例:ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPを使用したNG-VPLS
要件
表 1 は 、この例で使用するハードウェアと必要なソフトウェアを示しています。
| 機器 | コンポーネント | ソフトウェア |
|---|---|---|
6つのMXシリーズ5Gユニバーサルルーティングプラットフォーム |
DPC-4 10GE-X、DPC-40 1GE-X |
Junos OSリリース9.3R4以降 |
T Series コアルーター 1 台 |
FPC3、10GE-Xenpak |
Junos OSリリース9.3R4以降 |
EX4200イーサネットスイッチ x 8 |
EX4200仮想スイッチ |
Junos OSリリース9.3R4以降 |
M7iマルチサービスエッジルーター1台 |
ギガビットイーサネットインターフェイス |
Junos OSリリース9.3R4以降 |
概要とトポロジー
NG-VPLSの例の論理トポロジーを 図1に示します。
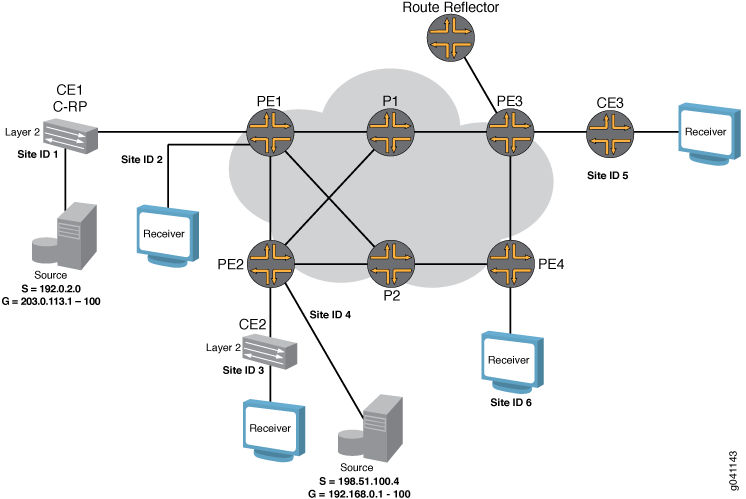
この例のルーターには、以下があらかじめ設定されています。
OSPFエリア0は、トラフィック制御を有効にしたすべてのPEルーターとPルーターで設定されています。
コアに面するすべてのインターフェイスは、
mplsプロトコルアドレスファミリーで設定されます。RSVP および MPLS プロトコルは、コアに面するすべてのインターフェイスで有効です。
すべてのMXシリーズルーターでは、ネットワークサービスモードがイーサネットに設定されています。ネットワークサービスモードは、
network-servicesステートメントを含め、ethernetオプションを指定することで設定されます。すべてのPEルーターは、自律システム
65000用に設定されています。
NG-VPLSの例の物理的なトポロジーを 図2に示します。トポロジーは、コアの冗長リンクに接続された6台のMXシリーズルーターで構成されています。4 台の MXシリーズ ルーターが PE ルーターとして機能し、2 台がコア ルーターとして機能します。
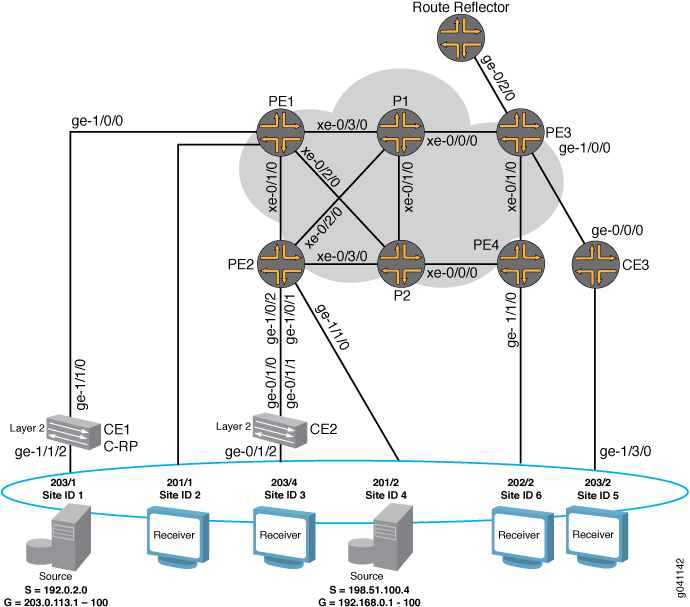
以下のトポロジーの詳細に注意してください。
ルートリフレクタは、BPG-VPLSのすべてのPEルーターへのファミリー
l2-vpnルートを反映するようにトポロジーで設定されています。GOLD VPLSルーティングインスタンスは、各PEルーターに2つのサイトで構成されています。
1 つの GOLD サイトは CE ルーターに接続され、もう 1 つは各 PE ルーターのテスト装置に直接接続されています。
VPLS トンネルサービスにLSIインターフェイスを使用できるようにするための
no-tunnel-servicesステートメントは、GOLD VPLSインスタンスに含まれています。ルーターCE1とルーターCE2は、CEルーターとして機能するEXシリーズバーチャルシャーシスイッチです。
ルーターCE3は、M7iルーターとして機能するCEルーターです。
2つのマルチキャストソースが設定されています。1つはルーターCE1(サイト1)に接続され、もう1つはルーターPE2(サイト4)に接続され、さまざまなシナリオをシミュレートします。
ルーターCE1はランデブーポイント(RP)として設定されています。
ユニキャストトラフィックは、すべてのテスト機器ポートで有効になり、GOLD VPLSインスタンスのすべてのサイトに送信されます。
設定
この例では、ポイントツーマルチポイント LSP を使用して次世代 VPLS を設定する方法を示します。以下のセクションで構成されています。
- PE ルーター インターフェイスの設定
- BGPベースVPLSにおける全PEルーターのルートリフレクタの設定
- ルートリフレクタを使用したBGPベースのVPLSの確立
- PEルーター間のポイントツーポイントLSPの設定
- PEルーター間での動的および静的ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPの設定
- ポイントツーマルチポイントリンク保護の設定
- NG-VPLS向けBGPベースVPLSルーティングインスタンスの設定
- VPLSのトンネルサービスの設定
- コントロールプレーンの検証
- データプレーンの検証
- 結果
PE ルーター インターフェイスの設定
ステップバイステップの手順
顧客向けのPEインターフェイスで、VLANタグを有効にし、カプセル化タイプを設定し、VPLSアドレスファミリーを有効にします。VPLSルーティングインスタンスには4つのインターフェイスカプセル化があり、ニーズに応じて選択できます。
ネットワークで、PE ルーター-to-CE ルーターリンク上の各論理インターフェイスが、VLAN ID
1000のパケットのみを受け入れるように設定する必要がある場合は、vlan-taggingステートメントを含め、encapsulationステートメントを含め、カプセル化タイプとしてvlan-vplsを指定します。また、vlan-idステートメントを含め、VLAN IDとして1000を指定します。[edit interfaces] ge-1/1/0 { vlan-tagging; encapsulation vlan-vpls; unit 1 { encapsulation vlan-vpls; vlan-id 1000; family vpls; } }この設定により、異なるVLAN IDを持つ複数の論理インターフェイスを設定し、各論理インターフェイスを異なるルーティングインスタンスに関連付けることができます。
ネットワークで PE ルーター 上の各物理インターフェイスルーター単一の VPLS インスタンスの一部としてイーサネット ポート全体を使用するようにリンクをCE設定する必要がある場合は、
encapsulationステートメントを含め、カプセル化タイプとしてethernet-vplsを指定します。[edit interfaces] ge-1/2/0 { encapsulation ethernet-vpls; unit 0 { family vpls; } }このカプセル化モードでは、複数の論理ユニット(VLAN)を作成することはできません。
ネットワークで、異なるカプセル化を混在CEするように PE ルーター上の単一の物理インターフェイスルーター各論理インターフェイスを設定する必要がある場合は、
encapsulationステートメントを含め、[edit interfaces interface-name]階層レベルでカプセル化タイプとしてflexible-ethernet-servicesを指定します。また、encapsulationステートメントを含め、[edit interfaces interface-name unit logical-unit-number]階層レベルでカプセル化タイプとしてvlan-vplsまたはvlan-cccを指定します。[edit interfaces] ge-1/2/0 { vlan-tagging; encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services; unit 1 { encapsulation vlan-vpls; } unit 2 { encapsulation vlan-ccc; } }ネットワークが、単一の物理インターフェイス上の異なる論理インターフェイスに設定されたシングルタグ付きVLANとデュアルタグ付きVLANの混在の使用をサポートする必要がある場合は、
encapsulationステートメントを含め、カプセル化タイプとしてflexible-vlan-taggingを指定します。コアに接続する CE ルーター インターフェイスを設定します。CE ルーターと PE ルーターの論理インターフェイス設定は、カプセル化タイプと VLAN ID が一致している必要があります。通常、CEデバイスがルーターであり、レイヤー2ドメインをレイヤー3ネットワークに終端する場合、IPアドレスはコアに面するCEルーターインターフェイスで設定されます。この例では、インターフェイスは VLAN ID
1000の単一のタグ付け用に設定されています。[edit interfaces] ge-1/1/0 { vlan-tagging; unit 1 { vlan-id 1000; family inet { address 198.51.100.4/24; } } }
BGPベースVPLSにおける全PEルーターのルートリフレクタの設定
ステップバイステップの手順
ルートリフレクタの設定は、BGPベースのサービス提供を有効にするための好ましい方法です。ルートリフレクタを設定することで、BGPピアセッションのフルメッシュの必要性が回避され、スケーリング性に優れています。BGPの冗長性は、単一のクラスター内で複数のルートリフレクタを使用することで実現できます。
BGPがレイヤ2 VPNおよびVPLS NLRIメッセージを伝送できるようにするには、ピアグループを作成し、
familyステートメントを含め、l2vpnオプションを指定してsignalingステートメントを含めます。ルートリフレクタクラスターを設定し、BGPピアセッションを完了するには、clusterステートメントを含め、クラスター IDのIPアドレスを指定します。次に、neighborステートメントを含め、クラスター内のクライアントピアBGPであるPEルーターのIPアドレスを指定します。[edit protocols] bgp { group RR { type internal; local-address 192.0.2.7; family l2vpn { signaling; } cluster 192.0.2.7; neighbor 192.0.2.1; # To PE1 neighbor 192.0.2.2; # To PE2 neighbor 192.0.2.3; # To PE3 neighbor 192.0.2.4; # To PE4 } }OSPFを設定し、ルートリフレクタでトラフィックエンジニアリングを有効にし、PEルーターから終端するエグレスLSPの制約付き最短パスファースト(CSPF)データベースを作成します。
[edit protocols] ospf { traffic-engineering; area 0.0.0.0 { interface all; interface fxp0.0 { disable; } } }MPLSコアに接続されたすべてのインターフェイスで、MPLSおよびRSVPプロトコルを有効にします。これにより、PE ルーターからの RSVP エグレス LSP が終了します。
[edit protocols] rsvp { interface all; interface fxp0.0 { disable; } } mpls { interface all; interface fxp0.0 { disable; } }
ルートリフレクタを使用したBGPベースのVPLSの確立
ステップバイステップの手順
BGPベースのVPLSでは、すべてのPEルーターが互いにBGPピアセッションのフルメッシュを持っているか、ルートリフレクタを持つ単一のピアを持っている必要があります。ルートリフレクタは、他のPEルーターから受信したルートを反映します。この例では、PE ルーターはルート リフレクタとのピア関係を確立するように設定されています。
すべてのPEルーターでルートリフレクタとのBGPクライアントピアセッションを確立するには、内部ピアグループを作成し、
local-addressステートメントを含めて、PEルーターのIPアドレスを指定します。また、neighborステートメントを含め、ルートリフレクタのIPアドレスを指定します。BGPがレイヤー2 VPNおよびVPLS NLRIメッセージを伝送できるようにするには、familyステートメントを含め、l2vpnオプションを指定してsignalingステートメントを含めます。[edit protocols] bgp { group to-RR { type internal; local-address 192.0.2.1; family l2vpn { signaling; } neighbor 192.0.2.7; # To the route reflector } }PEルーターからルートリフレクターへのポイントツーポイントRSVP LSPを設定します。LSPを作成するには、
