Configure External Path Computation Components
This section outlines the steps to install the cPCE container and cPCEPAdaptor in a Linux server environment that is running Ubuntu or Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). The cPCE and cPCEPAdaptor containers are packaged in a Docker image and run in the Docker Engine on the Linux host.
Overview
In the Figure 1, R1 is the Path Computation Client (PCC). Traffic engineered tunnels are configured and delegated to cPCE. This section provides information on how you can configure the connections between the cPCE, cPCEPAdaptor and the BGP link-state sessions necessary for topology acquisition.
You can install both the cPCE and cPCEPAdaptor on same server or on different hosts or routers that support the docker environment. The cPCEPAdaptor manages the PCEP sessions with the PCCs. Theis section describes how you can configure the gRPC connection between one or more PCCs and a cPCEPAdaptor. The cPCEPAdapter requires a set of gRPC connection parameters to be configured for establishing and maintaining a gRPC channel with the cPCE path computation service.
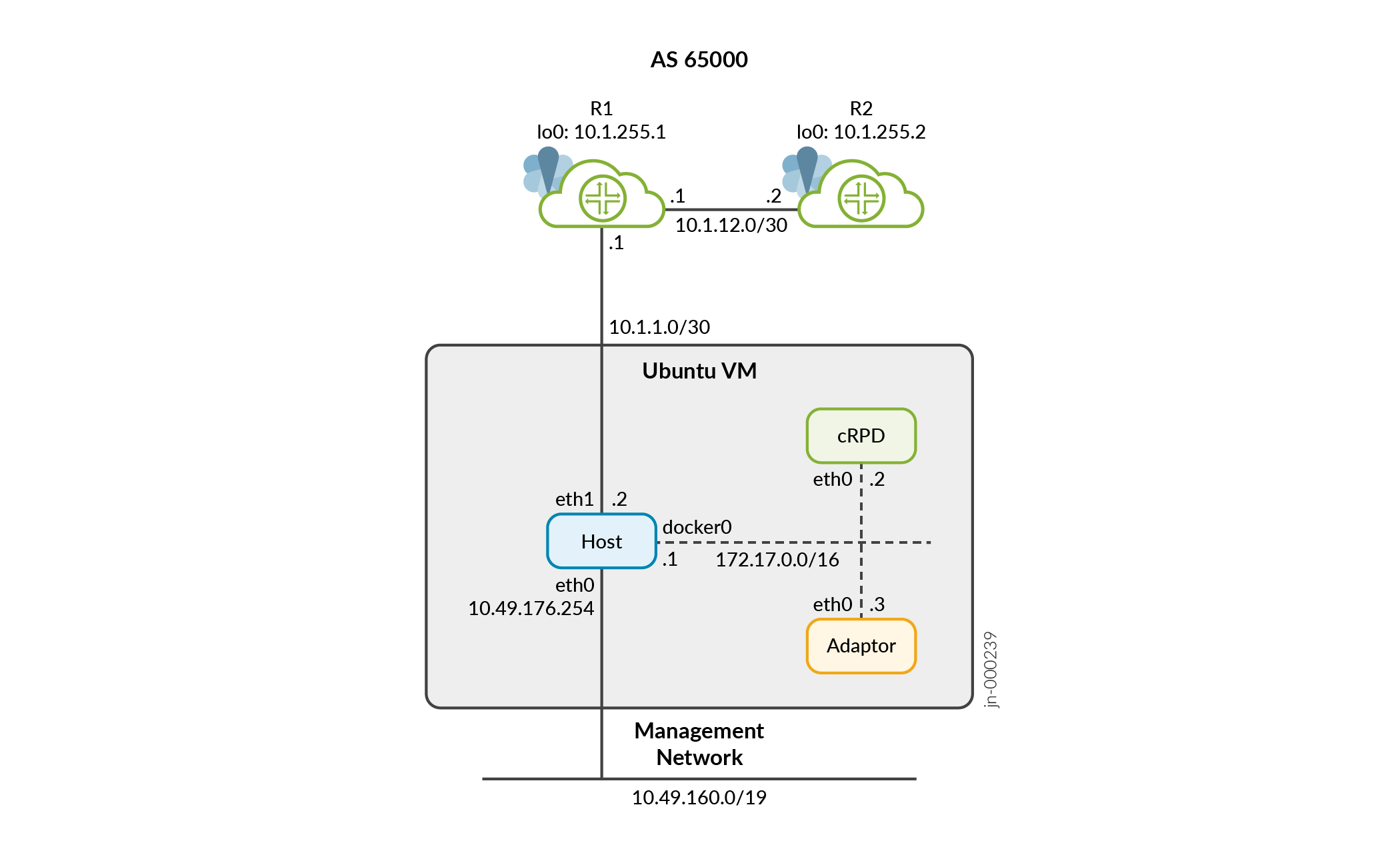
The PCC (R1) and cPCEPAdaptor communicate through standard PCEP messages. The cPCEPAdaptor and the cPCE communicate through gRPC messages. In this topology, IP address 10.1.255.1 is the loopback address or the router Id of the PCC (R1) router. The loopback address or the router Id of the PCC (R2) router is 10.1.255.2.
