Use this procedure to deploy and configure the vSRX Virtual Firewall as a virtual security
appliance in the Hyper-V environment using Hyper-V Manager.
Note the following for deploying vSRX Virtual Firewall on a Microsoft Hyper-V server:
Starting in Junos OS Release 15.1X49-D80 and Junos OS Release 17.3R1, you can deploy the vSRX
Virtual Firewall only on Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2012 R2 or 2012.
Starting in Junos OS Release 15.1X49-D100 and Junos OS Release 17.4R1, you can deploy the vSRX
Virtual Firewall on Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016.
Note: To upgrade an existing vSRX Virtual Firewall instance, see Migration, Upgrade, and
Downgrade in the vSRX Virtual Firewall Release
Notes.
To deploy vSRX Virtual Firewall using Hyper-V Manager:
-
Download the vSRX Virtual Firewall software image for Microsoft Hyper-V from
the Juniper Networks website. The vSRX Virtual Firewall
disk image supported by Microsoft Hyper-V is a virtual hard disk (VHD) format
file.
CAUTION:
Do not change the filename of the downloaded software image or the
installation will fail.
- Log onto your Hyper-V host computer using the Administrator
account.
- Open the Hyper-V Manager by selecting Start > Administrative
Tools > Hyper-V Manager. The welcome page for Hyper-V appears
the first time that you open Hyper-V Manager.
- Create a virtual machine by selecting Action > New
> Virtual Machine. The Before You Begin screen appears for the
New Virtual Machine Wizard. Click Next to move through
each page of the wizard, or you can click the name of a page in the
left pane to move directly to that page.
-
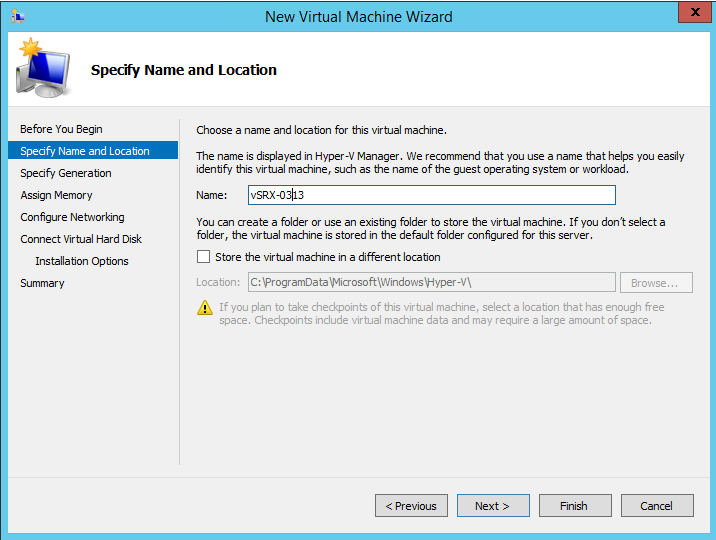
From the Specify Name and Location page (see Figure 1), enter a name and location for the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM that you are
creating and then click Next. We recommend that you keep
this name the same as the hostname you intend to assign to the vSRX Virtual
Firewall VM.
Figure 1: Specify Name and Location Page
-
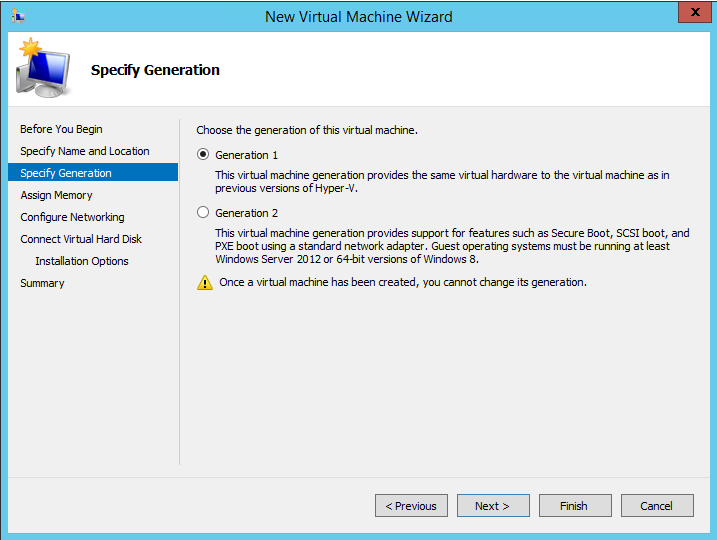
From the Specify Generation page (see Figure 2), keep the default setting of Generation 1 as the
generation of the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM and then click
Next.
