IDP Sensor Configuration
IDP Sensor Configuration allows administrators to configure settings for optimizing IDP performance on SRX Series Firewalls. It explains how to limit memory and session usage, control traffic drops when resources are exceeded and configure IDP Intelligent Bypass for managing high CPU utilization. It also covers handling conditions during failovers.
You cannot create application signatures with the IDP signature database. However, you can configure sensor settings to limit sessions and memory usage for Application Identification (AppID).
IDP Sensor Configuration Overview
Sensor configuration options are used to:
Log run conditions as IDP session capacity and memory limits are approached.
Analyze traffic dropped by IDP and application identification when the limits are exceeded.
You can configure the maximum amount of memory bytes that can be used to save packets for application identification for one TCP or UDP session. You can also configure a limit for global memory usage for application identification. AppID is disabled for a session after the system reaches the specified memory limit for the session. However, IDP continues to match patterns. The matched application is saved to cache so that the next session can use it. This protects the system from attackers trying to bypass AppID by purposefully sending large client-to-server packets.
Although you cannot create application signatures with the IDP signature database, you can configure the following sensor settings to limit the number of sessions running application identification and also to limit memory usage for application identification:
max-tcp-session-packet-memory—To configure memory and session limits for IDP AppID services, run the set security idp sensor-configuration application-identification max-tcp-session-packet-memory 5000 command.
memory-limit-percent—To set memory limit percentage for data plane available in the system, which can be used for IDP allocation, run the set security idp sensor-configuration global memory-limit-percent command. The supported percentage value is from 10 through 90.
drop-if-no-policy-loaded—At startup, traffic is ignored by IDP by default if the IDP policy is not yet loaded. The
drop-if-no-policy-loadedoption changes this behavior so that all sessions are dropped before the IDP policy is loaded.The following counter for the
show security idp counters flowcommand output analyzes dropped traffic due to thedrop-if-no-policy-loadedoption:Sessions dropped due to no policy 0
drop-on-failover—By default, IDP ignores failover sessions in an SRX Series chassis cluster deployment. The
drop-on-failoveroption changes this behavior and automatically drops sessions that are in the process of being inspected on the primary node when a failover to the secondary node occurs.The following counter for the
show security idp counters flowcommand output analyzes dropped failover traffic due to thedrop-on-failoveroption:Fail-over sessions dropped 0
drop-on-limit—By default, sessions are not dropped if the IDP session limit or resource limits are exceeded. In this case, IDP and other sessions are dropped only when the device’s session capacity or resources are depleted. The
drop-on-limitoption changes this behavior and drops sessions when resource limits are exceeded.The following counters for the
show security idp counters flowcommand output analyze dropped IDP traffic due to thedrop-on-limitoption:SM Sessions encountered memory failures 0 SM Packets on sessions with memory failures 0 SM Sessions dropped 0 Both directions flows ignored 0 IDP Stream Sessions dropped due to memory failure 0 IDP Stream Sessions ignored due to memory failure 0 IDP Stream Sessions closed due to memory failure 0 Number of times Sessions exceed high mark 0 Number of times Sessions drop below low mark 0 Memory of Sessions exceeds high mark 0 Memory of Sessions drops below low mark 0
The following counters for the
show security idp counters application-identificationcommand output analyze dropped AppID traffic due to thedrop-on-limitoption:AI-session dropped due to malloc failure before session create 0 AI-Sessions dropped due to malloc failure after create 0 AI-Packets received on sessions marked for drop due to malloc failure 0
The following options are used to trigger informative log messages about current run conditions. When set, the log messages are triggered whether the
drop-on-limitoption is set or not.max-sessions-offset—The
max-sessions-offsetoption sets an offset for the maximum IDP session limit. When the number of IDP sessions exceeds the maximum session limit, a warning is logged that conditions exist where IDP sessions could be dropped. When the number of IDP sessions drops below the maximum IDP session limit minus the offset value, a message is logged that conditions have returned to normal.Jul 19 04:38:13 4.0.0.254 RT_IDP: IDP_SESSION_LOG_EVENT: IDP: at 1374233893, FPC 4 PIC 1 IDP total sessions pass through high mark 100000. IDP may drop new sessions. Total sessions dropped 0. Jul 19 04:38:21 4.0.0.254 RT_IDP: IDP_SESSION_LOG_EVENT: IDP: at 1374233901, FPC 4 PIC 1 IDP total sessions drop below low mark 99000. IDP working in normal mode. Total sessions dropped 24373.
