为第 3 层 VPN 启用 Internet 接入
本主题提供以下示例:配置提供商边缘 (PE) 路由器以向 VPN 中的客户边缘 (CE) 路由器提供互联网访问,以及配置路由器通过网络地址转换器 (NAT) 将互联网流量路由到 CE 路由器。您使用的方法取决于各个网络的需求和规格。
通过 3 层 VPN 进行非 VRF Internet 访问
Junos OS 支持从第 3 层虚拟专用网 (VPN) 访问互联网。您还需要在[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name routing-options static route]层次结构级别配置next-table语句。配置后,此语句可以将默认路由从 VPN 表(路由实例)指向主路由表(默认实例)inet.0。主路由表存储所有互联网路由,是进行最终路由解析的地方。
以下章节介绍了在不使用 VPN 路由和转发 (VRF) 接口的情况下,为第 3 层 VPN 中的 CE 路由器提供互联网访问的方法。由于这些方法有效地绕过了第 3 层 VPN,因此未详细讨论。
CE 路由器独立于 PE 路由器访问互联网
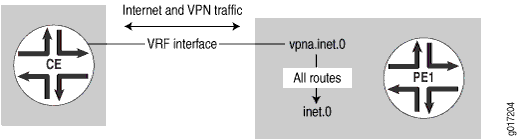
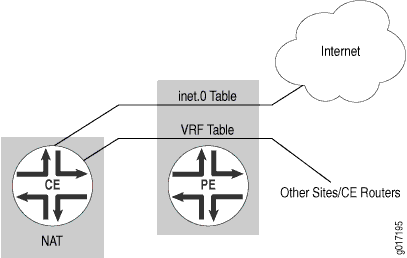
在此配置中,PE 路由器不提供互联网访问。CE 路由器将互联网流量发送到其他服务提供商,或发送到同一服务提供商但不同的路由器。PE 路由器仅处理第 3 层 VPN 流量(参见 图 1)。
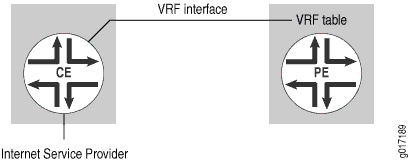
PE 路由器提供第 2 层互联网服务
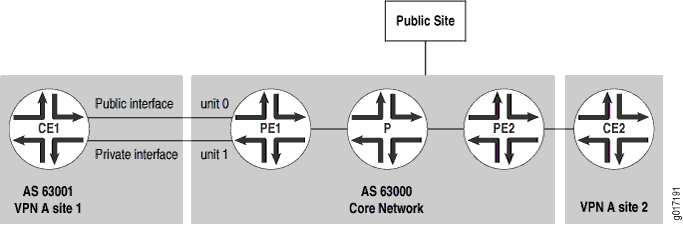
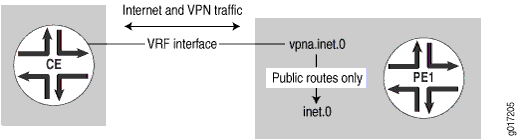
在此配置中,PE 路由器充当第 2 层设备,与另一台具有完整互联网路由的路由器提供第 2 层连接(例如电路交叉连接 [CCC])。CE 路由器可以只对 PE 路由器使用一个物理接口和两个逻辑接口,也可以对 PE 路由器使用多个物理接口(参见 图 2)。
 的路由器
的路由器
通过 3 层 VPN 的分布式互联网接入
在此场景中,PE 路由器提供对 CE 路由器的互联网访问。在以下示例中,假定互联网路由(或默认值)存在于为选定 CE 路由器提供互联网访问的 PE 路由器的 inet.0 表中。
从 VPN 访问 Internet 时,必须在 VPN 的专用地址和 Internet 上使用的公共地址之间执行网络地址转换 (NAT),除非 VPN 正在使用公共地址空间。本节包括如何为 VPN 提供互联网接入的几个示例,其中大多数示例需要 CE 路由器执行地址转换。 但是,通过单独的 NAT 设备路由互联网流量 的示例要求服务提供商使用连接到 PE 路由器的 NAT 设备提供 NAT 功能。
在所有示例中,必须将 VPN 的公共 IP 地址池(其条目与转换后的专用地址对应)添加到 inet.0 表中,并传播到互联网路由器,以接收来自公共目标的反向流量。
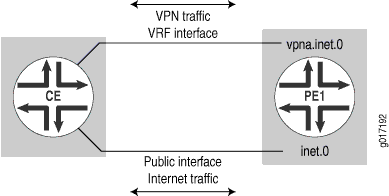
通过不同接口为第 3 层 VPN 路由 VPN 和互联网流量
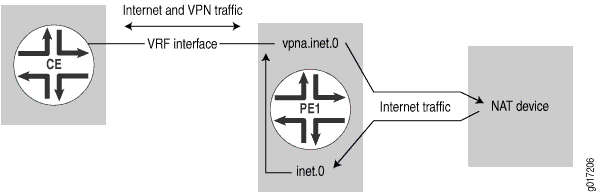
在此示例中,VPN 和 Internet 流量通过不同的接口路由。CE 路由器通过 VPN 接口发送 VPN 流量,并通过作为路由器 PE1 上主路由表一部分的单独接口发送互联网流量(CE 路由器可以使用一个具有两个逻辑单元的物理接口,也可以使用两个物理接口)。NAT 也会发生在 CE 路由器上(参见 图 3)。
 路由 VPN 和 Internet 流量
路由 VPN 和 Internet 流量
PE 路由器配置为安装 VPN 的公共 IP 地址池,并将其播发至其他核心路由器(用于返回流量)。VPN 流量正常路由。 图 4 显示了 PE 路由器的 VPN 配置。
 路由的 Internet 流量示例
路由的 Internet 流量示例
此示例中的配置具有以下功能:
-
路由器 PE1 使用两个逻辑接口通过帧中继封装连接到路由器 CE1。
-
路由器 PE1 和路由器 CE1 之间的路由协议为 EBGP。
-
路由器 CE1 的公共 IP 地址池通过
10.12.1.110.12.1.254(10.12.1.0/24)。 -
该
next-hop-self设置派生自fix-nh policy路由器 PE1 上的语句。PE 路由器被强制使用next-hop-self,以便仅对非 VPN 路由的 PE 路由器的环路地址进行下一跳解析(默认情况下,VPN – Internet 协议版本 4 [IPv4] 路由通过next-hop-self发送)。
您可以将路由器 CE1 配置为指向其公共接口的静态默认路由,用于其他所有作。
以下部分说明如何通过不同的接口路由 VPN 和 Internet 流量:
- 在路由器 PE1 上配置接口
- 在路由器 PE1 上配置路由选项
- 在路由器 PE1 上配置 BGP、IS-IS 和 LDP 协议
- 在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例
- 在路由器 PE1 上配置策略选项
- 不同接口路由的流量: 按路由器汇总的配置
在路由器 PE1 上配置接口
配置一个接口来处理 VPN 流量和一个接口来处理互联网流量:
[edit]
interfaces {
t3-0/2/0 {
dce;
encapsulation frame-relay;
unit 0 {
description "to CE1 VPN interface";
dlci 10;
family inet {
address 192.168.197.13/30;
}
}
unit 1 {
description "to CE1 public interface";
dlci 20;
family inet {
address 192.168.198.201/30;
}
}
}
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由选项
在路由器 PE1 上配置静态路由,以便在 inet.0 中安装到 CE 路由器的公共 IP 地址池的路由:
[edit]
routing-options {
static {
route 10.12.1.0/24 next-hop 192.168.198.202;
}
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置 BGP、IS-IS 和 LDP 协议
