Example: Configuring Multicast-Only Fast Reroute in a Multipoint LDP Domain
This example shows how to configure multicast-only fast reroute (MoFRR) to minimize packet loss in a network when there is a link failure.
Multipoint LDP MoFRR is used at the egress node of an MPLS network, where the packets are forwarded to an IP network. In the case of multipoint LDP MoFRR, the two paths toward the upstream provider edge (PE) router are established for receiving two streams of MPLS packets at the label-edge router (LER). One of the streams (the primary) is accepted, and the other one (the backup) is dropped at the LER. The backup stream is accepted if the primary path fails.
Requirements
No special configuration beyond device initialization is required before configuring this example.
In a multipoint LDP domain, for MoFRR to work, only the egress PE router needs to have MoFRR enabled. The other routers do not need to support MoFRR.
MoFRR is supported on MX Series platforms with MPC line cards.
As a prerequisite, the router must be set to network-services enhanced-ip mode, and all the line-cards in the platform must
be MPCs.
This example requires Junos OS Release 14.1 or later on the egress PE router.
Overview
In this example, Device R3 is the egress edge router. MoFRR is enabled on this device only.
OSPF is used for connectivity, though any interior gateway protocol (IGP) or static routes can be used.
For testing purposes, routers are used to simulate the source
and the receiver. Device R4 and Device R8 are configured to statically
join the desired group by using the set protocols igmp interface
interface-name static group group command.
In the case when a real multicast receiver host is not available,
as in this example, this static IGMP configuration is useful. On the
receivers, to make them listen to the multicast group address, this
example uses set protocols sap listen group.
MoFRR configuration includes a policy option that is not shown in this example, but is explained separately. The option is configured as follows:
stream-protection { policy policy-name; }
Topology
Figure 1 shows the sample network.
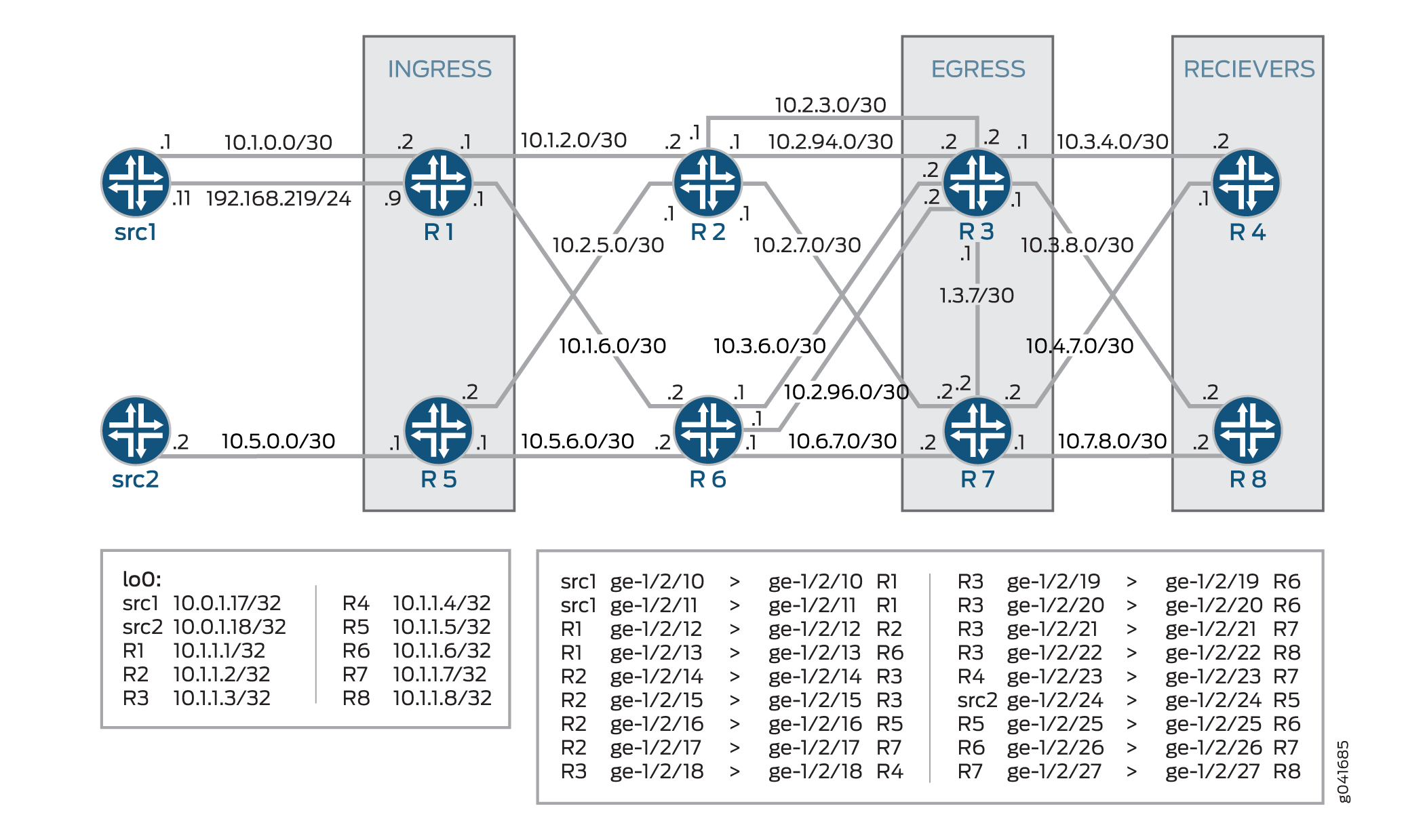
CLI Quick Configuration shows the configuration for all of the devices in Figure 1.
The section Configuration describes the steps on Device R3.
CLI Quick Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device src1
set interfaces ge-1/2/10 unit 0 description src1-to-R1 set interfaces ge-1/2/10 unit 0 family inet address 10.5.0.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/11 unit 0 description src1-to-R1 set interfaces ge-1/2/11 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.219.11/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.1.17/32 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive
Device src2
set interfaces ge-1/2/24 unit 0 description src2-to-R5 set interfaces ge-1/2/24 unit 0 family inet address 10.5.0.2/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.1.18/32 set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive
Device R1
set interfaces ge-1/2/12 unit 0 description R1-to-R2 set interfaces ge-1/2/12 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.2.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/12 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/13 unit 0 description R1-to-R6 set interfaces ge-1/2/13 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.6.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/13 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/10 unit 0 description R1-to-src1 set interfaces ge-1/2/10 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/11 unit 0 description R1-to-src1 set interfaces ge-1/2/11 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.219.9/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.1/32 set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols mpls interface all set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.1.1.1 set protocols bgp group ibgp export static-route-tobgp set protocols bgp group ibgp peer-as 65010 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.1.1.3 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.1.1.7 set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/12.0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/13.0 set protocols ldp interface lo0.0 set protocols ldp p2mp set protocols pim mldp-inband-signalling policy mldppim-ex set protocols pim rp static address 10.1.1.5 set protocols pim interface lo0.0 set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/10.0 set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/11.0 set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.219.11/32 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B then p2mp-lsp-root address 10.1.1.2 set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B then accept set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term A from source-address-filter 10.1.1.7/32 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term A from source-address-filter 10.1.0.0/30 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term A then accept set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 65010
