SCTP Configuration
Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) can be configured to perform stateful inspection on all SCTP traffic.
SCTP Configuration Overview
You must configure at least one SCTP profile to enable the security device to perform stateful inspection on all SCTP traffic. The stateful inspection of SCTP traffic will drop some anomalous SCTP packets.
The SCTP firewall supports deeper inspection of the profiles:
Packet filtering—The profile configuration of drop packets for special SCTP payload protocol and M3UA service enables packet filtering.
Limit-rate—Controls the M3UA and SCCP packets rate per association.
The SCTP deeper inspection requires the following settings:
Creating a SCTP profile
Configuring the filtering and limit parameters
Binding the SCTP profile to a policy
Example: Configuring a Security Policy to Permit or Deny SCTP Traffic
This example shows how to configure a security policy to permit or deny SCTP traffic.
Requirements
Before you begin:
-
Create zones. See Example: Creating Security Zones.
-
Configure an address book and create addresses for use in the policy. See Example: Configuring Address Books and Address Sets.
-
Create an application (or application set) that indicates that the policy applies to traffic of that type. See Example: Configuring Security Policy Applications and Application Sets.
-
Configure a GPRS SCTP profile. See Example: Configuring a GPRS SCTP Profile for Policy-Based Inspection to Reduce Security Risks.
Overview
The SCTP firewall implements a policy mechanism that is administratively used to determine the packets that can be passed or dropped. Policies can be configured for multiple addresses, address groups, or the entire zone.
In situations where only a few ports are used for SCTP traffic, the SCTP associations are not evenly distributed to Services Processing Units (SPUs). This occurs in the following cases:
-
Uneven hash results on the association ports pairs.
-
The number of port pairs is less than, or not much greater than, the number of SPUs.
This configuration example shows how to:
-
Deny SCTP traffic from the trust zone to the IP address 10.1.1.0/24 in the untrust zone.
-
Permit SCTP traffic from an IP address 10.1.2.0/24 in the trust zone to the untrust zone with the SCTP configuration specified in the roam2att profile.
Figure 1 shows the SCTP firewall implementation.
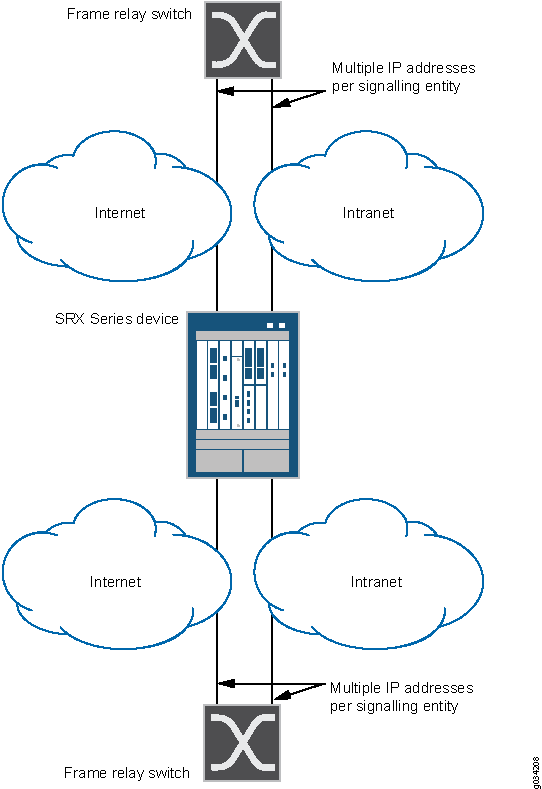
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration
mode.
set security zones security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/2 set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/1 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy deny-all match source-address any set security policies policy from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy deny-all match destination-address 10.1.1.0/24 set security policies policy from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy deny-all match application junos-gprs-sctp set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy deny-all then deny set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy allow-att-roaming match source-address 10.1.2.0/24 set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy allow-att-roaming match destination-address any set security policies policy from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy allow-att-roaming match application junos-gprs-sctp set security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy allow-att-roaming then permit application-services gprs-sctp-profile roam2att
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure a security policy to permit or deny SCTP traffic:
-
Configure the interfaces and security zones.
