예: IS-IS 트래픽 엔지니어링 지원 활성화
이 예는 레이블 스위칭 경로를 단축키로 사용하도록 IS-IS(Intermediate System to Intermediate System)를 구성하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
요구 사항
이 예를 구성하기 전에 디바이스 초기화를 제외한 특별한 구성은 필요하지 않습니다.
개요
MPLS 트래픽 엔지니어링은 특정 데이터 플로우를 최적(최단) 경로의 일부로 내부 게이트웨이 프로토콜(IGP)에 의해 계산된 데이터 링크가 아닌 설정된 LSP(Label-Switched Path)에 매핑합니다. 이 기능의 핵심은 LSP에 매핑할 트래픽을 결정하는 것입니다. 트래픽은 특정 목적지 접두사에 대한 다음 홉 라우터로 송신 LSR을 지정하여 터널의 수신 레이블 스위칭 라우터(LSR)에 있는 LSP에 매핑됩니다.
LSP가 목적지에 대한 전체 경로를 구성하지 않는다는 것을 이해하는 것이 중요합니다. 오히려 LSP는 경로의 다음 홉 세그먼트입니다. 따라서 경로 확인 과정에서 송신 LSR이 실행 가능한 다음 홉 후보로 간주되는 경우에만 패킷을 LSP에 매핑할 수 있습니다.
그림 1 은 이 예에서 사용되는 토폴로지입니다.
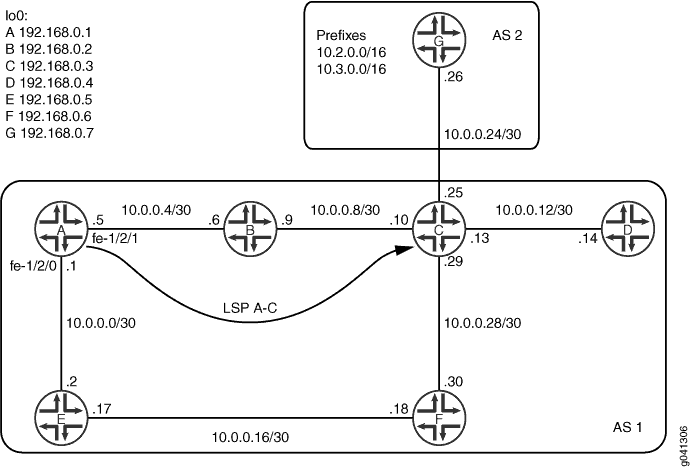
이 예에서 디바이스 C는 자율 시스템(AS) 2의 디바이스 G와 외부 BGP(EBGP) 피어 세션을 가지고 있습니다. 내부 BGP(IBGP) 피어가 AS 2의 서브넷에 액세스할 수 있도록 하기 위해 디바이스 C는 디바이스 G에 연결된 인터페이스에서 IS-IS(Intermediate System to Intermediate System)를 수동적으로 실행합니다. IS-IS는 외부 서브넷에 대한 정보를 가지고 있으며 inet.0 라우팅 테이블에 이러한 서브넷에 대한 경로를 입력합니다. BGP는 AS-external 경로의 다음 홉 주소를 확인할 때 IGP 경로를 사용합니다.
인터페이스에서 IS-IS(Intermediate System to Intermediate System)를 수동적으로 실행하는 대안은 넥스트 홉 자체 정책을 사용하는 것입니다.
디바이스 A는 디바이스 C에 대한 LSP를 보유합니다. 경로는 항상 디바이스 B를 통과하지 않고 디바이스 E를 통과하도록 구성됩니다.
트래픽 엔지니어링 바로 가기라고도 하는 IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol) 바로 가기는 AS의 링크 상태 IGP(OSPF 또는 IS-IS)가 최단 경로 우선(SPF) 계산에서 LSP를 고려할 수 있는 도구를 제공합니다. 패시브 외부 인터페이스를 사용하는 경우, IGP는 LSP를 LSP 송신 디바이스 너머의 대상을 향한 단일 데이터 링크로 간주합니다.