label-switched-pathステートメントを含め、LSPに意味のある名前を付け、toステートメントを含め、LSPエンドポイントとしてルートリフレクタのIPアドレスを指定します。このLSPは、ルートリフレクタから受信したルートのinet.3ルーティングテーブルのBGPネクストホップを解決するために必要です。[edit protocols] mpls { label-switched-path to-RR { to 192.0.2.7; } interface all; interface fxp0.0 { disable; } }
PEルーター間のポイントツーポイントLSPの設定
ステップバイステップの手順
次世代VPLSでは、ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPは、ブロードキャスト、マルチキャスト、未知のユニキャストフレームの伝送にのみ使用されます。その他のフレームは、ポイントツーポイントのRSVP LSPを使用して転送されます。これは、特に未知のフレーム、ブロードキャストフレーム、およびマルチキャストフレームのソース付近で、帯域幅をより効率的に使用できます。トレードオフは、各 PE ルーターが、他のすべての PE ルーターに接続する 1 つのポイントツーマルチポイント LSP のイングレスであり、他の PE ルーターに 1 つずつ接続される n ポイントツーポイント LSP が必要となるためです。
ポイントツーポイントLSPを作成するには、
label-switched-pathステートメントを含め、LSPに意味のある名前を付け、toステートメントを含め、LSPエンドポイントとして他のPEルーターのIPアドレスを指定します。この例は、ルーターPE1からルーターPE2、PE3、およびPE4へのLSPの設定を示しています。[edit protocols] mpls { label-switched-path to-PE2 { to 192.0.2.2; } label-switched-path to-PE3 { to 192.0.2.3; } label-switched-path to-PE4 { to 192.0.2.4; } }
PEルーター間での動的および静的ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPの設定
ステップバイステップの手順
この手順では、動的なポイントツーマルチポイント LSP の作成を有効にする方法と、静的なポイントツーマルチポイント LSP を設定する方法について説明します。静的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPで設定されたルーターでは、LSPはすぐに起動します。動的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPで設定されたルーターでは、ルートリフレクタまたはVPLSドメインに参加している他のPEルーターからBGPネイバー情報を受信した後にのみLSPが起動します。
VPLSインスタンスごとに、動的ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPを有効にしたPEルーターは、ポイントツーマルチポイントテンプレートに基づいて専用のポイントツーマルチポイントLSPを作成します。VPLSがBGPを介して新しいネイバーを発見するたびに、このネイバーのサブLSPがポイントツーマルチポイントLSPに追加されます。
VPLSインスタンスに n PEルーターが存在する場合、ルーターはネットワーク内に n ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPを作成し、各PEルーターはツリーのルートであり、残りの n-1 PEルーターは、ソースツーリーフのサブLSPを介して接続されたリーフノードとして含まれます。
このステップでは、LSP作成に動的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPテンプレートを使用するように、ルーターPE1とルーターPE2を設定します。これらのルーターは、新しいネイバーに対してルートリフレクターからアドバタイズされた新しいBGPルートを受信すると、そのネイバーへのポイントツーマルチポイントサブLSPを作成します。動的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPテンプレートを作成するには、
label-switched-pathステートメントを含め、LSPテンプレートに意味のある名前を付け、templateステートメントを含め、p2mpステートメントを含めます。また、リンク保護を有効にし、最適化タイマーを設定して、LSPパスを定期的に再最適化します。[edit protocols] mpls { label-switched-path vpls-GOLD-p2mp-template { template; # identify as a template optimize-timer 50; link-protection; # link protection is enabled on point-to-multipoint LSPs p2mp; } }このステップでは、静的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPを設定します。静的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPの作成は、ポイントツーポイントLSPの作成と似ていますが、各ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPの下に他のRSVPパラメーターを設定することもできます。
静的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPを作成するには、
label-switched-pathステートメントを含め、LSPに意味のある名前を付け、toステートメントを含め、LSPのエンドポイントであるPEルーターのIPアドレスを指定します。また、p2mpステートメントを含め、パス名を指定します。[edit protocols] mpls { label-switched-path to-pe2 { to 192.0.2.2; p2mp vpls-GOLD; } label-switched-path to-pe3 { to 192.0.2.3; p2mp vpls-GOLD; } label-switched-path to-pe1 { to 192.0.2.1; p2mp vpls-GOLD; } }
ポイントツーマルチポイントリンク保護の設定
ステップバイステップの手順
ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPは、トラフィックエンジニアリング用のRSVPリンク保護のみをサポートします。ノード保護はサポートされていません。リンク保護はオプションですが、ほとんどのネットワークで推奨される設定です。
コアに面するインターフェイスでリンク保護を有効にするには、
[edit protocols rsvp interface interface-name]階層レベルでlink-protectionステートメントを含めます。[edit protocols] rsvp { interface all; interface fxp0.0 { disable; } interface xe-0/3/0.0 { link-protection; } interface xe-0/2/0.0 { link-protection; } interface xe-0/1/0.0 { link-protection; } }ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPがRSVPリンク保護機能を使用できるようにします。リンク保護は、テンプレートを使用する静的ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPと動的ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPの両方に設定できます。
静的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPの場合は、各支社のサブLSPを設定します。リンク保護を有効にするには、
[edit protocols mpls label-switched-path label-switched-path-name]階層レベルでlink-protectionステートメントを含めます。[edit protocols mpls label-switched-path] label-switched-path to-pe2 { to 192.0.2.2; link-protection; p2mp vpls-GOLD; } label-switched-path to-pe3 { to 192.0.2.3; link-protection; p2mp vpls-GOLD; } label-switched-path to-pe1 { to 192.0.2.1; link-protection; p2mp vpls-GOLD; }テンプレートを使用した動的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPの場合、テンプレートのみでリンク保護を設定する必要があります。テンプレートを使用するすべてのポイントツーマルチポイントブランチLSPは、この設定を継承します。
動的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPのリンク保護を有効にするには、
[edit protocols mpls label-switched-path label-switched-path-name]階層レベルでlink-protectionステートメントを含めます。[edit protocols mpls label-switched-path] label-switched-path vpls-GOLD-p2mp-template { template; optimize-timer 50; link-protection; p2mp; }
NG-VPLS向けBGPベースVPLSルーティングインスタンスの設定
ステップバイステップの手順
NG-VPLSの場合、ルーティングインスタンスの設定は通常のVPLSルーティングインスタンスの場合と似ています。ルーティングインスタンスは、VPLSサイトを定義し、VPLS接続を作成します。以下のパラメータが設定されています。
インスタンスタイプ – VPLS
インターフェイス - CEルーターに接続するインターフェイス。
ルート識別子 – PEルーターで設定する各ルーティングインスタンスには、固有のルート識別子が必要です。ルート識別は、異なるVPNから受信した潜在的に同一のネットワーク到達可能性情報(NLRI)メッセージを区別するために、BGPによって使用されます。どのPEがルートを発信したのかを判断できるように、各PE上の各ルーティングインスタンスに一意のルート識別子を使用することが推奨されます。
VRFターゲット -
vrf-targetステートメントを使用してVRFターゲットコミュニティを設定すると、インポートされたルートを受け入れ、指定されたターゲットコミュニティでエクスポートされたルートをタグ付けするデフォルトのVRFインポートおよびエクスポートポリシーが生成されます。プロトコル – 次の手順で説明されているように、VPLSプロトコルを設定します。
NG-VPLSルーティングインスタンスを設定するには、