在路由器 PE1 上配置 BGP,以允许非 VPN 和 VPN 对等互连,并通告 VPN 的公共 IP 地址池:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group pe-pe {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.171;
family inet {
any;
}
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
export [fix-nh redist-static];
neighbor 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.179;
}
}
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置 IS-IS 以允许访问内部路由:
[edit protocols]
isis {
level 1 disable;
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置 LDP 以通过隧道传输 VPN 路由:
[edit protocols]
ldp {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
}
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置策略选项
您需要在路由器 PE1 上配置策略选项。 fix-nh 策略语句为所有非 VPN 路由设置 next-hop-self :
[edit]
policy-options {
policy-statement fix-nh {
then {
next-hop self;
}
}
}
redist-static策略语句会播发 VPN 的公共 IP 地址池:
[edit policy-options]
policy-statement redist-static {
term a {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 10.12.1.0/24 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
为以下内容 vpna配置导入和导出策略:
[edit policy-options]
policy-statement vpna-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpna-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
community vpna-comm members target:63000:100;
不同接口路由的流量: 按路由器汇总的配置
路由器 PE1
接口
interfaces {
t3-0/2/0 {
dce;
encapsulation frame-relay;
unit 0 {
description "to CE1 VPN interface";
dlci 10;
family inet {
address 192.168.197.13/30;
}
}
unit 1 {
description "to CE1 public interface";
dlci 20;
family inet {
address 192.168.198.201/30;
}
}
}
}
路由选项
routing-options {
static {
route 10.12.1.0/24 next-hop 192.168.198.202;
}
}
BGP 协议
protocols {
bgp {
group pe-pe {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.171;
family inet {
any;
}
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
export [ fix-nh redist-static];
neighbor 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.179;
}
}
}
IS-IS 协议
isis {
level 1 disable;
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
LDP 协议
ldp {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
}
路由实例
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
}
}
策略选项/策略声明
policy-options {
policy-statement fix-nh {
then {
next-hop self;
}
}
policy-statement redist-static {
term a {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 10.12.1.0/24 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
}
导入和导出策略
policy-statement vpna-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpna-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
community vpna-comm members target:63000:100;
通过同一接口和路由的路由 VPN 和传出互联网流量会通过不同的接口返回互联网流量
在此示例中,CE 路由器通过同一接口发送 VPN 和互联网流量,但通过不同的接口接收回传的互联网流量。PE 路由器在 VRF 表中有一条默认路由,指向主路由表 inet.0。它通过 inet.0 中的不同接口路由 VPN 公共 IP 地址池(返回 Internet 流量)(参见 图 5)。CE 路由器仍执行 NAT 功能。
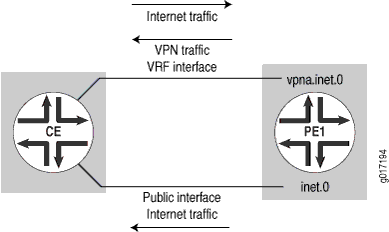 路由的返回 Internet 流量
路由的返回 Internet 流量
以下部分介绍如何通过同一接口路由 VPN 和传出 Internet 流量,以及如何通过不同的接口返回 Internet 流量:
路由器 PE1 的配置
