IPsec Security Services
Juniper Cloud-Native Router (JCNR) offers containerized routing functionality for both cloud-based and on-premise 5G environments. There is a growing demand for integrating security services with JCNR. This functionality can be achieved using host-based service chaining. The cloud-native router is integrated with Juniper's containerized SRX (cSRX) platform to provide security services such as IPsec.
Overview
Let us consider an IPsec security services use case with JCNR. In the figure below, the cloud-native router connects the provider edge (PE) routers in a service provider network. The customer edge (CE) routers or devices in the source network securely transfer data to the destination CEs via an IPsec tunnel. In the given scenario, the IPsec tunnel initiates from the cloud-native router's security services (cSRX) and terminates on the destination CEs. The cloud-native router and its peer PE provides the underlay connectivity to the IPsec tunnel.
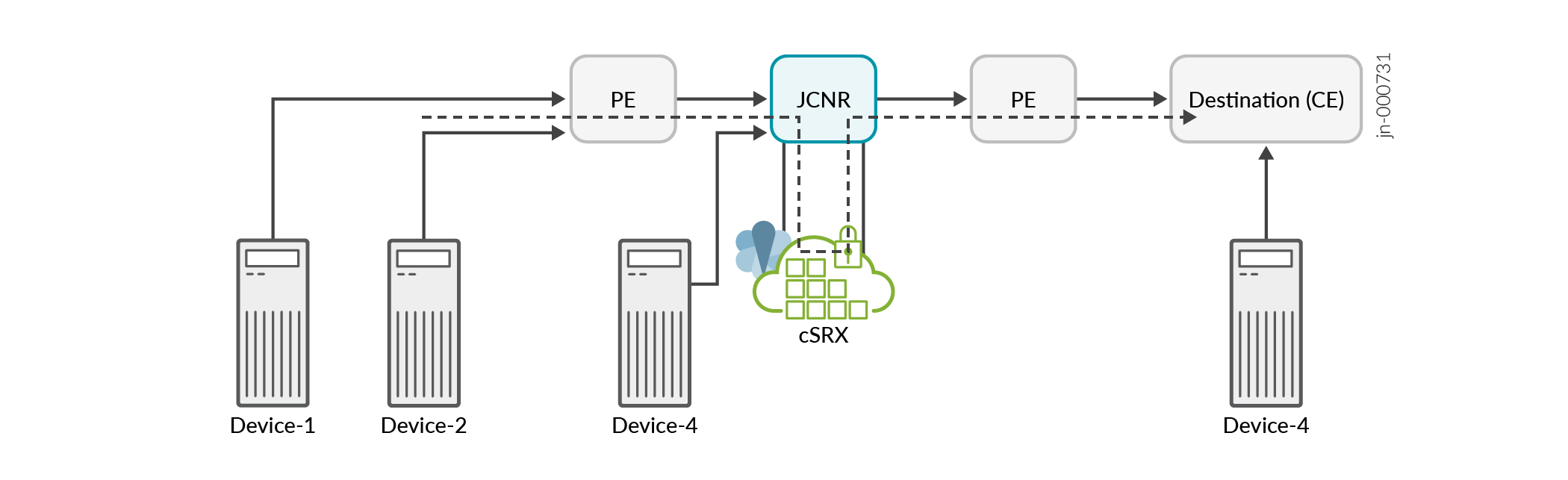
The cloud-native router is chained with a security service instance (cSRX) in the same Kubernetes cluster. The cSRX instance runs as a pod service in L3 mode.
A cloud-native router instance is service chained with only one instance of cSRX. It can support multiple IPSec tunnels.
Configuration
Cloud-Native Router can steer selective traffic through IPsec services. This is achieved by defining static routes to a destination via the cSRX interface. When the selective traffic is received on JCNR, it is forwarded to cSRX. The cSRX subjects the packet to IPsec encryption based on the configuration and forwards it to JCNR. Cloud-Native Router performs a route lookup in the untrust VRF and forwards traffic through the configured fabric interface. When IPsec packet is received from the remote end, Cloud-Native Router sends it to the security services. The cSRX decrypts the packet and forwards it to Cloud-Native Router on the trust interface. Cloud-Native Router then forwards the packet to the pod. The IP addresses of the tunnel endpoints are configured in Cloud-Native Router as static routes and advertised through an IGP to the remote end.
