Integrated DCI (VXLAN Stitching)
Overview
Integrated Data Center Interconnect (DCI) was introduced as a technology preview in Apstra version 4.2.0 and became GA as of Apstra version 4.2.1.
In Apstra version 4.2.0, this feature is classified as a Juniper Apstra Technology Preview feature. These features are "as is" and are for voluntary use. Juniper Support will attempt to resolve any issues that customers experience when using these features and create bug reports on behalf of support cases. However, Juniper may not provide comprehensive support services to Tech Preview features.
For additional information, refer to the Juniper Apstra Technology Previews page or contact JuniperSupport.
Apstra also supports two other types of DCI:
-
External Handoff where an external connection is set with a standard Layer 2 VLAN handoff external connection with traditional Flood MA VLAN learning. This extends a single Network/Broadcast domain with a traditional demarcation point.
-
OTT (over the top) Extending the Single EVPN-VXLAN domain between data centers.
For device information, see the Interconnect Gateway Leaf section of the Qualified Devices and NOS Versions page.
Integrated DCI, also known as VXLAN stitching, allows Apstra users to extend EVPN Type 2 and Type 5 routes between data centers using designated border leaf(s) to act as DCI gateways at each data center.
-
Apstra's Integrated DCI reference design follows RFE-9014 and draft-sharma-bess.
-
Each data center is treated as its own independent domain.
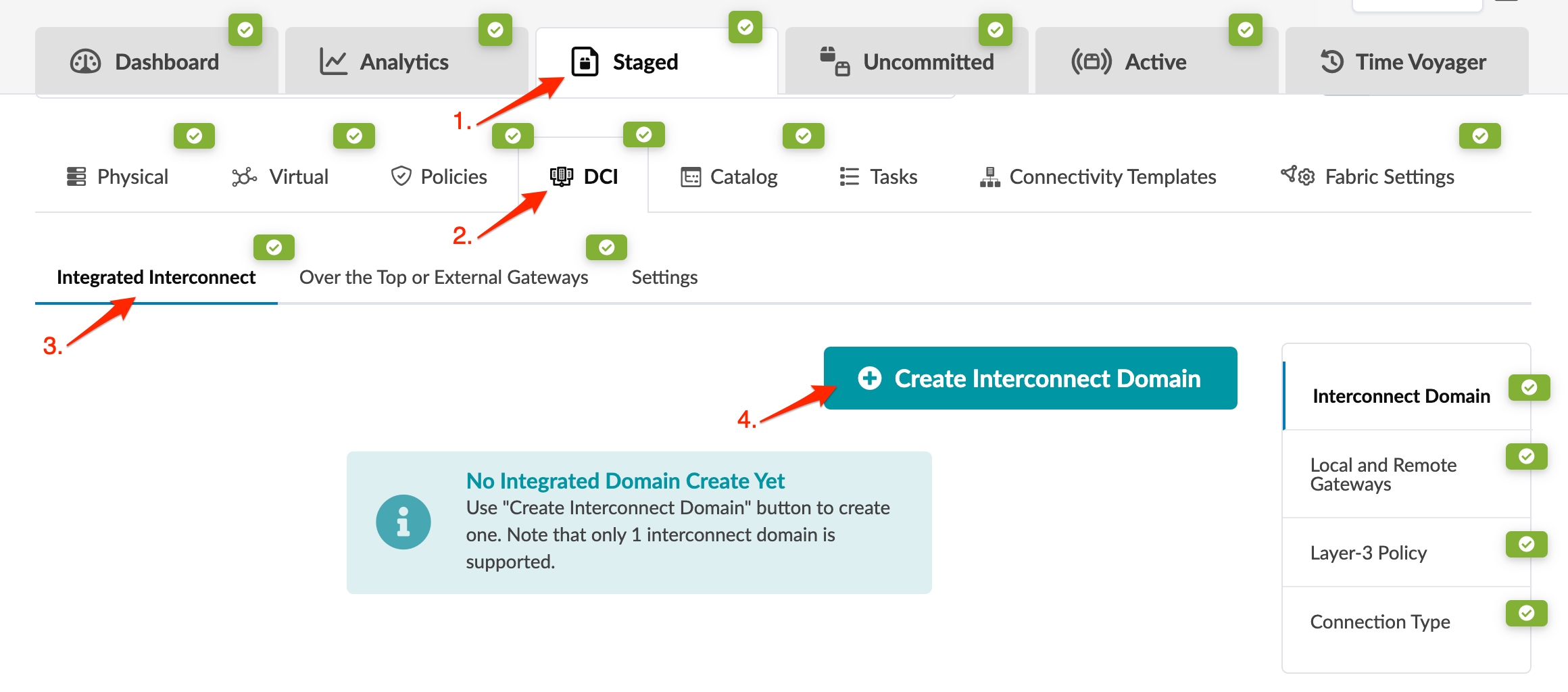
Configuring Integrated DCI within Apstra:
-
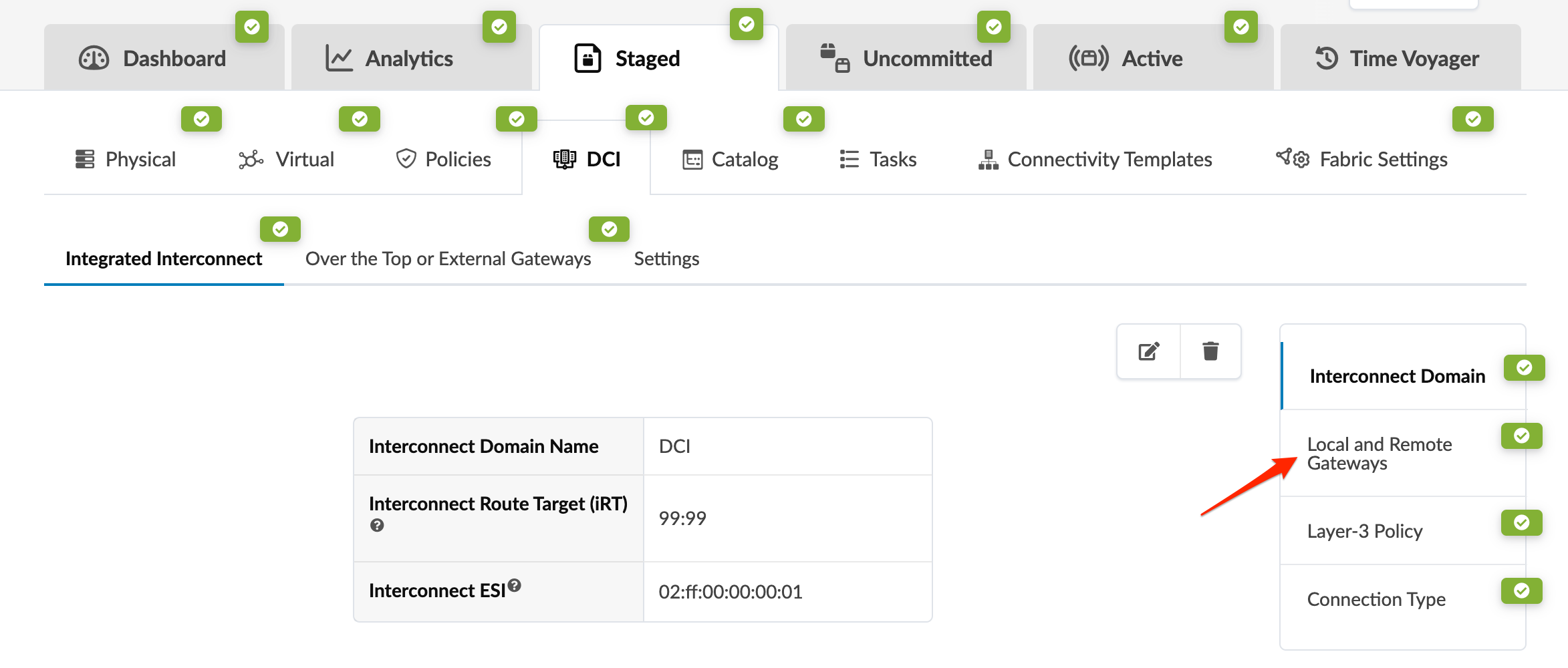
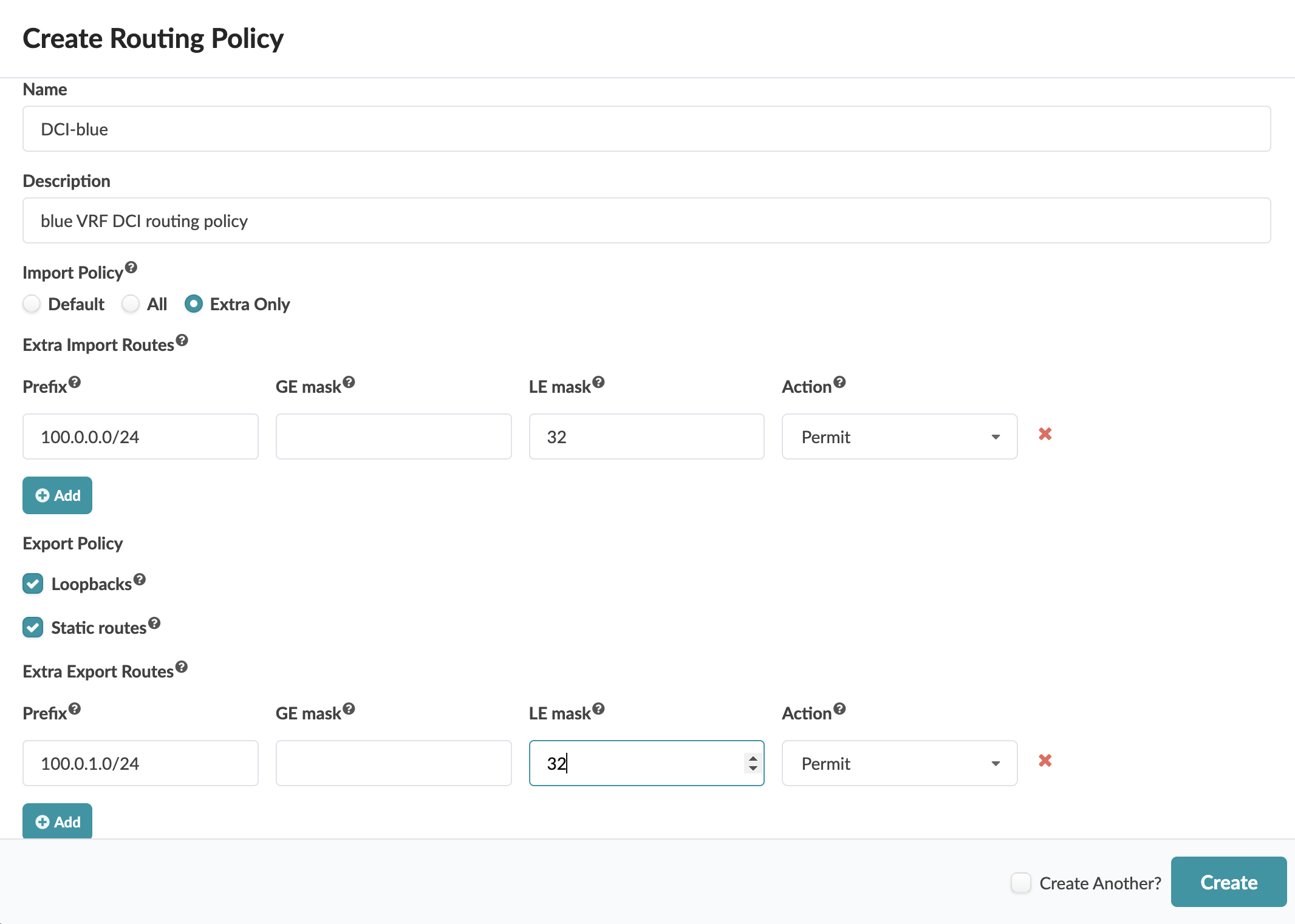
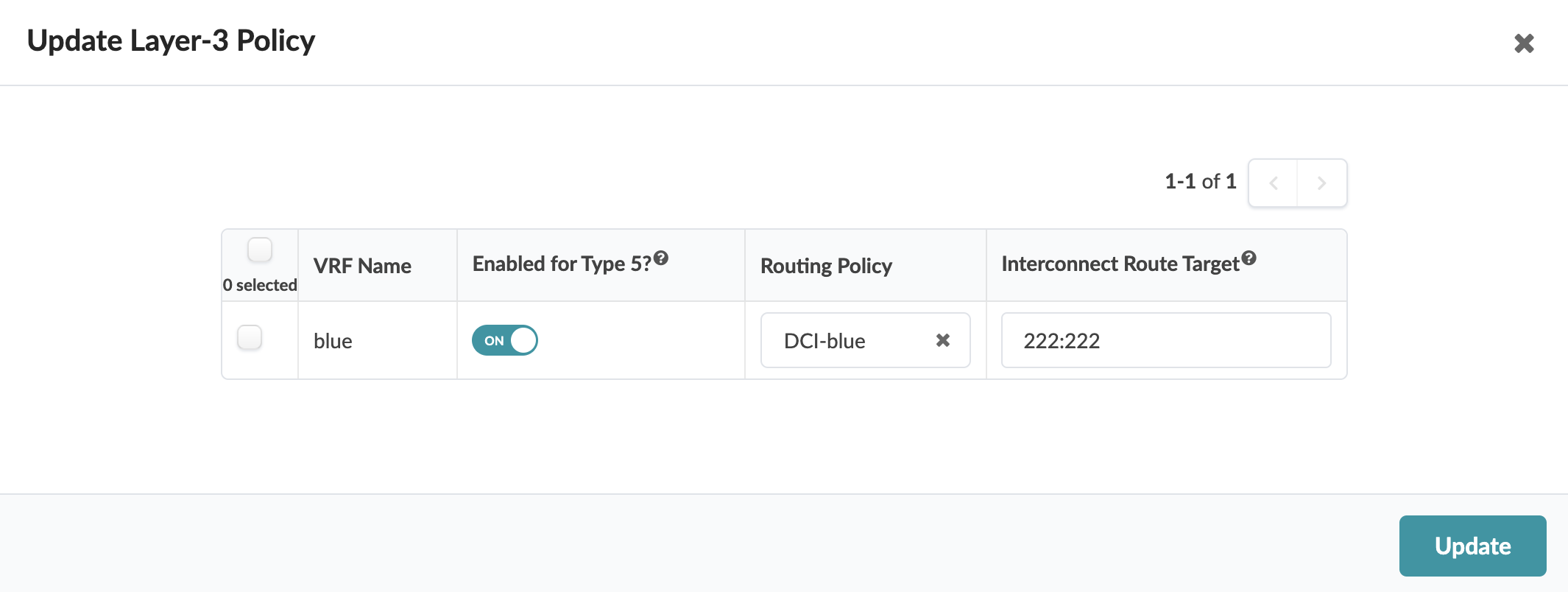
DCI configuration must be configured as part of each data center deployment/blueprint and use the same Interconnect Route Target (iRT).