此示例在通过不同 接口为第 3 层 VPN 路由 VPN 和互联网流量方面与路由器 PE1 的配置相同。它 使用第 3 层 VPN 通过不同接口路由 VPN 和 Internet 流量中所示的拓扑结构。VPN 路由表的默认路由配置方式不同。在 [edit routing-instances routing-instance-name routing-options] 层次结构级别,您可以配置一个默认静态路由,该路由安装在 vpna.inet.0 中并指向 inet.0 进行解析:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-table inet.0;
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
}
}
您还需要更改路由器 CE1 的配置(从与路由器 PE1 配置配合使用的配置(从通过第 3 层 VPN 的不同接口路由 VPN 和互联网流量中所述)来解释 PE 路由器的配置差异。
通过同一接口双向路由 VPN 和互联网流量(VPN 有公共地址)
本节介绍如何配置单个逻辑接口来处理进出互联网和 CE 路由器的 VPN 和互联网流量。只要 VPN 中没有专用地址,此接口就可以处理 VPN 和 Internet 流量。从 CE 路由器收到的 VPN 路由会通过路由表组添加到主路由表 inet.0 中。这使得 PE 路由器可以吸引来自互联网的返回流量(参见 图 6)。
 的接口
的接口
在此示例中,CE 路由器不需要执行 NAT,因为所有 VPN 路由都是公共的。CE 路由器有一个到 PE 路由器的接口,它向该路由器播发 VPN 路由。PE 路由器在 VRF 表中有一条默认路由,指向主路由表 inet.0。PE 路由器还通过路由表组将从 CE 路由器收到的 VPN 路由导入到 inet.0 中。
路由器 PE1 的以下配置使用的拓扑结构与 通过不同接口将 VPN 和互联网流量路由第 3 层 VPN 中的拓扑相同。此配置在路由器 PE1 和路由器 CE1 之间使用一个逻辑接口(而非两个)。
以下部分说明如何通过同一接口双向路由 VPN 和 Internet 流量(VPN 具有公共地址):
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由选项
配置路由表组定义,以便在路由表组 vpna.inet.0 和 inet.0 中安装 VPN 路由:
[edit]
routing-options {
rib-groups {
vpna-to-inet0 {
import-rib [ vpna.inet.0 inet.0 ];
}
}
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由协议
在路由器 PE1 上配置 MPLS、BGP、IS-IS 和 LDP 协议。此配置不包括 policy redist-static 层 [edit protocols bgp group pe-pe] 级的语句。VPN 路由直接发送到 IBGP。
在路由器 PE1 上配置 BGP,以允许非 VPN 和 VPN 对等互连,并播发 VPN 的公共 IP 地址池:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
}
bgp {
group pe-pe {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.171;
family inet {
any;
}
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
export fix-nh;
neighbor 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.173;
}
}
isis {
level 1 disable;
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
ldp {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
}
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例
本节介绍如何在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例。语句中 routing-options 定义的静态路由将互联网流量从 CE 路由器定向到 inet.0 路由表。语句定义 rib-group vpna-to-inet0 的路由表组将 VPN 路由添加到 inet.0。
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-table inet.0;
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
family inet {
unicast {
rib-group vpna-to-inet0;
}
}
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
}
}
您必须将路由器 CE1 配置为使用默认路由将所有流量转发到路由器 PE1。或者,可以使用 EBGP 从路由器 PE1 向路由器 CE1 播发默认路由。
通过同一接口双向路由的流量: 按路由器汇总的配置
路由器 PE1
此示例使用的配置与 通过不同接口为第 3 层 VPN 路由 VPN 和 Internet 流量中的配置相同。此配置在路由器 PE1 和路由器 CE1 之间使用一个逻辑接口(而非两个)。
路由选项
routing-options {
rib-groups {
vpna-to-inet0 {
import-rib [ vpna.inet.0 inet.0 ];
}
}
}
路由协议
protocols {
mpls {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
}
bgp {
group pe-pe {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.171;
family inet {
any;
}
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
export fix-nh;
neighbor 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.173;
}
}
isis {
level 1 disable;
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
ldp {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
}
}
路由实例