routing-instancesステートメントを含め、インスタンス名を指定します。また、instance-typeステートメントを含め、タイプとしてvplsを指定します。route-distinguisherステートメントを含め、ルーターに設定されたすべての VPN で一意のルート識別子を指定します。vrf-targetステートメントを含めてVRFルートターゲットを設定し、ルートターゲットを指定します。1つのルーターによってエクスポートされたルートターゲットは、同じVPLSに対して別のルーターによってインポートされたルートターゲットと一致する必要があります。[edit] routing-instances { GOLD { instance-type vpls; interface ge-1/0/0.1; interface ge-1/1/0.1; route-distinguisher 192.0.2.1:1; vrf-target target:65000:1; } }VPLSフラッディングにポイントツーマルチポイントLSPを使用するには、VPLSルーティングインスタンスの下でLSPを設定します。
VPLSフラッディングにポイントツーマルチポイントLSPを設定するには、
label-switched-path-templateステートメントを含め、[edit routing-instances routing-instances-name provider-tunnel rsvp-te]階層レベルでLSPテンプレートの名前を指定します。[edit] routing-instances { GOLD { instance-type vpls; interface ge-1/0/0.1; interface ge-1/1/0.1; route-distinguisher 192.0.2.1:1; provider-tunnel { rsvp-te { label-switched-path-template { vpls-GOLD-p2mp-template; } } } vrf-target target:65000:1; } }VPLSプロトコルを設定することで、VPLSドメイン内の異なるサイト間でVPLSを有効にすることができます。単一のVPLSルーティングインスタンスの下で複数のサイトを設定することができますが、最低のサイトIDが他のPEルーターへのVPLS擬似回線の構築に使用され、最低のサイトIDに関連付けられたラベルブロックがアドバタイズされることに注意してください。VPLS プロトコルには、以下のパラメータが設定されています。
サイト - VPLSサイトの名前。
サイト範囲 - VPLSで許可される最大サイトID。サイト範囲は、VPLS内のサイト数ではなく、VPLS内で許可される最大値のサイトIDを指定します。
サイト識別子 - VPLSサイトを一意に識別する1から65,534までの任意の番号。これは、関連するRFCではVE-IDとも呼ばれます。
PE-CEインターフェイス - このサイトに参加しているインターフェイス。
VPLS用トンネルサービス –
[edit protocol vpls tunnel-services]階層でトンネルインターフェイスを設定しない場合、ルーターはVPLS用にルーターで利用可能なトンネルインターフェイスを使用します。No-トンネル-services -
no-tunnel-servicesステートメントを含める場合、ルーターはそのVPLSインスタンスのトンネルサービスにラベルスイッチインターフェイス(LSI)を使用します。Macテーブルサイズ - VPLSメディアアクセス制御(MAC)アドレステーブルのサイズ。デフォルトは512アドレス、最大アドレスは65,536です。テーブルがいっぱいになると、新しいMACアドレスはテーブルに追加されなくなります。
VPLSプロトコルを設定するには、
[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name protocols]階層レベルでvplsステートメントを含めます。サイト範囲を設定するには、site-rangeステートメントを含め、VPLS内で許可される最大値のサイトIDを指定します。ルーターがLSIインターフェイスを使用するようにするには、no-tunnel-servicesステートメントを含めます。VPLSサイトを作成するには、siteステートメントを含め、サイト名を指定します。また、site-identifierステートメントを含め、サイトIDを指定します。次に、interfaceステートメントを含め、CE デバイスに接続されたインターフェイスのインターフェイス名を指定します。[edit] routing-instances { GOLD { instance-type vpls; interface ge-1/0/0.1; interface ge-1/1/0.1; route-distinguisher 192.0.2.1:1; provider-tunnel { rsvp-te { label-switched-path-template { vpls-GOLD-p2mp-template; } } } vrf-target target:65000:1; protocols { vpls { site-range 8; no-tunnel-services; site CE1 { site-identifier 1; interface ge-1/0/0.1; } site Direct { site-identifier 2; interface ge-1/1/0.1; } } } } }
VPLSのトンネルサービスの設定
ステップバイステップの手順
VPLS設定では、発信元トラフィックをカプセル化し、リモートサイトから送信されるトラフィックのカプセル化を解除するために、トンネルインターフェイスが必要です。トンネルインターフェイスが設定されていない場合、ルーターはデフォルトでルーター上で利用可能なトンネルインターフェイスの1つを選択します。このトンネルインターフェイスを設定するには、Junos OSで使用できる3つの方法があります。
トンネリングのプライマリデバイスとして使用する仮想トンネルインターフェイスを指定するには、
primaryステートメントを含め、[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name protocols vpls tunnel-services]階層レベルで使用する仮想トンネルインターフェイスを指定します。[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name] protocols { vpls { site-range 8; tunnel-services { primary vt-1/2/10; } } }仮想トンネルインターフェイスではなく、トンネルサービスにLSIインターフェイスを使用するようにルーターを設定するには、
[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name protocols vpls]階層レベルにno-tunnel-servicesステートメントを含めます。[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name] protocols { vpls { site-range 8; no-tunnel-services; } }MXシリーズルーターでは、トンネルサービスに使用するトンネルサービスインターフェイスを作成するトンネルサービスインターフェイスを作成する必要があります。トンネルサービスインターフェイスを作成するには、
bandwidthステートメントを含め、[edit chassis fpc slot-number pic slot-number tunnel-services]階層レベルでトンネルサービス用に予約する帯域幅をギガビット/秒で指定します。[edit chassis] fpc 1 { pic 3 { tunnel-services { bandwidth 1g; } } }
コントロールプレーンの検証
ステップバイステップの手順
このセクションでは show コントロールプレーンの検証に使用できるコマンド出力について説明します。また、トラブルシューティングのための方法論も示します。以下の点に注意してください。
この例には、6つのサイトがあります。ルーターPE1とルーターPE2には、それぞれ2つのサイトがあります。ルーターPE3とルーターPE4には、それぞれ1つのサイトがあります。すべてのサイトはGOLD VPLSインスタンスにあります。
VPLSでは、単一のVPLSルーティングインスタンスの下に複数のサイトが設定されている場合、サイトIDが最も小さいサイトのラベルブロックを使用して、リモートPE間の疑似配線を確立します。データトラフィックは、以下のいずれかの状態にあるCEデバイスに接続されたPEルーターインターフェイスに引き続き送信されることに注意してください。
LM – ローカルサイトIDは指定された最小値ではありません。ローカルサイトIDは最小ではありません。そのため、ローカルサイトIDは、疑似配線の確立やVPLSラベルブロックの配布には使用されません。
RM – リモートサイトIDは指定された最小値ではありません。リモートサイトIDは最小ではありません。そのため、リモートサイトIDは、疑似配線の確立やVPLSラベルブロックの配布には使用されていません。
VPLSラベルブロックの割り当て方法と使用方法の詳細については、 VPLSラベルブロック動作を理解するを参照してください。
設定全体が完了したら、VPLS接続の状態を確認できます。
以下の出力では、VPLS接続は特定のサイトの
Up状態を示し、残りのサイトはRMまたはLMの状態を示しています。これは、マルチホーミングサイトへのVPLS実装で予想される状態です。この例では、ルーターPE1にはサイトID
1でサイトCE1が設定されており、サイトID2でサイトDirectが設定されています。サイトCE1のラベルブロックは、リモートPEルーターにアドバタイズされ、リモートPEルーターからのデータパケットを受信するために使用されます。showコマンドの出力で、以下の点がわかります。ルーターPE1は、最も低いサイトID、すなわちサイトID
1を使用します。サイトID 1はデバイスCE1に使用されます。ルーターPE2は、最低のサイトID、すなわちサイトID
3を使用します。サイトID 3はデバイスCE2に使用されます。ルーターPE3とルーターPE4には、それぞれ1つのサイトが設定されています。
サイト
CE1の場合、接続サイト3はUp状態になり、接続サイト4はRM状態になります。サイト
Directでは、すべての接続がLM状態になります。サイト
Directのサイト ID は、このルーターのサイト1よりも大きくなっています。
ルーターPE1では、