The cPCE requires a set of connection parameters to establish a gRPC channel with the cRPD for path computation service.
Configure cPCE
To configure cPCE:
-
Set the root authentication password by entering a cleartext password, an
encrypted password, or an SSH public key string (DSA or RSA).
root@cRPD-cpce# set system root-authentication plain-text-passwordNew password: xxx Retype new password: xxx
-
Specify the IP address and the port number to build the gRPC connection
between cPCEPAdaptor and cPCE.
[edit system services]
root@cRPD-cpce# set extension-service request-response grpc clear-text port 50051root@cRPD-cpce# set extension-service request-response grpc clear-text address 0.0.0.0root@cRPD-cpce# set extension-service request-response grpc max-connections 30 -
Configure a policy statement to import the BGP-LS acquired topology into
the local traffic-engineering database.
[edit policy-options]
root@cRPD-cpce# set policy-statement bgpl2_rt_2_ted term 1 from family traffic-engineeringroot@cRPD-cpce# set policy-statement bgpl2_rt_2_ted term 1 then accept[edit protocols mpls]root@cRPD-cpce# set traffic-engineering database export policy bgpl2_rt_2_tedConfigure if cPCE is catering to segment routing traffic-engineering paths.
[edit protocols mpls]root@cRPD-cpce# set traffic-engineering database export l3-unicast-topology -
Configure the autonomous system number and establish reachability to the
network. For example, a static route to Router R1.
[edit routing-options]
root@cRPD-cpce# set autonomous-system 65000root@cRPD-cpce# set static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 172.17.0.1 -
Configure topology acquisition using BGP-LS on cPCE.
The PCC router should have IP
reachability with the cPCEPAdaptor and cPCE for PCEP session and BGP-LS
session establishment.
[edit protocols bgp]
root@cRPD-cpce# set group 65000 type internalroot@cRPD-cpce# set group 65000 passiveroot@cRPD-cpce# set group 65000 family traffic-engineering unicastroot@cRPD-cpce# set group 65000 allow 0.0.0.0/0 -
Apply templates (optional) that can be applied to the cPCE controlled LSPs
for computing paths and to enable specific timers. For example,
optimize-timer.
[edit protocols mpls]
root@cRPD-cpce# set lsp-external-controller remote-pce pce-controlled-lsp * label-switched-path-template t1root@cRPD-cpce# set label-switched-path t1 templateroot@cRPD-cpce# set label-switched-path t1 optimize-timer 45 -
Commit the configuration.
root@cRPD-cpce# commitcommit complete
Create and Configure cPCEPAdaptor
To configure cPCEPAdaptor:
-
Configure cPCEPAdaptor.
root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# set system root-authentication plain-text-passwordNew password: xxx Retype new password: xxx
-
Configure the gRPC request response service on the adaptor by specifying IP
address and the port number to establish the connection between the
cPCEPAdaptor and cPCE.
[edit system services]
root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# set extension-service request-response grpc clear-text address 0.0.0.0root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# set extension-service request-response grpc clear-text port 50051root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# set extension-service request-response grpc max-connections 30[edit services]root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# set path-computation-adaptor pce cRPD-cpce ipv4-address 172.17.0.2root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# set path-computation-adaptor pce cRPD-cpce port 50051root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# set path-computation-adaptor pce cRPD-cpce login-id rootroot@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# set path-computation-adaptor pce cRPD-cpce password xxxx -
Commit the configuration.
root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# commitcommit complete
Configure R1 as PCC
Establish a Path Computation Element Protocol (PCEP) connection with the cPCEPAdaptor or cPCE. R1 will also be configured to export the traffic-engineering topology to cPCE through BGP-LS.
-
Configure the interfaces of the Router R1.
[edit interfaces]
root@R1# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.1/30root@R1# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.12.1/30root@R1# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family mplsroot@R1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.255.1/32 -
Configure the BGP-LS traffic engineering database import policy.