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-table inet.0;
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
family inet {
unicast {
rib-group vpna-to-inet0;
}
}
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
}
}
通过同一接口双向路由 VPN 和互联网流量(VPN 有专用地址)
本节中的示例说明如何通过同一接口在两个方向上路由 VPN 和 Internet 流量(从 CE 路由器到 Internet,以及从 Internet 到 CE 路由器)。此示例中的 VPN 具有专用地址。如果可以在 CE 路由器上配置 EBGP,则可以使用通过 同一接口双向路由 VPN 和互联网流量中所述的配置(VPN 有公共地址)配置 PE 路由器,即使 VPN 有专用地址也是如此。
在本节介绍的示例中,CE 路由器使用单独的社区来通告其 VPN 路由和公共路由。PE 路由器有选择地仅将公共路由导入到 inet.0 路由表中。此配置可确保来自互联网的返回流量在 PE 和 CE 路由器之间使用与传出到公共互联网地址的 VPN 流量相同的接口(参见 图 7)。
在此示例中,CE 路由器与 PE 路由器有一个接口和一个 BGP 会话,并标记了不同社区的 VPN 路由和互联网路由。PE 路由器只有一个接口,可选择地将 VPN 的公共 IP 地址池的路由导入到 inet.0 中,并且 VRF 路由路由表中的默认路由指向 inet.0。
以下部分说明如何通过同一接口双向路由 VPN 和 Internet 流量(VPN 具有专用地址):
配置路由器 PE1 的路由选项
在路由器 PE1 上,配置路由表组以在 vpna.inet.0 和 inet.0 路由表中安装 VPN 路由:
[edit]
routing-options {
rib-groups {
vpna-to-inet0 {
import-policy import-public-addr-to-inet0;
import-rib [ vpna.inet.0 inet.0 ];
}
}
}
为路由器 PE1 配置路由实例
在路由器 PE1 上,配置路由实例。作为路由实例配置的一部分,配置安装在 vpna.inet.0 中并指向 inet.0 进行解析的静态路由。
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-table inet.0;
}
}
}
}
在 [edit routing-instances vpna protocols bgp] 层次结构级别,配置策略 (import-public-addr-to-inet0) 以将公共路由导入 inet.0,并将路由表组 (vpna-to-inet0) 以允许 BGP 将路由安装到多个路由表(vpna.inet.0 和 inet.0)中:
[edit routing-instances vpna]
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
import import-public-addr-to-inet0;
family inet {
unicast {
rib-group vpna-to-inet0;
}
}
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
配置路由器 PE1 的策略选项
配置路由器 PE1 的策略选项,以初始 (term a) 接受所有路由,然后将带有 public-comm 社区的路由安装到路由表 inet.0 (term b):
[edit]
policy-options {
policy-statement import-public-addr-to-inet0 {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
rib vpna.inet.0;
community [ public-comm private-comm ];
}
then accept;
}
term b {
from {
protocol bgp;
community public-comm;
}
to rib inet.0;
then accept;
}
term c {
then reject;
}
}
community private-comm members target:1:333;
community public-comm members target:1:111;
community vpna-comm members target:63000:100;
}
同一接口双向路由的流量(VPN 有专用地址): 按路由器汇总的配置
路由器 PE1
路由选项
[edit]
routing-options {
rib-groups {
vpna-to-inet0 {
import-policy import-public-addr-to-inet0;
import-rib [ vpna.inet.0 inet.0 ];
}
}
}
路由实例
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-table inet.0;
}
}
}
}
路由实例、协议、BGP
[edit routing-instances vpna]
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
family inet {
unicast {
rib-group vpna-to-inet0;
}
}
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
策略选项
[edit]
policy-options {
policy-statement import-public-addr-to-inet0 {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
rib vpna.inet.0;
community [ public-comm private-comm ];
}
then accept;
}
term b {
from {
protocol bgp;
community public-comm;
}
to rib inet.0;
then accept;
}
term c {
then reject;
}
}
community private-comm members target:1:333;
community public-comm members target:1:111;
community vpna-comm members target:63000:100;
