Aruba ClearPass
Learn about how the firewall communicate with Aruba ClearPass. You can learn about the Web API and user query function.
The firewall associate with Aruba ClearPass to control the user access from the user level based on their usernames or by the groups that they belong to, not the IP address of the device.
Communication Between ClearPass and Firewall
The firewall and the ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) communicate with each other to authenticate users and provide access to the Internet and internal, protected resources.
Benefits
-
Quick and easy access to data that help to manage and maintain your networks, clients, and devices.
-
Continuous monitoring and advance analytics that offer real-time visibility into your network.
How communication happens between the firewall and the ClearPass?
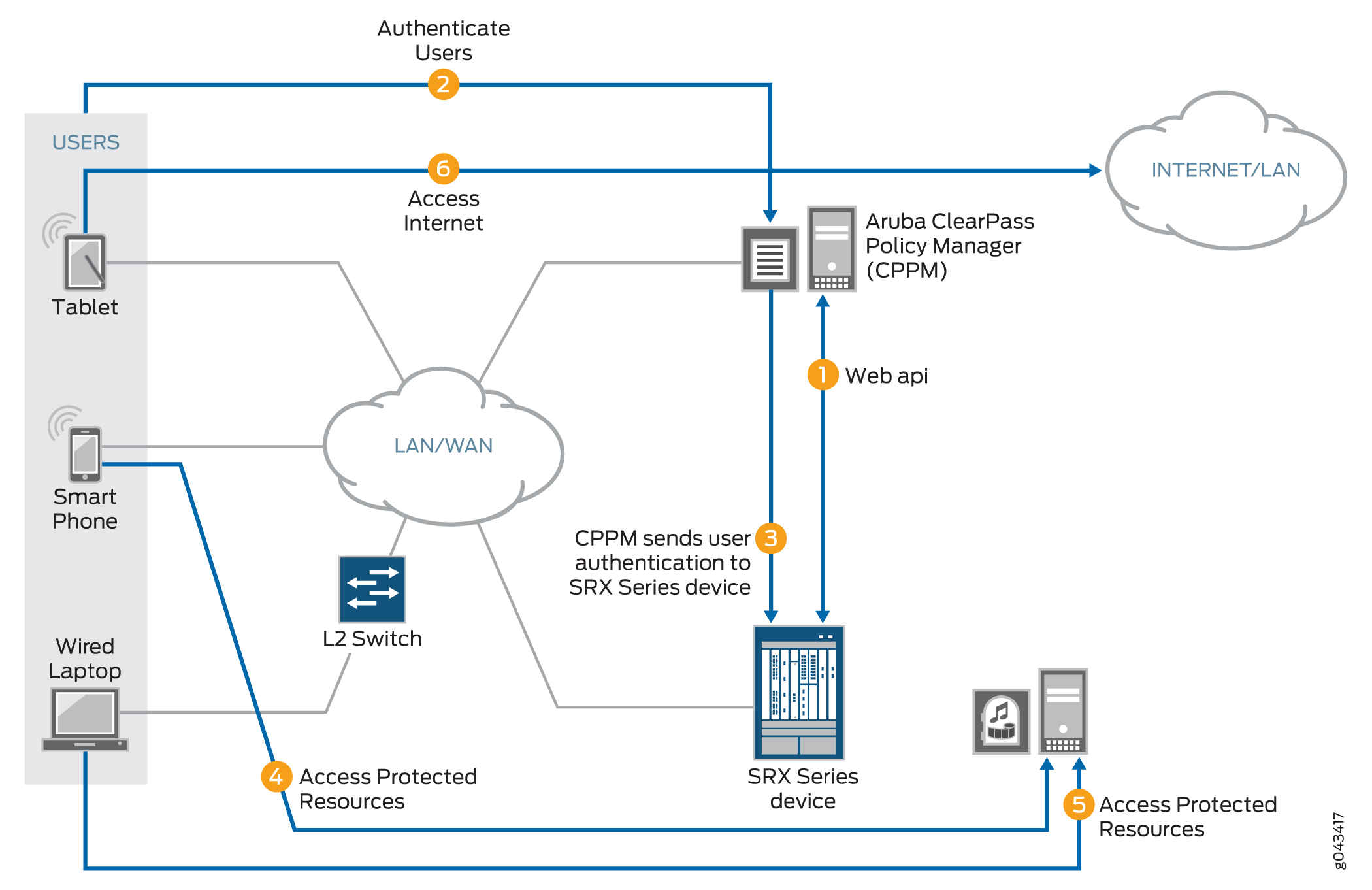
-
The ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) initiates a secure connection with the firewall using the Web API.
Three users join the network and are authenticated by the CPPM.
A tablet user joins the network across the corporate WAN.
A smartphone user joins the network across the corporate WAN.
A wireless laptop user joins the network from a wired laptop connected to a Layer 2 switch that is connected to the corporate LAN.
The CPPM sends the user authentication and identity information for the users who are logged in to the network to the firewall in POST request messages using the Web API.
When traffic from a user arrives at the firewall, the firewall:
Identifies a security policy that the traffic matches.
Locates an authentication entry for the user in the ClearPass authentication table.
Applies the security policy to the traffic after authenticating the user.
Traffic from the smartphone user who is requesting access to an internal, protected resource arrives at the firewall. Because all of the conditions identified in Step 3 are met and the security policy permits it, the firewall allows the user connection to the protected resource.
Traffic from the wired laptop user who is requesting access to a protected resource arrives at the firewall. Because all of the conditions identified in Step 3 are met and the security policy permits it, the firewall allows the user connection to the resource.
Traffic from the tablet user who is requesting access to the Internet arrives at the firewall. Because all of the conditions identified in Step 3 are met and the security policy permits it, the firewall allows the user connection to the Internet.
The UserID daemon gets the full IP-user mapping from the CPPM. For each authenticated user, the UserID daemon generates an entry in the Routing Engine authentication table.
The Routing Engine authentication table is common in that it holds authentication entries based on information from other authentication sources in addition to ClearPass. For example, it might also hold entries for users authenticated by Microsoft Active Directory.
The UserID daemon synchronizes the user authentication information from the Routing Engine authentication table to the ClearPass authentication table on the Packet Forwarding Engine. The ClearPass authentication table is dedicated to holding only ClearPass authentication information. See Figure 2.