show vpls connectionsコマンドを使用してVPLS接続の状態を確認します。user@PE1> show vpls connections Layer-2 VPN connections: Legend for connection status (St) EI -- encapsulation invalid NC -- interface encapsulation not CCC/TCC/VPLS EM -- encapsulation mismatch WE -- interface and instance encaps not same VC-Dn -- Virtual circuit down NP -- interface hardware not present CM -- control-word mismatch -> -- only outbound connection is up CN -- circuit not provisioned <- -- only inbound connection is up OR -- out of range Up -- operational OL -- no outgoing label Dn -- down LD -- local site signaled down CF -- call admission control failure RD -- remote site signaled down SC -- local and remote site ID collision LN -- local site not designated LM -- local site ID not minimum designated RN -- remote site not designated RM -- remote site ID not minimum designated XX -- unknown connection status IL -- no incoming label MM -- MTU mismatch MI -- Mesh-Group ID not availble BK -- Backup connection ST -- Standby connection Legend for interface status Up -- operational Dn -- down Instance: GOLD Local site: CE1 (1) connection-site Type St Time last up # Up trans 3 rmt Up Oct 6 16:27:23 2009 1 Remote PE: 192.0.2.2, Negotiated control-word: No Incoming label: 262171, Outgoing label: 262145 Local interface: lsi.1049353, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS Description: Intf - vpls GOLD local site 1 remote site 3 4 rmt RM 5 rmt Up Oct 6 16:27:27 2009 1 Remote PE: 192.0.2.3, Negotiated control-word: No Incoming label: 262173, Outgoing label: 262145 Local interface: lsi.1049354, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS Description: Intf - vpls GOLD local site 1 remote site 5 6 rmt Up Oct 6 16:27:31 2009 1 Remote PE: 192.0.2.4, Negotiated control-word: No Incoming label: 262174, Outgoing label: 800000 Local interface: lsi.1049355, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS Description: Intf - vpls GOLD local site 1 remote site 6 Local site: Direct (2) connection-site Type St Time last up # Up trans 3 rmt LM 4 rmt LM 5 rmt LM 6 rmt LMルーターPE4では、
show vpls connectionsコマンドを使用してVPLS接続の状態を確認します。サイト
2とサイト4がRM状態であることを確認します。この状態は、サイトがルーターPE1とルーターPE2で最も高いサイトIDで設定されていることを示します。ルーターPE4はサイトが1つだけ設定されているため、LM状態のサイトはありません。user@PE4> show vpls connections ... Instance: GOLD Local site: Direct (6) connection-site Type St Time last up # Up trans 1 rmt Up Oct 6 16:28:35 2009 1 Remote PE: 192.0.2.1, Negotiated control-word: No Incoming label: 800000, Outgoing label: 262174 Local interface: vt-1/2/10.1048576, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS Description: Intf - vpls GOLD local site 6 remote site 1 2 rmt RM 3 rmt Up Oct 6 16:28:35 2009 1 Remote PE: 192.0.2.2, Negotiated control-word: No Incoming label: 800002, Outgoing label: 262150 Local interface: vt-1/2/10.1048577, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS Description: Intf - vpls GOLD local site 6 remote site 3 4 rmt RM 5 rmt Up Oct 6 16:28:35 2009 1 Remote PE: 192.0.2.3, Negotiated control-word: No Incoming label: 800004, Outgoing label: 262150 Local interface: vt-1/2/10.1048578, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS Description: Intf - vpls GOLD local site 6 remote site 5各 PE ルーターで、
show bgp summaryコマンドを使用して、PE ルーター間または PE ルーターとルート リフレクター間の IBGP セッションが確立されていることを確認します。PEルーターがレイヤー2 VPNルートを交換する前に、セッションが動作している必要があります。以下の例では、ルーターPE1からの出力が、bgp.l2vpn.0とGOLD.l2vpn.0のルーティングテーブルが作成されていることを示しています。user@PE1> show bgp summary Groups: 1 Peers: 1 Down peers: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending bgp.l2vpn.0 4 4 0 0 0 0 Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State 192.0.2.7 65000 40 39 0 1 15:45 Establ bgp.l2vpn.0: 4/4/4/0 GOLD.l2vpn.0: 4/4/4/0 admin@PE2# run show bgp summary Groups: 1 Peers: 1 Down peers: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending bgp.l2vpn.0 4 4 0 0 0 0 inet6.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 inet.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State 192.0.2.7 65000 43 42 0 0 17:25 Establ bgp.l2vpn.0: 4/4/4/0 GOLD.l2vpn.0: 4/4/4/0
ルーターPE4では、
show route tableコマンドを使用して、他のPEルーターそれぞれに1つのレイヤー2 VPNルートがあることを確認します。ルーターPE3にも同様のshowコマンド出力があるはずです。user@PE4> show route table bgp.l2vpn.0 bgp.l2vpn.0: 5 destinations, 5 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 192.0.2.1:1:1:1/96 *[BGP/170] 00:23:18, localpref 100, from 192.0.2.7 AS path: I > to 10.10.9.1 via xe-0/0/0.0, label-switched-path to-PE1 192.0.2.1:1:2:1/96 *[BGP/170] 00:23:18, localpref 100, from 192.0.2.7 AS path: I > to 10.10.9.1 via xe-0/0/0.0, label-switched-path to-PE1 192.0.2.2:10:3:1/96 *[BGP/170] 00:23:18, localpref 100, from 192.0.2.7 AS path: I > to 10.10.9.1 via xe-0/0/0.0, label-switched-path to-PE2 192.0.2.2:10:4:1/96 *[BGP/170] 00:23:18, localpref 100, from 192.0.2.7 AS path: I > to 10.10.9.1 via xe-0/0/0.0, label-switched-path to-PE2 192.0.2.3:10:5:1/96 *[BGP/170] 00:23:18, localpref 100, from 192.0.2.7 AS path: I > to 10.10.8.1 via xe-0/1/0.0, label-switched-path to-PE3ルートリフレクタで、
show bgp summaryコマンドを使用して、ルーターが各PEルーターとIBGPピアセッションを持っていることを確認します。user@RR> show bgp summary Groups: 2 Peers: 5 Down peers: 1 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending bgp.l2vpn.0 6 6 0 0 0 0 inet.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State 192.0.2.1 65000 44 46 0 0 18:27 Establ bgp.l2vpn.0: 2/2/2/0 192.0.2.2 65000 43 45 0 0 18:22 Establ bgp.l2vpn.0: 2/2/2/0 192.0.2.3 65000 42 45 0 0 18:19 Establ bgp.l2vpn.0: 1/1/1/0 192.0.2.4 65000 43 45 0 0 18:15 Establ bgp.l2vpn.0: 1/1/1/0
NG-VPLSでは、ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPは未知のユニキャスト、ブロードキャスト、マルチキャストパケットのみを伝送します。NG-VPLSのPEルーター間には、ポイントツーポイントLSPのフルメッシュが必要です。ポイントツーポイントLSPは、
inet.3ルーティングテーブルでルートを作成します。これらのエントリーは、BGPピアから受信したレイヤー2 VPNルートを解決するために使用されます。その他のデータトラフィックはすべて、ポイントツーポイントLSPを介して送信されます。ルートリフレクタ用にポイントツーポイントLSPも作成されます。このLSPは、BGPネクストホップ解決のために
inet.3ルーティングテーブルにルートを作成します。ルーターPE1では、