}
通过单独的 NAT 设备路由互联网流量
在此示例中,CE 路由器不执行 NAT。它通过同一接口将 VPN 和互联网流量发送到 PE 路由器。PE 路由器通过两个接口连接到 NAT 设备。在 PE 路由器的 VRF 表中配置了一个接口,该接口指向 NAT 设备上的 VPN 接口,该接口可以为 VPN 路由互联网流量。另一个接口处于默认实例中;例如,公共路由表 inet.0 的一部分。PE 路由器和 NAT 设备之间可以有一个物理连接,另一个逻辑连接可以作为全局路由表的一部分,每个 VRF 表可以有一个逻辑连接,另一个接口可以建立(参见 图 8)。
 路由的 Internet 流量
路由的 Internet 流量
要求
此示例使用以下硬件和软件组件:
-
M Series 路由器
-
Junos OS 9.3 或更高版本
概述
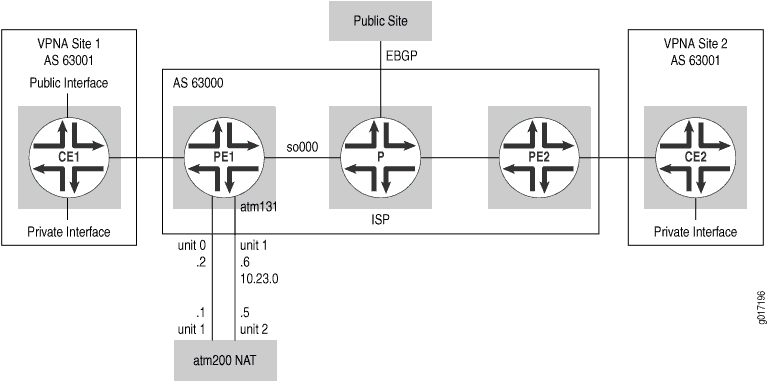
此示例的拓扑扩展了通过 第 3 层 VPN 的不同接口路由 VPN 和 Internet 流量中所示的拓扑。CE 路由器将 VPN 和互联网流量都发送到路由器 PE1。VPN 流量基于路由器 PE1 接收的 VPN 路由。使用路由器 PE1 与 NAT 设备的专用接口,将所有其他流量发送到 NAT 设备,然后 NAT 设备转换专用地址,并使用路由器的公共接口将流量发送回路由器 PE1(参见 图 9)。
拓扑学
配置
要通过单独的 NAT 设备路由互联网流量,请执行以下任务:
在路由器 PE1 上配置接口
分步过程
-
为来自路由器 CE1 的 VPN 流量配置接口:
[edit] interfaces { t3-0/2/0 { dce; encapsulation frame-relay; unit 0 { description "to CE1 VPN interface"; dlci 10; family inet { address 192.168.197.13/30; } } } } -
配置一个接口,用于进出 NAT 设备(单元 0)的 VPN 流量,以及一个用于进出 NAT 设备(单元 1)的互联网流量的接口:
[edit] interfaces { at-1/3/1 { atm-options { vpi 1 maximum-vcs 255; } unit 0 { description "to NAT VPN interface"; vci 1.100; family inet { address 10.23.0.2/32 { destination 10.23.0.1; } } } unit 1 { description "to NAT public interface"; vci 1.101; family inet { address 10.23.0.6/32 { destination 10.23.0.5; } } } } }
配置路由器 PE1 的路由选项
分步过程
-
在路由器 PE1 上配置静态路由,通过 NAT 设备将互联网流量引导至 CE 路由器。路由器 PE1 将此路由分发到 Internet。
[edit] routing-options { static { route 10.12.1.0/24 next-hop 10.23.0.5; } }
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由协议
分步过程
在路由器 PE1 上配置以下路由协议:
-
在路由器 PE1 上配置 MPLS。在 VRF 表中包括 NAT 设备的 VPN 接口。
[edit] protocols { mpls { interface so-0/0/0.0; interface at-1/3/1.0; } } -
在路由器 PE1 上配置 BGP。包括播发公共 IP 地址池的策略:
[edit] protocols { bgp { group pe-pe { type internal; local-address 10.255.14.171; family inet { any; } family inet-vpn { any; } export [ fix-nh redist-static ]; neighbor 10.255.14.177; neighbor 10.255.14.173; } } } -
在路由器 PE1 上配置 IS-IS:
[edit] protocols { isis { level 1 disable; interface so-0/0/0.0; interface lo0.0; } } -
在路由器 PE1 上配置 LDP:
[edit] protocols { ldp { interface so-0/0/0.0; } }
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例
分步过程
在路由器 PE1 上配置第 3 层 VPN 路由实例:
-
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例。作为路由实例配置的一部分,在
routing-options下,在 vpna.inet.0 中配置指向 NAT 设备的 VPN 接口的静态默认路由(这会将所有非 VPN 流量定向到 NAT 设备):[edit] routing-instances { vpna { instance-type vrf; interface t3-0/2/0.0; interface at-1/3/1.0; route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100; vrf-import vpna-import; vrf-export vpna-export; routing-options { static { route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 10.23.0.1; } } protocols { bgp { group to-CE1 { peer-as 63001; neighbor 192.168.197.14; } } } } } -
为路由器 PE1 上的第 3 层 VPN 路由实例配置路由策略:
policy-options { policy-statement fix-nh { then { next-hop self; } } policy-statement redist-static { term a { from { protocol static; route-filter 10.12.1.0/24 exact; } then accept; } term b { from protocol bgp; then accept; } term c { then accept; } } policy-statement vpna-import { term a { from { protocol bgp; community vpna-comm; } then accept; } term b { then reject; } } policy-statement vpna-export { term a { from protocol bgp; then { community add vpna-comm; accept; } } term b { then reject; } } community vpna-comm members target:63000:100; }
结果
在路由器 PE1 上的配置模式下,输入 show interfaces、show routing-options、show protocols、show routing-instances 和 show policy-options 命令,以确认您的配置。如果输出未显示预期的配置,请重复此示例中的说明以更正配置。
user@PE1# show interfaces
interfaces {
t3-0/2/0 {
dce;
encapsulation frame-relay;
unit 0 {
description "to CE1 VPN interface";
dlci 10;
family inet {
address 192.168.197.13/30;
}
}
}
at-1/3/1 {
atm-options {
vpi 1 maximum-vcs 255;
}
unit 0 {
description "to NAT VPN interface";
vci 1.100;
family inet {
address 10.23.0.2/32 {
destination 10.23.0.1;
}
}
}
unit 1 {
description "to NAT public interface";
vci 1.101;
family inet {
address 10.23.0.6/32 {
destination 10.23.0.5;
}
}
}
}
}
user@PE1# show routing-options
routing-options {
static {
route 10.12.1.0/24 next-hop 10.23.0.5;
}
}
user@PE1# show protocols
protocols {
mpls {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface at-1/3/1.0;
}
bgp {
group pe-pe {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.171;
family inet {
any;
}
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
export [ fix-nh redist-static ];
neighbor 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.173;
}
}
isis {
level 1 disable;
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
ldp {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
}
}
user@PE1# show routing-instances
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
interface at-1/3/1.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 10.23.0.1;
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
}
}
user@PE1# show policy-options
policy-options {
policy-statement fix-nh {
then {
next-hop self;
}
}
policy-statement redist-static {
term a {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 10.12.1.0/24 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
from protocol bgp;
then accept;
}
term c {
then accept;
}
}
policy-statement vpna-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpna-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
community vpna-comm members target:63000:100;
}
通过 3 层 VPN 集中访问互联网
本节介绍将 CE 路由器配置为作为 Internet 访问的中央站点的几种方法。来自其他站点(CE 路由器)的互联网流量使用该路由器的 VPN 接口路由到中枢 CE 路由器(也执行 NAT)。然后,中枢 CE 路由器将流量转发到通过 inet.0 表中标识的另一个接口连接到互联网的 PE 路由器。中枢 CE 路由器可以将默认路由播发至分支 CE 路由器。这种配置的缺点是所有流量在进入互联网之前都必须经过中央 CE 路由器,如果此路由器接收到过多的流量,则会导致网络延迟。但是,在企业网络中,流量可能必须路由到中央站点,因为大多数企业网络通过单个防火墙将 VPN 与 Internet 隔离开来。
本部分包括以下示例:
通过中枢 CE 路由器路由互联网流量
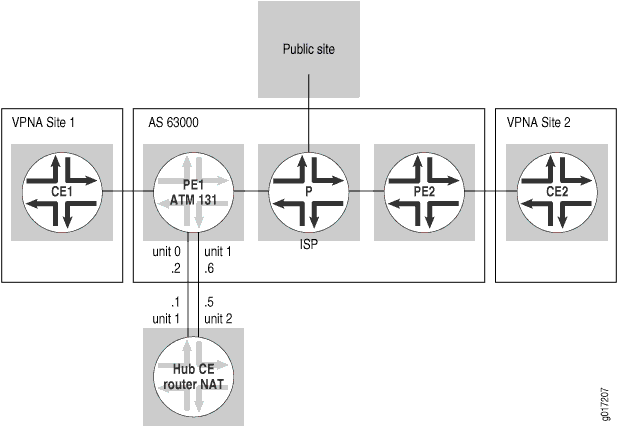
在此示例中,互联网流量通过集线器 CE 路由器路由。集线器 CE 路由器有两个到集线器 PE 路由器的接口:一个 VPN 接口和一个公共接口。它会对从中枢 PE 路由器通过 VPN 接口转发的流量执行 NAT,并将该流量从其公共接口转发回中枢 PE 路由器。中枢 PE 路由器的 VRF 表中有一条静态默认路由,该路由指向中枢 CE 路由器的 VPN 接口。它会将此默认路由通告到 VPN 的其余部分,从而将所有非 VPN 流量吸引到中枢 CE 路由。中枢 PE 路由器还会安装和分配 VPN 的公共 IP 地址空间(参见 图 10)。