Figure 2: User Information from the CPPM to the firewall Routing Engine Synchronized to the ClearPass Authentication Table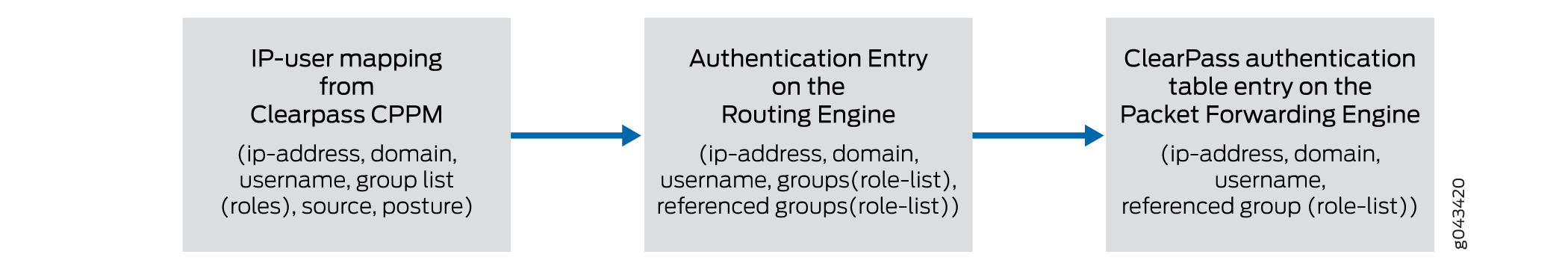
The firewall uses the authenticated user identity information in the following process. When a user attempts to access an internal, protected resource or the Internet, the device:
-
Checks the traffic generated by the user for a matching security policy. The source traffic must match all of the tuples specified in the security policy. The match includes the source-identity field, which specifies a username or a group name.
To identify a match, the firewall compares the username or the group name with the source-identity specification that is configured in a security policy, along with all other security policy values.
-
Checks the ClearPass authentication table for an authentication entry for the user, if a security policy match was found.
If it does not find an entry in the ClearPass authentication table, the firewall checks other local authentication tables, in the order that you specified, until a match is found. However, it does not check other local authentication tables if the user query function is configured.
The firewall can query the CPPM for individual user information, under certain circumstances, when it has not already received that information from the CPPM. This feature is referred to as user query.
Enforce Security with Aruba ClearPass
The firewall collaborate with Aruba ClearPass to protect your network resources by enforcing security at the user identity level and controlling user access to the Internet. The ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) can authenticate users across wired, wireless, and VPN infrastructures.
- Why you need Aruba ClearPass with Enforcement Security?
- How Aruba ClearPass with Enforcement Security works?
Why you need Aruba ClearPass with Enforcement Security?
Risk and Challenges—Use of company smartphones poses one of the biggest IT security risks to businesses.
Today’s network environments are more open to attacks of various kinds because they support anywhere, anytime, any device access, to a greater or lesser degree, and they allow a user to use multiple concurrently network-connected devices.
Attackers can gain access to nearby company-owned mobile devices and install malware on them that they can then use to capture data at any time.
Attackers can launch information-gathering ventures, stop business activity, and steal sensitive corporate data.
Need for Business—The proliferation of mobile devices and cloud services and securing them has become a fundamental strategic part of enterprise cybersecurity.
In a work environment that supports mobile devices, knowing the identity of the user is important.
An identity of the user provides IT administrators with improved advantage in identifying the source of the attack and stemming future potential attacks that follow the same strategy.
The ClearPass with enforcement security protects against malicious intrusions introduced through use of mobile devices and multiple concurrently connected devices.
Protection using ClearPass—The ClearPass with enforcement security can protect you against attacks and intrusions by allowing you to configure security policies that identify users by their usernames or by the groups that they belong to.
ClearPass identifies threats and attacks perpetrated against your network environment and provides this information to the CPPM.
As administrator of the CPPM, you can better align your security enforcement to protect against possible future attacks of the same kind.
If a user is logged in to the network with more than one device, you can keep track of their activity based on their identity and not only by their devices.
You can easily control their network access and any egregious activity on their behalf, whether intended or not.
How Aruba ClearPass with Enforcement Security works?
The Aruba ClearPass with enforcement security delivers the protection of the SCREENS, IDP and Content Security features to defend your network against a wide range of attack strategies. In addition to protecting the company’s network resources, the device can make available to the CPPM log records generated by these protective security features in response to attack or attack threats. Knowing about threats and specific attacks that have already occurred can help IT departments to identify noncompliant systems and exposed areas of the network. With this information, they can harden their security by enforcing device compliance and strengthening protection of their resources.
The ClearPass with enforcement security gives you granular control at the user level:
-
As administrator of the device, you can now specify in the identity source parameter of identity-awaresecurity policies a username or a role (group) name that the CPPM posts to the device. You are no longer restricted to relying solely on the IP address of the device as a means of identifying the user. Honing in on the user of the device, rather than only the device, enhances your control over security enforcement.
-
In addition to providing the firewall with authenticated user information, the CPPM can map a device type to a role and assign users to that role. It can then send that role mapping to the firewall. This capability allows you to control through security policies a user’s access to resources when they are using a specific type of device.
For example, suppose that the administrator of the CPPM configured a role called marketing-company-device and mapped to that role both company devices and members of the Marketing department. As administrator of the device, you could specify that role in a security policy as if it were a group. The security policy would then apply to all users mapped to the role, inherently controlling their network activity when they use that type of device type.
firewall security policies protect the company’s resources and enforce access control at a fine-grain level, taking advantage of the user authentication and identity information sent to the device from the CPPM. The CPPM acts as the authentication source. It uses its own internal RADIUS server to authenticate users. It can also rely on an external authentication source to perform the authentication for it, such as an external RADIUS server or Active Directory.
The CPPM authentication is triggered by requests from NAS devices such as switches and access controllers. The CPPM uses the XML portion of the RESTful Web services that the device exposes to it to send in POST request messages to the device authenticated user identity and device posture information.
The firewall and Aruba ClearPass simplify the complex and complicated security tasks required to safeguard company resources and enforce Internet access policy for mobile devices. This security is essential in a network environment that supports the mobile experience and that gives the user latitude to use a wide range of devices, including their own systems, smartphones, and tablets.
Web API Function
The firewall exposes to the CPPM its Web API daemon (webapi) interface that enables the CPPM to integrate with it and efficiently send authenticated user identity information to the device. The Web API daemon acts as an HTTP server in that it implements part of the RESTful Web services that supports concurrent HTTP and HTTPS requests. In this relationship, the CPPM is the client. The Web API daemon is restricted to processing only HTTP/HTTPS requests. Any other type of request it receives generates an error message.
If you are deploying the ClearPass Web API function and Web management at the same time, you must ensure that they use different HTTP or HTTPS service ports. However, for security considerations, we recommend that you use HTTPS instead of HTTP. HTTP is supported primarily for debugging purposes.
When you configure the Web API, you specify a certificate key if you are using HTTPS as the connection protocol. To ensure security, the HTTPS default certificate key size is 2048 bytes. If you do not specify a certificate size, the default size is assumed. There are three methods that you can use to specify a certificate:
-
Default certificate
-
Certificate generated by PKI
-
Custom certificate and certificate key
The Web API supports only the Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) format for the certificate and certificate key configuration.
