotiates them for IPsec. |
| IPsec proposal |
List protocols, algorithms, and security services to be negotiated with the remote IPsec peer. |
| Policies | |
| IKE policy |
Define a combination of security parameters (IKE proposals) to be used during IKE negotiation. |
| IPsec policy |
Contain rules and security policies to allow group VPN traffic between the zones specified. |
| Security policy |
Allows you to select the type of data traffic to secure through the IPsec SAs.
|
|
Profiles |
|
|
Key profile |
Define how the SRX Series Firewall devices use the static key profile to fetch the QKD keys on IPsec VPN to send traffic securely over the Internet.
|
| PPK Profile |
Indicate which key profile to use to establish quantum-safe IKE or IPsec SAs by referencing the key profile under the IKE gateway. |
| Certificates | |
| CA certificate | Verify identity of devices and authenticate communication link between them. |
| Local certificate | Generate PKI and enroll it with the CA certificate for verification. |
| KME certificate | Third-party certificate generated by vendor |
| Security Zones | |
| trust |
Network segment at the host zone |
| untrust |
Network segment at the destination server zone |
| vpn |
Network segment through which the SRX1 and SRX2 devices interact. |
|
Primary verification tasks |
Verify the established IKE and IPsec SAs are Quantum safe. |
Topology Overview
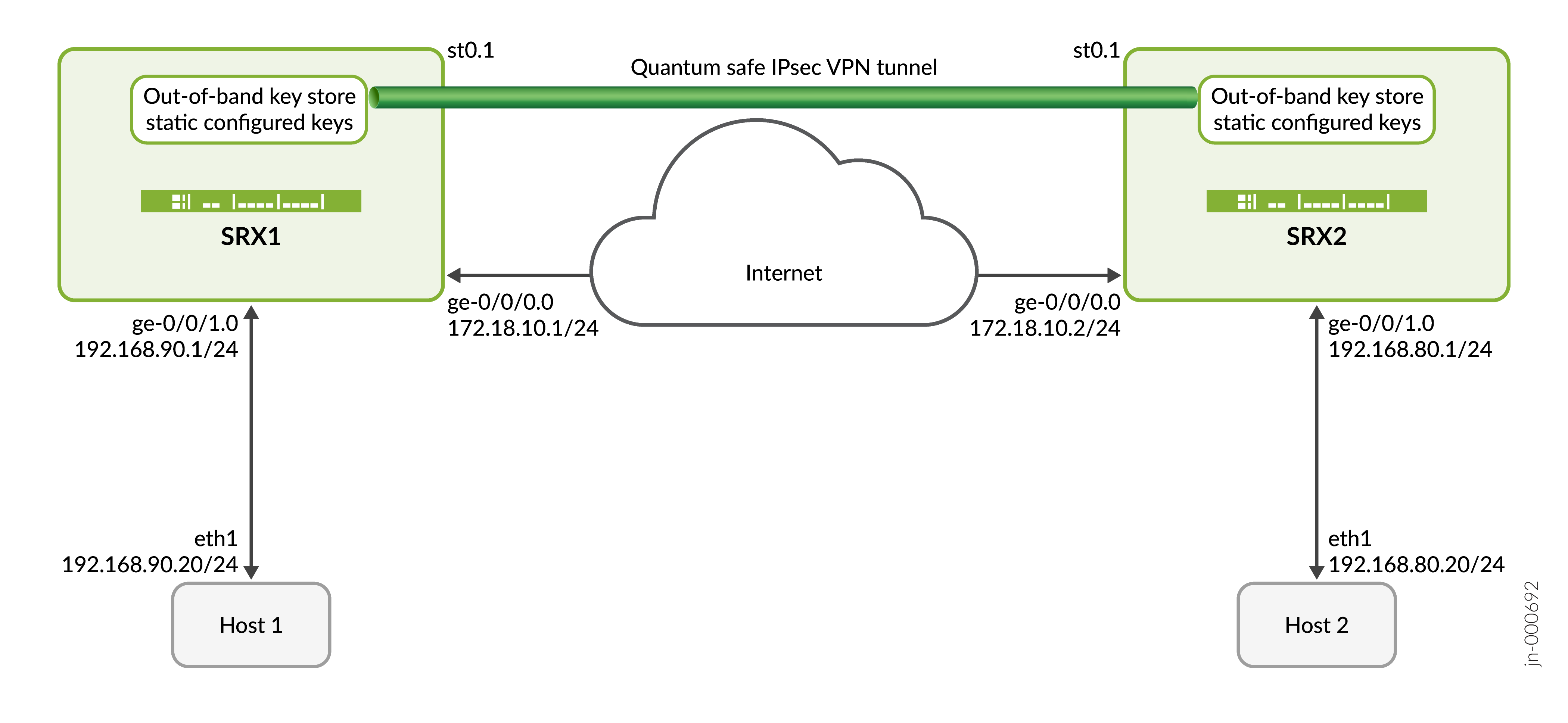
In this example, SRX1 initiates the negotiation of quantum safe IPsec tunnels with SRX2 using CLI configured static key. SRX2 responds to this request by verifying SRX1’s identity along with the key and establishes a quantum safe IPsec VPN. Once the tunnel is established, data traffic between Host1 and Host2 are secured using the established IPsec tunnel.
|
Hostname |
Role |
Function |
|---|---|---|
| SRX1 |
SRX Series Firewall capable of establishing IPsec tunnels |
Initiates IKE or IPsec SA negotiation and establishes Quantum-safe IPsec tunnels with SRX2 using static key configured on the SRX1. |
| SRX2 | SRX Series Firewall capable of establishing IPsec tunnels | Responds to the IKE or IPsec SA negotiation initiated by SRX1 and establishes Quantum-safe IPsec tunnels using static key configured on the SRX2. |
| Host1 | A Host inside the trusted zone or LAN side of SRX1 | Initiates client-side traffic toward Host2 |
| Host2 | A Host inside the trusted zone or LAN side of SRX2 | Responds to client-side traffic from Host1 |
Topology Illustration
Step-By-Step Configuration on SRX Series Firewall Devices
For complete sample configurations on the DUT, see:
This configuration is applicable for only SRX1 and SRX2 devices. You must make the appropriate device-specific configuration changes.
-
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@srx# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.1/24 user@srx# set st0 unit 1 family inet user@srx# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.90.1/24
-
Configure a key profile of type static with a key-id and a corresponding key.
[edit security key-manager profiles] user@srx# set km_profile_1 static key-id ascii-text test-key-id user@srx# set km_profile_1 static key ascii-text qjwbdip139u5mcy89m28pcgowerefnkjsdg
-
Configure the security zones.
[edit security zones] user@srx# set security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike user@srx# set security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 user@srx# set security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 user@srx# set security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping user@srx# set security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0
[edit security policies] user@srx# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any user@srx# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any user@srx# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any user@srx# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit user@srx# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any user@srx# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any user@srx# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any user@srx# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
[edit security ike proposal] user@srx# set IKE_PROP authentication-method pre-shared-keys user@srx# set IKE_PROP dh-group group14 user@srx# set IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 user@srx# set IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc user@srx# set IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600
[edit security ike policy] user@srx# set IKE_POL proposals IKE_PROP user@srx# set IKE_POL pre-shared-key ascii-text ipsec-test
[edit security ike gateway] user@srx# set IKE_GW ike-policy IKE_POL user@srx# set IKE_GW address 172.18.10.2 user@srx# set IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/0.0 user@srx# set IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.1 user@srx# set IKE_GW version v2-only user@srx# set IKE_GW ppk-profile km_profile_1
[edit security ipsec proposal] user@srx# set IPSEC_PROP protocol esp user@srx# set IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@srx# set IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc user@srx# set IPSEC_PROP lifetime-seconds 2400
[edit security ipsec policy] user@srx# set IPSEC_POL proposals IPSEC_PROP
[edit security ipsec vpn] user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN ike gateway IKE_GW user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy IPSEC_POL user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.90.0/24 user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.80.0/24 user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN establish-tunnels immediately
Verification
This section provides a list of show commands that you can use to verify the feature in this example.
|
Command |
Verification Task |
|---|---|
|
show security ike security-associations detail |
|
|
show security ipsec security-associations detail |
|
|
show security ipsec statistics |
|
|
show security key-manager profiles detail |
|
|
ping 192.168.80.20 source 192.168.90.20 count 4 |
- Verify IKE SAs
- Verify IPsec SAs
- Verify IPsec Statistics
- Verify Key Manager Profile
- Ping from HOST 1 to HOST 2
Verify IKE SAs
Purpose
Verify the IKE SAs
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ike
security-associations detail command to view the IKE SAs.
user@srx> show security ike security-associations detail IKE peer 172.18.10.2, Index 1, Gateway Name: IKE_GW
Role: Initiator, State: UP
Initiator cookie: dee592254e808a2b, Responder cookie: 51f6b1d4a8618332 Exchange type: IKEv2, Authentication method: Pre-shared-keys
Local gateway interface: ge-0/0/2.0 Routing instance: default
Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.2:500
Lifetime: Expires in 1286 seconds Reauth Lifetime: Disabled
IKE Fragmentation: Enabled, Size: 576 SRG ID: 0
Remote Access Client Info: Unknown Client Peer ike-id: 172.18.10.2
AAA assigned IP: 0.0.0.0
PPK-profile: km_profile_1 Optional: No
State : Used
Algorithms:
Authentication : hmac-sha256-128
Encryption : aes256-cbc Pseudo random function: hmac-sha256 Diffie-Hellman group : DH-group-14
Traffic statistics:
Input bytes : 1058
Output bytes : 1074
Input packets: 4
Output packets: 4
Input fragmented packets: 0
Output fragmented packets: 0
IPSec security associations: 4 created, 1 deleted Phase 2 negotiations in progress: 1
IPSec Tunnel IDs: 500002
Negotiation type: Quick mode, Role: Initiator, Message ID: 0 Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.2:500
Local identity: 172.18.10.1
Remote identity: 172.18.10.2 Flags: IKE SA is created
IPsec SA Rekey CREATE_CHILD_SA exchange stats:
Initiator stats: Responder stats:
Request Out : 0 Request In : 1
Response In : 0 Response Out : 1
No Proposal Chosen In : 0 No Proposal Chosen Out : 0
Invalid KE In : 0 Invalid KE Out : 0
TS Unacceptable In : 0 TS Unacceptable Out : 0
Res DH Compute Key Fail : 0 Res DH Compute Key Fail: 0 Res Verify SA Fail : 0
Res Verify DH Group Fail: 0 Res Verify TS Fail : 0
Meaning
The Role: Initiator, State: UP, PPK-profile:
km_profile_1 Optional: No, IPSec security associations:
4 created, and Flags: IKE SA is created fields
shows the IKE SAs are created successfully.
Verify IPsec SAs
Purpose
Verify the IPsec SAs
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ipsec
security-associations detail command to view the IPsec SAs.
user@srx> show security ipsec security-associations detail ID: 500002 Virtual-system: root, VPN Name: IPSEC_VPN Local Gateway: 172.18.10.1, Remote Gateway: 172.18.10.2 Traffic Selector Name: ts1 Local Identity: ipv4(192.168.90.0-192.168.90.255) Remote Identity: ipv4(192.168.80.0-192.168.80.255) TS Type: traffic-selector Version: IKEv2 Quantum Secured: Yes PFS group: N/A SRG ID: 0 DF-bit: clear, Copy-Outer-DSCP Disabled, Bind-interface: st0.1, Policy-name: IPSEC_POL Port: 500, Nego#: 0, Fail#: 0, Def-Del#: 0 Flag: 0 Multi-sa, Configured SAs# 0, Negotiated SAs#: 0 Tunnel events: Thu Mar 30 2023 23:43:42: IPsec SA negotiation succeeds (1 times) Location: FPC 0, PIC 0, KMD-Instance 0 Anchorship: Thread 1 Distribution-Profile: default-profile Direction: inbound, SPI: 0x983a0221, AUX-SPI: 0 , VPN Monitoring: - Hard lifetime: Expires in 1330 seconds Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited Soft lifetime: Expires in 662 seconds Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits) Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64 Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-immediately IKE SA Index: 1 Direction: outbound, SPI: 0x4112746b, AUX-SPI: 0 , VPN Monitoring: - Hard lifetime: Expires in 1330 seconds Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited Soft lifetime: Expires in 662 seconds Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits) Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64 Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-immediately IKE SA Index: 1
Meaning
The Version: IKEv2 Quantum Secured: Yes and
tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-immediately IKE SA
Index: 1 fields shows the IPsec SAs are created
successfully.
The sample output confirms the IPsec SAs.
Verify IPsec Statistics
Purpose
Verify the IPsec statistics.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ipsec
statistics command to view the IPsec statistics.
user@srx> show security ipsec statistics ESP Statistics: Encrypted bytes: 624 Decrypted bytes: 624 Encrypted packets: 4 Decrypted packets: 4 AH Statistics: Input bytes: 0 Output bytes: 0 Input packets: 0 Output packets: 0 Errors: AH authentication failures: 0, Replay errors: 0 ESP authentication failures: 0, ESP decryption failures: 0 Bad headers: 0, Bad trailers: 0 Invalid SPI: 0, TS check fail: 0 Exceeds tunnel MTU: 0 Discarded: 0
Meaning
The ESP Statistics and AH Statistics fields
shows the IPsec statistics.
Verify Key Manager Profile
Purpose
Verify the key manager profile.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security key-manager profiles
detail to view the key manager profile.
user@srx> show security key-manager profiles detail Name: km_profile_1, Index: 1, Type: Static Configured-at: 30.03.23 (23:22:43) Time-elapsed: 1 hrs 16 mins 3 secs Request stats: Received: 1 In-progress: 0 Success: 1 Failed: 0
Meaning
The Name: km_profile_1 and Type: Static
fields shows the key manager profile.
Ping from HOST 1 to HOST 2
Purpose
Verify the connectivity from HOST 1 to HOST 2.
Action
From operational mode, enter the ping 192.168.80.20 source 192.168.90.20 count 4 to view the connectivity from HOST 1 to HOST 2.
user@HOST1# ping 192.168.80.20 source 192.168.90.20 count 4 PING 192.168.80.20 (192.168.80.20): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 192.168.80.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=2.151 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.80.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.710 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.80.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.349 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.80.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.597 ms --- 192.168.80.1 ping statistics --- 4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.349/1.702/2.151/0.290 ms Data traffic is successfully flowing between the HOSTs
Meaning
The PING 192.168.80.20 (192.168.80.20): 56 data bytes
confirms the connectivity from HOST 1 to HOST 2.
Appendix 1: Set Commands on all Devices
Set command output on all devices.