You can customize the cSRX deployment by specifying a range of configuration parameters in the helm chart (values.yaml) for cSRX. Key configuration options include:
-
interfaceType: This is the type of interface on the cSRX to connect to JCNR. Must be set tovhostonly. -
interfaceConfigs: This is an array defining the interface IP address, gateway address and optionally routes. One of the interface IP must match thelocalAddresselement in theipSecTunnelConfigsarray. This will be the interface in the untrust zone. The routes should contain prefixes to steer decrypted traffic to Cloud-Native Router and reachability route for IPSec gateway. -
ipSecTunnelConfigs: This is an array defining the IPsec configuration details such as ike-phase1, proposal, policy and gateway configuration. Traffic selector should contain traffic that is expected to be encrypted. You can define one or multiple tunnel configurations. You can either define the tunnel configuration using the installation helm chart or configure them post-deployment using a configlet. -
jcnr_config: This is an array defining the routes to be configured in Cloud-Native Router to steer traffic from Cloud-Native Router to cSRX and to steer IPsec traffic from the remote IPsec gateway to the cSRX to apply the security service chain.
Configuring cSRX via Helm Chart
The cSRX configurations are required to bring up its containers and pods at the time of
installation. The IPSec tunnel configuration can be defined at the time of installation
or later using a configlet. The enableUserConfig flag in the cSRX helm
chart when set to true enables IPSec tunnel configuration via configlet.
By default the enableUserConfig flag is set to false in
values.yaml and therefore requires
ipSecTunnelConfigs to be configured at the time of installation. A
sample interface and tunnel configuration for multiple tunnels is provided below:
enableUserConfig: false # enable /disable user configuration
interfaceType: "vhost"
interfaceConfigs:
- name: ge-0/0/0
ip: 172.16.10.1/30 # should match ipSecTunnelConfigs localAddress if configured
gateway: 172.16.10.2 # gateway configuration
ip6: 2001:db8:172:16:10::1/64 # optional
ip6Gateway: 2001:db8:172:16:10::2 # optional
routes: # this field is optional
- "172.17.10.0/24"
- "172.18.10.0/24"
instance_parameters:
name: "untrust"
type: "vrf" # options include virtual-router or vrf
vrfTarget: 10:10
- name: ge-0/0/1
ip: 192.168.1.1/30 # should match ipSecTunnelConfigs localAddress if configured
gateway: 192.168.1.2 # gateway configuration
ip6: 2001:db8:192:168:1::1/64 # optional
ip6Gateway: 2001:db8:192:168:1::2 # optional
routes: # this field is optional
- "10.111.1.0/24"
- "10.112.1.0/24"
instance_parameters:
name: "trust"
type: "vrf" # options include virtual-router or vrf
vrfTarget: 11:11
ipSecTunnelConfigs: # untrust
- interface: ge-0/0/0 ## section ike-phase1, proposal, policy, gateway
gateway: 172.17.10.2
localAddress: 172.16.10.1
authenticationAlgorithm: sha-256
encryptionAlgorithm: aes-256-cbc
preSharedKey: "$9$zt3l3AuIRhev8FnNVsYoaApu0RcSyev8XO1NVYoDj.P5F9AyrKv8X"
trafficSelector:
- name: ts1
localIP: 10.111.1.0/24 ## IP cannot be 0.0.0.0/0
remoteIP: 10.221.1.0/24 ## IP cannot be 0.0.0.0/0
- interface: ge-0/0/1 ## section ike-phase1, proposal, policy, gateway
gateway: 172.18.10.2
localAddress: 172.16.10.1
authenticationAlgorithm: sha-256
encryptionAlgorithm: aes-256-cbc
preSharedKey: "$9$zt3l3AuIRhev8FnNVsYoaApu0RcSyev8XO1NVYoDj.P5F9AyrKv8X"
trafficSelector:
- name: ts2
localIP: 10.112.1.0/24 ## IP cannot be 0.0.0.0/0
remoteIP: 10.222.1.0/24 ## IP cannot be 0.0.0.0/0
jcnr_config:
- name: ge-0/0/0
routes:
- "10.221.1.0/24"
- "10.222.1.0/24"Configuring cSRX IPSec Tunnel Configuration via Configlets
You can configure the IPSec tunnels after cSRX has been deployed using a configlet. The
installation helm chart must have enableUserConfig flag value set to
true. The ipSecTunnelConfigs configuration snippet must not be defined.