[edit policy-options]
root@R1 set policy-statement TED_to_BGP-LS term 1 from protocol isisroot@R1 set policy-statement TED_to_BGP-LS term 1 from protocol ospfroot@R1 set policy-statement TED_to_BGP-LS term 1 then accept[edit protocols]root@R1 set mpls traffic-engineering database import policy TED_to_BGP-LS -
Configure the router ID and assign an autonomous system number.
.
[edit routing-options]
root@R1 set router-id 10.1.255.1root@R1 set autonomous-system 65000 -
Configure BGP internal group, the link-state address-family and assign the
export policy
edit [policy-options]
root@R1 set policy-statement export_TED then accept[edit protocols bgp]root@R1 set group 65000 type internalroot@R1 set group 65000 local-address 10.1.255.1root@R1 set group 65000 family traffic-engineering unicastroot@R1 set group 65000 export export_TEDroot@R1 set group 65000 allow 0.0.0.0/0root@R1 set group 65000 neighbor 172.17.0.2 -
Specify the loopback address of the PCC router as the local address and the
destination IP address of the host where cPCEPAdaptor instance is spawned.
Configure the destination port for the PCC (R1) router that connects to the
cPCEPAdaptor using PCEP and the PCE type.
[edit protocols pcep]
root@R1# set pce cPCE1 local-address 10.1.255.1root@R1# set pce cPCE1 destination-ipv4-address 172.17.0.3root@R1# set pce cPCE1 destination-port 4189root@R1# set pce cPCE1 pce-type activeroot@R1# set pce cPCE1 pce-type statefulroot@R1# set pce cPCE1 lsp-provisioningroot@R1# set pce cPCE1 spring-capability -
Configure IS-IS, Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP),
and segment routing to illustrate
external control through cPCE of both traffic engineering (SR-TE) and
RSVP-TE traffic engineered tunnels.
[edit protocols rsvp]
root@R1# set interface ge-0/0/1.0root@R1# set interface lo0.0[edit protocols isis]
root@R1# set interface ge-0/0/1.0root@R1# set interface lo0.0 passiveroot@R1# set source-packet-routing node-segment ipv4-index 401root@R1# set traffic-engineering l3-unicast-topology -
Configure RSVP-TE label-switched path (LSP) and enable external control.
[edit protocols mpls]
root@R1# set lsp-external-controller pccdroot@R1# set interface ge-0/0/1.0root@R1# set label-switched-path to-R2 to 10.1.255.2root@R1# set label-switched-path to-R2 lsp-external-controller pccd -
Configure SR-TE LSP and enable external control.
[edit protocols source-packet-routing]
root@R1# set lsp-external-controller pccd[edit protocols source-packet-routing]root@R1# set source-routing-path computels1 to 10.1.255.2root@R1# set source-routing-path computels1 lsp-external-controller pccdroot@R1# set source-routing-path computels1 primary p1 compute compute1root@R1# set compute-profile compute1 maximum-computed-segment-lists 1 -
Commit the configuration.
root@R1# commit
Configure Router R2
-
Configure interfaces of Router R2.
[edit interfaces]
root@R2# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.12.2/30root@R2# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family mplsroot@R2# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.255.2/32 -
Configure the router ID.
[edit routing-options]
root@R2# set router-id 10.1.255.2 -
Configure MPLS interface.
[edit protocols mpls]
root@R2# set interface ge-0/0/0.0 -
Configure IS-IS, RSVP, and
segment routing .
[edit protocols rsvp]
root@R2# set interface ge-0/0/0.0root@R2# set interface lo0.0[edit protocols isis]
root@R2# set interface ge-0/0/0.0root@R2# set interface lo0.0 passiveroot@R2# set source-packet-routing node-segment ipv4-index 402root@R2# set traffic-engineering l3-unicast-topology -
Commit the configuration.
root@R1# commit
See Also
Verify cPCEPAdaptor Status
-
Verify the gRPC connection and registration status.
root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# run show path-computation-adaptor pce statusPCE IP Port Type Status Elapsed PCE Name Time ------ ---- ---- ------ ------- -------- 172.17.0.2 50051 gRPC Connected 00:00:04 cRPD-cpceroot@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# run show path-computation-adaptor pce statusPCE IP Port Type Status Elapsed PCE Name Time ------ ---- ---- ------ ------- -------- 172.17.0.2 50051 gRPC Registered 00:15:52 cRPD-cpce -
Verify path computation client status. This command displays the list of
PCC routers that established PCEP connection with the cPCEPAdaptor.
root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# run show path-computation-adaptor pccPCC IP Port Session Status Elapsed ID Time ------ ---- ------- ------ ------- 10.1.255.1 53554 2 SessionUP 01:55:48 -
Verify the path computation client lsp information. This command displays
the list of LSPs reported from a given PCC connected to the
cPCEPAdaptor.