min-objcache-limit-lt—The
min-objcache-limit-ltoption sets a lower threshold for available cache memory. The threshold value is expressed as a percentage of available IDP cache memory. If the available cache memory drops below the lower threshold level, a message is logged stating that conditions exist where IDP sessions could be dropped because of memory allocation failures. For example, the following message shows that the IDP cache memory has dropped below the lower threshold and that a number of sessions have been dropped:Jul 19 04:07:33 4.0.0.254 RT_IDP: IDP_SESSION_LOG_EVENT: IDP: at 1374232053, FPC 4 PIC 1 IDP total available objcache(used 4253368304, limit 7247757312) drops below low mark 3986266515. IDP may drop new sessions. Total sessions dropped 1002593.
min-objcache-limit-ut—The
min-objcache-limit-utoption sets an upper threshold for available cache memory. The threshold value is expressed as a percentage of available IDP cache memory. If available IDP cache memory returns to the upper threshold level, a message is logged stating that available cache memory has returned to normal. For example, the following message shows the available IDP cache memory has increased above the upper threshold and it is performing normally:Jul 19 04:13:47 4.0.0.254 RT_IDP: IDP_SESSION_LOG_EVENT: IDP: at 1374232428, FPC 4 PIC 1 IDP total available objcache(used 2782950560, limit 7247757312) increases above high mark 4348654380. IDP working in normal mode. Total sessions dropped 13424632.
The message triggers only when available memory falls below the lower threshold and then rises above the upper threshold. Memory fluctuations above the lower threshold do not trigger the message.
In the IDP Intelligent Bypass default configuration, IDP attempts to inspect new and existing sessions, regardless of CPU utilization. This can lead to dropped packets, latency, and instability across the system during high CPU utilization events. To overcome unpredictable IDP packet processing behavior, you can enable the IDP Intelligent Bypass feature. This feature gives you the flexibility to bypass IDP or to drop the packets when the system CPU utilization reaches a high level, otherwise known as “Failing Open” (permit packets) or “Failing Closed” (dropping packets). By default, IDP Intelligent Bypass feature is not enabled. The following options are used to configure the IDP Intelligent Bypass feature.
idp-bypass-cpu-usage-overload—By default, IDP may consume 100 percent of available CPU and may begin dropping packets for all sessions inadvertently. To handle IDP packet processing behavior when the system CPU utilization reaches high threshold value, you can enable the IDP Intelligent Bypass feature. To enable IDP Intelligent Bypass feature, issue the
set security idp sensor-configuration flow idp-bypass-cpu-overloadcommand. By default, IDP Intelligent Bypass feature is not enabled.idp-bypass-cpu-threshold—IDP stops inspecting new sessions when CPU utilization reaches the defined threshold value. The default threshold CPU utilization value is 85 percent. When CPU utilization reaches threshold value, IDP keeps on bypassing new sessions until CPU utilization falls below the lower threshold value. Alternatively, if you set the
drop-on-limit, where IDP drops new session until CPU utilization falls below the lower threshold value. To configure the threshold value, issueset security idp sensor-configuration flow idp-bypass-cpu-thresholdcommand. You can set a threshold value in the range 0 through 99. This threshold value is expressed as a percentage.idp-bypass-cpu-tolerance—To configure the tolerance value, issue the
set security idp sensor-configuration flow idp-bypass-cpu-tolerancecommand. You can set a tolerance value in the range 1 through 99. The default tolerance value is 5. This tolerance value is expressed as a percentage.
You can calculate the CPU upper and lower threshold values by using the following equations:
CPU upper threshold value = CPU threshold + CPU tolerance value.
CPU lower threshold value = CPU threshold - CPU tolerance value.