Figure 2: Specify Generation Page
-
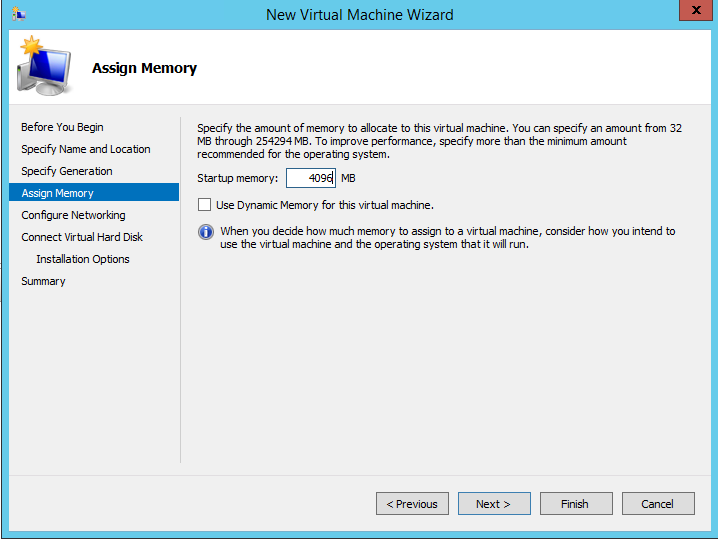
From the Assign Memory page (see Figure 3), enter 4096 MB as the amount of startup memory to
assign to the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM. Leave Use Dynamic Memory for
this virtual machine clear. Click Next.
Figure 3: Assign Memory Page
-
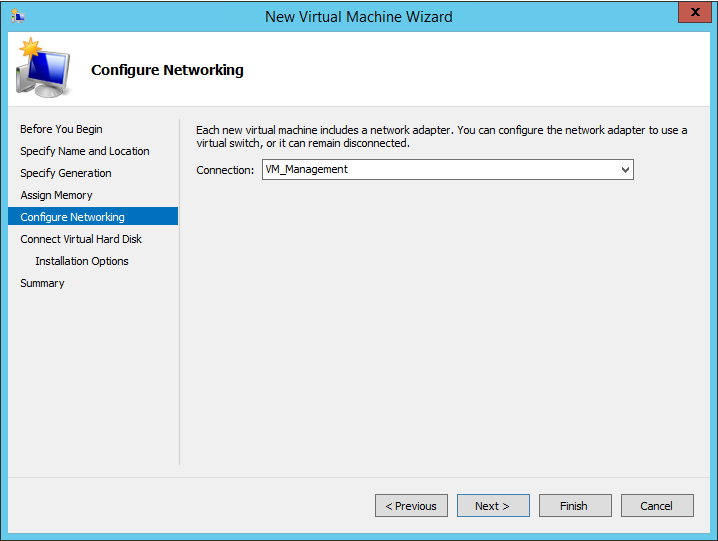
From the Configure Networking page (see Figure 4), select a virtual switch from a list of existing virtual switches on the
Hyper-V host computer to connect to the vSRX Virtual Firewall management
interface. The default is Not connected. Click
Next.
Note:
See Add vSRX Interfaces for the procedure on adding virtual
switches for the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM using the Virtual Switch
Manager.