If you enable the Web API on the default ports—HTTP (8080) or HTTPS (8443)—you must enable
host inbound traffic on the ports. If you enable it on any other TCP port, you must enable
host inbound traffic specifying the parameter any-service. For example:
user@host# set security zones security-zone trust host-inbound-traffic system-services any-service
The Web API daemon runs on the primary Routing Engine in a chassis cluster environment. After an Chassis Cluster switchover, the daemon will start automatically on the new primary Routing Engine. It has no effect on the Packet Forwarding Engine. Web API supports both the IPv4 and IPv6 address user entries obtained from CPPM.
- Integrity of Data Sent from ClearPass to the Firewall
- Data Size Restrictions and Other Constraints
- Posture States and the Posture Group
Integrity of Data Sent from ClearPass to the Firewall
The following requirements ensure that the data sent from the CPPM is not compromised:
-
The Web API implementation is restricted to processing only HTTP/HTTPS POST requests. Any other type of request that it receives generates an error message.
-
The Web API daemon analyzes and processes HTTP/HTTPS requests from only the following dedicated URL:
/api/userfw/v1/post-entry
-
The HTTP/HTTPS content that the CPPM posts to the device must be consistently formatted correctly. The correct XML format indicates a lack of compromise, and it ensures that user identity information is not lost.
Data Size Restrictions and Other Constraints
The following data size restrictions and limitations apply to the CPPM:
-
The CPPM must control the size of the data that it posts. Otherwise the Web API daemon is unable to process it. Presently the Web API can process a maximum of 2 megabytes of data.
-
The following limitations apply to XML data for role and device posture information. The Web API daemon discards XML data sent to it that exceeds these amounts (that is, the overflow data):
-
The firewall can process a maximum of 209 roles.
-
The firewall supports only one type of posture with six possible posture tokens, or values. Identity information for an individual user can have only one posture token.
-
The CPPM checks the health and posture of a firewall and it can send that information to the firewall as part of the user information that it posts.
-
You cannot define posture on the firewall. Also, firewall does not check posture information that it receives.
-
Posture States and the Posture Group
User, role, and posture token fields are distinct in the context of the CPPM. Each set of
user identity information contains user and role (group) identity and a posture token.
Because the firewall supports only user and role (group) fields, the posture token value
is mapped to a role by adding the prefix posture–. You can then use that
role in a security policy as a group and that policy will be applied to all traffic that
matches the policy.
The predefined posture identity states are:
-
posture-healthy (HEALTHY)
-
posture-checkup (CHECKUP)
-
posture-transition (TRANSITION)
-
posture-quarantine (QUARANTINE)
-
posture-infected (INFECTED)
-
posture-unknown (UNKNOWN)
User Query Function
You can obtain user authentication and identity information for an individual user when that information is not posted directly to the firewall by the ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM).
It can happen that the CPPM does not send user authentication information for a user, for various reasons. When traffic from that user arrives at the firewall, the firewall cannot authenticate the user. If you configure the device to enable the user query function, it can query the ClearPass webserver for authentication information for an individual user. The device bases the query on the IP address of the user’s device, which it obtains from the user’s access request traffic.
If the user query function is configured, the query process is triggered automatically when the device does not find an entry for the user in its ClearPass authentication table when it receives traffic from that user requesting access to a resource or the Internet. The firewall does not search its other authentication tables. Rather, it sends a query to the CPPM requesting authentication information for the user. In this example:
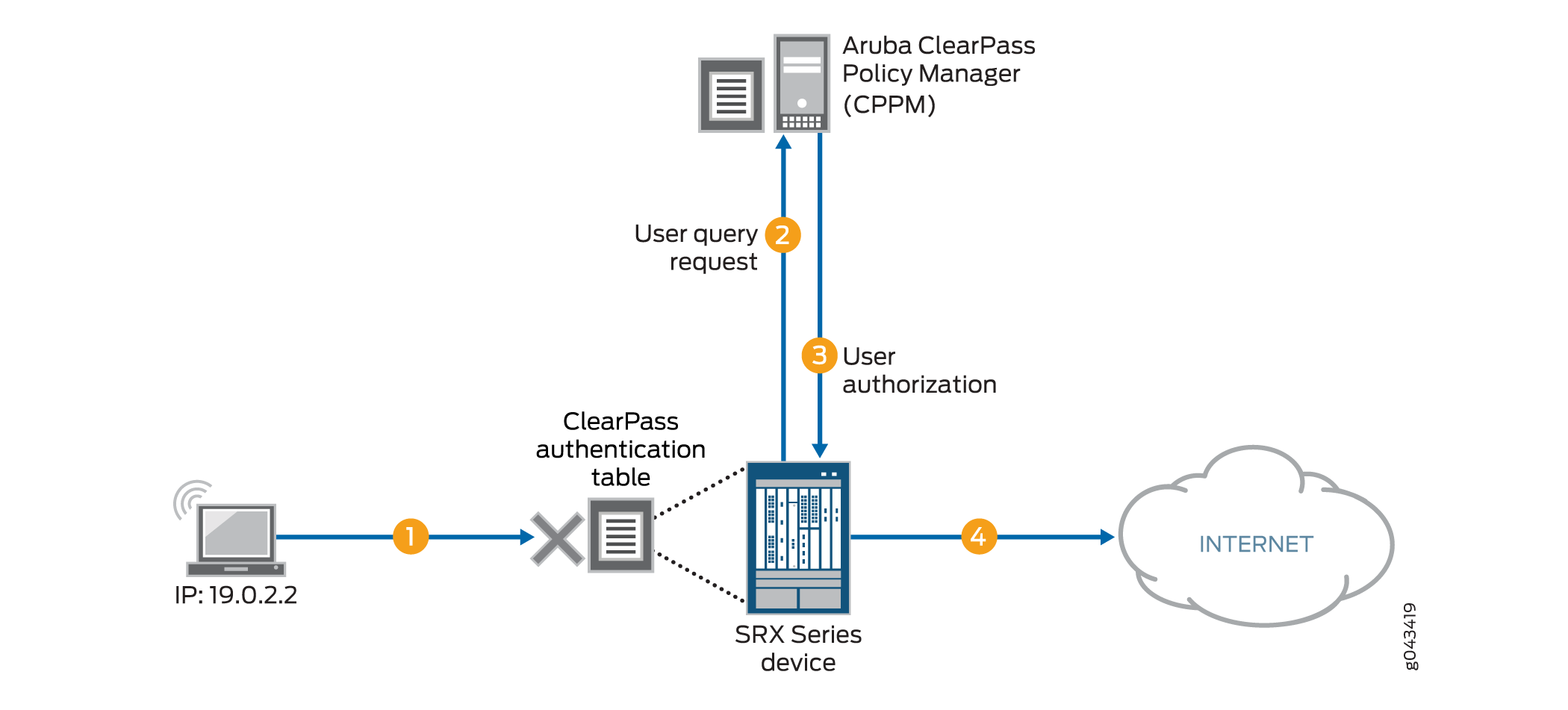
-
A user attempts to access a resource. The firewall receives the traffic requesting access. The firewall searches for an entry for the user in its ClearPass authentication table, but none is found.