(기본값) 및 IGP 바로 가기를 사용하는 traffic-engineering bgp 경우, 트래픽 엔지니어링 솔루션은 BGP AS-외부 경로 확인에만 사용됩니다. 그러나 AS 내부 목적지로의 트래픽도 LSP에 매핑할 수 있습니다. 이를 위해 은(는) traffic-engineering bgp-igp 활성화되어 있습니다. 따라서 RSVP는 MPLS 접두사를 inet.3 테이블이 아닌 inet.0 테이블에 설치합니다. 그 결과, MPLS LSP가 포워딩 테이블에 설치됩니다.
이 접근 방식은 과도한 트래픽이 서버 팜과 같은 AS 내의 특정 대상으로 라우팅될 때마다 실용적으로 적용됩니다.
IGP 바로 가기의 중요한 점은 단독으로 사용하든 트래픽 엔지니어링 BGP-IGP와 함께 사용하든 IGP 인접성이 LSP 간에 형성되지 않는다는 것입니다. IGP는 LSP를 단일 데이터 링크로 간주하지만 송신 라우터를 잠재적 피어로 않으며 LSP 전체에 Hello 메시지를 전달하지 않습니다. 또한 RSVP 메시지는 LSP를 통해 전달되지 않으므로 LSP가 다른 LSP 내에 의도치 않게 구축될 가능성을 방지합니다.
CLI 빠른 구성 은 그림 1의 모든 디바이스에 대한 구성을 보여줍니다. #configuration424__isis-shortcuts-step-by-step 섹션에서는 디바이스 A의 단계를 설명합니다.
구성
절차
CLI 빠른 구성
이 예를 빠르게 구성하려면, 아래 명령을 복사하여 텍스트 파일로 붙여 넣은 다음 모든 라인브레이크를 제거하고, 네트워크 구성을 일치하는 데 필요한 세부 사항을 바꾸고 계층 수준에서 명령을 CLI [edit] 로 복사해 붙여 넣습니다.
디바이스 A
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0001.00 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls traffic-engineering bgp-igp set protocols mpls label-switched-path test_path to 192.168.0.3 set protocols mpls label-switched-path test_path no-cspf set protocols mpls label-switched-path test_path primary through_E set protocols mpls path through_E 192.168.0.5 strict set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols isis traffic-engineering family inet shortcuts set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
디바이스 B
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.6/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.9/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.2/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0002.00 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
디바이스 C
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.10/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.13/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.25/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.29/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.3/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0003.00 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/3.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/3.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.3 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group external-peers type external set protocols bgp group external-peers export send-some-isis set protocols bgp group external-peers peer-as 2 set protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 10.0.0.26 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/2.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/2.0 level 2 passive set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/3.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set policy-options policy-statement send-some-isis term 1 from protocol isis set policy-options policy-statement send-some-isis term 1 from route-filter 10.0.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement send-some-isis term 1 from route-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement send-some-isis term 1 then accept set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.3 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
디바이스 D
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.14/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.4/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0004.00 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.4 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
디바이스 E
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.17/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.5/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0005.00 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.5 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
디바이스 F
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.18/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.30/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.6/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0006.00 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/2.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/2.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/2.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.6 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
디바이스 G
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.26/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.7/32 primary set interfaces lo0 unit 0family inet address 10.2.1.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0family inet address 10.3.1.1/32 set protocols bgp group external-peers type external set protocols bgp group external-peers export statics set protocols bgp group external-peers export send-directs set protocols bgp group external-peers peer-as 1 set protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 10.0.0.25 set policy-options policy-statement statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement send-directs term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement send-directs term 1 then accept set routing-options static route 10.2.0.0/32 reject set routing-options static route 10.2.0.0/32 install set routing-options static route 10.3.0.0/32 reject set routing-options static route 10.3.0.0/32 install set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.7 set routing-options autonomous-system 2
단계별 절차
다음 예제에서는 구성 계층에서 다양한 수준의 탐색이 필요합니다. CLI 탐색에 관한 정보는 CLI 사용자 가이드에서 구성 모드에서 CLI 편집기 사용을 참조하십시오.
