例:IS-IS トラフィック エンジニアリング サポートの有効化
この例では、ラベルスイッチパスをショートカットとして使用するようにIS-ISを設定する方法を示しています。
必要条件
この例を設定する前に、デバイス初期化以外の特別な設定を行う必要はありません。
概要
MPLSトラフィックエンジニアリングは、特定のデータフローを、内部ゲートウェイプロトコル(IGP)によって計算されたデータリンクではなく、確立されたラベルスイッチパス(LSP)にマッピングします。この機能の基本となるのは、どのトラフィックを LSP にマッピングするかを決定することです。エグレス LSR を特定の宛先プレフィックスのネクストホップ ルーターとして指定することで、トラフィックはトンネルのイングレス ラベルスイッチ ルーター(LSR)の LSP にマッピングされます。
LSPが宛先へのルート全体を構成するわけではないことを理解することが重要です。むしろ、LSP はルートのネクストホップ セグメントです。そのため、ルート解決プロセス中にエグレス LSR が実現可能なネクストホップ候補であると考えられる場合にのみ、パケットを LSP にマッピングできます。
図 1 は、この例で使用されているトポロジーを示しています。
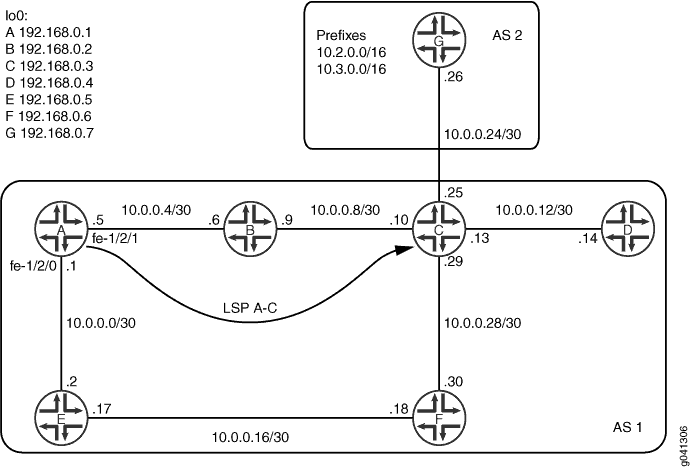
この例では、デバイス C は、自律システム(AS)2 でデバイス G と外部 BGP(EBGP)ピア セッションを持っています。内部 BGP(IBGP)ピアが AS 2 のサブネットにアクセスできるようにするために、デバイス C はデバイス G に接続するインターフェイス上で IS-IS を受動的に実行します。 IS-ISは外部サブネットに関する情報を持っており、これらのサブネットへのルートをinet.0ルーティングテーブルに入力します。BGPは、AS外部ルートのネクストホップアドレスを解決するときに、IGPルートを使用します。
インターフェイス上で IS-IS を受動的に実行する代わりに、ネクストホップ自己ポリシーを使用する方法があります。
デバイス A には、デバイス C への LSP があります。パスは、デバイスBを経由するのではなく、常にデバイスEを経由するように設定されています。
内部ゲートウェイプロトコル(IGP)のショートカットは、トラフィック制御ショートカットとも呼ばれ、AS内のリンク状態IGP(OSPFまたはIS-IS)が最短パスファースト(SPF)の計算でLSPを考慮するためのツールを提供します。パッシブ外部インターフェイスを使用している場合、IGPはLSPを、LSPエグレスデバイスを超えた宛先への単一のデータリンクと見なします。
traffic-engineering bgp(デフォルト)およびIGPショートカットを使用する場合、トラフィック制御ソリューションはBGP AS外部ルート解決にのみ使用されます。ただし、AS内部の宛先へのトラフィックもLSPにマッピングできます。これを実現するために、traffic-engineering bgp-igpが有効になっています。したがって、RSVP は MPLS プレフィックスを inet.3 テーブルではなく inet.0 テーブルにインストールします。その結果、MPLS LSP が転送テーブルにインストールされます。
このアプローチは、サーバーファームなど、AS内の特定の宛先に大量のトラフィックがルーティングされる場合に実用的です。
IGPのショートカットに関する重要な点は、単独で使用する場合でも、トラフィックエンジニアリングBGP-IGPと組み合わせて使用する場合でも、LSP間でIGP隣接関係が形成されることはないということです。IGPはLSPを単一のデータリンクとして認識しますが、egressルーターを潜在的なピアとは見なさず、LSP間でhelloメッセージを転送しません。また、RSVP メッセージが LSP を介して転送されることは決してないため、LSP が別の LSP 内で誤って構築される可能性を防ぎます。
CLI クイック構成 は、 図 1 のすべてのデバイスの設定を示しています。 セクション#configuration424__isis-shortcuts-step-by-stepでは 、デバイスAの手順について説明します。
構成
プロシージャ
CLIクイック構成
この例をすばやく設定するには、次のコマンドをコピーしてテキストファイルに貼り付け、改行を削除して、ネットワーク構成に合わせて必要な詳細を変更し、 [edit] 階層レベルのCLIにコマンドをコピー&ペーストしてください。
1 デバイスA 1
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0001.00 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls traffic-engineering bgp-igp set protocols mpls label-switched-path test_path to 192.168.0.3 set protocols mpls label-switched-path test_path no-cspf set protocols mpls label-switched-path test_path primary through_E set protocols mpls path through_E 192.168.0.5 strict set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols isis traffic-engineering family inet shortcuts set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
1 デバイスB 1
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.6/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.9/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.2/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0002.00 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
1 デバイスC 1
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.10/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.13/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.25/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.29/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.3/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0003.00 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/3.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/3.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.3 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group external-peers type external set protocols bgp group external-peers export send-some-isis set protocols bgp group external-peers peer-as 2 set protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 10.0.0.26 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/2.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/2.0 level 2 passive set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/3.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set policy-options policy-statement send-some-isis term 1 from protocol isis set policy-options policy-statement send-some-isis term 1 from route-filter 10.0.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement send-some-isis term 1 from route-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement send-some-isis term 1 then accept set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.3 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