Device R2
set interfaces ge-1/2/12 unit 0 description R2-to-R1 set interfaces ge-1/2/12 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.2.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/12 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/14 unit 0 description R2-to-R3 set interfaces ge-1/2/14 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.3.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/14 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/16 unit 0 description R2-to-R5 set interfaces ge-1/2/16 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.5.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/16 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/17 unit 0 description R2-to-R7 set interfaces ge-1/2/17 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.7.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/17 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/15 unit 0 description R2-to-R3 set interfaces ge-1/2/15 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.94.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/15 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.2/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family mpls set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols mpls interface all set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp p2mp set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.219.11/32 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B then p2mp-lsp-root address 10.1.1.2 set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 65010
Device R3
set chassis network-services enhanced-ip set interfaces ge-1/2/14 unit 0 description R3-to-R2 set interfaces ge-1/2/14 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.3.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/14 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/18 unit 0 description R3-to-R4 set interfaces ge-1/2/18 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.4.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/18 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/19 unit 0 description R3-to-R6 set interfaces ge-1/2/19 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.6.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/19 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/21 unit 0 description R3-to-R7 set interfaces ge-1/2/21 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.7.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/21 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/22 unit 0 description R3-to-R8 set interfaces ge-1/2/22 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.8.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/22 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/15 unit 0 description R3-to-R2 set interfaces ge-1/2/15 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.94.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/15 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/20 unit 0 description R3-to-R6 set interfaces ge-1/2/20 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.96.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/20 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.3/32 primary set routing-options autonomous-system 65010 set routing-options multicast stream-protection set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols mpls interface all set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.1.1.3 set protocols bgp group ibgp peer-as 10 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.1.1.1 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.1.1.5 set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp p2mp set protocols pim mldp-inband-signalling policy mldppim-ex set protocols pim interface lo0.0 set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/18.0 set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/22.0 set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.219.11/32 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B then accept set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term A from source-address-filter 10.1.0.1/30 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term A then accept set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static then accept
Device R4