IS-IS 트래픽 엔지니어링 단축키 구성:
인터페이스를 구성합니다.
[edit interfaces] user@A# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 user@A# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso user@A# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls user@A# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 user@A# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso user@A# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls user@A# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 user@A# set lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0001.00
인터페이스에서 신호 전송 프로토콜을 활성화합니다.
[edit protocols rsvp] user@A# set interface lo0.0 user@A# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 user@A# set interface fe-1/2/1.0
인터페이스에 MPLS 활성화합니다.
[edit protocols mpls] user@A# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 user@A# set interface fe-1/2/1.0
레이블 스위칭 경로를 구성합니다.
test_path라는 단일 LSP는 디바이스 A에서 디바이스 C로 구성됩니다. LSP 명시적 경로 객체(ERO)는 디바이스 E를 통해 엄격한 홉을 사용하도록 지정되므로 LSP는 최단 경로 우선(OSPF) A–B–C와 다른 경로를 사용합니다. LSP는 RSVP를 사용하여 시그널링되지만, CSPF는 실행되지 않습니다.
[edit protocols mpls] user@A# set label-switched-path test_path to 192.168.0.3 user@A# set label-switched-path test_path no-cspf user@A# set label-switched-path test_path primary through_E user@A# set path through_E 192.168.0.5 strict
BGP 및 IGP 목적지 모두에 대해 트래픽 엔지니어링을 구성합니다.
IGP 바로 가기도 활성화되면 IGP는 계산에 LSP를 사용할 수 있습니다. 계산 결과는 inet.0 테이블에 입력됩니다.
[edit protocols mpls] user@A# set traffic-engineering bgp-igp
디바이스 간의 내부 BGP(IBGP) 피어링을 구성합니다.
[edit protocols bgp group int] user@A# set type internal user@A# set local-address 192.168.0.1 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.0.5 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.0.6 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.0.2 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.0.3
인터페이스에서 IS-IS(Intermediate System to Intermediate System)를 활성화하고 링크 메트릭을 설정합니다.
[edit protocols isis] user@A# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable user@A# set interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable user@A# set interface lo0.0
IPv4 주소 패밀리에 대한 다음 홉으로 MPLS LSP를 사용하도록 IS-IS(Intermediate System to Intermediate System)를 구성합니다.
IGP 수신 라우터는 SPF(Shortest-Path-First) 계산을 수행하는 라우터이기 때문에 IGP 바로 가기만 활성화하면 됩니다.
IGP 단축키가 프로토콜과 라우팅 테이블 관계에 어떤 영향을 미치는지 이해하는 것이 중요합니다. IGP는 LSP 송신 지점의 서브넷 다운스트림에 대해 SPF 계산을 수행하지만 이러한 계산 결과는 inet.3 테이블에만 입력됩니다. 동시에 IGP는 기존의 SPF 계산을 수행하고 이러한 계산 결과를 inet.0 테이블에 입력합니다. 그 결과 IGP가 inet.3 테이블에 항목을 만들더라도 BGP는 여전히 경로 확인을 위해 해당 테이블에 가시성을 가진 유일한 프로토콜입니다. 따라서 AS-internal 목적지로의 포워딩은 여전히 inet.0 IGP 경로를 사용하며 LSP는 BGP 다음 홉 해결에만 사용됩니다. IGP 다음 홉 해결에 LSP를 사용하려면 을 구성해야
traffic-engineering bgp-igp합니다.[edit protocols isis] user@A# set traffic-engineering family inet shortcuts
라우터 ID 및 AS(Autonomous System) 번호를 구성합니다.
