运营商间 VPN
了解载波至载波 VPN
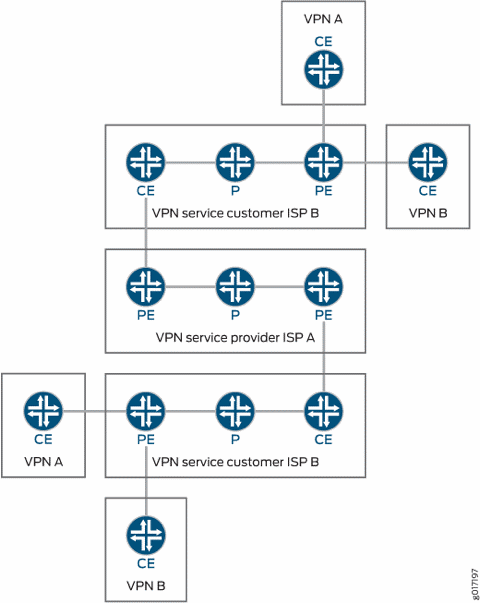
VPN 服务提供商的客户可能是最终客户的服务提供商。以下是两种主要类型的载波至载波 VPN(如 RFC 4364 中所述):
作为客户的互联网服务提供商 — VPN 客户是使用 VPN 服务提供商的网络连接其地理位置不同的区域网络的 ISP。客户不必在其区域网络中配置 MPLS。
作为客户的 VPN 服务提供商 - VPN 客户本身就是一个 VPN 服务提供商,为其客户提供 VPN 服务。运营商至运营商 VPN 服务客户依靠骨干 VPN 服务提供商实现站点间连接。客户 VPN 服务提供商需要在其区域网络内运行 MPLS。
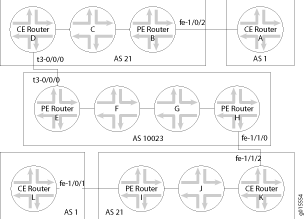
图 1 展示了用于载波至载波 VPN 服务的网络架构。
本主题涵盖以下内容:
作为客户的互联网服务提供商
在这种类型的载波至载波 VPN 配置中,ISP A 将其网络配置为向 ISP B 提供互联网服务。ISP B 向需要互联网服务的客户提供连接,但实际的互联网服务由 ISP A 提供。
这种类型的载波至载波 VPN 配置具有以下特征:
载波至载波 VPN 服务客户 (ISP B) 不需要在其网络上配置 MPLS。
载波至载波 VPN 服务提供商 (ISP A) 必须在其网络上配置 MPLS。
还必须在运营商至运营商 VPN 服务客户和运营商至运营商 VPN 服务提供商网络中连接在一起的 CE 路由器和 PE 路由器上配置 MPLS。
VPN 服务提供商作为客户
VPN 服务提供商的客户本身也可以是 VPN 服务提供商。在这种配置(也称为分层或递归 VPN)中,客户 VPN 服务提供商的 VPN-IPv4 路由被视为外部路由,主干 VPN 服务提供商不会将其导入其 VRF 表。骨干 VPN 服务提供商仅将客户 VPN 服务提供商的内部路由导入其 VRF 表。
表 1 显示了提供商间 VPN 和载波至载波 VPN 之间的异同。
特征 |
ISP 客户 |
VPN 服务提供商客户 |
|---|---|---|
客户边缘设备 |
AS 边界路由器 |
PE 路由器 |
IBGP 会话 |
携带 IPv4 路由 |
携带带有关联标签的外部 VPN-IPv4 路由 |
客户网络内的转发 |
MPLS 是可选的 |
MPLS 是必需的 |
支持 VPN 服务,因为从 Junos OS 17.1R1 版开始,QFX10000交换机支持客户。
为提供互联网服务的客户配置运营商至运营商 VPN
您可以为希望提供基本互联网服务的客户配置载波至载波 VPN 服务。载波至载波 VPN 服务提供商必须在其网络中配置 MPLS,但此配置对于运营商服务客户是可选的。 载波至载波 VPN 架构 显示了此类服务中的路由器或交换机如何互连。
要配置载波至载波 VPN,请执行以下部分中介绍的任务:
配置载波至载波 VPN 服务客户的 CE 路由器
载波至载波 VPN 服务客户的路由器(或交换机)相对于服务提供商的 PE 路由器或交换机充当 CE 路由器。以下章节介绍如何配置载波至载波 VPN 服务客户的 CE 路由器或交换机:
配置 MPLS
要在客户的 CE 路由器或交换机上配置 MPLS,请添加 mpls 以下语句:
mpls {
traffic-engineering bgp-igp;
interface interface-name;
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 BGP
要配置组来整理客户的内部路由,请包含以下 bgp 语句:
bgp {
group group-name {
type internal;
local-address address;
neighbor address;
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)必须能够向 VPN 服务提供商的路由器发送标签。通过在 BGP 组的配置中包含语 labeled-unicast 句来启用此功能:
bgp {
group group-name {
export internal;
peer-as as-number;
neighbor address {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含 bgp 语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 OSPF
要在客户的 CE 路由器或交换机上配置 OSPF,请添加以下 ospf 语句:
ospf {
area area-id {
interface interface-name {
passive;
}
interface interface-name;
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置策略选项
要在客户的 CE 路由器或交换机上配置策略选项,请添加以下 policy-statement 语句:
policy-statement statement-name {
term term-name {
from protocol [ospf direct ldp];
then accept;
}
term term-name {
then reject;
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit policy-options][edit logical-systems logical-system-name policy-options]
配置载波至载波 VPN 服务提供商的 PE 路由器
服务提供商的 PE 路由器连接到客户的 CE 路由器,并通过提供商的网络转发客户的 VPN 流量。
以下章节介绍如何配置载波至载波 VPN 服务提供商的 PE 路由器:
配置 MPLS
要在提供商的 PE 路由器或交换机上配置 MPLS,请包含以下 mpls 语句:
mpls {
interface interface-name;
interface interface-name;
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 BGP
要配置与提供商网络另一端的提供商 PE 路由器的 BGP 会话,请添加以下 bgp 语句:
bgp {
group group-name {
type internal;
local-address address;
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
neighbor address;
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 IS-IS
要在提供商的 PE 路由器或交换机上配置 IS-IS,请包含以下 isis 语句:
isis {
interface interface-name;
interface interface-name {
passive;
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 LDP
要在提供商的 PE 路由器或交换机上配置 LDP,请添加以下 ldp 语句:
ldp {
interface interface-name;
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置路由实例
要使用客户的 CE 路由器或交换机配置第 3 层 VPN 服务,请在路由实例的配置中包含语 labeled-unicast 句,以便 PE 路由器(或交换机)可以向客户的 CE 路由器或交换机发送标签:
routing-instance-name {
instance-type vrf;
interface interface-name;
route-distinguisher address;
vrf-import policy-name;
vrf-export policy-name;
protocols {
bgp {
group group-name {
peer-as as-number;