1 デバイスD 1
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.14/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.4/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0004.00 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.4 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
1 デバイスE 1
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.17/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.5/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0005.00 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.5 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
デバイスF
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.18/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.30/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.6/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0006.00 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/2.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/2.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/2.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.6 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
1 デバイスG 1
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.26/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.7/32 primary set interfaces lo0 unit 0family inet address 10.2.1.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0family inet address 10.3.1.1/32 set protocols bgp group external-peers type external set protocols bgp group external-peers export statics set protocols bgp group external-peers export send-directs set protocols bgp group external-peers peer-as 1 set protocols bgp group external-peers neighbor 10.0.0.25 set policy-options policy-statement statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement send-directs term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement send-directs term 1 then accept set routing-options static route 10.2.0.0/32 reject set routing-options static route 10.2.0.0/32 install set routing-options static route 10.3.0.0/32 reject set routing-options static route 10.3.0.0/32 install set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.7 set routing-options autonomous-system 2
手順
次の例では、設定階層のいくつかのレベルに移動する必要があります。CLIのナビゲーションについては、CLIユーザー・ガイド の コンフィギュレーション・モードでのCLIエディタの使用を参照してください。
IS-IS トラフィック制御のショートカットを設定するには:
インターフェイスを設定します。
[edit interfaces] user@A# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 user@A# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso user@A# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls user@A# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 user@A# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso user@A# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls user@A# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 user@A# set lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0001.00
インターフェイスでシグナリングプロトコルを有効にします。
[edit protocols rsvp] user@A# set interface lo0.0 user@A# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 user@A# set interface fe-1/2/1.0
インターフェイスでMPLSを有効にします。
[edit protocols mpls] user@A# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 user@A# set interface fe-1/2/1.0
ラベルスイッチパスを設定します。
test_pathという名前の単一のLSPが、デバイスAからデバイスCに設定されます。LSPの明示的なルートオブジェクト(ERO)は、デバイスEを介して厳密なホップを使用するように指定されているため、LSPはOSPFのA-B-Cの最短パスとは異なるパスを取ります。LSP は RSVP を使用してシグナリングされていますが、CSPF は実行されていません。
[edit protocols mpls] user@A# set label-switched-path test_path to 192.168.0.3 user@A# set label-switched-path test_path no-cspf user@A# set label-switched-path test_path primary through_E user@A# set path through_E 192.168.0.5 strict
BGPとIGPの両方の宛先のトラフィック制御を設定します。