Sample helm charts are provided in the installer bundle—
/csrx_examples/values-user-config-csrx.yaml for cSRX only
installation and
/charts/junos-csrx/csrx_examples/values-user-config-unified.yaml for
unified JCNR and cSRX installation. An example helm chart is provided below:
enableUserConfig: true # enable /disable user configuration
interfaceType: "vhost"
interfaceConfigs:
- name: ge-0/0/0
ip: 172.16.10.1/30 # should match ipSecTunnelConfigs localAddress if configured
gateway: 172.16.10.2 # gateway configuration
ip6: 2001:db8:172:16:10::1/64 # optional
ip6Gateway: 2001:db8:172:16:10::2 # optional
routes: # this field is optional
- "172.17.10.0/24"
- "172.18.10.0/24"
instance_parameters:
name: "untrust"
type: "vrf" # options include virtual-router or vrf
vrfTarget: 10:10
- name: ge-0/0/1
ip: 192.168.1.1/30 # should match ipSecTunnelConfigs localAddress if configured
gateway: 192.168.1.2 # gateway configuration
ip6: 2001:db8:192:168:1::1/64 # optional
ip6Gateway: 2001:db8:192:168:1::2 # optional
routes: # this field is optional
- "10.111.1.0/24"
- "10.112.1.0/24"
instance_parameters:
name: "trust"
type: "vrf" # options include virtual-router or vrf
vrfTarget: 11:11
jcnr_config:
- name: ge-0/0/0
routes:
- "10.221.1.0/24"
- "10.222.1.0/24"You can create IPSec tunnels or modify tunnel configuration after deployment using a
configlet. A sample configlet has been provided in the installer
bundle—/csrx_examples/ipsec-tunnel-config-cr.yaml for cSRX only
installation and
/charts/junos-csrx/csrx_examples/ipsec-tunnel-config-cr.yaml for unified
JCNR and cSRX installation. An example configlet is provided below:
# Example configlet CR to configure an IPsec tunnel on a CSRX
apiVersion: configplane.juniper.net/v1
kind: Configlet
metadata:
name: example-csrx-cr
namespace: jcnr
labels:
app: csrx
annotations:
juniper.net/device: csrx
spec:
config: |-
set security ike proposal ike-phase-171-1-1-1-0-proposal dh-group group5
set security ike proposal ike-phase-171-1-1-1-0-proposal encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
set security ike proposal ike-phase-171-1-1-1-0-proposal authentication-algorithm sha-256
set security ike proposal ike-phase-171-1-1-1-0-proposal authentication-method pre-shared-keys
set security ike proposal ike-phase-171-1-1-1-0-proposal lifetime-seconds 3600
set security ike policy ike-phase-171-1-1-1-0-policy proposals ike-phase-171-1-1-1-0-proposal
set security ike policy ike-phase-171-1-1-1-0-policy pre-shared-key ascii-text "$9$zt3l3AuIRhev8FnNVsYoaApu0RcSyev8XO1NVYoDj.P5F9AyrKv8X"
set security ike gateway remote-171-1-1-1-0 ike-policy ike-phase-171-1-1-1-0-policy
set security ike gateway remote-171-1-1-1-0 address 181.1.1.1
set security ike gateway remote-171-1-1-1-0 external-interface ge-0/0/0.0
set security ike gateway remote-171-1-1-1-0 local-address 171.1.1.1
set security ike gateway remote-171-1-1-1-0 version v2-only
set security ipsec proposal ipsec-171-1-1-1-0-proposal protocol esp
set security ipsec proposal ipsec-171-1-1-1-0-proposal encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
set security ipsec proposal ipsec-171-1-1-1-0-proposal authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128
set security ipsec proposal ipsec-171-1-1-1-0-proposal lifetime-seconds 18000
set security ipsec policy ipsec-171-1-1-1-0-policy perfect-forward-secrecy keys group5
set security ipsec policy ipsec-171-1-1-1-0-policy proposals ipsec-171-1-1-1-0-proposal
set security ipsec vpn ipsec-remote-171-1-1-1-0 bind-interface st0.0
set security ipsec vpn ipsec-remote-171-1-1-1-0 ike gateway remote-171-1-1-1-0
set security ipsec vpn ipsec-remote-171-1-1-1-0 ike ipsec-policy ipsec-171-1-1-1-0-policy
set security ipsec vpn ipsec-remote-171-1-1-1-0 establish-tunnels immediately
set security ipsec vpn ipsec-remote-171-1-1-1-0 traffic-selector ts1 local-ip 100.1.1.0/24
set security ipsec vpn ipsec-remote-171-1-1-1-0 traffic-selector ts1 remote-ip 200.1.1.0/24
set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic system-services all
set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic protocols allConfiguration Example
Let us look at a configuration example for Cloud-Native Router with security services.