neighbor address {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit routing-instances][edit logical-systems logical-system-name routing-instances]
配置策略选项
要配置策略语句以从客户的 CE 路由器或交换机导入路由,请包含以下 policy-statement 语句:
policy-statement policy-name {
term term-name {
from {
protocol bgp;
community community-name;
}
then accept;
}
term term-name {
then reject;
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit policy-options][edit logical-systems logical-system-name policy-options]
要配置策略语句以将路由导出到客户的 CE 路由器或交换机,请添加 policy-statement 和 community 语句:
policy-statement policy-name {
term term-name {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add community-name;
accept;
}
}
term term-name {
then reject;
}
}
community community-name members value;
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit policy-options][edit logical-systems logical-system-name policy-options]
另见
载波至载波 VPN 示例 — 客户提供互联网服务
在此示例中,运营商客户不需要在其网络上配置 MPLS 和 LDP。但是,运营商提供商必须在其网络上配置 MPLS 和 LDP。
有关配置信息,请参阅以下部分:
- 载波至载波服务的网络拓扑
- 路由器 A 的配置
- 路由器 B 的配置
- 路由器 C 的配置
- 路由器 D 的配置
- 路由器 E 的配置
- 路由器 F 的配置
- 路由器 G 的配置
- 路由器 H 的配置
- 路由器 I 的配置
- 路由器 J 的配置
- 路由器 K 的配置
- 路由器 L 的配置
路由器 A 的配置
在此示例中,路由器 A 代表最终客户。您可以将此路由器配置为 CE 设备。
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group to-routerB {
export attached;
peer-as 21;
as-override;
neighbor 192.168.197.169;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement attached {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
路由器 B 的配置
路由器 B 可以充当网关路由器,负责聚合最终客户并将其连接到网络。如果配置了全网状 IBGP 会话,则可以使用路由反射器。
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.179;
neighbor 10.255.14.175;
neighbor 10.255.14.181;
neighbor 10.255.14.176;
neighbor 10.255.14.178;
neighbor 10.255.14.177;
}
group to-vpn-blue {
peer-as 1;
neighbor 192.168.197.170;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/0/3.0;
interface fe-1/0/2.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
}
路由器 C 的配置
配置路由器 C:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.176;
neighbor 10.255.14.179;
neighbor 10.255.14.175;
neighbor 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.178;
neighbor 10.255.14.181;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-0/3/3.0;
interface fe-0/3/0.0;
}
}
}
路由器 D 的配置
路由器 D 是相对于 AS 10023 的 CE 路由器。在载波至载波 VPN 中,CE 路由器必须能够向运营商提供商发送标签;这是通过 labeled-unicast 组 to-isp-red中的语句完成的。
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
interface t3-0/0/0.0;
}
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.175;
neighbor 10.255.14.179;
neighbor 10.255.14.176;
neighbor 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.178;
neighbor 10.255.14.181;
}
group to-isp-red {
export internal;
peer-as 10023;
neighbor 192.168.197.13 {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-0/3/0.0;
interface t3-0/0/0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
}
policy options {
policy-statement internal {
term a {
from protocol [ ospf direct ];
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
}
路由器 E 的配置
此配置设置 inet-vpn 与路由器 H 的 IBGP 会话,以及与路由器 D 的 VPN 的 PE 路由器部分。由于在此示例中需要路由器 D 发送标签,因此请使用 labeled-unicast 虚拟路由和转发 (VRF) 表中的语句配置 BGP 会话。
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
interface at-0/1/0.0;
}
bgp {
group pe-pe {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.171;
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
neighbor 10.255.14.173;
}
}
isis {
interface at-0/1/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
ldp {
interface at-0/1/0.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
vpn-isp1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:21;
vrf-import vpn-isp1-import;
vrf-export vpn-isp1-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group to-isp1 {