Set Commands on SRX1
set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 static key-id ascii-text test-key-id set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 static key ascii-text qjwbdip139u5mcy89m28pcgowerefnkjsdg set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.1/24 set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.90.1/24 set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 set security zones security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit set security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-method pre-shared-keys set security ike proposal IKE_PROP dh-group group14 set security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 set security ike proposal IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ike proposal IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600 set security ike policy IKE_POL proposals IKE_PROP set security ike policy IKE_POL pre-shared-key ascii-text ipsec-test set security ike gateway IKE_GW ike-policy IKE_POL set security ike gateway IKE_GW address 172.18.10.2 set security ike gateway IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/0.0 set security ike gateway IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.1 set security ike gateway IKE_GW version v2-only set security ike gateway IKE_GW ppk-profile km_profile_1 set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP protocol esp set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP lifetime-seconds 2400 set security ipsec policy IPSEC_POL proposals IPSEC_PROP set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN ike gateway IKE_GW set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy IPSEC_POL set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.90.0/24 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.80.0/24 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN establish-tunnels immediately
Set Commands on SRX2
set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 static key-id ascii-text test-key-id set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 static key ascii-text qjwbdip139u5mcy89m28pcgowerefnkjsdg set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.2/24 set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.80.1/24 set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 set security zones security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit set security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-method pre-shared-keys set security ike proposal IKE_PROP dh-group group14 set security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 set security ike proposal IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ike proposal IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600 set security ike policy IKE_POL proposals IKE_PROP set security ike policy IKE_POL pre-shared-key ascii-text “ipsec-test” set security ike gateway IKE_GW ike-policy IKE_POL set security ike gateway IKE_GW address 172.18.10.1 set security ike gateway IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/0.0 set security ike gateway IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.2 set security ike gateway IKE_GW version v2-only set security ike gateway IKE_GW ppk-profile km_profile_1 set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP protocol esp set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP lifetime-seconds 2400 set security ipsec policy IPSEC_POL proposals IPSEC_PROP set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN ike gateway IKE_GW set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy IPSEC_POL set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.80.0/24 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN establish-tunnels immediately
Appendix 2: Show Configuration Output on DUT
SRX1
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show
security key-manager profiles, show security
key-manager, show interfaces, show
security zones, show security policies,
show security ike proposal IKE_PROP, show security
ike policy IKE_POL, show security ike gateway
IKE_GW, show security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP,
show security ipsec policy IPSEC_POL, and show
security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN commands. If the output does not
display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in
this example to correct it.
user@srx1# show security key-manager profiles
km_profile_1 {
static {
key-id ascii-text "$9$.mz6pu1hyKBI8X-boajHqmF/hcylK836"; ## SECRET-DATA
key ascii-text "$9$5Q6AhclXNbtuIcyeXxGDikfT369A0Bn/vWLNY2aZUjPQAp0BEcFnyleMXxGDi.mT9CuhSeIElMLXwsaZUikPpu1hSen/eW8XbwJGD"; ## SECRET-DATA
}
}
user@srx1# show security key-manager
profiles {
km_profile_1 {
static {
key-id ascii-text "$9$.mz6pu1hyKBI8X-boajHqmF/hcylK836"; ## SECRET-DATA
key ascii-text "$9$5Q6AhclXNbtuIcyeXxGDikfT369A0Bn/vWLNY2aZUjPQAp0BEcFnyleMXxGDi.mT9CuhSeIElMLXwsaZUikPpu1hSen/eW8XbwJGD"; ## SECRET-DATA
}
}
}
user@srx1# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.2/24;
address 172.18.10.1/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.80.1/24;
address 192.168.90.1/24;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family mpls;
}
}
st0 {
unit 1 {
family inet;
}
}
user@srx1# show security zones
security-zone untrust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ike;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0.0;
}
}
security-zone vpn {
interfaces {
st0.1;
}
}
security-zone trust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0;
}
}
user@srx1# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone vpn {
policy vpn_out {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
from-zone vpn to-zone trust {
policy vpn_in {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
user@srx1# show security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-method pre-shared-keys; dh-group group14; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600;
user@srx1# show security ike policy IKE_POL proposals IKE_PROP; pre-shared-key ascii-text "$9$z0C63/tp0Icrvz39p0Ihcs24aZjqmTn9p"; ## SECRET-DATA
user@srx1# show security ike gateway IKE_GW ike-policy IKE_POL; address [ 172.18.10.1 172.18.10.2 ]; external-interface ge-0/0/0.0; local-address 172.18.10.1; version v2-only; ppk-profile km_profile_1;
user@srx1# show security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP protocol esp; authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 2400;
user@srx1# show security ipsec policy IPSEC_POL proposals IPSEC_PROP;
user@srx1# show security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN
bind-interface st0.1;
ike {
gateway IKE_GW;
ipsec-policy IPSEC_POL;
}
traffic-selector ts1 {
local-ip 192.168.90.0/24;
remote-ip 192.168.80.0/24;
}
establish-tunnels immediately;
SRX2
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show
security key-manager profiles, show security
key-manager, show interfaces, show
security zones, show security policies,
show security ike proposal IKE_PROP, show security
ike policy IKE_POL, show security ike gateway
IKE_GW, show security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP,
show security ipsec policy IPSEC_POL, and show
security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN commands. If the output does not
display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in
this example to correct it.
user@srx2# show security key-manager profiles
km_profile_1 {
static {
key-id ascii-text "$9$Hk5FCA0IhruOvWx-2gGDikT3IRhSrvQF"; ## SECRET-DATA
key ascii-text "$9$zDD33CuyrvNVY0BhreMN-jHqmQF/Ctu1R9A8X7V4oGDikT3uO1RSr69evMLN-jHqf5FtpBylMhSvL7N2gGDiqmTOBEylM9AMXxNY2UjH"; ## SECRET-DATA
}
}user@srx2# show security key-manager
profiles {
km_profile_1 {
static {
key-id ascii-text "$9$Hk5FCA0IhruOvWx-2gGDikT3IRhSrvQF"; ## SECRET-DATA
key ascii-text "$9$zDD33CuyrvNVY0BhreMN-jHqmQF/Ctu1R9A8X7V4oGDikT3uO1RSr69evMLN-jHqf5FtpBylMhSvL7N2gGDiqmTOBEylM9AMXxNY2UjH"; ## SECRET-DATA
}
}
}user@srx2# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.90.1/24;
address 192.168.80.1/24;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family mpls;
}
}
st0 {
unit 1 {
family inet;
}
}user@srx2# show security zones
security-zone untrust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ike;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0.0;
}
}
security-zone vpn {
interfaces {
st0.1;
}
}
security-zone trust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0;
}
}user@srx2# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone vpn {
policy vpn_out {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
from-zone vpn to-zone trust {
policy vpn_in {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}user@srx2# show security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-method pre-shared-keys; dh-group group14; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600;
user@srx2# show security ike policy IKE_POL proposals IKE_PROP; pre-shared-key ascii-text "$9$zTi03/tp0Icrvz39p0Ihcs24aZjqmTn9p"; ## SECRET-DATA
user@srx2# show security ike gateway IKE_GW ike-policy IKE_POL; address 172.18.10.1; external-interface ge-0/0/0.0; local-address 172.18.10.2; version v2-only; ppk-profile km_profile_1;
user@srx2# show security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP protocol esp; authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 2400;
user@srx2# show security ipsec policy IPSEC_POL
proposals IPSEC_PROP;
[edit]
user@srx2# show security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN
bind-interface st0.1;
ike {
gateway IKE_GW;
ipsec-policy IPSEC_POL;
}
traffic-selector ts1 {
local-ip 192.168.80.0/24;
remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24;
}
establish-tunnels immediately;
Example: Configure Static Keys Profile for AutoVPN
Use this configuration example to secure an IPsec AutoVPN infrastructure by configuring the static key profile.
You can secure an IPsec AutoVPN infrastructure by configuring the static key profile.
In this configuration example, the Hub, Spoke 1, and Spoke 2 use static key profiles to fetch the QKD keys on IPsec VPN. The QKD keys help send traffic securely over the Internet.
|
Reading Time |
Less than an hour |
|
Configuration Time |
Less than an hour |
- Example Prerequisites
- Before You Begin
- Functional Overview
- Topology Overview
- Topology Illustration
- Step-By-Step Configuration on Hub
- Step-By-Step Configuration on Spoke Devices
- Verification
- Appendix 1: Set Commands on all Devices
- Appendix 2: Show Configuration Output on DUT
Example Prerequisites
|
Hardware requirements |
|
|
Software requirements |
Junos OS Release 22.4R1 or later. |
Before You Begin
|
Benefits |
|
|
Useful Resources |
|
|
Know more |
|
|
Hands-on experience |
|
|
Learn more |
Obtain the address of the certificate authority (CA) and the information they require (such as the challenge password) then you submits requests for local certificates. See Understanding Local Certificate Requests. Enroll the digital certificates in each device. See Example: Loading CA and Local Certificates Manually. |
Functional Overview
| IPsec VPN |
Deploys a hub-and-spoke IPsec VPN topology where spokes are connected by VPN tunnels that send traffic through the hub. These VPN tunnels are later configured to use quantum keys making them quantum-safe VPN tunnels. |
| IKE gateway |
Establishes a secure connection, the IKE gateway uses the IKE policy to limit itself to the configured group of CAs (ca-profiles) while validating the certificate. |
| Proposals | |
| IKE proposal |
Defines the algorithms and keys used to establish the secure IKE connection with the peer security gateway. IKE creates the dynamic SAs and negotiates them for IPsec. |
| IPsec proposal |
Lists protocols, algorithms, and security services to be negotiated with the remote IPsec peer. |
| Policies | |
| IKE policy |
Defines a combination of security parameters (IKE proposals) to be used during IKE negotiation. |
| IPsec policy |
Contains rules and security policies to allow group VPN traffic between the zones specified. |
| Security policy |
Allows you to select the type of data traffic to secure through the IPsec SAs.
|
|
Profiles |
|
|
Key profile |
Define how the SRX Series Firewall devices communicate with the KME devices to retrieve QKD keys from the external KME server. Key profiles are configured on the hub (HUB_KM_PROFILE_1) and spokes (SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 and SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1) separately.
|
| PPK Profile |
Indicates which key profile to use to establish quantum-safe IKE or IPsec SAs by referencing the key profile under the IKE gateway. |
| Certificates | |
| CA certificate | Verifies identity of devices and authenticate communication link between them. |
| Local certificate | Generates PKI and enroll it with the CA certificate for verification. |
| KME certificate | Third-party certificate generated by vendor. |
| Security Zones | |
| trust |
Network segment at the host zone. |
| untrust |
Network segment at the destination server zone. |
| vpn |
Network segment through which the hub-and-spoke interacts. |
|
Primary verification tasks |
Verify the established IKE and IPsec SAs are Quantum safe. |
Topology Overview
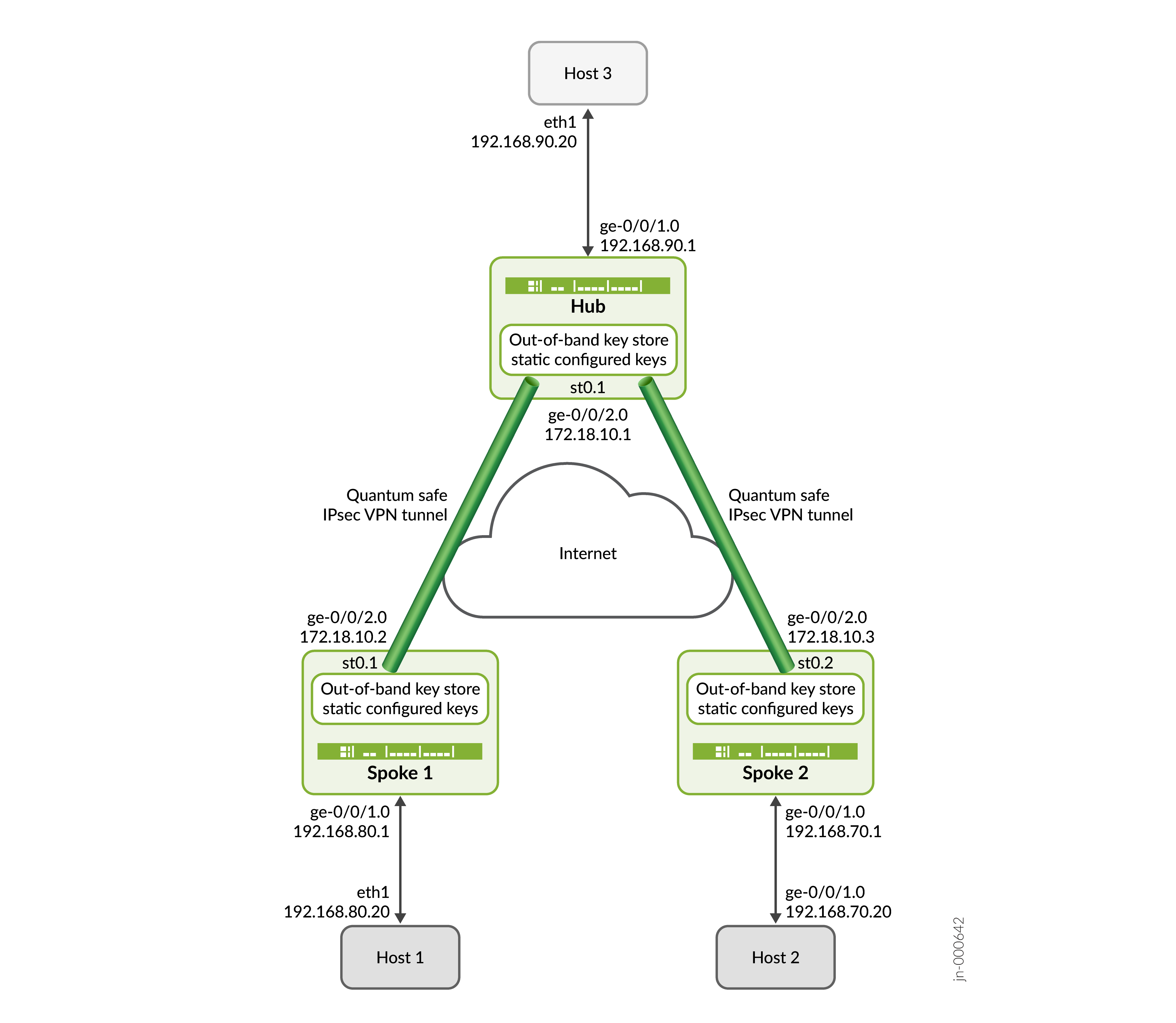
In this example, SPOKE 1 and SPOKE 2 initiate the negotiation of quantum-safe IPsec tunnels with the Hub using CLI-configured static key. The Hub responds to the requests by verifying the identity of Spoke 1 and Spoke 2 along with their respective keys and establishes a quantum-safe IPsec VPN with both the spokes. Once the tunnels are established, data traffic between Host 1 and Host 3, and between Host 2 and Host 3 are secured using the established IPsec tunnels.
|
Hostname |
Role |
Function |
|---|---|---|
| Hub | SRX Series Firewall capable of establishing IPsec tunnels | Responds to IKE or IPsec SA negotiation initiated by SPOKE 1 and SPOKE 2 and establishes quantum-safe IPsec tunnels using static key configured on the Hub device. |
| Spoke 1 | SRX Series Firewall capable of establishing IPsec tunnels | Initiates IKE/IPsec SA negotiation and establishes quantum-safe IPsec tunnels with the Hub using static key configured on the Spoke 1. |
| Spoke 2 | SRX Series Firewall capable of establishing IPsec tunnels | Initiates IKE or IPsec SA negotiation and establishes quantum-safe IPsec tunnels with the Hub using static key configured on the Spoke 2. |
| Host 1 | Host inside the trusted zone or LAN side of Spoke 1 | Initiates client-side traffic toward Host 3. |
| Host 2 | Host inside the trusted zone or LAN side of Spoke 2 | Initiates client-side traffic toward Host 3. |
| Host 3 | Host inside the trusted zone or LAN side of HUB | Responds to client-side traffic from Host 1 and Host 2. |
Topology Illustration
Step-By-Step Configuration on Hub
For complete sample configurations on the DUT, see:
This configuration is applicable for only the Hub devices. You must make the appropriate device-specific configuration changes.
-
Configure the hub interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@hub# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.1/24 user@hub# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.90.1/24 user@hub# set st0 unit 1 family inet
-
Configure the CA profile and CA certificate.