Consider the following network topology: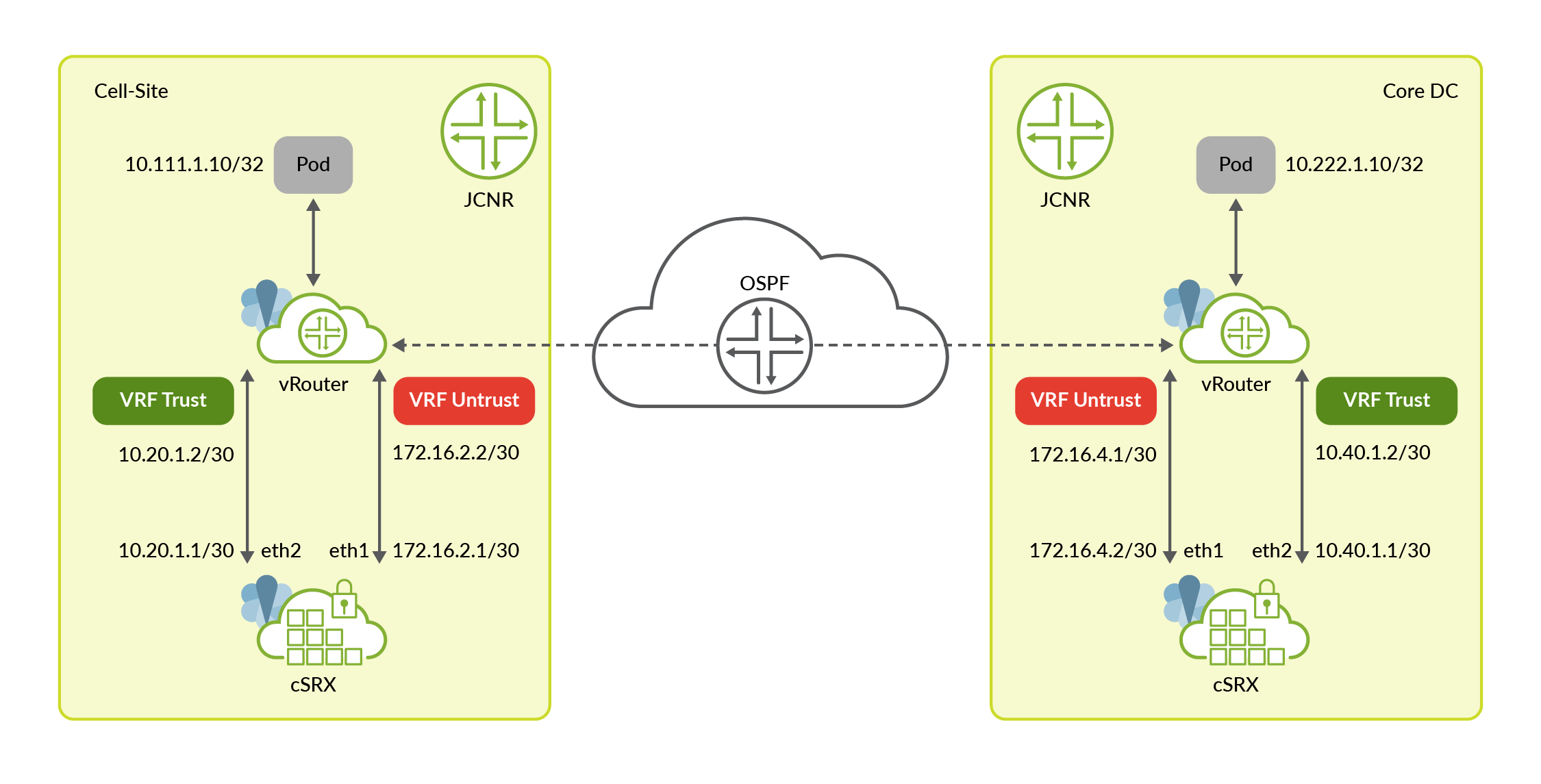
The topology consists of a Cloud-Native Router on the cell-site and a Cloud-Native Router
in the core data center. Both JCNRs are service chained with cSRX. The core data center can
also have any other physical or virtual firewall function as the tunnel endpoint. The
traffic between pods 10.111.1.10 and 10.222.1.10 must be
encrypted through an IPsec tunnel. The IP addresses and gateway addresses for the
cSRX-Cloud-Native Router interface are also illustrated.
cSRX connects with JCNR’s forwarding plane (vRouter) using two interfaces:
- ge-0/0/1 interface is used to send traffic from Cloud-Native Router to security services for IPsec encryption and from security services to Cloud-Native Router after IPsec decryption. This interface is a part of the trust zone in cSRX and trust VRF in JCNR.
- ge-0/0/0 interface is used to send traffic from security services to Cloud-Native Router after IPsec encryption and from Cloud-Native Router to security services for IPsec decryption. This interface is part of the untrust zone in cSRX and untrust VRF in JCNR.