set interfaces ge-1/2/18 unit 0 description R4-to-R3 set interfaces ge-1/2/18 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.4.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/18 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/23 unit 0 description R4-to-R7 set interfaces ge-1/2/23 unit 0 family inet address 10.4.7.1/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.4/32 set protocols igmp interface ge-1/2/18.0 version 3 set protocols igmp interface ge-1/2/18.0 static group 232.1.1.1 group-count 2 set protocols igmp interface ge-1/2/18.0 static group 232.1.1.1 source 192.168.219.11 set protocols igmp interface ge-1/2/18.0 static group 232.2.2.2 source 10.2.7.7 set protocols sap listen 232.1.1.1 set protocols sap listen 232.2.2.2 set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols mpls interface all set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols pim mldp-inband-signalling policy mldppim-ex set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/23.0 set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/18.0 set protocols pim interface lo0.0 set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static then accept set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.219.11/32 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B then p2mp-lsp-root address 10.1.1.2 set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 65010
Device R5
set interfaces ge-1/2/24 unit 0 description R5-to-src2 set interfaces ge-1/2/24 unit 0 family inet address 10.5.0.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/16 unit 0 description R5-to-R2 set interfaces ge-1/2/16 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.5.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/16 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/25 unit 0 description R5-to-R6 set interfaces ge-1/2/25 unit 0 family inet address 10.5.6.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/25 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.5/32 set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols mpls interface all set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.1.1.5 set protocols bgp group ibgp export static-route-tobgp set protocols bgp group ibgp peer-as 65010 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.1.1.7 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.1.1.3 set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/16.0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/25.0 set protocols ldp p2mp set protocols pim interface lo0.0 set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/24.0 set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 65010
Device R6
set interfaces ge-1/2/13 unit 0 description R6-to-R1 set interfaces ge-1/2/13 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.6.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/13 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/19 unit 0 description R6-to-R3 set interfaces ge-1/2/19 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.6.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/19 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/25 unit 0 description R6-to-R5 set interfaces ge-1/2/25 unit 0 family inet address 10.5.6.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/25 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/26 unit 0 description R6-to-R7 set interfaces ge-1/2/26 unit 0 family inet address 10.6.7.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/26 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/20 unit 0 description R6-to-R3 set interfaces ge-1/2/20 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.96.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/20 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.6/30 set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols mpls interface all set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp p2mp
Device R7
set interfaces ge-1/2/17 unit 0 description R7-to-R2 set interfaces ge-1/2/17 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.7.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/17 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/21 unit 0 description R7-to-R3 set interfaces ge-1/2/21 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.7.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/21 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/23 unit 0 description R7-to-R4 set interfaces ge-1/2/23 unit 0 family inet address 10.4.7.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/23 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/26 unit 0 description R7-to-R6 set interfaces ge-1/2/26 unit 0 family inet address 10.6.7.