peer-as 21;
neighbor 192.168.197.14 {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement vpn-isp1-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpn-isp1-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpn-isp1-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpn-isp1-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
community vpn-isp1-comm members target:69:21;
}
路由器 F 的配置
将路由器 F 配置为标签交换路由器:
[edit]
protocols {
isis {
interface so-0/2/0.0;
interface at-0/3/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
ldp {
interface so-0/2/0.0;
interface at-0/3/0.0;
}
}
路由器 G 的配置
将路由器 G 配置为标签交换路由器:
[edit]
protocols {
isis {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface so-1/0/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
ldp {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface so-1/0/0.0;
}
}
路由器 H 的配置
路由器 H 充当 AS 10023 的 PE 路由器。以下配置与路由器 F 的配置类似:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
interface fe-1/1/0.0;
interface so-1/0/0.0;
}
bgp {
group pe-pe {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.173;
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
neighbor 10.255.14.171;
}
}
isis {
interface so-1/0/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
ldp {
interface so-1/0/0.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
vpn-isp1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface fe-1/1/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.173:21;
vrf-import vpn-isp1-import;
vrf-export vpn-isp1-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group to-isp1 {
peer-as 21;
neighbor 192.168.197.94 {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement vpn-isp1-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpn-isp1-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpn-isp1-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpn-isp1-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
community vpn-isp1-comm members target:69:21;
}
路由器 I 的配置
将路由器 I 配置为连接到基本互联网服务客户(路由器 L):
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
interface fe-1/0/1.0;
interface fe-1/1/3.0;
}
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.181;
neighbor 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.179;
neighbor 10.255.14.175;
neighbor 10.255.14.176;
neighbor 10.255.14.178;
}
group to-vpn-green {
peer-as 1;
neighbor 192.168.197.198;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/0/1.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/1/3.0;
}
}
}
路由器 J 的配置
将路由器 J 配置为标签交换路由器:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.178;
neighbor 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.181;
neighbor 10.255.14.175;
neighbor 10.255.14.176;
neighbor 10.255.14.179;
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
interface fe-1/0/3.0;
}
}
路由器 K 的配置
路由器 K 在与运营商提供商的连接结束时充当 CE 路由器。与路由器 D 的配置一样,包括 labeled-unicast EBGP 会话的语句:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
interface fe-1/1/2.0;
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
}
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.181;
neighbor 10.255.14.178;
neighbor 10.255.14.175;
neighbor 10.255.14.176;
neighbor 10.255.14.179;
}
group to-isp-red {
export internal;
peer-as 10023;
neighbor 192.168.197.93 {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
interface fe-1/1/2.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement internal {
term a {
from protocol [ ospf direct ];
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
}
路由器 L 的配置
将路由器 L 配置为运营商至运营商 VPN 服务的最终客户:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group to-routerI {