IGPのショートカットも有効になっている場合、IGPは計算にLSPを使用することができます。計算の結果は inet.0 テーブルに入力されます。
[edit protocols mpls] user@A# set traffic-engineering bgp-igp
デバイス間の内部BGP(IBGP)ピアリングを設定します。
[edit protocols bgp group int] user@A# set type internal user@A# set local-address 192.168.0.1 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.0.5 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.0.6 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.0.2 user@A# set neighbor 192.168.0.3
インターフェイスでIS-ISを有効にし、リンクメトリックを設定します。
[edit protocols isis] user@A# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable user@A# set interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable user@A# set interface lo0.0
IPv4 アドレス ファミリーのネクスト ホップとして MPLS LSP を使用するように IS-IS を設定します。
ingressルーターでIGPショートカットを有効にする必要があるのは、それが最短パスファースト(SPF)計算を実行するルーターだからです。
IGPのショートカットがプロトコルとルーティングテーブルの関係にどのように影響するかを理解することが重要です。IGPは、LSPのエグレスポイントのダウンストリームのサブネットに対してSPF計算を行いますが、これらの計算結果はinet.3テーブルにのみ入力されます。同時に、IGP は従来の SPF 計算を実行し、これらの計算結果を inet.0 テーブルに入力します。その結果、IGPはinet.3テーブルにエントリーを行っていますが、BGPは依然として、ルート解決の目的でそのテーブルを可視化できる唯一のプロトコルです。そのため、AS内部の宛先への転送は引き続きinet.0 IGPルートを使用し、LSPはBGPネクストホップの解決にのみ使用されます。LSPをIGPネクストホップ解決に使用する場合は、
traffic-engineering bgp-igpを設定する必要があります。[edit protocols isis] user@A# set traffic-engineering family inet shortcuts
ルーターIDと自律システム(AS)番号を設定します。
[edit routing-options] user@A# set router-id 192.168.0.1 user@A# set autonomous-system 1
業績
設定モードから、 show interfaces、 show protocols、および show routing-options コマンドを入力して設定を確認します。出力結果に意図した設定内容が表示されない場合は、この例の手順を繰り返して設定を修正します。
user@A# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 0{
family inet {
address 10.0.0.1/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
fe-1/2/1{
unit 0
family inet {
address 10.0.0.5/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0{
family inet {
address 192.168.0.1/32;
}
family iso {
address 49.0002.0192.0168.0001.00;
}
}
}
user@A# show protocols
rsvp {
interface lo0.0;
interface fe-1/2/0.0;
interface fe-1/2/1.0;
}
mpls {
traffic-engineering bgp-igp;
label-switched-path test_path {
to 192.168.0.3;
no-cspf;
primary through_E;
}
path through_E {
192.168.0.5 strict;
}
interface fe-1/2/0.0;
interface fe-1/2/1.0;
}
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.0.1;
neighbor 192.168.0.5;
neighbor 192.168.0.6;
neighbor 192.168.0.2;
neighbor 192.168.0.3;
}
}
isis {
traffic-engineering {
family inet {
shortcuts;
}
}
interface fe-1/2/0.0 {
level 1 disable;
}
interface fe-1/2/1.0 {
level 1 disable;
}
interface lo0.0;
}
user@A# show routing-options
router-id 192.168.0.1;
autonomous-system 1;
デバイスの設定が完了したら、設定モードから コミット を入力します。
検証
設定が正常に機能していることを確認します。
ネクストホップの検証
目的
MPLS LSP が、想定されるルートのネクスト ホップとして使用されていることを確認します。
アクション
動作モードから、 show route コマンドを入力します。
user@A> show route
inet.0: 21 destinations, 21 routes (21 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 4d 09:07:26
> via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.1/32 *[Local/0] 4d 09:07:26
Local via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.4/30 *[Direct/0] 4d 09:07:28
> via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.5/32 *[Local/0] 4d 09:07:28
Local via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.8/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.12/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.16/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.20/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.24/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.28/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 30
to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.2.0.0/32 *[BGP/170] 02:22:30, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 2 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
10.2.1.1/32 *[BGP/170] 02:20:23, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 2 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
10.3.0.0/32 *[BGP/170] 02:22:30, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 2 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