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/26 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/27 unit 0 description R7-to-R8 set interfaces ge-1/2/27 unit 0 family inet address 10.7.8.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/27 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.7/32 set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols mpls interface all set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.1.1.7 set protocols bgp group ibgp export static-route-tobgp set protocols bgp group ibgp peer-as 65010 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.1.1.5 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.1.1.1 set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/17.0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/21.0 set protocols ldp interface ge-1/2/26.0 set protocols ldp p2mp set protocols pim mldp-inband-signalling policy mldppim-ex set protocols pim interface lo0.0 set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/27.0 set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.219.11/32 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B then accept set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term A from source-address-filter 10.1.0.1/30 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term A then accept set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 65010 set routing-options multicast stream-protection policy mldppim-ex
Device R8
set interfaces ge-1/2/22 unit 0 description R8-to-R3 set interfaces ge-1/2/22 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.8.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/22 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/27 unit 0 description R8-to-R7 set interfaces ge-1/2/27 unit 0 family inet address 10.7.8.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/27 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.8/32 set protocols igmp interface ge-1/2/22.0 version 3 set protocols igmp interface ge-1/2/22.0 static group 232.1.1.1 group-count 2 set protocols igmp interface ge-1/2/22.0 static group 232.1.1.1 source 192.168.219.11 set protocols igmp interface ge-1/2/22.0 static group 232.2.2.2 source 10.2.7.7 set protocols sap listen 232.1.1.1 set protocols sap listen 232.2.2.2 set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface all set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols pim mldp-inband-signalling policy mldppim-ex set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/27.0 set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/22.0 set protocols pim interface lo0.0 set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp term static then accept set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B from source-address-filter 192.168.219.11/32 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B then p2mp-lsp-root address 10.1.1.2 set policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex term B then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 65010
Configuration
Procedure
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires that you navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To configure Device R3:
Enable enhanced IP mode.
[edit chassis] user@R3# set network-services enhanced-ip
Configure the device interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@R3# set ge-1/2/14 unit 0 description R3-to-R2 user@R3# set ge-1/2/14 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.3.2/30 user@R3# set ge-1/2/14 unit 0 family mpls user@R3# set ge-1/2/18 unit 0 description R3-to-R4 user@R3# set ge-1/2/18 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.4.1/30 user@R3# set ge-1/2/18 unit 0 family mpls user@R3# set ge-1/2/19 unit 0 description R3-to-R6 user@R3# set ge-1/2/19 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.6.2/30 user@R3# set ge-1/2/19 unit 0 family mpls user@R3# set ge-1/2/21 unit 0 description R3-to-R7 user@R3# set ge-1/2/21 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.7.1/30 user@R3# set ge-1/2/21 unit 0 family mpls user@R3# set ge-1/2/22 unit 0 description R3-to-R8 user@R3# set ge-1/2/22 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.8.1/30 user@R3# set ge-1/2/22 unit 0 family mpls user@R3# set ge-1/2/15 unit 0 description R3-to-R2 user@R3# set ge-1/2/15 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.94.2/30 user@R3# set ge-1/2/15 unit 0 family mpls user@R3# set ge-1/2/20 unit 0 description R3-to-R6 user@R3# set ge-1/2/20 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.96.2/30 user@R3# set ge-1/2/20 unit 0 family mpls user@R3# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.3/32 primary
Configure the autonomous system (AS) number.
user@R3# set routing-options autonomous-system 6510
Configure the routing policies.