Let us look at the configuration steps:
- Configure the cSRX helm chart with correct
interfaceConfigs,ipSecTunnelConfigsandjcnr_configfor the topology.- Helm chart configuration for cell-site JCNR:
junos-csrx: # Default values for cSRX. # This is a YAML-formatted file. # Declare variables to be passed into your templates. common: registry: enterprise-hub.juniper.net/ repository: jcnr-container-prod/ csrxInit: repository: image: csrx-init tag: R25.1-25 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: #limits: # memory: 1Gi # cpu: 1 #requests: # memory: 1Gi # cpu: 1 csrx: repository: image: csrx tag: 25.1R1.8 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: limits: hugepages-1Gi: 6Gi memory: 4Gi requests: hugepages-1Gi: 6Gi memory: 4Gi csrxTelemetry: repository: image: contrail-telemetry-exporter tag: 25.1.0.25 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: # kubeconfigpath: path to the kubeconfig file (to override the default path /etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf) # kubeConfigPath: /path/to/kubeconfig # nodeAffinity: Can be used to inject nodeAffinity for cSRX # you may label the nodes where we wish to deploy cSRX and inject affinity accordingly nodeAffinity: #- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/worker # operator: Exists #- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master # operator: DoesNotExist - key: kubernetes.io/hostname operator: In values: - node2 replicas: 1 interfaceType: "vhost" interfaceConfigs: - name: ge-0/0/0 ip: 172.16.2.1/30 # --> Interface IP in Untrust VRF, should match ipSecTunnelConfigs localAddress if configured gateway: 172.16.2.2 # --> gateway configuration ip6: 2001:172:16:2::1/126 # optional ip6Gateway: 2001:172.16.2::2 # optional routes: # --> Route to remote tunnel endpoint - "172.16.4.0/24" instance_parameters: name: "untrust" type: "vrf" # options include virtual-router or vrf vrfTarget: 10:10 - name: ge-0/0/1 ip: 10.20.1.1/30 # --> Interface IP in the Trust VRF gateway: 10.20.1.2 # --> gateway configuration ip6: 2001:10:20:1::1/126 # optional ip6Gateway: 2001:10:20:1::2 # optional routes: # --> Route to local application subnet - "10.111.1.0/24" instance_parameters: name: "trust" type: "vrf" # options include virtual-router or vrf vrfTarget: 11:11 ipSecTunnelConfigs: # untrust - interface: ge-0/0/0 ## section ike-phase1, proposal, policy, gateway gateway: 172.16.4.1 # --> Remote tunnel endpoint localAddress: 172.16.2.1 # --> Local Untrust Interface IP authenticationAlgorithm: sha-256 encryptionAlgorithm: aes-256-cbc preSharedKey: "$9$zt3l3AuIRhev8FnNVsYoaApu0RcSyev8XO1NVYoDj.P5F9AyrKv8X" trafficSelector: - name: ts1 localIP: 10.111.1.0/24 # --> Traffic selector based on local application subnet remoteIP: 10.222.1.0/24 # --> Traffic selector based on remote application subnet jcnr_config: - name: ge-0/0/1 routes: - "10.222.1.0/24" # --> cRPD route to remote application subnet via trust interface #csrx_flavor: specify the csrx deployment model. Corresponding values for csrx control and data cpus #must be provided based on the flavor mentioned below. Following are possible options: # CSRX-2CPU-4G # CSRX-4CPU-8G # CSRX-6CPU-12G # CSRX-8CPU-16G # CSRX-16CPU-32G # CSRX-20CPU-48G csrx_flavor: CSRX-2CPU-4G csrx_ctrl_cpu: "0x01" csrx_data_cpu: "0x02" -
Helm chart configuration for remote JCNR:
# Default values for cSRX. # This is a YAML-formatted file. # Declare variables to be passed into your templates. common: registry: enterprise-hub.juniper.net/ repository: jcnr-container-prod/ csrxInit: image: csrx-init tag: f4tgt33 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: #limits: # memory: 1Gi # cpu: 1 #requests: # memory: 1Gi # cpu: 1 csrx: image: csrx tag: 24.2R1.14 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: limits: hugepages-1Gi: 4Gi memory: 4Gi requests: hugepages-1Gi: 4Gi memory: 4Gi # uncomment below if you are using a private registry that needs authentication # registryCredentials - Base64 representation of your Docker registry credentials # secretName - Name of the Secret object that will be created #imagePullSecret: #registryCredentials: <base64-encoded-credential> #secretName: regcred # nodeAffinity: Can be used to inject nodeAffinity for cSRX # you may label the nodes where we wish to deploy cSRX and inject affinity accordingly # nodeAffinity: #- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/worker # operator: Exists #- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master # operator: DoesNotExist replicas: 1 interfaceType: "vhost" interfaceConfigs: - name: ge-0/0/0 ip: 172.16.4.1/30 # --> Interface IP in Untrust VRF, should match ipSecTunnelConfigs localAddress if configured gateway: 172.16.4.2 # --> gateway configuration ip6: 2001:172:16:4::1/126 # optional ip6Gateway: 2001:172.16.4::2 # optional routes: # --> Route to remote tunnel endpoint - "172.16.2.0/24" instance_parameters: name: "untrust" type: "vrf" # options include virtual-router or vrf vrfTarget: 10:10 - name: ge-0/0/1 ip: 10.40.1.1/30 # --> Interface IP in the Trust VRF gateway: 10.40.1.2 # --> gateway configuration ip6: 2001:10:40:1::1/126 # optional ip6Gateway: 2001:10:40:1::2 # optional routes: # --> Route to local application subnet - "10.222.1.0/24" instance_parameters: name: "trust" type: "vrf" # options include virtual-router or vrf vrfTarget: 11:11 ipSecTunnelConfigs: # untrust - interface: ge-0/0/0 ## section ike-phase1, proposal, policy, gateway gateway: 172.16.2.1 # --> Remote tunnel endpoint localAddress: 172.16.4.1 # --> Local Untrust Interface IP authenticationAlgorithm: sha-256 encryptionAlgorithm: aes-256-cbc preSharedKey: "$9$zt3l3AuIRhev8FnNVsYoaApu0RcSyev8XO1NVYoDj.P5F9AyrKv8X" trafficSelector: - name: ts1 localIP: 10.222.1.0/24 # --> Traffic selector based on local application subnet remoteIP: 10.111.1.0/24 # --> Traffic selector based on remote application subnet jcnr_config: - name: ge-0/0/0 routes: - "10.222.1.0/24" # --> cRPD route to local application subnet via untrust interface - name: ge-0/0/1 routes: - "10.111.1.0/24" # --> cRPD route to remote application subnet via trust interface #csrx_flavor: specify the csrx deployment model. Corresponding values for csrx control and data cpus #must be provided based on the flavor mentioned below. Following are possible options: # CSRX-2CPU-4G # CSRX-4CPU-8G # CSRX-6CPU-12G # CSRX-8CPU-16G # CSRX-16CPU-32G # CSRX-20CPU-48G csrx_flavor: CSRX-2CPU-4G csrx_ctrl_cpu: "0x01" csrx_data_cpu: "0x02"Once you have configured the helm chart, you must deploy cSRX.
Please review the Deploying Service Chain (cSRX) with JCNR topic for details on how to deploy cSRX for service chaining with JCNR.
- Helm chart configuration for cell-site JCNR:
-
Configure the Cloud-Native Router fabric interface (
ens192) to participate in the IGP running in the core. The configuration is performed in the untrust VRF.-
Example configlet for OSPF on the cell-site JCNR:
apiVersion: configplane.juniper.net/v1 kind: Configlet metadata: name: configlet-ipsec-ospf # <-- Configlet resource name namespace: jcnr spec: config: |- set policy-options policy-statement export_static_ospf from protocol local set policy-options policy-statement export_static_ospf from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement export_static_ospf then accept set routing-instances untrust protocols ospf export export_static_ospf set routing-instances untrust protocols ospf area 0 interface ens192 set interfaces ens192 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.0.11/24 set routing-instances untrust interface ens192 crpdSelector: matchLabels: node: worker
-
Example configlet for OSPF on the remote JCNR:
apiVersion: configplane.juniper.net/v1 kind: Configlet metadata: name: configlet-ipsec-ospf # <-- Configlet resource name namespace: jcnr spec: config: |- set policy-options policy-statement export_static_ospf from protocol local set policy-options policy-statement export_static_ospf from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement export_static_ospf then accept set routing-instances untrust protocols ospf export export_static_ospf set routing-instances untrust protocols ospf area 0 interface ens192 set interfaces ens192 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.0.12/24 set routing-instances untrust interface ens192 crpdSelector: matchLabels: node: worker
-
-
Deploy the application pods with an interface attached to the trust VRF in JCNR.
-
Application pod on the cell-site:
apiVersion: "k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1" kind: NetworkAttachmentDefinition metadata: name: net-trust spec: config: '{ "cniVersion":"0.4.0", "name": "net-trust", "plugins": [ { "type": "jcnr", # --> CNI plugin is jcnr "args": { "vrfName": "trust", # --> VRF name is trust "vrfTarget": "10:10" }, "kubeConfig":"/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" } ] }' --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: pktgen-ce1 labels: app: pktgen-odu annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: | [ { "name": "net-trust", "interface":"net1", "cni-args": { "interfaceType":"veth", "mac":"aa:bb:cc:dd:50:11", "ipConfig":{ "ipv4":{ "address":"10.111.1.10/24", # --> IP address of the pod "gateway":"10.111.1.1", "routes":[ "10.222.1.0/24"] }, "ipv6":{ "address":"2001:0db8:10:111:1::10/126", "gateway":"2001:0db8:10:111:1::10", "routes":["2001:0db8:10:222:1::0/126"] } } } } ] spec: affinity: <trimmed...> -
Application pod on the remote site:
apiVersion: "k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1" kind: NetworkAttachmentDefinition metadata: name: net-trust spec: config: '{ "cniVersion":"0.4.0", "name": "net-trust", "plugins": [ { "type": "jcnr", # --> CNI plugin is jcnr "args": { "vrfName": "trust", # --> VRF name is trust "vrfTarget": "10:10" }, "kubeConfig":"/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" } ] }' --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: pktgen-ce1 labels: app: pktgen-odu annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: | [ { "name": "net-trust", "interface":"net1", "cni-args": { "interfaceType":"veth", "mac":"aa:bb:cc:dd:50:22", "ipConfig":{ "ipv4":{ "address":"10.222.1.10/24", # --> IP address of the pod "gateway":"10.222.1.1", "routes":[ "10.111.1.0/24"] }, "ipv6":{ "address":"2001:0db8:10:222:1::10/126", "gateway":"2001:0db8:10:222:1::10", "routes":["2001:0db8:10:111:1::0/126"] } } } } ] spec: affinity: <trimmed...>
-
Verify Configuration
You can verify the configuration and traffic flows in cRPD, cSRX and vRouter.
