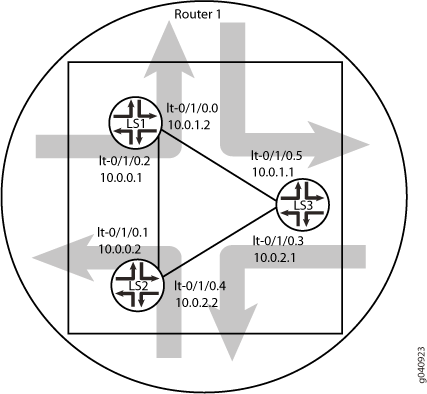
예: 동일한 라우터 내의 논리적 시스템에서 IS-IS 구성
이 예는 단일 물리적 라우터에서 실행되는 여러 논리적 시스템을 사용하여 IS-IS 네트워크를 구성하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 논리적 시스템은 논리적 터널 인터페이스에 의해 연결됩니다.
요구 사항
논리적 터널(lt) 인터페이스를 사용하여 논리적 시스템을 연결해야 합니다. 예: MX 시리즈 라우터 및 EX 시리즈 스위치에서 논리적 터널 인터페이스를 사용하여 동일한 디바이스 내에서 논리적 시스템 연결을 참조하십시오.
개요
이 예는 하나의 물리적 라우터에서 실행되는 세 개의 논리적 시스템이 있는 IS-IS 구성을 보여줍니다. 각 논리적 시스템에는 자체 라우팅 테이블이 있습니다. 이 구성은 IS-IS 도메인에 참여하는 모든 논리적 터널 인터페이스에서 프로토콜을 활성화합니다.
구성
CLI 빠른 구성
이 예를 빠르게 구성하려면, 아래 명령을 복사하여 텍스트 파일로 붙여 넣은 다음 모든 라인브레이크를 제거하고, 네트워크 구성을 일치하는 데 필요한 세부 사항을 바꾸고 계층 수준에서 명령을 CLI [edit] 로 복사해 붙여 넣은 다음, 구성 모드에서 commit을 입력합니다.
set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 description LS1->LS2 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 peer-unit 1 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 family iso set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 description LS1->LS3 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 peer-unit 5 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.1.2/30 set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 family iso set logical-systems LS1 interfaces lo0 unit 1 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1001.00 set logical-systems LS1 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.0 set logical-systems LS1 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.2 set logical-systems LS1 protocols isis interface lo0.1 passive set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 description LS2->LS1 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 peer-unit 2 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family iso set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 description LS2->LS3 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 peer-unit 3 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 family inet address 10.0.2.2/30 set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 family iso set logical-systems LS2 interfaces lo0 unit 2 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.2002.00 set logical-systems LS2 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.1 set logical-systems LS2 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.4 set logical-systems LS2 protocols isis interface lo0.2 passive set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 description LS3->LS2 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 peer-unit 4 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 family inet address 10.0.2.1/30 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 family iso set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 description LS3->LS1 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 encapsulation ethernet set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 peer-unit 0 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 family inet address 10.0.1.1/30 set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 family iso set logical-systems LS3 interfaces lo0 unit 3 family iso address 49.0001.1234.1600.2231.00 set logical-systems LS3 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.5 set logical-systems LS3 protocols isis interface lt-0/1/0.3 set logical-systems LS3 protocols isis interface lo0.3 passive
절차
단계별 절차
다음 예제에서는 구성 계층에서 다양한 수준의 탐색이 필요합니다. CLI 탐색에 관한 정보는 CLI 사용자 가이드에서 구성 모드에서 CLI 편집기 사용을 참조하십시오.
논리적 시스템에서 IS-IS(Intermediate System to Intermediate System)를 구성하려면:
논리적 시스템 LS2에 연결하는 논리적 시스템 LS1에서 논리적 터널 인터페이스를 구성합니다.
[edit logical-systems LS1] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 description LS1->LS2 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 peer-unit 1 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 2 family iso
논리적 시스템 LS3에 연결하는 논리적 시스템 LS1에서 논리적 터널 인터페이스를 구성합니다.
[edit logical-systems LS1] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 description LS1->LS3 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 peer-unit 5 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.1.2/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 0 family iso
논리적 시스템 LS1에 연결하는 논리적 시스템 LS2에서 논리적 터널 인터페이스를 구성합니다.