[edit policy-options policy-statement mldppim-ex] user@R3# set term B from source-address-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger user@R3# set term B from source-address-filter 192.168.219.11/32 orlonger user@R3# set term B then accept user@R3# set term A from source-address-filter 10.1.0.1/30 orlonger user@R3# set term A then accept [edit policy-options policy-statement static-route-tobgp] user@R3# set term static from protocol static user@R3# set term static from protocol direct user@R3# set term static then accept
Configure PIM.
[edit protocols pim] user@R3# set mldp-inband-signalling policy mldppim-ex user@R3# set interface lo0.0 user@R3# set interface ge-1/2/18.0 user@R3# set interface ge-1/2/22.0
Configure LDP.
[edit protocols ldp] user@R3# set interface all user@R3# set p2mp
Configure an IGP or static routes.
[edit protocols ospf] user@R3# set traffic-engineering user@R3# set area 0.0.0.0 interface all user@R3# set area 0.0.0.0 interface fxp0.0 disable user@R3# set area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive
Configure internal BGP.
[edit protocols bgp group ibgp] user@R3# set local-address 10.1.1.3 user@R3# set peer-as 65010 user@R3# set neighbor 10.1.1.1 user@R3# set neighbor 10.1.1.5
Configure MPLS and, optionally, RSVP.
[edit protocols mpls] user@R3# set interface all [edit protocols rsvp] user@R3# set interface all
Enable MoFRR.
[edit routing-options multicast] user@R3# set stream-protection
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show chassis, show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options, and show routing-options commands. If the output does not display
the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example
to correct the configuration.
user@R3# show chassis network-services enhanced-ip;
user@R3# show interfaces
ge-1/2/14 {
unit 0 {
description R3-to-R2;
family inet {
address 10.2.3.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/2/18 {
unit 0 {
description R3-to-R4;
family inet {
address 10.3.4.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/2/19 {
unit 0 {
description R3-to-R6;
family inet {
address 10.3.6.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/2/21 {
unit 0 {
description R3-to-R7;
family inet {
address 10.3.7.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/2/22 {
unit 0 {
description R3-to-R8;
family inet {
address 10.3.8.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/2/15 {
unit 0 {
description R3-to-R2;
family inet {
address 10.2.94.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/2/20 {
unit 0 {
description R3-to-R6;
family inet {
address 10.2.96.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.15.1/32;
address 10.1.1.3/32 {
primary;
}
}
}
}
user@R3# show protocols
rsvp {
interface all;
}
mpls {
interface all;
}
bgp {
group ibgp {
local-address 10.1.1.3;
peer-as 65010;
neighbor 10.1.1.1;
neighbor 10.1.1.5;
}
}
ospf {
traffic-engineering;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface all;
p2mp;
}
pim {
mldp-inband-signalling {
policy mldppim-ex;
}
interface lo0.0;
interface ge-1/2/18.0;
interface ge-1/2/22.0;
}
user@R3# show policy-options
policy-statement mldppim-ex {
term B {
from {
source-address-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger;
source-address-filter 192.168.219.11/32 orlonger;
}
then accept;
}
term A {
from {
source-address-filter 10.1.0.1/30 orlonger;
}
then accept;
}
}
policy-statement static-route-tobgp {
term static {
from protocol [ static direct ];
then accept;
}
}
user@R3# show routing-options
autonomous-system 65010;
multicast {
stream-protection;
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Checking the LDP Point-to-Multipoint Forwarding Equivalency Classes
- Examining the Label Information
- Checking the Multicast Routes
- Checking the LDP Point-to-Multipoint Traffic Statistics
Checking the LDP Point-to-Multipoint Forwarding Equivalency Classes
Purpose
Make sure the MoFRR is enabled, and determine what labels are being used.