-
Verify cRPD configuration for trust and untrust VRFs via the cRPD shell. The configuration is available under the cni configuration group.
user@host > show configuration groups cni | display set set groups cni apply-flags omit set groups cni apply-macro ht jcnr set groups cni routing-instances untrust instance-type vrf set groups cni routing-instances untrust routing-options rib untrust.inet6.0 static route 2001:db8:172:16:10::1/128 qualified-next-hop 2001:db8:172:16:10::1 interface vhostge-0_0_0-90aca656-8b86-4d1d-a8 set groups cni routing-instances untrust routing-options static route 172.16.10.1/32 qualified-next-hop 172.16.10.1 interface vhostge-0_0_0-90aca656-8b86-4d1d-a8 set groups cni routing-instances untrust interface vhostge-0_0_0-90aca656-8b86-4d1d-a8 set groups cni routing-instances untrust route-distinguisher 10:10 set groups cni routing-instances untrust vrf-target target:10:10 set groups cni routing-instances trust instance-type vrf set groups cni routing-instances trust routing-options rib trust.inet6.0 static route 2001:db8:10:20:1::1/128 qualified-next-hop 2001:db8:10:20:1::1 interface vhostge-0_0_1-90aca656-8b86-4d1d-a8 set groups cni routing-instances trust routing-options static route 10:20:1.1/32 qualified-next-hop 10:20:1.1 interface vhostge-0_0_1-90aca656-8b86-4d1d-a8 set groups cni routing-instances trust routing-options static route 10.222.1.0/24 qualified-next-hop 10.20.1.1 interface vhostge-0_0_1-90aca656-8b86-4d1d-a8 set groups cni routing-instances trust interface vhostge-0_0_1-90aca656-8b86-4d1d-a8 set groups cni routing-instances trust route-distinguisher 11:11 set groups cni routing-instances trust vrf-target target:11:11
-
Verify the cRPD Routing Tables:
user@host > show route table trust.inet.0 trust.inet.0: 5 destinations, 5 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 10.20.1.1/32 *[Static/5] 03:59:00 > via vhostge-0_0_1-a6c764da-a46d-4832-b5 10.20.1.2/32 *[Local/0] 03:59:00 Local via vhostge-0_0_1-a6c764da-a46d-4832-b5 10.111.1.1/32 *[Local/0] 03:59:00 Local via jvknet1-88e1126 10.111.1.10/32 *[Static/5] 03:59:00 > via jvknet1-88e1126 10.222.1.0/24 *[Static/5] 03:59:00 > via vhostge-0_0_1-a6c764da-a46d-4832-b5
user@host > show route table untrust.inet.0 untrust.inet.0: 9 destinations, 9 routes (9 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 10.111.1.0/24 *[Static/5] 04:00:31 > via vhostge-0_0_0-a6c764da-a46d-4832-b5 10.222.1.0/24 *[OSPF/150] 03:56:03, metric 0, tag 0 > to 172.16.0.12 via ens192 172.16.0.0/24 *[Direct/0] 04:00:31 > via ens192 172.16.0.11/32 *[Local/0] 04:00:31 Local via ens192 172.16.1.0/24 *[OSPF/10] 03:56:03, metric 2 > to 172.16.0.12 via ens192 172.16.2.1/32 *[Static/5] 04:00:31 > via vhostge-0_0_0-a6c764da-a46d-4832-b5 172.16.2.2/32 *[Local/0] 04:00:31 Local via vhostge-0_0_0-a6c764da-a46d-4832-b5 172.16.4.1/32 *[OSPF/150] 03:56:03, metric 0, tag 0 > to 172.16.0.12 via ens192
-
Login to the cSRX shell using the
kubectl exec -it csrx_pod_name -n jcnr -- bashcommand. Typeclito navigate to the CLI mode. Verify the cSRX configuration, security associations and flows:user@host> show configuration ## Last commit: 2024-10-01 10:25:50 UTC by root version 20240621.103832_builder.r1429411; system { root-authentication { encrypted-password *disabled*; ## SECRET-DATA } services { ssh { root-login allow; } } } interfaces { ge-0/0/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address 172.16.2.1/30; } } } ge-0/0/1 { unit 0 { family inet { address 10.20.1.1/30; } } } st0 { unit 0 { family