Example: Configuring IPv6 Source Guard and Neighbor Discovery Inspection to Protect a Switch from IPv6 Address Spoofing
This example describes how to enable IPv6 source guard and neighbor discovery inspection on a specified VLAN to protect an EX Series switch against IPv6 address spoofing attacks. IPv6 source guard and neighbor discovery inspection support introduced on EX2200 and EX3300 switches in Junos OS Release 14.1X53-D10.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
One EX2200 or EX3300 switch
Junos OS Release 14.1X53-D10 or later for EX Series switches
A DHCPv6 server to provide IPv6 addresses to network devices on the switch
Before you configure IPv6 source guard and neighbor discovery inspection to prevent IPv6 address spoofing attacks, be sure you have:
Connected the DHCPv6 server to the switch.
Configured the VLAN to which you are adding DHCPv6 security features. See Configuring VLANs for EX Series Switches.
Overview and Topology
Ethernet LAN switches are vulnerable to attacks on security that involve spoofing (forging) of source MAC addresses or source IPv6 addresses. These spoofed packets are sent from hosts connected to untrusted access interfaces on the switch. For more information on IPv6 address spoofing attacks, see IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Inspection.
IPv6 source guard and neighbor discovery inspection mitigate the risk of IPv6 spoofing attacks by using the DHCPv6 snooping table. Also known as the binding table, the DHCPv6 snooping table contains the valid bindings of IPv6 addresses to MAC addresses. When a packet is sent from a host attached to an untrusted access interface on the switch, IPv6 source guard verifies the source IPv6 address and MAC address of the packet against the DHCPv6 snooping table. If there is no match in the table, the switch does not forward the packet—that is, the packet is discarded. Neighbor discovery inspection verifies neighbor discovery messages sent between IPv6 nodes on the same network link against the DHCPv6 snooping table, and also discards the packet if no match is found.
This example shows how to configure these important port security features on a switch
that is connected to a DHCPv6 server. The setup for this example includes the VLAN sales on the switch. Figure 1 illustrates the topology for this example.
The trunk interface connecting to the DHCPv6 server interface is a trusted port by default.
Topology
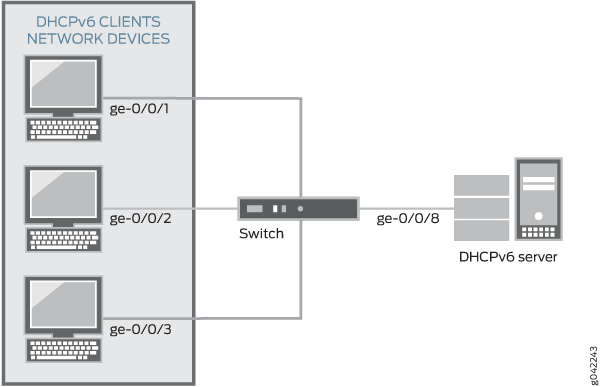
The components of the topology for this example are shown in Table 1.
| Properties | Settings |
|---|---|
Switch hardware |
One EX2200 or EX3300 switch |
VLAN name and ID |
sales, tag |
VLAN subnets |
192.0.2.16/28 192.0.2.17 through 192.0.2.30 192.0.2.31 is the subnet's broadcast address |
Interfaces in |
ge-0/0/1, ge-0/0/2, ge-0/0/3, ge-0/0/8 |
Interface connecting to DHCPv6 server |
ge-0/0/8 |
In this example, the switch has already been configured as follows:
All access ports are untrusted, which is the default setting.
The trunk port (ge-0/0/8) is trusted, which is the default setting.
The VLAN (sales) has been configured to include the specified interfaces.
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure IPv6 source guard and neighbor discovery inspection, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit] set ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port vlan sales examine-dhcpv6 set ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port vlan sales ipv6-source-guard set ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port vlan sales neighbor-discovery-inspection
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure IPv6 source guard and neighbor discovery inspection (and thereby, also automatically configure DHCPv6 snooping) on the VLAN:
Enable DHCPv6 snooping on the VLAN:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port vlan sales] user@switch# set examine-dhcpv6
Configure IPv6 source guard on the VLAN:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port vlan sales] user@switch# set ipv6-source-guard
Configure neighbor discovery inspection on the VLAN:
[edit ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port vlan sales] user@switch# set neighbor-discovery-inspection
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch> show ethernet-switching-options secure-access-port
vlan sales {
examine-dhcpv6;
ipv6-source-guard;
neighbor-discovery-inspection;
}
}
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying That DHCPv6 Snooping Is Working Correctly on the Switch
- Verifying That Neighbor Discovery Inspection Is Working Correctly on the Switch
Verifying That DHCPv6 Snooping Is Working Correctly on the Switch
Purpose
Verify that DHCPv6 snooping is working on the switch.
Action
Send DHCPv6 requests from network devices (in this example, these are DHCPv6 clients) connected to the switch.
Display the DHCPv6 snooping information when the port on which the DHCPv6 server connects to the switch is trusted. The following is the output when requests are sent from the MAC addresses and the server has provided the IPv6 addresses and leases:
user@switch> show dhcpv6 snooping binding DHCP Snooping Information: MAC address IP address Lease (seconds) Type VLAN Interface 00:10:94:00:00:01 2001:db8::10:0:3 3599992 dynamic sales ge-0/0/1.0 00:10:94:00:00:01 fe80::210:94ff:fe00:1 3599992 dynamic sales ge-0/0/1.0 00:10:94:00:00:02 2001:db8::10:0:5 3599992 dynamic sales ge-0/0/2.0 00:10:94:00:00:02 fe80::210:94ff:fe00:2 3599992 dynamic sales ge-0/0/2.0 00:10:94:00:00:03 2001:db8::10:0:7 3599992 dynamic sales ge-0/0/3.0 00:10:94:00:00:03 fe80::210:94ff:fe00:3 3599992 dynamic sales ge-0/0/3.0
Meaning
The output shows the assigned IP address, the MAC address, the VLAN name, and
the time, in seconds, leased to the IP address. Because IPv6 hosts usually have more than
one IP address assigned to each of their IPv6-enabled network interfaces, there are two entries
added for each client: one with the link-local IP address, which is used by the client for
DHCP transactions, and another with the IP address assigned by the server. The link-local
address always has the prefix fe80::/10.
Verifying That Neighbor Discovery Inspection Is Working Correctly on the Switch
Purpose
Verify that neighbor discovery inspection is working on the switch.
Action
Send neighbor discovery packets from network devices connected to the switch.
Display the neighbor discovery information:
user@switch> show neighbor-discovery-inspection statistics ND inspection statistics: Interface Packets received ND inspection pass ND inspection failed ge-0/0/1.0 7 5 2 ge-0/0/2.0 10 10 0 ge-0/0/3.0 12 12 0
Meaning
The sample output shows the number of neighbor discovery packets received and inspected per interface, and lists the number of packets passed and the number that failed the inspection on each interface. The switch compares the neighbor discovery requests and replies against the entries in the DHCPv6 snooping database. If a MAC address or IPv6 address in the neighbor discovery packet does not match a valid entry in the database, the packet is dropped.
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