show mpls lspコマンドを使用して、to-PE2、to-PE3、to-PE4、およびto-RRLSPがUp状態であることを確認します。user@PE1> show mpls lsp ingress unidirectional Ingress LSP: 7 sessions To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname 192.0.2.2 192.0.2.1 Up 0 * to-PE2 192.0.2.3 192.0.2.1 Up 0 * to-PE3 192.0.2.4 192.0.2.1 Up 0 * to-PE4 192.0.2.7 192.0.2.1 Up 0 * to-RR Total 4 displayed, Up 4, Down 0 admin@PE2# run show mpls lsp ingress unidirectional Ingress LSP: 7 sessions To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname 192.0.2.1 192.0.2.2 Up 0 * to-PE1 192.0.2.3 192.0.2.2 Up 0 * to-PE3 192.0.2.4 192.0.2.2 Up 0 * to-PE4 192.0.2.7 192.0.2.2 Up 0 * to-RR Total 4 displayed, Up 4, Down 0 admin@PE3# run show mpls lsp ingress unidirectional Ingress LSP: 7 sessions To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname 192.0.2.1 192.0.2.3 Up 0 * to-PE1 192.0.2.2 192.0.2.3 Up 0 * to-PE2 192.0.2.4 192.0.2.3 Up 0 * to-PE4 192.0.2.7 192.0.2.3 Up 0 * to-RR Total 4 displayed, Up 4, Down 0 admin@PE4# run show mpls lsp ingress unidirectional Ingress LSP: 7 sessions To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname 192.0.2.1 192.0.2.4 Up 0 * to-PE1 192.0.2.2 192.0.2.4 Up 0 * to-PE2 192.0.2.3 192.0.2.4 Up 0 * to-PE3 192.0.2.7 192.0.2.4 Up 0 * to-RR Total 4 displayed, Up 4, Down 0
VPLSインスタンスごとに、PEルーターは専用のポイントツーマルチポイントLSPを作成します。この例では、ルーターPE1とルーターPE2は、ポイントツーマルチポイントの動的テンプレートを使用するように設定されています。
動的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPの場合、VPLSがBGPを介して新しいレイヤー2 VPNネイバーを発見するたびに、このネイバーPEルーターのVPLSインスタンスにソースツーリーフサブLSPが追加されます。
ルーターPE1で、
show mpls lspコマンドを使用して、3つのソースからリーフへのサブLSPが作成されていることを確認します。user@PE1> show mpls lsp ingress p2mp Ingress LSP: 1 sessions P2MP name: 192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, P2MP branch count: 3 To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname 192.0.2.4 192.0.2.1 Up 0 * 192.0.2.4:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD 192.0.2.3 192.0.2.1 Up 0 * 192.0.2.3:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD 192.0.2.2 192.0.2.1 Up 0 * 192.0.2.2:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD Total 3 displayed, Up 3, Down 0
ルーターPE2で、
show mpls lspコマンドを使用して、3つのソースツーリーフサブLSPが作成されていることを確認します。user@PE2> show mpls lsp p2mp ingress Ingress LSP: 1 sessions P2MP name: 192.0.2.2:10:vpls:GOLD, P2MP branch count: 3 To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname 192.0.2.4 192.0.2.2 Up 0 * 192.0.2.4:192.0.2.2:10:vpls:GOLD 192.0.2.3 192.0.2.2 Up 0 * 192.0.2.3:192.0.2.2:10:vpls:GOLD 192.0.2.1 192.0.2.2 Up 0 * 192.0.2.1:192.0.2.2:10:vpls:GOLD Total 3 displayed, Up 3, Down 0
このステップでは、ルーターPE3とルーターPE4は、静的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPを使用しています。静的なポイントツーマルチポイント LSP の場合、すべての PE ルーターへのソースからリーフへのサブ LSP は手動で設定されます。
ルーターPE3では、
show mpls lspコマンドを使用して、3つのソースからリーフへのサブLSPが設定されていることを確認します。user@PE3> show mpls lsp p2mp ingress Ingress LSP: 1 sessions P2MP name: vpls-GOLD, P2MP branch count: 3 To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname 192.0.2.1 192.0.2.3 Up 0 * to-pe1 192.0.2.4 192.0.2.3 Up 0 * to-pe4 192.0.2.2 192.0.2.3 Up 0 * to-pe2 Total 3 displayed, Up 3, Down 0
ルーターPE4で、
show mpls lspコマンドを使用して、3つのソースからリーフへのサブLSPが設定されていることを確認します。user@PE4> show mpls lsp ingress p2mp Ingress LSP: 1 sessions P2MP name: vpls-GOLD, P2MP branch count: 3 To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname 192.0.2.1 192.0.2.4 Up 0 * to-pe1 192.0.2.3 192.0.2.4 Up 0 * to-pe3 192.0.2.2 192.0.2.4 Up 0 * to-pe2 Total 3 displayed, Up 3, Down 0
PE ルーターによって作成された各ポイントツーマルチポイント LSP は、RSVP-TE ポイントツーマルチポイント セッション オブジェクトを使用して識別できます。セッションオブジェクトは、VPLSルートをアドバタイズするときに、BGPによってPMSIトンネル属性として渡されます。このトンネル属性を使用して、受信した送信元からリーフへのサブLSP追加要求(RSVP-Pathメッセージ)は、トラフィックがこの送信元からリーフへのサブLSPに到着すると、ルーターが右側のVPLSインスタンスでメッセージを終了し、発信元PEも識別するようにラベル割り当てをサポートします。これにより、送信元 MACアドレス学習がサポートされます。
ルーターPE1では、
show rsvp sessionコマンドを使用して、動的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSPのRSVPセッションがUpされ、リンク保護がdesiredとして設定されていることを確認します。BGPで送信されるポイントツーマルチポイントセッションオブジェクトが54337であることに注意してください。user@PE1> show rsvp session detail p2mp ingress Ingress RSVP: 7 sessions P2MP name: 192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, P2MP branch count: 3 192.0.2.2 From: 192.0.2.1, LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0 LSPname: 192.0.2.2:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, LSPpath: Primary P2MP LSPname: 192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD Suggested label received: -, Suggested label sent: - Recovery label received: -, Recovery label sent: 262145 Resv style: 1 SE, Label in: -, Label out: 262145 Time left: -, Since: Tue Oct 6 16:27:23 2009 Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak Infbps m 20 M 1500 Port number: sender 2 receiver 54337 protocol 0 Link protection desired Type: Protection down PATH rcvfrom: localclient Adspec: sent MTU 1500 Path MTU: received 1500 PATH sentto: 10.10.2.2 (xe-0/1/0.0) 371 pkts RESV rcvfrom: 10.10.2.2 (xe-0/1/0.0) 370 pkts Explct route: 10.10.2.2 Record route: <self> 10.10.2.2
ルーターPE4は、静的なポイントツーマルチポイントLSP用に設定されています。これらのLSPにはリンク保護は設定されていません。
show rsvp sessionコマンドを使用して、BGPで送信されるポイントツーマルチポイントセッションオブジェクトが42873であることを確認します。user@PE4> show rsvp session detail p2mp ingress Ingress RSVP: 7 sessions P2MP name: vpls-GOLD, P2MP branch count: 3 192.0.2.1 From: 192.0.2.4, LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0 LSPname: to-pe1, LSPpath: Primary P2MP LSPname: vpls-GOLD Suggested label received: -, Suggested label sent: - Recovery label received: -, Recovery label sent: 390416 Resv style: 1 SE, Label in: -, Label out: 390416 Time left: -, Since: Tue Oct 6 15:28:33 2009 Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak Infbps m 20 M 1500 Port number: sender 10 receiver 42873 protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: localclient Adspec: sent MTU 1500 Path MTU: received 1500 PATH sentto: 10.10.9.1 (xe-0/0/0.0) 524 pkts RESV rcvfrom: 10.10.9.1 (xe-0/0/0.0) 447 pkts Explct route: 10.10.9.1 10.10.3.1 Record route: <self> 10.10.9.1 10.10.3.1