export attached;
peer-as 21;
neighbor 192.168.197.197;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement attached {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
另见
为提供 VPN 服务的客户配置运营商至运营商 VPN
您可以为需要 VPN 服务的客户配置载波至载波 VPN 服务。
要将客户和提供商网络中的路由器(或交换机)配置为启用运营商至运营商 VPN 服务,请执行以下部分中的步骤:
配置载波至载波客户的 PE 路由器
载波至载波客户的 PE 路由器(或交换机)连接到最终客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)。
以下章节介绍如何配置载波至载波客户的 PE 路由器(或交换机):
配置 MPLS
要在载波至载波客户的 PE 路由器(或交换机)上配置 MPLS,请包含以下 mpls 语句:
mpls {
interface interface-name;
interface interface-name;
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 BGP
在到载波至载波客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)的 IBGP 会话配置中包含该 labeled-unicast 语句,并将该 family-inet-vpn 语句包含在到网络另一端的载波至载波 PE 路由器(或交换机)的 IBGP 会话配置中:
bgp {
group group-name {
type internal;
local-address address;
neighbor address {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
resolve-vpn;
}
}
}
neighbor address {
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 OSPF
要在载波至载波客户的 PE 路由器(或交换机)上配置 OSPF,请添加以下 ospf 语句:
ospf {
area area-id {
interface interface-name {
passive;
}
interface interface-name;
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 LDP
要在载波至载波客户的 PE 路由器(或交换机)上配置 LDP,请包含以下 ldp 语句:
ldp {
interface interface-name;
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
在路由实例中配置 VPN 服务
要在载波至载波客户的 PE 路由器(或交换机)上为最终客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)配置 VPN 服务,请包含以下语句:
instance-type vrf;
interface interface-name;
route-distinguisher address;
vrf-import policy-name;
vrf-export policy-name;
protocols {
bgp {
group group-name {
peer-as as-number;
neighbor address;
}
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name][edit logical-systems logical-system-name routing-instances routing-instance-name]
配置策略选项
要配置策略选项以导入和导出最终客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)之间的路由,请包括 policy-statement 和 community 语句:
policy-statement policy-name {
term term-name {
from {
protocol bgp;
community community-name;
}
then accept;
}
term term-name {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement policy-name {
term term-name {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add community-name;
accept;
}
}
term term-name {
then reject;
}
}
community community-name members value;
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit policy-options][edit logical-systems logical-system-name policy-options]
配置载波至载波客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)
载波至载波客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)连接到提供商的 PE 路由器(或交换机)。完成以下部分中的说明,配置载波至载波客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机):
配置 MPLS
在载波至载波客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)的 MPLS 配置中,包括到提供商的 PE 路由器(或交换机)和客户网络中的 P 路由器(或交换机)的接口:
mpls {
traffic-engineering bgp-igp;
interface interface-name;
interface interface-name;
}
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 BGP
在载波至载波客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)的 BGP 配置中,配置一个组,其中包含 labeled-unicast 将 VPN 服务扩展到连接到最终客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)的语句:
bgp {
group group-name {
type internal;
local-address address;
neighbor address {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含 bgp 语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
要配置组以将带标记的内部路由发送到提供商的 PE 路由器(或交换机),请添加以下 bgp 语句:
bgp {
group group-name {
export internal;
peer-as as-number;
neighbor address {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 OSPF 和 LDP
要在载波至载波客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)上配置 OSPF 和 LDP,请添加 ospf 和 ldp 语句:
ospf {
area area-id {
interface interface-name {
passive;
}
