What is SD-WAN?
What is SD-WAN?
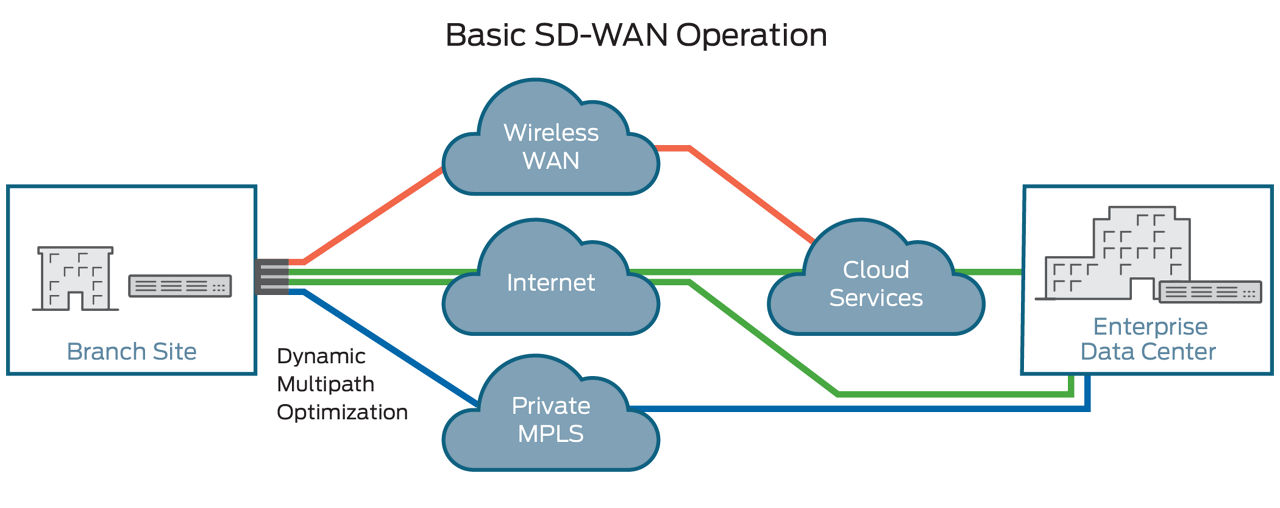
Software-defined wide-area networking (SD-WAN) is an automated, programmatic approach to managing enterprise network connectivity and circuit costs. It extends software-defined networking (SDN) into an application that businesses can use to quickly create a smart hybrid WAN.
Consisting of business-grade IP VPN, broadband Internet, and wireless services, SD-WAN enables you to cost-efficiently manage applications, particularly in the cloud. Traffic is automatically and dynamically forwarded across the most appropriate and efficient WAN path based on network conditions, application traffic security and quality-of-service (QoS) requirements, and circuit cost. You can set the routing policies.
SD-WAN Benefits
Businesses are rapidly adopting SD-WAN technology because of its comprehensive financial and operational benefits.
- Lowers WAN OpEx, CapEx, and overall total cost of ownership.
- Provides greater business agility and responsiveness to keep pace with IT innovations.
- Supports multiple, secure, high-performance connections, eliminating backhaul penalties imposed by MPLS networks.
- Improves performance by enabling load sharing across connections and adjusting traffic flows based on network conditions.
- Supports the automated provisioning of, and changes to, premium network services such as VPNs, firewalls, security, WAN optimization, and application delivery control.
- Supports zero touch provisioning (ZTP).
- Improves network security by encrypting WAN traffic and segmenting the network to minimize damage if breaches occur.
Problems Addressed by SD-WAN
Managing the WAN traditionally has been one of the most expensive and rigid aspects of running an enterprise network. SD-WAN eases this burden by proactively responding to real-time network conditions. It uses programmable network devices that you can modify remotely and through dynamic best-path routing, both of which improve cost, agility, and performance.
SD-WAN Uses and Functions
SD-WAN software running on CPE (customer premises equipment) monitors the conditions of all public and private-line services and determines how to route each type of application traffic. For instance, the default might be to send voice-over-IP (VoIP) traffic over an MPLS VPN service. However, if the MPLS connection becomes congested, the SD-WAN might switch that traffic over to a broadband Internet or 4G LTE wireless circuit. In this way, the SD-WAN enables automatic load balancing and network congestion management for best performance and least-cost effective routing.
SD-WAN FAQs
So, what is an SD-WAN?
Simply put, an SD-WAN is an automated, programmable wide-area network that dynamically and securely routes traffic based on applications policies, network conditions, or WAN circuit priority.
What are the benefits of SD-WAN?
SD-WAN enables local breakout from your various sites, directly to the cloud, which reduces latency and improves application performance. It also reduces costs by eliminating the need to backhaul traffic to a central location, which was the conventional architecture before SD-WAN. Its application-aware path selection further reduces circuit and telecom costs because it allows you to use a less expensive broadband link for non-essential traffic.
Are all SD-WAN solutions the same?
Most of today’s SD-WAN solutions are built on a conventional tunnel-based approach. Tunnels such as IPSec add additional, expensive overhead through the use of headers. This approach consumes precious bandwidth and reduces application performance. Also, application and session visibility are reduced as all application traffic is assigned to a tunnel across, say an MPLS link. Hence, telemetry like latency, jitter, and packet loss is available at the tunnel level only.
Alternatively, a session-centric approach, used in Juniper’s AI-driven SD-WAN, provides granular session-level performance. For example, you can view the latency, jitter, and packet loss for an individual Microsoft Teams video call. And if the link cannot provide the required SLA, then that individual session is instantly routed to a better performing link.
What is an AI-driven SD-WAN?
An AI-driven SD-WAN brings AI-powered insights, anomaly detection, and automated troubleshooting to the SD-WAN. It enables IT administrators to deliver better network experiences to their end users with minimal operational burden on the IT staff. Juniper Mist WAN Assurance delivers this AI capability to the SD-WAN, and correlates SD-WAN performance with wireless and wired network performance. In this way, complete insight and visibility is provided, from client to cloud.
What SD-WAN technology, solutions, and products does Juniper offer?
Juniper offers AI-driven SD-WAN, which combines Juniper Mist WAN Assurance, driven by Mist AI, with Session Smart technology. Juniper SD-WAN delivers the insights, anomaly detection, and automated troubleshooting for day 2 operations.
Session Smart is a unique approach that focuses on applications and user experiences by operating at a more granular session level. For example, a Zoom call is a session. Session Smart Routers can be deployed at remote, distributed sites or as headend devices at your data center or in your cloud, including Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. Session Smart Routers can be managed on premises with the Session Smart Conductor or in the Mist Cloud.






