[edit security zones] user@host# set security-zone trust interfaces ge-0/0/2 user@host# set security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/1
-
Create the security policy to permit traffic from the trust zone to the untrust zone.
[edit security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust] user@host# set policy allow-att-roaming match source-address 10.1.2.0/24 user@host# set policy allow-att-roaming match destination-address any user@host# set policy allow-att-roaming match application junos-gprs-sctp user@host# set policy allow-att-roaming then permit application-services gprs-sctp-profile roam2att
-
Create the security policy to deny traffic from the trust zone to the untrust zone.
[edit security policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust] user@host# set policy deny-all match source-address any user@host# set policy deny-all match destination-address 10.1.1.0/24 user@host# set policy deny-all match application junos-gprs-sctp user@host# set policy deny-all then deny
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show security policies command. If the
output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions
in this example to correct the configuration.
[edit]
user@host# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone untrust {
policy deny-all {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address 10.1.1.0/24;
application junos-gprs-sctp;
}
then {
deny;
}
}
policy allow-att-roaming {
match {
source-address 10.1.2.0/24;
destination-address any;
application junos-gprs-sctp;
}
then {
permit {
application-services {
gprs-sctp-profile roam2att;
}
}
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Example: Configuring a GPRS SCTP Profile for Policy-Based Inspection to Reduce Security Risks
In the GPRS architecture, the fundamental cause of security threats to an operator’s network is the inherent lack of security in the GPRS tunneling protocol (GTP). This example shows how to configure a GPRS SCTP profile for policy-based inspection to reduce the GTP's security risks.
Requirements
Before you begin, understand the GPRS SCTP hierarchy and its options.
Overview
In this example, you configure a GPRS SCTP profile by setting
the limit rate parameter and the payload protocol parameter for SCTP
inspection. If your policy includes the nat-only option,
the payload IP addresses are translated, but they are not inspected.
The SCTP commands can be applied only to the policy configured with an SCTP profile.
If you remove the SCTP profile from the policy, the packets are forwarded without any inspection, and the IP address list in the packet payload will not be translated, even if the related static NAT is configured.
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration
mode.
set security gprs sctp profile roam2att limit rate address 10.1.1.0 sccp 100 set security gprs sctp profile roam2att limit rate address 10.1.1.0 ssp 10 set security gprs sctp profile roam2att limit rate address 10.1.1.0 sst 50 set security gprs sctp profile roam2att drop payload-protocol all set security gprs sctp profile roam2att permit payload-protocol dua
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure a GPRS SCTP profile:
Configure the limit rate parameter.
The limit rate is per association.
[edit security gprs sctp profile roam2att] user@host# set limit rate address 10.1.1.0 sccp 100 user@host# set limit rate address 10.1.1.0 ssp 10 user@host# set limit rate address 10.1.1.0 sst 50
Configure the payload protocol to drop all SCTP payload messages.
[edit security gprs sctp profile roam2att] user@host# set drop payload-protocol all
Configure the payload protocol to allow certain SCTP payload messages.
[edit security gprs sctp profile roam2att] user@host# set permit payload-protocol dua
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show security gprs command. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
[edit]
user@host# show security gprs
sctp {
profile roam2att {
drop {
payload-protocol all;
}
permit {
payload-protocol dua;
}
limit {
rate {
address 10.1.1.0 {
sccp 100;
ssp 10;
sst 50;
}
}
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
Verifying SCTP Profile Configuration
Purpose
Verify the SCTP profile configuration.
Action
From configuration mode, enter the show configuration security gprs sctp profile roam2att command.
user@host> show configuration security gprs sctp profile roam2att
drop {
payload-protocol all;
}
permit {
payload-protocol dua;
}
limit {
rate {
address 10.1.1.0 {
sccp 100;
ssp 10;
sst 50;
}
}
}Meaning
The output displays information about the SCTP payload messages allowed and SCTP payload messages that are dropped. Verify the following information:
Dropped SCTP payload messages
Allowed SCTP payload messages
