Configuration Examples
The following sections provide Drain Mode configuration examples for different OS and device combinations.
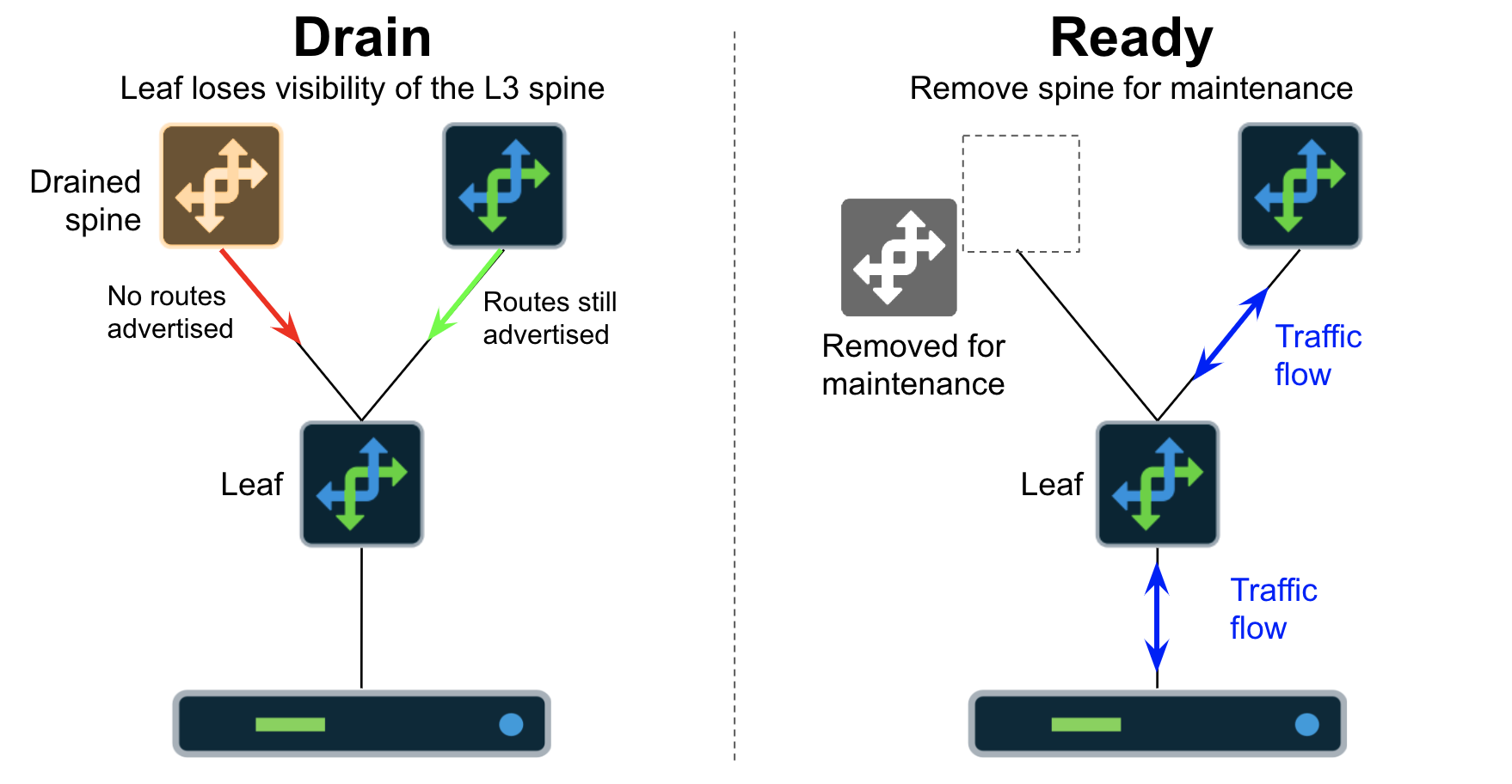
Drain Spine Devices (L2 and L3 Blueprints)
The following occurs when draining the Spine:
-
Outbound routes are removed from the device’s routing table.