Figure 4: Configure Networking Page
-
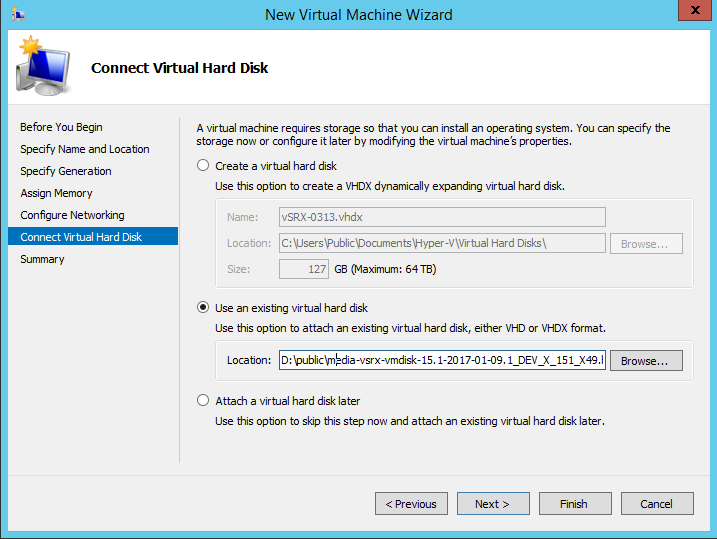
From the Connect Virtual Hard Disk page (see Figure 5), click Use an existing virtual hard disk and browse
to the location of the vSRX Virtual Firewall virtual hard disk (VHD) file
(downloaded in Step 1). Click Next.
Figure 5: Connect Virtual Hard Disk Page
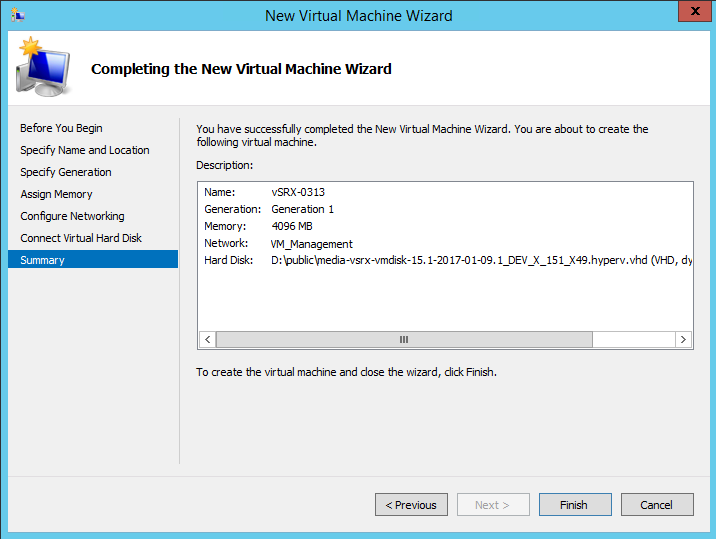
- After you have finished configuring the new virtual machine,
verify your selections in the Summary page (see Figure 6) and then click Finish to
complete the installation.
Figure 6: Summary Page
-
Right-click the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM and select
Settings from the context menu.
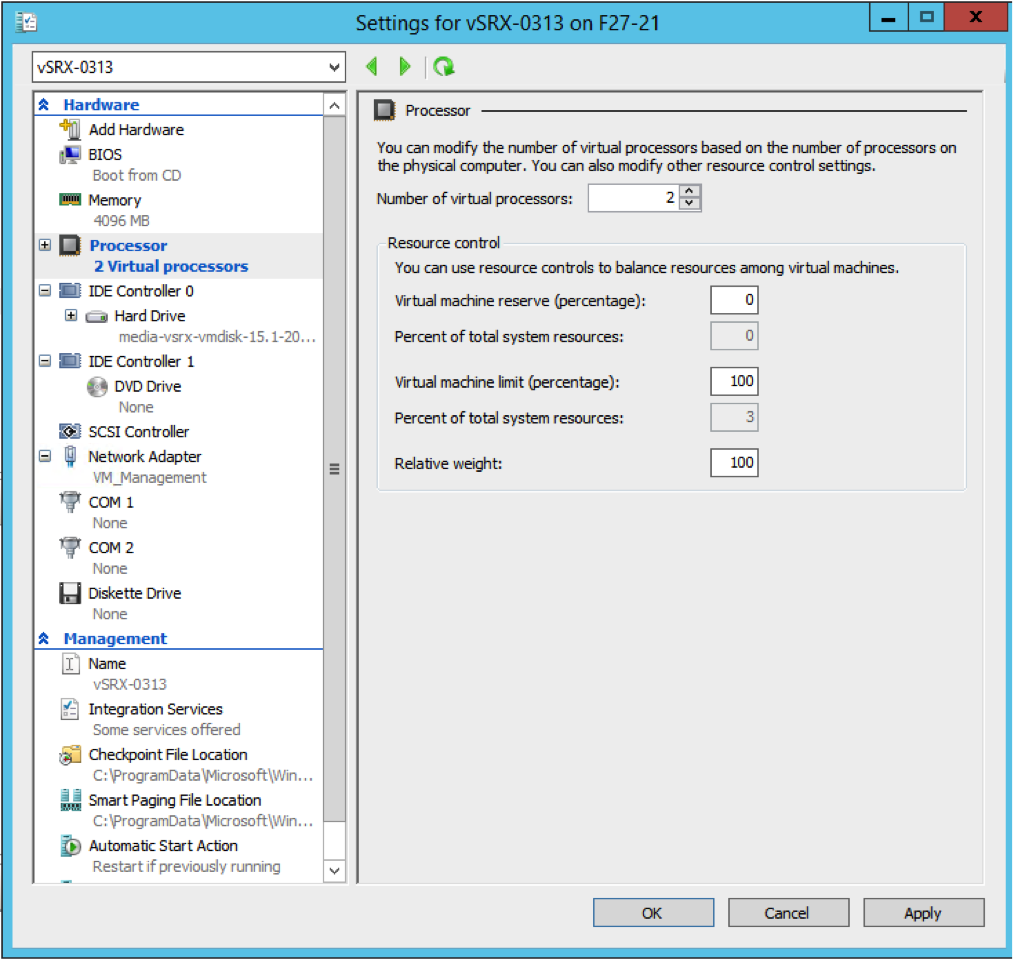