10.3.1.1/32 *[BGP/170] 02:20:23, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 2 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
192.168.0.1/32 *[Direct/0] 4d 09:08:47
> via lo0.0
192.168.0.2/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 10
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
192.168.0.3/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
192.168.0.4/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/1.0
to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.5/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 10
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.6/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:42:24, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.7/32 *[BGP/170] 02:20:23, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 2 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
inet.3: 5 destinations, 6 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.12/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:41:21, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
10.0.0.24/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:41:21, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
10.0.0.28/30 *[IS-IS/18] 01:41:21, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
192.168.0.3/32 *[RSVP/7/1] 01:41:21, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
[IS-IS/18] 01:41:21, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
192.168.0.4/32 *[IS-IS/18] 01:41:21, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0, label-switched-path test_path
iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
49.0002.0192.0168.0001/72
*[Direct/0] 4d 09:08:47
> via lo0.0
mpls.0: 4 destinations, 4 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0 *[MPLS/0] 4d 09:10:00, metric 1
Receive
1 *[MPLS/0] 4d 09:10:00, metric 1
Receive
2 *[MPLS/0] 4d 09:10:00, metric 1
Receive
13 *[MPLS/0] 4d 09:10:00, metric 1
Receive
意味
IS-ISは、LSPエグレスデバイスのダウンストリームの宛先への最短パスとしてLSPを選択します。さらに、IGPはLSPを使用して外部サブネット10.0.0.24/30に到達するため、BGPは10.2.0.0および10.3.0.0へのルートにもLSPを使用します。
ネクストホップの self がデバイス C で使用された場合でも、BGP は IGP パスよりも LSP を選択します。
RSVP セッションの確認
目的
RSVP セッションに関する情報を表示します
アクション
動作モードから、 show rsvp session brief コマンドを入力します。
user@A> show rsvp session brief Ingress RSVP: 1 sessions To From State Rt Style Labelin Labelout LSPname 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 Up 0 1 FF - 299776 test_path Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0 Egress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Transit RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
user@E> show rsvp session brief Ingress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Egress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Transit RSVP: 1 sessions To From State Rt Style Labelin Labelout LSPname 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 Up 0 1 FF 299776 299808 test_path Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
user@F> show rsvp session brief Ingress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Egress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Transit RSVP: 1 sessions To From State Rt Style Labelin Labelout LSPname 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 Up 0 1 FF 299808 3 test_path Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
user@C> show rsvp session brief Ingress RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0 Egress RSVP: 1 sessions To From State Rt Style Labelin Labelout LSPname 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 Up 0 1 FF 3 - test_path Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0 Transit RSVP: 0 sessions Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
意味
4 つのルーティング デバイスすべてで、LSP のイングレスおよびエグレス IP アドレスが表示されます。このパスは、デバイス A でイングレス パスとして示され、LSP で転送されるパケットには 299776 のラベルが割り当てられます。デバイス E では、LSP がトランジットされており、299776 のラベルで到着するパケットには、299808 の発信ラベルが付けられます。ラベルは、隣接するLSR(ラベルスイッチルーター)間でのみ意味を持ちます。デバイスFは、受信ラベル299808を送信ラベル3と交換します。デバイス C (エグレス) は、ラベル 3 をポップし、標準の IP 最長一致ルート ルックアップによって受信したパケットをルーティングします。