Action
user@R3> show ldp p2mp fec LDP P2MP FECs: P2MP root-addr 10.1.1.1, grp: 232.1.1.1, src: 192.168.219.11 MoFRR enabled Fec type: Egress (Active) Label: 301568 P2MP root-addr 10.1.1.1, grp: 232.1.1.2, src: 192.168.219.11 MoFRR enabled Fec type: Egress (Active) Label: 301600
Meaning
The output shows that MoFRR is enabled, and it shows that the labels 301568 and 301600 are being used for the two multipoint LDP point-to-multipoint LSPs.
Examining the Label Information
Purpose
Make sure that the egress device has two upstream interfaces for the multicast group join.
Action
user@R3> show route label 301568 detail
mpls.0: 18 destinations, 18 routes (18 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
301568 (1 entry, 1 announced)
*LDP Preference: 9
Next hop type: Flood
Address: 0x2735208
Next-hop reference count: 3
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 1397
Address: 0x2735d2c
Next-hop reference count: 3
Next hop: 10.3.8.2 via ge-1/2/22.0
Label operation: Pop
Load balance label: None;
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 1395
Address: 0x2736290
Next-hop reference count: 3
Next hop: 10.3.4.2 via ge-1/2/18.0
Label operation: Pop
Load balance label: None;
State: <Active Int AckRequest MulticastRPF>
Local AS: 65010
Age: 54:05 Metric: 1
Validation State: unverified
Task: LDP
Announcement bits (1): 0-KRT
AS path: I
FECs bound to route: P2MP root-addr 10.1.1.1, grp: 232.1.1.1, src: 192.168.219.11
Primary Upstream : 10.1.1.3:0--10.1.1.2:0
RPF Nexthops :
ge-1/2/15.0, 10.2.94.1, Label: 301568, weight: 0x1
ge-1/2/14.0, 10.2.3.1, Label: 301568, weight: 0x1
Backup Upstream : 10.1.1.3:0--10.1.1.6:0
RPF Nexthops :
ge-1/2/20.0, 10.2.96.1, Label: 301584, weight: 0xfffe
ge-1/2/19.0, 10.3.6.1, Label: 301584, weight: 0xfffe
user@R3> show route label 301600 detail
mpls.0: 18 destinations, 18 routes (18 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
301600 (1 entry, 1 announced)
*LDP Preference: 9
Next hop type: Flood
Address: 0x27356b4
Next-hop reference count: 3
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 1520
Address: 0x27350f4
Next-hop reference count: 3
Next hop: 10.3.8.2 via ge-1/2/22.0
Label operation: Pop
Load balance label: None;
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 1481
Address: 0x273645c
Next-hop reference count: 3
Next hop: 10.3.4.2 via ge-1/2/18.0
Label operation: Pop
Load balance label: None;
State: <Active Int AckRequest MulticastRPF>
Local AS: 65010
Age: 54:25 Metric: 1
Validation State: unverified
Task: LDP
Announcement bits (1): 0-KRT
AS path: I
FECs bound to route: P2MP root-addr 10.1.1.1, grp: 232.1.1.2, src: 192.168.219.11
Primary Upstream : 10.1.1.3:0--10.1.1.6:0
RPF Nexthops :
ge-1/2/20.0, 10.2.96.1, Label: 301600, weight: 0x1
ge-1/2/19.0, 10.3.6.1, Label: 301600, weight: 0x1
Backup Upstream : 10.1.1.3:0--1.1.1.2:0
RPF Nexthops :
ge-1/2/15.0, 10.2.94.1, Label: 301616, weight: 0xfffe
ge-1/2/14.0, 10.2.3.1, Label: 301616, weight: 0xfffeMeaning
The output shows the primary upstream paths and the backup upstream paths. It also shows the RPF next hops.
