Subscriber-Aware and Application-Aware Traffic Treatment Overview
This topic contains an overview of subscriber-aware and application-aware traffic treatment.
Introduction
Junos Subscriber Aware identifies the mobile or fixed-line subscriber associated with a data session, and enforces traffic treatment based on policies assigned to the subscriber. This permits highly customizable differentiated services for subscribers. A subscriber policy can be based on Layer 7 application information for the IP flow (for example, YouTube) or can be based on Layer 3/Layer 4 information for the IP flow (for example, the source and destination IP address). Junos Subscriber Aware resides on an MX Series router.
Subscriber-aware policies can specify the following actions:
-
Redirecting HTTP traffic to another URL or IP address
-
Forwarding packets to a routing instance so that packets are directed to external service chains ( predefined sequence of services)
-
Setting the forwarding class
-
Setting the maximum bit rate
-
Performing HTTP header enrichment (provided by Junos Web Aware, which resides on the same MX Series router as Junos Subscriber Aware)
-
Setting the gating status to blocked or allowed
Subscriber-aware policies can also specify the time of day that the policies are in effect.
Access-Independent Subscriber Traffic Treatment
Subscriber identification for both mobile access and wireline access provides a unified experience for the subscriber, regardless of the connection method.
Junos Subscriber Aware resides on an MX Series router that is located between the gateway of the access network and the public network and network services, as shown in Figure 1. Subscribers may be controlled by a broadband network gateway (BNG) in a wireline access network, by a gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) in a 2G or 3G network architecture, or by a Packet Data Network Gateway (PGW) in a 4G/LTE network architecture.
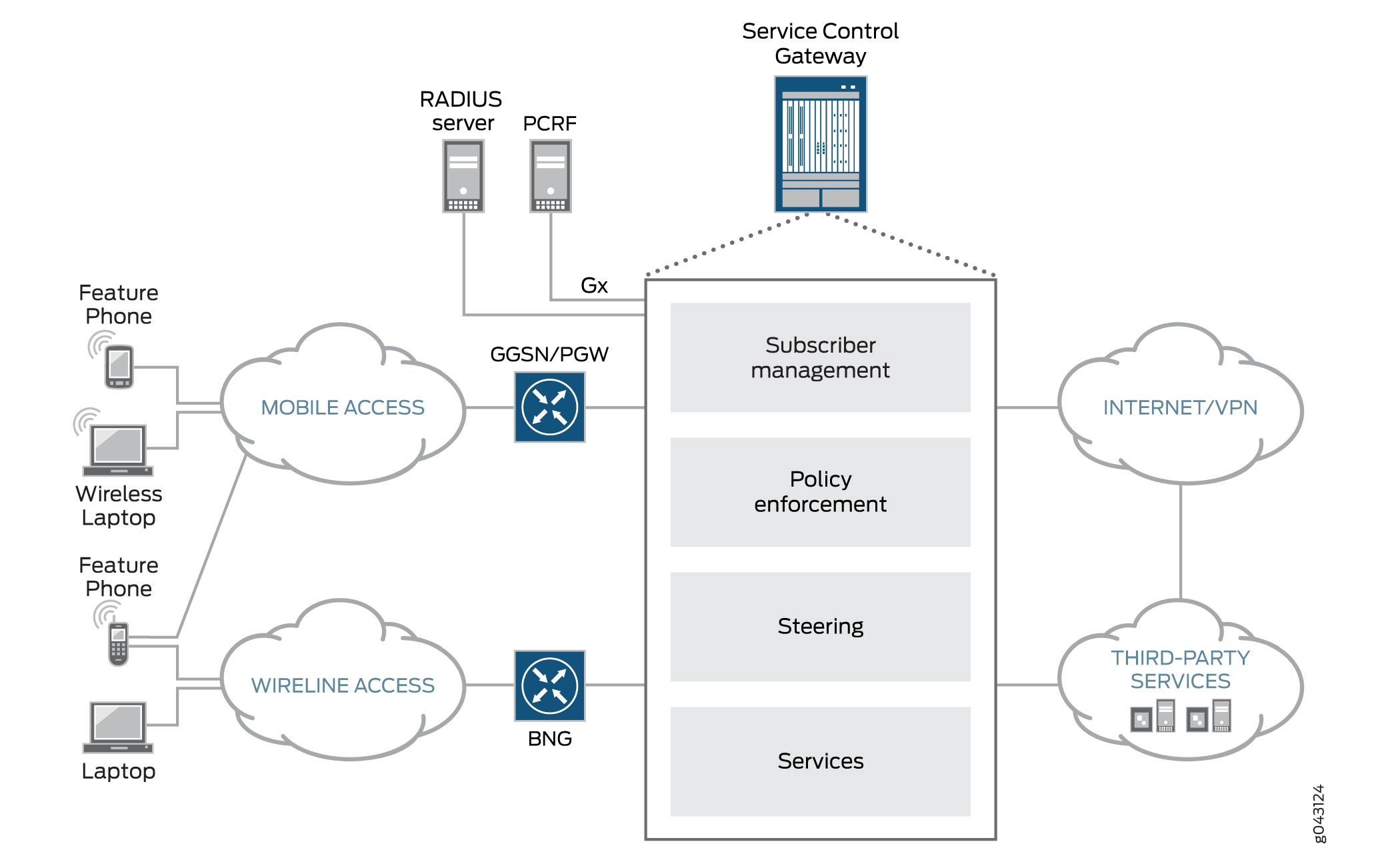
Subscriber Identification Methods
You can use the following methods to identify subscribers:
-
IP-based—Processes a RADIUS accounting start request to identify the subscriber. An IP-based subscriber session is for one unique user IP address.
-
IFL-based—Requires you to configure a subscriber name and specify a set of MX Series router access interfaces for the subscriber. Junos Subscriber Aware assigns all data sessions received on those interfaces to the configured subscriber.
Application Identification
Layer 7 application identification is provided by Junos Application Aware, which performs deep packet inspection (DPI) to determine whether the subscriber’s data packets match an application signature. When an application is identified, the appropriate subscriber policy is applied to the packets. Juniper Networks provides a set of predefined application signatures that you can download and that are periodically updated. You can also configure your own custom application signatures.
Junos Subscriber Aware and Junos Application Aware reside on the same MX Series router, allowing policy control on a single platform.
Policy Control Methods
Subscriber-aware policies can be controlled dynamically by a policy and charging rules function (PCRF) server, can be activated by a RADIUS server, or can be under static control.
Under dynamic control, a PCRF either sends policies to the MX Series router or activates predefined policies that you configured on the MX Series router. Dynamic policy control is provided by Junos Policy Control, which resides on the same MX Series router as Junos Subscriber Aware.
Under RADIUS server control, the RADIUS server controls the activation of your predefined polices but does not send policies to the MX Series router.
Under static control, your predefined policies are not controlled by a PCRF or RADIUS server.
Subscriber-Aware Data Session Logging and Reporting
Junos Subscriber Aware can log data for subscriber-aware data sessions and send that data in an IPFIX format to an external log collector. These logs can include subscriber information, application information, HTTP metadata, data volume, time-of-day information, and source and destination details. You can then use the external collector, which is not a Juniper Networks product, to perform analytics that provide you with insights about subscriber and application usage, enabling you to create packages and policies that increase revenue.
Usage Monitoring
For subscriber data sessions that are under the dynamic policy control of a PCRF, Junos Subscriber Aware can monitor the volume of traffic or amount of time the subscriber uses during a session, and send reports to the PCRF. The PCRF can use this information to adjust the policies for a subscriber.