[edit routing-options] user@A# set router-id 192.168.0.1 user@A# set autonomous-system 1
결과
구성 모드에서 , show protocols, 및 show routing-options 명령을 입력하여 show interfaces구성을 확인합니다. 출력 결과가 의도한 구성대로 표시되지 않으면 이 예의 지침을 반복하여 구성을 수정하십시오.
user@A# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 0{
family inet {
address 10.0.0.1/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
fe-1/2/1{
unit 0
family inet {
address 10.0.0.5/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0{
family inet {
address 192.168.0.1/32;
}
family iso {
address 49.0002.0192.0168.0001.00;
}
}
}
user@A# show protocols
rsvp {
interface lo0.0;
interface fe-1/2/0.0;
interface fe-1/2/1.0;
}
mpls {
traffic-engineering bgp-igp;
label-switched-path test_path {
to 192.168.0.3;
no-cspf;
primary through_E;
}
path through_E {
192.168.0.5 strict;
}
interface fe-1/2/0.0;
interface fe-1/2/1.0;
}
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.0.1;
neighbor 192.168.0.5;
neighbor 192.168.0.6;
neighbor 192.168.0.2;
neighbor 192.168.0.3;
}
}
isis {
traffic-engineering {
family inet {
shortcuts;
}
}
interface fe-1/2/0.0 {
level 1 disable;
}
interface fe-1/2/1.0 {
level 1 disable;
}
interface lo0.0;
}
user@A# show routing-options
router-id 192.168.0.1;
autonomous-system 1;
디바이스 구성을 마쳤으면 구성 모드에서 commit 을 입력합니다.
확인
구성이 올바르게 작동하고 있는지 확인합니다.
다음 홉 확인
목적
MPLS LSP가 예상 경로에서 다음 홉으로 사용되는지 확인합니다.
행동
운영 모드에서 명령을 입력합니다 show route .
user@A> show route
inet.0: 21 destinations, 21 routes (21 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 4d 09:07:26
> via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.1/32 *[Local/0] 4d 09:07:26
Local via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.4/30 *[Direct/0] 4d 09:07:28
> via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.5/32 *[Local/0] 4d 09:07:28
Local via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.8/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.12/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.16/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.20/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.24/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.28/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 30
to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.2.0.0/32 *[BGP/170] 02:22:30, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 2 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
10.2.1.1/32 *[BGP/170] 02:20:23, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 2 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
10.3.0.0/32 *[BGP/170] 02:22:30, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 2 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
10.3.1.1/32 *[BGP/170] 02:20:23, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 2 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
192.168.0.1/32 *[Direct/0] 4d 09:08:47
> via lo0.0
192.168.0.2/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 10
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
192.168.0.3/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
192.168.0.4/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.5/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 10
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.6/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.7/32 *[BGP/170] 02:20:23, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 2 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
inet.3: 5 destinations, 6 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.12/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:41:21, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
10.0.0.24/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:41:21, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
10.0.0.28/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:41:21, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
192.168.0.3/32 *[RSVP/7/1] 01:41:21, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
[IS-IS/18] 01:41:21, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
192.168.0.4/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:41:21, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
49.0002.0192.0168.0001/72
*[Direct/0] 4d 09:08:47
> via lo0.0
mpls.0: 4 destinations, 4 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0 *[MPLS/0] 4d 09:10:00, metric 1
Receive
1 *[MPLS/0] 4d 09:10:00, metric 1
Receive
2 *[MPLS/0] 4d 09:10:00, metric 1
Receive
13 *[MPLS/0] 4d 09:10:00, metric 1
Receive
의미
IS-IS(Intermediate System to Intermediate System)는 LSP 송신 디바이스의 대상 다운스트림에 대한 최단 경로로 LSP를 선택합니다. 또한 IGP는 LSP를 사용하여 외부 서브넷 10.0.0.24/30에 도달하기 때문에 BGP는 10.2.0.0 및 10.3.0.0에 대한 경로에서도 LSP를 사용합니다.