interface interface-name;
}
}
ldp {
interface interface-name;
}
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置策略选项
要在载波至载波客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)上配置策略选项,请包含以下 policy-statement 语句:
policy-statement policy-statement-name {
term term-name {
from protocol [ ospf direct ldp ];
then accept;
}
term term-name {
then reject;
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit policy-options][edit logical-systems logical-system-name policy-options]
配置提供商的 PE 路由器或交换机
载波至载波提供商的 PE 路由器(或交换机)连接到运营商客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机)。完成以下部分中的说明以配置提供商的 PE 路由器(或交换机):
配置 MPLS
在 MPLS 配置中,指定至少两个接口:一个连接到客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机),另一个连接到提供商网络另一端的 PE 路由器(或交换机):
interface interface-name; interface interface-name;
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit protocols mpls][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols mpls]
配置 PE 到 PE BGP 会话
要在提供商的 PE 路由器(或交换机)上配置 PE 到 PE BGP 会话,以允许 VPN-IPv4 路由在 PE 路由器(或交换机)之间传递,请包含以下 bgp 语句:
bgp {
group group-name {
type internal;
local-address address;
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
neighbor address;
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含此语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置 IS-IS 和 LDP
要在提供商的 PE 路由器(或交换机)上配置 IS-IS 和 LDP,请添加 isis 和 ldp 语句:
isis {
interface interface-name;
interface interface-name {
passive;
}
}
ldp {
interface interface-name;
}
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit protocols][edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
配置策略选项
要在提供商的 PE 路由器(或交换机)上配置策略语句,以便将路由导出到运营商客户网络以及从运营商客户网络导入路由,请添加 policy-statement 和 community 语句:
policy-statement statement-name {
term term-name {
from {
protocol bgp;
community community-name;
}
then accept;
}
term term-name {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement statement-name {
term term-name {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add community-name;
accept;
}
}
term term-name {
then reject;
}
}
community community-name members value;
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit policy-options][edit logical-systems logical-system-name policy-options]
配置路由实例以向 CE 路由器发送路由
要在提供商的 PE 路由器(或交换机)上配置路由实例,以便将带标记的路由发送到运营商客户的 CE 路由器(或交换机),请包含以下语句:
instance-type vrf;
interface interface-name;
route-distinguisher value;
vrf-import policy-name;
vrf-export policy-name;
protocols {
bgp {
group group-name {
peer-as as-number;
neighbor address {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
}
您可以在以下层级包含这些语句:
[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name][edit logical-systems logical-system-name routing-instances routing-instance-name]
另见
载波至载波 VPN 示例 — 客户提供 VPN 服务
在此示例中,运营商客户 必须在 其网络上运行某种形式的 MPLS(资源预留协议 [RSVP] 或 LDP),以便向最终客户提供 VPN 服务。在以下示例中,路由器 B 和路由器 I 充当 PE 路由器(或交换机),如果这些路由器交换 VPN-IPv4 路由,则它们之间需要一条正常运行的 MPLS 路径。
有关配置信息,请参阅以下部分:
- 载波至载波服务的网络拓扑
- 路由器 A 的配置
- 路由器 B 的配置
- 路由器 C 的配置
- 路由器 D 的配置
- 路由器 E 的配置
- 路由器 F 的配置
- 路由器 G 的配置
- 路由器 H 的配置
- 路由器 I 的配置
- 路由器 J 的配置
- 路由器 K 的配置
- 路由器 L 的配置
路由器 A 的配置
在此示例中,路由器 A 充当最终客户的 CE 路由器。在路由器 A 上配置默认 family inet BGP 会话:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group to-routerB {
export attached;
peer-as 21;
neighbor 192.168.197.169;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement attached {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
路由器 B 的配置
由于路由器 B 是最终客户 CE 路由器(路由器 A)的 PE 路由器,因此您需要配置路由实例 (vpna)。将 IBGP 会话上的语句配置 labeled-unicast 到路由器 D,然后通过路由器 I 为网络另一端的 IBGP 会话进行配置 family-inet-vpn :
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
interface fe-1/0/3.0;
}
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.179;