The firewall requests authentication for the user from the CPPM.
The CPPM authenticates the user and returns the user authentication and identity information to the device.
The firewall creates an entry for the user in its ClearPass authentication table, and grants the user access to the Internet.
You can control when the device sends its requests automatically by configuring the following two mechanisms:
-
The
delay-query-timeparameterTo determine the value to set for the
delay-query-timeparameter, it helps to understand the events and duration involved in how user identity information is transferred to the device from ClearPass. Thedelay-query-timeparameter influences the query process:A delay is incurred from when the CPPM initially posts user identity information to the device using the Web API to when the device can update its local ClearPass authentication table with that information.
The user identity information must first pass through the ClearPass device’s control plane and the control plane of the device. In other words, this process can delay when the firewall can enter the user identity information in its ClearPass authentication table.
While this process is taking place, traffic might arrive at the device that is generated by an access request from a user whose authentication and identity information is in transit from ClearPass to the device.
Rather than allow the device to respond automatically by sending a user query immediately, you can set a
delay-query-timeparameter, specified in seconds, that allows the device to wait for a period of time before sending the query.After the delay timeout expires, the firewall sends the query to the CPPM and creates a pending entry in the Routing Engine authentication table. During this period, the traffic matches the default policy and is dropped or allowed, depending on the policy configuration.
If there are many query requests in the queue, the firewall can maintain multiple concurrent connections to ClearPass to increase throughput. However, to ensure that ClearPass is not stressed by these connections, the number of concurrent connections is constrained to no more than 20 (<=20). You cannot change this value.
-
A default policy, which is applied to a packet if the firewall does not find an entry for the user associated with the traffic in its ClearPass authentication table.
The system default policy is configured to drop packets. You can override this action by configuring a policy that specifies a different action to apply to this traffic.
|
Active Directory Is Configured |
ClearPass User Query Function Is Enabled |
CLI Check Result |
|---|---|---|
|
No |
No |
Pass |
|
No |
Yes |
Pass |
|
Yes |
No |
Pass |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Fail |
To avoid the failure condition reflected in the bottom row of the table, you must disable either Active Directory or the user query function. If both are configured, the system displays the following error message:
The priority of CP auth source is higher than AD auth source, and the CP user-query will shadow all AD features. Therefore, please choose either disabling CP user-query or not configuring AD.
In its response to the user query request, the ClearPass web server returns information for the user’s device whose IP address was specified in the request. This response includes a time stamp, which is expressed in UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) as defined by ISO 8601.
Here are some examples:
-
2016-12-30T09:30:10.678123Z
-
2016-12-30T09:30:10Z
-
2016-06-06T00:31:52-07:00
|
Format Component |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
YYYY |
two-digit month |
|
DD |
two-digit day of month |
|
hh |
two-digits of hour (00 through 23) |
|
mm |
two-digits of minute |
|
ss |
two-digits of second |
|
s |
one or more digits representing a decimal fraction of a second |
|
TZD |
time zone designator: Z or +hh:mm or -hh:mm |
Filter and Rate-limit Threat and Attack Logs
The firewall transmits the threat and attack logs recorded to the ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM). CPPM can use the log data to harden the security. You can also configure the threats and attacks related to a specific device and their users. For more information, see Example: Configure ClearPass to Filter and Rate-limit Threat and Attack Logs.
- How ClearPass Detect Threats and Attacks and Notifies the CPPM
- Threat and Attack Logs Sent to Aruba ClearPass
How ClearPass Detect Threats and Attacks and Notifies the CPPM
When the firewall detect threat and attack events, the event is recorded in the firewall event log. The firewall uses syslog to forward the logs to the CPPM. The CPPM can evaluate the logs and take action based on matching conditions. As administrator of ClearPass, you can use the information from the firewall and define appropriate actions on the CPPM to harden your security.
Junos OS on the firewall generates over 100 different types of log entries issued by more than 10 of its modules. Among the firewall that generate threat and attack logs are SCREENS, IDP, and Content Security. To avoid overburdening the firewall and the log server, the ClearPass allows you to configure the firewall to send to the CPPM only attack and threat log entries that were written to the event log in response to activity detected by the SCREENS, IDP, and Content Security features.
You can set the following conditions to control the log transmission:
-
A log stream filter to ensure that only threat and attack logs are sent.
-
A rate limiter to control the transmission volume. The device log transmission will not exceed the rate-limiting conditions that you set.
For the CPPM to analyze the log information that the sends to it, the content must be formatted in a standard, structured manner. The firewall log transmission follows the syslog protocol, which has a message format that allows vendor-specific extensions to be provided in a structured way.
|
Log Entry Component |
Meaning |
Format |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Priority |
pri = LOG_USER + severity. Version is always 1 |
pri version |
<14>1 |
|
Time and Time Zone |
When the log was recorded and in what time zone. |
y-m-dThs.ms+time zone
|
2014-07-24T1358.362+08:00 |
|
Device/Host Name |
Name of the device from which the event log was sent. This value is configured by the user. |
string, hostname |
bjsolar |
|
Service Name |
Firewall feature that issued the event log. |
string service |
SERVICE_IDP |
|
Application Name |
Application that generated the log entry. |
string application-name |
NONE |
|
PID |
Process ID. The process ID is not meaningful in this context, so pid is replaced by “-”. The value “-” is a placeholder for process ID. |
pid |
- |
|
Errmsg Tag |
Log ID name, error message tag. |
string, log-name and tag |
IDP_ATTACK_LOG_EVENT |
|
Errmsg Tag Square Bracket |
Log content enclosed in square brackets. |
[ ] |
- |
|
OID |
Product ID provided by the chassis daemon (chassisd). |
junos@oid |
junos@2636.1.1.1.2.86 |
|
Epoch Time |
The time when the log was generated after the epoch. |
number |
1421996988 |
Threat and Attack Logs Sent to Aruba ClearPass
The firewall and enforcement feature collaborates with Aruba ClearPass in protecting a company’s resources against potential and actual attacks through use of attack and threat event logs. These logs that are generated by the Firewall SCREENS, IDP, and Content Security components clearly identify the types of attacks and threats that threaten a company’s network security.
