このページで
レイヤー3 VPN設定のSCU
レイヤー3 VPNでのSCUの設定
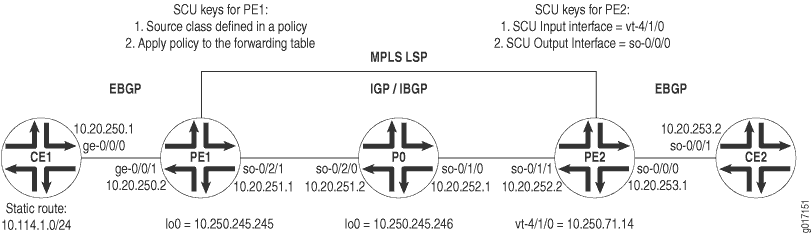
図 1 は、レイヤー3 VPNトポロジーを表示します。CE1およびCE2は、プロバイダルーターPE1、P0、およびPE2を介してVPNによって接続されたカスタマーエッジ(CE)ルーターです。ルーターCE1とPE1の間でEBGPが確立され、IBGPがIS-IS/MPLS/LDPコアを介してルーターPE1とPE2を接続し、ルーターPE2とCE2の間に2つ目のEBGP接続が流れます。
ルーターCE1で、PE1へのEBGP接続を設定してVPNを開始します。10.114.1.0/24の静的ルートをインストールし、このルートをEBGPネイバーにアドバタイズします。
ルーターCE1
[edit]
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.250.1/30;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
static {
route 10.114.1.0/24 reject;
}
autonomous-system 100;
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-pe1 {
local-address 10.20.250.1;
export inject-direct;
peer-as 300;
neighbor 10.20.250.2;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement inject-direct {
term 1 {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 10.114.1.0/24 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term 2 {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
}
PE1で、VRFルーティングインスタンスを介してCE1へのEBGP接続を完了します。BGP トラフィックをコミュニティに入れる VRF インスタンスのエクスポートポリシーと、VPN ネイバーからの同様のコミュニティトラフィックを受け入れるインポートポリシーを設定します。最後に、IS-IS、MPLS、LDP コア上で動作するルーター PE2 との IBGP 関係を設定します。
ルーターPE1
[edit]
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.250.2/30;
}
}
}
so-0/2/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.251.1/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.250.245.245/32;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 300;
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface so-0/2/1;
}
bgp {
group ibgp {
type internal;
local-address 10.250.245.245;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
neighbor 10.250.71.14;
}
}
isis {
interface so-0/2/1;
}
ldp {
interface so-0/2/1;
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement red-import {
from {
protocol bgp;
community red-com;
}
then accept;
}
policy-statement red-export {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add red-com;
accept;
}
}
community red-com members target:20:20;
}
routing-instances {
red {
instance-type vrf;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
route-distinguisher 10.250.245.245:100;
vrf-import red-import;
vrf-export red-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group to-ce1 {
local-address 10.20.250.2;
peer-as 100;
neighbor 10.20.250.1;
}
}
}
}
}
P0 で、PE1 と PE2 にある IBGP ネイバーを接続します。すべてのインターフェイスにVPN関連のプロトコル(MPLS、LDP、IGP)を含めることを忘れないでください。
ルーターP0
[edit]
interfaces {
so-0/1/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.252.1/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
so-0/2/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.251.2/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.250.245.246/32;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 300;
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface so-0/1/0;
interface so-0/2/0;
}
isis {
interface all;
}
ldp {
interface all;
}
}
PE2で、ルーターPE1とのIBGP関係を完了します。VRFルーティングインスタンスを介してCE2へのEBGP接続を確立します。BGP トラフィックをコミュニティに配置する VRF インスタンスのエクスポート ポリシーと、VPN ネイバーからの同様のコミュニティ トラフィックを受け入れるインポート ポリシーを設定します。次に、CE1からのスタティックルートを GOLD1というソースクラスに追加するポリシーを確立します。また、このSCUポリシーを転送テーブルにエクスポートします。最後に、 vt インターフェイスをSCU入力インターフェイスとして設定し、CE向けのインターフェイス so-0/0/0 をSCU出力インターフェイスとして確立します。
ルーターPE2
[edit]
interfaces {
so-0/1/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.252.2/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