[edit security pki] user@hub# set ca-profile Root-CA ca-identity Root-CA user@hub# set ca-profile Root-CA enrollment url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll user@hub# set ca-profile Root-CA revocation-check disable
-
From the operational mode, bind the CA certificate to CA profile.
user@hub> request security pki ca-certificate enroll ca-profile Root-CA user@hub> request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id HUB_CRT size 2048 type rsa user@hub> request security pki local-certificate enroll certificate-id HUB_CRT challenge-password <different> domain-name hub.juniper.net email hub@juniper.net subject DC=juniper,CN=hub.juniper.net,OU=security,O=juniper,L=sunnyvale,ST=california,C=us ca-profile Root-CA
-
Configure the static key manager profile.
[edit security key-manager profiles] user@hub# set HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 static key-id ascii-text test-key-id user@hub# set HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 static key ascii-text qjwbdip139u5mcy89m28pcgowerefnkjsdg
Configure the hub-spoke on the IPsec VPN. This includes configuring the security zones, security policies, and relevant certificates for authenticating device identities and their communication links.
[edit security ike proposal] user@hub# set HUB_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures user@hub# set HUB_IKE_PROP dh-group group14 user@hub# set HUB_IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 user@hub# set HUB_IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc user@hub# set HUB_IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600
[edit security ike policy] user@hub# set HUB_IKE_POL proposals HUB_IKE_PROP user@hub# set HUB_IKE_POL certificate local-certificate HUB_CRT
[edit security ike gateway] user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.1 user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW ike-policy HUB_IKE_POL user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/2.0 user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW local-identity distinguished-name user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW dynamic ike-user-type group-ike-id user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW dynamic distinguished-name wildcard C=us,DC=juniper user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW ppk-profile HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW version v2-only
[edit security ipsec proposal] user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
[edit security ipsec policy] user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_POL proposals HUB_IPSEC_PROP
[edit security ipsec vpn] user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_VPN ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy HUB_IPSEC_POL user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.90.0/24 user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0
[edit security zones] user@hub# set security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike user@hub# set security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 user@hub# set security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 user@hub# set security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping user@hub# set security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0
[edit security policies] user@hub# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any user@hub# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any user@hub# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any user@hub# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit user@hub# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any user@hub# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any user@hub# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any user@hub# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
Step-By-Step Configuration on Spoke Devices
For complete sample configurations on the DUT, see:
This configuration is applicable for Spoke 1 and Spoke 2 devices. For other devices, you must make appropriate device-specific configuration changes.
-
Configure the spoke interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@spoke# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.2/24 user@spoke# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.80.1/24 user@spoke# set st0 unit 1 family inet
-
Configure hub-spoke on the IPsec VPN. This includes configuring the security zones, security policies, and relevant certificates for authenticating device identities and their communication links.
[edit security ike proposal] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP dh-group group14 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600
[edit security ike policy] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_POL proposals SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_POL certificate local-certificate SPOKE_1_CRT
[edit security ike gateway] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW address 172.18.10.1 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.2 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW ike-policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/2.0 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW local-identity distinguished-name user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW remote-identity distinguished-name user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW ppk-profile SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW version v2-only
[edit security ipsec proposal] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
[edit security ipsec policy] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL proposals SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP
[edit security ipsec vpn] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.80.0/24 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24
[edit security zones] user@spoke# set security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike user@spoke# set security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 user@spoke# set security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 user@spoke# set security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping user@spoke# set security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0
[edit security policies] user@spoke# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any user@spoke# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any user@spoke# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any user@spoke# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit user@spoke# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any user@spoke# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any user@spoke# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any user@spoke# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
[edit security pki ] user@spoke# set ca-profile Root-CA ca-identity Root-CA user@spoke# set ca-profile Root-CA enrollment url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll user@spoke# set ca-profile Root-CA revocation-check disable
user@spoke> request security pki ca-certificate enroll ca-profile Root-CA user@spoke> request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id SPOKE_1_CRT size 2048 type rsa user@spoke> request security pki local-certificate enroll certificate-id SPOKE_1_CRT challenge-password <different> domain-name spoke_1.juniper.net email spoke_1@juniper.net subject DC=juniper,CN=spoke_1.juniper.net,OU=security,O=juniper,L=sunnyvale,ST=california,C=us ca-profile Root-CA
-
Configure the static key manager profile.
[edit security key-manager profiles] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 static key-id ascii-text test-key-id user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 static key ascii-text qjwbdip139u5mcy89m28pcgowerefnkjsdg
Verification
This section provides a list of show commands that you can use to verify the feature in this example.
| Command | Verification Task |
|---|---|
|
show security ike security-associations detail |
|
|
show security ipsec security-associations detail |
|
|
show security ipsec statistics |
|
|
show security key-manager profiles detail |
|
|
ping 192.168.90.20 source 192.168.80.20 count 4 |
- Verify IKE SAs
- Verify IPsec SAs
- Verify IPsec Statistics
- Verify Key Manager Profile
- Ping from Host 1 to Host 3 or vice versa
- Ping from Host 2 to Host 3 or vice versa
Verify IKE SAs
Purpose
Verify the IKE SAs.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ike
security-associations detail command to view the IKE SAs.
user@hub> show security ike security-associations detail
IKE peer 172.18.10.2, Index 2123, Gateway Name: HUB_IKE_GW
Role: Responder, State: UP
Initiator cookie: 0e40ccdcee1b54bd, Responder cookie: 43964f5cc4d4491c
Exchange type: IKEv2, Authentication method: RSA-signatures
Local gateway interface: ge-0/0/2.0
Routing instance: default
Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.2:500
Lifetime: Expires in 2840 seconds
Reauth Lifetime: Disabled
IKE Fragmentation: Enabled, Size: 576
Remote Access Client Info: Unknown Client
Peer ike-id: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=spoke.juniper.net
AAA assigned IP: 0.0.0.0
PPK-profile: HUB_KM_PROFILE_1
Optional: No
State : Used
Algorithms:
Authentication : hmac-sha256-128
Encryption : aes256-cbc
Pseudo random function: hmac-sha256
Diffie-Hellman group : DH-group-14
Traffic statistics:
Input bytes : 2610
Output bytes : 2571
Input packets: 5
Output packets: 5
Input fragmented packets: 4
Output fragmented packets: 4
IPSec security associations: 2 created, 0 deleted
Phase 2 negotiations in progress: 1
IPSec Tunnel IDs: 500440
Negotiation type: Quick mode, Role: Responder, Message ID: 0
Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.2:500
Local identity: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=hub.juniper.net
Remote identity: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=spoke.juniper.net
Flags: IKE SA is created
IPsec SA Rekey CREATE_CHILD_SA exchange stats:
Initiator stats: Responder stats:
Request Out : 0 Request In : 0
Response In : 0 Response Out : 0
No Proposal Chosen In : 0 No Proposal Chosen Out : 0
Invalid KE In : 0 Invalid KE Out : 0
TS Unacceptable In : 0 TS Unacceptable Out : 0
Res DH Compute Key Fail : 0 Res DH Compute Key Fail: 0
Res Verify SA Fail : 0
Res Verify DH Group Fail: 0
Res Verify TS Fail : 0
IKE peer 172.18.10.3, Index 2124, Gateway Name: HUB_IKE_GW
Role: Responder, State: UP
Initiator cookie: 651bf4a52a9375ec, Responder cookie: d9a9c95c27e3f929
Exchange type: IKEv2, Authentication method: RSA-signatures
Local gateway interface: ge-0/0/2.0
Routing instance: default
Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.3:500
Lifetime: Expires in 2901 seconds
Reauth Lifetime: Disabled
IKE Fragmentation: Enabled, Size: 576
Remote Access Client Info: Unknown Client
Peer ike-id: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=spoke_2.juniper.net
AAA assigned IP: 0.0.0.0
PPK-profile: HUB_KM_PROFILE_1
Optional: No
State : Used
Algorithms:
Authentication : hmac-sha256-128
Encryption : aes256-cbc
Pseudo random function: hmac-sha256
Diffie-Hellman group : DH-group-14
Traffic statistics:
Input bytes : 2610
Output bytes : 2571
Input packets: 5
Output packets: 5
Input fragmented packets: 4
Output fragmented packets: 4
IPSec security associations: 2 created, 0 deleted
Phase 2 negotiations in progress: 1
IPSec Tunnel IDs: 500441
Negotiation type: Quick mode, Role: Responder, Message ID: 0
Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.3:500
Local identity: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=hub.juniper.net
Remote identity: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=spoke_2.juniper.net
Flags: IKE SA is created
IPsec SA Rekey CREATE_CHILD_SA exchange stats:
Initiator stats: Responder stats:
Request Out : 0 Request In : 0
Response In : 0 Response Out : 0
No Proposal Chosen In : 0 No Proposal Chosen Out : 0
Invalid KE In : 0 Invalid KE Out : 0
TS Unacceptable In : 0 TS Unacceptable Out : 0
Res DH Compute Key Fail : 0 Res DH Compute Key Fail: 0
Res Verify SA Fail : 0
Res Verify DH Group Fail: 0
Res Verify TS Fail : 0
Meaning
The Role: Responder, State: UP, PPK-profile:
HUB_KM_PROFILE_1, IPSec security associations: 2
created, 0 deleted, and Flags: IKE SA is
created fields shows the IKE SAs are created successfully.
Verify IPsec SAs
Purpose
Verify the IPsec SAs.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ipsec
security-associations detail command to view the IPsec
SAs.
user@hub> show security ipsec security-associations detail
ID: 500440 Virtual-system: root, VPN Name: HUB_IPSEC_VPN
Local Gateway: 172.18.10.1, Remote Gateway: 172.18.10.2
Traffic Selector Name: ts1
Local Identity: ipv4(192.168.90.0-192.168.90.255)
Remote Identity: ipv4(192.168.80.0-192.168.80.255)
TS Type: traffic-selector
Version: IKEv2
Quantum Secured: Yes
PFS group: N/A
Passive mode tunneling: Disabled
DF-bit: clear, Copy-Outer-DSCP Disabled, Bind-interface: st0.1, Policy-name: HUB_IPSEC_POL
Port: 500, Nego#: 0, Fail#: 0, Def-Del#: 0 Flag: 0
Multi-sa, Configured SAs# 0, Negotiated SAs#: 0
Tunnel events:
Thu Jul 20 2023 10:44:19: IPsec SA negotiation succeeds (1 times)
Location: FPC 0, PIC 0
Anchorship: Thread 1
Distribution-Profile: default-profile
Direction: inbound, SPI: 0x649d371f, AUX-SPI: 0
, VPN Monitoring: -
Hard lifetime: Expires in 2840 seconds
Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited
Soft lifetime: Expires in 2183 seconds
Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed
Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits)
Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64
Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled
tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-responder-only
IKE SA Index: 2123
Direction: outbound, SPI: 0xd5ef611e, AUX-SPI: 0
, VPN Monitoring: -
Hard lifetime: Expires in 2840 seconds
Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited
Soft lifetime: Expires in 2183 seconds
Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed
Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits)
Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64
Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled
tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-responder-only
IKE SA Index: 2123
ID: 500441 Virtual-system: root, VPN Name: HUB_IPSEC_VPN
Local Gateway: 172.18.10.1, Remote Gateway: 172.18.10.3
Traffic Selector Name: ts1
Local Identity: ipv4(192.168.90.0-192.168.90.255)
Remote Identity: ipv4(192.168.70.0-192.168.70.255)
TS Type: traffic-selector
Version: IKEv2
Quantum Secured: Yes
PFS group: N/A
Passive mode tunneling: Disabled
DF-bit: clear, Copy-Outer-DSCP Disabled, Bind-interface: st0.1, Policy-name: HUB_IPSEC_POL
Port: 500, Nego#: 0, Fail#: 0, Def-Del#: 0 Flag: 0
Multi-sa, Configured SAs# 0, Negotiated SAs#: 0
Tunnel events:
Thu Jul 20 2023 10:45:19: IPsec SA negotiation succeeds (1 times)
Location: FPC 0, PIC 0
Anchorship: Thread 1
Distribution-Profile: default-profile
Direction: inbound, SPI: 0xa0d3ba32, AUX-SPI: 0
, VPN Monitoring: -
Hard lifetime: Expires in 2901 seconds
Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited
Soft lifetime: Expires in 2258 seconds
Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed
Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits)
Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64
Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled
tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-responder-only
IKE SA Index: 2124
Direction: outbound, SPI: 0xe54414e3, AUX-SPI: 0
, VPN Monitoring: -
Hard lifetime: Expires in 2901 seconds
Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited
Soft lifetime: Expires in 2258 seconds
Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed
Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits)
Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64
Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled
tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-responder-only
IKE SA Index: 2124
Meaning
The Quantum Secured: Yes, Passive mode tunneling:
Disabled, Policy-name: HUB_IPSEC_POL, and
IPsec SA negotiation succeeds (1 times) fields shows
the IPsec SAs are created successfully.
Verify IPsec Statistics
Purpose
Verify the IPsec statistics.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ipsec
statistics command to view the IPsec statistics.
user@hub> show security ipsec statistics ESP Statistics: Encrypted bytes: 1248 Decrypted bytes: 1248 Encrypted packets: 8 Decrypted packets: 8 AH Statistics: Input bytes: 0 Output bytes: 0 Input packets: 0 Output packets: 0 Errors: AH authentication failures: 0, Replay errors: 0 ESP authentication failures: 0, ESP decryption failures: 0 Bad headers: 0, Bad trailers: 0 Invalid SPI: 0, TS check fail: 0 Exceeds tunnel MTU: 0 Discarded: 0
Meaning
The ESP Statistics and AH Statistics fields
shows the IPsec statistics.
Verify Key Manager Profile
Purpose
Verify the key manager profile.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security key-manager profiles
detail command to view the key manager profile.
user@hub> show security key-manager profiles detail
Name: HUB_KM_PROFILE_1, Index: 4, Type: Static
Configured-at: 20.07.23 (09:59:06)
Time-elapsed: 1 hrs 2 mins 7 secs
Request stats:
Received: 2
In-progress: 0
Success: 2
Failed: 0Meaning
The Name: HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 and Type: Static
fields shows the key manager profile
Ping from Host 1 to Host 3 or vice versa
Purpose
Verify the connectivity from Host 1 to Host 3.
Action
From operational mode, enter the ping 192.168.90.20 source
192.168.80.20 count 4 command to view the connectivity from
Host 1 to Host 3.
user@HOST1# ping 192.168.90.20 source 192.168.80.20 count 4 PING 192.168.90.20 (192.168.90.20): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=2.151 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.710 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.349 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.597 ms --- 192.168.90.20 ping statistics --- 4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.349/1.702/2.151/0.290 ms Data traffic is successfully flowing between the HOSTs
Meaning
The PING 192.168.80.20 (192.168.80.20): 56 data bytes
confirms the connectivity from HOST 1 to HOST 3.
Ping from Host 2 to Host 3 or vice versa
Purpose
Verify the connectivity from Host 2 to Host 3.
Action
From operational mode, enter the ping 192.168.90.20 source
192.168.80.20 count 4 to view the connectivity from Host 2 to
Host 3.
user@HOST1# ping 192.168.90.20 source 192.168.70.20 count 4 PING 192.168.90.20 (192.168.90.20): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=2.151 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.710 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.349 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.597 ms --- 192.168.90.20 ping statistics --- 4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.349/1.702/2.151/0.290 ms Data traffic is successfully flowing between the HOSTs
Meaning
The PING 192.168.80.20 (192.168.80.20): 56 data bytes
confirms the connectivity from HOST 2 to HOST 3.
Appendix 1: Set Commands on all Devices
Set command output on all devices.