ルーターPE1では、
show route tableコマンドを使用して、ルーターPE1がルーターリフレクタからルーターPE2へのレイヤー2 VPNルートを受信し、ルートに20361のポイントツーマルチポイントトンネル識別子を含むPMSIオブジェクトが含まれていることを確認します。user@PE1> show route table GOLD.l2vpn.0 detail GOLD.l2vpn.0: 6 destinations, 6 routes (6 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) ! ! 192.0.2.2:10:3:1/96 (1 entry, 1 announced) *BGP Preference: 170/-101 Route Distinguisher: 192.0.2.2:10 PMSI: Flags 0:RSVP-TE:label[0:0:0]:Session_13[192.0.2.2:0:20361:192.0.2.2] Next hop type: Indirect Next-hop reference count: 7 Source: 192.0.2.7 Protocol next hop: 192.0.2.2 Indirect next hop: 2 no-forward State: <Secondary Active Int Ext> Local AS: 65000 Peer AS: 65000 Age: 4:25:25 Metric2: 1 Task: BGP_65000.192.0.2.7+63544 Announcement bits (1): 0-GOLD-l2vpn AS path: I (Originator) Cluster list: 192.0.2.7 AS path: Originator ID: 192.0.2.2 Communities: target:65000:1 Layer2-info: encaps:VPLS, control flags:, mtu: 0, site preference: 100 Import Accepted Label-base: 262145, range: 8 Localpref: 100 Router ID: 192.0.2.7 Primary Routing Table bgp.l2vpn.0 PMSI: Flags 0:RSVP-TE:label[0:0:0]:Session_13[192.0.2.2:0:20361:192.0.2.2]ルーターPE2では、
show rsvp sessionコマンドを使用して、20361のPMSIトンネル識別子オブジェクトがルーターPE1に表示されているPMSIトンネル識別子オブジェクトと一致していることを確認します。user@PE2> show rsvp session p2mp detail Ingress RSVP: 7 sessions P2MP name: 192.0.2.2:10:vpls:GOLD, P2MP branch count: 3 192.0.2.1 From: 192.0.2.2, LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0 LSPname: 192.0.2.1:192.0.2.2:10:vpls:GOLD, LSPpath: Primary P2MP LSPname: 192.0.2.2:10:vpls:GOLD Suggested label received: -, Suggested label sent: - Recovery label received: -, Recovery label sent: 262171 Resv style: 1 SE, Label in: -, Label out: 262171 Time left: -, Since: Tue Oct 6 16:31:47 2009 Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak Infbps m 20 M 1500 Port number: sender 1 receiver 20361 protocol 0 Link protection desired Type: Protection down PATH rcvfrom: localclient Adspec: sent MTU 1500 Path MTU: received 1500 PATH sentto: 10.10.2.1 (xe-0/1/0.0) 379 pkts RESV rcvfrom: 10.10.2.1 (xe-0/1/0.0) 379 pkts Explct route: 10.10.2.1 Record route: <self> 10.10.2.1
データプレーンの検証
ステップバイステップの手順
前の手順を使用してコントロールプレーンを確認したら、データプレーンを検証できます。このセクションでは show データプレーンの検証に使用できるコマンド出力について説明します。
ルーターPE1では、
show vpls connections extensive | match Floodコマンドを使用して、すべてのサイトのポイントツーマルチポイントLSP名とステータスを確認します。192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLDLSPの600のフラッドネクストホップ識別子に注目してください。user@PE1> show vpls connections extensive | match Flood Ingress RSVP-TE P2MP LSP: 192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, Flood next-hop ID: 600
ルーターPE1では、
show vpls connections extensiveコマンドを使用して、すべてのサイトのポイントツーマルチポイントLSP名とステータスを確認します。user@PE1> show vpls connections extensive Instance: GOLD Local site: CE1 (1) Number of local interfaces: 1 Number of local interfaces up: 1 IRB interface present: no ge-1/0/0.1 lsi.1049353 3 Intf - vpls GOLD local site 1 remote site 3 lsi.1049346 4 Intf - vpls GOLD local site 1 remote site 4 Interface flags: VC-Down lsi.1049354 5 Intf - vpls GOLD local site 1 remote site 5 lsi.1049355 6 Intf - vpls GOLD local site 1 remote site 6 Label-base Offset Range Preference 262169 1 8 100 connection-site Type St Time last up # Up trans 3 rmt Up Oct 6 16:27:23 2009 1 Remote PE: 192.0.2.2, Negotiated control-word: No Incoming label: 262171, Outgoing label: 262145 Local interface: lsi.1049353, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS Description: Intf - vpls GOLD local site 1 remote site 3 RSVP-TE P2MP lsp: Ingress branch LSP: 192.0.2.2:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, State: Up Egress branch LSP: 192.0.2.1:192.0.2.2:10:vpls:GOLD, State: Up Connection History: Oct 6 16:27:23 2009 status update timer Oct 6 16:27:23 2009 PE route changed Oct 6 16:27:23 2009 Out lbl Update 262145 Oct 6 16:27:23 2009 In lbl Update 262171 Oct 6 16:27:23 2009 loc intf up lsi.1049353 4 rmt RM RSVP-TE P2MP lsp: Ingress branch LSP: 192.0.2.2:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, State: Up 5 rmt Up Oct 6 16:27:27 2009 1 Remote PE: 192.0.2.3, Negotiated control-word: No Incoming label: 262173, Outgoing label: 262145 Local interface: lsi.1049354, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS Description: Intf - vpls GOLD local site 1 remote site 5 RSVP-TE P2MP lsp: Ingress branch LSP: 192.0.2.3:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, State: Up Egress branch LSP: to-pe1, State: Up Connection History: Oct 6 16:27:27 2009 status update timer Oct 6 16:27:27 2009 PE route changed Oct 6 16:27:27 2009 Out lbl Update 262145 Oct 6 16:27:27 2009 In lbl Update 262173 Oct 6 16:27:27 2009 loc intf up lsi.1049354 6 rmt Up Oct 6 16:27:31 2009 1 Remote PE: 192.0.2.4, Negotiated control-word: No Incoming label: 262174, Outgoing label: 800000 Local interface: lsi.1049355, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS Description: Intf - vpls GOLD local site 1 remote site 6 RSVP-TE P2MP lsp: Ingress branch LSP: 192.0.2.4:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, State: Up Egress branch LSP: to-pe1, State: Up Connection History: Oct 6 