The firewall filters from the overall log entries the logs that report on threat and attack events, and it forwards these log entries to the ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) to be used in assessing and enforcing the company’s security policy. The firewall transmits the logs in volumes determined by the rate-limiting conditions that you set.
|
Log Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
RT_SCREEN_ICMP |
ICMP attack |
|
RT_SCREEN_ICMP_LS |
|
|
RT_SCREEN_IP |
IP attack |
|
RT_SCREEN_IP_LS |
|
|
RT_SCREEN_TCP |
TCP attack |
|
RT_SCREEN_TCP_LS |
|
|
RT_SCREEN_TCP_DST_IP |
TCP destination IP attack |
|
RT_SCREEN_TCP_DST_IP_LS |
|
|
RT_SCREEN_TCP_SRC_IP |
TCP source IP attack |
|
RT_SCREEN_TCP_SRC_IP_LS |
|
|
RT_SCREEN_UDP |
UDP attack |
|
RT_SCREEN_UDP_LS |
|
|
AV_VIRUS_DETECTED_MT |
Virus infection A virus was detected by the antivirus scanner. |
|
AV_VIRUS_DETECTED_MT_LS |
|
|
ANTISPAM_SPAM_DETECTED_MT |
spam The identified e-mail was detected to be spam. |
|
ANTISPAM_SPAM_DETECTED_MT_LS |
|
|
IDP_APPDDOS_APP_ATTACK_EVENT |
Application-level distributed denial of service (AppDDoS) attack The AppDDoS attack occurred when the number of client transactions exceeded the user-configured connection, context, and time binding thresholds. |
|
IDP_APPDDOS_APP_ATTACK_EVENT_LS |
|
|
IDP_APPDDOS_APP_STATE_EVENT |
AppDDoS attack The AppDDoS state transition occurred when the number of application transactions exceeded the user-configured connection or context thresholds. |
|
IDP_APPDDOS_APP_STATE_EVENT_LS |
|
|
IDP_ATTACK_LOG_EVENT |
Attack discovered by IDP IDP generated a log entry for an attack. |
|
IDP_ATTACK_LOG_EVENT_LS |
ClearPass with JIMS
The firewall relies on Juniper Identity Management Service (JIMS) and ClearPass for user identity information. You can configure ClearPass and Juniper Identity Management Service (JIMS) at the same time. When you configure ClearPass and JIMS at the same time, the firewall can query JIMS for user identification entries, and ClearPass can push these entries to the devices through the Web API. For more information, see Example: Configure ClearPass with JIMS.
How ClearPass works with JIMS?
When a user gets authenticated by CPPM, the CPPM uses a Web API to push user or device information to a firewall. The firewall builds up the authentication entry or device information for the user, and the user traffic can pass-through the firewall based on security policy. When windows Active Directory client log on to domain, firewall obtains client’s user or device information from JIMS via batch query. The authentication table gets updated with entry provided by JIMS. The user traffic can pass-through the device based on security policy.
When both JIMS IP query and ClearPass user query are enabled, firewall always queries ClearPass first. If CPPM returns with IP-user mapping information, then the information is subsequently added to authentication table. If CPPM does not return the IP-user mapping information or if a firewall receives a response from CPPM without IP-user mapping, then the firewall queries JIMS to obtain IP-user or group mapping.