Set Commands on Hub
set security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP dh-group group14 set security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 set security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600 set security ike policy HUB_IKE_POL proposals HUB_IKE_PROP set security ike policy HUB_IKE_POL certificate local-certificate HUB_CRT set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.1 set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW ike-policy HUB_IKE_POL set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/2.0 set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW local-identity distinguished-name set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW dynamic ike-user-type group-ike-id set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW dynamic distinguished-name wildcard C=us,DC=juniper set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW ppk-profile HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW version v2-only set security ipsec proposal HUB_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp set security ipsec proposal HUB_IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 set security ipsec proposal HUB_IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ipsec policy HUB_IPSEC_POL proposals HUB_IPSEC_PROP set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy HUB_IPSEC_POL set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.90.0/24 set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.1/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.90.1/24 set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 set security zones security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
Set Commands on Spoke 1
set security pki ca-profile Root-CA ca-identity Root-CA set security pki ca-profile Root-CA enrollment url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll set security pki ca-profile Root-CA revocation-check disable request security pki ca-certificate enroll ca-profile Root-CA request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id SPOKE_1_CRT size 2048 type rsa request security pki local-certificate enroll certificate-id SPOKE_1_CRT challenge-password <different> domain-name spoke_1.juniper.net email spoke_1@juniper.net subject DC=juniper,CN=spoke_1.juniper.net,OU=security,O=juniper,L=sunnyvale,ST=california,C=us ca-profile Root-CA set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 static key-id ascii-text test-key-id set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 static key ascii-text qjwbdip139u5mcy89m28pcgowerefnkjsdg set security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures set security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP dh-group group14 set security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 set security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600 set security ike policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL proposals SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP set security ike policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL certificate local-certificate SPOKE_1_CRT set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW address 172.18.10.1 set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.2 set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW ike-policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/2.0 set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW local-identity distinguished-name set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW remote-identity distinguished-name set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW ppk-profile SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW version v2-only set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ipsec policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL proposals SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.80.0/24 set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.2/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.80.1/24 set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 set security zones security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
Set Commands on Spoke 2
set security pki ca-profile Root-CA ca-identity Root-CA set security pki ca-profile Root-CA enrollment url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll set security pki ca-profile Root-CA revocation-check disable request security pki ca-certificate enroll ca-profile Root-CA request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id SPOKE_2_CRT size 2048 type rsa request security pki local-certificate enroll certificate-id SPOKE_2_CRT challenge-password <different> domain-name spoke_2.juniper.net email spoke_2@juniper.net subject DC=juniper,CN=spoke_2.juniper.net,OU=security,O=juniper,L=sunnyvale,ST=california,C=us ca-profile Root-CA set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1 static key-id ascii-text test-key-id set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1 static key ascii-text qjwbdip139u5mcy89m28pcgowerefnkjsdg set security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures set security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP dh-group group14 set security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 set security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600 set security ike policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL proposals SPOKE_IKE_PROP set security ike policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL certificate local-certificate SPOKE_2_CRT set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW address 172.18.10.1 set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.3 set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW ike-policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/2.0 set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW local-identity distinguished-name set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW remote-identity distinguished-name set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW ppk-profile SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1 set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW version v2-only set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ipsec policy SPOKE_2_IPSEC_POL proposals SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.2 set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy SPOKE_2_IPSEC_POL set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.70.0/24 set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.3/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.70.1/24 set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 set security zones security-zone vpn interfaces st0.2 set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
Appendix 2: Show Configuration Output on DUT
Hub
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show
security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP, show security ike
policy HUB_IKE_POL, show security ike gateway
HUB_IKE_GW, show security ipsec proposal
HUB_IPSEC_PROP, show security ipsec policy
HUB_IPSEC_POL, show security ipsec vpn
HUB_IPSEC_VPN, show interfaces, show
security zones, and show security policies
commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the
configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
user@hub# show security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP dh-group group14; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600;
user@hub# show security ike policy HUB_IKE_POL
proposals HUB_IKE_PROP;
certificate {
local-certificate HUB_CRT;user@hub# show security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW
ike-policy HUB_IKE_POL;
dynamic {
distinguished-name {
wildcard C=us,DC=juniper;
}
ike-user-type group-ike-id;
}
local-identity distinguished-name;
external-interface ge-0/0/2.0;
local-address 172.18.10.1;
version v2-only;
ppk-profile HUB_KM_PROFILE_1;user@hub# show security ipsec proposal HUB_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp; authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc;
user@hub# show security ipsec policy HUB_IPSEC_POL proposals HUB_IPSEC_PROP;
user@hub# show security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN
bind-interface st0.1;
ike {
gateway HUB_IKE_GW;
ipsec-policy HUB_IPSEC_POL;
}
traffic-selector ts1 {
local-ip 192.168.90.0/24;
remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0;
}user@hub# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.90.1/24;
address 192.168.80.1/24;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
}
}
}
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family mpls;
}
}
st0 {
unit 1 {
family inet;
}
}user@hub# show security zones
security-zone untrust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ike;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0.0;
ge-0/0/2.0;
}
}
security-zone vpn {
interfaces {
st0.1;
}
}
security-zone trust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0;
}
}
user@hub# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone vpn {
policy vpn_out {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
from-zone vpn to-zone trust {
policy vpn_in {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}Spoke 1
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show
security pki ca-profile Root-CA, show security key-manager
profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1, show security ike proposal
SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP, show security ike policy
SPOKE_1_IKE_POL, show security ike gateway
SPOKE_1_IKE_GW, show security ipsec proposal
SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP, show security ipsec policy
SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL, show security ipsec vpn
SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN, show interfaces, show
security zones, show security policies, and
show security pki commands. If the output does not display
the intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in this
example to correct it.
user@spoke1# show security pki ca-profile Root-CA
ca-identity Root-CA;
enrollment {
url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll;
}
revocation-check {
disable;
}
user@spoke1# show security key-manager profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1
static {
key-id ascii-text "$9$cJ5SvLdVYoZjs2qmTFAt1RhSMXoaZUjqWL"; ## SECRET-DATA
key ascii-text "$9$mfF/IRSWX-9AORhyW8aZUj.PQFn/tuz3lKMXbwgoJGqf/Ctu1RTzhSyeW8aZUHkPn6AIEyO1SeMWdVgoJUjqCA0IEyz3yKvW-d4aZ"; ## SECRET-DATA
}
user@spoke1# show security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures; dh-group group14; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600;
user@spoke1# show security ike policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL
proposals SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP;
certificate {
local-certificate SPOKE_1_CRT;
}
user@spoke1# show security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW ike-policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL; address 172.18.10.1; local-identity distinguished-name; remote-identity distinguished-name; external-interface ge-0/0/2.0; local-address 172.18.10.2; version v2-only; ppk-profile SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1;
user@spoke1# show security ipsec proposal SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp; authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc;
user@spoke1# show security ipsec policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL proposals SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP;
user@spoke1# show security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN
bind-interface st0.1;
ike {
gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW;
ipsec-policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL;
}
traffic-selector ts1 {
local-ip 192.168.80.0/24;
remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24;
}user@spoke1# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.90.1/24;
address 192.168.80.1/24;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
}
}
}
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family mpls;
}
}
st0 {
unit 1 {
family inet;
}
}
user@spoke1# show security zones
security-zone untrust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ike;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/2.0;
}
}
security-zone vpn {
interfaces {
st0.1;
}
}
security-zone trust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0;
}
}user@spoke1# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone vpn {
policy vpn_out {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
from-zone vpn to-zone trust {
policy vpn_in {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
user@spoke1# show security pki
ca-profile Root-CA {
ca-identity Root-CA;
enrollment {
url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll;
}
revocation-check {
disable;
}
}Spoke 2
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show
security pki, show security key-manager,
show security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP, show
security ike policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL, show security ike
gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW, show security ipsec proposal
SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP, show security ipsec vpn
SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN, show interfaces, show
security zones, and show security policies
commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the
configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
user@spoke2# show security pki
ca-profile Root-CA {
ca-identity Root-CA;
enrollment {
url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll;
}
revocation-check {
disable;
}
}
user@spoke2# show security key-manager
profiles {
SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1 {
static {
key-id ascii-text "$9$C4Y8ABEleWx-wM8goGjPf369A1hx7-VwgIE"; ## SECRET-DATA
key ascii-text "$9$15SRyKdVYGjqvW7Vw2GUn/CtBIcylK8XSr4aZjPfz369ORKM8X-VhSwY2oGUn/Cu0IleWdb27-YoZG.mz36CtOMWxdb2Sr2aJGq.Fn/"; ## SECRET-DATA
}
}
}
user@spoke2# show security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures; dh-group group14; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600;
user@spoke2# show security ike policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL
proposals SPOKE_IKE_PROP;
certificate {
local-certificate SPOKE_2_CRT;
}
user@spoke2# show security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW ike-policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL; address 172.18.10.1; local-identity distinguished-name; remote-identity distinguished-name; external-interface ge-0/0/2.0; local-address 172.18.10.3; version v2-only; ppk-profile SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1;
user@spoke2# show security ipsec proposal SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp; authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc;
user@spoke2# show security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN
bind-interface st0.2;
ike {
gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW;
ipsec-policy SPOKE_2_IPSEC_POL;
}
traffic-selector ts1 {
local-ip 192.168.70.0/24;
remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24;
}user@spoke2# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.90.1/24;
address 192.168.80.1/24;
address 192.168.70.1/24;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
address 172.18.10.3/24;
}
}
}
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family mpls;
}
}
st0 {
unit 1 {
family inet;
}
unit 2 {
family inet;
}
}user@spoke2# show security zones
security-zone untrust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ike;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/2.0;
}
}
security-zone vpn {
interfaces {
st0.2;
}
}
security-zone trust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0;
}
}user@spoke2# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone vpn {
policy vpn_out {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
from-zone vpn to-zone trust {
policy vpn_in {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}Configure Quantum Key Manager Key Profile for Junos Key Manager
This example shows how to configure quantum key profile for Junos key manager. Configure the quantum key manager key profile to generate and send the generated keys to establish quantum safe IPsec VPN tunnel.
Requirements
-
Hardware requirements —Juniper Networks® SRX1500 Firewall and higher-numbered device models or Juniper Networks® vSRX Virtual Firewall (vSRX3.0).
-
Software requirements—Junos OS Release 22.4R1 or later with JUNOS ike and JUNOS Key Manager packages.
-
Use any QKD device supporting ETSI Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) Rest API standard for communication.
-
Load the local certificates on the device. We recommended you to provide full path to the certificate.
Overview
The SRX Series Firewall devices use the IPsec VPN to send traffic securely over the Internet. Configure the quantum key manager key profile in the IPsec VPN, to re-authenticate the existing IKE SA and a new key and key.
The quantum key manager key profile uses secure key distribution method based on QKD to generate and distribute keys that are quantum safe. These keys are dynamic.
Configuration
-
Configure the CA certificate.
user@host# set security pki ca-profile Root-CA ca-identity Root-CA user@host# set security pki ca-profile Root-CA enrollment url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll user@host# set security pki ca-profile Root-CA revocation-check disable
-
Load the CA certificate.
user@host> request security pki local-certificate load certificate-id SAE_A filename SAE_A.cert key SAE_A.key
-
Enroll the CA certificate.
user@host> request security pki ca-certificate enroll ca-profile Root-CA
-
Configure the quantum key manager profile.
user@host# set security key-manager profiles KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager url https://kme.juniper.net user@host# set security key-manager profiles KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-sae-id SAE_A user@host# set security key-manager profiles KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-certificate-id SAE_A_CERT user@host# set security key-manager profiles KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager trusted-cas Root-CA
Verification
Purpose
Verify the quantum key manager key profile and keys.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security pki ca-certificate ca-profile
Root-CA to view the CA profile and CA certificates.
user@host> show security pki ca-certificate ca-profile Root-CA
LSYS: root-logical-system
CA profile: Root-CA
Certificate identifier: Root-CA
Issued to: Root-CA, Issued by: C = IN, ST = WestBengal, O = JuniperNetworks, CN = Root-CA
Validity:
Not before: 09-11-2023 09:03 UTC
Not after: 03-24-2044 09:03 UTC
Public key algorithm: rsaEncryption(4096 bits)
Keypair Location: Keypair generated locallyFrom operational mode, enter the show security pki local-certificate
certificate-id SAE_A_CERT to view the PKI local certificates.
user@host> show security pki local-certificate certificate-id SAE_A_CERT
LSYS: root-logical-system
Certificate identifier: SAE_A_CERT
Issued to: SAE_A, Issued by: C = IN, ST = WestBengal, O = JuniperNetworks, CN = ROOT_CA
Validity:
Not before: 08-28-2023 04:54 UTC
Not after: 03-10-2044 04:54 UTC
Public key algorithm: rsaEncryption(2048 bits)
Keypair Location: Keypair generated locallyFrom operational mode, enter the request security key-manager profiles get
profile-keys name km_profile_1 peer-sae-id SAE_B to view peer device key
manager profile and keys.
user@host> request security key-manager profiles get profile-keys name km_profile_1 peer-sae-id SAE_B
- Response:
- Status: SUCCESS
- Name: km_profile_1
- Type: quantum-key-manager
- Key-size: 256 bits
- Key-count: 1
- Key-ids:
- 002420bd-7a03-4725-9c41-6969d8e1815a
- Keys:
- 728d21c4a05fe2f73c7b2f58d1e3631dc68fcfaca16be12ca3fc7715079db0f9From operational mode, enter the show security key-manager profiles name
KM_PROFILE_1 detail to view key manager profile details.
user@host> show security key-manager profiles name KM_PROFILE_1 detail
Name: KM_PROFILE_1, Index: 2, Type: quantum-key-manager
Configured-at: 11.09.23 (02:04:32)
Time-elapsed: 0 hrs 20 mins 23 secs
Url: https://kme.juniper.net
Local-sae-id: SAE_A
Local-certificate-id: SAE_A_CERT
Trusted-cas: [ Root-CA ]
Peer-sae-ids: N/A
Default-key-size: N/A
Request stats:
Received: 0
In-progress: 0
Success: 0
Failed: 0Meaning
The show security pki ca-certificate ca-profile Root-CA displays PKI CA
profile name, certificate identifier, validity, public key algorithm, and so on.
The show security pki local-certificate certificate-id SAE_A_CERT
displays the local CA profile name, certificate identifier, validity, public key
algorithm, and so on.
The request security key-manager profiles get profile-keys name km_profile_1
peer-sae-id SAE_B displays peer device key manager profile and keys.
The show security key-manager profiles name KM_PROFILE_1 detail displays
the security key manager profile name, URL, requests, and so on.
Example: Configure Quantum Key Manager Key Profile for Site-to-Site IPsec VPN
Use this configuration example to secure an IPsec Site-to-Site VPN infrastructure by configuring the quantum key manager key profile.
You can secure an IPsec Site-to-Site VPN infrastructure by configuring the quantum key manager key profile.