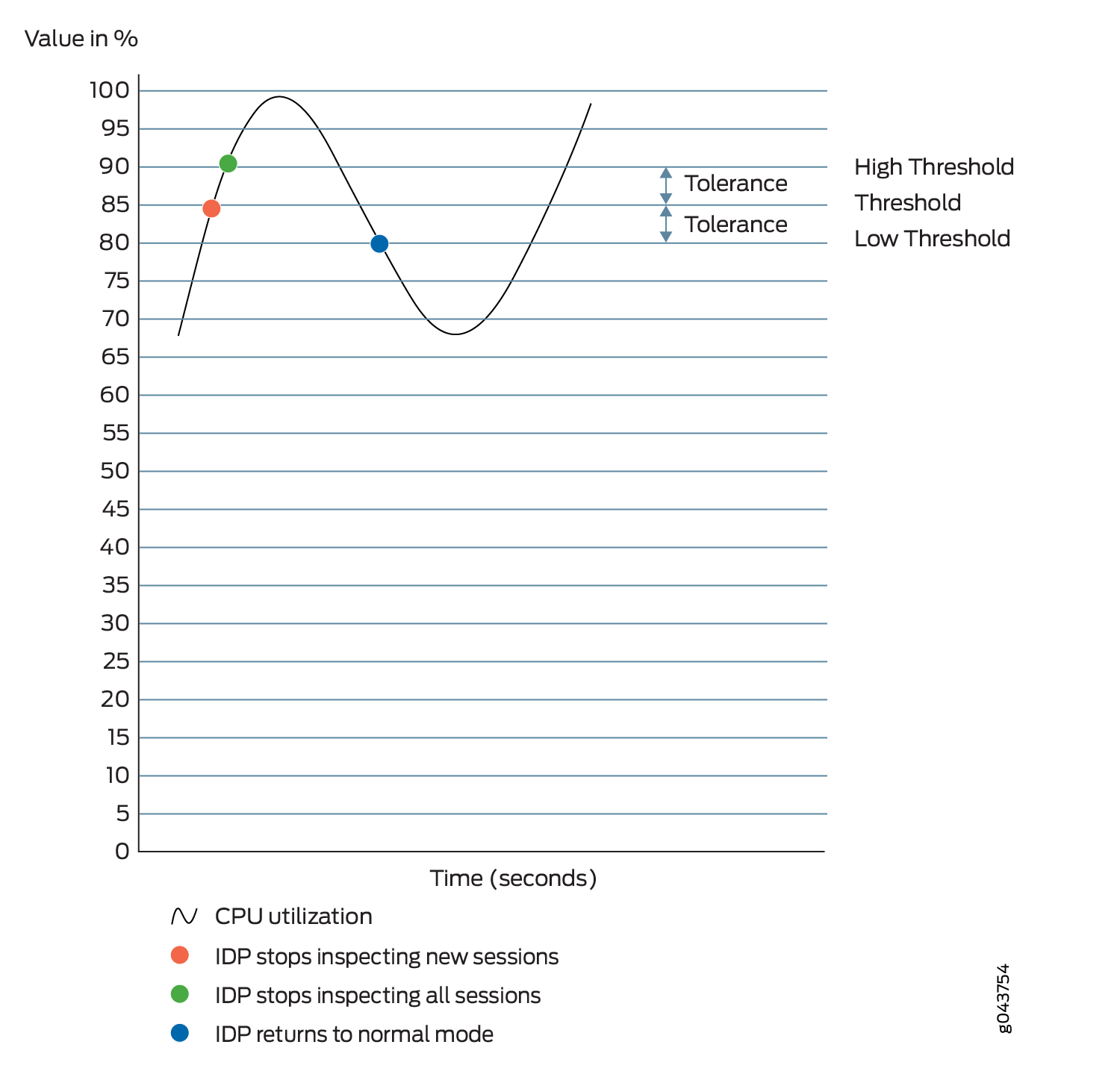
When the system CPU utilization exceeds the threshold value,
IDP stops inspecting new sessions, but continues to inspect existing
sessions. In this state, if drop-on-limit is set, IDP starts
dropping new sessions. Log messages are triggered to indicate new
sessions are dropped. For example, the following message states that
IDP CPU utilization has crossed the threshold value and IDP may drop
new sessions:
FPC 0 PIC 1 IDP CPU usage 86 crossed threshold value 85. IDP may drop new sessions. Total sessions dropped 2
When the system CPU utilization exceeds the upper threshold value, IDP stops inspecting the
packets of existing sessions and new sessions. In this state, no packets can
go through IDP inspection. If drop-on-limit is set, IDP
drops all sessions. Log messages are triggered to indicate all sessions are
dropped. For example, the following message states that IDP CPU utilization
has crossed the upper threshold value, and IDP stops inspecting the packets
of the existing sessions and new sessions:
FPC 0 PIC 1 IDP CPU usage 92 crossed upper threshold value 90. IDP may drop packets of existing sessions as well as new sessions. Total sessions dropped 21
When the system CPU utilization falls below the lower threshold value, IDP starts inspecting new session and returns to normal mode. IDP will not inspect existing discarded sessions. Log messages are triggered to indicate IDP starts inspecting new session and returned to normal mode. For example, the following message states that IDP CPU utilization falls below the lower threshold value, and IDP returns to normal mode:
FPC 0 PIC 1 IDP CPU usage 75 dropped below lower threshold value 80. IDP working in normal mode. Total sessions dropped 25
IDP Protection Modes
IDP protection modes adjust the inspection parameters for efficient
inspection of traffic in the device. To enable the IDP protection
modes, issue the security-configuration protection-mode mode command at the [edit security idp sensor-configuration] hierarchy level.