When the IP-user or group mapping is received from both JIMS and CPPM, firewall considers the latest authentication entries and overwrites the existing authentication entries.
You can set a delay-query-time parameter, specified in seconds, that
allows the device to wait for a period of time before sending the query. The delay time
should be the same value for ClearPass and JIMS. Otherwise, an error message is displayed
and the commit check fails.
When the IP-user or group mapping is received from both JIMS and CPPM, the device considers the latest authentication entries and overwrites the existing authentication entries.
Different Scenarios of how ClearPass works with JIMS
A detailed explanation with scenarios of how ClearPass with JIMS works is as follows:
Scenario 1: What Firewall Does If CPPM Responds with IP-User or Group Mapping Information
Figure 4 shows when an firewall queries CPPM for IP-user or group mapping information and adds to the authentication table.
-
A user attempts to access a resource. When the firewall receives the traffic request, it searches for an entry for the user in its ClearPass authentication table and the local Active Directory authentication table, but the user information is not found.
-
The firewall queries ClearPass for user identity.
-
The ClearPass sends the IP-user or group mapping information to the firewall.
-
The firewall adds the information to the authentication table.
Figure 4: What Firewall Does If CPPM Responds with IP-User or Group Mapping Information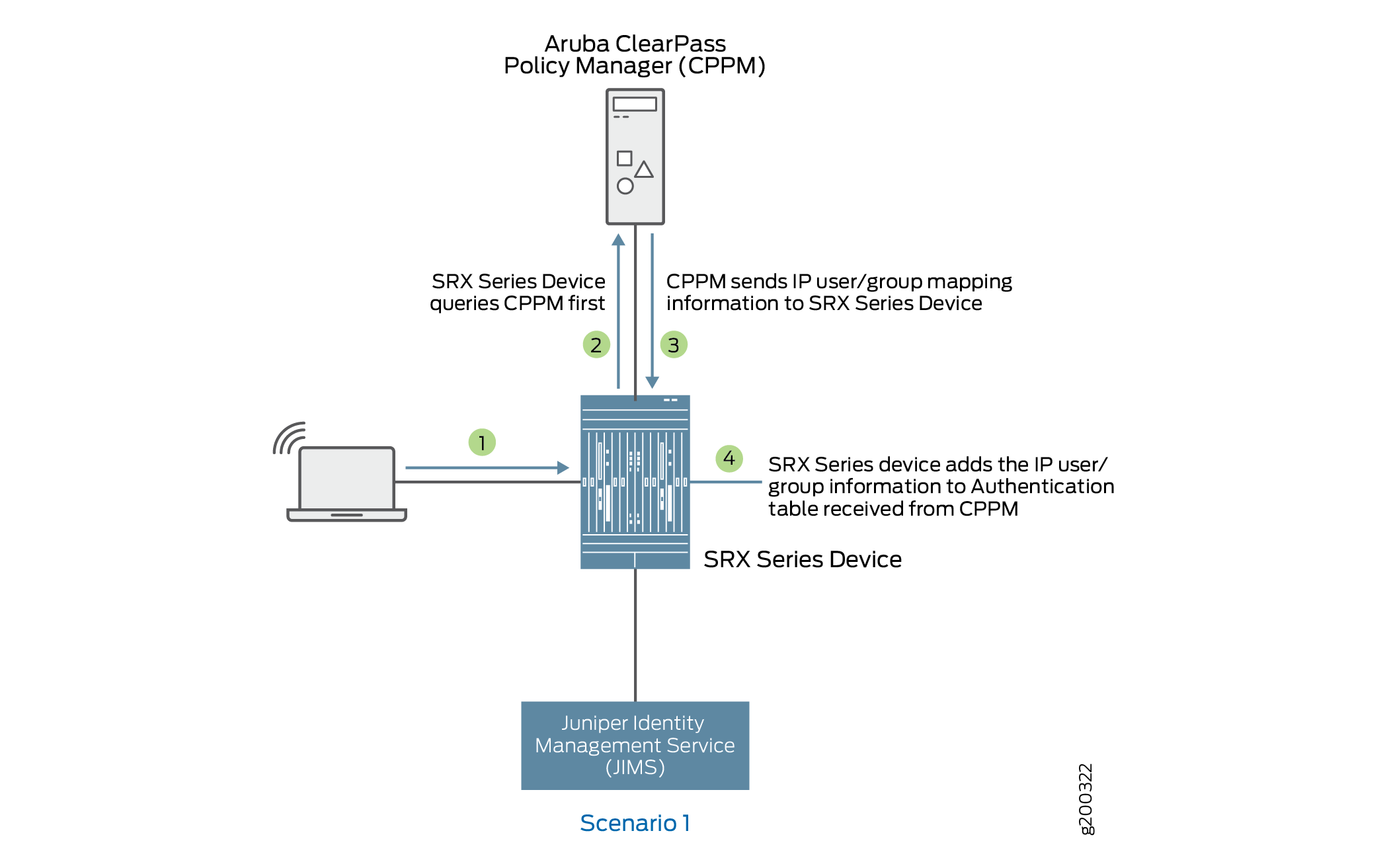
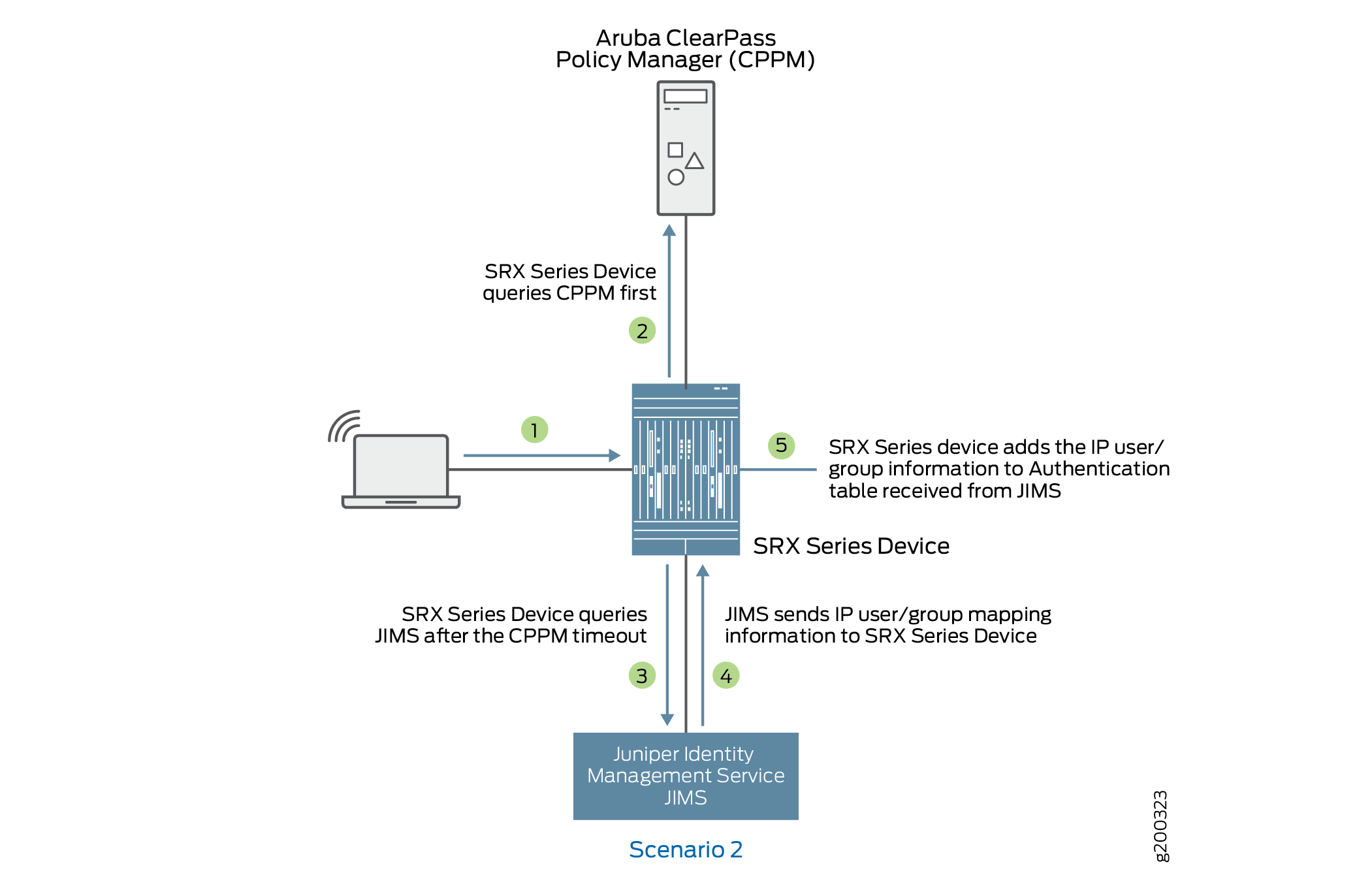
Scenario 2: What Firewall Does If CPPM Does Not Respond or CPPM Responds with No IP-User or Group Mapping Information
Figure 5 shows when an firewall queries JIMS if there is no response or no IP-user or group mapping information received from CPPM.
-
A user attempts to access a resource. When the firewall receives the traffic request, it searches for an entry for the user in its ClearPass authentication table and JIMS authentication table, but the user information is not found.
-
The firewall queries ClearPass for user identity.
-
If the firewall does not receive a response from ClearPass, the firewall queries JIMS.
-
The JIMS sends IP-user or group mapping information to the firewall.
-
The firewall adds the information received from JIMS to the authentication table.
Domain and Interested Groups
How the user identity group information is managed on the device is dominated by two concepts: Domain group and Interested group.
Domain Group
The device follows the usual course in regard to how it handles usernames in domain
namespaces. It makes use of the namespace to distinguish names that are the same–such as
admin—but that are from different sources and are in different domains.
Because they belong to different domains, the names are not in conflict.