-
The steps below guide you through the process for each blueprint and deployment.
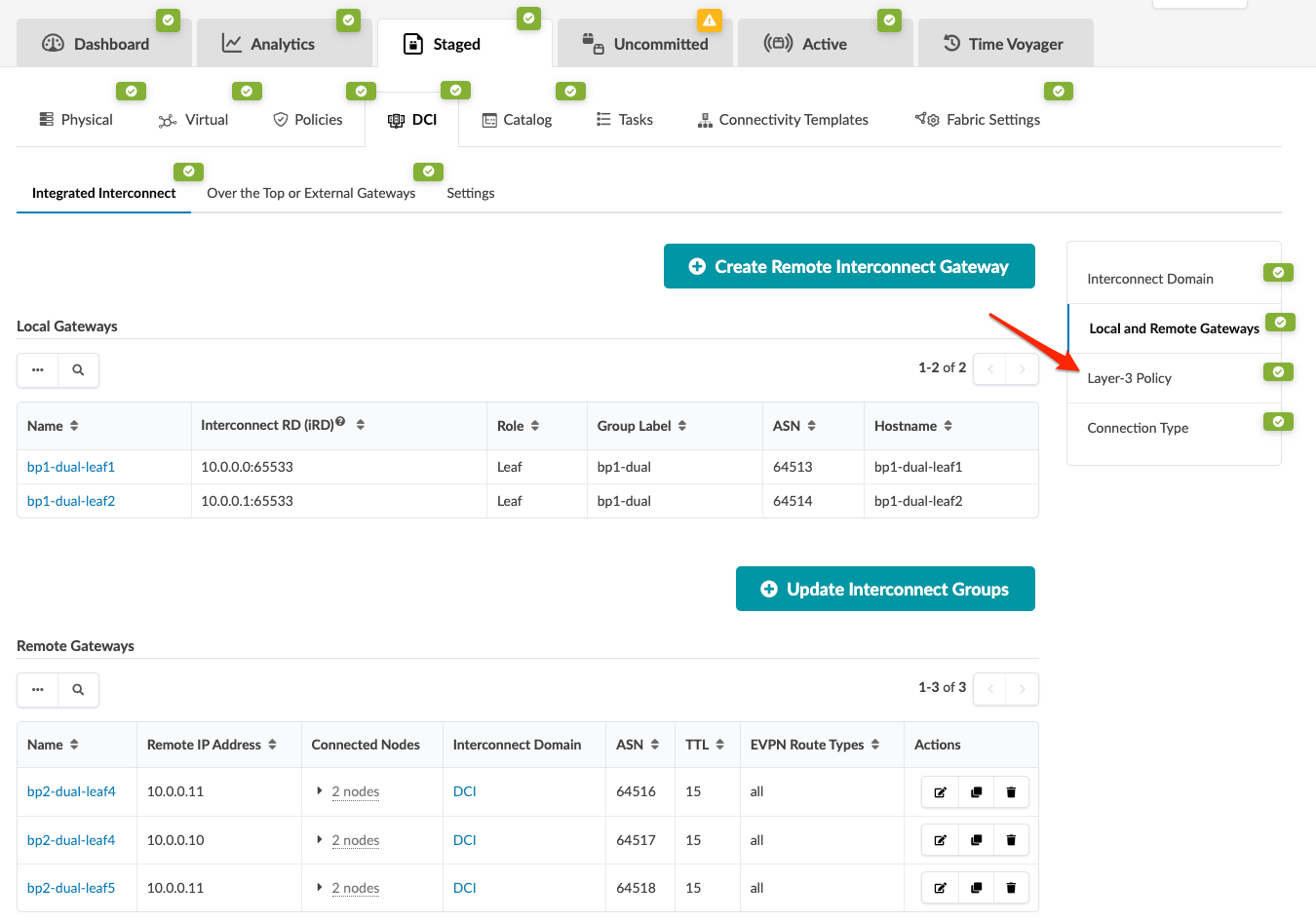
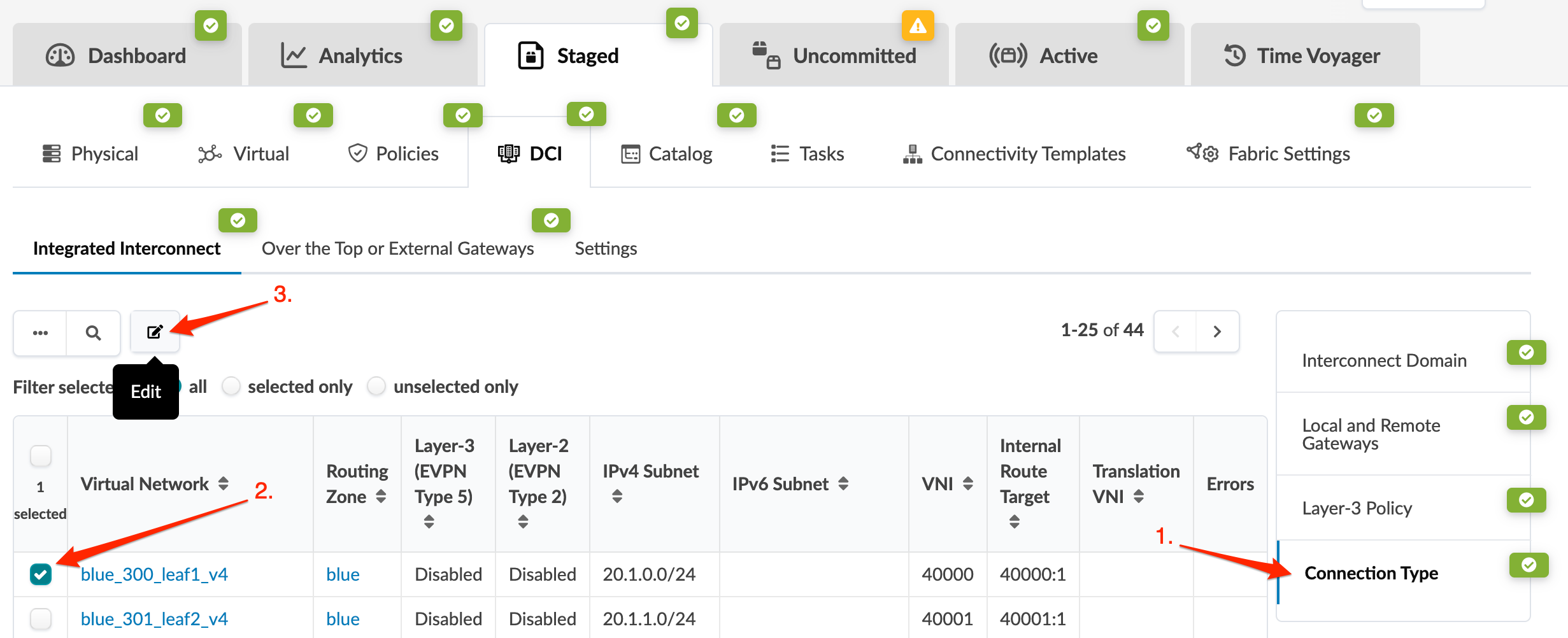