inet; } } } routing-options { static { route 172.16.4.0/24 next-hop 172.16.2.2/32; route 10.111.1.0/24 next-hop 10.20.1.2/32; } } security { ike { proposal ike-phase-172-16-2-1-proposal { authentication-method pre-shared-keys; dh-group group5; authentication-algorithm sha-256; encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc; lifetime-seconds 3600; } policy ike-phase-172-16-2-1-policy { proposals ike-phase-172-16-2-1-proposal; pre-shared-key ascii-text "$9$zt3l3AuIRhev8FnNVsYoaApu0RcSyev8XO1NVYoDj.P5F9AyrKv8X"; ## SECRET-DATA } gateway remote-172-16-2-1 { ike-policy ike-phase-172-16-2-1-policy; address 172.16.4.1; external-interface ge-0/0/0.0; local-address 172.16.2.1; version v2-only; } } ipsec { proposal ipsec-172-16-2-1-proposal { protocol esp; } policy ipsec-172-16-2-1-policy { perfect-forward-secrecy { keys group5; } proposals ipsec-172-16-2-1-proposal; } vpn ipsec-remote-172-16-2-1 { bind-interface st0.0; ike { gateway remote-172-16-2-1; ipsec-policy ipsec-172-16-2-1-policy; } traffic-selector ts1 { local-ip 10.111.1.0/24; remote-ip 10.222.1.0/24; } establish-tunnels immediately; } } policies { default-policy { permit-all; } } zones { security-zone untrust { host-inbound-traffic { system-services { all; } protocols { all; } } interfaces { ge-0/0/0.0; st0.0; } } security-zone trust { host-inbound-traffic { system-services { all; } protocols { all; } } interfaces { ge-0/0/1.0; } } } }user@host> show security ike security-associations Index State Initiator cookie Responder cookie Mode Remote Address 73 UP 6895337b7ae4b449 2bdca7788a896e50 IKEv2 172.16.4.1
user@host> show security ipsec security-associations Total active tunnels: 1 Total IPsec sas: 1 ID Algorithm SPI Life:sec/kb Mon lsys Port Gateway <500002 ESP:3des/sha1 0x0283e69b 2132/ unlim - root 500 172.16.4.1 >500002 ESP:3des/sha1 0xbdd5cc1e 2132/ unlim - root 500 172.16.4.1
user@host> show security ipsec statistics ESP Statistics: Encrypted bytes: 2878576 Decrypted bytes: 1739472 Encrypted packets: 21166 Decrypted packets: 20708 AH Statistics: Input bytes: 0 Output bytes: 0 Input packets: 0 Output packets: 0 Errors: AH authentication failures: 0, Replay errors: 0 ESP authentication failures: 0, ESP decryption failures: 0 Bad headers: 0, Bad trailers: 0 Invalid SPI: 0, TS check fail: 0 Exceeds tunnel MTU: 0 Discarded: 0
user@host> show security flow session Session ID: 2, Policy name: N/A, Timeout: N/A, Session State: Valid In: 172.16.4.1/0 --> 172.16.2.1/0;esp, Conn Tag: 0x0, If: ge-0/0/0.0, Pkts: 0, Bytes: 0, Session ID: 2696, Policy name: N/A, Timeout: N/A, Session State: Valid In: 172.16.4.1/20915 --> 172.16.2.1/10740;esp, Conn Tag: 0x0, If: ge-0/0/0.0, Pkts: 7, Bytes: 952, Total sessions: 2
-
You can also verify the flow in the vRouter CLI:
# flow -l Flow table(size 161218560, entries 629760) … Index Source:Port/Destination:Port Proto(V) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 58256<=>206532 172.16.4.1:0 50 (1) 172.16.2.1:0 (Gen: 53, K(nh):1, Action:F, Flags:, QOS:-1, S(nh):26, Stats:14479/1969144, SPort 63031, TTL 0, Sinfo 0.0.0.0) 202824<=>382336 10.111.1.10:67 1 (2) 10.222.1.10:0 (Gen: 5, K(nh):2, Action:F, Flags:, QOS:-1, S(nh):18, Stats:14754/1445892, SPort 51876, TTL 0, Sinfo 8.0.0.0) 206532<=>58256 172.16.2.1:0 50 (1) 172.16.4.1:0 (Gen: 53, K(nh):1, Action:F, Flags:, QOS:-1, S(nh):27, Stats:14494/2174100, SPort 55303, TTL 0, Sinfo 6.0.0.0) 382336<=>202824 10.222.1.10:67 1 (2) 10.111.1.10:0 (Gen: 5, K(nh):2, Action:F, Flags:, QOS:-1, S(nh):14, Stats:14479/1418942, …