-
Routes to destinations with the device’s ASN (Autonomous System Numbers) in the AS-PATH are removed from all devices in the network.
-
Packets are forwarded through remaining ECMP (Equal Cost Multi-Path) paths for all destinations.
It is highly unlikely that a single in-flight packet will be lost. This is dependent however, on the L3 ECMP to L2 path hashing algorithms in the hardware and NOS.
Drain (NX-OS)
ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
route-map Drain deny 10
match ip address prefix-list Drain
exit
!
neighbor 172.16.0.1 remote-as 64514
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-map Drain out
route-map Drain in
exit
exit
neighbor 172.16.0.3 remote-as 64514
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-map Drain out
route-map Drain in
exit
exit Drain (Junos)
[edit policy-options]
+ route-filter-list Drain {
+ 0.0.0.0/0 upto /32;
+ }
[edit policy-options]
+ policy-statement Drain {
+ term Drain-10 {
+ from {
+ family inet;
+ route-filter-list Drain;
+ }
+ then reject;
+ }
+ }
[edit protocols bgp group l3clos-s neighbor 172.16.0.7]
+ import ( Drain );
- export ( SPINE_TO_LEAF_FABRIC_OUT && BGP-AOS-Policy );
+ export ( Drain );
[edit protocols bgp group l3clos-s neighbor 172.16.0.9]
+ import ( Drain );
- export ( SPINE_TO_LEAF_FABRIC_OUT && BGP-AOS-Policy );
+ export ( Drain );
[edit protocols bgp group l3clos-s neighbor 172.16.0.11]
+ import ( Drain );
- export ( SPINE_TO_LEAF_FABRIC_OUT && BGP-AOS-Policy );
+ export ( Drain );
[edit protocols bgp group l3clos-s-evpn neighbor 10.0.0.0]
+ import ( Drain );
- export ( SPINE_TO_LEAF_EVPN_OUT );
+ export ( Drain );
[edit protocols bgp group l3clos-s-evpn neighbor 10.0.0.1]