In this configuration example, The SRX1 and SRX2 devices use the quantum key manager profile to fetch the QKD keys on IPsec VPN. The QKD keys help send traffic securely over the Internet.
|
Reading Time |
Less than an hour |
|
Configuration Time |
Less than an hour |
- Example Prerequisites
- Before You Begin
- Functional Overview
- Topology Overview
- Topology Illustration
- Step-By-Step Configuration on SRX Series Firewall Devices
- Verification
- Appendix 1: Set Commands on all Devices
- Appendix 2: Show Configuration Output on DUT
Example Prerequisites
|
Hardware requirements |
Juniper Networks® SRX1500 Firewall or higher-numbered device models or Juniper Networks® vSRX Virtual Firewall (vSRX3.0) |
|
Software requirements |
Junos OS Release 22.4R1 or later. |
Before You Begin
|
Benefits |
|
|
Useful Resources |
|
|
Know more |
|
|
Hands-on experience |
|
|
Learn more |
Functional Overview
| IPsec VPN |
Deploys a hub-and-spoke IPsec VPN topology where spokes are connected by VPN tunnels that send traffic through the hub. These VPN tunnels are later configured to use quantum keys making them quantum-safe VPN tunnels. |
| IKE gateway |
Establishes a secure connection. The IKE gateway uses the IKE policy to limit itself to the configured group of certificate authority (CA) profiles while validating the certificate. |
| Proposals | |
| IKE proposal |
Defines the algorithms and keys used to establish the secure IKE connection with the peer security gateway. IKE creates the dynamic security associations (SAs) and negotiates them for IPsec. |
| IPsec proposal |
Lists protocols, algorithms, and security services to be negotiated with the remote IPsec peer. |
| Policies | |
| IKE policy |
Defines a combination of security parameters (IKE proposals) to be used during IKE negotiation. |
| IPsec policy |
Contains rules and security policies to allow group VPN traffic between the zones specified. |
| Security policy |
Allows you to select the type of data traffic to secure through the IPsec SAs.
|
|
Profiles |
|
|
Key profile |
Defines how the SRX Series Firewall devices communicate with the KME devices to retrieve QKD keys from the external KME server. Key profiles are configured on the hub (HUB_KM_PROFILE_1) and spokes (SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 and SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1) separately.
|
| PPK Profile |
Indicates which key profile to use to establish quantum-safe IKE or IPsec SAs by referencing the key profile under the IKE gateway. |
| Certificates | |
| CA certificate | Verifies identity of devices and authenticate communication link. |
| Local certificate | Generates PKI and enroll it with the CA certificate for verification. |
| KME certificate | Third-party certificate generated by vendor. |
| Security Zones | |
| trust |
Network segment at the host zone. |
| untrust |
Network segment at the destination server zone. |
| vpn |
Network segment through which the hub and spokes interact. |
|
Primary verification tasks |
Verify the established IKE and IPsec SAs are Quantum safe. |
Topology Overview
In this example, we secure the SRX1 and SRX2 IPsec VPN tunnels by using quantum keys generated by third-party KME devices. The KME devices (KME-A and KME-B) are connected to each other through a quantum channel that is highly secure and capable of threat identification. Using this channel, the SRX1 and SRX2 devices retrieve quantum keys from their corresponding KME device and merge it with the existing keys to make the VPN tunnels quantum secure.
|
Hostname |
Role |
Function |
|---|---|---|
| SRX1 | SRX Series Firewall device capable of establishing IPsec tunnels | Initiates IKE or IPsec SA negotiation and establishes quantum-safe IPsec tunnels with SRX2 using QKD key fetched from KME-A QKD device. |
| SRX2 | SRX Series Firewall device capable of establishing IPsec tunnels | Responds to IKE or IPsec SA negotiation and establishes quantum-safe IPsec tunnels using QKD key from KME-B QKD device. |
| HOST1 | Host inside the trusted zone or LAN side of SRX1 | Initiates client-side traffic toward HOST 2 |
| HOST2 | Host inside the trusted zone or LAN side of SRX2 | Responds to client-side traffic from HOST 1. |
| KME-A | Third-party vendor QKD device | Provides QKD keys in response to key requests from SRX1. |
| KME-B | Third-party vendor QKD device | Provides QKD keys in response to key requests from SRX2. |
Topology Illustration
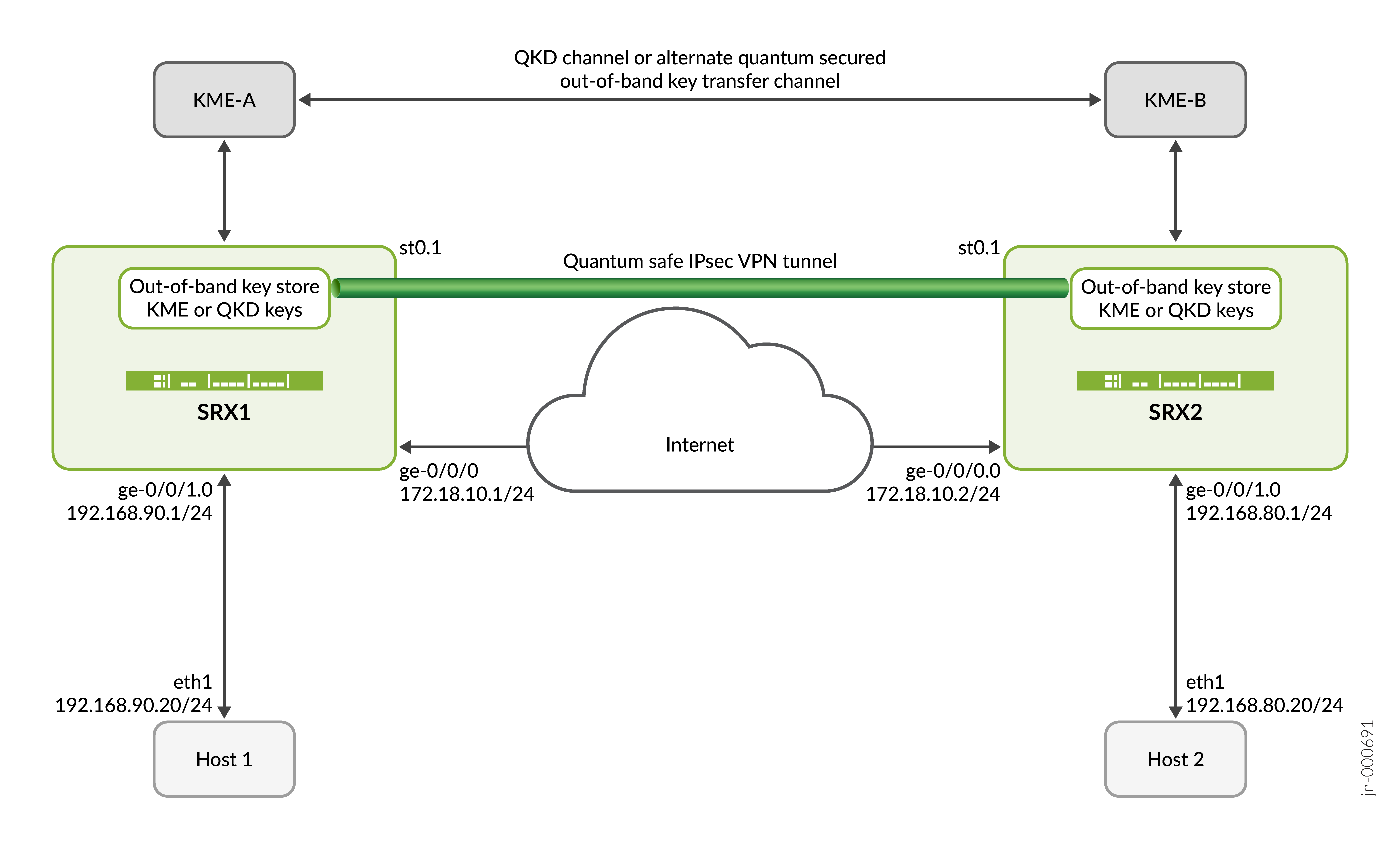
Step-By-Step Configuration on SRX Series Firewall Devices
For complete sample configurations on the DUT, see:
This configuration is applicable to SRX1 and SRX2 devices. For other devices, you must make the appropriate device-specific configuration changes.
-
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@srx# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.1/24 user@srx# set st0 unit 1 family inet user@srx# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.90.1/24
-
Configure a key profile of type quantum-key-manager with the must or recommended parameters.
Define the CA certificate, configure the URL of the KME server, configure the SAE-ID to be used by the local end, configure the corresponding certificate for the local SAE-ID, and configure the previously defined CA certificate.
[edit security pki] user@srx# set ca-profile ROOT_CA_CERT ca-identity RootCA
[edit security key-manager profiles] user@srx# set km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager url https://www.kme_a-qkd-server.net
[edit security key-manager profiles] user@srx# set km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager local-sae-id SAE_A user@srx# set km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager local-certificate-id SAE_A_CERT user@srx# set km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager trusted-cas ROOT_CA_CERT
Configure Site-to-Site IPsec VPN. This includes configuring the security zones, security policies, and relevant certificates for authenticating device identities and their communication links.
[edit security zones] user@srx# set security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike user@srx# set security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 user@srx# set security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 user@srx# set security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping user@srx# set security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0
[edit security policies] user@srx# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any user@srx# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any user@srx# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any user@srx# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit user@srx# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any user@srx# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any user@srx# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any user@srx# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
[edit security ike proposal] user@srx# set IKE_PROP authentication-method pre-shared-keys user@srx# set IKE_PROP dh-group group14 user@srx# set IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 user@srx# set IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc user@srx# set IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600
[edit security ike policy] user@srx# set IKE_POL proposals IKE_PROP user@srx# set IKE_POL pre-shared-key ascii-text ipsec-test
[edit security ike gateway] user@srx# set IKE_GW ike-policy IKE_POL user@srx# set IKE_GW address 172.18.10.2 user@srx# set IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/0.0 user@srx# set IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.1 user@srx# set IKE_GW version v2-only user@srx# set IKE_GW ppk-profile km_profile_1
[edit security ipsec proposal] user@srx# set IPSEC_PROP protocol esp user@srx# set IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@srx# set IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc user@srx# set IPSEC_PROP lifetime-seconds 2400
[edit security ipsec policy] user@srx# set IPSEC_POL proposals IPSEC_PROP
[edit security ipsec vpn] user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN ike gateway IKE_GW user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy IPSEC_POL user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.90.0/24 user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.80.0/24 user@srx# set IPSEC_VPN establish-tunnels immediately
Verification
This section provides a list of show commands that you can use to verify the feature in this example.
| Command | Verification Task |
|---|---|
|
show security ike security-associations detail |
|
|
show security ipsec security-associations detail |
|
|
show security ipsec statistics |
Verify IPsec encryption and decryption statistics. |
|
show security key-manager profiles detail |
Verify key profile statistics. |
|
ping 192.168.80.20 source 192.168.90.20 count 5 |
Ping from HOST 1 to HOST 2 or vice versa. |
- Verify IKE SAs
- Verify IPsec SAs
- Verify IPsec Statistics
- Verify Key Manager Profile
- Ping from HOST 1 to HOST 2 or vice versa
Verify IKE SAs
Purpose
Verify the IKE SAs.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ike
security-associations detail command to view the IKE SAs.
user@srx> show security ike security-associations detail IKE peer 172.18.10.2, Index 21, Gateway Name: IKE_GW Role: Initiator, State: UP Initiator cookie: 5a417d46cef3207d, Responder cookie: 57b9a17516bee31b Exchange type: IKEv2, Authentication method: Pre-shared-keys Local gateway interface: ge-0/0/2.0 Routing instance: default Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.2:500 Lifetime: Expires in 3445 seconds Reauth Lifetime: Disabled IKE Fragmentation: Enabled, Size: 576 SRG ID: 0 Remote Access Client Info: Unknown Client Peer ike-id: 172.18.10.2 AAA assigned IP: 0.0.0.0 PPK-profile: km_profile_1 Optional: No State : Used Algorithms: Authentication : hmac-sha256-128 Encryption : aes256-cbc Pseudo random function: hmac-sha256 Diffie-Hellman group : DH-group-14 Traffic statistics: Input bytes : 783 Output bytes : 831 Input packets: 2 Output packets: 2 Input fragmented packets: 0 Output fragmented packets: 0 IPSec security associations: 2 created, 0 deleted Phase 2 negotiations in progress: 1 IPSec Tunnel IDs: 500003 Negotiation type: Quick mode, Role: Initiator, Message ID: 0 Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.2:500 Local identity: 172.18.10.1 Remote identity: 172.18.10.2 Flags: IKE SA is created IPsec SA Rekey CREATE_CHILD_SA exchange stats: Initiator stats: Responder stats: Request Out : 0 Request In : 0 Response In : 0 Response Out : 0 No Proposal Chosen In : 0 No Proposal Chosen Out : 0 Invalid KE In : 0 Invalid KE Out : 0 TS Unacceptable In : 0 TS Unacceptable Out : 0 Res DH Compute Key Fail : 0 Res DH Compute Key Fail: 0 Res Verify SA Fail : 0 Res Verify DH Group Fail: 0 Res Verify TS Fail : 0
Meaning
The Role: Initiator, State: UP, PPK-profile:
km_profile_1, IPSec security associations: 2 created, 0
deleted Phase 2 negotiations in progress: 1, and Flags:
IKE SA is created fields shows the IKE SAs are created
successfully.
Verify IPsec SAs
Purpose
Verify the IPsec SAs.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ipsec
security-associations detail command to view the IPsec
SAs.
user@srx> show security ipsec security-associations detail ID: 500003 Virtual-system: root, VPN Name: IPSEC_VPN Local Gateway: 172.18.10.1, Remote Gateway: 172.18.10.2 Traffic Selector Name: ts1 Local Identity: ipv4(192.168.90.0-192.168.90.255) Remote Identity: ipv4(192.168.80.0-192.168.80.255) TS Type: traffic-selector Version: IKEv2 Quantum Secured: Yes PFS group: N/A SRG ID: 0 DF-bit: clear, Copy-Outer-DSCP Disabled, Bind-interface: st0.1, Policy-name: IPSEC_POL Port: 500, Nego#: 0, Fail#: 0, Def-Del#: 0 Flag: 0 Multi-sa, Configured SAs# 0, Negotiated SAs#: 0 Tunnel events: Fri Mar 31 2023 01:41:52: IPsec SA negotiation succeeds (1 times) Location: FPC 0, PIC 0, KMD-Instance 0 Anchorship: Thread 1 Distribution-Profile: default-profile Direction: inbound, SPI: 0xd1e1549c, AUX-SPI: 0 , VPN Monitoring: - Hard lifetime: Expires in 1916 seconds Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited Soft lifetime: Expires in 1349 seconds Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits) Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64 Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-immediately IKE SA Index: 21 Direction: outbound, SPI: 0xb5883167, AUX-SPI: 0 , VPN Monitoring: - Hard lifetime: Expires in 1916 seconds Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited Soft lifetime: Expires in 1349 seconds Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits) Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64 Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-immediately IKE SA Index: 21
Meaning
The Quantum Secured: Yes, Policy-name:
IPSEC_POL, IPsec SA negotiation succeeds (1
times), and tunnel-establishment:
establish-tunnels-immediately IKE SA Index: 21 fields shows the
IPsec SAs are created successfully.
Verify IPsec Statistics
Purpose
Verify the IPsec statistics.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ipsec
statistics command to view the IPsec statistics.
user@srx> show security ipsec statistics ESP Statistics: Encrypted bytes: 780 Decrypted bytes: 780 Encrypted packets: 5 Decrypted packets: 5 AH Statistics: Input bytes: 0 Output bytes: 0 Input packets: 0 Output packets: 0 Errors: AH authentication failures: 0, Replay errors: 0 ESP authentication failures: 0, ESP decryption failures: 0 Bad headers: 0, Bad trailers: 0 Invalid SPI: 0, TS check fail: 0 Exceeds tunnel MTU: 0 Discarded: 0
Meaning
The ESP Statistics and AH Statistics fields
shows the IPsec statistics.