Checking the Multicast Routes
Purpose
Examine the IP multicast forwarding table to make sure that there is an upstream RPF interface list, with a primary and a backup interface.
Action
user@R3> show ldp p2mp path
P2MP path type: Transit/Egress
Output Session (label): 10.1.1.2:0 (301568) (Primary)
Egress Nexthops: Interface ge-1/2/18.0
Interface ge-1/2/22.0
RPF Nexthops: Interface ge-1/2/15.0, 10.2.94.1, 301568, 1
Interface ge-1/2/20.0, 10.2.96.1, 301584, 65534
Interface ge-1/2/14.0, 10.2.3.1, 301568, 1
Interface ge-1/2/19.0, 10.3.6.1, 301584, 65534
Attached FECs: P2MP root-addr 10.1.1.1, grp: 232.1.1.1, src: 192.168.219.11 (Active)
P2MP path type: Transit/Egress
Output Session (label): 10.1.1.6:0 (301584) (Backup)
Egress Nexthops: Interface ge-1/2/18.0
Interface ge-1/2/22.0
RPF Nexthops: Interface ge-1/2/15.0, 10.2.94.1, 301568, 1
Interface ge-1/2/20.0, 10.2.96.1, 301584, 65534
Interface ge-1/2/14.0, 10.2.3.1, 301568, 1
Interface ge-1/2/19.0, 10.3.6.1, 301584, 65534
Attached FECs: P2MP root-addr 10.1.1.1, grp: 232.1.1.1, src: 192.168.219.11 (Active)
P2MP path type: Transit/Egress
Output Session (label): 10.1.1.6:0 (301600) (Primary)
Egress Nexthops: Interface ge-1/2/18.0
Interface ge-1/2/22.0
RPF Nexthops: Interface ge-1/2/15.0, 10.2.94.1, 301616, 65534
Interface ge-1/2/20.0, 10.2.96.1, 301600, 1
Interface ge-1/2/14.0, 10.2.3.1, 301616, 65534
Interface ge-1/2/19.0, 10.3.6.1, 301600, 1
Attached FECs: P2MP root-addr 10.1.1.1, grp: 232.1.1.2, src: 192.168.219.11 (Active)
P2MP path type: Transit/Egress
Output Session (label): 10.1.1.2:0 (301616) (Backup)
Egress Nexthops: Interface ge-1/2/18.0
Interface ge-1/2/22.0
RPF Nexthops: Interface ge-1/2/15.0, 10.2.94.1, 301616, 65534
Interface ge-1/2/20.0, 10.2.96.1, 301600, 1
Interface ge-1/2/14.0, 10.2.3.1, 301616, 65534
Interface ge-1/2/19.0, 10.3.6.1, 301600, 1
Attached FECs: P2MP root-addr 10.1.1.1, grp: 232.1.1.2, src: 192.168.219.11 (Active)Meaning
The output shows primary and backup sessions, and RPF next hops.
Checking the LDP Point-to-Multipoint Traffic Statistics
Purpose
Make sure that both primary and backup statistics are listed.
Action
user@R3> show ldp traffic-statistics p2mp
P2MP FEC Statistics:
FEC(root_addr:lsp_id/grp,src) Nexthop Packets Bytes Shared
10.1.1.1:232.1.1.1,192.168.219.11, Label: 301568
10.3.8.2 0 0 No
10.3.4.2 0 0 No
10.1.1.1:232.1.1.1,192.168.219.11, Label: 301584, Backup route
10.3.4.2 0 0 No
10.3.8.2 0 0 No
10.1.1.1:232.1.1.2,192.168.219.11, Label: 301600
10.3.8.2 0 0 No
10.3.4.2 0 0 No
10.1.1.1:232.1.1.2,192.168.219.11, Label: 301616, Backup route
10.3.4.2 0 0 No
10.3.8.2 0 0 No
Meaning
The output shows both primary and backup routes with the labels.