此示例的配置与 通过单独的 NAT 设备路由互联网流量中所述的配置几乎相同。不同之处在于,路由器 PE1 配置为向其他 CE 路由器通告静态默认路由(参见 图 11)。
 提供的 Internet 访问
提供的 Internet 访问
以下章节介绍如何通过中枢 CE 路由器路由互联网流量来配置集中互联网访问:
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例
为路由器 PE1 配置路由实例。作为此配置的一部分,在 下 routing-options,配置要安装在 vpna.inet.0 中的默认静态路由 (route 0.0.0.0/0),并将路由指向中枢 CE 路由器的 VPN 接口 (10.23.0.1)。另外,在路由实例下配置 BGP,将默认路由导出到本地 CE 路由器:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
interface at-1/3/1.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 10.23.0.1;
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
export export-default;
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
}
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置策略选项
在路由器 PE1 上配置策略选项。作为此配置的一部分,路由器 PE1 应将静态默认路由导出到(在policy-statement vpna-export语句中term b配置)中vpna的所有远程 PE 路由器:
[edit]
policy-options {
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term c {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement export-default {
term a {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
from protocol bgp;
then accept;
}
term c {
then reject;
}
}
}
中枢 CE 路由器路由的互联网流量:按路由器汇总的配置
路由器 PE1
路由器 PE1 的配置与 通过单独的 NAT 设备路由互联网流量中的示例几乎完全相同。不同之处在于,路由器 PE1 配置为向其他 CE 路由器通告静态默认路由。
路由实例
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
interface at-1/3/1.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 10.23.0.1;
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
export export-default;
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
}
}
策略选项
policy-options {
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term c {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement export-default {
term a {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
from protocol bgp;
then accept;
}
term c {
then reject;
}
}
}
通过多个 CE 路由器路由互联网流量
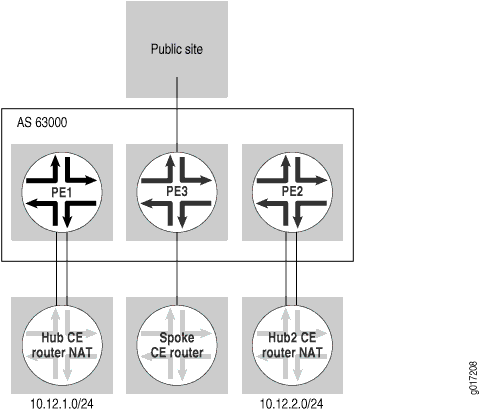
本节中的示例是 通过第 3 层 VPN 进行集中式 Internet 访问中所述的扩展。此示例通过多个执行类似功能的集线器 CE 路由器为不同的站点提供不同的出口点。每个中枢 CE 路由器都使用不同的路由目标标记默认路由,并允许分支 CE 路由器选择应用于 Internet 访问的中枢站点( 参见图 12)。
 的集线器 CE 路由器
的集线器 CE 路由器
此示例使用两台处理 NAT 和互联网流量的集线器 CE 路由器:
-
带社区的
public-comm1Hub1 CE 路由器标记0/0(目标:1:111) -
带社区的
public-comm2Hub2 CE 路由器标记0/0(目标:1:112)
此示例中的分支 CE 路由器配置为偏向 Hub2 进行 Internet 访问。
以下部分介绍如何配置两个中枢 CE 路由器来处理互联网流量和 NAT:
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例
在路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
interface at-1/3/1.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 10.23.0.1;
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
export export-default;
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
}
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置策略选项
路由器 PE1 的策略选项与通过集线器 CE 路由器路由互联网流量中的策略选项相同,但此示例中的配置在语句中export包括了一个附加社区 public-comm1:
[edit]
policy-options {
policy-statement vpna-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpna-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then {
community add public-comm1;
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term c {
then reject;
}
}
community public-comm1 members target:1:111;