neighbor 10.255.14.175 {
family inet {
labeled-unicast {
resolve-vpn;
}
}
}
}
neighbor 10.255.14.181 {
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/0/3.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface fe-1/0/3.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.179:21;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group vpna-06 {
peer-as 1;
neighbor 192.168.197.170;
}
}
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement vpna-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpna-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
community vpna-comm members target:100:1001;
}
路由器 C 的配置
将路由器 C 配置为本地 AS 中的标签交换路由器:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
traffic-engineering bgp-igp;
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-0/3/3.0;
interface fe-0/3/0.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface fe-0/3/0.0;
interface fe-0/3/3.0;
}
}
路由器 D 的配置
路由器 D 充当 AS 10023 网络提供的 VPN 服务的 CE 路由器。在处理流向路由器 B (10.255.14.179) 的 group int的 BGP 组配置中,包括语 labeled-unicast 句。您还需要配置 BGP 组 to-isp-red ,以便将带标记的内部路由发送到 PE 路由器(路由器 E)。
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
traffic-engineering bgp-igp;
interface fe-0/3/0.0;
interface t3-0/0/0.0;
}
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.175;
neighbor 10.255.14.179 {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
group to-isp-red {
export internal;
peer-as 10023;
neighbor 192.168.197.13 {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-0/3/0.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface fe-0/3/0.0;
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement internal {
term a {
from protocol [ ospf direct ];
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
}
路由器 E 的配置
路由器 E 和路由器 H 都是 PE 路由器。配置 PE 路由器到 PE 路由器 BGP 会话,以允许 VPN-IPv4 路由在这两台 PE 路由器之间传递。在路由器 E 上配置路由实例,以将标记的路由发送到 CE 路由器(路由器 D)。
配置路由器 E:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
interface at-0/1/0.0;
}
bgp {
group pe-pe {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.171;
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
neighbor 10.255.14.173;
}
}
isis {
interface at-0/1/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
ldp {
interface at-0/1/0.0;
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement vpn-isp1-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpn-isp1-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpn-isp1-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpn-isp1-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
community vpn-isp1-comm members target:69:21;
}
routing-instances {
vpn-isp1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.171:21;
vrf-import vpn-isp1-import;
vrf-export vpn-isp1-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group to-isp1 {
peer-as 21;
neighbor 192.168.197.14 {
as-override;
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
路由器 F 的配置
配置路由器 F 以交换通过其接口运行的路由的标签:
[edit]
protocols {
isis {
interface so-0/2/0.0;
interface at-0/3/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
ldp {
interface so-0/2/0.0;
interface at-0/3/0.0;
}
}
路由器 G 的配置
配置路由器 G:
[edit]
protocols {
isis {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface so-1/0/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
ldp {
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface so-1/0/0.0;
}
}
路由器 H 的配置
路由器 H 的配置与路由器 E 的配置类似:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
interface fe-1/1/0.0;
interface so-1/0/0.0;
}
bgp {
group pe-pe {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.173;
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