Any group that is part of an IP-user mapping will always belong to a domain, whether that domain is a specific domain or the GLOBAL domain. If a domain name is not specified in the IP-user mapping, then the GLOBAL domain is assumed.
|
Does the IP-User Mapping Contain a Domain Name? |
What Domain Is Applied to the Group? |
|---|---|
|
No For example: IP, , user1, group-list The second comma serves as a placeholder for the domain name and the GLOBAL domain is applied. |
Groups included in group-list belong to the GLOBAL domain. |
|
Yes For example: IP, domain1, user1, group-list In this example, the IP-user mapping specifies the domain name as domain1. |
The domain name, domain1, is included in the IP-user mapping from the CPPM, and it is used. It is retained in the entry for the authenticated user in the ClearPass authentication table on the Packet Forwarding Engine. |
Interested Group
A group qualifies as an interested group if it is referenced by a security policy–that is, if it is specified in a policy’s source-identity field. On the Routing Engine authentication table, each user entry contains a group referenced by a policy list that identifies the names of the groups for which a security policy exists. If a group included in a user entry is not currently used in a security policy, it is not included in this list. A group can move in and out of the groups referenced by a policy list.
-
Interested group lists
An interested group list, or a list of groups referenced by policies, is a subset of overall groups. It is the intersection of the group list in a user authentication entry and the source-identity list for security policies. That is, any group included in a ClearPass authentication table user entry qualifies as an interested group. The Routing Engine synchronizes to the user entry in the ClearPass authentication table on the Packet Forwarding Engine only those groups that are referenced by security policies.
Here is how it works:
-
The UserID daemon gets the full IP-user role (group) mapping from the CPPM.
-
For each group, the UserID daemon identifies whether it is an interested group by determining if there is a security policy that references it. Any qualifying groups are included in the groups referenced by a policy list on the Routing Engine. The UserID daemon synchronizes to the user entry in the ClearPass authentication table on the Packet Forwarding Engine interested groups along with the rest of the user authentication and identity information.
The interested groups list for a user entry on the Routing Engine can change, based on the following events:
-
A new security policy is configured that references a group included in the user entry on the Routing Engine but that is not already in the entry’s referenced groups list.
-
A currently configured security policy that references a group in its source-identity is deleted.
Consider the following example:
-
Assume that the CPPM posted the following information for two users to the firewall:
192.51.100.1, abe, group1, group2, group3, group4, healthy 192.0.2.21, john, group1, group5, healthy
-
After the device maps the posture, defining it as a group, the two user entries in the device Routing Engine authentication table appear as follows:
192.51.100.1, abe, group1, group2, group3, group4, posture-healthy 192.0.2.21, john, group1, group5, posture-healthy
-
Assume that several security policies include source-identity fields that reference one of the following: group1, group3, posture-healthy.
The intersection of the preceding sets—the original group list and the list of security policies that refer to the groups—results in the following interested groups list:
-
For the user john, the groups referenced by policy list includes group1 and posture-healthy.
-
For the user abe, the groups referenced by policy list includes group1, group3, and posture-healthy.
-
Now suppose that the security policy whose source-identity field specified group1 was deleted. The groups referenced by policy lists for the user authentication entries for the two users—john and abe—would be changed, producing the following results:
-
For the user john, the list would include only posture-healthy.
-
For the user abe, the list would include group3 and posture-healthy.
-
Table 6 shows the effect on the ClearPass authentication table when a group is not referenced by a security policy, and therefore is not an interested group.
|
Security Policies Configuration and Modification |
Resulting Effect on ClearPass Authentication Table Packet Forwarding Engine Entries |
|---|---|
|
Case 1: The firewall gets the IP-user mapping for a user from the CPPM. None of the groups in the user mapping are referenced by security policies. |
|
|
IP-user mapping from the CPPM: 203.0.113.9, ,user1, g1, g2, g3, g4 |
The user authentication entry written to the ClearPass authentication table in the Packet Forwarding Engine for this user does not contain any groups. 203.0.113.9 , ,user1 |
|
Case 2: The firewall gets the IP-user mapping for a user from the CPPM. It checks the groups list against the security policies list and finds that two of the groups are referenced by security policies. |
|
|
IP-user mapping on the Routing Engine: 192.0.2.1, domain1, user2, g1, g2, g3, g4 |
The user authentication entry written to the ClearPass authentication table on the Packet Forwarding Engine for this user includes the following groups that are included in the groups referenced by the policy list on the Routing Engine: 192.0.2.1, domain1, user2, g2, g4 |
When a user has already been authenticated by another source
It can happen that the device Routing Engine authentication table and the individual Microsoft Active Directory authentication table on the Packet Forwarding Engine, for example, contain an entry for a user who was authenticated by Active Directory. As usual, the CPPM sends the IP-user mapping for the user to the device. The device must resolve the problem because its Routing Engine authentication table is common to both Active Directory and ClearPass.
Here is how the device handles the situation:
-
On the Routing Engine authentication table:
-
The device overwrites the Active Directory authentication entry for the user in its common Routing Engine authentication table with the newly generated one from the IP-user mapping for the user from the CPPM.
There is now no IP address or username conflict.
-
-
On the Packet Forwarding Engine:
-
The device deletes the existing Active Directory authentication entry for the user from the Active Directory authentication table.
This will delete active sessions associated with the IP address.
-
The device generates a new entry for the CPPM-authenticated user in the Packet Forwarding Engine ClearPass authentication table.
Traffic associated with the IP-user mapping entry will initiate new sessions based on user authentication in the ClearPass authentication table.
-
ClearPass Authentication Table
The firewall receives information from the CPPM. The firewall extracts the user authentication and identity information, and analyzes it. The firewall creates a ClearPass authentication table on the Packet Forwarding Engine side to hold this user information. When the firewall receives the information from ClearPass, the firewall generates entries in the ClearPass authentication table for the authenticated users. When the firewall receives an access request from a user, it can check its ClearPass authentication table to verify that the user is authenticated, and then apply the security policy that matches the traffic from the user.
The default priority value for the ClearPass authentication table is 110. You must change the local authentication table entry from 100 to 120 to direct the firewall to check the ClearPass authentication table first if there are other authentication tables on the Packet Forwarding Engine.
- How the Firewall manages the ClearPass Authentication Table?
- User Authentication Entries in the ClearPass Authentication Table
How the Firewall manages the ClearPass Authentication Table?
The firewall gets authenticated user identity information from the CPPM, generates entries in its ClearPass authentication table, and manages those entries in relation to security policies and user events. ClearPass acts as the authentication source for the firewall. The CPPM sends to the firewall identity information about users that it has authenticated. The UserID daemon process in the firewall receives this information, processes it, and synchronizes it to the Packet Forwarding Engine side in the independent ClearPass authentication table that is generated for this purpose.
As administrator of the device, you can use the authenticated user identity information in security policies to control access to your protected resources and the Internet.