1. Create Interconnect Domain
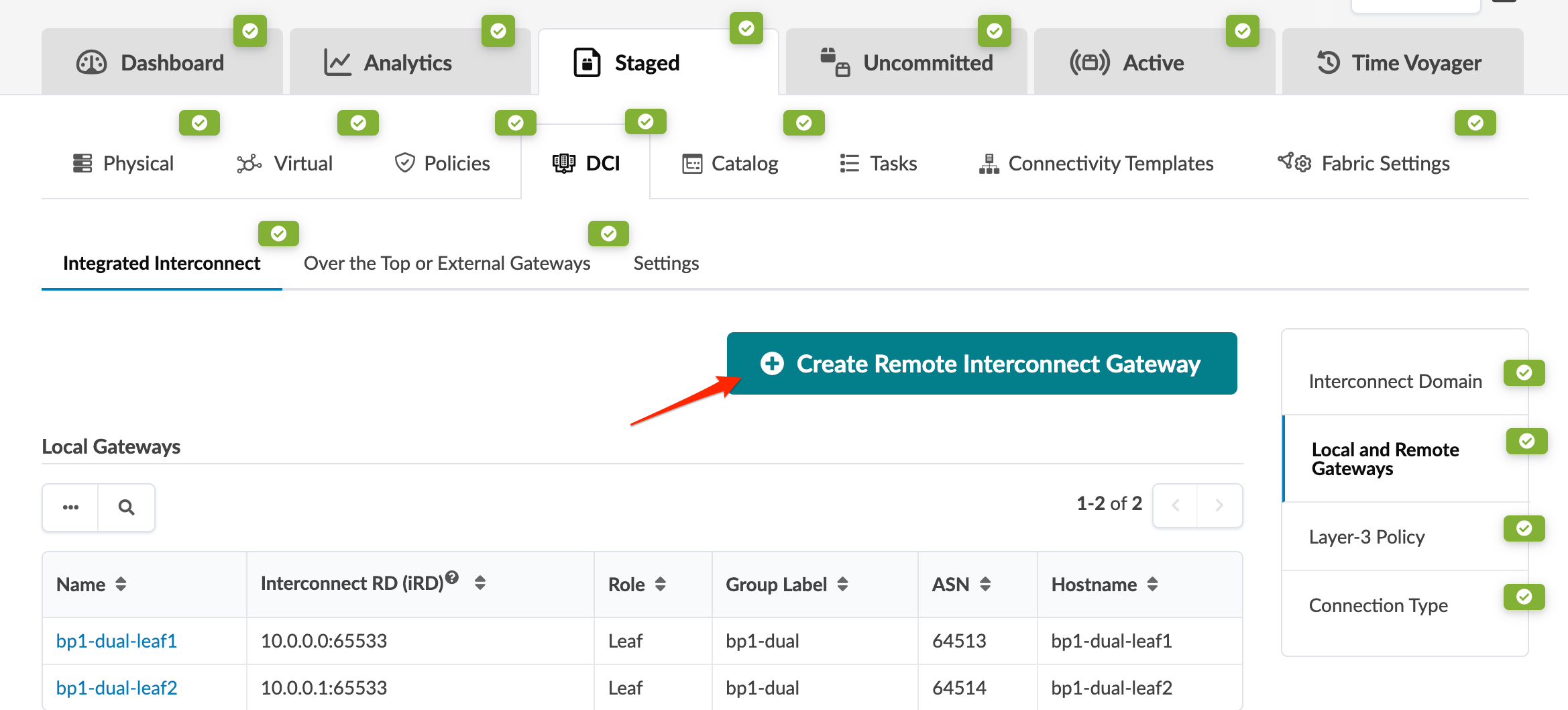
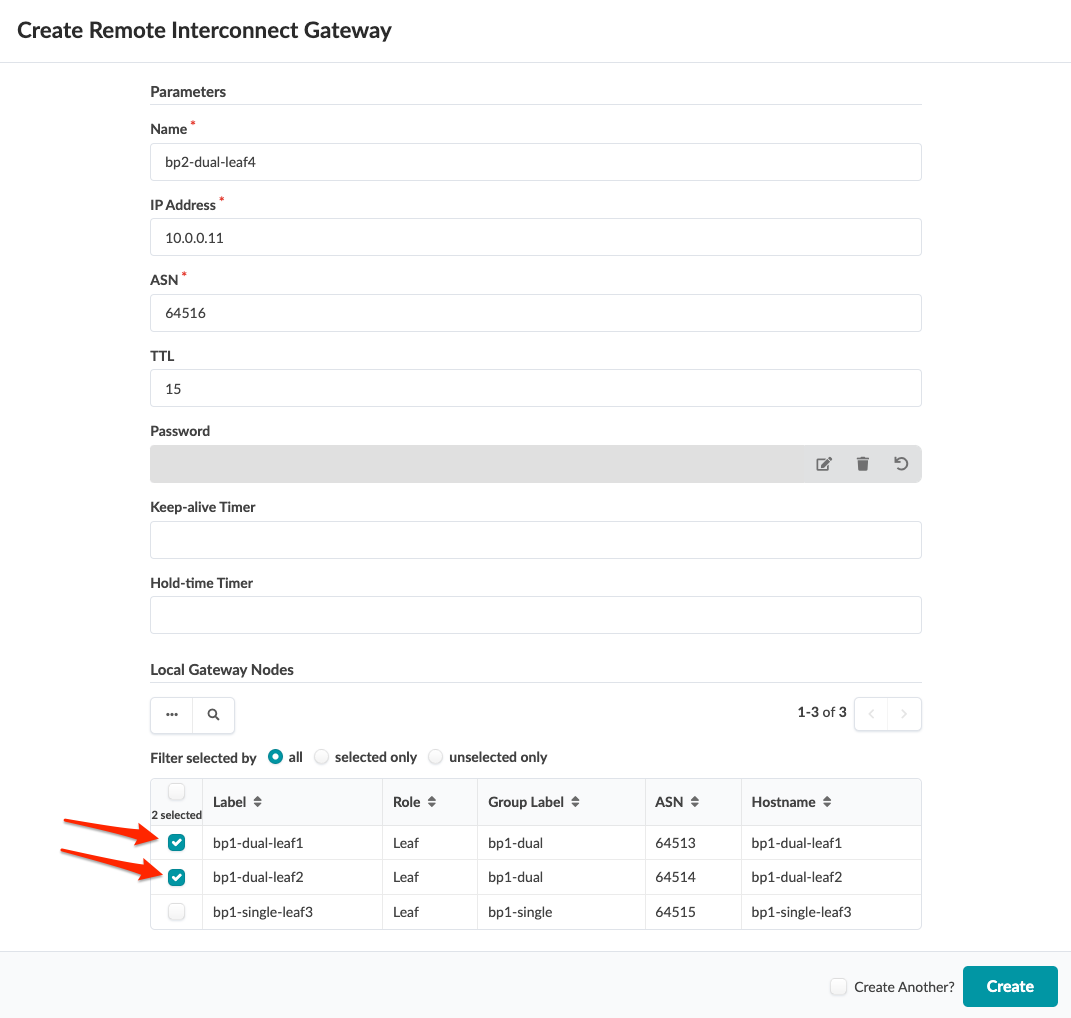
2. Create Remote Interconnect Gateway