Verify Key Manager Profile
Purpose
Verify the key manager profile.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security key-manager profiles
detail command to view the key manager profile.
user@srx> show security key-manager profiles detail Name: km_profile_1, Index: 3, Type: Quantum-key-manager Configured-at: 31.03.23 (01:40:50) Time-elapsed: 0 hrs 11 mins 30 secs Url: https://www.kme_a-qkd-server.net Local-sae-id: SAE_A Local-certificate-id: SAE_A_CERT Trusted-cas: [ ROOT_CA_CERT ] Peer-sae-ids: N/A Default-key-size: N/A Request stats: Received: 1 In-progress: 0 Success: 1 Failed: 0
Meaning
The Name: km_profile_1 and Quantum-key-manager
fields shows the key manager profile.
Ping from HOST 1 to HOST 2 or vice versa
Purpose
Verify the connectivity from HOST 1 to HOST 2.
Action
From operational mode, enter the ping 192.168.80.20 source
192.168.90.20 count 5 to view the connectivity from HOST 1 to
HOST 2.
user@HOST1# ping 192.168.80.20 source 192.168.90.20 count 5 PING 192.168.80.20 (192.168.80.20): 56 data bytes count 5 64 bytes from 192.168.80.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=0.998 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.80.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.594 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.80.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.395 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.80.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.536 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.80.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=1.838 ms --- 192.168.80.1 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 0.998/1.472/1.838/0.277 ms Data traffic is successfully flowing between the HOSTs
Meaning
The PING 192.168.80.20 (192.168.80.20): 56 data bytes count
5 confirms the connectivity from HOST 1 to HOST 2.
Appendix 1: Set Commands on all Devices
Set command output on all devices.
Set Commands on SRX1
set security pki ca-profile ROOT_CA_CERT ca-identity RootCA set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager url https://www.kme_a-qkd-server.net set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager local-sae-id SAE_A set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager local-certificate-id SAE_A_CERT set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager trusted-cas ROOT_CA_CERT set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.1/24 set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.90.1/24 set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 set security zones security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit set security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-method pre-shared-keys set security ike proposal IKE_PROP dh-group group14 set security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 set security ike proposal IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ike proposal IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600 set security ike policy IKE_POL proposals IKE_PROP set security ike policy IKE_POL pre-shared-key ascii-text ipsec-test set security ike gateway IKE_GW ike-policy IKE_POL set security ike gateway IKE_GW address 172.18.10.2 set security ike gateway IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/0.0 set security ike gateway IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.1 set security ike gateway IKE_GW version v2-only set security ike gateway IKE_GW ppk-profile km_profile_1 set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP protocol esp set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP lifetime-seconds 2400 set security ipsec policy IPSEC_POL proposals IPSEC_PROP set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN ike gateway IKE_GW set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy IPSEC_POL set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.90.0/24 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.80.0/24 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN establish-tunnels immediately
Set Commands on SRX2
set security pki ca-profile ROOT_CA_CERT ca-identity RootCA set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager url https://www.kme_a-qkd-server.net set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager local-sae-id SAE_B set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager local-certificate-id SAE_B_CERT set security key-manager profiles km_profile_1 quantum-key-manager trusted-cas ROOT_CA_CERT set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.2/24 set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.80.1/24 set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 set security zones security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit set security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-method pre-shared-keys set security ike proposal IKE_PROP dh-group group14 set security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 set security ike proposal IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ike proposal IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600 set security ike policy IKE_POL proposals IKE_PROP set security ike policy IKE_POL pre-shared-key ascii-text ipsec-test set security ike gateway IKE_GW ike-policy IKE_POL set security ike gateway IKE_GW address 172.18.10.1 set security ike gateway IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/0.0 set security ike gateway IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.2 set security ike gateway IKE_GW version v2-only set security ike gateway IKE_GW ppk-profile km_profile_1 set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP protocol esp set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP lifetime-seconds 2400 set security ipsec policy IPSEC_POL proposals IPSEC_PROP set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN ike gateway IKE_GW set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy IPSEC_POL set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.80.0/24 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24 set security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN establish-tunnels immediately
Appendix 2: Show Configuration Output on DUT
Show command output on the DUT.
SRX1
user@srk1# show security pki
ca-profile ROOT_CA_CERT {
ca-identity RootCA;
}
user@srk1# show security key-manager
profiles {
km_profile_1 {
quantum-key-manager {
url https://www.kme_a-qkd-server.net;
local-sae-id SAE_A;
local-certificate-id SAE_A_CERT;
trusted-cas ROOT_CA_CERT;
}
}
}user@srk1# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.90.1/24;
address 192.168.80.1/24;
address 192.168.70.1/24;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
address 172.18.10.3/24;
}
}
}
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family mpls;
}
}
st0 {
unit 1 {
family inet;
}
unit 2 {
family inet;
}
}user@srk1# show security zones
security-zone untrust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ike;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0.0;
}
}
security-zone vpn {
interfaces {
st0.1;
}
}
security-zone trust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0;
}
}user@srk1# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone vpn {
policy vpn_out {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
from-zone vpn to-zone trust {
policy vpn_in {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}user@srk1# show security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-method pre-shared-keys; dh-group group14; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600;
user@srk1# show security ike policy IKE_POL proposals IKE_PROP; pre-shared-key ascii-text "$9$Nadwg4aUH.5Nds4aUiHuO1RhrvWxVs4"; ## SECRET-DATA
user@srk1# show security ike gateway IKE_GW ike-policy IKE_POL; address 172.18.10.2; external-interface ge-0/0/0.0; local-address 172.18.10.1; version v2-only; ppk-profile km_profile_1;
user@srk1# show security ipsec proposal IPSEC_PROP protocol esp; authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 2400;
user@srk1# show security ipsec policy IPSEC_POL proposals IPSEC_PROP;
user@srk1# show security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN
bind-interface st0.1;
ike {
gateway IKE_GW;
ipsec-policy IPSEC_POL;
}
traffic-selector ts1 {
local-ip 192.168.90.0/24;
remote-ip 192.168.80.0/24;
}
establish-tunnels immediately;SRX 2
user@srx2# show security key-manager
profiles {
km_profile_1 {
quantum-key-manager {
url https://www.kme_a-qkd-server.net;
local-sae-id SAE_B;
local-certificate-id SAE_B_CERT;
trusted-cas ROOT_CA_CERT;
}
}
}user@srx2# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.90.1/24;
address 192.168.80.1/24;
address 192.168.70.1/24;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
address 172.18.10.3/24;
}
}
}
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family mpls;
}
}
st0 {
unit 1 {
family inet;
}
unit 2 {
family inet;
}
}user@srx2# show security zones
security-zone untrust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ike;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0.0;
}
}
security-zone vpn {
interfaces {
st0.1;
}
}
security-zone trust {
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0;
}
}user@srx2# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone vpn {
policy vpn_out {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
from-zone vpn to-zone trust {
policy vpn_in {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}user@srx2# show security ike proposal IKE_PROP authentication-method pre-shared-keys; dh-group group14; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600;
user@srx2# show security ike gateway IKE_GW ike-policy IKE_POL; address 172.18.10.1; external-interface ge-0/0/0.0; local-address 172.18.10.2; version v2-only; ppk-profile km_profile_1;
user@srx2# show security ike policy IKE_POL proposals IKE_PROP; pre-shared-key ascii-text "$9$P5z6/Cu1EyP5F/CuB1-VwYgJDi.TF/"; ## SECRET-DATA
user@srx2# show security ipsec policy IPSEC_POL proposals IPSEC_PROP;
user@srx2# show security ipsec vpn IPSEC_VPN
bind-interface st0.1;
ike {
gateway IKE_GW;
ipsec-policy IPSEC_POL;
}
traffic-selector ts1 {
local-ip 192.168.80.0/24;
remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24;
}
establish-tunnels immediately;Example: Configure Quantum-Secured IPsec AutoVPN Topology Using Quantum Key Manager Key Profile
Use this configuration example to secure an IPsec AutoVPN infrastructure by configuring the quantum key manager key profile.
The Hub, Spoke 1, and Spoke 2 use quantum key manager key profiles to communicate with KME Hub, KME Spoke 1, and KME Spoke 2 to fetch the QKD keys and establish then IPsec VPN tunnels.
Reading Time |
Less than an hour. |
Configuration Time |
Less than an hour. |
- Example Prerequisites
- Before You Begin
- Functional Overview
- Topology Overview
- Topology Illustration
- Step-By-Step Configuration on Hub
- Step-By-Step Configuration on Spoke Devices
- Verification
- Appendix 1: Set Commands on all Devices
- Appendix 2: Show Configuration Output on DUT
Example Prerequisites
Hardware requirements |
|
Software requirements |
Junos OS Release 22.4R1 or later. |
Before You Begin
Benefits |
|
Useful Resources |
|
Know more |
|
Hands-on Experience |
|
Learn more |
Functional Overview
Table 20 provides a quick summary of the configuration components deployed in this example.
| IPsec VPN | Deploy a hub-and-spoke IPsec VPN topology where spokes are connected by VPN tunnels that send traffic through the hub. These VPN tunnels are later configured to use quantum keys making them quantum-safe VPN tunnels. |
| IKE gateway | Establish a secure connection, the IKE gateway uses the IKE policy to limit itself to the configured group of CAs (ca-profiles) while validating the certificate. |
| Proposals | |
| IKE proposal | Define the algorithms and keys used to establish the secure IKE connection with the peer security gateway. IKE creates the dynamic SAs and negotiates them for IPsec. |
| IPsec proposal | List protocols, algorithms, and security services to be negotiated with the remote IPsec peer. |
| Policies | |
| IKE policy | Define a combination of security parameters (IKE proposals) to be used during IKE negotiation. |
| IPsec policy | Contain rules and security policies to allow group VPN traffic between the zones specified. |
| Security policy | Allows you to select the type of data traffic to secure through the IPsec SAs.
|
Profiles |
|
| Key profile | Define how the SRX devices communicate with the KME devices to retrieve QKD keys from the external KME server. Key profiles are configured on the hub (HUB_KM_PROFILE_1) and spokes (SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 and SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1) separately. Configure SPOKE-1 and SPOKE-2 for applications and services to retrieve QKD keys from external server.
|
| PPK Profile | Indicate which key profile to use to establish quantum-safe IKE or IPsec SAs by referencing the key profile under the IKE gateway. |
| Certificates | |
| CA certificate | Verify identity of devices and authenticate communication link between them. |
| Local certificate | Generate PKI and enroll it with the CA certificate for verification. |
| KME certificate | Third-party certificate generated by vendor. |
| Security Zones | |
| trust | Network segment at the host zone. |
| untrust | Network segment at the destination server zone. |
| vpn | Network segment through which the hub and spokes interact. |
Primary verification tasks |
Verify the established IKE and IPsec SAs are Quantum safe. |
Topology Overview
In this example, we secure the hub-and-spoke IPsec VPN tunnels using quantum keys generated by third-party KME devices. The KME devices (KME-Hub, KME-Spoke 1, and KME-Spoke 2) are connected to each other through a quantum channel that is highly secure and capable of threat identification. Using this channel, the Hub and Spoke devices retrieve quantum keys from their corresponding KME device and merge it with the existing keys to make the VPN tunnels quantum secure.
Topology Components |
Role |
Function |
|---|---|---|
Hub |
SRX Series Firewall capable of establishing IPsec tunnels | Responds to IKE or IPsec SA negotiation and establishes Quantum-safe IPsec tunnels using QKD key from KME-HUB QKD device on SPOKE-1 and SPOKE-2. |
SPOKE-1 |
SRX Series Firewall capable of establishing IPsec tunnels | Initiates IKE or IPsec SA negotiation and establishes Quantum-safe IPsec tunnels with hub using QKD key from KME-SPOKE-1 QKD device. |
SPOKE-2 |
SRX Series Firewall capable of establishing IPsec tunnels | Initiates IKE or IPsec SA negotiation and establishes Quantum-safe IPsec tunnels with hub using QKD key from KME-SPOKE-2 QKD device. |
HOST-1 |
Host inside the trusted zone or LAN side of SPOKE 1. Host 1 is secured by SPOKE 1. |
Initiates client-side traffic toward HOST-3 |
HOST-2 |
Host inside the trusted zone or LAN side of SPOKE 2. Host 2 is secured by SPOKE 2. |
Initiates client-side traffic toward HOST-3 |
HOST- 3 |
Host inside the trusted zone or LAN side of hub. Host 3 is secured by Hub. |
Responds to client-side traffic from HOST-1 and HOST-2 |
KME-HUB |
Third-party QKD device | Provides QKD keys in response to key requests from HUB |
KME-SPOKE-1 |
Third-party QKD device | Provides QKD keys in response to key requests from SPOKE-1 |
KME-SPOKE-2 |
Third-party QKD device | Provides QKD keys in response to key requests from SPOKE-2 |
Topology Illustration
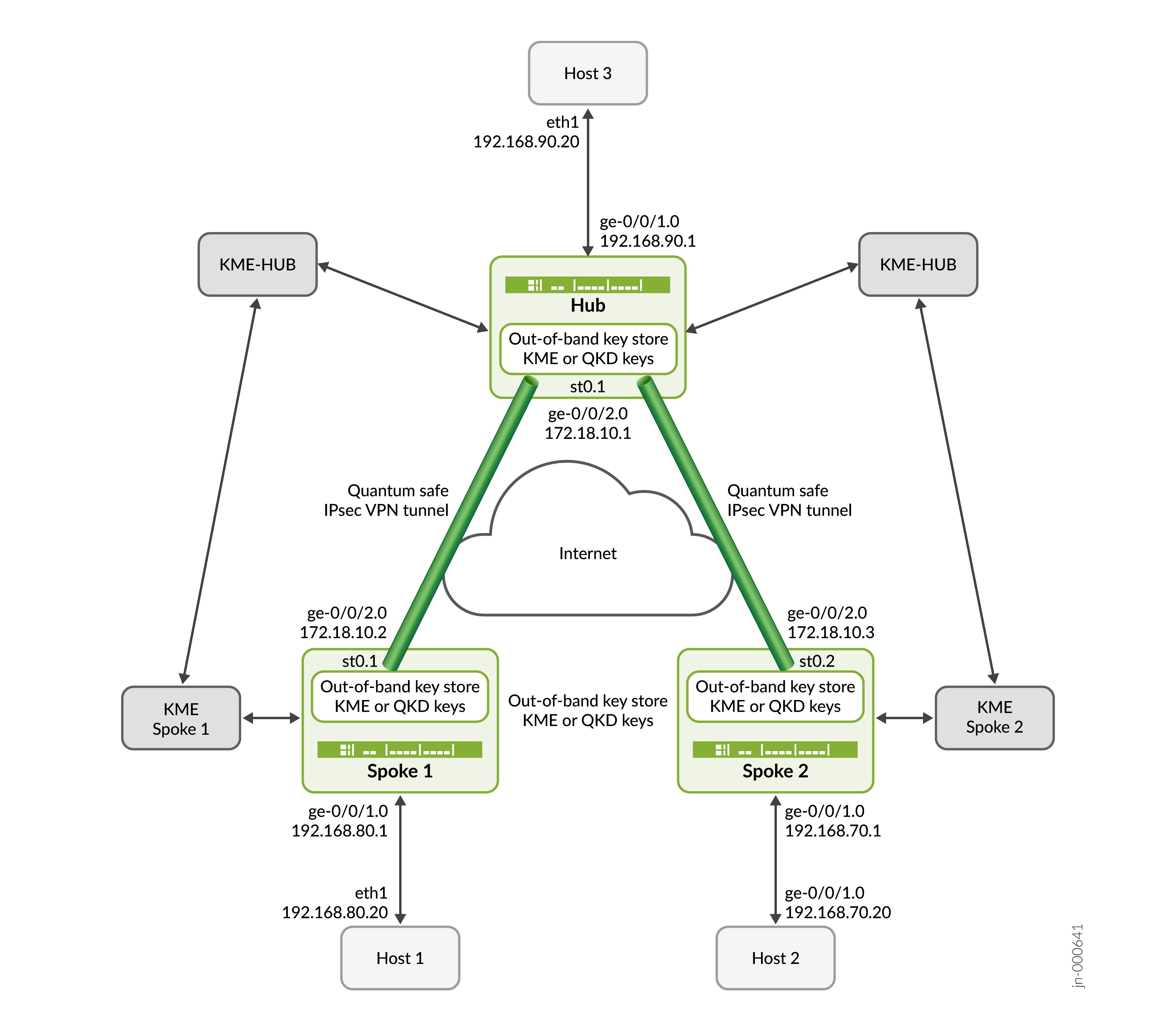
Step-By-Step Configuration on Hub
For complete sample configurations on the hub and spoke devices, see:
Configure the hub interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@hub# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.1/24 user@hub# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.90.1/24 user@hub# set st0 unit 1 family inet
Configure hub-spoke the IPsec VPN. This includes configuring the security zones, security policies, and relevant certificates for authenticating device identities and their communication links.