+ import ( Drain );
- export ( SPINE_TO_LEAF_EVPN_OUT );
+ export ( Drain );
[edit protocols bgp group l3clos-s-evpn neighbor 10.0.0.2]
+ import ( Drain );
- export ( SPINE_TO_LEAF_EVPN_OUT );
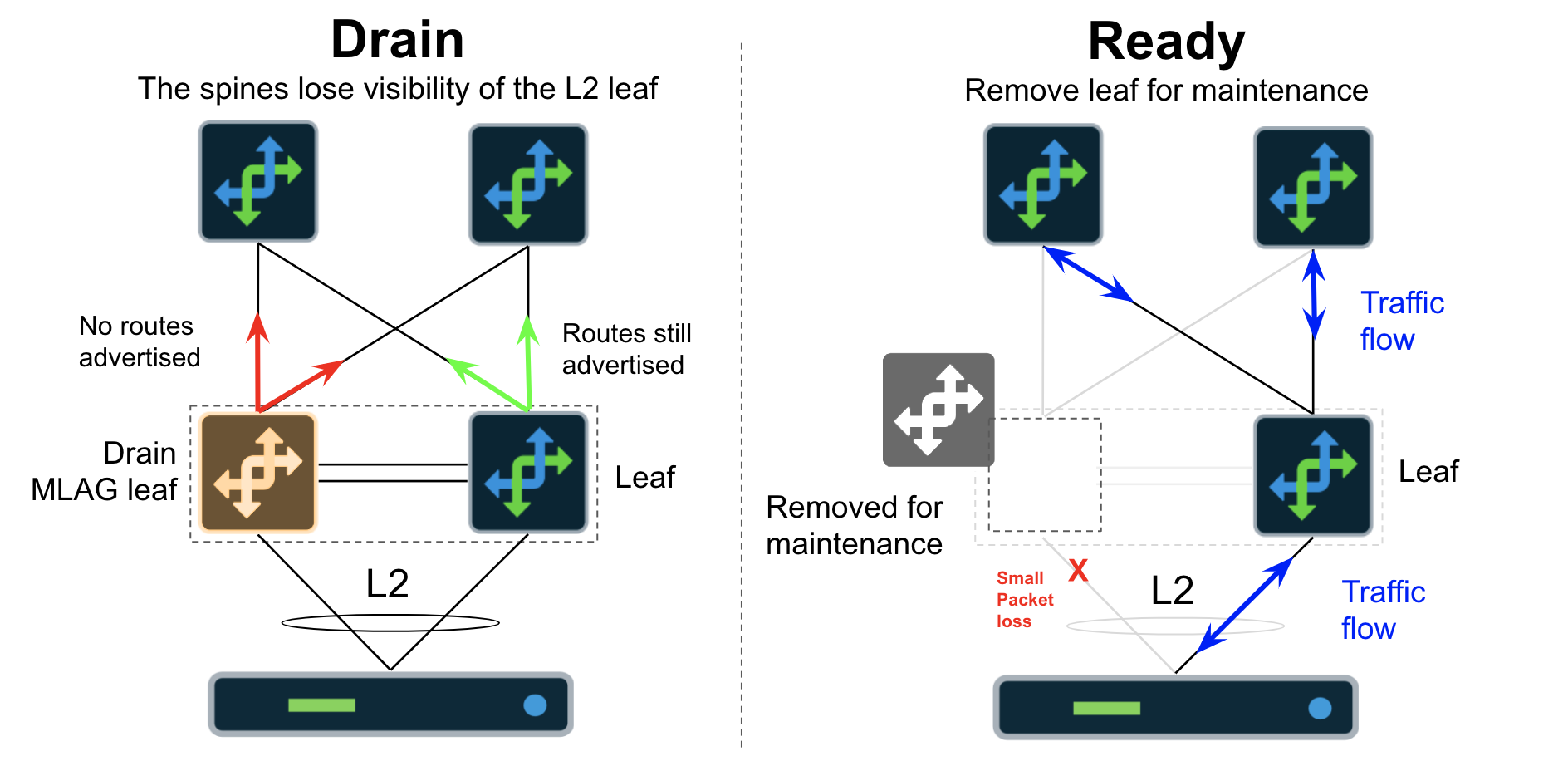
+ export ( Drain ); Drain Leaf Devices (Server-Facing Ports w/ MLAG)
The following occurs when draining Leaf devices with a server-facing port in an MLAG:
-
A route-map is placed on all BGP neighbors restricting inbound and outbound routes.
-
Server facing interfaces are shutdown.
-
MLAG peer interfaces are shutdown.
What happens at L3:
-
Outbound routes are removed from the device’s routing table.
-
Routes to destinations with the device’s ASN in the AS-PATH are removed from all devices in the network.
-
Packets are forwarded through remaining ECMP paths for all destinations.
It is highly unlikely that a single in-flight packet will be lost, however, this is dependent on the L3 ECMP to L2 path hashing algorithms in the hardware and NOS.
What happens at L2:
-
Server interfaces to this device will go DOWN.
-
Packets from the server that happen to be hashed onto this device via MLAG may be dropped depending on where they are in the forwarding process.
-
Packets from the server that happen to be hashed onto this device via MLAG may be forwarded over the MLAG peer link depending on where they are in the forwarding process.
-
Flows will be reestablished on the alternate MLAG interfaces.
-
New flows will be established on the remaining MLAG interfaces.
Drain (NX-OS)
interface Ethernet1/1
shutdown
exit
!
interface Ethernet1/2
shutdown
exit
!
interface port-channel1
shutdown
exit
!
ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
ipv6 prefix-list DrainV6 seq 5 permit 0::0/0 le 128
route-map Drain deny 10
match ip address prefix-list Drain
exit
!
route-map DrainV6 deny 10
match ipv6 address prefix-list DrainV6
exit
!
router bgp 64514
neighbor 10.0.0.0 remote-as 64512
address-family l2vpn evpn
route-map Drain out
route-map Drain in
exit
exit
neighbor 172.16.0.0 remote-as 64512
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-map Drain out
route-map Drain in
exit
exit Drain (EOS)
interface Ethernet5 shutdown exit ! interface Ethernet6 shutdown exit ! interface port-channel1 shutdown exit ! interface port-channel2 shutdown exit ! ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 route-map Drain deny 10 match ip address prefix-list Drain exit ! router bgp 102 neighbor 10.10.4.0 route-map Drain out neighbor 10.10.4.0 route-map Drain in neighbor 10.10.4.8 route-map Drain out neighbor 10.10.4.8 route-map Drain in default neighbor 10.10.4.19 route-map MlagPeer out neighbor 10.10.4.19 route-map Drain out neighbor 10.10.4.19 route-map Drain in !
Undrain (NS-OS)
What happens at L2:
-
Server interface to this device will go UP
-
New flows will be hashed onto the newly available MLAG interface
interface Ethernet1/1
no shutdown
exit
!
interface Ethernet1/2
no shutdown
exit
!
interface port-channel1
no shutdown
exit
!
no ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
no ipv6 prefix-list DrainV6 seq 5 permit 0::0/0 le 128
no route-map Drain deny 10
!
no route-map DrainV6 deny 10
!
router bgp 64514
neighbor 10.0.0.0 remote-as 64512
address-family l2vpn evpn
default route-map Drain out
default route-map Drain in
exit
exit Undrain (EOS)
What happens at L2:
-
Server interface to this device will go UP
-
New flows will be hashed onto the newly available MLAG interface
interface Ethernet5 no shutdown exit ! interface Ethernet6 no shutdown exit ! interface port-channel1 no shutdown exit ! interface port-channel2 no shutdown exit ! no ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 no route-map Drain deny 10 ! router bgp 102 default neighbor 10.10.4.0 route-map Drain out default neighbor 10.10.4.0 route-map Drain in default neighbor 10.10.4.8 route-map Drain out default neighbor 10.10.4.8 route-map Drain in default neighbor 10.10.4.19 route-map Drain out neighbor 10.10.4.19 route-map MlagPeer out default neighbor 10.10.4.19 route-map Drain in !
