|
Software release
|
For information on which MPCs support these MICs, see MIC/MPC Compatibility. For information
on which MICs are supported on MX Series routers, see MICs Supported by MX Series Routers.
|
|
Description
|
-
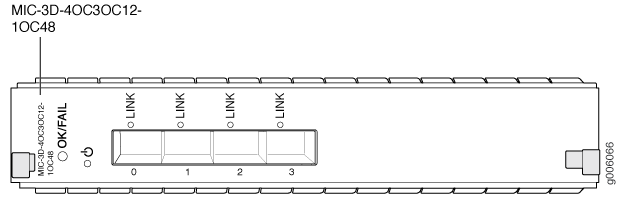
4-port: 4 OC3/STM1 or OC12/STM4 ports
The ports can be configured to support a combination of OC3,
OC12, and OC48 rates. In the combination, you can configure only one
port (port 0) to support OC48, whereas OC3 or OC12 can be configured
on all four ports.
-
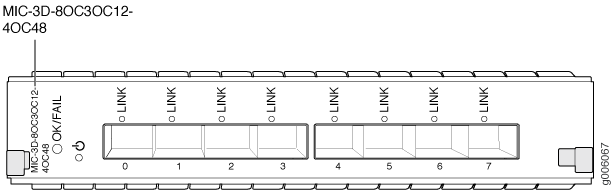
8-port: 8 OC3/STM1 or OC12/STM4 ports
The ports can be configured to support a combination of OC3, OC12, and OC48 rates. In the
combination
(when the device is in the multi-rate
mode), you can configure only two ports
(port 0 and port 1) to support OC48, whereas you can
configure all eight ports to support OC3 or
OC12.
If the multi-rate mode is disabled, you can configure four
ports (port 0, port 1, port 2, and port 3) to support OC48.
To disable the multi-rate mode, use the CLI statement
set chassis fpc slot pic
slot
no-multi-rate.
-
Power requirement:
-
Weight:
-
Model number:
|
|
Hardware features
|
|
|
Software features
|
-
Per-port SONET/SDH framing
-
Local and remote loopback on each port
-
Optical diagnostics and monitoring
-
Clocking options: internal or external/loop mode.
-
Unified in-service software upgrade (unified ISSU)
-
Encapsulations:
-
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) fast reroute
-
MPLS CCC (circuit cross-connect)
-
MPLS TCC (translational cross-connect)
-
Cisco High-Level Data Link Control
-
Cisco HDLC CCC
-
Cisco HDLC TCC
-
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
-
PPP for CCC
-
PPP for TCC
-
Flexible Frame Relay
-
Frame Relay
-
Frame Relay for CCC
-
Frame Relay for TCC
-
PPP over Frame Relay
Note:
Ethernet over Frame Relay is not supported.
|
|
Cables and connectors
|
Tip:
You
can use the Hardware
Compatibility Tool to find information about the pluggable
transceivers supported on your Juniper Networks device.
The list of supported transceivers for the MX Series is located
at https://pathfinder.juniper.net/hct/category/#catKey=100001&modelType;=All&pf;=MX+Series.
|
|
LEDs
|
OK/FAIL LED, one bicolor:
LINK LED, one green per port:
-
Off—Not enabled
-
Green—Online with no alarms or failures
-
Yellow—Online with alarms for remote failures
-
Red—Active with a local alarm; router has detected
a failure
|
|
Alarms, errors, and events
|
SONET alarms:
-
Loss of light (LOL)
-
Loss of signal (LOS)
-
Loss of frame (LOF)
-
Phase lock loop (PLL)
-
Severely errored frame (SEF)
-
Alarm indicator signal–line (AIS-L)
-
Alarm indicator signal–path (AIS-P)
-
Remote defect indicator–line (RDI-L)
-
Remote defect indicator–path (RDI-P)
-
Loss of pointer–path (LOP-P)
-
Bit error rate–signal degrade (BERR-SD)
-
Bit error rate–signal fail (BERR-SF)
-
Payload label mismatch–Path (PLM-P)
-
Unequipped–path (UNEQ-P)
-
Remote error indicator–path (REI-P)
SDH alarms:
-
Loss of light (LOL)
-
Phase lock loop (PLL)
-
Loss of frame (LOF)
-
Loss of signal (LOS)
-
Severely errored frame (SEF)
-
Multiplex-section alarm indicator signal (MS-AIS)
-
H Path alarm indicator signal (HP-AIS)
-
Loss of pointer (LOP)
-
Bit error rate–signal degrade (BER-SD)
-
Bit error rate–signal fail (BER-SF)
-
Multiplex section–far end receive failure (MS-FERF)
-
High order path–far end receive failure (HP-FERF)
-
High order path–payload label mismatch (HP-PLM)
-
Remote error indicator (REI)
-
Unequipped (UNEQ)
|