user@host# set security-configuration
protection-mode mode
There are four IDP protection modes:
All IDP protection modes inspect CTS (Client To Server) traffic.
Mode |
Description |
|---|---|
Perimeter-Full |
Inspects all STC(Server To Client) traffic. Processes TCP errors without any optimization. This is the default mode. |
Perimeter |
Inspects all STC traffic. Processes TCP errors with optimization. For TCP packets, if SYN is received in a window and has a TCP error flag set, then process the TCP error and take appropriate action. Drop the current packet and ignore inspection on the entire session. |
Datacenter-Full |
Disables all STC traffic inspection. Processes TCP errors without any optimization. Datacenter-Full can be used in situations where the SRX Series Firewall is only responsible for protecting servers whose response traffic is not deemed interesting for analysis. Datacenter-Full should not be used in cases where the SRX Series Firewall is responsible for protecting clients. |
Datacenter |
Disables all STC traffic inspection. Processes TCP errors with optimization. For TCP packets, if SYN is received in a window and has a TCP error flag set, then process the TCP error and take appropriate action. Drop the current packet and ignore inspection on the entire session. Datacenter configuration is optimized to provide balanced protection and performance. |
See Also
Example: Improve Logging and Traffic Analysis with IDP Sensor Configuration Options
This example shows how to improve logging and traffic analysis by configuring IDP sensor configuration options. In addition, you can use these options to log run conditions as IDP session capacity and memory limits are approached, and to analyze traffic dropped by IDP and application identification when exceeding these limitations.
Requirements
Before you begin:
Configure network interfaces.
Download the signature database. See Updating the IDP Signature Database Manually. Application signatures are available as part of the security package provided by Juniper Networks. You download predefined application signatures along with the security package updates.
Overview
The IDP sensor monitors the network and detects suspicious and anomalous network traffic based on specific rules defined in IDP rulebases. It applies attack objects to traffic based on protocols or applications. Application signatures enable the sensor to identify known and unknown applications running on nonstandard ports and to apply the correct attack objects.
The default behavior of IDP is to ignore the sessions when:
IDP policy is not configured in the device
Resource limits (memory or active sessions) are reached
In case of Chassis Cluster, for fail over sessions
If traffic availability is considered more important than security, then it is recommended to continue to use the above mentioned default behavior of IDP. However, If security is considered more important than availability, then it is recommended to change the default behavior with the configuration provided in this example.
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set security idp sensor-configuration application-identification max-tcp-session-packet-memory 5000 set security idp sensor-configuration flow drop-if-no-policy-loaded set security idp sensor-configuration flow drop-on-failover set security idp sensor-configuration flow drop-on-limit set security idp sensor-configuration flow max-sessions-offset 5 set security idp sensor-configuration flow min-objcache-limit-lt 21 set security idp sensor-configuration flow min-objcache-limit-ut 56
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For instructions on how to do that, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To set IDP sensor configuration options:
Specify the memory limits for application identification.
[edit security idp sensor-configuration] user@host# set application-identification max-tcp-session-packet-memory 5000
Specify that traffic is dropped before the IDP policy is loaded.
[edit security idp sensor-configuration flow] user@host# set drop-if-no-policy-loaded
Specify that failover sessions in an SRX Series chassis cluster deployment are dropped.
[edit security idp sensor-configuration flow] user@host# set drop-on-failover
Specify that sessions are dropped when resource limits are exceeded.
[edit security idp sensor-configuration flow] user@host# set drop-on-limit
Run the
delete drop-on-limitcommand to prevent sessions drops when resource limits are exceeded.Configure an offset value for the maximum IDP session limit.
[edit ssecurity idp sensor-configuration flow] user@host# set max-sessions-offset 5
Set a lower threshold for available cache memory.
[edit security idp sensor-configuration flow] user@host# set min-objcache-limit-lt 21
Set an upper threshold for available cache memory.
