IPsec VPN Traffic Flow in a Single MX Series Router (ECMP-Based Consistent Hashing) and Scaled-Out SRX Series Firewalls (Standalone)
In this topic, you’ll see how IPsec traffic flows in a topology that includes a single MX Series router with ECMP-based Consistent Hashing load balancing and standalone SRX Series Firewalls.
See Figure 1 for the topology. In this topology, you must:
- Configure a single MX Series router with two interfaces for the IPSEC VR and Internet routing instances.
- Configure each SRX Series Firewall for AutoVPN and assign the same anycast IP to the loopback interface of the IKE endpoint IP address. Ensure all the SRX Series Firewalls are in IPsec responder-only mode.
- The IPsec tunnels that are initiated from the IPsec initiator behind the MX Series router uses the same SRX Series Firewall IKE endpoint IP address with unique traffic selector. The SRX Series Firewall uses the same traffic selector to install unique Auto Route Insertion (ARI) routes to attract the return data traffic from the server to the correct IPsec tunnel. ARI automatically inserts a static route for the remote network from the Internet side. A route is created based on the remote IP address configured in the traffic selector and is inserted into the IPSEC VR routing instance. See Understanding Auto route Insertion.
- Configure the forwarding table with a load balancing policy with source hash for anycast IP route. The MX Series receives the anycast IP route on IPSEC VR instance and advertises using external BGP to the MX Series on the IPSEC VR side. The MX Series router imports this routes on the IPSEC VR instance using load balancing consistent hash policy.
- The MX Series router on the trust side has ECMP routes for anycast IP address.
Figure 1 illustrates the step-by-step traffic flow.
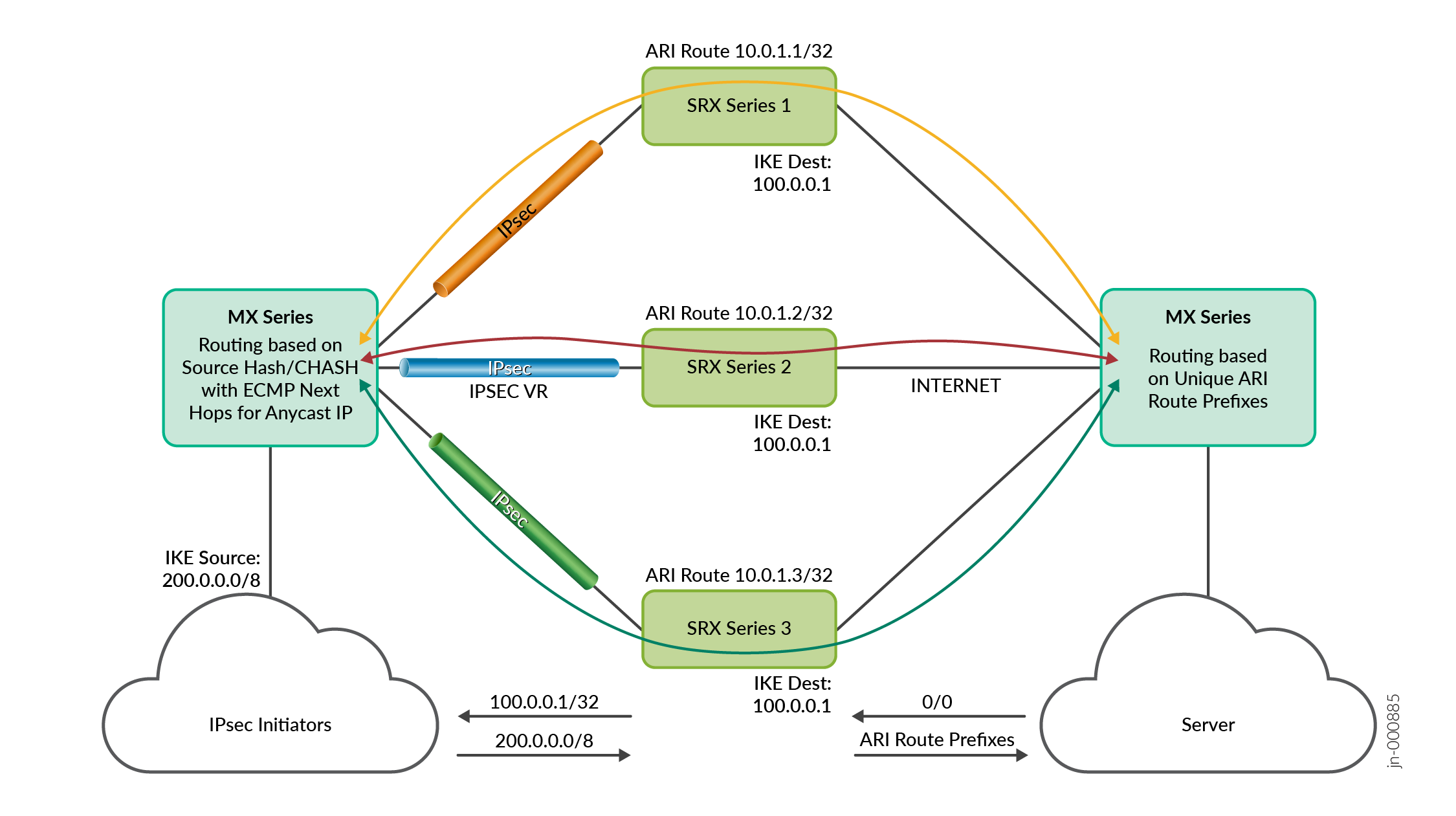
The MX Series router is a single device configured with multiple logical interfaces toward scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls on the IPSEC VR and Internet direction.
The IKE traffic initiated from IPsec initiator router reaches the MX Series router on the IPSEC VR instance and matches the ECMP anycast IP route. The traffic takes one of the ECMP next hops to the SRX Series Firewalls based on the calculated source IP-based hash value.
The SRX Series Firewalls anchors the IKE session and installs the ARI route. The firewalls advertise the ARI route toward the Internet instance of the MX Series router.
The clients connected to the IPsec initiator router initiates the traffic that passes through the IPsec VPN tunnel and reaches the anchored IPsec tunnel on the SRX Series Firewall. The router forwards the cleartext packets from the IPsec VPN tunnel to the Internet direction, allowing the traffic to reach the server.
The IPsec data reply traffic from the server to the client reaches the MX Series router on the Internet instance. The router forwards the traffic through the unique ARI route to the SRX Series Firewall, which anchors the tunnel.
The SRX Series Firewall encrypts and sends the traffic over the tunnel to the IPsec initiator and then to the client.
When an SRX Series Firewall is down, Consistent Hashing on the MX Series router ensures that the sessions on the other SRX Series Firewall continue without any disruption. The impacted SRX Series Firewalls redistribute the IPsec sessions and initiate a new session. DPD timers ensure traffic redistribution during SRX Series Firewall failure or the link failure.
