ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring IS-IS on Logical Systems Within the Same Router
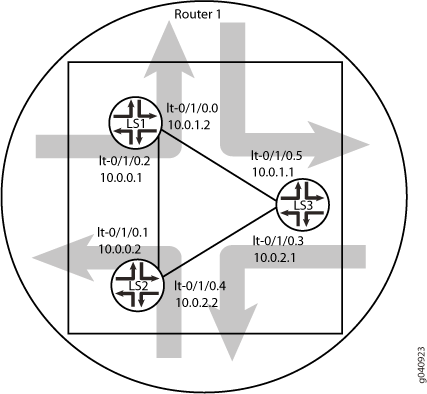
This example shows how to configure an IS-IS network by using multiple logical systems that are running on a single physical router. The logical systems are connected by logical tunnel interfaces.
Requirements
You must connect the logical systems by using logical tunnel (lt) interfaces. See Example: Connecting Logical Systems Within the Same Device Using Logical Tunnel Interfaces on MX Series Routers and EX Series Switches.
Overview
This example shows an IS-IS configuration with three logical systems running on one physical router. Each logical system has its own routing table. The configuration enables the protocol on all logical tunnel interfaces that participate in the IS-IS domain.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 description LS1->LS2 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 peer-unit 1 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 family iso set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 description LS1->LS3 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 peer-unit 5 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.1.2/30 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 family iso set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lo0 unit 1 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1001.00 set logical-systems LS1 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.0 set logical-systems LS1 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.2 set logical-systems LS1 protocols isis interface lo0.1 passive set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 description LS2->LS1 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 peer-unit 2 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family iso set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 description LS2->LS3 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 peer-unit 3 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 family inet address 10.0.2.2/30 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 family iso set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lo0 unit 2 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.2002.00 set logical-systems LS2 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.1 set logical-systems LS2 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.4 set logical-systems LS2 protocols isis interface lo0.2 passive set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 description LS3->LS2 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 peer-unit 4 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 family inet address 10.0.2.1/30 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 family iso set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 description LS3->LS1 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 peer-unit 0 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 family inet address 10.0.1.1/30 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 family iso set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lo0 unit 3 family iso address 49.0001.1234.1600.2231.00 set logical-systems LS3 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.5 set logical-systems LS3 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.3 set logical-systems LS3 protocols isis interface lo0.3 passive
Procedure
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To configure IS-IS on logical systems:
Configure the logical tunnel interface on Logical System LS1 connecting to Logical System LS2.
[edit logical-systems LS1] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 description LS1->LS2 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 peer-unit 1 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 family iso
Configure the logical tunnel interface on Logical System LS1 connecting to Logical System LS3.
[edit logical-systems LS1] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 description LS1->LS3 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 peer-unit 5 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.1.2/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 family iso
Configure the logical tunnel interface on Logical System LS2 connecting to Logical System LS1.
[edit logical-systems LS2] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 description LS2->LS1 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 peer-unit 2 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family iso
Configure the logical tunnel interface on Logical System LS2 connecting to Logical System LS3.
[edit logical-systems LS2] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 description LS2->LS3 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 peer-unit 3 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 family inet address 10.0.2.2/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 family iso
Configure the logical tunnel interface on Logical System LS3 connecting to Logical System LS2.
[edit logical-systems LS3] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 description LS3->LS2 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 peer-unit 4 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 family inet address 10.0.2.1/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 family iso
Configure the logical tunnel interface on Logical System LS3 connecting to Logical System LS1.
[edit logical-systems LS3] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 description LS3->LS1 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 peer-unit 0 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 family inet address 10.0.1.1/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 family iso
Configure the ISO address on the loopback interface for the three logical systems.
[edit logical-systems LS1] user@host# set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1001.00 user@host# set protocols isis interface lo0.1 passive
[edit logical-systems LS2] user@host# set interfaces lo0 unit 2 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.2002.00 user@host# set protocols isis interface lo0.2 passive
[edit logical-systems LS3] user@host# set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family iso address 49.0001.1234.1600.2231.00 user@host# set protocols isis interface lo0.3 passive
Configure IS-IS on all the interfaces.
[edit logical-systems LS1 protocols isis] user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.0 user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.2
[edit logical-systems LS2 protocols isis] user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.1 user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.4
[edit logical-systems LS3 protocols isis] user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.5 user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.3
If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit] user@host# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by issuing the show logical-systems command. If the output
does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions
in this example to correct the configuration.