[edit security idp sensor-configuration flow] user@host# set min-objcache-limit-ut 56
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show security idp command. If the output
does not display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration
instructions in this example to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show security idp
sensor-configuration {
application-identification {
max-tcp-session-packet-memory 5000;
}
flow {
drop-on-limit;
drop-on-failover;
drop-if-no-policy-loaded;
max-sessions-offset 5;
min-objcache-limit-lt 21;
min-objcache-limit-ut 56;
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Verify IDP Sensor Configuration Settings
Purpose
Verify the IDP sensor configuration settings.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security
idp sensor-configuration command.
user@host> show security idp sensor-configuration
application-identification {
max-tcp-session-packet-memory 5000;
}
flow {
drop-on-limit;
drop-on-failover;
drop-if-no-policy-loaded;
max-sessions-offset 5;
min-objcache-limit-lt 21;
min-objcache-limit-ut 56;
}
}
Meaning
The show security idp sensor-configuration command displays all sensor configuration options that are set with
certain values.
Verify IDP Counters
Purpose
Verify the IDP counters.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security
idp counters flow command.
Sample Output
IDP counters: IDP counter type Value Fast-path packets 0 Slow-path packets 0 Session construction failed 0 Session limit reached 0 Session inspection depth reached 0 Memory limit reached 0 Not a new session 0 Invalid index at ageout 0 Packet logging 0 Policy cache hits 0 Policy cache misses 0 Policy cache entries 0 Maximum flow hash collisions 0 Flow hash collisions 0 Gates added 0 Gate matches 0 Sessions deleted 0 Sessions aged-out 0 Sessions in-use while aged-out 0 TCP flows marked dead on RST/FIN 0 Policy init failed 0 Number of times Sessions exceed high mark 0 Number of times Sessions drop below low mark 0 Memory of Sessions exceeds high mark 0 Memory of Sessions drops below low mark 0 SM Sessions encountered memory failures 0 SM Packets on sessions with memory failures 0 IDP session gate creation requests 0 IDP session gate creation acknowledgements 0 IDP session gate hits 0 IDP session gate timeouts 0 Number of times Sessions crossed the CPU threshold value that is set 0 Number of times Sessions crossed the CPU upper threshold 0 Sessions constructed 0 SM Sessions ignored 0 SM Sessions dropped 0 SM Sessions interested 0 SM Sessions not interested 749 SM Sessions interest error 0 Sessions destructed 0 SM Session Create 0 SM Packet Process 0 SM ftp data session ignored by idp 0 SM Session close 0 SM Client-to-server packets 0 SM Server-to-client packets 0 SM Client-to-server L7 bytes 0 SM Server-to-client L7 bytes 0 Client-to-server flows ignored 0 Server-to-client flows ignored 0 Both directions flows ignored 0 Fail-over sessions dropped 0 Sessions dropped due to no policy 0 IDP Stream Sessions dropped due to memory failure 0 IDP Stream Sessions ignored due to memory failure 0 IDP Stream Sessions closed due to memory failure 0 IDP Stream Sessions accepted 0 IDP Stream Sessions constructed 0 IDP Stream Sessions destructed 0 IDP Stream Move Data 0 IDP Stream Sessions ignored on JSF SSL Event 0 IDP Stream Sessions not processed for no matching rules 0 IDP Stream stbuf dropped 0 IDP Stream stbuf reinjected 0 Busy pkts from stream plugin 0 Busy pkts from pkt plugin 0 bad kpp 0 Lsys policy id lookup failed sessions 0 Busy packets 0 Busy packet Errors 0 Dropped queued packets (async mode) 0 Dropped queued packets failed(async mode) 0 Reinjected packets (async mode) 0 Reinjected packets failed(async mode) 0 AI saved processed packet 0 AI-session dropped due to malloc failure before session create 0 AI-Sessions dropped due to malloc failure after create 0 AI-Packets received on sessions marked for drop due to malloc failure 0 busy packet count incremented 0 busy packet count decremented 0 session destructed in pme 0 session destruct set in pme 0 kq op hold 0 kq op drop 0 kq op route 0 kq op continue 0 kq op error 0 kq op stop 0 PME wait not set 0 PME wait set 0 PME KQ run not called 0
Meaning
The show security idp counters flow command
displays all counters that are used for analyzing dropped failover
traffic, dropped IDP traffic, and dropped application identification
traffic.
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
