Example: Applying Firewall Filters to Multiple Supplicants on Interfaces Enabled for 802.1X or MAC RADIUS Authentication
On supported switches, firewall filters that you apply to interfaces enabled for 802.1X or MAC RADIUS authentication are dynamically combined with the per-user policies sent to the switch from the RADIUS server. The switch uses internal logic to dynamically combine the interface firewall filter with the user policies from the RADIUS server and create an individualized policy for each of the multiple users or nonresponsive hosts that are authenticated on the interface.
This example describes how dynamic firewall filters are created for multiple supplicants on an 802.1X-enabled interface (the same principles shown in this example apply to interfaces enabled for MAC RADIUS authentication):
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Supported Junos OS Release for the switches
A supported switch
One RADIUS authentication server. The authentication server acts as the backend database and contains credential information for hosts (supplicants) that have permission to connect to the network.
Before you apply firewall filters to an interface for use with multiple supplicants, be sure you have:
Set up a connection between the switch and the RADIUS server. See Example: Connecting a RADIUS Server for 802.1X to an EX Series Switch.
Configured 802.1X authentication on the switch, with the authentication mode for interface ge-0/0/2 set to multiple. See Configuring 802.1X Interface Settings (CLI Procedure) and Example: Setting Up 802.1X for Single-Supplicant or Multiple-Supplicant Configurations on an EX Series Switch.
Configured users on the RADIUS authentication server.
Overview and Topology
Topology
When the 802.1X configuration on an interface is set to multiple supplicant mode, the system dynamically combines interface firewall filter with the user policies sent to the switch from the RADIUS server during authentication and creates separate terms for each user. Because there are separate terms for each user authenticated on the interface, you can, as shown in this example, use counters to view the activities of individual users that are authenticated on the same interface.
When a new user (or a nonresponsive host) is authenticated on an interface, the system adds a term to the firewall filter associated with the interface, and the term (policy) for each user is associated with the MAC address of the user. The term for each user is based on the user-specific filters set on the RADIUS server and the filters configured on the interface. For example, as shown in Figure 1, when User1 is authenticated by the EX Series switch, the system creates the firewall filter dynamic-filter-example. When User2 is authenticated, another term is added to the firewall filter, and so on.
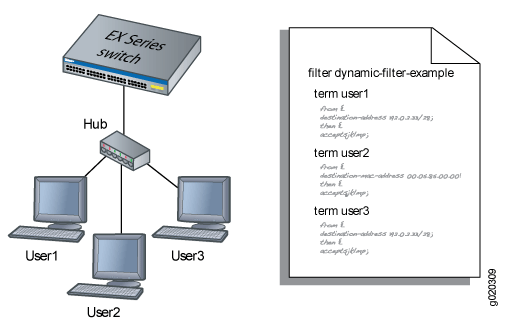
This is a conceptual model of the internal process—you cannot access or view the dynamic filter.
If the firewall filter on the interface is modified after the user (or nonresponsive host) is authenticated, the modifications are not reflected in the dynamic filter unless the user is reauthenticated.
In this example, you configure a firewall filter to count the requests made by each endpoint authenticated on interface ge-0/0/2 to the file server, which is located on subnet 192.0.2.16/28, and set policer definitions to rate limit the traffic. Figure 2 shows the network topology for this example.
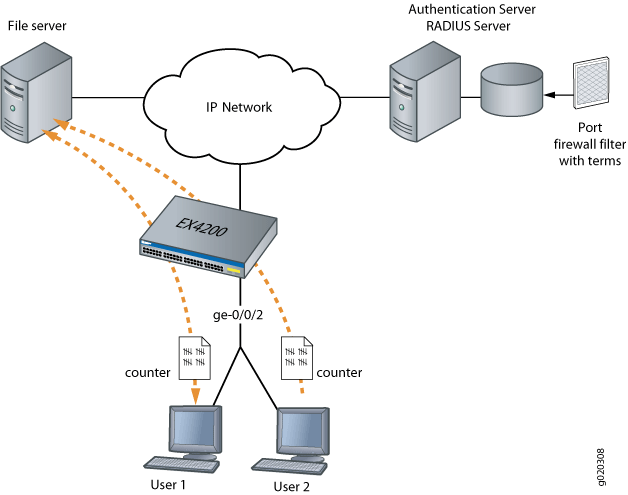
Configuration
To configure firewall filters for multiple supplicants on 802.1X-enabled interfaces:
Configuring Firewall Filters on Interfaces with Multiple Supplicants
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure firewall filters for multiple supplicants on an 802.1X-enabled interface copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/2 supplicant multiple
set firewall family ethernet-switching filter filter1 term term1 from destination-address 192.0.2.16/28
set firewall policer p1 if-exceeding bandwidth-limit 1m
set firewall policer p1 if-exceeding burst-size-limit 1k
set firewall family ethernet-switching filter filter1 term term1 then count counter1
set firewall family ethernet-switching filter filter1 term term2 then policer p1Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure firewall filters on an interface enabled for multiple supplicants:
Configure interface ge-0/0/2 for multiple supplicant mode authentication:
[edit protocols dot1x] user@switch# set authenticator interface ge-0/0/2 supplicant multiple
Set policer definition:
user@switch# show policer p1 |display set set firewall policer p1 if-exceeding bandwidth-limit 1m set firewall policer p1 if-exceeding burst-size-limit 1k set firewall policer p1 then discard
Configure a firewall filter to count packets from each user and a policer that limits the traffic rate. As each new user is authenticated on the multiple supplicant interface, this filter term will be included in the dynamically created term for the user:
[edit firewall family ethernet-switching] user@switch# set filter filter1 term term1 from destination-address 192.0.2.16/28 user@switch# set filter filter1 term term1 then count counter1 user@switch# set filter filter1 term term2 then policer p1
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch> show configuration
firewall {
family ethernet-switching {
filter filter1 {
term term1 {
from {
destination-address {
192.0.2.16/28;
}
}
then count counter1;
term term2 {
from {
destination-address {
192.0.2.16/28;
}
}
then policer p1;
}
}
}
policer p1 {
if-exceeding {
bandwidth-limit 1m;
burst-size-limit 1k;
}
then discard;
}
}
protocols {
dot1x {
authenticator
interface ge-0/0/2 {
supplicant multiple;
}
}
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks:
Verifying Firewall Filters on Interfaces with Multiple Supplicants
Purpose
Verify that firewall filters are functioning on the interface with multiple supplicants.
Action
Check the results with one user authenticated on the interface. In this case, the user is authenticated on ge-0/0/2:
user@switch> show dot1x firewall Filter: dot1x_ge-0/0/2 Counters counter1_dot1x_ge-0/0/2_user1 100
When a second user, User2, is authenticated on the same interface, ge-0/0/2, you can verify that the filter includes the results for both of the users authenticated on the interface:
user@switch>
show dot1x firewallFilter: dot1x-filter-ge-0/0/0 Counters counter1_dot1x_ge-0/0/2_user1 100 counter1_dot1x_ge-0/0/2_user2 400
Meaning
The results displayed by the show dot1x firewall command output reflect the dynamic filter created with the authentication
of each new user. User1 accessed the file server located at the specified
destination address 100 times, while User2 accessed the same file
server 400 times.