[edit logical-systems LS2] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 description LS2->LS1 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 peer-unit 2 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 1 family iso
논리적 시스템 LS3에 연결하는 논리적 시스템 LS2에 논리적 터널 인터페이스를 구성합니다.
[edit logical-systems LS2] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 description LS2->LS3 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 peer-unit 3 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 family inet address 10.0.2.2/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 4 family iso
논리적 시스템 LS2에 연결하는 논리적 시스템 LS3에서 논리적 터널 인터페이스를 구성합니다.
[edit logical-systems LS3] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 description LS3->LS2 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 peer-unit 4 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 family inet address 10.0.2.1/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 3 family iso
논리적 시스템 LS1에 연결하는 논리적 시스템 LS3에서 논리적 터널 인터페이스를 구성합니다.
[edit logical-systems LS3] user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 description LS3->LS1 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 encapsulation ethernet user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 peer-unit 0 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 family inet address 10.0.1.1/30 user@host# set interfaces lt-0/1/0 unit 5 family iso
3개의 논리적 시스템에 대한 루프백 인터페이스에서 ISO 주소를 구성합니다.
[edit logical-systems LS1] user@host# set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1001.00 user@host# set protocols isis interface lo0.1 passive
[edit logical-systems LS2] user@host# set interfaces lo0 unit 2 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.2002.00 user@host# set protocols isis interface lo0.2 passive
[edit logical-systems LS3] user@host# set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family iso address 49.0001.1234.1600.2231.00 user@host# set protocols isis interface lo0.3 passive
모든 인터페이스에 IS-IS(Intermediate System to Intermediate System)를 구성합니다.
[edit logical-systems LS1 protocols isis] user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.0 user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.2
[edit logical-systems LS2 protocols isis] user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.1 user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.4
[edit logical-systems LS3 protocols isis] user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.5 user@host# set interface lt-0/1/0.3
디바이스 구성을 완료하면 해당 구성을 커밋합니다.
[edit] user@host# commit
결과
구성 모드에서 명령을 실행하여 show logical-systems 구성을 확인합니다. 출력 결과가 의도한 구성대로 표시되지 않으면 이 예의 지침을 반복하여 구성을 수정하십시오.
user@host# show logical-systems
LS1 {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 0 {
description LS1->LS3;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 5;
family inet {
address 10.0.1.2/30;
}
family iso;
}
unit 2 {
description LS1->LS2;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 1;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.1/30;
}
family iso;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 1 {
family iso {
address 49.0001.1720.1600.1001.00;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
isis {
interface lt-0/1/0.0;
interface lt-0/1/0.2;
interface lo0.1 {
passive;
}
}
}
}
LS2 {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 1 {
description LS2->LS1;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 2;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.2/30;
}
family iso;
}
unit 4 {
description LS2->LS3;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 3;
family inet {
address 10.0.2.2/30;
}
family iso;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 2 {
family iso {
address 49.0001.1720.1600.2002.00;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
isis {
interface lt-0/1/0.1;
interface lt-0/1/0.4;
interface lo0.2 {
passive;
}
}
}
}
LS3 {
interfaces {
lt-0/1/0 {
unit 3 {
description LS3->LS2;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 4;
family inet {
address 10.0.2.1/30;
}
family iso;
}
unit 5 {
description LS3->LS1;
encapsulation ethernet;
peer-unit 0;
family inet {
address 10.0.1.1/30;
}
family iso;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 3 {
family iso {
address 49.0001.1234.1600.2231.00;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
isis {
interface lt-0/1/0.3;
interface lt-0/1/0.5;
interface lo0.3 {
passive;
}
}
}
}
확인
구성이 올바르게 작동하고 있는지 확인합니다.
논리적 시스템이 작동 중인지 확인하기
목적
인터페이스가 올바르게 구성되었는지 확인합니다.