root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# run show path-computation-adaptor pcc ip 10.1.255.1 lspTo From State PLSP LSP Setup Control LSP ID ID Type Type Name -- ---- ----- ---- --- ----- ------- ---- 10.1.255.2 10.1.255.1 ACTIVE 1 4 RSVP Delegated to-R2 10.1.255.2 10.1.255.1 ACTIVE 2 0 SR Delegated computels1/p1 Total LSPs: 2 -
Verify the path computation client lsp information for segment
routing.
root@CPCE1-pcepAdaptor# run show path-computation-adaptor pcc ip 10.1.255.1 lsp-name computels1/p1LSP Name: computels1/p1, PLSP ID: 2 PCC ID: 10.1.255.1 Source: 10.1.255.1, Destination: 10.1.255.2 Setup Type: SR Control Type: Delegated (SRP ID: 400018) LSP ID: 0, Tunnel ID: 2, Ext Tunnel ID: 10.1.255.2 State: ACTIVE, Since: 0 Lspflags: Delegate: 1, Sync: 41, Remove: 0, Administrative: 1 Operational: 2, Create: 0, P2MP: 0, Fragmentation: 0 Attributes: Metric Type: TE Priorities (Setup/Hold): 0/0 Include All: 0, Include Any: 0, Exclude All: 0 Eq Cost Tie Breaker: RANDOM Bandwidth: 1036 Computed Path: SID: 1048575 ERO: 10.1.12.1-10.1.12.2 Metrics: 0 Recorded Route: RRO: 10.1.12.1-10.1.12.2 Statistics: RROSID: 1048575 Recent Path Request ID: 10025 Recent Path Response ID: 10023 Total Path Computation Requests sent: 2 Total Path Computation Responses received: 1 Total Unsolicited responses received: 0 Average time for computing the path by cPCE: 9 msec Recent LSP-ID notified to cPCE: 0 Recent LSP-ID received from cPCE: 0 Recent Notified State: Up
Verify BGP on cPCE
-
Verify BGP configuration.
[edit protocols]
root@cRPD-cpce# run show bgp summaryThreading mode: BGP I/O Default eBGP mode: advertise - accept, receive - accept Groups: 1 Peers: 1 Down peers: 0 Unconfigured peers: 1 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending lsdist.0 7 7 0 0 0 0 Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Accepted/Damped... 10.1.255.1 65000 52365 52348 0 0 2w2d 8:29:55 Establ lsdist.0: 7/7/7/0 -
Verify LSP configuration.
root@cRPD-cpce# run show mpls lspIngress LSP: 1 sessions To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname 10.1.255.2 10.1.255.1 Up 0 * 10.1.255.1-to-R2 Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
Verify PCC Status
-
Verify the PCEP session status and LSP summary between the PCC (R1) and the
connected PCEs.
root@R1> show path-computation-client statusSession Type Provisioning Status Uptime cPCE1 Stateful Active On Up 2161 LSP Summary Total number of LSPs : 1 Static LSPs : 0 Externally controlled LSPs : 1 Externally provisioned LSPs : 0/16000 (current/limit) Orphaned LSPs : 0 cPCE1 (main) Delegated : 1 Externally provisioned : 0
root@R1> show mpls lsp ingressIngress LSP: 1 sessions To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname 10.1.255.2 10.1.255.1 Up 0 * to-R2 Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
root@R1> show ospf neighborAddress Interface State ID Pri Dead 10.1.12.2 ge-0/0/1.0 Full 10.1.255.2 128 31
-
Verify LSP configuration.
[edit]
root@R1# run show spring-traffic-engineering lspTo State LSPname 10.1.255.2 Up computels1 Total displayed LSPs: 1 (Up: 1, Down: 0)
root@R1# run show spring-traffic-engineering lsp detailName: computels1 Tunnel-source: Static configuration Tunnel Forward Type: SRMPLS To: 10.1.255.2 Te-group-id: 0 State: Up Path: p1 Path Status: NA Outgoing interface: ge-0/0/1.0 Delegation info: Control-status: Externally controlled Routing-status: Externally routed Auto-translate status: Disabled Auto-translate result: N/A BFD status: N/A BFD name: N/A Segment ID : 128 ERO Valid: true SR-ERO hop count: 1 Hop 1 (Strict): NAI: IPv4 Adjacency ID, 10.1.12.1 -> 10.1.12.2 SID type: 20-bit label, Value: 1048575 Total displayed LSPs: 1 (Up: 1, Down: 0)