- From the Settings dialog box, under the Hardware section,
select Processor. The Processor pane appears (see Figure 7). Enter 2 in the Number of virtual processors field (the default is 1).
Figure 7: Processor Pane
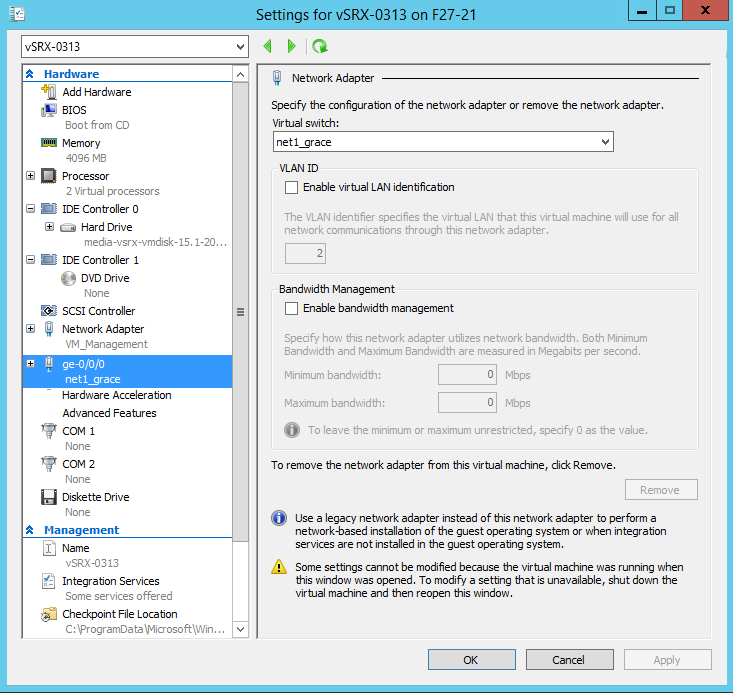
- From the Settings dialog box, under the Hardware section,
select Network Adapter. The Network Adapter pane appears
(see Figure 8).
From the Virtual switch drop-down list, select a virtual switch to assign to a network adapter to
be used by the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM (see Add vSRX
Interfaces for details on adding virtual switches). Each network
adapter that is defined for a vSRX Virtual Firewall is mapped to a specific
interface.