16:27:31 2009 status update timer Oct 6 16:27:31 2009 PE route changed Oct 6 16:27:31 2009 Out lbl Update 800000 Oct 6 16:27:31 2009 In lbl Update 262174 Oct 6 16:27:31 2009 loc intf up lsi.1049355 Local site: Direct (2) Number of local interfaces: 1 Number of local interfaces up: 1 IRB interface present: no Interface name Remote site ID Description ge-1/1/0.1 lsi.1049347 3 Intf - vpls GOLD local site 2 remote site 3 Interface flags: VC-Down lsi.1049348 4 Intf - vpls GOLD local site 2 remote site 4 Interface flags: VC-Down lsi.1049350 5 Intf - vpls GOLD local site 2 remote site 5 Interface flags: VC-Down lsi.1049352 6 Intf - vpls GOLD local site 2 remote site 6 Interface flags: VC-Down Label-base Offset Range Preference 262177 1 8 100 connection-site Type St Time last up 3 rmt LM RSVP-TE P2MP lsp: Ingress branch LSP: 192.0.2.2:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, State: Up 4 rmt LM RSVP-TE P2MP lsp: Ingress branch LSP: 192.0.2.2:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, State: Up 5 rmt LM RSVP-TE P2MP lsp: Ingress branch LSP: 192.0.2.3:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, State: Up 6 rmt LM RSVP-TE P2MP lsp: Ingress branch LSP: 192.0.2.4:192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, State: Up Ingress RSVP-TE P2MP LSP: 192.0.2.1:1:vpls:GOLD, Flood next-hop ID: 600Junos OSリリース9.0以降では、フラッドネクストホップルートが複合ネクストホップとして識別されます。ルーターPE1では、
show route forwarding-table family vpls vpn GOLD detailコマンドを使用して、3つの複合フラッドネクストホップルートがパケット転送エンジンにインストールされていることを確認します。user@PE1> show route forwarding-table family vpls vpn GOLD detail Routing table: GOLD.vpls VPLS: Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif default perm 0 dscd 518 1 00:00:28:28:28:02/48 user 0 ucst 617 4 ge-1/1/0.1 00:00:28:28:28:06/48 user 0 indr 1048576 4 10.10.3.2 Push 800000, Push 390384(top) 621 2 xe-0/2/0.0 lsi.1049353 intf 0 indr 1048574 3 10.10.2.2 Push 262145 598 2 xe-0/1/0.0 lsi.1049354 intf 0 indr 1048575 4 10.10.1.2 Push 262145, Push 302272(top) 602 2 xe-0/3/0.0 lsi.1049355 intf 0 indr 1048576 4 10.10.3.2 Push 800000, Push 390384(top) 621 2 xe-0/2/0.0 00:14:f6:75:78:00/48 user 0 indr 1048575 4 10.10.1.2 Push 262145, Push 302272(top) 602 2 xe-0/3/0.0 00:19:e2:57:e7:c0/48 user 0 ucst 604 4 ge-1/0/0.1 0x30003/51 user 0 comp 613 2 0x30002/51 user 0 comp 615 2 0x30001/51 user 0 comp 582 2 ge-1/0/0.1 intf 0 ucst 604 4 ge-1/0/0.1 ge-1/1/0.1 intf 0 ucst 617 4 ge-1/1/0.1また、
show route forwarding-table family vpls extensiveコマンドを使用して、フラッド識別子を照合し、フラッドラベルをメモすることもできます。ポイントツーマルチポイントLSPに対応するラベルを一致させるには、show rsvp session ingress p2mpコマンドを使用します。ルーターPE1では、
show route forwarding-table family vpls vpn GOLD extensive | find 0x30003/51コマンドを使用して、複合ネクストホップルートと関連するポイントツーマルチポイントLSPラベルの詳細を取得します。user@PE1> show route forwarding-table family vpls vpn GOLD extensive | find 0x30003/51 Destination: 0x30003/51 Route type: user Route reference: 0 Route interface-index: 0 Flags: sent to PFE Nexthop: Next-hop type: composite Index: 613 Reference: 2 Nexthop: Next-hop type: composite Index: 556 Reference: 4 Next-hop type: unicast Index: 604 Reference: 4 Next-hop interface: ge-1/0/0.1 Next-hop type: unicast Index: 617 Reference: 4 Next-hop interface: ge-1/1/0.1 Destination: 0x30002/51 Route type: user Route reference: 0 Route interface-index: 0 Flags: sent to PFE Nexthop: Next-hop type: composite Index: 615 Reference: 2 Nexthop: Next-hop type: composite Index: 556 Reference: 4 Next-hop type: unicast Index: 604 Reference: 4 Next-hop interface: ge-1/0/0.1 Next-hop type: unicast Index: 617 Reference: 4 Next-hop interface: ge-1/1/0.1 Nexthop: Next-hop type: composite Index: 603 Reference: 3 Next-hop type: flood Index: 600 Reference: 2 Nexthop: 10.10.2.2 Next-hop type: Push 262145 Index: 599 Reference: 1 Next-hop interface: xe-0/1/0.0 Nexthop: 10.10.3.2 Next-hop type: Push 390496 Index: 622 Reference: 1 Next-hop interface: xe-0/2/0.0 Nexthop: 10.10.1.2 Next-hop type: Push 302416 Index: 618 Reference: 1 Next-hop interface: xe-0/3/0.0 Destination: 0x30001/51 Route type: user Route reference: 0 Route interface-index: 0 Flags: sent to PFE Nexthop: Next-hop type: composite Index: 582 Reference: 2 Nexthop: Next-hop type: composite Index: 556 Reference: 4 Next-hop type: unicast Index: 604 Reference: 4 Next-hop interface: ge-1/0/0.1 Next-hop type: unicast Index: 617 Reference: 4 Next-hop interface: ge-1/1/0.1 Nexthop: Next-hop type: composite Index: 603 Reference: 3 Next-hop type: flood Index: 600 Reference: 2 Nexthop: 10.10.2.2 Next-hop type: Push 262145 Index: 599 Reference: 1 Next-hop interface: xe-0/1/0.0 Nexthop: 10.10.3.2 Next-hop type: Push 390496 Index: 622 Reference: 1 Next-hop interface: xe-0/2/0.0 Nexthop: 10.10.1.2 Next-hop type: Push 302416 Index: 618 Reference: 1 Next-hop interface: xe-0/3/0.0 Destination: ge-1/0/0.1 Route type: interface Route reference: 0 Route interface-index: 84 Flags: sent to PFE Next-hop type: unicast Index: 604 Reference: 4 Next-hop interface: ge-1/0/0.1 Destination: ge-1/1/0.1 Route type: interface Route reference: 0 Route interface-index: 86 Flags: sent to PFE Next-hop type: unicast Index: 617 Reference: 4 Next-hop interface: ge-1/1/0.1ルーターPE1では、
show vpls mac-table instance GOLDコマンドを使用して、VPLSドメインに接続されたCEルーターの学習したMACアドレスを確認します。user@PE1> show vpls mac-table instance GOLD MAC flags (S -static MAC, D -dynamic MAC, SE -Statistics enabled, NM -Non configured MAC) Routing instance : GOLD Bridging domain : __GOLD__, VLAN : NA MAC MAC Logical address flags interface 00:00:28:28:28:02 D ge-1/1/0.1 00:00:28:28:28:04 D lsi.1049353 00:14:f6:75:78:00 D lsi.1049354 00:19:e2:51:7f:c0 D lsi.1049353 00:19:e2:57:e7:c0 D ge-1/0/0.1ルーターPE1では、
