Understand Express Path for CSDS Architecture
Read this topic to learn about offloading services in the CSDS Architecture using Express Path mechanism.
Overview
The Connected Security Distributed Services (CSDS) Architecture improves network performance by efficiently managing the processing of data traffic for both new and existing sessions through a mechanism called Express Path.
Express Path is a key feature within the CSDS Architecture where the vSRX Virtual Firewall can offload security services to the MX Series router using the session-offloading method. Express Path allows direct processing and forwarding of traffic flows in the router, bypassing the firewall in the datapath. However, the firewall retains its management capabilities for these offloaded flows even as the router handles the processing. Express Path redistributes the session processing tasks between the firewalls and routers.
A session is a record of the traffic flow in a stateful connection on a firewall. A flow consists of related packets that share identical characteristics—such as source IP, destination IP, source port, destination port, and protocol—and match specific criteria. The CSDS Architecture uses the Express Path mechanism for offloading the flow. The Express Path session-offloading process allows the firewall to determine when a session doesn't require deep packet inspection (DPI) and subsequently transfers the session to a router.
Benefits
-
Enhanced resource utilization—Enhances resource utilization across the forwarding and services layers by efficiently distributing session processing workloads in the CSDS topology.
-
Optimized performance—Improves network performance by allowing routers to process session data directly, thereby reducing processing overhead and latency.
-
Improved throughput—Improves overall system throughput by minimizing the need for repetitive data inspection.
-
Enhanced security—Provides robust security by leveraging session-aware forwarding and inspecting only the required sessions.
Session-Offloading Workflow
The Figure 1 illustrates the session offloading workflow between the firewalls and the router.
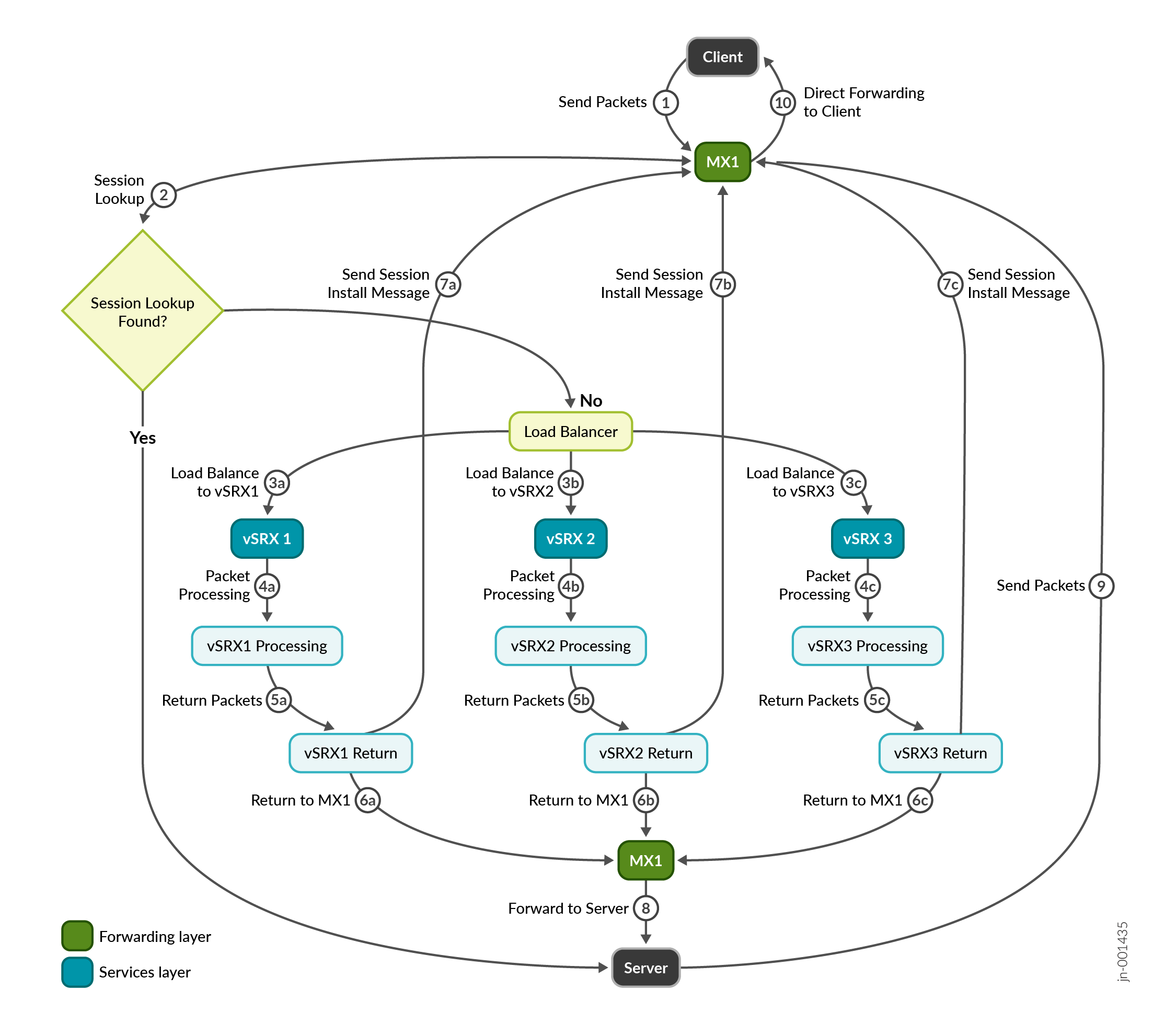
The following steps describe the CSDS traffic workflow using Express Path:
A client initiates traffic destined for a server, and the packets first arrive at the router.
The router performs a session lookup. If it finds an existing session record for this traffic (indicating it was previously offloaded), the router forwards the packets directly to the server after a standard route lookup, bypassing the firewall inspection.
If the router doesn't find a matching session, it treats the traffic as new and load-balances the packets across the available firewalls in the CSDS topology for further inspection and processing.
The firewalls process the packets to perform DPI.
The firewalls prepare the return packets based on the results of the DPI.
After processing and inspection, the firewall sends the packet back to the router.
The firewalls record session details in the session table present on the router.
Once the router updates the session table, subsequent packets that belong to the established session find a match during the session lookup (as described in Step 2). The router performs route lookup and forwards the traffic directly to the server.
The server sends its return traffic packets back to the router.
As the session is established and offloaded, the router performs a session lookup and forwards the return traffic directly to the client.
WHAT's NEXT
Read the following topics to know more.