The collection of user identity information that the device obtains from the CPPM and uses to create entries in its global Routing Engine authentication table that is synchronized to its individual ClearPass authentication table is referred to as a mapping, or, more commonly, an IP-user mapping because the username and the related group list are mapped to the IP address of the user’s device.
For each user authentication entry in the ClearPass authentication table, a group list identifies the groups that a user belongs to in addition to other information such as the posture token, which indicates state of the device, such as whether it is healthy.
User Authentication Entries in the ClearPass Authentication Table
You can use a username or a group name in security policies to identity a user and not rely directly on the IP address of the device used, because the IP address of the firewall is tied to the username and its groups in the ClearPass authentication table entry. For each user authentication entry in the ClearPass authentication table, a group list identifies the groups that a user belongs to in addition to other information such as the posture token, which indicates state of the device, such as whether it is healthy. The ClearPass authentication will manage up to 2048 sessions for each user for whom there is a user identity and authentication entry in the authentication table.
For each user entry, the number of groups, or roles, in the entry cannot exceed 200. After the capacity is reached, additional roles are discarded and the following syslog message is sent:
userid_get_and_check_adauth_num: src_ip ip-address user domain:user dropped.record numrecord-number has arrived max num of db
The CPPM posts user information to the device in the following format. The device does not use all of this information.
<userfw-entries>
<userfw-entry>
<source>Aruba ClearPass</source>
<timestamp>2016-01-29T0310Z</timestamp>
<operation>logon</operation>
<IP>192.0.2.123</IP>
<domain>my-company-domain</domain>
<user>user1</user>
<role-list>
<role>human-resources-grp</role>
<role>[User Authenticated],/role>
</role-list>
<posture>HEALTHY</posture>
<device_category>Computer</device_category>
</userfw-entry>
</userfw-entries>
Here is the format for a ClearPass authentication table entry for a user, followed by an example entry and a description of its components.
IP-address, domain, user, user-group-list
In the following example, the user belongs to two groups, the human-resources-grp group and the posture-healthy group. The firewall converts the posture information from the CPPM to a group name. You might configure a security policy that allows all users access to the marketing server if their devices belong to the posture-healthy group (role).
192.0.2.11 , my-company-domain, lin, human-resources-grp, posture-healthy
-
IP address
This is the IP address of the device used.
-
The name of the domain that the user belongs to.
In this example, the domain name is “my-company-domain.” The default domain name GLOBAL is used if a domain name is not provided.
-
The username
The username is the user’s login name used to connect to the network, which, in this example, is lin.
This name is constant regardless of the device used.
When you configure a security policy whose source-identity tuple identifies the source of the traffic by username or group name, not by the IP address of the device used, it is as if the security policy were device independent; it applies to the user’s activity regardless of the device used.
-
One or more groups that a user belongs to
It is here where the concept of interested groups and their relationship to security policies comes into play. An interested group is a group that is referenced in a security policy. The concept of interested groups is covered later in this topic.
Note that if a user is connected to the network using multiple devices, there might be more than one IP-user mapping for that user. Each mapping would have its own set of values—that is, domain name and group-list—in conjunction with the username and IP address.
For example, the following three IP address-to-username mappings might exist for the user abe who is connected to the network using three separate devices:
203.0.113.5 abe, marketing-grp, posture-healthy 192.0.2.34 abe, marketing-grp, posture-transition 203.0.133.19 abe, marketing-grp, posture-unknown
Assume that the firewall receives a logout message for 110.208.132.23, abe. The following partial user authentication entry shows that the user abe is now logged in to the network using only two devices:
192.0.2.34 abe, marketing-grp, posture-transition 203.0.133.19 abe, marketing-grp, posture-unknown
If more than 2048 sessions are associated with a single authentication entry in the ClearPass authentication table, the active directory for ClearPass will not manage the sessions that caused the overflow. Consequently, there will be no user identification information for those sessions reported in the session close log for those sessions.
ClearPass Timeout Setting
What is timeout setting for Aruba ClearPass?
Authentication entries in the Aruba ClearPass authentication table contain a timeout value after which the entry expires. You can protect invalid user authentication entries in an authentication table from expiring before the user can be validated by configuring a timeout setting that is specific to invalid entries. The invalid authentication entry timeout setting is separate from the common authentication entry timeout setting that is applied to valid entries.
For the ClearPass feature, if an unauthenticated user attempts to join the network and the IP address of the user’s device is not found—that is, it is not in the Packet Forwarding Engine—the device queries Aruba ClearPass for the user’s information. If the query is unsuccessful, the system generates an INVALID authentication entry for the user. If you configure a value for the invalid timeout setting, that timeout is applied to the entry. If you don't configure the invalid entry timeout, then its default timeout of 30 minutes is applied to the new entry. The invalid entry timeout is also applied to entries whose state is changed from valid or pending to INVALID.
How timeout setting for Aruba ClearPass works?
Use the following command to configure the invalid authentication entry timeout for entries in the ClearPass authentication table. Here, invalid authentication entries in the ClearPass authentication table expires 22 minutes after they are created.
user@host# set services user-identification authentication-source aruba-clearpass invalid-authentication-entry-timeout 22
-
When you initially configure the invalid authentication entry timeout value for ClearPass, it is applied to any invalid authentication entries that are generated after it was configured. However, all existing invalid authentication entries retain the default timeout of 30 minutes.
-
If you do not configure the invalid authentication entry timeout setting, the default timeout of 30 minutes is applied to all invalid authentication entries.
If you configure the invalid authentication entry timeout setting and delete it later, the default value is applied to new invalid authentication entries generated after the deletion. However, any existing invalid authentication entries to which a configured value had been applied previously retain that value.
-
If you change the setting for the invalid authentication entry timeout value, the new value is applied to all invalid authentication entries that were created after the value was changed. However, all existing invalid authentication entries retain the former invalid authentication entry timeout setting applied to them. Those entries to which the default value of 30 minutes had been applied previously retain that setting.
-
When the pending or valid state of an entry is changed to invalid, the invalid authentication entry timeout setting is applied to it.
When the state of an invalid authentication entry is changed to pending or valid, the invalid authentication entry timeout setting is no longer applicable to it. The timeout value set for the common authentication entry timeout is applied to it.
Table 7: Invalid Authentication Timeout for Invalid Entries in the ClearPass Authentication Table Invalid Entry Timeout Setting
Intial Invalid Entry Timeout Setting
Elapse Time
New Invalid Entry Timeout Configuration Setting
Final Timeout Setting for Existing Invalid Entry
New invalid authentication entry
50
50
Existing invalid entry timeout
20
5
50
15
Existing invalid entry timeout
0
40
20
0
Existing invalid entry timeout
40
20
0
20