See Requirements for vSRX on Microsoft Hyper-V for a summary of
interface names and mappings for a vSRX Virtual Firewall VM.
Note: If you need to add a network adapter to assign to a virtual
switch, click Add Hardware > Network Adapter > Add.
Figure 8: Network Adapter
Pane
-
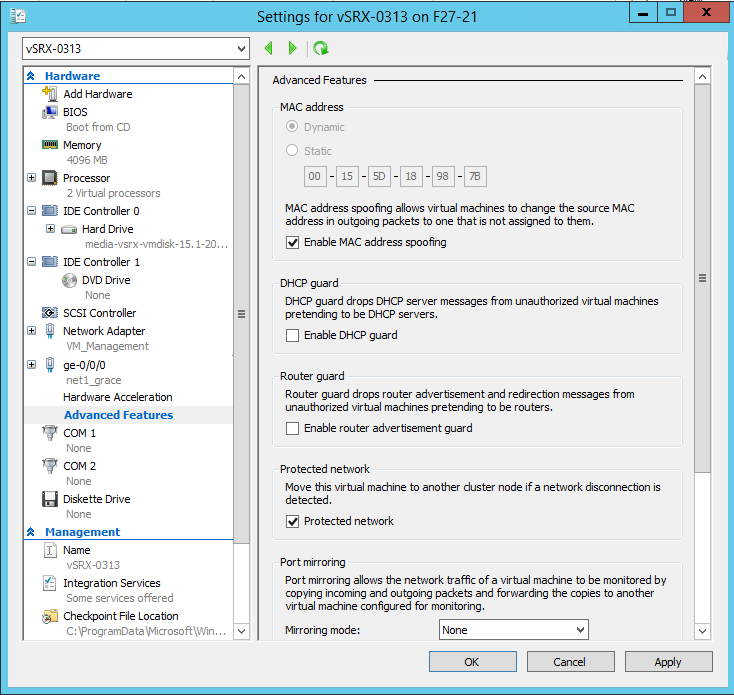
Enable the MAC address spoofing function for the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM if a
network adapter is to be used as an interface for Layer 2 mode
support on the vSRX
Virtual Firewall. From the Network Adapter pane select Advanced
Features. The Advanced Features pane appears (see Figure 9). Click the Enable MAC address spoofing check box.
MAC address spoofing allows each network adapter to change its source MAC
address for outgoing packets to one that is not assigned to them. Enabling
MAC address spoofing ensures those packets are not dropped by the network
adapter if the source MAC address fails to match the outgoing interface MAC
address.
Click OK when you complete your vSRX Virtual Firewall
VM selections.
Figure 9: Network Adapter Advanced Features Pane
-
On Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016, you will need to enable nested virtualization
for the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM before you power on the vSRX Virtual Firewall
instance. This procedure can only be performed in the Hyper-V environment using
Windows PowerShell (see, Deploy vSRX
in a Hyper-V Host Using Windows PowerShell, Step 9). You cannot
enable nested virtualization from the Hyper-V Manager because nessted
virtualization is not supported on Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2012.
Note: This step is applicable only for vSRX Virtual Firewall (which uses and
requires nested virtualization) and not for vSRX Virtual Firewall
3.0.
Note:
Nested virtualization can only be configured on a host running Microsoft
Hyper-V Server 2016. In addition, Dynamic Memory must be disabled on the
virtual machine containing the nested instance of Hyper-V.
-
Launch and power on the vSRX Virtual Firewall instance in the Hyper-V Manager
by selecting the vSRX Virtual Firewall VM from the list of virtual machines.
Right-click and select Start from the context menu (or
select Action > Start).
-
Configure the basic settings for the vSRX Virtual Firewall (see Configure vSRX
Using the CLI).
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
15.1X49-D80
Starting in Junos OS Release 15.1X49-D80 and Junos OS Release 17.3R1, you can deploy
the vSRX Virtual Firewall only on Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2012 R2 or
2012.
15.1X49-D100
Starting in Junos OS Release 15.1X49-D100 and Junos OS Release 17.4R1, you can
deploy the vSRX Virtual Firewall on Microsoft Hyper-V Server
2016.