community public-comm2 members target:1:112;
community vpna-comm members target:63000:100;
}
路由器 PE2 的配置与路由器 PE1 的配置相同,只是路由器 PE2 通过社区 public-comm2导出默认路由。
在路由器 PE3 上配置路由实例
在路由器 PE3 上配置路由实例 vpna :
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t1-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.173:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
protocols {
rip {
group to-vpn12 {
export export-CE;
neighbor t1-0/2/0.0;
}
}
}
}
}
在路由器 PE3 上配置策略选项
为路由器 PE3 配置 vrf-import 策略,以根据在 路由器 PE1 上配置策略选项中指定的其他社区选择 Internet 出口点:
[edit]
policy-options {
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from protocol rip;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpna-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community public-comm1;
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then reject;
}
term b {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpna-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term c {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement export-CE {
from protocol bgp;
then accept;
}
community vpna-comm members target:69:100;
community public-comm1 members target:1:111;
community public-comm2 members target:1:112;
}
通过多台 CE 路由器路由互联网流量:按路由器汇总的配置
路由器 PE1
此配置是 通过集线器 CE 路由器路由互联网流量中示例的扩展。它通过使用多个执行类似功能的集线器 CE 路由器,为各个站点提供不同的出口点。
路由实例
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
interface at-1/3/1.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 10.23.0.1;
}
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-CE1 {
export export-default;
peer-as 63001;
neighbor 192.168.197.14;
}
}
}
}
}
策略选项
policy-options {
policy-statement vpna-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpna-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then {
community add public-comm1;
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term c {
then reject;
}
}
community public-comm1 members target:1:111;
community public-comm2 members target:1:112;
community vpna-comm members target:63000:100;
}
路由器 PE2
路由器 PE2 的配置与路由器 PE1 的配置相同,只是路由器 PE2 通过社区 public-comm2导出默认路由。
路由器 PE3
路由实例
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface t1-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.173:100;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
protocols {
rip {
group to-vpn12 {
export export-CE;
neighbor t1-0/2/0.0;
}
}
}
}
}
策略选项
policy-options {
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from protocol rip;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpna-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community public-comm1;
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then reject;
}
term b {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpna-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term c {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement export-CE {
from protocol bgp;
then accept;
}
community vpna-comm members target:69:100;
community public-comm1 members target:1:111;
community public-comm2 members target:1:112;
}