neighbor 10.255.14.171;
}
}
isis {
interface so-1/0/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
ldp {
interface so-1/0/0.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
vpn-isp1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface fe-1/1/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.173:21;
vrf-import vpn-isp1-import;
vrf-export vpn-isp1-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group to-isp1 {
peer-as 21;
neighbor 192.168.197.94 {
as-override;
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement vpn-isp1-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpn-isp1-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpn-isp1-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpn-isp1-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
community vpn-isp1-comm members target:69:21;
}
路由器 I 的配置
路由器 I 充当最终客户的 PE 路由器。以下配置类似于路由器 B 的配置:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
interface fe-1/0/1.0;
interface fe-1/1/3.0;
}
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.181;
neighbor 10.255.14.177 {
family inet {
labeled-unicast {
resolve-vpn;
}
}
}
neighbor 10.255.14.179 {
family inet-vpn {
any;
}
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/1/3.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface fe-1/1/3.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface fe-1/0/1.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.181:21;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group vpna-0 {
peer-as 1;
neighbor 192.168.197.198;
}
}
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement vpna-import {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community vpna-comm;
}
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement vpna-export {
term a {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add vpna-comm;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
community vpna-comm members target:100:1001;
}
路由器 J 的配置
配置路由器 J 以交换通过其接口运行的路由的标签:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
traffic-engineering bgp-igp;
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
interface fe-1/0/3.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
interface fe-1/0/3.0;
}
}
路由器 K 的配置
路由器 K 的配置与路由器 D 的配置类似:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
traffic-engineering bgp-igp;
interface fe-1/1/2.0;
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
}
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.177;
neighbor 10.255.14.181 {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
group to-isp-red {
export internal;
peer-as 10023;
neighbor 192.168.197.93 {
family inet {
labeled-unicast;
}
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement internal {
term a {
from protocol [ ospf direct ];
then accept;
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
}
路由器 L 的配置
在此示例中,路由器 L 是最终客户的 CE 路由器。在路由器 L 上配置默认家庭 inet BGP 会话:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group to-I {
export attached;
peer-as 21;
neighbor 192.168.197.197;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement attached {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
另见
LDP 和载波至载波 VPN 的多个实例
通过配置多个 LDP 路由实例,您可以使用 LDP 将载波至载波 VPN 中的标签从核心提供商 PE 路由器播发到客户运营商 CE 路由器。当运营商客户是基本 ISP 并希望将完整的互联网路由限制到其 PE 路由器时,让 LDP 以这种方式播发标签特别有用。通过使用 LDP 而非 BGP,运营商客户可以保护其其他内部路由器免受整个互联网的影响。当运营商客户希望为其客户提供第 3 层 VPN 或第 2 层 VPN 服务时,多实例 LDP 也很有用。
有关如何为运营商的运营商 VPN 配置多个 LDP 路由实例的示例,请参阅 https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/mpls/topics/example/multiple-instance-ldp-configuring-detailed-solutions.html。
另见
变更历史表
是否支持某项功能取决于您使用的平台和版本。使用 功能浏览器 查看您使用的平台是否支持某项功能。