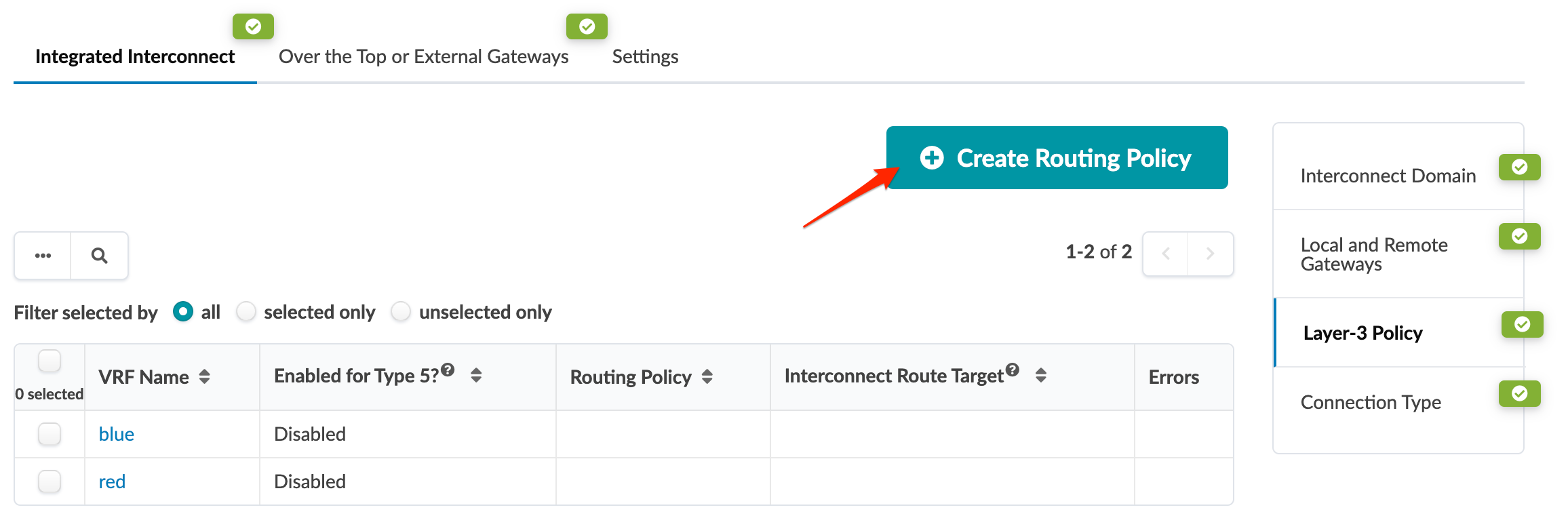
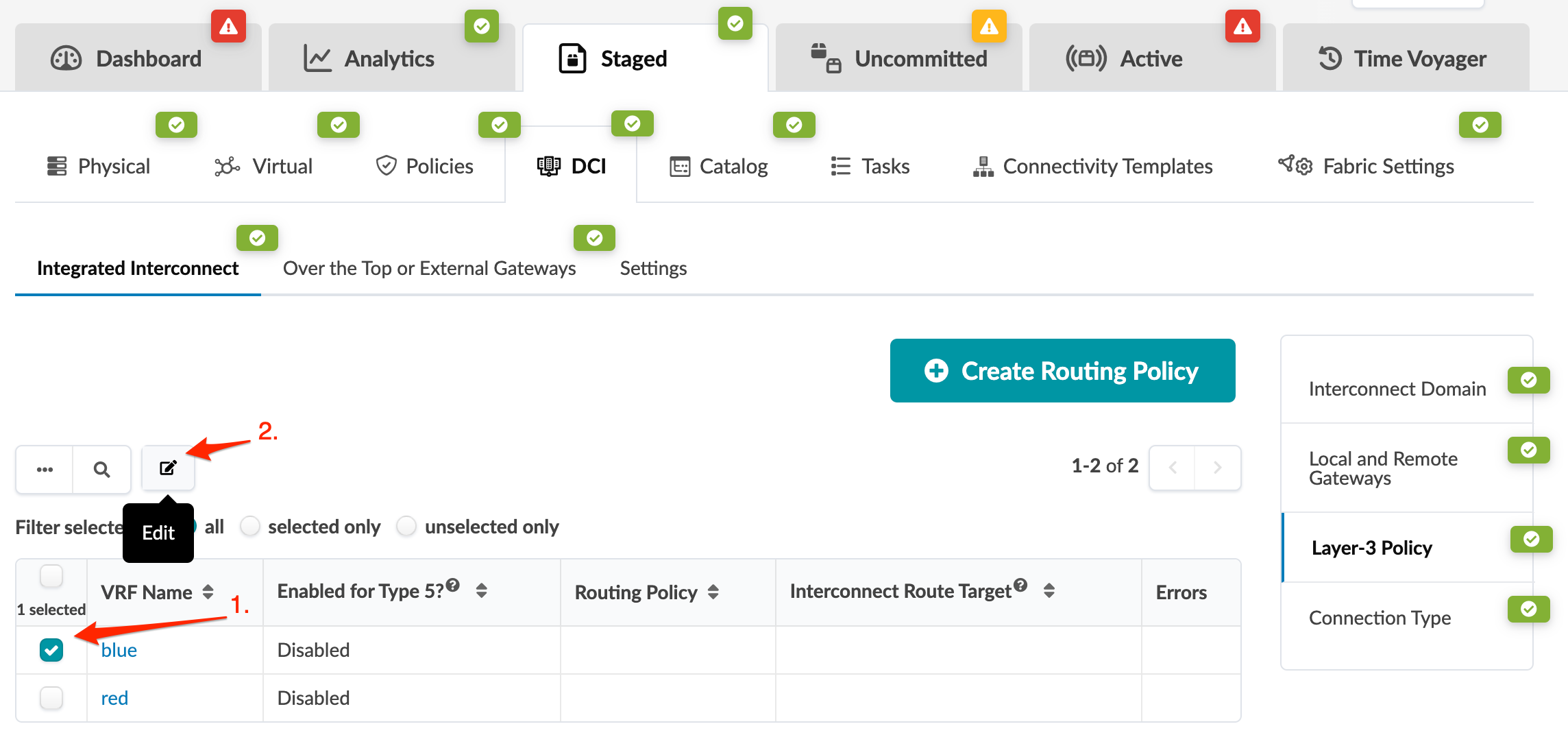
3. Create Routing Policy
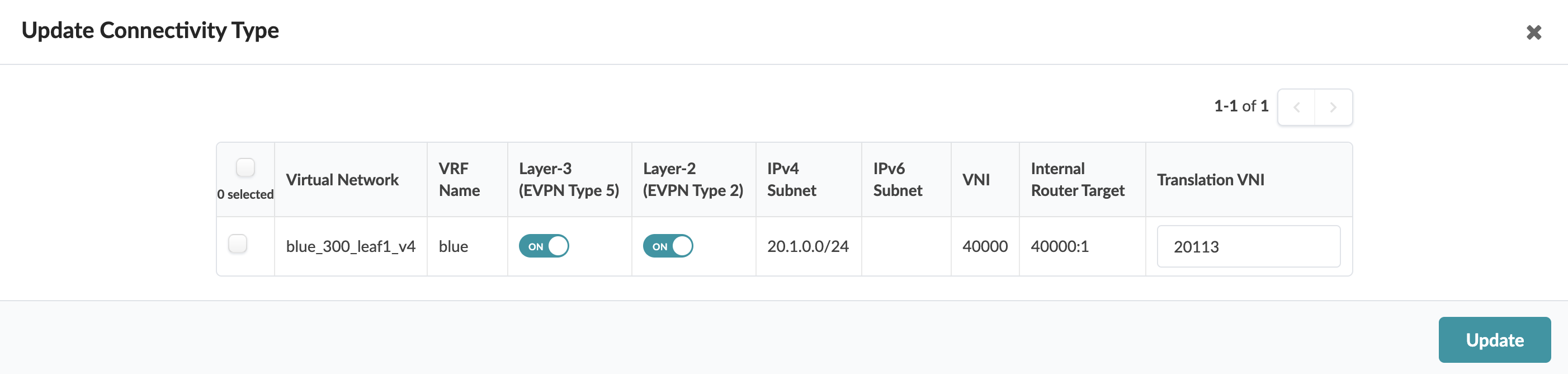
4. Update Connectivity Type
5. Configure ESI MAC MSB
All data centers must be configured to use a different ESI MAC MSB (most significant byte). Refer to Update ESI MAC MSB for details.
6. Configure Remote DCI Gateway
After configuring ESI MAC MSB, repeat the above steps to configure the remote DCI gateway.