행동
user@host> show interfaces terse
Interface Admin Link Proto Local Remote
...
lt-0/1/0 up up
lt-0/1/0.0 up up inet 10.0.1.2/30
iso
lt-0/1/0.1 up up inet 10.0.0.2/30
iso
lt-0/1/0.2 up up inet 10.0.0.1/30
iso
lt-0/1/0.3 up up inet 10.0.2.1/30
iso
lt-0/1/0.4 up up inet 10.0.2.2/30
iso
lt-0/1/0.5 up up inet 10.0.1.1/30
iso
...
논리적 시스템 간 연결 검증
목적
논리적 시스템 라우팅 항목을 확인하고 논리적 시스템을 ping하여 IS-IS 인접 항목이 설정되었는지 확인합니다.
행동
user@host> show route logical-system LS1
inet.0: 5 destinations, 5 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:37:52
> via lt-0/1/0.2
10.0.0.1/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:37:52
Local via lt-0/1/0.2
10.0.1.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:37:52
> via lt-0/1/0.0
10.0.1.2/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:37:52
Local via lt-0/1/0.0
10.0.2.0/30 *[IS-IS/15] 3w0d 01:37:13, metric 20
> to 10.0.1.1 via lt-0/1/0.0
to 10.0.0.2 via lt-0/1/0.2
iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
49.0001.1720.1600.1001/72
*[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:37:52
> via lo0.1
user@host> show route logical-system LS2
inet.0: 5 destinations, 5 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:01
> via lt-0/1/0.1
10.0.0.2/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:38:01
Local via lt-0/1/0.1
10.0.1.0/30 *[IS-IS/15] 3w0d 01:37:01, metric 20
to 10.0.0.1 via lt-0/1/0.1
> to 10.0.2.1 via lt-0/1/0.4
10.0.2.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:01
> via lt-0/1/0.4
10.0.2.2/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:38:01
Local via lt-0/1/0.4
iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
49.0001.1720.1600.2002/72
*[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:01
> via lo0.2
user@host> show route logical-system LS3
inet.0: 5 destinations, 5 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.0/30 *[IS-IS/15] 3w0d 01:37:10, metric 20
to 10.0.2.2 via lt-0/1/0.3
> to 10.0.1.2 via lt-0/1/0.5
10.0.1.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:10
> via lt-0/1/0.5
10.0.1.1/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:38:11
Local via lt-0/1/0.5
10.0.2.0/30 *[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:11
> via lt-0/1/0.3
10.0.2.1/32 *[Local/0] 3w0d 01:38:11
Local via lt-0/1/0.3
iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
49.0001.1234.1600.2231/72
*[Direct/0] 3w0d 01:38:11
> via lo0.3
LS1에서 LS3 ping
user@host> set cli logical-system LS1
user@host:LS1> ping 10.0.2.1 PING 10.0.2.1 (10.0.2.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.2.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=63 time=1.264 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.2.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=1.189 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.2.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=1.165 ms ^C --- 10.0.2.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.165/1.206/1.264/0.042 ms
LS3에서 LS1 ping
user@host> set cli logical-system LS3
user@host:LS3> ping 10.0.0.1 PING 10.0.0.1 (10.0.0.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=63 time=1.254 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=1.210 ms ^C --- 10.0.0.1 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.210/1.232/1.254/0.022 ms
LS1에서 LS2 ping
user@host> set cli logical-system LS1
user@host:LS1> ping 10.0.2.2 PING 10.0.2.2 (10.0.2.2): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.2.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=1.240 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.2.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.204 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.2.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.217 ms ^C --- 10.0.2.2 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.204/1.220/1.240/0.015 ms
LS2에서 LS1 ping
user@host> set cli logical-system LS2
user@host:LS2> ping 10.0.1.2 PING 10.0.1.2 (10.0.1.2): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.1.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=1.308 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.235 ms ^C --- 10.0.1.2 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.235/1.272/1.308/0.037 ms
LS2에서 LS3 ping
user@host> set cli logical-system LS2
user@host:LS2> ping 10.0.1.1 PING 10.0.1.1 (10.0.1.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=1.253 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.194 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.212 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.221 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=1.195 ms ^C --- 10.0.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.194/1.215/1.253/0.022 ms
LS3에서 LS2 ping
user@host> set cli logical-system LS3
user@host:LS3> ping 10.0.0.2 PING 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=1.240 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.217 ms ^C --- 10.0.0.2 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.217/1.228/1.240/0.012 ms