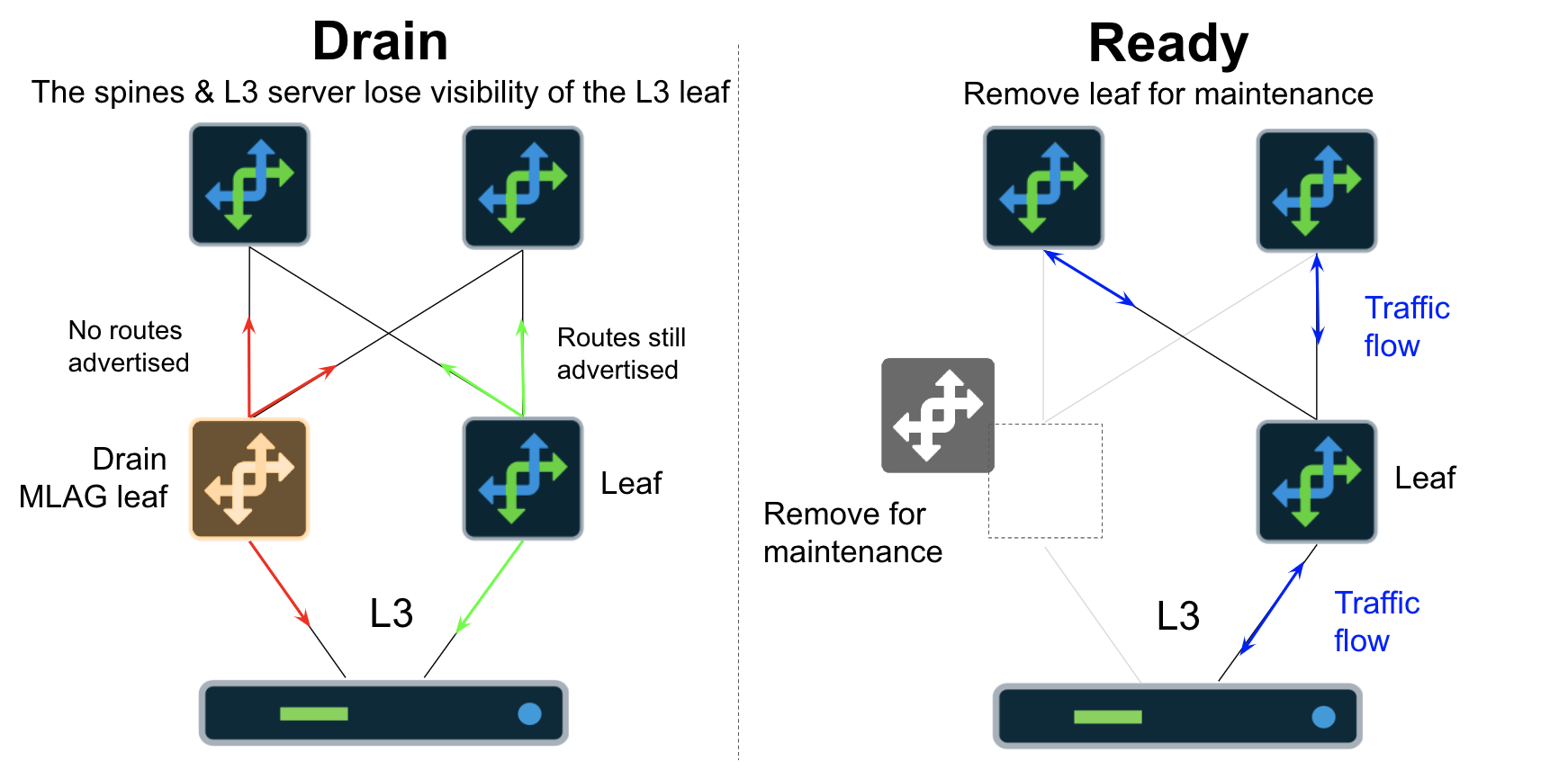
Drain Leaf Devices (L2 Server-Facing Ports no MLAG)
The following occurs when draining a Leaf device with a server-facing port with no MLAG:
-
A route-map is placed on all BGP neighbors restricting inbound and outbound routes
-
Server facing interfaces are shutdown
Drain (Junos)
[interfaces replace: ae1] + disable; [interfaces replace: xe-0/0/2] + disable; [interfaces replace: xe-0/0/3] + disable; [routing-instances blue protocols bgp group l3rtr neighbor 192.168.0.11] - import ( RoutesFromExt-blue-Default_immutable ); - export ( RoutesToExt-blue-Default_immutable ); + import ( Drain ); + export ( Drain ); [routing-instances red protocols bgp group l3rtr neighbor 192.168.0.7] - import ( RoutesFromExt-red-Default_immutable ); - export ( RoutesToExt-red-Default_immutable ); + import ( Drain ); + export ( Drain ); [protocols bgp group l3clos-l neighbor 172.16.0.2] - export ( LEAF_TO_SPINE_FABRIC_OUT && BGP-AOS-Policy ); + import ( Drain ); + export ( Drain ); [protocols bgp group l3clos-l neighbor 172.16.0.8] - export ( LEAF_TO_SPINE_FABRIC_OUT && BGP-AOS-Policy ); + import ( Drain ); + export ( Drain ); [protocols bgp group l3clos-l-evpn neighbor 10.0.0.3] - export ( LEAF_TO_SPINE_EVPN_OUT && EVPN_EXPORT ); + import ( Drain ); + export ( Drain && EVPN_EXPORT ); [protocols bgp group l3clos-l-evpn neighbor 10.0.0.4] - export ( LEAF_TO_SPINE_EVPN_OUT && EVPN_EXPORT ); + import ( Drain ); + export ( Drain && EVPN_EXPORT ); [protocols bgp group l3rtr neighbor 192.168.0.3] - import ( RoutesFromExt-default-Default_immutable ); - export ( RoutesToExt-default-Default_immutable ); + import ( Drain ); + export ( Drain ); + [policy-options route-filter-list Drain] + 0.0.0.0/0 upto /32; + [policy-options policy-statement Drain term Drain-10 from] + route-filter-list Drain; + family inet; + [policy-options policy-statement Drain term Drain-10] + then reject
Drain (NX-OS)
interface Ethernet1/41
shutdown
exit
!
ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
route-map Drain deny 10
match ip address prefix-list Drain
exit
!
router bgp 64516
neighbor 172.16.0.8 remote-as 64512
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-map Drain out
route-map Drain in
exit
exit
neighbor 172.16.0.22 remote-as 64513
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-map Drain out
route-map Drain in
exit
exit
exit
! Drain (EOS)
interface Ethernet5
shutdown
exit
!
ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
route-map Drain deny 10
match ip address prefix-list Drain
exit
!
router bgp 104
default neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map RoutesToExt out
neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map Drain out
default neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map RoutesFromExt in
neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map Drain in
neighbor 10.10.4.4 route-map Drain out
neighbor 10.10.4.4 route-map Drain in
neighbor 10.20.30.4 route-map Drain out
neighbor 10.20.30.4 route-map Drain in
neighbor 10.10.4.12 route-map Drain out
neighbor 10.10.4.12 route-map Drain in
neighbor 10.20.30.5 route-map Drain out
neighbor 10.20.30.5 route-map Drain in
vrf Finance
default neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map RoutesToExt-Finance out
neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map Drain out
default neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map RoutesFromExt-Finance in
neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map Drain in
exit
! Undrain (NX-OS)
interface Ethernet1/41
no shutdown
exit
!
no ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
no route-map Drain deny 10
!
router bgp 64516
neighbor 172.16.0.8 remote-as 64512
address-family ipv4 unicast
default route-map Drain out
default route-map Drain in
exit
exit
neighbor 172.16.0.10 remote-as 64512
address-family ipv4 unicast
default route-map Drain out
default route-map Drain in
exit
exit
neighbor 10.0.0.1 remote-as 64513
address-family l2vpn evpn
default route-map Drain out
default route-map Drain in
exit
exit
neighbor 172.16.0.20 remote-as 64513
address-family ipv4 unicast
default route-map Drain out
default route-map Drain in
exit
exit
neighbor 172.16.0.22 remote-as 64513
address-family ipv4 unicast
default route-map Drain out
default route-map Drain in
exit
exit
exit
! Undrain (EOS)
interface Ethernet5
no shutdown
exit
!
no ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
no route-map Drain deny 10
!
router bgp 104
default neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map Drain out
neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map RoutesToExt out
default neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map Drain in
neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map RoutesFromExt in
default neighbor 10.10.4.4 route-map Drain out
default neighbor 10.10.4.4 route-map Drain in
default neighbor 10.20.30.4 route-map Drain out
default neighbor 10.20.30.4 route-map Drain in
default neighbor 10.10.4.12 route-map Drain out
default neighbor 10.10.4.12 route-map Drain in
default neighbor 10.20.30.5 route-map Drain out
default neighbor 10.20.30.5 route-map Drain in
vrf Finance
default neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map Drain out
neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map RoutesToExt-Finance out
default neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map Drain in
neighbor 9.0.0.1 route-map RoutesFromExt-Finance in
exit
! Drain Leaf Devices (L3 Connected Servers)
Drain (EOS)
ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 route-map Drain deny 10 match ip address prefix-list Drain exit ! router bgp 102 neighbor 10.10.4.0 route-map Drain out neighbor 10.10.4.0 route-map Drain in neighbor 10.10.4.8 route-map Drain out neighbor 10.10.4.8 route-map Drain in neighbor 11.0.0.1 route-map Drain out neighbor 11.0.0.1 route-map Drain in !
Undrain (EOS)
no ip prefix-list Drain seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 no route-map Drain deny 10 ! router bgp 102 default neighbor 10.10.4.0 route-map Drain out default neighbor 10.10.4.0 route-map Drain in default neighbor 10.10.4.8 route-map Drain out default neighbor 10.10.4.8 route-map Drain in default neighbor 11.0.0.1 route-map Drain out default neighbor 11.0.0.1 route-map Drain in !