디바이스 C에서 다음 홉 자체를 사용하는 경우에도 BGP는 IGP 경로를 통해 LSP를 선택합니다.
RSVP 세션 확인
목적
RSVP 세션에 대한 정보 표시
행동
운영 모드에서 명령을 입력합니다 show rsvp session brief .
user@A> show rsvp session brief Ingress RSVP: 1 sessions To From State Rt Style Labelin Labelout LSPname 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 Up 0 1 FF - 299776 test_path Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0 Egress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Transit RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
user@E> show rsvp session brief Ingress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Egress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Transit RSVP: 1 sessions To From State Rt Style Labelin Labelout LSPname 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 Up 0 1 FF 299776 299808 test_path Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
user@F> show rsvp session brief Ingress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Egress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Transit RSVP: 1 sessions To From State Rt Style Labelin Labelout LSPname 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 Up 0 1 FF 299808 3 test_path Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
user@C> show rsvp session brief Ingress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Egress RSVP: 1 sessions To From State Rt Style Labelin Labelout LSPname 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 Up 0 1 FF 3 - test_path Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0 Transit RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
의미
4개의 라우팅 디바이스 모두에서 LSP의 수신 및 송신 IP 주소가 표시됩니다. 경로는 디바이스 A에서 수신 경로로 표시되며 LSP에서 전송된 패킷에는 레이블 299776가 할당됩니다. 디바이스 E에서 LSP는 전송되며, 299776 레이블로 도착하는 패킷에는 발신 레이블 299808이 부여됩니다. 레이블은 이웃하는 레이블 스위칭 라우터(LSR) 사이에서만 의미가 있습니다. 디바이스 F는 수신 레이블 299808 발신 레이블 3으로 스왑합니다. 송신 디바이스 C는 레이블 3을 팝하고 표준 IP longest-match 경로 조회를 통해 수신된 패킷을 라우팅합니다.
다른 트래픽 엔지니어링 설정으로 경로 확인
목적
이(가) 사용될 때와 (기본)이 사용될 때 traffic-engineering bgp-igp traffic-engineering bgp IGP 및 BGP 경로에 사용되는 경로를 확인합니다.
행동
를 구성합니다
traffic-engineering bgp.각 라우팅 인스턴스에서 하나의 MPLS 트래픽 엔지니어링 설정만 구성할 수 있으므로 이렇게 하면 구성에서 제거
traffic-engineering bgp-igp됩니다.[edit protocols mpls] user@A# set traffic-engineering bgp user@A# commit
show route forwarding-table(기본)이 구성된 경우traffic-engineering bgp명령을 사용하여 경로를 확인합니다.user@A> show route forwarding-table destination 10.2.1.1 Routing table: default.inet Internet: Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif 10.2.1.1/32 user 0 indr 262145 6 10.0.0.2 Push 299776 1013 2 fe-1/2/0.0user@A> show route forwarding-table destination 192.168.0.3 Routing table: default.inet Internet: Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif 192.168.0.3/32 user 1 10.0.0.6 ucst 938 11 fe-1/2/1.0