異なるトラフィック制御設定によるパスの確認
目的
traffic-engineering bgp-igpを使用する場合とtraffic-engineering bgp(デフォルト)を使用する場合、IGPおよびBGPルートに使用されるパスを確認します。
アクション
traffic-engineering bgpを設定します。これにより、各ルーティング インスタンスで構成できるMPLSトラフィックエンジニアリング設定は 1 つだけであるため、構成から
traffic-engineering bgp-igpが削除されます。[edit protocols mpls] user@A# set traffic-engineering bgp user@A# commit
traffic-engineering bgp(デフォルト)が設定されている場合、show route forwarding-tableコマンドを使用してパスをチェックします。user@A> show route forwarding-table destination 10.2.1.1 Routing table: default.inet Internet: Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif 10.2.1.1/32 user 0 indr 262145 6 10.0.0.2 Push 299776 1013 2 fe-1/2/0.0user@A> show route forwarding-table destination 192.168.0.3 Routing table: default.inet Internet: Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif 192.168.0.3/32 user 1 10.0.0.6 ucst 938 11 fe-1/2/1.0
traffic-engineering bgp(デフォルト)が設定されている場合、tracerouteコマンドを使用してパスをチェックします。user@A> traceroute 10.2.1.1 traceroute to 10.2.1.1 (10.2.1.1), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 11.086 ms 1.587 ms 1.603 ms MPLS Label=299776 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 2 10.0.0.18 (10.0.0.18) 1.455 ms 1.477 ms 1.442 ms MPLS Label=299808 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 3 10.0.0.29 (10.0.0.29) 2.240 ms 1.045 ms 1.243 ms 4 10.2.1.1 (10.2.1.1) 1.363 ms 1.389 ms 1.374 msuser@A> traceroute 192.168.0.3 traceroute to 192.168.0.3 (192.168.0.3), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.6 (10.0.0.6) 1.759 ms 1.872 ms 2.281 ms 2 bb03-cclab-lo0.spglab.juniper.net (192.168.0.3) 2.119 ms 2.157 ms 1.598 ms
traffic-engineering bgp-igpを設定します。各ルーティング インスタンスで構成できるMPLSトラフィックエンジニアリング設定は 1 つだけであるため、構成から
traffic-engineering bgpが削除されます。[edit protocols mpls] user@A# set traffic-engineering bgp-igp user@A# commit
traffic-engineering bgp-igpが設定されている場合に、show route forwarding-tableコマンドを使用してパスを確認します。user@A> show route forwarding-table destination 10.2.1.1 Routing table: default.inet Internet: Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif 10.2.1.1/32 user 0 indr 262145 6 10.0.0.2 Push 299776 1013 2 fe-1/2/0.0user@A> show route forwarding-table destination 192.168.0.3 Routing table: default.inet Internet: Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif 192.168.0.3/32 user 1 10.0.0.2 Push 299776 1013 8 fe-1/2/0.0
tracerouteコマンドを使用して、traffic-engineering bgp-igpが設定されている場合にパスを確認します。user@A> traceroute 10.2.1.1 traceroute to 10.2.1.1 (10.2.1.1), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 2.348 ms 1.475 ms 1.434 ms MPLS Label=299776 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 2 10.0.0.18 (10.0.0.18) 1.507 ms 2.307 ms 1.911 ms MPLS Label=299808 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 3 10.0.0.29 (10.0.0.29) 1.743 ms 1.645 ms 1.940 ms 4 10.2.1.1 (10.2.1.1) 2.041 ms 1.977 ms 2.233 msuser@A> traceroute 192.168.0.3 traceroute to 192.168.0.3 (192.168.0.3), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 1.721 ms 2.558 ms 2.229 ms MPLS Label=299776 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 2 10.0.0.18 (10.0.0.18) 2.505 ms 1.462 ms 1.408 ms MPLS Label=299808 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1 3 bb03-cclab-lo0.spglab.juniper.net (192.168.0.3) 1.371 ms 1.422 ms 1.351 ms
意味
traffic-engineering bgpが設定されている場合、最初のトレースはBGPで学習した10.2.0.0/16プレフィックスに属する宛先へのトレースで、LSPに続きます。2 番目のトレースは、IS-IS で学習された 192.168.0.3 ルート(デバイス C のループバック インターフェイス アドレス)へのもので、IS-IS ルートに続いています。これらの結果は、転送テーブルで観察された結果と一致します。転送テーブルは、inet.0 のルートのみに基づいて構築されます。BGP は inet.3 を調べて、BGP プレフィックスのネクストホップへの最適パスとして LSP を選択し、その LSP を利用して inet.0 にルートを追加できます。そして、inet.0 ルートから転送テーブルにエントリーが作成されます。デフォルトでは、他のプロトコルは inet.3 を参照できず、inet.3 ルートは inet.0 には入力されません。そのため、192.168.0.3 の転送エントリーは、inet.0 の宛先への唯一のルートである IS-IS ルートから作成されます。
traffic-engineering bgp-igpが設定されている場合、10.2.1.1への最初のトレースは引き続きLSPに続きます。192.168.0.3 への 2 番目のトレースも LSP に続いています。これらの結果は、転送テーブルで観察されたものと一致しており、LSPがIGPネクストホップ解決に使用されていることを示しています。