Configure the hub to fetch the CA certificate from the CA server, or load a locally available CA certificate from the device.
Note:The KME certificates need to configured as per third-party vendor instructions.
Configure the IPsec proposal and policy. Configure the IKE policy, proposal and gateway for the IPsec VPN.
[edit security zones] user@hub# set security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike user@hub# set security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 user@hub# set security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 user@hub# set security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping user@hub# set security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0
[edit security policies] user@hub# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any user@hub# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any user@hub# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any user@hub# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit user@hub# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any user@hub# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any user@hub# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any user@hub# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
[edit security pki] user@hub# set ca-profile Root-CA ca-identity Root-CA user@hub# set ca-profile Root-CA enrollment url url-to-CA-server user@hub# set ca-profile Root-CA revocation-check disable
user@hub> request security pki ca-certificate enroll ca-profile Root-CA
user@hub> request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id HUB_CRT size 2048 type rsa user@hub> request security pki local-certificate enroll certificate-id HUB_CRT challenge-password password domain-name hub.juniper.net email hub@juniper.net subject DC=juniper,CN=hub.juniper.net,OU=security,O=juniper,L=sunnyvale,ST=california,C=us ca-profile Root-CA user@hub> request security pki local-certificate load certificate-id SAE_HUB filename SAE_HUB.cert key SAE_HUB.key
[edit security ike proposal] user@hub# set HUB_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures user@hub# set HUB_IKE_PROP dh-group group14 user@hub# set HUB_IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 user@hub# set HUB_IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc user@hub# set HUB_IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600
[edit security ike policy] user@hub# set HUB_IKE_POL proposals HUB_IKE_PROP user@hub# set HUB_IKE_POL certificate local-certificate HUB_CRT
[edit security ike gateway] user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.1 user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW ike-policy HUB_IKE_POL user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/2.0 user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW local-identity distinguished-name user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW dynamic ike-user-type group-ike-id user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW dynamic distinguished-name wildcard C=us,DC=juniper user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW version v2-only
[edit security ipsec proposal] user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
[edit security ipsec vpn] user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_VPN ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy HUB_IPSEC_POL user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.90.0/24 user@hub# set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0
[edit security ipsec policy] user@hub# set HUB_IPSEC_POL proposals HUB_IPSEC_PROP
Configure the quantum key manager key profile to retrieve quantum keys from the corresponding KME-Hub device.
[edit security key-manager profiles] user@hub# set HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager url kme-server-urlset security key-manager profiles HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-sae-id SAE_HUB user@hub# set HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-certificate-id SAE_HUB_CERT user@hub# set HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager trusted-cas Root-CA
Bind the quantum key manager key profile as the IKE gateway ppk-profile to make the VPN tunnels quantum-safe.
[edit security ike gateway] user@hub# set HUB_IKE_GW ppk-profile HUB_KM_PROFILE_1
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Step-By-Step Configuration on Spoke Devices
For complete sample configurations on the devices, see:
This configuration is applicable for Spoke 1 and Spoke 2 devices, you must make the appropriate device-specific configuration changes.
Configure the spoke interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@spoke# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.2/24 user@spoke# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.80.1/24 user@spoke# set st0 unit 1 family inet
Configure hub-spoke the IPsec VPN. This includes configuring the security zones, security policies, and relevant certificates for authenticating device identities and their communication links.
Configure the hub to fetch the CA certificate from the CA server, or load a locally available CA certificate from the device.
Note:The KME certificates need to configured as per third-party vendor instructions.
Configure the IPsec proposal and policy. Configure the IKE policy, proposal and gateway for the IPsec VPN.
[edit security zones] user@spoke# set security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike user@spoke# set security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 user@spoke# set security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 user@spoke# set security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping user@spoke# set security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0
[edit security policies] user@spoke# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any user@spoke# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any user@spoke# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any user@spoke# set from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit user@spoke# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any user@spoke# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any user@spoke# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any user@spoke# set from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
[edit security pki] user@spoke# set ca-profile Root-CA ca-identity Root-CA user@spoke# set ca-profile Root-CA enrollment url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll user@spoke# set ca-profile Root-CA revocation-check disable
user@spoke> request security pki ca-certificate enroll ca-profile Root-CA
user@spoke> request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id SPOKE_1_CRT size 2048 type rsa user@spoke> request security pki local-certificate enroll certificate-id SPOKE_1_CRT challenge-password <password> domain-name spoke_1.juniper.net email spoke_1@juniper.net subject DC=juniper,CN=spoke_1.juniper.net,OU=security,O=juniper,L=sunnyvale,ST=california,C=us ca-profile Root-CA user@spoke> request security pki local-certificate load certificate-id SAE_SPOKE_1 filename SAE_SPOKE_1.cert key SAE_SPOKE_1.key
[edit security ike proposal] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP dh-group group14 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600
[edit security ike policy] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_POL proposals SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_POL certificate local-certificate SPOKE_1_CRT
[edit security ike gateway] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW address 172.18.10.1 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.2 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW ike-policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/2.0 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW local-identity distinguished-name user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW remote-identity distinguished-name user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW version v2-only
[edit security ipsec proposal] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
[edit security ipsec vpn] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.80.0/24 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24
[edit security ipsec policy] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL proposals SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP
Configure the quantum key manager key profile to retrieve quantum keys from the corresponding spoke device.
[edit security key-manager profiles] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager url https://www.kme_spoke_1-qkd-server.net user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-sae-id SAE_SPOKE_1 user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-certificate-id SAE_SPOKE_1_CERT user@spoke# set profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager trusted-cas Root-CA
Bind the quantum key manager key profile as the IKE gateway ppk-profile to make the VPN tunnels quantum-safe.
[edit security ike gateway] user@spoke# set SPOKE_1_IKE_GW ppk-profile SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
This section provides a list of show commands that you can use to verify the feature in this example.
| Command | Verification Task |
|---|---|
|
show security ike security-associations detail |
Verify the IKE SAs. |
|
show security ipsec security-associations detail |
Verify the IPsec SAs. |
|
show security ipsec statistics |
Verify IPsec encryption and decryption statistics. |
|
show security key-manager profiles detail |
Verify key profile statistics. |
|
ping 192.168.90.20 source 192.168.80.20 count 4 |
Ping from Host 1 to Host 3. |
|
ping 192.168.90.20 source 192.168.70.20 count 4 |
Ping from Host 2 to Host 3. |
- Verify IKE SAs
- Verify IPsec SAs
- Verify IPsec Statistics
- Verify Key Manager Profile
- Ping from Host 1 to Host 3
- Ping from Host 2 to Host 3
Verify IKE SAs
Purpose
Verify the IKE SAs.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ike security-associations detail command to view the IKE SAs.
user@hub> show security ike security-associations detail
IKE peer 172.18.10.3, Index 2161, Gateway Name: HUB_IKE_GW
Role: Responder, State: UP
Initiator cookie: bccc74c70f0b81b9, Responder cookie: 872d364f15b29c28
Exchange type: IKEv2, Authentication method: RSA-signatures
Local gateway interface: ge-0/0/2.0
Routing instance: default
Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.3:500
Lifetime: Expires in 3464 seconds
Reauth Lifetime: Disabled
IKE Fragmentation: Enabled, Size: 576
Remote Access Client Info: Unknown Client
Peer ike-id: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=spoke_2.juniper.net
AAA assigned IP: 0.0.0.0
PPK-profile: HUB_KM_PROFILE_1
Optional: No
State : Used
Algorithms:
Authentication : hmac-sha256-128
Encryption : aes256-cbc
Pseudo random function: hmac-sha256
Diffie-Hellman group : DH-group-14
Traffic statistics:
Input bytes : 2661
Output bytes : 2586
Input packets: 5
Output packets: 5
Input fragmented packets: 4
Output fragmented packets: 4
IPSec security associations: 2 created, 0 deleted
Phase 2 negotiations in progress: 1
IPSec Tunnel IDs: 500446
Negotiation type: Quick mode, Role: Responder, Message ID: 0
Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.3:500
Local identity: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=hub.juniper.net
Remote identity: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=spoke_2.juniper.net
Flags: IKE SA is created
IPsec SA Rekey CREATE_CHILD_SA exchange stats:
Initiator stats: Responder stats:
Request Out : 0 Request In : 0
Response In : 0 Response Out : 0
No Proposal Chosen In : 0 No Proposal Chosen Out : 0
Invalid KE In : 0 Invalid KE Out : 0
TS Unacceptable In : 0 TS Unacceptable Out : 0
Res DH Compute Key Fail : 0 Res DH Compute Key Fail: 0
Res Verify SA Fail : 0
Res Verify DH Group Fail: 0
Res Verify TS Fail : 0
IKE peer 172.18.10.2, Index 2162, Gateway Name: HUB_IKE_GW
Role: Responder, State: UP
Initiator cookie: 5e17d5924c619788, Responder cookie: 15f1e3c4252ba6f8
Exchange type: IKEv2, Authentication method: RSA-signatures
Local gateway interface: ge-0/0/2.0
Routing instance: default
Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.2:500
Lifetime: Expires in 3464 seconds
Reauth Lifetime: Disabled
IKE Fragmentation: Enabled, Size: 576
Remote Access Client Info: Unknown Client
Peer ike-id: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=spoke.juniper.net
AAA assigned IP: 0.0.0.0
PPK-profile: HUB_KM_PROFILE_1
Optional: No
State : Used
Algorithms:
Authentication : hmac-sha256-128
Encryption : aes256-cbc
Pseudo random function: hmac-sha256
Diffie-Hellman group : DH-group-14
Traffic statistics:
Input bytes : 2645
Output bytes : 2586
Input packets: 5
Output packets: 5
Input fragmented packets: 4
Output fragmented packets: 4
IPSec security associations: 2 created, 0 deleted
Phase 2 negotiations in progress: 1
IPSec Tunnel IDs: 500447
Negotiation type: Quick mode, Role: Responder, Message ID: 0
Local: 172.18.10.1:500, Remote: 172.18.10.2:500
Local identity: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=hub.juniper.net
Remote identity: C=us, DC=juniper, ST=california, L=sunnyvale, O=juniper, OU=security, CN=spoke.juniper.net
Flags: IKE SA is created
IPsec SA Rekey CREATE_CHILD_SA exchange stats:
Initiator stats: Responder stats:
Request Out : 0 Request In : 0
Response In : 0 Response Out : 0
No Proposal Chosen In : 0 No Proposal Chosen Out : 0
Invalid KE In : 0 Invalid KE Out : 0
TS Unacceptable In : 0 TS Unacceptable Out : 0
Res DH Compute Key Fail : 0 Res DH Compute Key Fail: 0
Res Verify SA Fail : 0
Res Verify DH Group Fail: 0
Res Verify TS Fail : 0 Meaning
The sample output confirms the IKE SAs.
Verify IPsec SAs
Purpose
Verify the IPsec SAs.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ipsec security-associations detail command to view the IPsec SAs.
user@hub> show security ipsec security-associations detail
ID: 500446 Virtual-system: root, VPN Name: HUB_IPSEC_VPN
Local Gateway: 172.18.10.1, Remote Gateway: 172.18.10.3
Traffic Selector Name: ts1
Local Identity: ipv4(192.168.90.0-192.168.90.255)
Remote Identity: ipv4(192.168.70.0-192.168.70.255)
TS Type: traffic-selector
Version: IKEv2
Quantum Secured: Yes
PFS group: N/A
Passive mode tunneling: Disabled
DF-bit: clear, Copy-Outer-DSCP Disabled, Bind-interface: st0.1, Policy-name: HUB_IPSEC_POL
Port: 500, Nego#: 0, Fail#: 0, Def-Del#: 0 Flag: 0
Multi-sa, Configured SAs# 0, Negotiated SAs#: 0
Tunnel events:
Fri Jul 21 2023 00:31:08: IPsec SA negotiation succeeds (1 times)
Location: FPC 0, PIC 0
Anchorship: Thread 1
Distribution-Profile: default-profile
Direction: inbound, SPI: 0xcf48c0c9, AUX-SPI: 0
, VPN Monitoring: -
Hard lifetime: Expires in 3464 seconds
Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited
Soft lifetime: Expires in 2778 seconds
Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed
Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits)
Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64
Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled
tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-responder-only
IKE SA Index: 2161
Direction: outbound, SPI: 0x86c9ba76, AUX-SPI: 0
, VPN Monitoring: -
Hard lifetime: Expires in 3464 seconds
Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited
Soft lifetime: Expires in 2778 seconds
Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed
Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits)
Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64
Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled
tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-responder-only
IKE SA Index: 2161
ID: 500447 Virtual-system: root, VPN Name: HUB_IPSEC_VPN
Local Gateway: 172.18.10.1, Remote Gateway: 172.18.10.2
Traffic Selector Name: ts1
Local Identity: ipv4(192.168.90.0-192.168.90.255)
Remote Identity: ipv4(192.168.80.0-192.168.80.255)
TS Type: traffic-selector
Version: IKEv2
Quantum Secured: Yes
PFS group: N/A
Passive mode tunneling: Disabled
DF-bit: clear, Copy-Outer-DSCP Disabled, Bind-interface: st0.1, Policy-name: HUB_IPSEC_POL
Port: 500, Nego#: 0, Fail#: 0, Def-Del#: 0 Flag: 0
Multi-sa, Configured SAs# 0, Negotiated SAs#: 0
Tunnel events:
Fri Jul 21 2023 00:31:08: IPsec SA negotiation succeeds (1 times)
Location: FPC 0, PIC 0
Anchorship: Thread 1
Distribution-Profile: default-profile
Direction: inbound, SPI: 0x4275d756, AUX-SPI: 0
, VPN Monitoring: -
Hard lifetime: Expires in 3464 seconds
Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited
Soft lifetime: Expires in 2772 seconds
Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed
Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits)
Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64
Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled
tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-responder-only
IKE SA Index: 2162
Direction: outbound, SPI: 0xe37b5568, AUX-SPI: 0
, VPN Monitoring: -
Hard lifetime: Expires in 3464 seconds
Lifesize Remaining: Unlimited
Soft lifetime: Expires in 2772 seconds
Mode: Tunnel(0 0), Type: dynamic, State: installed
Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha256-128, Encryption: aes-cbc (256 bits)
Anti-replay service: counter-based enabled, Replay window size: 64
Extended-Sequence-Number: Disabled
tunnel-establishment: establish-tunnels-responder-only
IKE SA Index: 2162Meaning
The sample output confirms the IPsec SAs.