traceroute(기본)이 구성된 경우traffic-engineering bgp명령을 사용하여 경로를 확인합니다.user@A> traceroute 10.2.1.1 traceroute to 10.2.1.1 (10.2.1.1), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 11.086 ms 1.587 ms 1.603 ms MPLS Label=299776 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 2 10.0.0.18 (10.0.0.18) 1.455 ms 1.477 ms 1.442 ms MPLS Label=299808 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 3 10.0.0.29 (10.0.0.29) 2.240 ms 1.045 ms 1.243 ms 4 10.2.1.1 (10.2.1.1) 1.363 ms 1.389 ms 1.374 msuser@A> traceroute 192.168.0.3 traceroute to 192.168.0.3 (192.168.0.3), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.6 (10.0.0.6) 1.759 ms 1.872 ms 2.281 ms 2 bb03-cclab-lo0.spglab.juniper.net (192.168.0.3) 2.119 ms 2.157 ms 1.598 ms
를 구성합니다
traffic-engineering bgp-igp.각 라우팅 인스턴스에서 하나의 MPLS 트래픽 엔지니어링 설정만 구성할 수 있으므로 이렇게 하면 구성에서 제거
traffic-engineering bgp됩니다.[edit protocols mpls] user@A# set traffic-engineering bgp-igp user@A# commit
show route forwarding-table이(가) 구성된 경우traffic-engineering bgp-igp명령을 사용하여 경로를 확인합니다.user@A> show route forwarding-table destination 10.2.1.1 Routing table: default.inet Internet: Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif 10.2.1.1/32 user 0 indr 262145 6 10.0.0.2 Push 299776 1013 2 fe-1/2/0.0user@A> show route forwarding-table destination 192.168.0.3 Routing table: default.inet Internet: Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif 192.168.0.3/32 user 1 10.0.0.2 Push 299776 1013 8 fe-1/2/0.0
traceroute이(가) 구성된 경우traffic-engineering bgp-igp명령을 사용하여 경로를 확인합니다.user@A> traceroute 10.2.1.1 traceroute to 10.2.1.1 (10.2.1.1), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 2.348 ms 1.475 ms 1.434 ms MPLS Label=299776 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 2 10.0.0.18 (10.0.0.18) 1.507 ms 2.307 ms 1.911 ms MPLS Label=299808 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 3 10.0.0.29 (10.0.0.29) 1.743 ms 1.645 ms 1.940 ms 4 10.2.1.1 (10.2.1.1) 2.041 ms 1.977 ms 2.233 msuser@A> traceroute 192.168.0.3 traceroute to 192.168.0.3 (192.168.0.3), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 1.721 ms 2.558 ms 2.229 ms MPLS Label=299776 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 2 10.0.0.18 (10.0.0.18) 2.505 ms 1.462 ms 1.408 ms MPLS Label=299808 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 3 bb03-cclab-lo0.spglab.juniper.net (192.168.0.3) 1.371 ms 1.422 ms 1.351 ms
의미
이(가) 구성되면 traffic-engineering bgp 첫 번째 추적은 BGP-Learned 10.2.0.0/16 접두사에 속하는 대상에 대한 것이며 LSP를 따릅니다. 두 번째 추적은 IS-IS에서 학습한 192.168.0.3 경로(디바이스 C의 루프백 인터페이스 주소)에 대한 것으로, IS-IS 경로를 따릅니다. 이러한 결과는 포워딩 테이블에서 관찰한 내용과 일치합니다. 포워딩 테이블은 inet.0의 경로만을 기반으로 구축됩니다. BGP는 inet.3을 살펴보고 BGP 접두사의 다음 홉에 대한 최적의 경로로 LSP를 선택할 수 있으며, 해당 LSP를 활용하여 inet.0에 경로를 추가할 수 있습니다. 그런 다음 inet.0 경로에서 포워딩 테이블로 항목이 만들어집니다. 다른 프로토콜은 기본적으로 inet.3을 참조할 수 없으며, inet.3 경로는 inet.0에 입력되지 않습니다. 따라서 192.168.0.3의 포워딩 항목은 inet.0의 해당 목적지로 가는 유일한 경로(IS-IS 경로)에서 생성됩니다.
이(가) 구성되면 traffic-engineering bgp-igp 10.2.1.1에 대한 첫 번째 추적이 계속해서 LSP를 따릅니다. 192.168.0.3에 대한 두 번째 추적도 LSP를 따릅니다. 이러한 결과는 LSP가 IGP 다음 홉 해결에 사용된다는 것을 보여주는 포워딩 테이블에서 관찰한 내용과 일치합니다.