so-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
accounting {
source-class-usage {
output;
}
}
address 10.20.253.1/30;
}
}
}
vt-4/1/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
accounting {
source-class-usage {
input;
}
}
address 10.250.71.14/32;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 300;
forwarding-table {
export inject-customer2-dest-class;
}
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface so-0/1/1;
interface vt-4/1/0;
}
bgp {
group ibgp {
type internal;
local-address 10.250.71.14;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
neighbor 10.250.245.245;
}
}
isis {
interface so-0/1/1;
}
ldp {
interface so-0/1/1;
}
}
routing-instances {
red {
instance-type vrf;
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface vt-4/1/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.250.71.14:100;
vrf-import red-import;
vrf-export red-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group to-ce2 {
local-address 10.20.253.1;
peer-as 400;
neighbor 10.20.253.2;
}
}
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement red-import {
from {
protocol bgp;
community red-com;
}
then accept;
}
policy-statement red-export {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add red-com;
accept;
}
}
policy-statement inject-customer2-dest-class {
term term-gold1-traffic {
from {
route-filter 10.114.1.0/24 exact;
}
then source-class GOLD1;
}
}
community red-com members target:20:20;
}
ルーターCE2で、PE2へのEBGP接続を完了してVPNパスを完成させます。
ルーターCE2
[edit]
interfaces {
so-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.253.2/30;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 400;
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-pe2 {
local-address 10.20.253.2;
export inject-direct;
peer-as 300;
neighbor 10.20.253.1;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement inject-direct {
from {
protocol direct;
}
then accept;
}
}
機能の検証
SCUがレイヤー3 VPNで正しく機能していることを確認するには、次のコマンドを使用します。
show interfaces interface-name statisticsshow interfaces source-class source-class-name interface-nameshow interfaces interface-name(extensive|detail)show route(extensive|detail)clear interface interface-name statistics
SCU統計は、 output ステートメントを設定したアウトバウンドSCUインターフェイスで常に確認する必要があります。SCUの機能を確認するには、次の手順に従います。
SCU対応ルーターのすべてのカウンターをクリアし、空であることを確認します。
イングレスCEルーターから2番目のCEルーターにpingを送信して、SCU対応VPNルート全体でSCUトラフィックを生成します。
アウトバウンド インターフェイスでカウンターが正しく増加していることを確認します。
次のセクションは、設定例で使用されるこれらのコマンドの出力を示しています。
user@pe2> clear interfaces statistics all
user@pe2> show interfaces so-0/0/0.0 statistics
Logical interface so-0/0/0.0 (Index 6) (SNMP ifIndex 113)
Flags: Point-To-Point SNMP-Traps Encapsulation: PPP
Protocol inet, MTU: 4470
Source class Packets Bytes
GOLD1 0 0
Addresses, Flags: Is-Preferred Is-Primary
user@pe2> show interfaces source-class GOLD1 so-0/0/0.0
Protocol inet
Source class Packets Bytes
GOLD1 0 0
user@ce1> ping 10.20.253.2 source 10.114.1.1 rapid count 10000
user@scu> show interfaces source-class GOLD1 so-0/0/0.0
Protocol inet
Source class Packets Bytes
GOLD1 20000 1680000
user@scu> show interfaces so-0/0/0.0 statistics
Logical interface so-0/0/0.0 (Index 6) (SNMP ifIndex 113)
Flags: Point-To-Point SNMP-Traps Encapsulation: PPP
Protocol inet, MTU: 4470
Source class Packets Bytes
GOLD1 20000 1680000
Addresses, Flags: Is-Preferred Is-Primary
Destination: 10.20.253/24, Local: 10.20.253.1