show vpls statisticsコマンドを使用して、VPLSインスタンスのパケット統計情報を使用して、ブロードキャスト、マルチキャスト、およびユニキャストトラフィックフローを検証します。user@PE1> show vpls statistics VPLS statistics: Instance: GOLD Local interface: lsi.1049347, Index: 72 Current MAC count: 0 Local interface: lsi.1049348, Index: 73 Current MAC count: 0 Local interface: lsi.1049346, Index: 82 Current MAC count: 0 Local interface: lsi.1049353, Index: 83 Remote PE: 192.0.2.2 Current MAC count: 2 Local interface: ge-1/0/0.1, Index: 84 Broadcast packets: 421 Broadcast bytes : 26944 Multicast packets: 3520 Multicast bytes : 261906 Flooded packets : 509043345 Flooded bytes : 130315095486 Unicast packets : 393836428 Unicast bytes : 100822118854 Current MAC count: 1 (Limit 1024) Local interface: ge-1/1/0.1, Index: 86 Broadcast packets: 0 Broadcast bytes : 0 Multicast packets: 0 Multicast bytes : 0 Flooded packets : 22889544 Flooded bytes : 5859702144 Unicast packets : 472 Unicast bytes : 30838 Current MAC count: 1 (Limit 1024) Local interface: lsi.1049354, Index: 88 Remote PE: 192.0.2.3 Current MAC count: 1 Local interface: lsi.1049350, Index: 89 Current MAC count: 0 Local interface: lsi.1049355, Index: 90 Remote PE: 192.0.2.4 Current MAC count: 0 Local interface: lsi.1049352, Index: 91 Current MAC count: 0
結果
この例の設定、検証、テストの部分は完了です。次のセクションは参考用です。
ルーターPE1に関連する設定例は以下の通りです。
PE1の設定
chassis {
dump-on-panic;
fpc 1 {
pic 3 {
tunnel-services {
bandwidth 1g;
}
}
}
network-services ethernet;
}
interfaces {
xe-0/1/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.10.2.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
xe-0/2/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.10.3.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
xe-0/3/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.10.1.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/0/0 {
vlan-tagging;
encapsulation vlan-vpls;
unit 1 {
encapsulation vlan-vpls;
vlan-id 1000;
family vpls;
}
}
ge-1/1/0 {
vlan-tagging;
encapsulation vlan-vpls;
unit 1 {
encapsulation vlan-vpls;
vlan-id 1000;
family vpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.0.2.1/24;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 65000;
}
protocols {
rsvp {
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
mpls {
label-switched-path to-RR {
to 192.0.2.7;
}
label-switched-path vpls-GOLD-p2mp-template {
template;
optimize-timer 50;
link-protection;
p2mp;
}
label-switched-path to-PE2 {
to 192.0.2.2;
}
label-switched-path to-PE3 {
to 192.0.2.3;
}
label-switched-path to-PE4 {
to 192.0.2.4;
}
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
bgp {
group to-RR {
type internal;
local-address 192.0.2.1;
family l2vpn {
signaling;
}
neighbor 192.0.2.7;
}
}
ospf {
traffic-engineering;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
}
}
routing-instances {
GOLD {
instance-type vpls;
interface ge-1/0/0.1;
interface ge-1/1/0.1;
route-distinguisher 192.0.2.1:1;
provider-tunnel {
rsvp-te {
label-switched-path-template {
vpls-GOLD-p2mp-template;
}
}
}
vrf-target target:65000:1;
protocols {
vpls {
site-range 8;
no-tunnel-services;
site CE1 {
site-identifier 1;
interface ge-1/0/0.1;
}
site Direct {
site-identifier 2;
interface ge-1/1/0.1;
}
}
}
}
}
ルーターPE2に関連する設定例は以下の通りです。
PE2の設定
chassis {
dump-on-panic;
aggregated-devices {
ethernet {
device-count 1;
}
}
fpc 1 {
pic 3 {
tunnel-services {
bandwidth 1g;
}
}
}
}
interfaces {
xe-0/1/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.10.2.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
xe-0/2/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.10.5.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
xe-0/3/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.10.4.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/0/1 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae0;
}
}
ge-1/0/2 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae0;
}
}
ge-1/1/0 {
vlan-tagging;
encapsulation vlan-vpls;
unit 1 {
encapsulation vlan-vpls;
vlan-id 1000;
family vpls;
}
}
ae0 {
vlan-tagging;
encapsulation vlan-vpls;
unit 1 {
encapsulation vlan-vpls;
vlan-id 1000;
family vpls;
}
}
fxp0 {
apply-groups [ re0 re1 ];
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.0.2.2/24;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 65000;
}
protocols {
rsvp {
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
mpls {
label-switched-path to-RR {
to 192.0.2.7;
}
label-switched-path vpls-GOLD-p2mp-template {
template;
optimize-timer 50;
link-protection;
p2mp;
}
label-switched-path to-PE1 {
to 192.0.2.1;
}
label-switched-path to-PE3 {
to 192.0.2.3;
}
label-switched-path to-PE4 {
to 192.0.2.4;
}
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
bgp {
group to-RR {
type internal;
local-address 192.0.2.2;
family l2vpn {
signaling;
}
neighbor 192.0.2.7;
}
}
ospf {
traffic-engineering;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
}
}
routing-instances {
GOLD {
instance-type vpls;
interface ge-1/1/0.1;
interface ae0.1;
route-distinguisher 192.0.2.2:10;
provider-tunnel {
rsvp-te {
label-switched-path-template {
vpls-GOLD-p2mp-template;
}
}
}
vrf-target target:65000:1;
protocols {
vpls {
site-range 8;
site CE1 {
site-identifier 3;
interface ae0.1;
}
site Direct {
site-identifier 4;
interface ge-1/1/0.1;
}
}
}
}
}