user@host# show logical-systems
LS1 {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 0 {
description LS1->LS3;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 5;
family inet {
address 10.0.1.2/30;
}
family iso;
}
unit 2 {
description LS1->LS2;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 1;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.1/30;
}
family iso;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 1 {
family iso {
address 49.0001.1720.1600.1001.00;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
isis {
interface lt-0/1/0.0;
interface lt-0/1/0.2;
interface lo0.1 {
passive;
}
}
}
}
LS2 {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 1 {
description LS2->LS1;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 2;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.2/30;
}
family iso;
}
unit 4 {
description LS2->LS3;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 3;
family inet {
address 10.0.2.2/30;
}
family iso;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 2 {
family iso {
address 49.0001.1720.1600.2002.00;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
isis {
interface lt-0/1/0.1;
interface lt-0/1/0.4;
interface lo0.2 {
passive;
}
}
}
}
LS3 {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 3 {
description LS3->LS2;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 4;
family inet {
address 10.0.2.1/30;
}
family iso;
}
unit 5 {
description LS3->LS1;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 0;
family inet {
address 10.0.1.1/30;
}
family iso;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 3 {
family iso {
address 49.0001.1234.1600.2231.00;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
isis {
interface lt-0/1/0.3;
interface lt-0/1/0.5;
interface lo0.3 {
passive;
}
}
}
} Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
Verifying That the Logical Systems Are Up
Purpose
Make sure that the interfaces are properly configured.
Action
user@host> show interfaces terse
Interface Admin Link Proto Local Remote
...
lt-0/1/0 up up
lt-0/1/0.0 up up inet 10.0.1.2/30
iso
lt-0/1/0.1 up up inet 10.0.0.2/30
iso
lt-0/1/0.2 up up inet 10.0.0.1/30
iso
lt-0/1/0.3 up up inet 10.0.2.1/30
iso
lt-0/1/0.4 up up inet 10.0.2.2/30
iso
lt-0/1/0.5 up up inet 10.0.1.1/30
iso
... Verifying Connectivity Between the Logical Systems
Purpose
Make sure that the IS-IS adjacencies are established by checking the logical system routing entries and by pinging the logical systems.
Action
user@host> show route logical-system LS1
inet.0: 5 destinations, 5 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:37:52
> via lt-0/1/0.2
10.0.0.1/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:37:52
Local via lt-0/1/0.2
10.0.1.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:37:52
> via lt-0/1/0.0
10.0.1.2/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:37:52
Local via lt-0/1/0.0
10.0.2.0/30 *[IS-IS/15] 3w0d 01:37:13, metric 20
> to 10.0.1.1 via lt-0/1/0.0
to 10.0.0.2 via lt-0/1/0.2
iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
49.0001.1720.1600.1001/72
*[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:37:52
> via lo0.1
user@host> show route logical-system LS2
inet.0: 5 destinations, 5 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:01
> via lt-0/1/0.1
10.0.0.2/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:38:01
Local via lt-0/1/0.1
10.0.1.0/30 *[IS-IS/15] 3w0d 01:37:01, metric 20
to 10.0.0.1 via lt-0/1/0.1
> to 10.0.2.1 via lt-0/1/0.4
10.0.2.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:01
> via lt-0/1/0.4
10.0.2.2/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:38:01
Local via lt-0/1/0.4
iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
49.0001.1720.1600.2002/72
*[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:01
> via lo0.2
user@host> show route logical-system LS3
inet.0: 5 destinations, 5 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.0/30 *[IS-IS/15] 3w0d 01:37:10, metric 20
to 10.0.2.2 via lt-0/1/0.3
> to 10.0.1.2 via lt-0/1/0.5
10.0.1.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:10
> via lt-0/1/0.5
10.0.1.1/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:38:11
Local via lt-0/1/0.5
10.0.2.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:11
> via lt-0/1/0.3
10.0.2.1/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:38:11
Local via lt-0/1/0.3
iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
49.0001.1234.1600.2231/72
*[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:11
> via lo0.3
From LS1, Ping LS3
user@host> set cli logical-system LS1
user@host:LS1> ping 10.0.2.1 PING 10.0.2.1 (10.0.2.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.2.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=63 time=1.264 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.2.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=1.189 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.2.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=1.165 ms ^C --- 10.0.2.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.165/1.206/1.264/0.042 ms
From LS3, Ping LS1
user@host> set cli logical-system LS3
user@host:LS3> ping 10.0.0.1 PING 10.0.0.1 (10.0.0.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=63 time=1.254 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=1.210 ms ^C --- 10.0.0.1 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.210/1.232/1.254/0.022 ms
From LS1, Ping LS2
user@host> set cli logical-system LS1
user@host:LS1> ping 10.0.2.2 PING 10.0.2.2 (10.0.2.2): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.2.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=1.240 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.2.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.204 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.2.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.217 ms ^C --- 10.0.2.2 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.204/1.220/1.240/0.015 ms
From LS2, Ping LS1
user@host> set cli logical-system LS2
user@host:LS2> ping 10.0.1.2 PING 10.0.1.2 (10.0.1.2): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.1.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=1.308 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.235 ms ^C --- 10.0.1.2 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.235/1.272/1.308/0.037 ms
From LS2, Ping LS3
user@host> set cli logical-system LS2
user@host:LS2> ping 10.0.1.1 PING 10.0.1.1 (10.0.1.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=1.253 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.194 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.212 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.221 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=1.195 ms ^C --- 10.0.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.194/1.215/1.253/0.022 ms
From LS3, Ping LS2
user@host> set cli logical-system LS3
user@host:LS3> ping 10.0.0.2 PING 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=1.240 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.217 ms ^C --- 10.0.0.2 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.217/1.228/1.240/0.012 ms