Verify IPsec Statistics
Purpose
Verify the IPsec statistics.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security ipsec statistics command to view the IPsec statistics.
user@hub> show security ipsec statistics ESP Statistics: Encrypted bytes: 1560 Decrypted bytes: 1560 Encrypted packets: 10 Decrypted packets: 10 AH Statistics: Input bytes: 0 Output bytes: 0 Input packets: 0 Output packets: 0 Errors: AH authentication failures: 0, Replay errors: 0 ESP authentication failures: 0, ESP decryption failures: 0 Bad headers: 0, Bad trailers: 0 Invalid SPI: 0, TS check fail: 0 Exceeds tunnel MTU: 0 Discarded: 0
Meaning
The sample output confirms the IPsec statistics.
Verify Key Manager Profile
Purpose
Verify the key manager profile.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security key-manager profiles detail command and verify the Success field in the Request stats option.
user@hub> show security key-manager profiles detail
Name: HUB_KM_PROFILE_1, Index: 6, Type: Quantum-key-manager
Configured-at: 21.07.23 (00:14:00)
Time-elapsed: 0 hrs 19 mins 24 secs
Url: https://kme.juniper.net:8080
Local-sae-id: SAE_HUB
Local-certificate-id: SAE_HUB_CERT
Trusted-cas: [ ROOT_CA_CERT ]
Peer-sae-ids: N/A
Default-key-size: N/A
Request stats:
Received: 2
In-progress: 0
Success: 2
Failed: 0
Meaning
The sample output confirms the quantum key manager profile.
Ping from Host 1 to Host 3
Purpose
Verify the connectivity from Host 1 to Host 3.
Action
From operational mode, enter the ping 192.168.90.20 source 192.168.80.20 count 5 command to view the connectivity from Host 1 to Host 3.
user@host1# ping 192.168.90.20 source 192.168.80.20 count 5 PING 192.168.90.20 (192.168.90.20): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=2.151 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.710 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.349 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.597 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=1.515 ms --- 192.168.90.20 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.349/1.702/2.151/0.290 ms Data traffic is successfully flowing between the HOSTs
Meaning
The sample output confirms the connectivity from Host 1 to Host 3.
Ping from Host 2 to Host 3
Purpose
Verify the connectivity from Host 2 to Host 3.
Action
From operational mode, enter the ping 192.168.90.20 source 192.168.80.20 count 5 command to view the connectivity from Host 2 to Host 3.
user@host2# ping 192.168.90.20 source 192.168.70.20 count 5 PING 192.168.90.20 (192.168.90.20): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=2.151 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.710 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.349 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.597 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.90.20: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=1.759 ms --- 192.168.90.20 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.349/1.702/2.151/0.290 ms Data traffic is successfully flowing between the HOSTs
Meaning
The sample output confirms the connectivity from Host 2 to Host 3.
Appendix 1: Set Commands on all Devices
Set command output on all devices.
Set Commands on Hub
set security pki ca-profile Root-CA ca-identity Root-CA set security pki ca-profile Root-CA enrollment url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll set security pki ca-profile Root-CA revocation-check disable request security pki ca-certificate enroll ca-profile Root-CA request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id HUB_CRT size 2048 type rsa request security pki local-certificate enroll certificate-id HUB_CRT challenge-password <password> domain-name hub.juniper.net email hub@juniper.net subject DC=juniper,CN=hub.juniper.net,OU=security,O=juniper,L=sunnyvale,ST=california,C=us ca-profile Root-CA request security pki local-certificate load certificate-id SAE_HUB filename SAE_HUB.cert key SAE_HUB.key set security key-manager profiles HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager url https://www.kme_hub-qkd-server.net set security key-manager profiles HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-sae-id SAE_HUB set security key-manager profiles HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-certificate-id SAE_HUB_CERT set security key-manager profiles HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager trusted-cas Root-CA set security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures set security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP dh-group group14 set security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 set security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600 set security ike policy HUB_IKE_POL proposals HUB_IKE_PROP set security ike policy HUB_IKE_POL certificate local-certificate HUB_CRT set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.1 set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW ike-policy HUB_IKE_POL set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/2.0 set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW local-identity distinguished-name set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW dynamic ike-user-type group-ike-id set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW dynamic distinguished-name wildcard C=us,DC=juniper set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW ppk-profile HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 set security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW version v2-only set security ipsec proposal HUB_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp set security ipsec proposal HUB_IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 set security ipsec proposal HUB_IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ipsec policy HUB_IPSEC_POL proposals HUB_IPSEC_PROP set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy HUB_IPSEC_POL set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.90.0/24 set security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.1/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.90.1/24 set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 set security zones security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
Set Commands on Spoke 1
set security pki ca-profile Root-CA ca-identity Root-CA set security pki ca-profile Root-CA enrollment url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll set security pki ca-profile Root-CA revocation-check disable request security pki ca-certificate enroll ca-profile Root-CA request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id SPOKE_1_CRT size 2048 type rsa request security pki local-certificate enroll certificate-id SPOKE_1_CRT challenge-password <password> domain-name spoke_1.juniper.net email spoke_1@juniper.net subject DC=juniper,CN=spoke_1.juniper.net,OU=security,O=juniper,L=sunnyvale,ST=california,C=us ca-profile Root-CA request security pki local-certificate load certificate-id SAE_SPOKE_1 filename SAE_SPOKE_1.cert key SAE_SPOKE_1.key set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager url https://www.kme_spoke_1-qkd-server.net set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-sae-id SAE_SPOKE_1 set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-certificate-id SAE_SPOKE_1_CERT set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager trusted-cas Root-CA set security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures set security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP dh-group group14 set security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 set security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600 set security ike policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL proposals SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP set security ike policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL certificate local-certificate SPOKE_1_CRT set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW address 172.18.10.1 set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.2 set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW ike-policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/2.0 set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW local-identity distinguished-name set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW remote-identity distinguished-name set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW ppk-profile SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1 set security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW version v2-only set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ipsec policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL proposals SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.1 set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.80.0/24 set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.2/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.80.1/24 set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 set security zones security-zone vpn interfaces st0.1 set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
Set Commands on Spoke 2
set security pki ca-profile Root-CA ca-identity Root-CA set security pki ca-profile Root-CA enrollment url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll set security pki ca-profile Root-CA revocation-check disable request security pki ca-certificate enroll ca-profile Root-CA request security pki generate-key-pair certificate-id SPOKE_2_CRT size 2048 type rsa request security pki local-certificate enroll certificate-id SPOKE_2_CRT challenge-password <password> domain-name spoke_2.juniper.net email spoke_2@juniper.net subject DC=juniper,CN=spoke_2.juniper.net,OU=security,O=juniper,L=sunnyvale,ST=california,C=us ca-profile Root-CA request security pki local-certificate load certificate-id SAE_SPOKE_2 filename SAE_SPOKE_2.cert key SAE_SPOKE_2.key set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager url https://www.kme_spoke_2-qkd-server.net set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-sae-id SAE_SPOKE_2 set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager local-certificate-id SAE_SPOKE_2_CERT set security key-manager profiles SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1 quantum-key-manager trusted-cas Root-CA set security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures set security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP dh-group group14 set security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP authentication-algorithm sha-256 set security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP lifetime-seconds 3600 set security ike policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL proposals SPOKE_IKE_PROP set security ike policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL certificate local-certificate SPOKE_2_CRT set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW address 172.18.10.1 set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW local-address 172.18.10.3 set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW ike-policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW external-interface ge-0/0/2.0 set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW local-identity distinguished-name set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW remote-identity distinguished-name set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW ppk-profile SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1 set security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW version v2-only set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 set security ipsec proposal SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc set security ipsec policy SPOKE_2_IPSEC_POL proposals SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN bind-interface st0.2 set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN ike ipsec-policy SPOKE_2_IPSEC_POL set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 192.168.70.0/24 set security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.18.10.3/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.70.1/24 set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services ike set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 set security zones security-zone vpn interfaces st0.2 set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match source-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match destination-address any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out match application any set security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn policy vpn_out then permit set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match source-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match destination-address any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in match application any set security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust policy vpn_in then permit
Appendix 2: Show Configuration Output on DUT
Show command output on the DUT.
Hub
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show security pki ca-profile Root-CA, show security key-manager, show security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP, show security ike policy HUB_IKE_POL, show security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW, show security ipsec proposal HUB_IPSEC_PROP, show security ipsec policy HUB_IPSEC_POL, show security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN, show security zones security-zone untrust, show security zones security-zone trust, show security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn, show security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust, and show interfaces commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
user@hub# show security pki ca-profile Root-CA
ca-identity Root-CA;
enrollment {
url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll;
}
revocation-check {
disable;
}user@hub# show security key-manager
profiles {
km_profile_1 {
static {
key-id ascii-text "$9$7VNs4UDkPT3Hq9A01yrWLxNYoPfTz3924"; ## SECRET-DATA
key ascii-text "$9$RraElM7NbwgJ-VkPTFAtxNdws4GUHqmTaZ36AtOBwY24UHfTz9A0JGu1IhrlGDjHmTFn/9p0fT39p0hc-VwgGiPfzn9pJGqfQnpurev8xds2aDjqX7"; ## SECRET-DATA
}
}
HUB_KM_PROFILE_1 {
quantum-key-manager {
url https://www.kme_hub-qkd-server.net;
local-sae-id SAE_HUB;
local-certificate-id SAE_HUB_CERT;
trusted-cas Root-CA;
}
}
}
user@hub# show security ike proposal HUB_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures; dh-group group14; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600;
user@hub# show security ike policy HUB_IKE_POL
proposals HUB_IKE_PROP;
certificate {
local-certificate HUB_CRT;
}user@hub# show security ike gateway HUB_IKE_GW
ike-policy HUB_IKE_POL;
dynamic {
distinguished-name {
wildcard C=us,DC=juniper;
}
ike-user-type group-ike-id;
}
local-identity distinguished-name;
external-interface ge-0/0/2.0;
local-address 172.18.10.1;
version v2-only;
ppk-profile HUB_KM_PROFILE_1;
user@hub# show security ipsec proposal HUB_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp; authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc;
user@hub# show security ipsec policy HUB_IPSEC_POL proposals HUB_IPSEC_PROP;
user@hub# show security ipsec vpn HUB_IPSEC_VPN
bind-interface st0.1;
ike {
gateway HUB_IKE_GW;
ipsec-policy HUB_IPSEC_POL;
}
traffic-selector ts1 {
local-ip 192.168.90.0/24;
remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0;
}user@hub# show security zones security-zone untrust
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ike;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0.0;
ge-0/0/2.0;
}user@hub# show security zones security-zone trust
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0;
}
user@hub# show security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn
policy vpn_out {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}user@hub# show security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust
policy vpn_in {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}user@hub# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.90.1/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
}
}
}
st0 {
unit 1 {
family inet;
}
}Spoke 1
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show security pki ca-profile Root-CA, show security key-manager profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1, show security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP, show security ike policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL, show security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW, show security ipsec proposal SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP, show security ipsec policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL, show security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN, show interfaces, show security zones security-zone untrust, show security zones security-zone trust, show security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn, and show security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
user@spoke1# show security pki ca-profile Root-CA
ca-identity Root-CA;
enrollment {
url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll;
}
revocation-check {
disable;
}user@spoke1# show security key-manager profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1
quantum-key-manager {
url https://www.kme_spoke_1-qkd-server.net;
local-sae-id SAE_SPOKE_1;
local-certificate-id SAE_SPOKE_1_CERT;
trusted-cas Root-CA;
}user@spoke1# show security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures; dh-group group14; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600;
user@spoke1# show security ike policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL
proposals SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP;
certificate {
local-certificate SPOKE_1_CRT;
}user@spoke1# show security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW ike-policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL; address 172.18.10.1; local-identity distinguished-name; remote-identity distinguished-name; external-interface ge-0/0/2.0; local-address 172.18.10.2; version v2-only; ppk-profile SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1;
user@spoke1# show security ipsec proposal SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp; authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc;
user@spoke1# show security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN
bind-interface st0.1;
ike {
gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW;
ipsec-policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL;
}
traffic-selector ts1 {
local-ip 192.168.80.0/24;
remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24;
}user@spoke1# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.90.1/24;
address 192.168.80.1/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
}
}
}
st0 {
unit 1 {
family inet;
}
} user@spoke1# show security zones security-zone untrust
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ike;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0.0;
ge-0/0/2.0;
}user@spoke1# show security zones security-zone trust
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0;
}
user@spoke1# show security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn
policy vpn_out {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}user@spoke1# security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust
policy vpn_in {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}Spoke 2
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show security pki ca-profile Root-CA, show security key-manager profiles SPOKE_1_KM_PROFILE_1, show security ike proposal SPOKE_1_IKE_PROP, show security ike policy SPOKE_1_IKE_POL, show security ike gateway SPOKE_1_IKE_GW, show security ipsec proposal SPOKE_1_IPSEC_PROP, show security ipsec policy SPOKE_1_IPSEC_POL, show security ipsec vpn SPOKE_1_IPSEC_VPN, show interfaces, show security zones security-zone untrust, show security zones security-zone trust, show security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn, and show security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
user@spoke2# show security pki ca-profile Root-CA
ca-identity Root-CA;
enrollment {
url https://ca-server.juniper.net/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll;
}
revocation-check {
disable;
}user@spoke2# show security key-manager profiles SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1
quantum-key-manager {
url https://www.kme_spoke_2-qkd-server.net;
local-sae-id SAE_SPOKE_2;
local-certificate-id SAE_SPOKE_2_CERT;
trusted-cas Root-CA;
}user@spoke2# show security ike proposal SPOKE_2_IKE_PROP authentication-method rsa-signatures; dh-group group14; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600;
user@spoke2# show security ike policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL
##
## Warning: Referenced proposal is not defined
##
proposals SPOKE_IKE_PROP;
certificate {
local-certificate SPOKE_2_CRT;
}
user@spoke2# show security ike gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW ike-policy SPOKE_2_IKE_POL; address 172.18.10.1; local-identity distinguished-name; remote-identity distinguished-name; external-interface ge-0/0/2.0; local-address 172.18.10.3; version v2-only; ppk-profile SPOKE_2_KM_PROFILE_1;
user@spoke2# show security ipsec proposal SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP protocol esp; authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc;
user@spoke2# show security ipsec policy SPOKE_2_IPSEC_POL
proposals SPOKE_2_IPSEC_PROP;
[edit]
user@spoke2# show security ipsec vpn SPOKE_2_IPSEC_VPN
bind-interface st0.2;
ike {
gateway SPOKE_2_IKE_GW;
ipsec-policy SPOKE_2_IPSEC_POL;
}
traffic-selector ts1 {
local-ip 192.168.70.0/24;
remote-ip 192.168.90.0/24;
}user@spoke2# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.90.1/24;
address 192.168.80.1/24;
address 192.168.70.1/24;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.18.10.1/24;
address 172.18.10.2/24;
address 172.18.10.3/24;
}
}
}
st0 {
unit 1 {
family inet;
}
unit 2 {
family inet;
}
}
user@spoke2# show security zones security-zone untrust
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ike;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0.0;
ge-0/0/2.0;
}user@spoke2# show security zones security-zone vpn
interfaces {
st0.1;
st0.2;
}
user@spoke2# show security zones security-zone trust
host-inbound-traffic {
system-services {
ping;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0;
}
user@spoke2# show security policies from-zone trust to-zone vpn
policy vpn_out {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
user@spoke2# show security policies from-zone vpn to-zone trust
policy vpn_in {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}